Synthesis, Antifungal Activities and Molecular Docking Studies of Benzoxazole and Benzothiazole Derivatives
Abstract
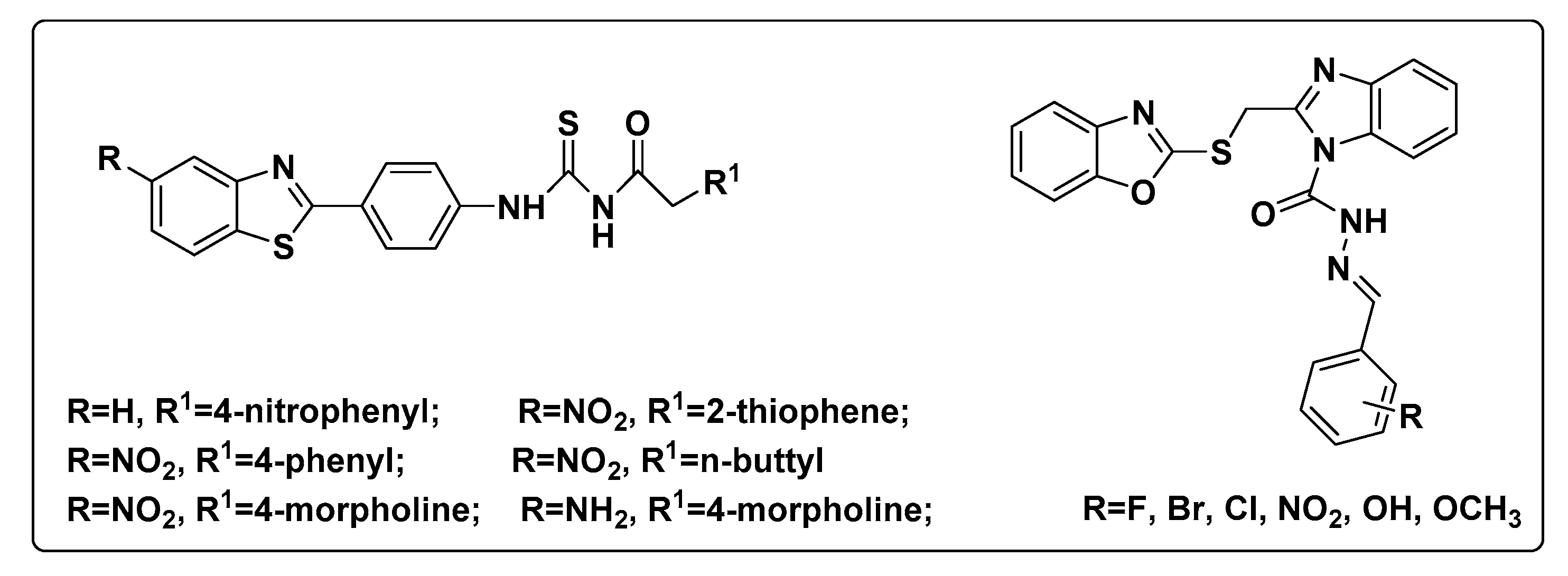
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
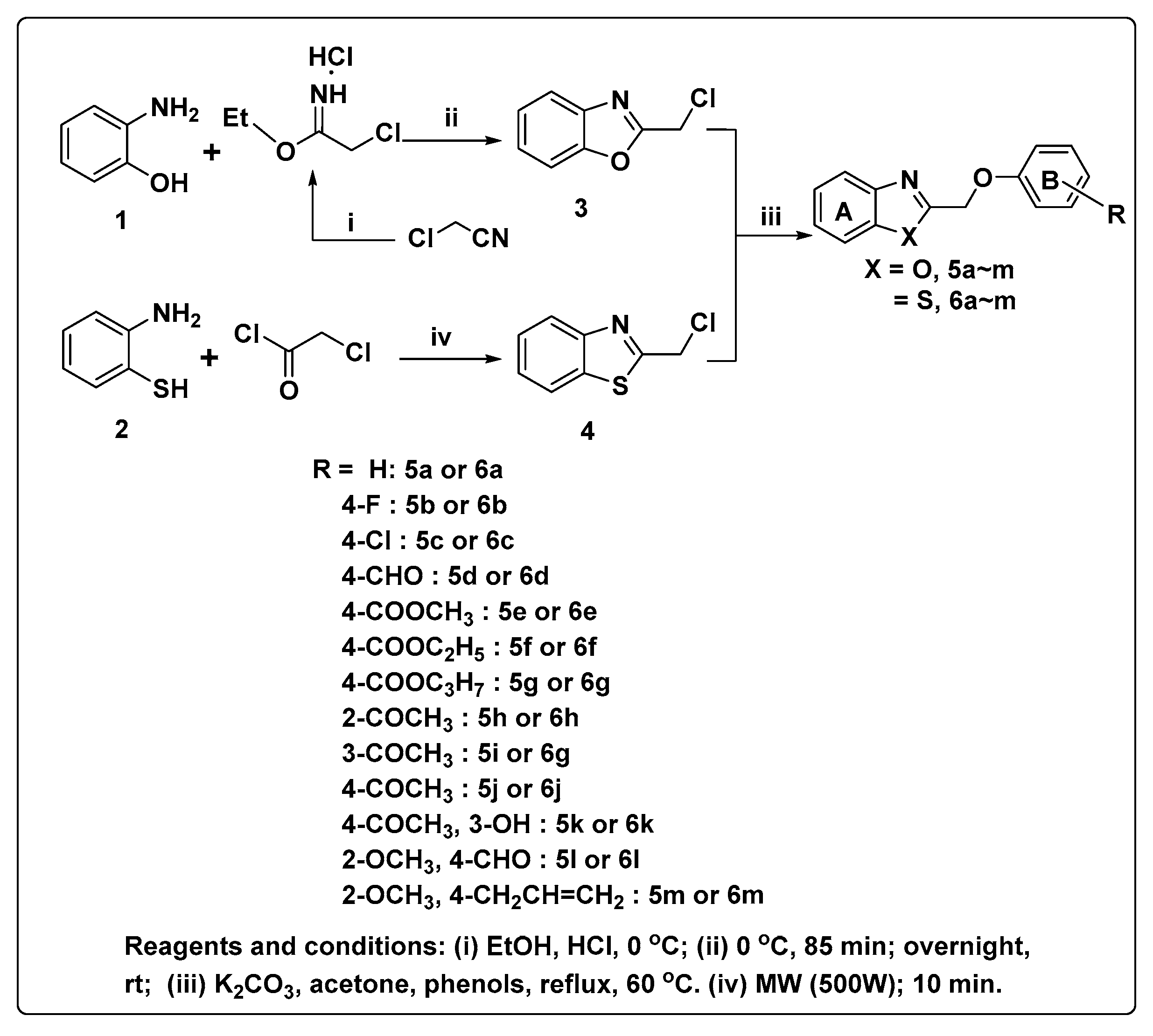
2.1. Chemistry
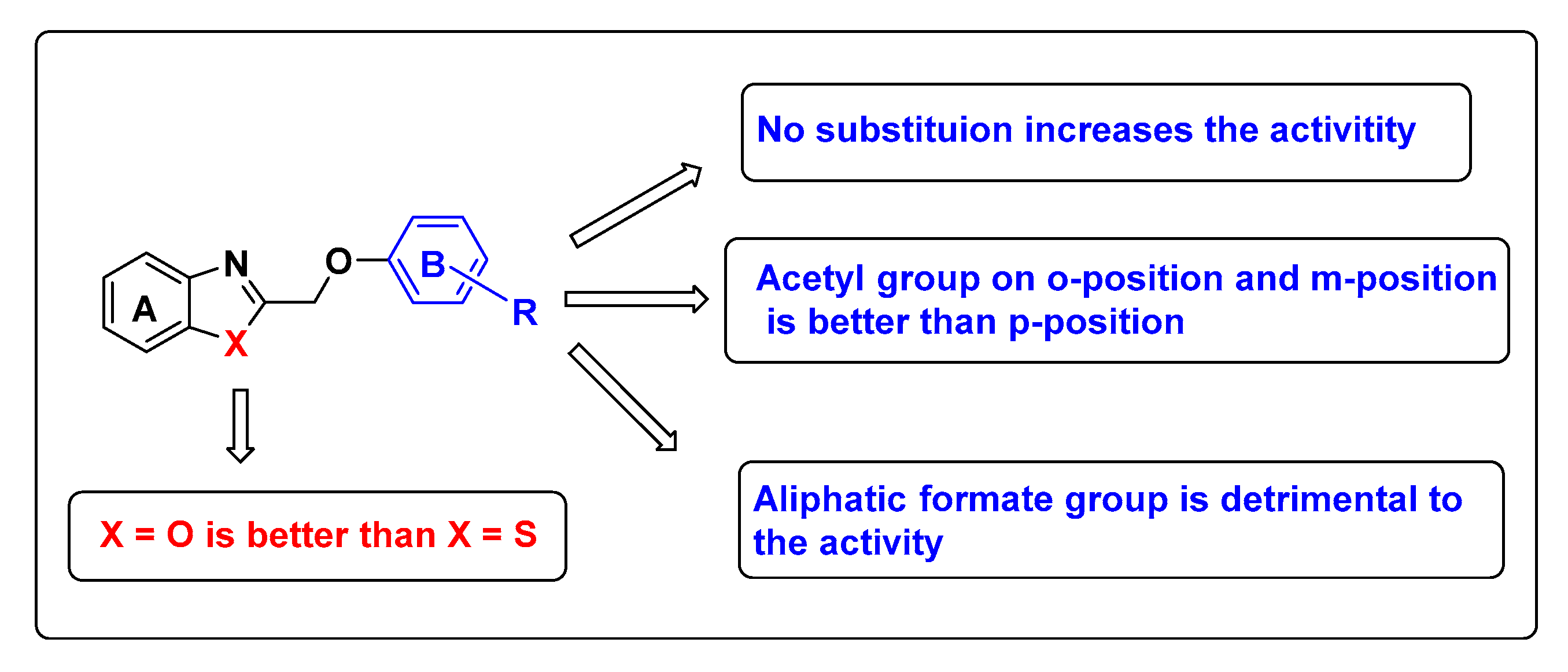
2.2. Antifungal Activity and Structure-Activity Relationships
2.2.1. Antifungal Activity of the Benzoxazole Derivatives
2.2.2. Antifungal Activity of the Benzothiazole Derivatives
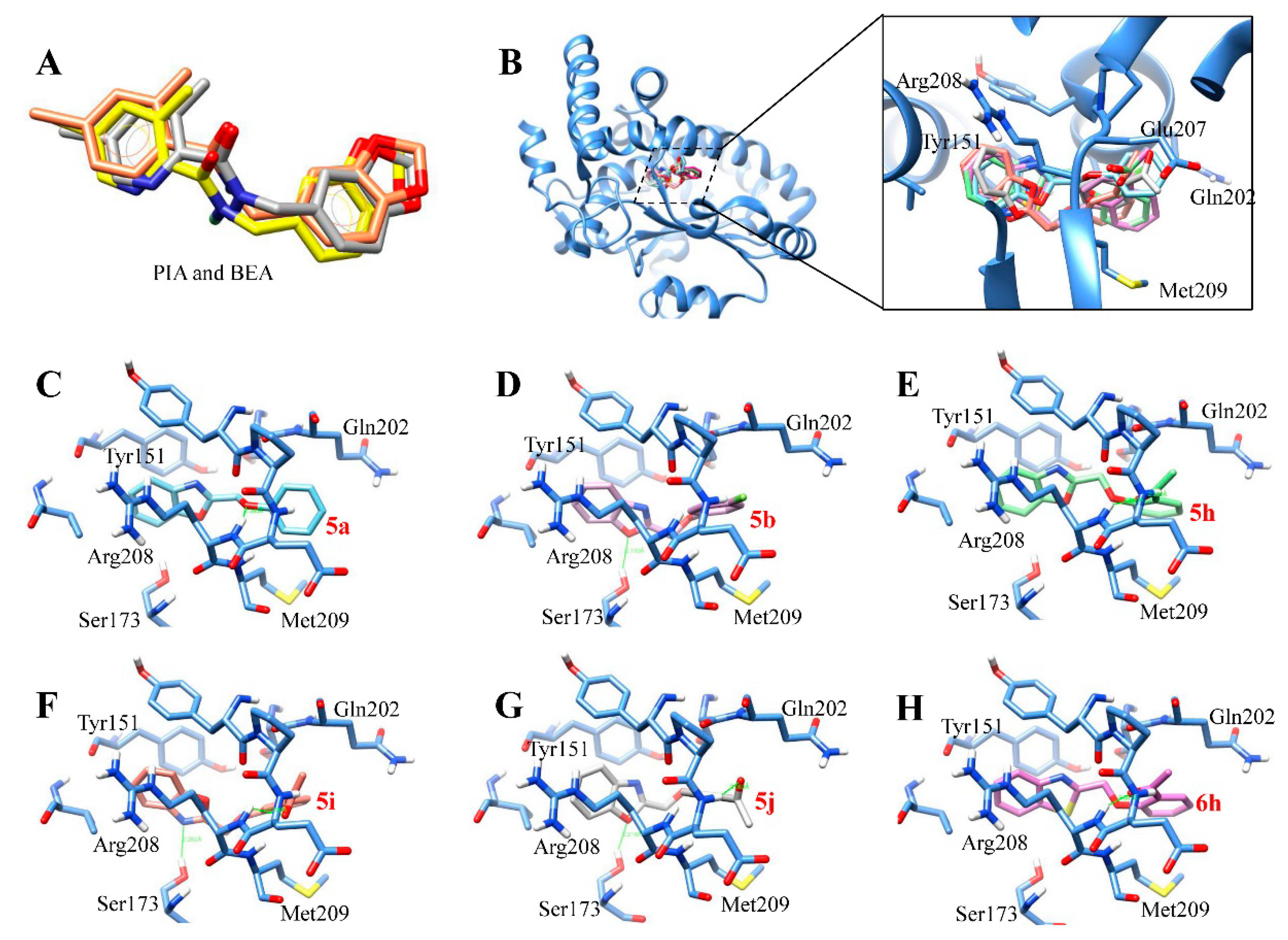
2.3. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the Benzoxazole and Benzothiazole Derivatives (5a–m, 6a–m)
3.2. Antifungal Bioassay
3.3. Molecular Docking Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.Q.; Tang, J.J.; Zhang, A.L.; Gao, J.-M. Secondary metabolites from the endophytic Botryosphaeria dothidea of Melia azedarach and their antifungal, antibacterial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meepagala, K.M.; Kuhajek, J.M.; Sturtz, G.D.; Wedge, D.E.; Vulgarone, B. The antifungal constituent in the steam-distilled fraction of Artemisia douglasiana. J. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 29, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pérez-García, A.; Romero, D.; de Vicente, A. Plant protection and growth stimulation by microorganisms: Biotechnological applications of Bacilli in agriculture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Ishihara, K.; Yuasa, H.; Huang, J.W. Antimicrobial activity of medicinal plant extracts used by indigenous people in Taiwan. Plant. Pathol. Bull. 2005, 14, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Noolvi, M.N.; Patel, H.M.; Kaur, M. Benzothiazoles: Search for anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, I.; Jennings, S.A.; Vishnuvajjala, B.R.; Westwell, A.D.; Stevens, M.F. Antitumor benzothizoles 16. Synthesis and pharmaceutical properties of antitumor 2(4-aminophenyl)benzothizoles amino acid prodrugs. J. Med. Chem 2002, 45, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.L.