Network-Based Differential Analysis to Identify Molecular Features of Tumorigenesis for Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma
Abstract
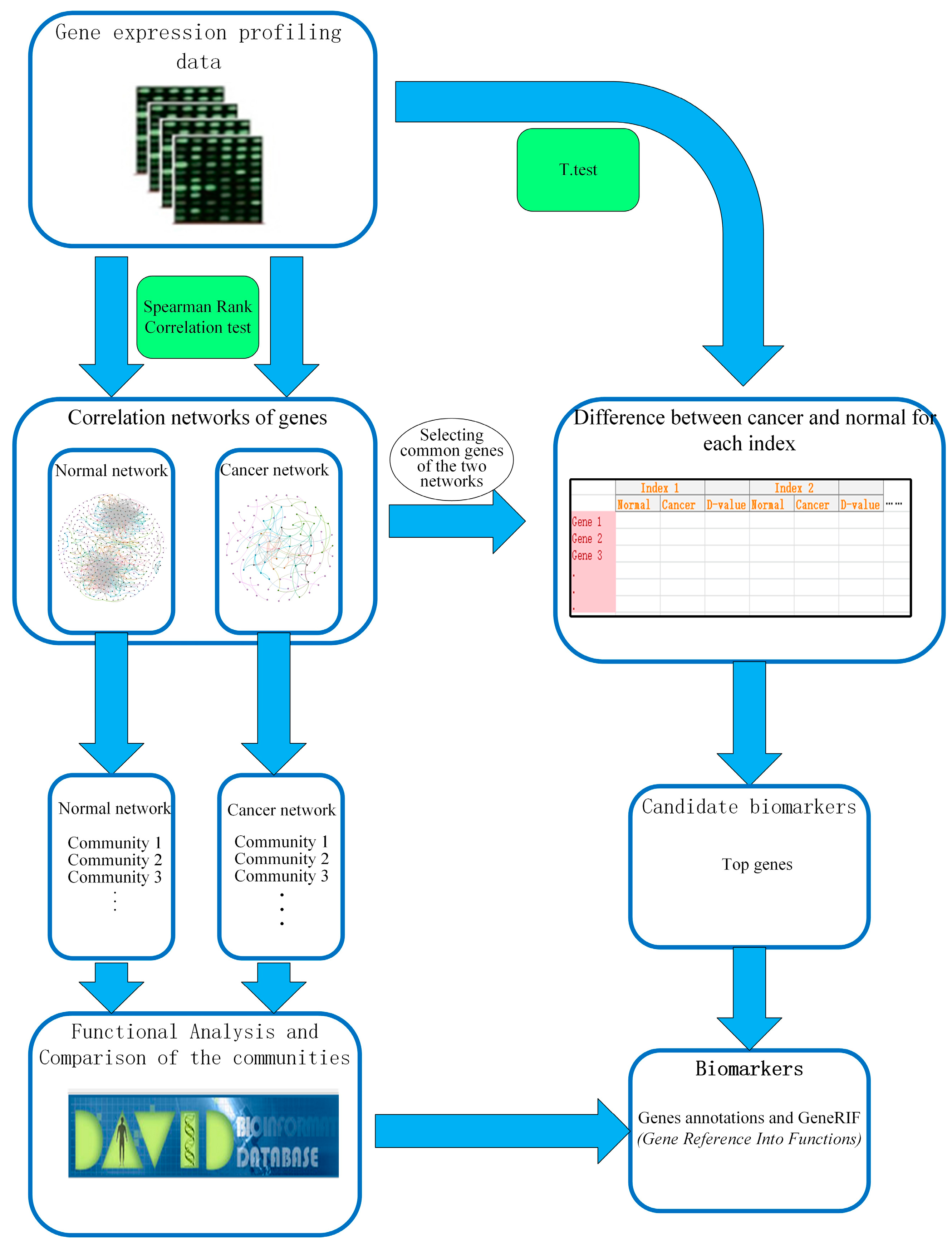
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Gene Networks
2.1.1. Comparison of the Communities between Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma and Normal
2.1.2. Differential Analysis Based on Global Centrality Indexes
2.1.3. Differential Analysis Based on Local Centrality Indexes
2.1.4. Performance Comparison
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Data Source and Data Processing
4.2. Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient
4.3. Centrality Measures
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Pisani, P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, M.W.; Burgers, K.G.; Fry, V.T. Esophageal cancer. Am. Fam. Phys. 2017, 95, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, J.; Puett, D. Cancer Bioinformatics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M. The sequence of the human genome (abstract only). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Biology, Montreal, QC, Canada, 22–25 April 2001; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Esteller, M.; Pandolfi, P.P. The epitranscriptome of noncoding RNAs in cancer. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E. Hmdb 3.0-the human metabolome database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraja, V.; Eslick, G.D. Forthcoming prognostic markers for esophageal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 5, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.Q.; Hu, N.; Burton, V.H.; Yang, H.H.; Su, H.; Conway, C.M.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Ding, T.; Xu, Y. PLCE1 mRNA and protein expression and survival of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Li, C.; Du, Z.; Yao, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Xu, L.; Li, E. Network based analyses of gene expression profile of LCN2 overexpression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Hu, N.; Yang, H.H.; Wang, C.; Takikita, M.; Wang, Q.H.; Giffen, C.; Clifford, R.; Hewitt, S.M.; Shou, J.Z. Global gene expression profiling and validation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and its association with clinical phenotypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2955–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Pleszczynska, E.; Ruland, F. Grade Models and Methods for Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Timmons, J.A.; Claes, W.; Ola, L. Considerations when using the significance analysis of microarrays (SAM) algorithm. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, H.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, G.S.; Wysocki, A. Interactions between extracellular matrix and growth factors in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2009, 17, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinka, R.; Kapoor, R.; Sistla, P.G.; Raj, T.A.; Pande, G. Alterations in cell-extracellular matrix interactions during progression of cancers. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 219196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, E.D. Extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 1981, 91, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Paradies, N.E.; Fedorchaiken, M.; Brackenbury, R. E-cadherin mediates adhesion and suppresses cell motility via distinct mechanisms. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Zheng, H.