Cationic High Molecular Weight Lignin Polymer: A Flocculant for the Removal of Anionic Azo-Dyes from Simulated Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cationic Lignin Preparation
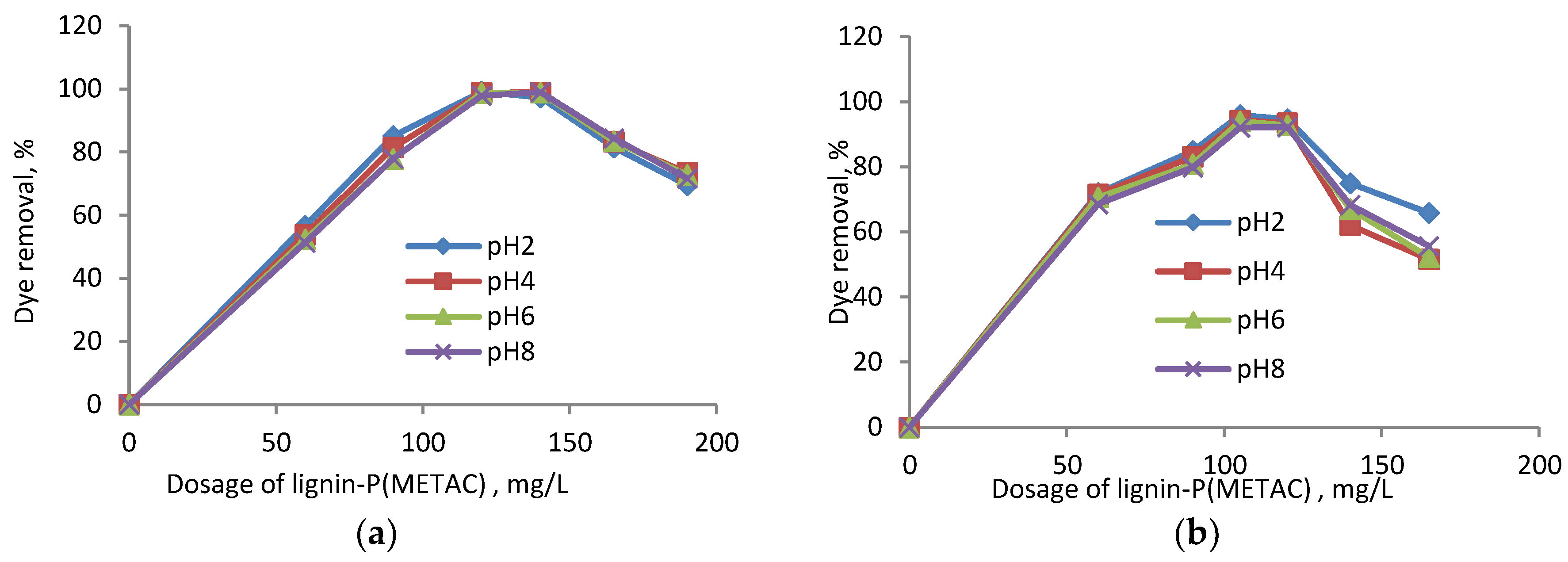
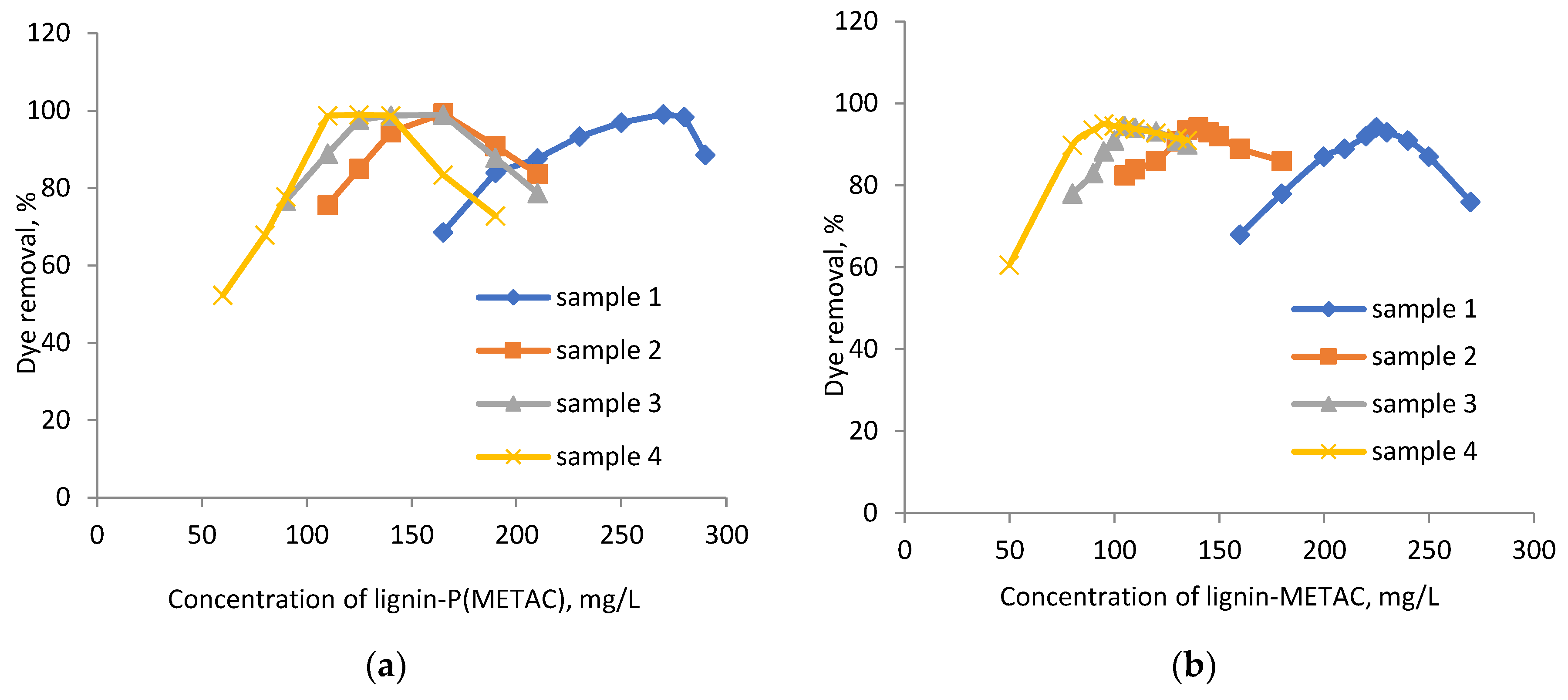
2.2. Effects of Dosage and pH
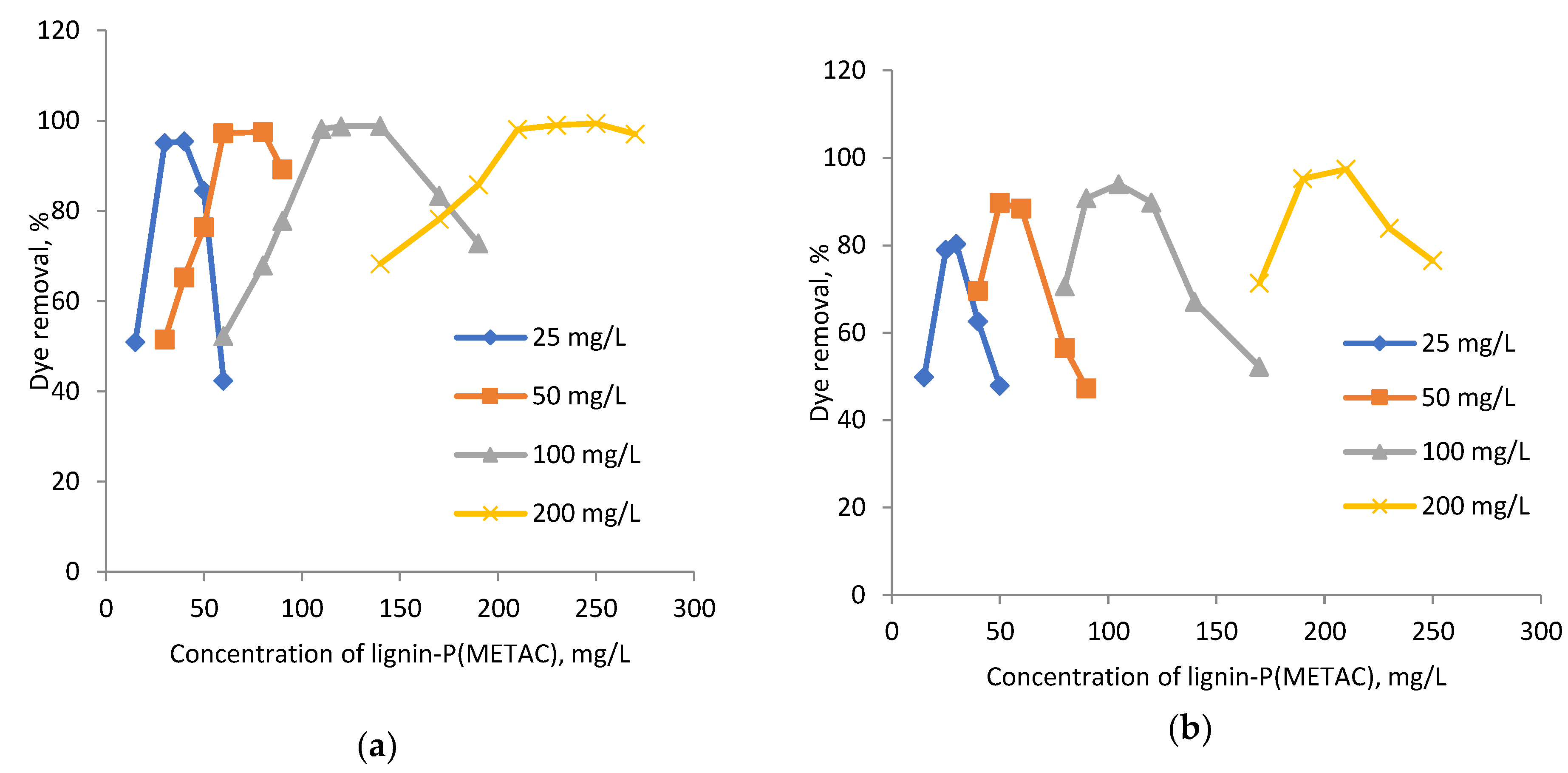
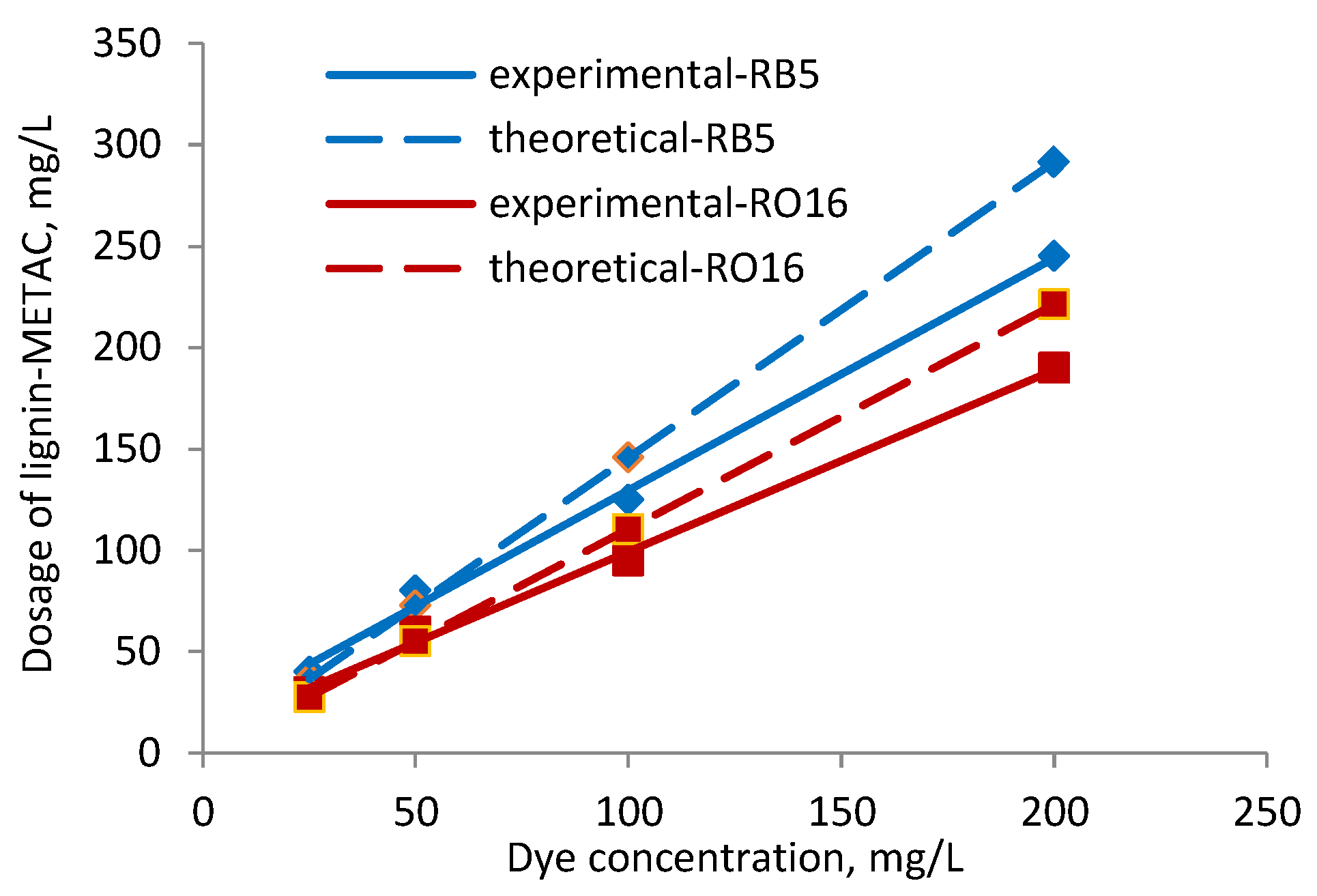
2.3. Effect of Dye Concentration
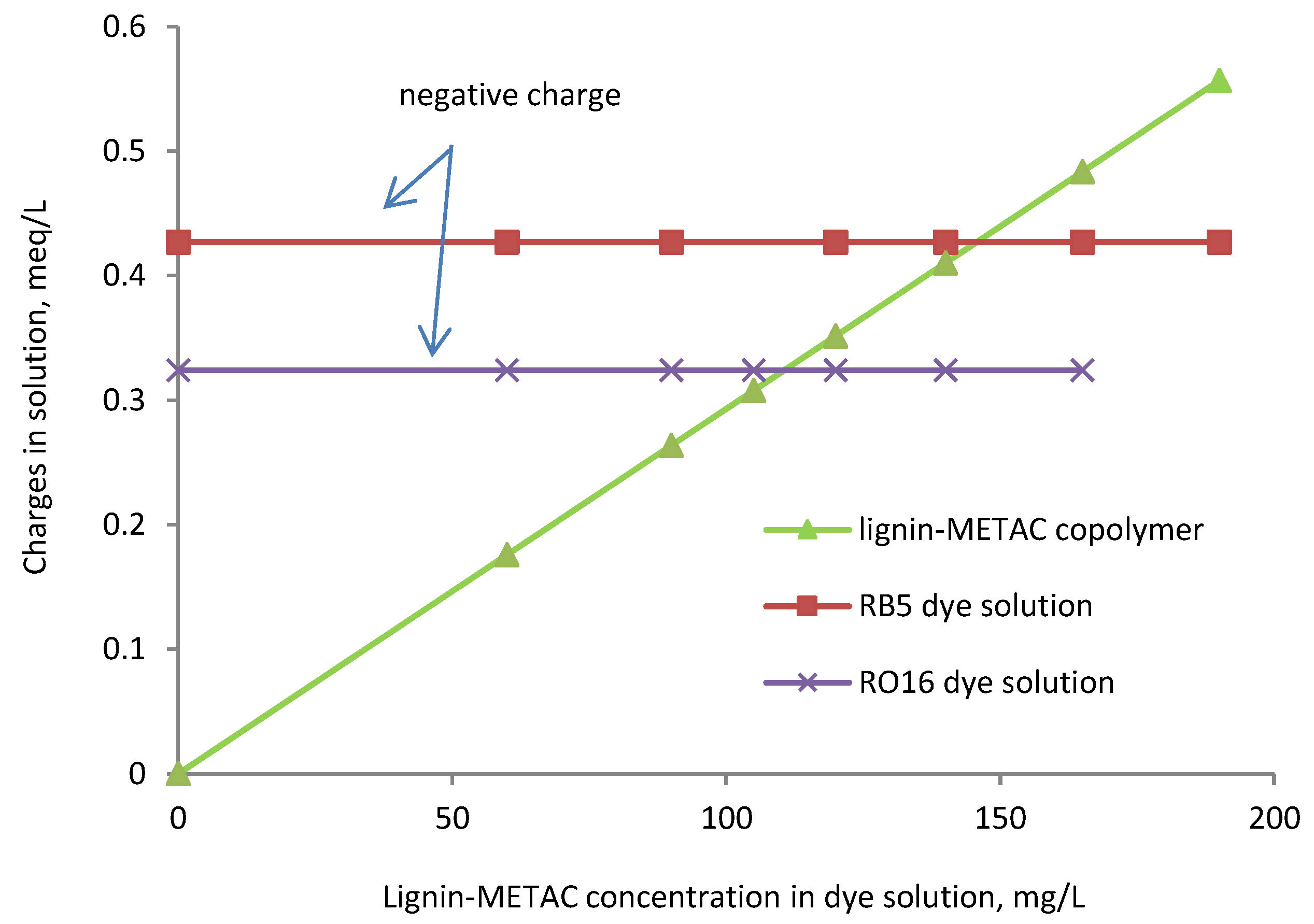
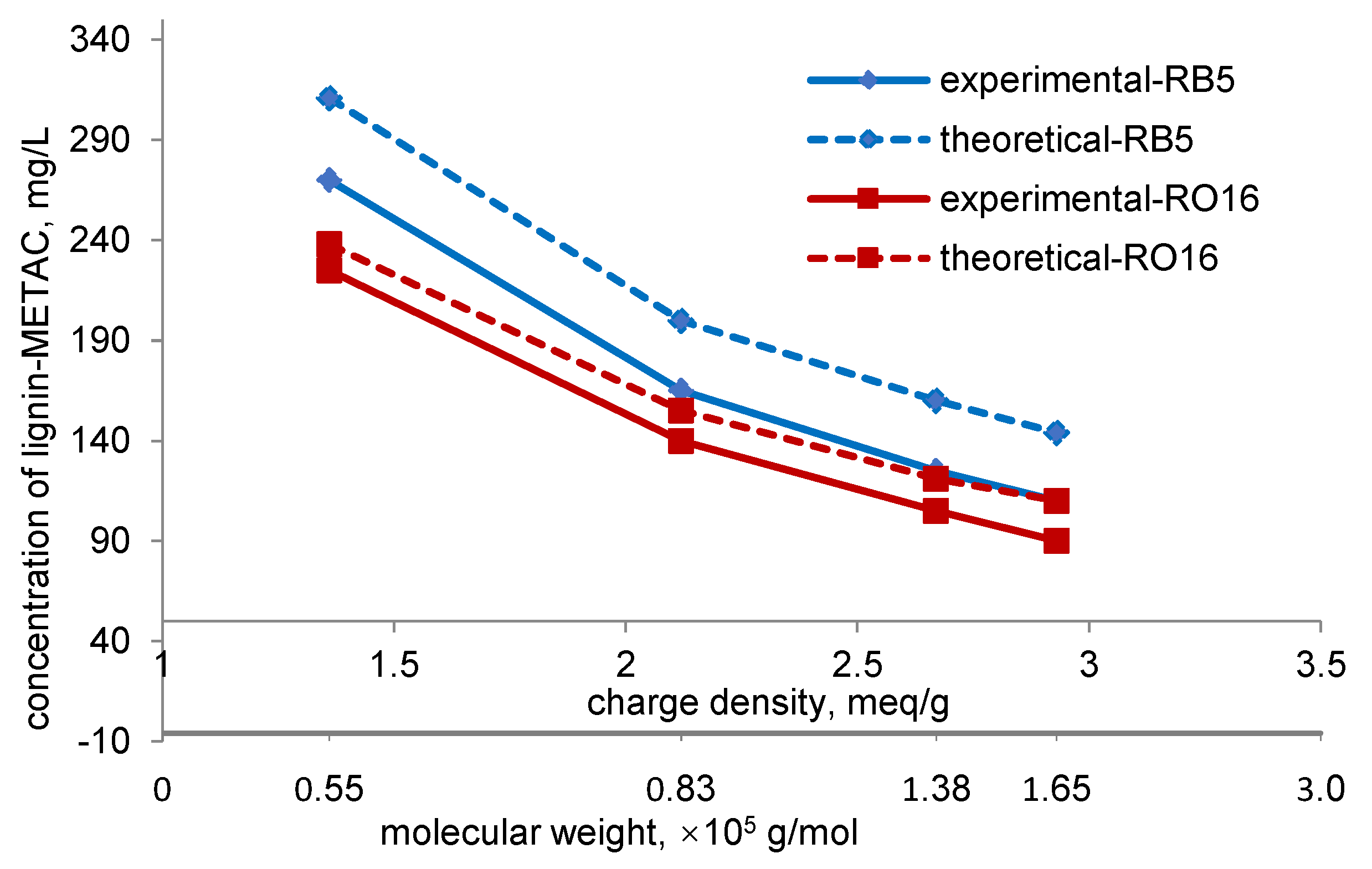
2.4. Effect of Charge Density and Mw of Lignin-METAC Polymer
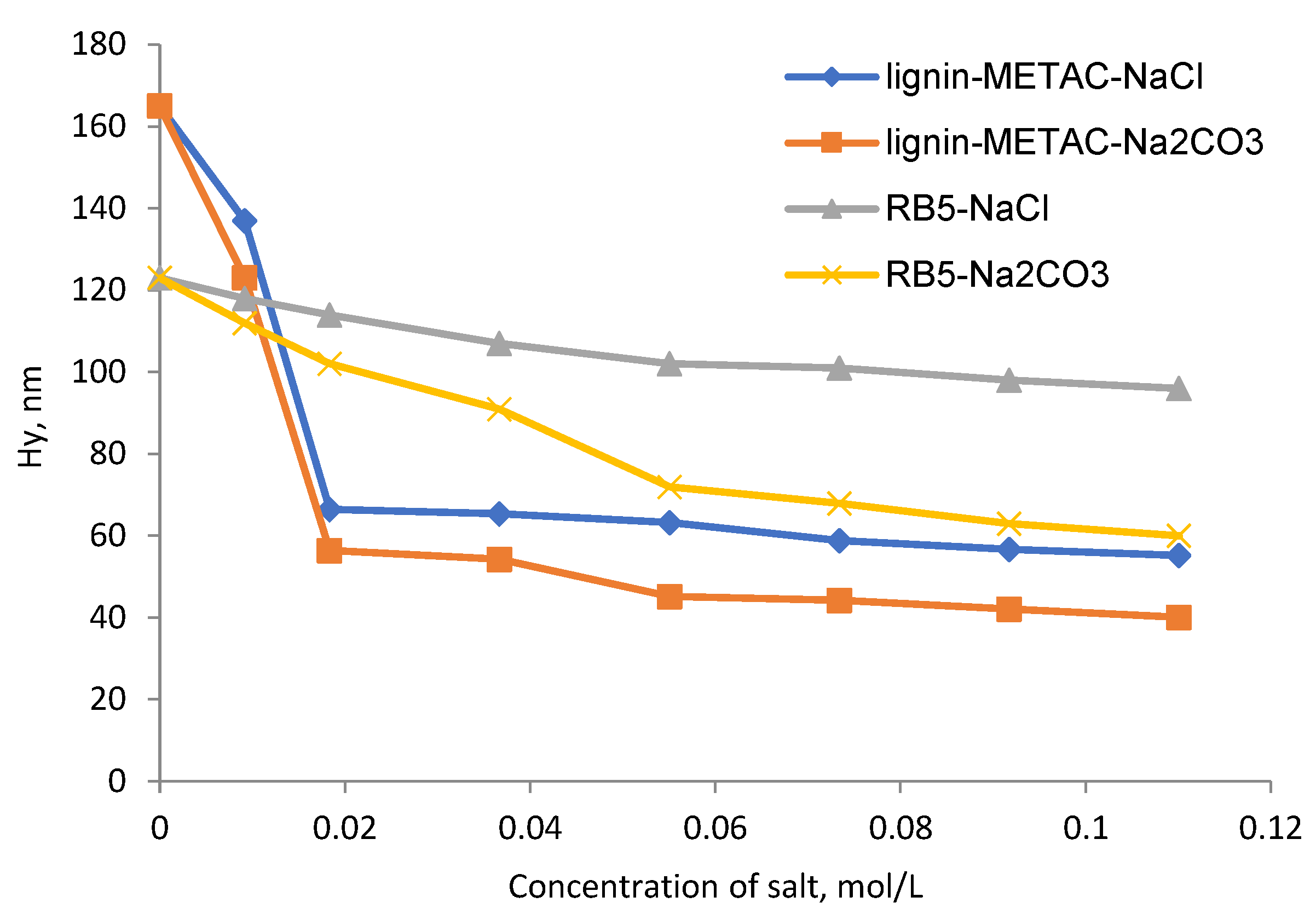
2.5. Effect of Inorganic Salts
2.6. COD Removal
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Cationic Lignin-METAC
3.3. Charge Density Analysis
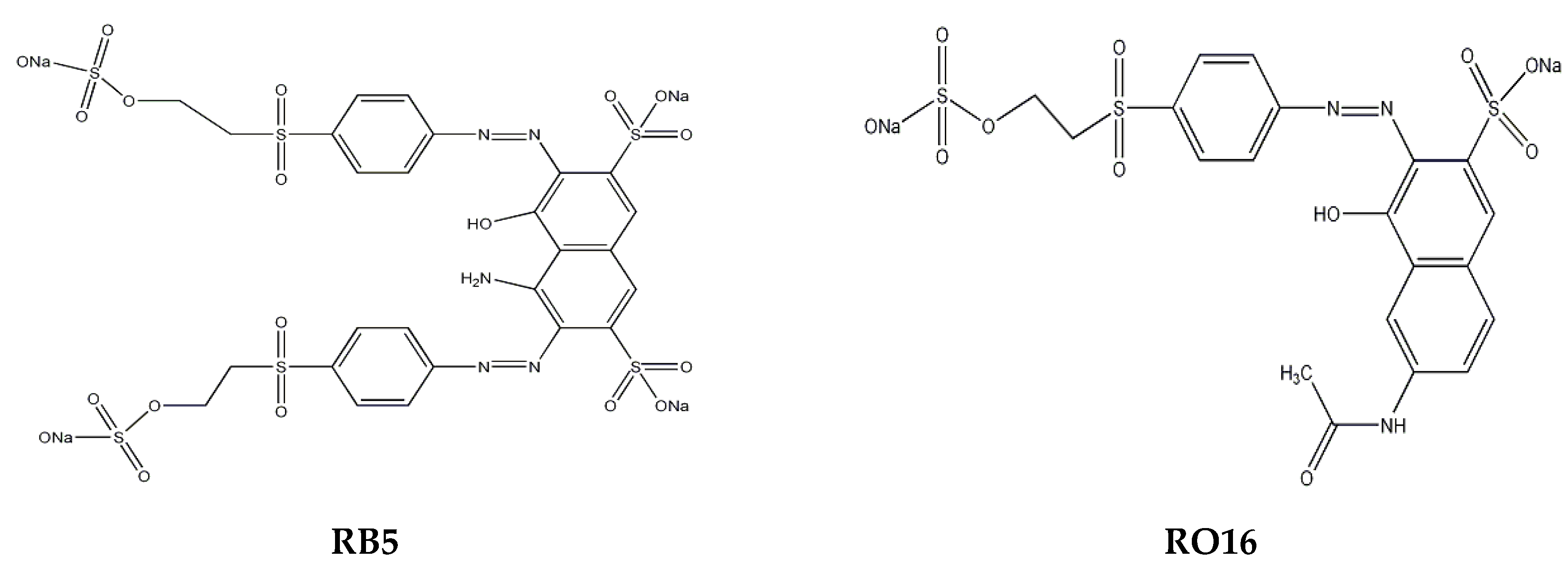
3.4. Preparation of Dye Solutions
3.5. Hydrodynamic Diameter (Hy) Measurement
3.6. Dye Removal Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iscen, C.F.; Kiran, I.; Ilhan, S. Biosorption of reactive black 5 dye by penicillium restrictum: The kinetic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buthelezi, S.P.; Olaniran, A.O.; Pillay, B. Textile dye removal from wastewater effluents using bioflocculants produced by indigenous bacterial isolates. Molecules 2012, 17, 14260–14274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, S.M.D.G.U.; Bonilla, K.A.S.; de Souza, A.A.U. Removal of COD and color from hydrolyzed textile azo dye by combined