Compound K Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Human Liver Cancer Cells by Regulating STAT3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
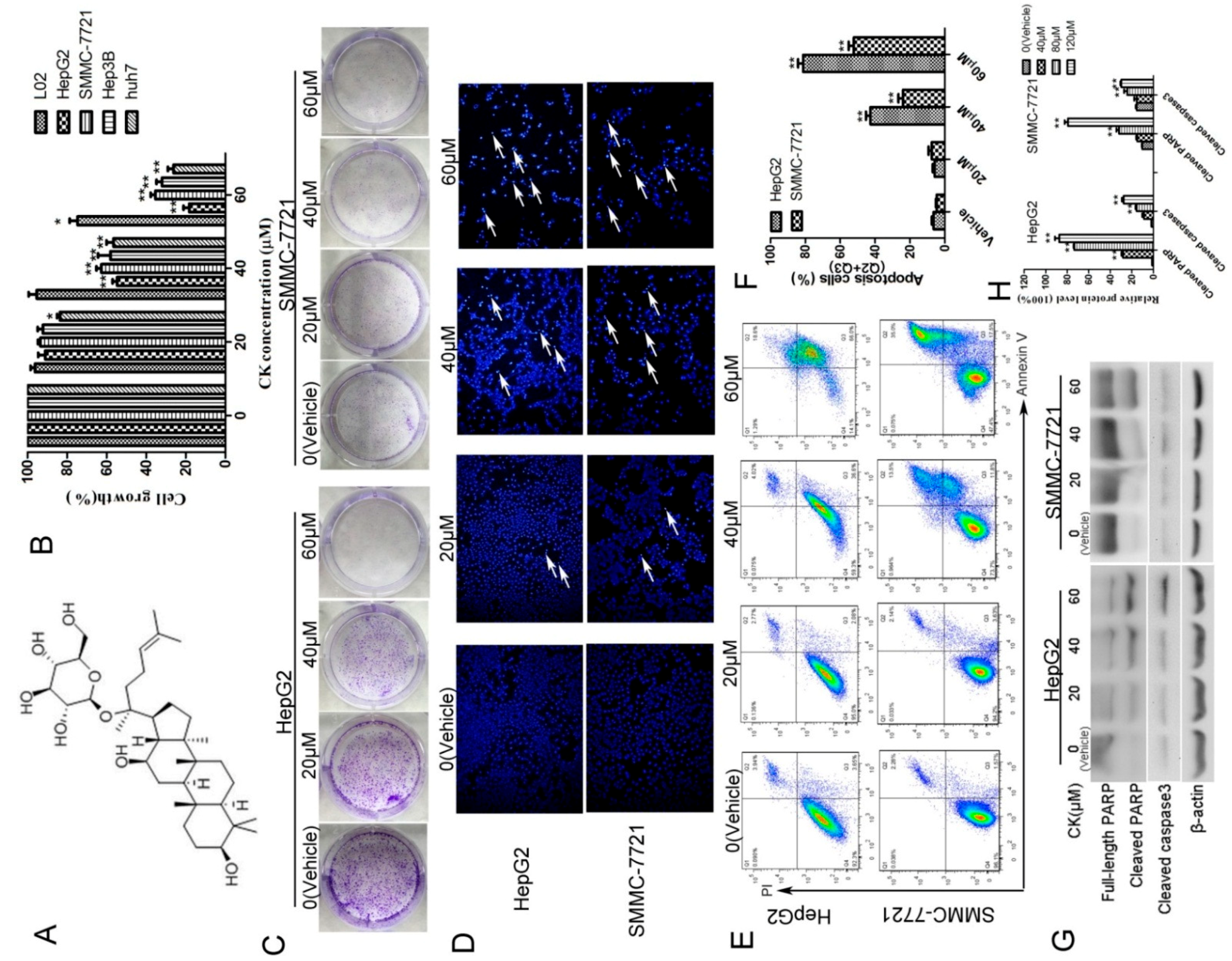
2.1. CK Inhibited the Growth of HepG2 and SMMC-7721 Cells by Inducing Apoptosis
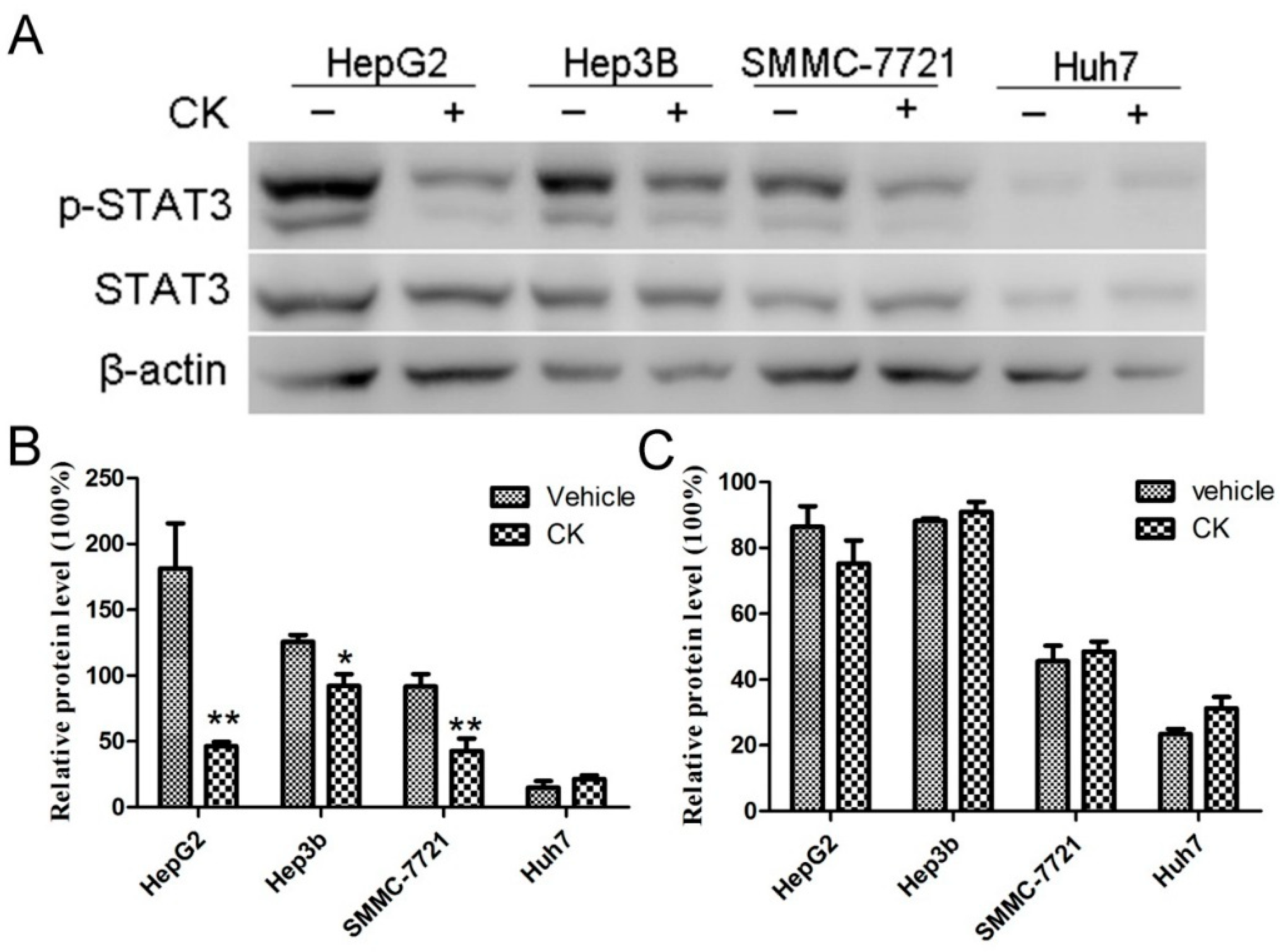
2.2. CK Downregulated p-STAT3 Levels in Different HCC Cell Lines
2.3. CK Inhibited p-STAT3 Expression in HepG2 and SMMC-7721 Cells
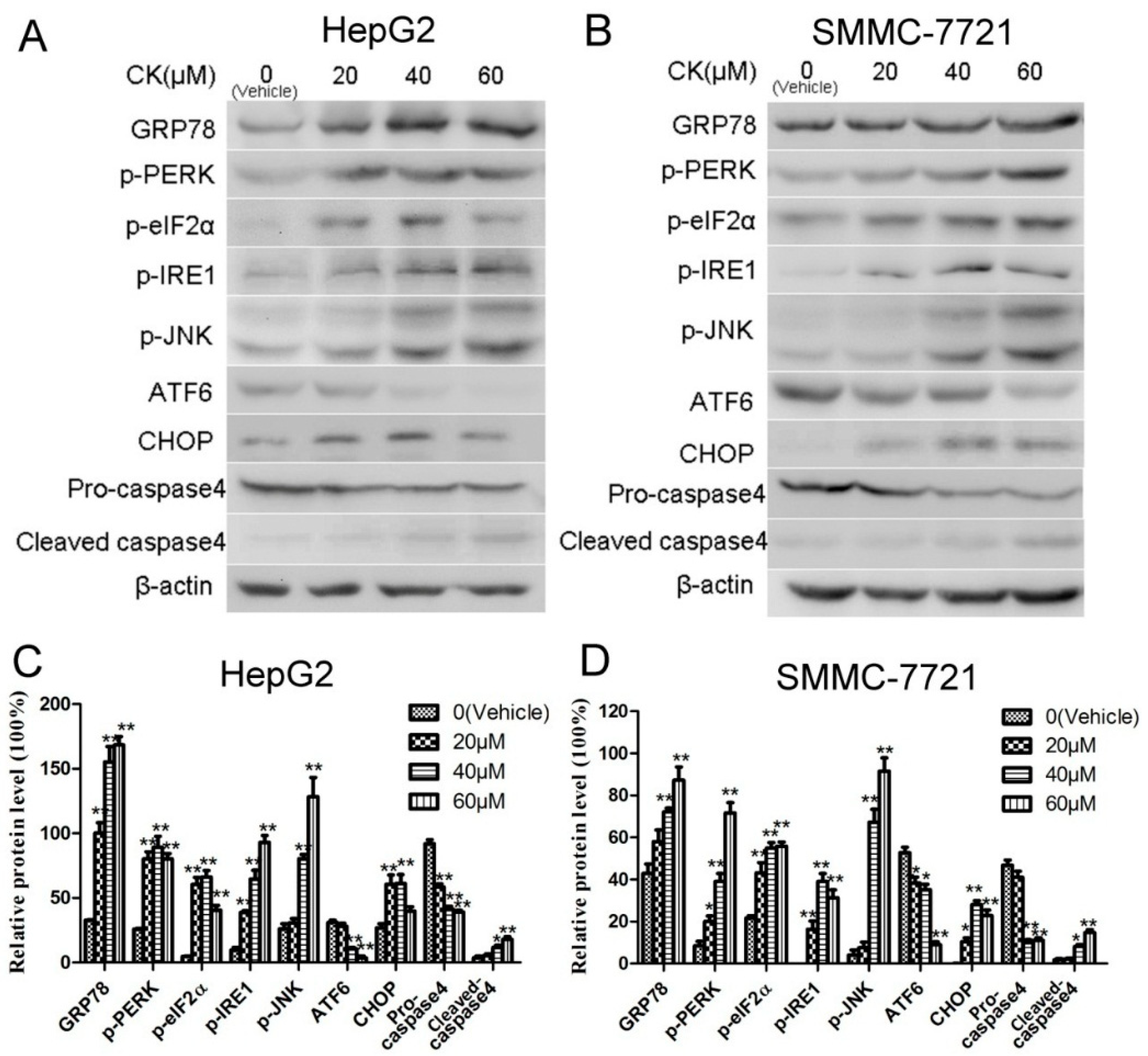
2.4. CK Induced ERS in HepG2 and SMMC-7721 Cells
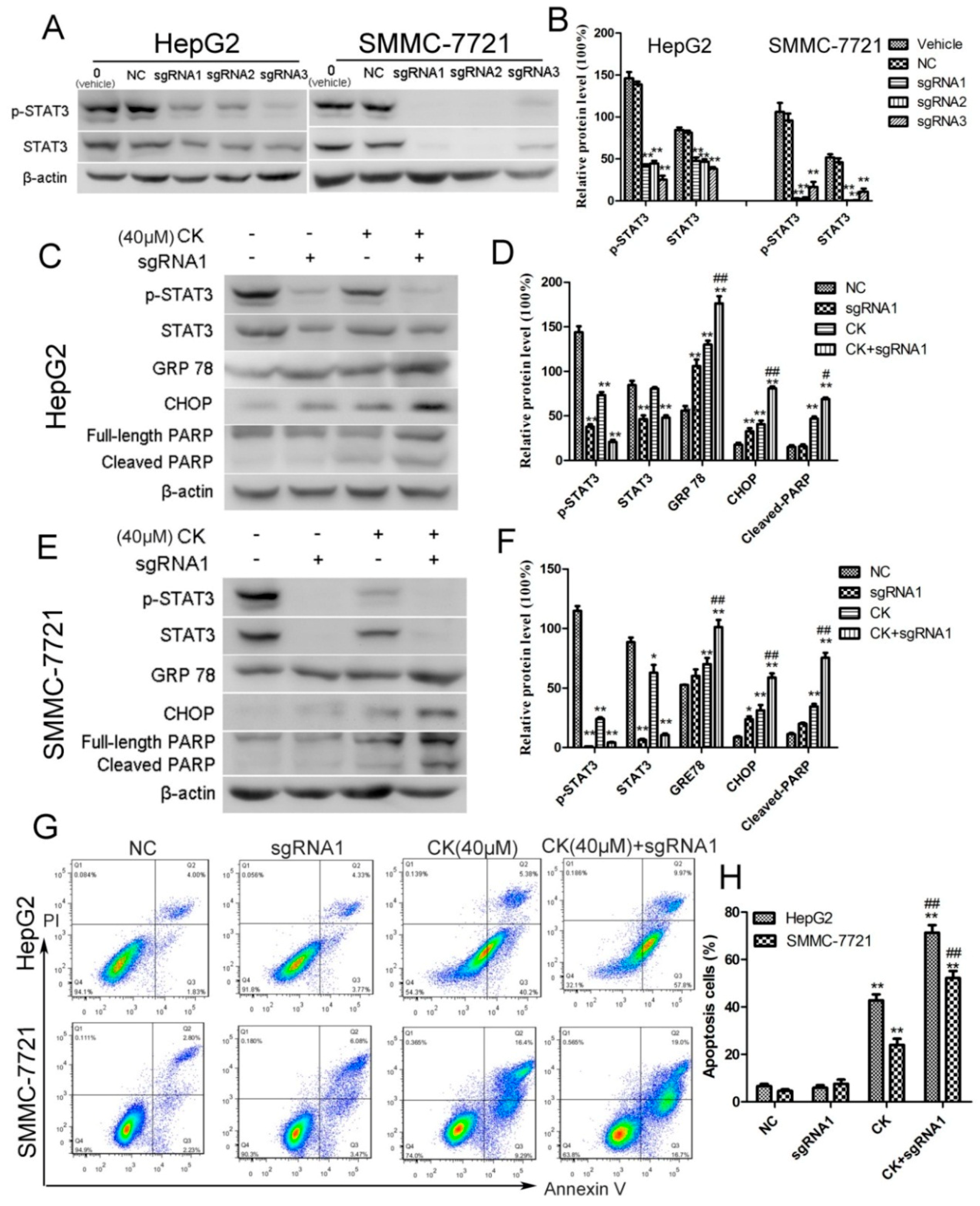
2.5. STAT3 Inhibition Enhanced ERS and Apoptosis in HepG2 and SMMC-7721 Cells
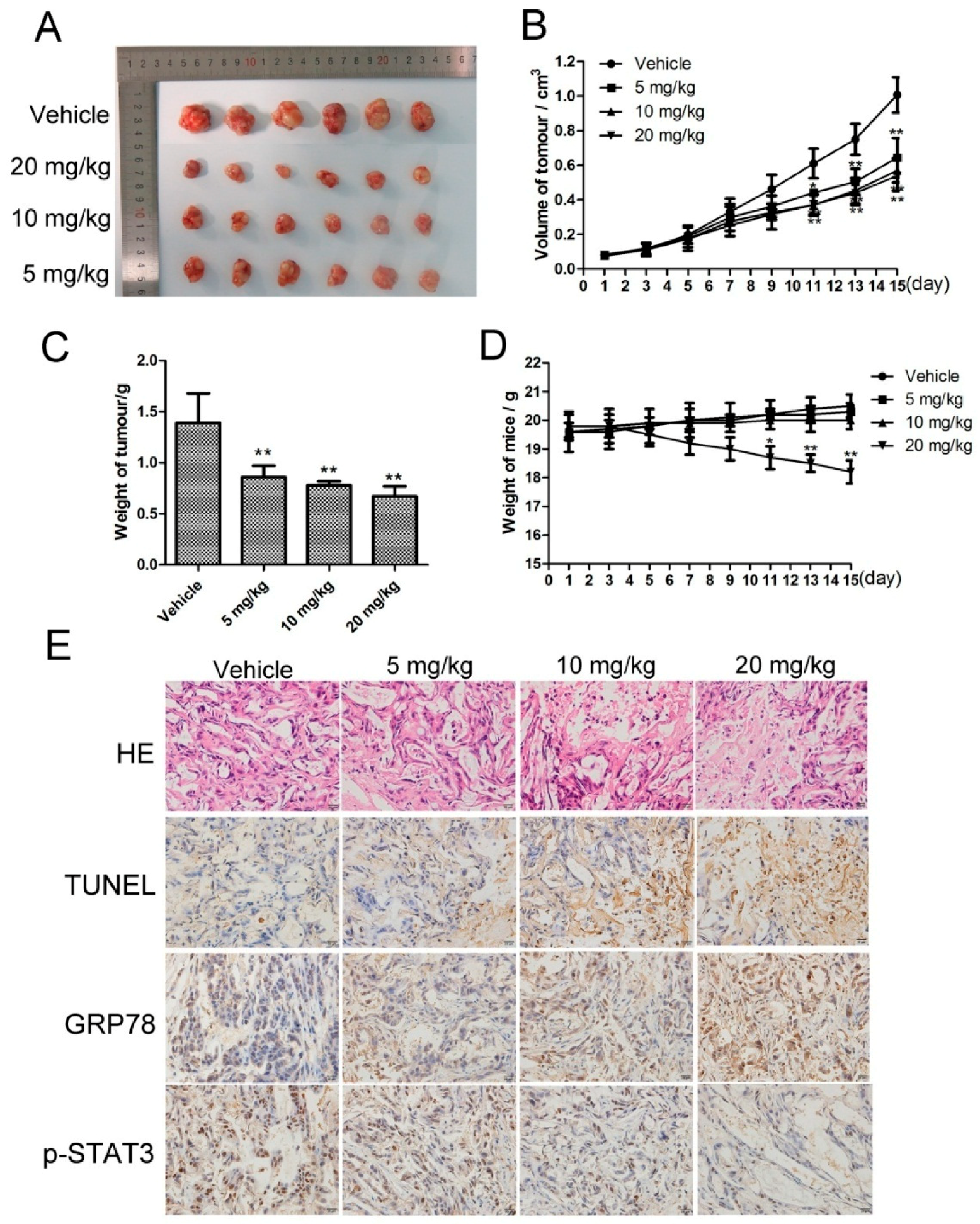
2.6. CK Inhibited In Vivo Tumor Growth, and STAT3 and ERS Were Involved in the Antitumor Effects
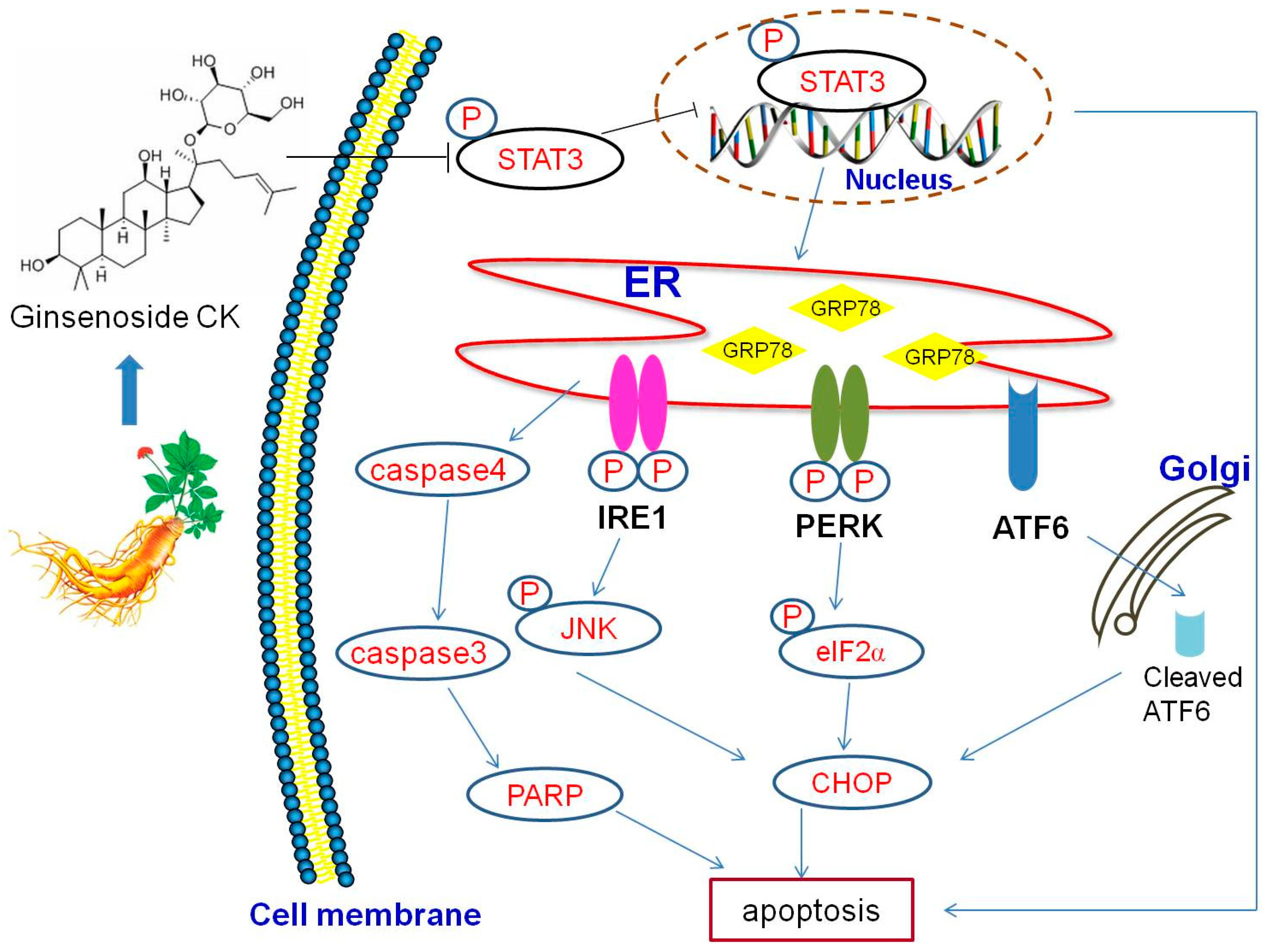
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Growth Assay
4.3. Colony-Forming Assay
4.4. Fluorescent Staining
4.5. Annexin V/PI Double Staining
4.6. ICC Staining Assay
4.7. IHC Staining Assay
4.8. IF Assay
4.9. EMSA
4.10. CRISPR/Cas9 Mediated STAT3 Knockdown
4.11. Western Blot Analysis
4.12. Animals and Tumor Implantation
4.13. HE Staining
4.14. TUNEL Assay
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attele, A.S.; Wu, J.A.; Yuan, C.S. Ginseng pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, D.; Pantuso, T. Panax ginseng. Am. Fam. Physician 2003, 68, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nag, S.A.; Qin, J.J.