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Ren, W.; Liao, W.; Duan, Z.; Li, L.; Cao, Y. Immunoglobulin expression and its biological significance in cancer cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 5, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.G. The role of matrix stiffness in regulating cell behavior. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilak, F.; Cohen, D.M.; Estes, B.T.; Gimble, J.M.; Liedtke, W.; Chen, C.S. Control of stem cell fate by physical interactions with the extracellular matrix. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombach, M.P.; Porter, M.A.; Fowler, J.H.; Mucha, P.J. Core-periphery structure in networks. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2013, 74, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekkapongpisit, M.; Wannatung, T.; Usantad, T.S.; Triwitayakorn, K.; Smith, D.R. cDNA-AFLP analysis of differential gene expression in human hepatoma cells (HepG2) upon dengue virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Qin, W.X.; He, X.H.; Shu, H.Q.; Yao, G.F.; Wan, D.F.; Gu, J.R. Differential gene expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells induced by apoptosis-related gene BNIPL-2. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, N.M.; Ceresa, B.P. Protein kinase G facilitates EGFR-mediated cell death in MDA-MB-468 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 346, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakoh, T.; Uekawa, N.; Terauchi, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Ishigami, A.; Shimada, J.I.; Maruyama, M. Implicatio of p53-dependent cellular senescence related gene, TARSH in tumor suppression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 380, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyanarayanan, A.; Karunagaran, D. microRNA-145 modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting SIP1 in human cervical cancer cells. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 40, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhong, B.L.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H. Microrna-145 inhibits cell migration and invasion and regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by targeting connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 22, 3925–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Szabolcs, M.; Terwilliger, J.D.; Efstratiadis, A. Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma in mice expressing a probasin-Neu oncogenic transgene. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emlet, D.R.; Schwartz, R.; Brown, K.A.; Pollice, A.A.; Smith, C.A.; Shackney, S.E. HER2 expression as a potential marker for response to therapy targeted to the EGFR. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vong, S.; Kalluri, R. The role of stromal myofibroblast and extracellular matrix in tumor angiogenesis. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Sun, R.; Deng, N.; Guo, T.; Cao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zou, B.; Zhang, S.; Jing, T. miR-29a/b enhances cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by regulating SPARC and COL3A1 gene expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L. Myosin light chain kinase is responsible for high proliferative ability of breast cancer cells via anti-apoptosis involving P38 pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignesh, S.; Nicolas, G.; Stemmler, M.P.; Kleemann, J.A.; Thomas, B.; Simone, B. The ZEB1/miR-200c feedback loop regulates invasion via actin interacting proteins MYLK and TKS5. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27083–27096. [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich, S.; Streltsov, A.; Schmidt, F.; Thangapandi, V.R.; Reinhardt, D.; Klusmann, J.H. LincRNAs MONC and MIR100HG act as oncogenes in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapkova, I.; Skarda, J.; Rouleau, C.; Thys, A.; Notarnicola, C.; Janikova, M.; Bernex, F.; Rypka, M.; Vanderwinden, J.M.; Faure, S. High expression of the RNA-binding protein RBPMS2 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, L.A.N.; Guimera, R. Complex networks: Lies, damned lies and statistics. Nat. Phys. 2006, 2, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Koh, D.I.; Choi, W.I.; Jeon, B.N.; Jeong, D.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.H.; Hur, M.W. ZBTB2 increases PDK4 expression by transcriptional repression of RelA/p65. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfarouk, K.O.; Verduzco, D.; Rauch, C.; Muddathir, A.K.; Bashir, A.H.H.; Elhassan, G.O.; Ibrahim, M.E.; Orozco, J.D.P.; Cardone, R.A.; Reshkin, S.J. Glycolysis, tumor metabolism, cancer growth and dissemination. Oncoscience 2014, 1, 777–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, 10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lang, R.; Bi, M.; Guo, L.; Lu, S.H. ECRG2, a novel candidate of tumor suppressor gene in the esophageal carcinoma, interacts directly with metallothionein 2A and links to apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 302, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Bi, M.; Su, T.; Liu, H.; Lu, S.H. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel esophageal cancer related gene. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Hu, Z.; Li, M.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Jiang, W.; Lu, S.H. ECRG2 inhibits cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis through the down-regulation of uPA/plasmin activity. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2274–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Lu, S.H.; Cui, Y. ECRG2 regulates ECM degradation and uPAR/FPRL1 pathway contributing cell invasion/migration. Cancer Lett. 2010, 290, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Hellwig, B.; Hammad, S.; Othman, A.; Lohr, M.; Chen, Z.; Boehm, D.; Gebhard, S.; Petry, I.; Lebrecht, A. A comprehensive analysis of human gene expression profiles identifies stromal immunoglobulin k C as a compatible prognostic marker in human solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.T.; Nagaokitamoto, H.; Ohga, N.; Akiyama, K.; Maishi, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Shinohara, N.; Taketomi, A.; Shindoh, M.; Hida, Y. Suprabasin as a novel tumor endothelial cell marker. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Tan, M.; Bishop, J.A.; Jia, L.; Bai, W.; Gaykalova, D.A.; Takenori, O.; Vikani, A.R.; Yuri, A.; Li, R.J. Suprabasin is hypomethylated and associated with metastasis in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niess, H.; Camaj, P.; Mair, R.; Renner, A.; Zhao, Y.; Jäckel, C.; Nelson, P.J.; Jauch, K.W.; Bruns, C.J. Overexpression of IFN-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3 (IFIT3) in pancreatic cancer: Cellular “pseudoinflammation” contributing to an aggressive phenotype. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3306–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.T.; Kwag, S.J.; Park, H.J.; Jung, E.J.; Jeong, C.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, S.K.; Kang, K.R.; Hah, Y.S. Decreased expression of heat shock protein 20 in colorectal cancer and its implication in tumorigenesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, S.; Yamashita, S.; Tanabe, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Yoshida, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Kojima, M.; Shinmura, K.; Saito, Y.; Hiraoka, N. Frequent PTPRK-RSPO3 fusions and RNF43 mutations in colorectal traditional serrated adenoma. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sol, R.M.; Nicolás, G.E.; Christian, E.P.; Luciana, R.V.; Hernán, C.L.; Carolina, S.L.; Melisa, T.J.; Claudia, K.E.; Natalia, R. RUNX1 and FOXP3 interplay regulates expression of breast cancer related genes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6552–6565. [Google Scholar]