ozonation and biological treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, S.S.; Moghaddam, M.A.; Arami, M. Coagulation/flocculation process for dye removal using sludge from water treatment plant: optimization through response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, K.; Woo, S.H.; Lee, D.S. Simultaneous removal of COD and Direct Red 80 in a mixed anaerobic sulfate-reducing bacteria culture. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Hameed, B. Fixed-bed adsorption of reactive azo dye onto granular activated carbon prepared from waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absalan, G.; Asadi, M.; Kamran, S.; Sheikhian, L.; Goltz, D.M. Removal of reactive red-120 and 4-(2-pyridylazo) resorcinol from aqueous samples by Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using ionic liquid as modifier. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Madeira, L.M.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Treatment of textile dye wastewaters using ferrous sulphate in a chemical coagulation/flocculation process. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorimotlagh, Z.; Soltani, R.D.C.; Khataee, A.R.; Shahriyar, S.; Nourmoradi, H. Adsorption of a textile dye in aqueous phase using mesoporous activated carbon prepared from Iranian milk vetch. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, Y.; Ashori, A.; Azadeh, E.; Abdulkhani, A. Removal of acid orange 7 and remazol black 5 reactive dyes from aqueous solutions using a novel biosorbent. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2012, 32, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, P. Dye removal from wastewater using activated carbon developed from sawdust: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 113, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, A.W.M.; Barford, J.P.; Mckay, G. A comparative study on the kinetics and mechanisms of removal of Reactive Black 5 by adsorption onto activated carbons and bone char. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Song, S.; Zhou, H.; Ying, H.; Chen, J.C.I. reactive black 5 decolorization by combined sonolysis and ozonation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szygula, A.; Guibal, E.; Palacin, M.A.; Ruiza, M.; Sastre, A.M. Removal of an anionic dye (Acid Blue 92) by coagulation-flocculation using chitosan. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2979–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, A.B.; Cervantes, F.J.; van Lier, J.B. Review paper on current technologies for decolourisation of textile wastewaters: Perspectives for anaerobic biotechnology. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2369–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guibal, E.; Roussy, J. Coagulation and flocculation of dye-containing solutions using a biopolymer (Chitosan). React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sen, G.; Jha, U.; Pal, S. Novel biodegradable polymeric flocculant based on polyacrylamide-grafted tamarind kernel polysaccharide. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9638–9644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonoozi, M.H.; Moghaddam, M.R.A.; Arami, M. Coagulation/flocculation of dye-containing solutions using polyaluminium chloride and alum. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.K.; Mandre, N.R.; Panda, A.B.; Pal, S. Amylopectin grafted with poly (acrylic acid): Development and application of a high performance flocculant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Pal, S.; Rana, V.K.; Ghorai, S. Amphoteric amylopectin: A novel polymeric flocculant. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Cai, T.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R. Flocculation of both anionic and cationic dyes in aqueous solutions by the amphoteric grafting flocculant carboxymethyl chitosan-graft-polyacrylamide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.P.; Chen, Y.Z.; Yuan, S.J.; Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q. Synthesis and characterization of a novel cationic chitosan-based flocculant with a high water-solubility for pulp mill wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5267–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szygula, A.; Guibal, E.; Ruiz, M.; Sastre, A.M. The removal of sulphonated azo-dyes by coagulation with chitosan. Colloid Surf. A 2008, 330, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ge, X.W.; Yu, H.Q. Gamma radiation-induced grafting of a cationic monomer onto chitosan as a flocculant. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.J.; Hou, Q.X.; Kong, F.G.; Fatehi, P. Production of cationic xylan-METAC copolymer as a flocculant for textile industry. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 124, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.; Parhiala, K.; Wang, S.; Fatehi, P. Preparation of cationic softwood kraft lignin and its application in dye removal. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kong, F.; Gao, W.; Fatehi, P. Novel process for generating cationic lignin based flocculant. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 6595–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusufi, A.; Dzubiella, J.; Likos, C.N.; von Ferber, C.; Lowen, H. Effective interactions between star polymers and colloidal particles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2001, 13, 6177–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Li, H.J.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, R.H.; Yang, H.; Li, A.M.; Cheng, R.S. Efficient flocculation of an anionic dye from aqueous solutions using a cellulose-based flocculant. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Chuong, C.S.; Khatoon, A.; Wani, W.A.; Kumar, R.; Rafatullah, M. Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: Novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30801–30818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, T.W.; La Mer, V.K. The energetics of flocculation and redispersion by polymers. J. Colloid Sci. 1964, 19, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Fatehi, P.; Ni, Y. Chitosan as a flocculant for pre-hydrolysis liquor of kraft-based dissolving pulp production process. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1630–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fatehi, P.; Ni, Y. Removal of inhibitors from pre-hydrolysis liquor of kraft-based dissolving pulp production process using adsorption and flocculation processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 116, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razali, M.A.A.; Sanusi, N.; Ismail, H.; Othman, N.; Ariffin, A. Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for optimization of cassava starch grafted polyDADMAC synthesis for cationic properties. Starch-Stärke 2012, 64, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisschops, I.; Spanjers, H. Literature review on textile wastewater characterization. Environ. Technol. 2003, 24, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Zhang, Y.K.; Hao, C.; Dai, X.H.; Zhou, Z.L.; Si, N.C. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis of aminated lignin by a Mannich reaction and its decolorizing properties for anionic azo-dyes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 28156–28164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, D.J.; Shin, W.S.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, M.C.; Han, M.H.; Ha, T.W.; Kim, Y.H. Decolorization of reactive dyes using inorganic coagulants and synthetic polymer. Dyes Pigm. 2007, 73, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouisni, L.; Holt-Hindle, P.; Maki, K.; Paleologou, M. The lignoforce system (TM): a new process for the production of high-quality lignin from black liquor. Pulp Pap-Can. 2014, 115, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- James, N.S.; Cheruku, R.R.; Missert, J.R.; Sunar, U.; Pandey, R.K. Measurement of cyanine dye photobleaching in photosensitizer cyanine dye conjugates could help in optimizing light dosimetry for improved photodynamic therapy of cancer. Molecules 2018, 23, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Li, E.; Liu, J.; Li, S. Using natural biomacromolecules for adsorptive and enzymatic removal of aniline blue from water. Molecules 2018, 23, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |


| Lignin-METAC Copolymer | METAC/Lignin Molar Ratio | Charge Density, meq/g | Mn, ×106 g/mol | Mw, ×106 g/mol | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 0.8 | 1.36 | 0.32 | 0.55 | 1.718 |
| Sample 2 | 1.0 | 2.12 | 0.45 | 0.83 | 1.844 |
| Sample 3 | 1.3 | 2.67 | 0.96 | 1.38 | 1.438 |
| Sample 4 | 1.6 | 2.93 | 1.15 | 1.65 | 1.434 |