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Tan, Y.; Wu, Q.Y.; Xi, Z.; Yang, G.F. Design and syntheses of novel N-(benzothiazol-5-yl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione and N-(benzothiazol-5-yl)isoindoline-1,3-dione as potent protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6172–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, A.; Sawhney, S.N. Antimalarials III. Benzothiazole amino alcohols. J. Med. Chem. 1968, 11, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musser, J.H.; Kubrak, D.M.; Chang, J.; DiZio, S.M.; Hite, M.; Hand, J.M.; Lewis, A.J. Leukotriene D4 antagonists and 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. synthesis of benzoheterocyclic [(methoxyphenyl)amino]oxoalkanoic acid esters. J. Med. Chem. 1987, 30, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sheng, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; Dong, G.; Wang, S.; Che, X.; Ji, H.; Miao, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhang, W. Design, synthesis and antifung al activity of isosteric analogues of benzoheterocyclic N-myristoyltransferase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3531–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S.; Rashid, N.; Jones, P.G.; Ali, M.; Hussain, R. Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of some thiourea derivatives bearing benzothiazole moiety as potential antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, S.; Tahlan, S.; Lim, S.M.; Ramasamy, K.; Mani, V.; Shah, S.A.A.; Narasimhan, B. Benzoxazole derivatives: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Luong, T.T.M.; Dan, W.-J.; Ren, Y.; Nien, H.X.; Zhang, A.-L.; Gao, J.-M. Natural products as sources of new fungicides (IV): Synthesis and biological evaluation of isobutyrophenone analogs as potential inhibitors of class-II fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Dan, W.