Discovery of 4,5-Dihydro-1H-thieno[2′,3′:2,3]thiepino [4,5-c]pyrazole-3-carboxamide Derivatives as the Potential Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
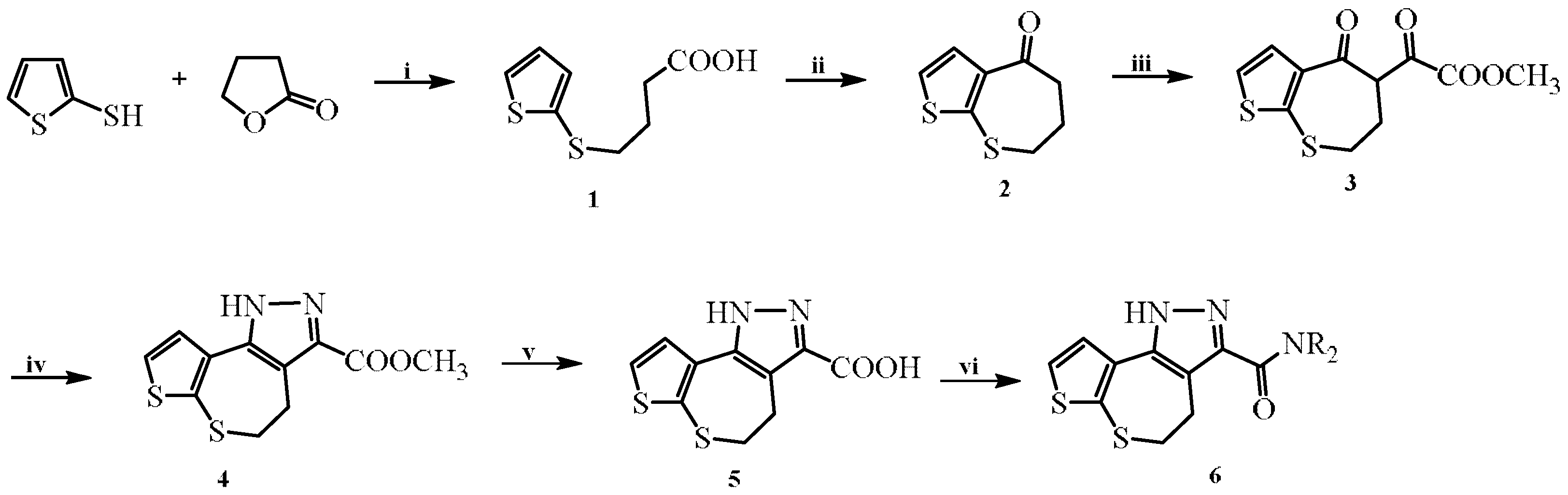
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Biological Evaluation
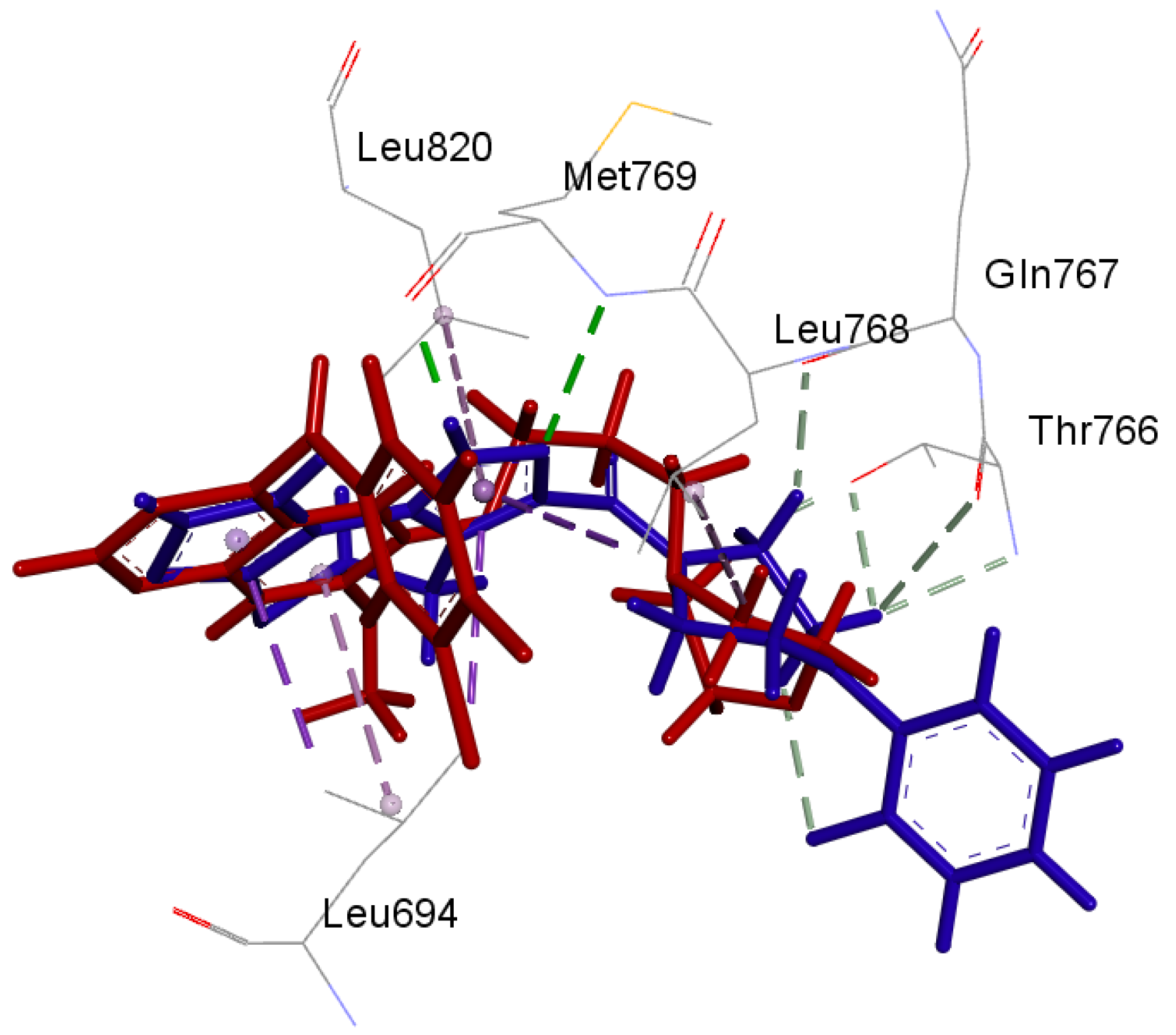
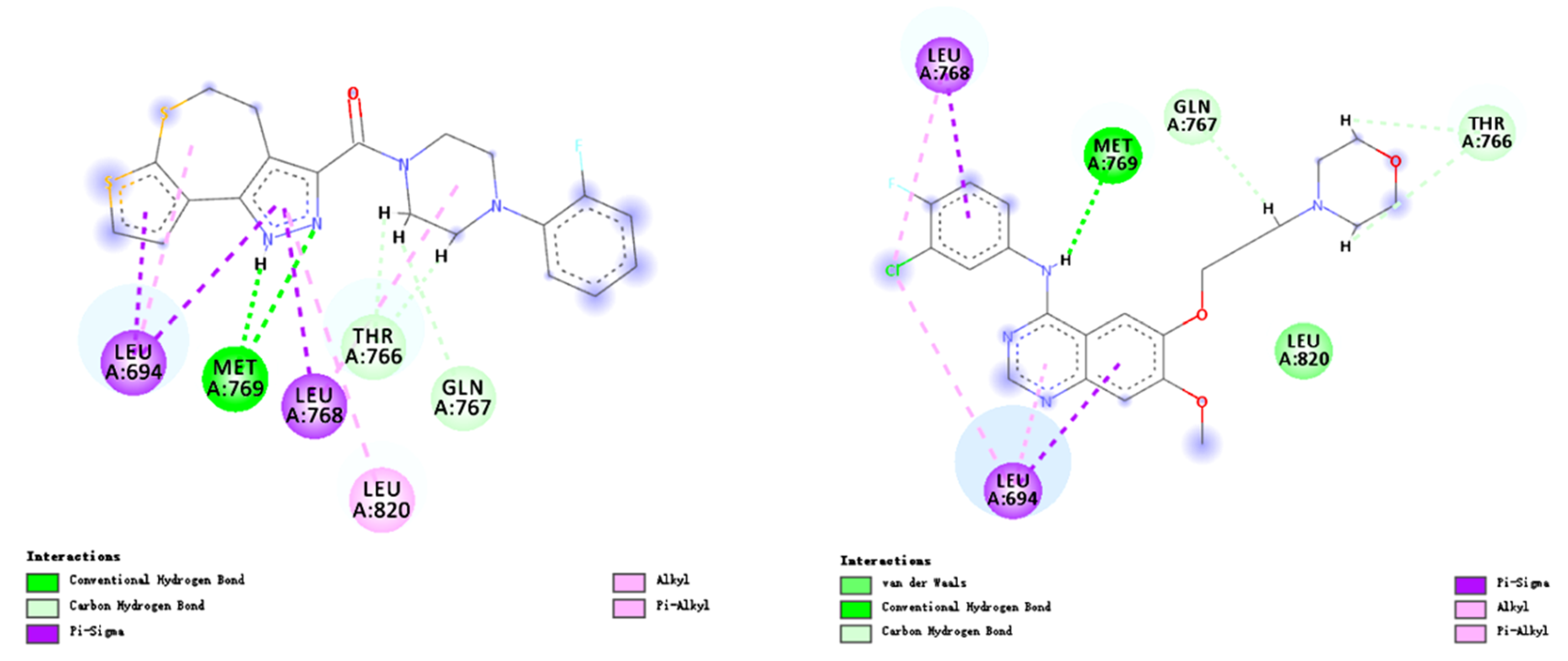
2.3. Docking Study
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. Synthesis of 4-(Thiophen-2-ylthio)butanoic Acid (1)
3.1.2. Synthesis of 6,7-Dihydrothieno[2,3-b]thiepin-4(5H)-one (2)
3.1.3. Synthesis of Methyl Oxo(4-oxo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-b]thiepin-5-yl)acetate (3)
3.1.4. Synthesis of Methyl 4,5-dihydro-1H-thieno[2′,3′:2,3]thiepino[4,5-c] pyrazole-3-carboxylate (4)
3.1.5. Synthesis of 4,5-Dihydro-1H-thieno[2′,3′:2,3]thiepin[4,5-c]pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid (5)
3.1.6. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 4,5-Dihydro-1H-thieno[2′,3′:2,3]thiepino[4,5-c]pyrazole-3-carboxamides (6a–6l)
3.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.3. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonello, A.; Tarozzi, A.; Morroni, F.; Cavalli, A.; Rosini, M.; Hrelia, P.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Melchiorre, C. Multitarget-directed drug design strategy: A novel molecule designed to block epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and to exert proapoptotic effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6642–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscatello, D.K.; Holgado-Madruga, M.; Godwin, A.K.; Ramirez, G.; Gunn, G.; Zoltick, P.W.; Biegel, J.A.; Hayes, R.L.; Wong, A.J. Frequent expression of a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in multiple human tumors. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 5536–5539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salomon, D.S.; Brandt, R.; Ciardiello, F.; Normanno, N. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 1995, 19, 183–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Berezov, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Drebin, J.; Murali, R.; Greene, M.I. ErbB receptors: From oncogenes to targeted cancer therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.J.; Kumar, R. Epidermal growth factor receptor family tyrosine kinases as signal integrators and therapeutic targets. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assefa, H.; Kamath, S.; Buolamwini, J.K. 3D-QSAR and docking studies on 4-anilinoquinazoline and 4-anilinoquinoline epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2003, 17, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P. Protein kinases—The major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, D.W.; Bridges, A.J.; Denny, W.A.; Doherty, A.; Greis, K.D.; Hicks, J.L.; Hook, K.E.; Keller, P.R.; Leopold, W.R.; Loo, J.A.; et al. Specific, irreversible inactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor and erbB2, by a new class of tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12022–12027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, J.D.; Barbacci, E.G.; Iwata, K.K.; Arnold, L.; Boman, B.; Cunningham, A.; DiOrio, C.; Doty, J.; Morin, M.J.; Moyer, M.P.; et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4838–4848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Liu, Y.; Lemmon, M.A.; Radhakrishnan, R. Erlotinib binds both inactive and active conformations of the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain. Biochem. J. 2012, 448, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponticello, G.S.; Freedman, M.B.; Habecker, C.N.; Holloway, M.K.; Amato, J.S.; Conn, R.S.; Baldwin, J.J. Utilization of α, β-unsaturated acids as Michael acceptors for the synthesis of thieno[2,3-b]thiopyrans. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Yin, B.Z.; Jiang, G.J.; Imafuku, K. Synthesis of isochroman-fused pyrazolone and pyrimidine derivatives. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1990, 27, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.R.; Yin, J.G.; Wang, J.J. Synthesis of isochromano[4,3-C]pyrazole substituted with biheterocycle at 3-position. J. Yantai Univ. Nat. Sci. Eng. Ed. 2002, 15, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.F.; Guo, J.L.; Ji, Y.M.; Pan, G.F.; Liu, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.P. Reciprocal negative regulation between EGFR and DEPTOR plays an important role in the progression of lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.J.; Kao, L.T. Cytotoxic enhancement of hexapeptide-conjugated micelles in EGFR high-expressed cancer cells. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Luan, T.; Kong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.F. Synthesis and anti-tumor activities of 4-anilinoquinoline derivatives. Molecules 2016, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the all target compounds are available from the authors. |
| No. | Substituents | IC50 (μM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A549 | HepG2 | ||
| 6a | 4-methylpiperazin-1-yl | 23.44 ± 3.32 | >200 |
| 6b | 4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl | 21.38 ± 14.39 | >200 |
| 6c | 4-(4-methylphenyl)piperazin-1-yl | 11.03 ± 1.96 | >200 |
| 6d | 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl | 13.13 ± 1.21 | >200 |
| 6e | 4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl | 92.71 ± 23.90 | >200 |