- Corona, W.; Karkera, D.J.; Patterson, R.H.; Saini, N.; Trachiotis, G.D.; Korman, L.Y.; Liu, B.; Alexander, E.P.; De La Pena, A.S.; Marcelo, A.B. Analysis of Sciellin (SCEL) as a candidate gene in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 1417–1419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marquardt, J.U.; Quasdorff, M.; Varnholt, H.; Curth, H.M.; Mesghenna, S.; Protzer, U.; Goeser, T.; Nierhoff, D. Neighbor of punc E11, a novel oncofetal marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Kuhn, M.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Minguez, P.; Doerks, T.; Stark, M.; Muller, J.; Bork, P. The string database in 2011: Functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D561–D568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, W.; Huo, W.; Huo, P.; Yang, H. Identification of biomarkers for ischemic cardiomyopathy based on microarray data analysis. Cardiol. J. 2017, 24, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Mansouri, V.; Mahdavi, S.M.; Valizadeh, R.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Zali, M.R. Introducing crucial protein panel of gastric adenocarcinoma disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2017, 10, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Pan, L. Identification of logic relationships between genes and subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of esophageal squamous carcinoma used in the work are available from the authors. |

| Community 1 | Community 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Term | p-Value | Cluster | Term | p-Value |
| 1 | Extracellular matrix | 9.52 × 10−6 | 1 | Notch signaling pathway | 4.00 × 10−4 |
| Secreted | 0.0013 | Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like calcium-binding | 0.0315 | ||
| Extracellular region | 0.01416 | conserved site | 0.0316 | ||
| 2 | Muscle contraction | 1.60 × 10−7 | EGF-type asparagine hydroxylation site | 0.0340 | |
| Actin-binding | 0.0153 | EGF-like, conserved site | 0.0456 | ||
| Cytoskeleton | 0.0386 | EGF_CA | 0.0469 | ||
| 3 | Cell membrane | 8.50 × 10−4 | 2 | Golgi apparatus | 0.0229 |
| Membrane | 0.0058 | ||||
| Plasma membrane | 0.0026 | ||||
| Community A | Community B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Term | p-Value | Cluster | Term | p-Value |
| 1 | muscle contraction | 1.07 × 10−6 | 1 | proteinaceous extracellular matrix | 2.95 × 10−5 |
| stress fiber | 7.67 × 10−4 | extracellular matrix | 4.34 × 10−5 | ||
| focal adhesion | 0.0029 | extracellular region | 0.0226 | ||
| cytoskeleton | 0.0388 | extracellular matrix | 3.53 × 10−7 | ||
| cell junction | 0.0753 | secreted | 7.31 × 10−5 | ||
| 2 | immunoglobulin I-set | 0.0049 | signal peptide | 3.45 × 10−4 | |
| signal | 0.0013 | ||||
| compositionally biased region: Cysrich | 0.004 | ||||
| 2 | collagen catabolic process | 6.22 × 10−6 | |||
| extracellular matrix | 4.34 × 10−5 | ||||
| collagen fibril organization | 2.34 × 10−4 | ||||
| extracellular matrix organization | 0.0057 | ||||
| endoplasmic reticulum lumen | 0.0079 | ||||
| extracellular region | 0.0226 | ||||