-J.; Tang, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Nandinsuren, T.; Zhang, A.-L.; Gao, J.-M. Natural products as sources of new fungicides (III): Antifungal activity of 2,4-dihydroxy-5-methylacetophenone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, T.; Wakabayashi, T. Synthesis of 2-(4-aryl-1E,3E-butadienyl) benzoxazoleby the horner-wadsworth-emmons reaction. Heterocycles 1995, 41, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, C.R.; Dolbier, W.R., Jr.; Médebielle, M. Synthesis and reactivity of halogeno-difluoromethyl aromatics and heterocycles: Application to the synthesis of gem-difluorinated bioactive compounds. J. Fluorine Chem. 2001, 109, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ma, S. Recent Advances in The Discovery of N-Myristoyltransferase Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popp, F.D.; McEwen, W.E. Polyphosphoric acids as a reagent in organic chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1958, 58, 321–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, Y.H.; Heeschen, J.P. Mechanism of polyphosphoric acid and phosphorus pentoxide–methanesulfonic acid as synthetic reagents for benzoxazole formation. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 3552–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; Che, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Yao, J.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, W. Design and synthesis of antifungal benzoheterocyclic derivatives by scaffold hopping. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peprah, K.; Zhu, X.Y.; Eyunni, S.V.; Etukala, J.R.; Setola, V.; Roth, B.L.; Ablordeppey, S.Y. Structure–activity relationship studies of SYA 013, a homopiperazine analog of haloperidol. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Li, Z.; Fang, Q.; Feng, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Gu, G.; Tian, Y.; Liu, P.; et al. Discovery and extensive in vitro evaluations of NK-HDAC-1: A chiral histone deacetylase inhibitor as a promising lead. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3066–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, M.; Kataoka, T. Studies on benzothiazoline derivatives. III. Reactions of 2,2-disubstituted benzothiazolines with haloacyl halides or acid anhydrides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1979, 27, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharghi, H.; Asemani, O. Methanesulfonic Acid/SiO2 as an efficient combination for the synthesis of 2-substituted aromatic and aliphatic benzothiazoles from carboxylic acids. Synth. Commun. 2009, 39, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, G.R.; Miranda, H.V.; Santos, I.C.; Santos, I; Outeiro, T.F.; Paulo, A. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of fluorinated styryl benzazoles as amyloid-probes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7698–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njoya, Y.; Gellis, A.; Crozet, M.P.; Vanelle, P. Efficient synthesis of new 6-nitrobenzothiazoles using microwave irradiation. Sulfur Lett. 2003, 26, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellis, A.; Boufatah, N.; Vanelle, P. Rapid microwave-promoted synthesis of new sulfonylmethylbenzothiazoles in water. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Lee, K.; Kim, D. Using reverse docking for target identification and its applications for drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Dis. 2016, 11, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nile, A.H.; Tripathi, A.; Yuan, P.; Mousley, C.J.; Suresh, S.; Wallace, I.M.; Shah, S.D.; Pohlhaus, D.T.; Temple, B.; Nislow, C.; et al. PITPs as targets for selectively interfering with phosphoinositide signaling in cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pries, V.; Nöcker, C.; Khan, D.; Johnen, P.; Hong, Z.; Tripathi, A.; Keller, A.