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Ginsenosides as Anticancer Agents: In vitro and in vivo Activities, Structure-Activity Relationships, and Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.K.; Choo, M.K.; Kim, E.J.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Antiallergic activity of ginsenoside Rh2. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xue, W.; Zhao, W.J.; Li, K.X. Pharmacokinetics and dopamine/acetylcholine releasing effects of ginsenoside Re in hippocampus and mPFC of freely moving rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Moon, C.K.; Lee, B.H. Antitumor activity of a novel ginseng saponin metabolite in human pulmonary adenocarcinoma cells resistant to cisplatin. Cancer Lett. 1999, 144, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, C.; Hasegawa, H.; Murata, J.; Saiki, I. The expression of in vivo antimetastatic effect of ginseng protopanaxatriol saponins is mediated by their intestinal bacterial metabolites after oral administration. J. Tradit. Med. 1997, 14, 180–185. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.Y.; Yuan, H.D.; Chung, I.K.; Chung, S.H. Compound K, intestinal metabolite of ginsenoside, attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation via AMPK activation in human hepatoma cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.U.; Bae, E.A.; Han, M.J. Hepatoprotective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced liver injury. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, S.J.; Song, H.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, E.O.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, S.H. Inhibition of JAK1/STAT3 signaling mediates compound K-induced apoptosis in human multiple myeloma U266 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liao, J.; Gong, C.; Sun, C.; Zhou, X.; Wei, X.; Zhang, T.; Gao, Q.; Ma, D.; et al. Quercetin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress to enhance cDDP cytotoxicity in ovarian cancer: Involvement of STAT3 signaling. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Perumal, E.; Li, F.; Nachiyappan, A.; Dai, X.; Swamy, S.N.; Ahn, K.S.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.H.; et al. Potential role of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival, proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haura, E.B.; Zheng, Z.; Song, L.; Cantor, A.; Bepler, G. Activated epidermal growth factor receptor-Stat-3 signaling promotes tumor survival in vivo in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8288–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, K.; Resat, H. Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Sandur, S.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sung, B.; Ichikawa, H. Targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 for prevention and therapy of cancer: Modern target but ancient solution. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1091, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Jove, R. The STATs of cancer—New molecular targets come of age. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.T.; Chu, P.Y.; Shiau, C.W.