| extracellular matrix | 3.53 × 10−7 | ||||
| Ehlers–Danlos syndrome | 3.34 × 10−5 | ||||
| collagen triple helix repeat | 0.0010 | ||||
| hydroxylation | 0.0015 | ||||
| collagen | 0.0016 | ||||
| Gene | Degree | p-Value | Gene | Eigenvector | p-Value | Gene | Core Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1orf116 | 61 | 1.6 × 10−14 | SORBS1 | 1 | 1.7 × 10−5 | C1orf116 | 0.50 | 1.6 × 10−14 |
| NEXN | 48 | 0.0145 | COL3A1 | 0.93 | 1.5 × 10−11 | BNIPL | 0.40 | 3.8 × 10−15 |
| BNIPL | 45 | 3.8 × 10−15 | MYLK | 0.90 | 0.0057 | PRSS27 | 0.38 | 4.0 × 10−12 |
| ERBB3 | 44 | 7.8 × 10−16 | PGM5 | 0.87 | 7.4 × 10−7 | ERBB3 | 0.34 | 7.8 × 10−16 |
| SCN7A | 43 | 0.000108 | MIR100HG | 0.68 | 0.0003 | CNFN | 0.33 | 4.4 × 10−17 |
| PRSS27 | 40 | 4.0 × 10−12 | RBPMS2 | 0.60 | 0.0002 | PRKG1 | 0.28 | 0.01496 |
| MRGPRF | 37 | 0.0002 | SCN7A | 0.58 | 0.0001 | PDK4 | 0.26 | 1.6 × 10−5 |
| PRKG1 | 37 | 0.0149 | C1orf116 | 0.56 | 1.6 × 10−14 | CCDC64B | 0.26 | 2.7 × 10−14 |
| ABI3BP | 36 | 3.5 × 10−5 | MIR145 | 0.56 | 0.0003 | YOD1 | 0.24 | 4.6 × 10−12 |
| MIR145HG | 33 | 0.0003 | CCDC64B | 0.50 | 2.7 × 10−14 | METRNL | 0.24 | 3.7 × 10−10 |
| Gene | Local Degree | p-Value | Gene | Local Eigenvector | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAM3D | 0.63 | 5.2 × 10−13 | SBSN | 0.95 | 1.2 × 10−16 |
| SBSN | 0.58 | 4.7 × 10−5 | OGN | 0.95 | 5.2 × 10−13 |
| SPINK7 | 0.56 | 7.9 × 10−6 | IFIT3 | 0.93 | 1.7 × 10−14 |
| HSPB6 | 0.55 | 1.6 × 10−5 | PDK4 | 0.90 | 8.4 × 10−6 |
| LINC01279 | 0.50 | 0.1191 | RSPO3 | 0.89 | 0.003063 |
| SCEL | 0.47 | 3.5 × 10−5 | ABI3BP | 0.87 | 6.2 × 10−13 |
| SMIM5 | 0.47 | 8.4 × 10−6 | HSPB6 | 0.84 | 5.8 × 10−17 |
| OGN | 0.47 | 1.2 × 10−16 | FAM3D | 0.75 | 4.7 × 10−5 |
| YOD1 | 0.47 | 1.7 × 10−14 | SPINK7 | 0.72 | 4.6 × 10−12 |
| PELI1 | 0.46 | 1.7 × 10−5 | SORBS1 | 0.70 | 6.48 × 10−8 |
| GNG2 | 0.44 | 0.00306 | LINC01279 | 0.70 | 0.00236 |
| IFIT3 | 0.43 | 6.4 × 10−8 | PELI1 | 0.70 | 7.92 × 10−6 |
| IGDCC4 | 0.43 | 0.00236 | GNG2 | 0.70 | 0.091054 |
| IGK | 0.43 | 0.09105 | IGK | 0.70 | 3.76 × 10−5 |
| RSAD2 | 0.43 | 3.7 × 10−5 | RSAD2 | 0.68 | 3.56 × 10−5 |
| R | Gene | Description | Degree | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACTA2 | actin, alpha 2, smooth muscle, aorta | 8 | 0.45 |
| 2 | PRKG1 | protein kinase, cGMP-dependent, type I | 7 | 0.40 |
| 3 | GNB1 | G protein subunit beta 1 | 7 | 0.05 |
| 4 | COL1A2 | collagen type I alpha 2 chain | 6 | 0.18 |
| 5 | ITGA1 | integrin subunit alpha 1 | 6 | 0.06 |
| 6 | MYH11 | myosin heavy chain 11 | 6 | 0.04 |
| 7 | COL3A1 | collagen type III alpha 1 chain | 5 | 0.15 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Y.; Pan, L. Network-Based Differential Analysis to Identify Molecular Features of Tumorigenesis for Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma. Molecules 2018, 23, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010088
Jiang S, Zhang Q, Su Y, Pan L. Network-Based Differential Analysis to Identify Molecular Features of Tumorigenesis for Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010088
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Suxia, Qi Zhang, Yansen Su, and Linqiang Pan. 2018. "Network-Based Differential Analysis to Identify Molecular Features of Tumorigenesis for Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma" Molecules 23, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010088
APA StyleJiang, S., Zhang, Q., Su, Y., & Pan, L. (2018). Network-Based Differential Analysis to Identify Molecular Features of Tumorigenesis for Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma. Molecules, 23(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010088