-L.; Fitz, M.; Perruccio, F.; Filipuzzi, I.; et al. Target Identification and Mechanism of Action of Picolinamide and Benzamide Chemotypes with Antifungal Properties. Cell. Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipuzzi, I.; Cotesta, S.; Perruccio, F.; Knapp, B.; Fu, Y.; Studer, C.; Pries, V.; Riedl, R.; Helliwell, S.B.; Petrovic, K.T.; et al. High-Resolution Genetics Identifies the Lipid Transfer Protein Sec14p as Target for Antifungal Ergolines. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandinsuren, T.; Shi, W.; Zhang, A.L.; Bai, Y.B.; Gao, J.-M. Natural products as sources of new fungicides (II): Antiphytopathogenic activity of 2,4-dihydroxyphenyl ethanone derivatives. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Shi, X.-W.; Gao, J.-M. Antifungal and antibacterial metabolites from an endophytic Aspergillus sp. associated with Melia azedarach. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, A.-L.; Gao, J.-M. Metabolites from Aspergillus fumigatus, an endophytic fungus associated with Melia azedarach, and their antifungal, antifeedant, and toxic activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chi, B.; Wang, W.-W.; Gao, J.-M.; Wan, J. Exploring the possible binding mode of trisubstituted benzimidazoles analogues in silico for novel drug designtargeting Mtb FtsZ. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds the benzoxazole and benzothiazole derivatives are available from the authors. |

| Cpd. | Average Values of Inhibition Rate (%) to Eight Pathogens | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F. n. | F. g. | F. s. | A. s. | C. g. | V. m. | M. o. | B. c. | |
| 5a | 85 | 87 | 100 | 92 | 100 | 100 | 95 | 100 |
| 5b | 51 | 30 | 85 | 69 | 70 | 43 | 72 | 80 |
| 5c | 44 | 30 | 41 | 57 | 37 | 39 | 44 | 68 |
| 5d | 38 | 45 | 43 | 34 | 57 | 44 | 38 | 78 |