| Dye | Molecular Formula | Mw, g/mol | Purity, % | λmax, nm | Anionic Charge Density, meq/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RB5 | C26H21N5Na4O19S6 | 991.82 | 55 | 597 | 4.27 |
| RO16 | C20H17N3Na2O11S3 | 617.54 | ≥70 | 493 | 3.24 |
| Dye | Linear Correlation | R² |
|---|---|---|
| RB5 | y = 1.1443x+ 15.217 | 0.9960 |
| RO16 | y = 0.9426x+ 4.1304 | 0.9963 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Kong, F.; Fatehi, P.; Hou, Q. Cationic High Molecular Weight Lignin Polymer: A Flocculant for the Removal of Anionic Azo-Dyes from Simulated Wastewater. Molecules 2018, 23, 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082005
Wang S, Kong F, Fatehi P, Hou Q. Cationic High Molecular Weight Lignin Polymer: A Flocculant for the Removal of Anionic Azo-Dyes from Simulated Wastewater. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082005
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shoujuan, Fangong Kong, Pedram Fatehi, and Qingxi Hou. 2018. "Cationic High Molecular Weight Lignin Polymer: A Flocculant for the Removal of Anionic Azo-Dyes from Simulated Wastewater" Molecules 23, no. 8: 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082005
APA StyleWang, S., Kong, F., Fatehi, P., & Hou, Q. (2018). Cationic High Molecular Weight Lignin Polymer: A Flocculant for the Removal of Anionic Azo-Dyes from Simulated Wastewater. Molecules, 23(8), 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082005