| 6f | 4-(2-methylphenyl)piperazin-1-yl | 3.79 ± 13.39 | >200 |
| 6g | 4-(2-fluorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl | 9.68 ± 1.95 | >200 |
| 6h | 4-(2-chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl | 28.68 ± 11.71 | >200 |
| 6i | 4-(diphenylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl | 104.98 ± 44.66 | >200 |
| 6j | pyrrolidin-1-yl | 25.98 ± 8.00 | >200 |
| 6k | piperidin-1-yl | 27.94 ± 13.79 | >200 |
| 6l | morpholin-4-yl | 12.62 ± 14.76 | >200 |
| Gifitinib | 8.58 ± 1.65 | >200 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, J.; Lu, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Jin, Z.; Zhan, X.; Hu, J.; Wan, D.C.-c.; Hu, C. Discovery of 4,5-Dihydro-1H-thieno[2′,3′:2,3]thiepino [4,5-c]pyrazole-3-carboxamide Derivatives as the Potential Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081980
Ke J, Lu Q, Wang X, Sun R, Jin Z, Zhan X, Hu J, Wan DC-c, Hu C. Discovery of 4,5-Dihydro-1H-thieno[2′,3′:2,3]thiepino [4,5-c]pyrazole-3-carboxamide Derivatives as the Potential Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081980
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Jia, Qi Lu, Xin Wang, Rui Sun, Zhe Jin, Xiaoyi Zhan, Jianshu Hu, David Chi-cheong Wan, and Chun Hu. 2018. "Discovery of 4,5-Dihydro-1H-thieno[2′,3′:2,3]thiepino [4,5-c]pyrazole-3-carboxamide Derivatives as the Potential Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors" Molecules 23, no. 8: 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081980
APA StyleKe, J., Lu, Q., Wang, X., Sun, R., Jin, Z., Zhan, X., Hu, J., Wan, D. C.-c., & Hu, C. (2018). Discovery of 4,5-Dihydro-1H-thieno[2′,3′:2,3]thiepino [4,5-c]pyrazole-3-carboxamide Derivatives as the Potential Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules, 23(8), 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081980