| 5e | 44 | 38 | 41 | 37 | 33 | 46 | 25 | 33 |
| 5f | 28 | 34 | 57 | 43 | 49 | 49 | 44 | 62 |
| 5g | 26 | 30 | 47 | 57 | 45 | 36 | 53 | 61 |
| 5h | 62 | 30 | 89 | 69 | 56 | 80 | 55 | 72 |
| 5i | 59 | 30 | 87 | 63 | 61 | 90 | 81 | 79 |
| 5j | 39 | 49 | 78 | 43 | 57 | 53 | 50 | 33 |
| 5k | 18 | 24 | 23 | 9 | 25 | 20 | 19 | 44 |
| 5l | 33 | 40 | 23 | 29 | 45 | 29 | 34 | 39 |
| 5m | 35 | 27 | 58 | 56 | 47 | 72 | 50 | 58 |
| 6a | 35 | 56 | 49 | 36 | 47 | 36 | 39 | 93 |
| 6b | 28 | 30 | 34 | 26 | 29 | 36 | 25 | 36 |
| 6c | 21 | 32 | 28 | 34 | 57 | 19 | 72 | 67 |
| 6d | 16 | 32 | 51 | 16 | 35 | 43 | 34 | 45 |
| 6e | 33 | 18 | 28 | 5 | 22 | 38 | 16 | 22 |
| 6f | 8 | 30 | 23 | 9 | 18 | 12 | 6 | 33 |
| 6g | 3 | 20 | 32 | 3 | 14 | 53 | 62 | 11 |
| 6h | 39 | 71 | 69 | 28 | 81 | 46 | 44 | 52 |
| 6i | 20 | 24 | 19 | 32 | 32 | 16 | 25 | 52 |
| 6j | 18 | 28 | 23 | 9 | 18 | 9 | 20 | 28 |
| 6k | 1 | 14 | 34 | 16 | 26 | 22 | 24 | 59 |
| 6l | 31 | 28 | 34 | 46 | 25 | 12 | 25 | 81 |
| 6m | 16 | 56 | 50 | 20 | 32 | 36 | 48 | 59 |
| Hy | 69 | 71 | 88 | 63 | 20 | 16 | 100 | 100 |
| Cpd. | IC50 ± SD/(μg/mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F. n. | F. g. | F. s. | A. s. | C. g. | V. m. | M. o. | B. c. | |
| 5a | 45.00 ± 2.71 | 20.59 ± 2.34 | 12.27 ± 0.88 | 23.23 ± 1.58 | 25.94 ± 2.53 | 23.52 ± 1.63 | 65.25 ± 2.98 | 19.92 ± 3.34 |
| 5b | >100 | >100 | 15.98 ± 1.15 | 32.10 ± 7.11 | 32.78 ± 2.11 | >100 | 30.61 ± 0.73 | 23.78 ± 1.55 |
| 5c | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 50.04 ± 6.03 |
| 5f | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 73.04 ± 3.54 |
| 5g | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 77.41 ± 3.16 |
| 5h | 94.48 ± 2.28 | >100 | 4.34 ± 0.13 | 33.32 ± 2.82 | >100 | 31.34 ± 2.64 | >100 | 35.52 ± 2.95 |
| 5i | >100 | >100 | 17.61 ± 0.93 | 73.09 ± 4.10 | 83.35 ± 1.04 | 37.98 ± 2.75 | 73.62 ± 5.12 | 42.01 ± 2.76 |
