Structural Optimization of Foldamer-Dendrimer Conjugates as Multivalent Agents against the Toxic Effects of Amyloid Beta Oligomers
Abstract
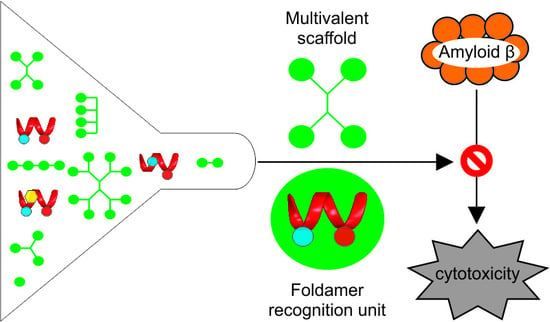
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Side Chain Alteration on Aβ Binding
2.2. Quantitative Study of the Effects of Multivalency and Topology on Aβ Binding
2.3. Effects of Multivalency on Biological Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. General Methods for the Synthesis of α-Peptidic Scaffolds and β-Peptidic Recognition Segments
3.2.2. Synthesis of Compounds 2a–2i and 7
3.2.3. Synthesis of Compound 3
3.2.4. Synthesis of Compound 4
3.2.5. Synthesis of Compound 5
3.2.6. Synthesis of Compound 6
3.2.7. Synthesis of Compound 8
3.2.8. Synthesis of Compound 9
3.3. Preparation of Aβ Samples
3.4. ITC Measurements
3.5. Ex Vivo Testing Aβ (1–42) Toxicity on Acute Hippocampal Slices
3.6. Impedance Based Measurement of Aβ Toxicity on Neuroblastoma Cells
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eisele, Y.S.; Monteiro, C.; Fearns, C.; Encalada, S.E.; Wiseman, R.L.; Powers, E.T.; Kelly, J.W. Targeting protein aggregation for the treatment of degenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aguzzi, A.; O’connor, T. Protein aggregation diseases: Pathogenicity and therapeutic perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science 2002, 298, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haass, C.; Selkoe, D.J. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: Lessons from the Alzheimer’s amyloid [beta]-peptide. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayed, R.; Head, E.; Thompson, J.L.; McIntire, T.M.; Milton, S.C.; Cotman, C.W.; Glabe, C.G. Common structure of soluble amyloid oligomers implies common mechanism of pathogenesis. Science 2003, 300, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Vassar, R. Targeting the β secretase BACE1 for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golde, T.E.; Koo, E.H.; Felsenstein, K.M.; Osborne, B.A.; Miele, L. γ-Secretase inhibitors and modulators. BBA-Biomembranes 2013, 1828, 2898–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Taguchi, H.; Hara, M.; Planque, S.A.; Mitsuda, Y.; Paul, S. Metal-dependent amyloid β-degrading catalytic antibody construct. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 180, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeMattos, R.B.; Bales, K.R.; Cummins, D.J.; Dodart, J.C.; Paul, S.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Peripheral anti-Aβ antibody alters CNS and plasma Aβ clearance and decreases brain Aβ burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8850–8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoll, J.A.; Wilkinson, D.; Holmes, C.; Steart, P.; Markham, H.; Weller, R.O. Neuropathology of human Alzheimer disease after immunization with amyloid-β peptide: A case report. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoll, J.A.; Barton, E.; Boche, D.; Neal, J.W.; Ferrer, I.; Thompson, P.; Vlachouli, C.; Wilkinson, D.; Bayer, A.; Games, D.; et al. Aβ species removal after Aβ42 immunization. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neur. 2006, 65, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, C.A.; Ng, V.; McLaurin, J. Small molecule inhibitors of Aβ-aggregation and neurotoxicity. Drug Dev. Res. 2009, 70, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruinsma, I.B.; Karawajczyk, A.; Schaftenaar, G.; de Waal, R.M.; Verbeek, M.M.; van Delft, F.L. A rational design to create hybrid β-sheet breaker peptides to inhibit aggregation and toxicity of amyloid-β. MedChemComm 2011, 2, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guisasola, E.E.B.; Andujar, S.A.; Hubin, E.; Broersen, K.; Kraan, I.M.; Méndez, L.; Delpiccolo, C.M.L.; Masman, M.F.; Rodríguez, A.M.; Enriz, R.D. New mimetic peptides inhibitors of Aβ aggregation. Molecular guidance for rational drug design. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 95, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.; Nadimpally, K.C.; Mondal, T.; Thalluri, K.; Mandal, B. Inhibition of Alzheimer’s amyloid-β peptide aggregation and its disruption by a conformationally restricted α/β hybrid peptide. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2245–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.A.; Poirier, M.A. Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkin, M.R.; Tang, Y.; Wells, J.A. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions: Progressing toward the reality. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.E.; Bayly, A.R.; Abell, C.; Skidmore, J. Small molecules, big targets: Drug discovery faces the protein–protein interaction challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkin, M.R.; Wells, J.A. Small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions: Progressing towards the dream. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Thornton, J.M. Analysis of protein-protein interaction sites using surface patches. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 272, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogan, A.A.; Thorn, K.S. Anatomy of hot spots in protein interfaces. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 280, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sela-Culang, I.; Kunik, V.; Ofran, Y. The structural basis of antibody-antigen recognition. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.M.; Wolchok, J.D.; Old, L.J. Antibody therapy of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, L.M.; Surana, R.; Wang, S. Monoclonal antibodies: Versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, H.M.; Horne, W.S. Folding and function in α/β-peptides: Targets and therapeutic applications. Cur.r Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 28, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, G.; Huc, I. Synthetic foldamers. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5933–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, C.M.; Choi, S.; Shandler, S.; DeGrado, W.F. Foldamers as versatile frameworks for the design and evolution of function. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinek, T.A.; Fülöp, F. Peptidic foldamers: Ramping up diversity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gademann, K.; Ernst, M.; Hoyer, D.; Seebach, D. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Cyclo-β-tetrapeptide as a Somatostatin Analogue. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.M.; Barrick, S.; Hager, M.V.; McFedries, A.; Homan, E.A.; Rabaglia, M.E.; Keller, M.P.; Attie, A.D.; Saghatelian, A.; Bisello, A.; et al. A potent α/β-peptide analogue of GLP-1 with prolonged action in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12848–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, W.S.; Boersma, M.D.; Windsor, M.A.; Gellman, S.H. Sequence-Based Design of α/β-Peptide Foldamers That Mimic BH3 Domains. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2853–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabrele, C.; Martinek, T.A.; Reiser, O.; Berlicki, Ł. Peptides containing β-amino acid patterns: Challenges and successes in medicinal chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9718–9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fülöp, L.; Mándity, I.M.; Juhász, G.; Szegedi, V.; Hetényi, A.; Wéber, E.; Bozsó, Z.; Simon, D.; Benkő, M.; Király, Z.; et al. A foldamer-dendrimer conjugate neutralizes synaptotoxic β-amyloid oligomers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olajos, G.; Bartus, E.; Schuster, I.; Lautner, G.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Szögi, T.; Fülöp, L.; Martinek, T.A. Multivalent foldamer-based affinity assay for selective recognition of Aβ oligomers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Vorobyov, I.; Allen, T.W. The different interactions of lysine and arginine side chains with lipid membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 11906–11920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozes, E.; Hunya, A.; Posa, A.; Penke, B.; Datki, Z. A novel method for the rapid determination of beta-amyloid toxicity on acute hippocampal slices using MTT and LDH assays. Brain Res. Bull. 2012, 87, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, N.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Abassi, Y.A. The xCELLigence system for real-time and label-free monitoring of cell viability. Mamm. Cell Viability 2011, 740, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hettiarachchi, N.; Dallas, M.; Al-Owais, M.; Griffiths, H.; Hooper, N.; Scragg, J.; Boyle, J.; Peers, C. Heme oxygenase-1 protects against Alzheimer’s amyloid-β1-42-induced toxicity via carbon monoxide production. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, A.C. The role of apoptotic pathways in Alzheimer’s disease neurodegeneration and cell death. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2005, 2, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozso, Z.; Penke, B.; Simon, D.; Laczkó, I.; Juhász, G.; Szegedi, V.; Kasza, A.; Soós, K.; Hetényi, A.; Wéber, E.; et al. Controlled in situ preparation of Aβ (1–42) oligomers from the isopeptide “iso-Aβ (1–42)”, physicochemical and biological characterization. Peptides 2010, 31, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, L.; Walter, F.R.; Bocsik, A.; Veszelka, S.; Ózsvári, B.; Puskás, L.G.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Deli, M.A. Kinetic analysis of the toxicity of pharmaceutical excipients Cremophor EL and RH40 on endothelial and epithelial cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boas, U.; Heegaard, P.M. Dendrimers in drug research. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; MacKay, J.A.; Fréchet, J.M.; Szoka, F.C. Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chafekar, S.M.; Malda, H.; Merkx, M.; Meijer, E.W.; Viertl, D.; Lashuel, H.A.; Baas, F.; Scheper, W. Branched KLVFF Tetramers Strongly Potentiate Inhibition of β-Amyloid Aggregation. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, J.; Kim, D.J. Multivalent & multifunctional ligands to β-amyloid. Curr. Pharm. Design 2009, 15, 637–658. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski, T.; Goñi, F. Immunotherapeutic approaches for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2015, 85, 1162–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |






| Compound | KD ITC (nM−1) | ΔG (kcal M−1) | ΔH (kcal M−1) | −TΔS (kcal M−1) | KD ELISA (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | 27.63 ± 7.74 1 | −9.97 | 51.33 | 61.30 | 0.95 ± 0.06 |
| 239.62 ± 68.67 2 | −8.73 | 0.31 | 9.04 | ||
| 2b | 53.20 ± 38.70 1 | −9.59 | 6.57 | 16.16 | 5.36 ± 1.42 |
| 373.40 ± 104.33 2 | −8.78 | 0.64 | 9.42 | ||
| 2c | 2.53 ± 1.81 1 | −11.34 | 1.96 | 13.30 | 1.92 ± 0.21 |
| 175.20 ± 46.41 2 | −8.91 | 0.76 | 9.67 | ||
| 2d | ND | ND | ND | ND | 7.70 ± 3.06 |
| 2e | ND | ND | ND | ND | 2.71 ± 0.21 |
| 2f | 19.30 ± 9.40 1 | −10.17 | 2.48 | 12.66 | 1.79 ± 0.09 |
| 816.40 ± 466.90 2 | −8.03 | 0.27 | 8.30 | ||
| 2g | 34.10 ± 10.00 1 | −9.85 | 4.88 | 14.73 | 1.34 ± 0 04 |
| 652.30 ± 158.50 2 | −8.16 | 0.37 | 8.53 | ||
| 2h | 8.61 ± 5.64 1 | −10.64 | 7.39 | 18.02 | 1.35 ± 0.08 |
| 78.99 ± 45.92 2 | −9.37 | 0.35 | 9.72 | ||
| 2i | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1.59 ± 0 08 |
| Compound | KD (nM−1) | ΔG (kcal M−1) | ΔH (kcal M−1) | −TΔS (kcal M−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2376.1 ± 214.4 * | −7.42 * | 0.36 * | 7.77 * |
| 3 | 721.4 ± 120.1 * | −8.10 * | 1.14 * | 9.24 * |
| 4 | 18.5 ± 13.9 1 | −10.20 | 2.16 | 12.36 |
| 155.0 ± 130.9 2 | −8.98 | 0.28 | 9.26 | |
| 5 | 6.9 ± 1.4 1 | −10.38 | 10.01 | 20.39 |
| 281.1 ± 38.7 2 | −8.25 | 2.55 | 10.80 | |
| 6 | 69.0 ± 12.0 1 | −9.45 | 49.4 | 58.85 |
| 193.4 ± 30.5 2 | −8.88 | 0.31 | 9.17 | |
| 7 | 16.2 ± 8.9 1 | −10.27 | 9.29 | 19.56 |
| 127.6 ± 56.7 2 | −9.09 | 0.23 | 9.32 | |
| 8 | 4.1 ± 2.5 1 | −11.07 | 2.31 | 13.38 |
| 374.0 ± 102.0 2 | −8.48 | 0.51 | 8.99 | |
| 9 | 35.0 ± 19.7 1 | −9.83 | 6.01 | 15.84 |
| 372.1 ± 212.8 2 | −8.48 | 1.18 | 9.66 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartus, É.; Olajos, G.; Schuster, I.; Bozsó, Z.; Deli, M.A.; Veszelka, S.; Walter, F.R.; Datki, Z.; Szakonyi, Z.; Martinek, T.A.; et al. Structural Optimization of Foldamer-Dendrimer Conjugates as Multivalent Agents against the Toxic Effects of Amyloid Beta Oligomers. Molecules 2018, 23, 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102523
Bartus É, Olajos G, Schuster I, Bozsó Z, Deli MA, Veszelka S, Walter FR, Datki Z, Szakonyi Z, Martinek TA, et al. Structural Optimization of Foldamer-Dendrimer Conjugates as Multivalent Agents against the Toxic Effects of Amyloid Beta Oligomers. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102523
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartus, Éva, Gábor Olajos, Ildikó Schuster, Zsolt Bozsó, Mária A. Deli, Szilvia Veszelka, Fruzsina R. Walter, Zsolt Datki, Zsolt Szakonyi, Tamás A. Martinek, and et al. 2018. "Structural Optimization of Foldamer-Dendrimer Conjugates as Multivalent Agents against the Toxic Effects of Amyloid Beta Oligomers" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102523
APA StyleBartus, É., Olajos, G., Schuster, I., Bozsó, Z., Deli, M. A., Veszelka, S., Walter, F. R., Datki, Z., Szakonyi, Z., Martinek, T. A., & Fülöp, L. (2018). Structural Optimization of Foldamer-Dendrimer Conjugates as Multivalent Agents against the Toxic Effects of Amyloid Beta Oligomers. Molecules, 23(10), 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102523