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, Y.S.; Hung, M.H.; Chen, L.J.; Chen, P.L.; Su, J.C.; Lin, P.Y.; et al. STAT3 mediates regorafenib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5768–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.; Oxford, A.E.; Tawara, K.; Jorcyk, C.L.; Oxford, J.T. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Cartilage Pathophysiology; Contributing Factors to Apoptosis and Osteoarthritisv. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, M.; Fan, Z.H.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, S.S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhou, P.; et al. Protective effects of a G. lucidum proteoglycan on INS-1 cells against IAPP-induced apoptosis via attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress and modulating CHOP/JNK pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, Y. The Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Cardiovascular Disease and Exercise. Int. J. Vasc. Med. 2017, 2017, 2049217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Im, M.; Ma, J.Y. A novel herbal formula, SGE, induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cancer cell death and alleviates cachexia symptoms induced by colon-26 adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16284–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchetti, F.; Crinelli, R.; Cesarini, E.; Canonico, B.; Guidi, L.; Zerbinati, C.; Di Sario, G.; Zamai, L.; Magnani, M.; Papa, S.; et al. Endothelial cells, endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxysterols. Redox Biol. 2017, 13, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iurlaro, R.; Muñoz-Pinedo, C. Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2640–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamuro, A.; Kishino, T.; Ohshima, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kimura, T.; Kasai, A.; Maeda, S. Caspase-4 directly activates caspase-9 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 115, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavami, S.; Yeganeh, B.; Stelmack, G.L.; Kashani, H.H.; Sharma, P.; Cunnington, R.; Rattan, S.; Bathe, K.; Klonisch, T.; Dixon, I.M.; et al. Apoptosis, autophagy and ER stress in mevalonate cascade inhibition-induced cell death of human atrial fibroblasts. J. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.F.; Wang, S.N.; Wu, C.F.; Yeh, Y.T.; Chai, C.Y.; Chunag, S.C.; Sheen, M.C.; Lee, K.T. Altered p-STAT3 (tyr705) expression is associated with histological grading and intratumour microvessel density in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.L.; Lee, C.H.; Chen, C.M.; Cheng, C.W.; Chen, P.N.; Ying, T.H.; Hsieh, Y.H. Protodioscin Induces Apoptosis Through ROS-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress via the JNK/p38 Activation Pathways in Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, R.; Guo, Q.; Li, J.; Bao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Hua, B. Norcantharidin inhibits IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK2/STAT3/TWIST signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, G.; Lou, Z.; Xu, G.; Zhang, G. Cryptotanshinone enhances the effect of Arsenic trioxide in treating liver cancer cell by inducing apoptosis through downregulating phosphorylated-STAT3 in vitro and in vivo. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.Z.; Ming, Y.L.; Chen, L.H.; Zheng, G.H.; Liu, S.S.; Chen, Q.X. Compound K-induced apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma MHCC97-H cells in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, C.W.; Son, Y.M.; Gu, M.J.; Kim, G.; Lee, I.K.; Kye, Y.C.; Kim, H.W.; Song, K.D.; Chu, H.; Park, B.C.; et al. A Bacterial Metabolite, Compound K, Induces Programmed Necrosis in MCF-7 Cells via GSK3β. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Karin, M. NF-κB and STAT3 - key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Jing, Y.; Cao, L.; Gong, C.; Gong, Z.; Cao, X. A novel synthetic Asiatic acid derivative induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation and mobility of gastric cancer cells by suppressing STAT3 signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 10, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilamathi, M.; Sivaramakrishnan, V. Artesunate acts as fuel to fire in sensitizing HepG2 cells towards TRAIL mediated apoptosis via STAT3 inhibition and DR4 augmentation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.; Guo, S.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Hu, T. Intestinal metabolite compound K of ginseng saponin potently attenuates metastatic growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by augmenting apoptosis via a Bid-mediated mitochondrial pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12753–12760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyadomari, S.; Mori, M. Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrin, R.; Arumugam, S.; Soetikno, V.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Pitchaimani, V.; Karuppagounder, V.; Sreedhar, R.; Harima, M.; Suzuki, H.; Miyashita, S.; et al. Curcumin ameliorates streptozotocin induced liver damage through modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis in diabetic rats. Free Radic. 2015, 49, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Kanda, T.; Nakamoto, S.; Haga, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Nakamura, M.; Wu, S.; Mikata, R.; Yokosuka, O. Knockdown of glucose-regulated protein 78 enhances poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage in human pancreatic cancer cells exposed to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitomi, J.; Katayama, T.; Eguchi, Y.; Kudo, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Koyama, Y.; Manabe, T.; Yamagishi, S.; Bando, Y.; Imaizumi, K.; et al. Involvement of caspase-4 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and Abeta-induced cell death. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Meng, X.B.; Yu, Y.L.; Sun, G.B.; Xu, X.D.; Zhang, X.P.; Dong, X.; Ye, J.X.; Xu, H.B.; Sun, Y.F.; et al. Elatoside C protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes through the reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress partially depending on STAT3 activation. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, W.; Tao, J.; Xin, P.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Wei, M. Fasudil protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress and modulating SERCA activity: The differential role for PI3K/Akt and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Wang, B.; Li, H.; Chai, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S.; Stefan, H. A kindling model of pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy in Sprague-Dawley rats induced by Coriaria lactone and its possible mechanism. Epilepsia 2003, 44, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Q.; Jiao, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X. Compound K Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Human Liver Cancer Cells by Regulating STAT3. Molecules 2018, 23, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061482
Zhang X, Zhang S, Sun Q, Jiao W, Yan Y, Zhang X. Compound K Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Human Liver Cancer Cells by Regulating STAT3. Molecules. 2018; 23(6):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061482
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuan, Silin Zhang, Qitong Sun, Wenjun Jiao, Yan Yan, and Xuewu Zhang. 2018. "Compound K Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Human Liver Cancer Cells by Regulating STAT3" Molecules 23, no. 6: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061482
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhang, S., Sun, Q., Jiao, W., Yan, Y., & Zhang, X. (2018). Compound K Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in Human Liver Cancer Cells by Regulating STAT3. Molecules, 23(6), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23061482