| 5j | >100 | >100 | 16.53 ± 1.89 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 5m | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 59.65 ± 5.0 | >100 | >100 |
| 6a | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 62.62 ± 2.17 |
| 6c | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 61.20 ± 4.91 |
| 6h | >100 | 23.39 ± 1.29 | 15.55 ± 1.35 | >100 | 29.61 ± 1.39 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 6l | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | 50.42 ± 5.75 |
| Hy | 8.47 ± 1.72 | 59.93 ± 2.19 | 38.92 ± 3.17 | 54.16 ± 1.46 | >100 | >150 | 35.40 ± 2.38 | 4.72 ± 0.52 |
| Cpd. | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Inhibit Constant (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 5a | −6.89 | 8.92 |
| 5b | −6.86 | 9.39 |
| 5h | −7.38 | 3.9 |
| 5i | −7.66 | 2.44 |
| 5j | −7.85 | 1.78 |
| 6h | −7.76 | 2.06 |
| PIA a | −6.96 | 7.97 (9.4) c |
| BEA b | −7.54 | 2.99 (1.7) c |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, B.; Li, D.; Zhang, A.-L.; Gao, J.-M. Synthesis, Antifungal Activities and Molecular Docking Studies of Benzoxazole and Benzothiazole Derivatives. Molecules 2018, 23, 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102457
Luo B, Li D, Zhang A-L, Gao J-M. Synthesis, Antifungal Activities and Molecular Docking Studies of Benzoxazole and Benzothiazole Derivatives. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102457
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Bo, Ding Li, An-Ling Zhang, and Jin-Ming Gao. 2018. "Synthesis, Antifungal Activities and Molecular Docking Studies of Benzoxazole and Benzothiazole Derivatives" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102457
APA StyleLuo, B., Li, D., Zhang, A.-L., & Gao, J.-M. (2018). Synthesis, Antifungal Activities and Molecular Docking Studies of Benzoxazole and Benzothiazole Derivatives. Molecules, 23(10), 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102457







