The Genus Alnus, A Comprehensive Outline of Its Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemical Constituents
2.1. Diarylheptanoids
2.2. Polyphenols
2.3. Flavonoids
2.4. Triterpenoids and Steroids
2.5. Other Compounds
3. Biological Activities
3.1. Anticancer Activity
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activities
3.4. Antimicrobial and Antiviral Activities
3.5. Hepatoprotective Activity
3.6. DNA Damage Protection Activity
3.7. Anti-Adipogenic Activity
3.8. Anti-Atopic Activity
3.9. Insecticidal Activity
3.10. Other Activities
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae. Available online: http://frps.eflora.cn/frps/Alnus (accessed on 23 June 2011).
- Sati, S.C.; Sati, N.; Sati, O.P. Bioactive constituents and medicinal importance of genus Alnus. Phcog. Rev. 2011, 5, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, S.Y.; Yook, C.S.; Jin, C.; Lee, Y.S. A new diarylheptanoid glycoside from the stem bark of Alnus hirsuta and protective effects of diarylheptanoid derivatives in human HepG2 cells. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novaković, M.; Stanković, M.; Vučković, I.; Todorović, N.; Trifunović, S.; Tešević, V.; Vajs, V.; Milosavljević, S. Diarylheptanoids from Alnus glutinosa bark and their chemoprotective effect on human lymphocytes DNA. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.W.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.I.; Nishioka, I. Dimeric ellagitannins from Alnus japonica. Phytoehtmistry 1992, 31, 2835–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenweber, E. Flavonoids from Alnus crispa, A. japonica, A. koehnei and A. sinuata. Phytochemistry 1974, 13, 2318–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Suga, T.; Aoki, T.; Kawad, Y.; Ohta, S.; Ohta, E. C31-secodammarane-type triterpenoid saponins from the flowers of Alnus pendula. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M.J.; Phan, T.S.; Truong, T.T.C.; Matsunami, K.; Otsuka, H. Mangiferonic acid, 22-hydroxyhopan-3-one, and physcion as specific chemical markers for Alnus nepalensis. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; She, G. Naturally occurring diarylheptanoids. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1687–1708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.C.; Wang, M.H. Antioxidative activity and anti-inflammatory effects of diarylheptanoids isolated from Alnus hirsuta. J. Wood Sci. 2011, 57, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaković, M.; Pešić, M.; Trifunović, S.; Vučković, I.; Todorović, N.; Podolski-Renić, A.; Dinić, J.; Stojković, S.; Tešević, V.; Vajs, V.; et al. Diarylheptanoids from the bark of black alder inhibit the growth of sensitive and multi-drug resistant non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Phytochemistry 2014, 97, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ra, J.C.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, Y.H. An anti-influenza component of the bark of Alnus japonica. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ra, J.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Sohn, D.H. Antioxidative and Hepatoprotective Compositions Containing Diarylheptanoids from Alnus japonica. U.S. Patent 2011/0144039 A1, 16 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.J. Method of Making Health Drink for Reducing Hangover Using Alnus japonica Extract and Green Tea Leaf Extract. Korea Patent KR 2006023093, 13 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Ahn, H.R.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, S.H. Preparative isolation and purification of antioxidative diarylheptanoid derivatives from Alnus japonica by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 3344–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.H.; Kim, S.K.; Ra, G.C.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Sohn, D.H.; Kim, Y.H. Antioxidative and hepatoprotective diarylheptanoids from the bark of Alnus japonica. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedini, A.; Chollet, S.; Angelis, A.; Borie, N.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Reynaud, R.; Gangloff, S.C.; Renault, J.H.; Hubert, J. Bioactivity-guided identification of antimicrobial metabolites in Alnus glutinosa bark and optimization of oregonin purification by centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1029, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahija, S.; Čakar, J.; Vidic, D.; Maksimović, M.; Parić, A. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn., Alnus incana (L.) Moench and Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. extracts. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 2317–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinić, J.; Ranđelović, T.; Stanković, T.; Dragoj, M.; Isaković, A.; Novaković, M.; Pešić, M. Chemo-protective and regenerative effects of diarylheptanoids from the bark of black alder (Alnus glutinosa) in human normal keratinocytes. Fitoterapia 2015, 105, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinić, J.; Novaković, M.; Podolski-Renić, A.; Stojković, S.; Mandić, B.; Tešević, V.; Vajs, V.; Isaković, A.; Pešić, M. Antioxidative activity of diarylheptanoids from the bark of black alder (Alnus glutinosa) and their interaction with anticancer drugs. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Gonzalez, A.J.; Acero, N.; Munoz-Mingarro, D.; López-Lázaro, M.; Martín-Cordero, C. Cytotoxic activity of hirsutanone, a diarylheptanoid isolated from Alnus glutinosa leaves. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acero, N.; Mingarro, D.M. Effect on tumor necrosis factor-α production and antioxidant ability of black alder, as factors related to its anti-inflammatory properties. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, S.J.; Kim, D.; Park, K.H.; Lee, W.S.; Ryu, Y.B. Diarylheptanoids from Alnus japonica inhibit papain-like protease of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 2036–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrand, L.; Kim, J.Y.; Byun, B.S.; Im-aram, A.; Lee, J.; Suh, J.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Tsang, B.K. The diarylheptanoid hirsutenone sensitizes chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin via modulation of apoptosis-inducing factor and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liao, H.B.; Guo, D.H.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Rahman, K. Antidepressant-like effects of 3, 60-disinapoyl sucrose on hippocampal neuronal plasticity and neurotrophic signal pathway in chronically mild stressed rats. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Z.; Huang, C.L.; Yu, B.Y.; Hu, Y.; Mu, L.H.; Liu, P. Effect of Tenuifoliside A isolated from Polygala tenuifolia on the ERK and PI3K pathways in C6 glioma cells. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.H.; Liu, P.; Ma, L.; Liao, H.B.; Xie, T.T.; Mu, L.H.; Liu, Y.M. Study on antidepressant components of sucrose ester from Polygala tenuifolia. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2008, 33, 1278–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroyanagl, M.; Shimomae, M.; Nagashima, Y.; Muto, N.; Okuda, T.; Kawahara, N.; Nakane, T.; Sano, T. New diarylheptanoids from Alnus japonica and their antioxidative activity. Chem. Pham. Bull. 2005, 53, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Jang, E.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, M.S.; Seo, S.J.; Lee, M.W. Hirsutenone inhibits lipopolysaccharide-activated NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediator production by suppressing Toll-like receptor 4 and ERK activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.Y.; Cai, X.F.; Na, M.K.; Lee, J.J.; Bae, K.H. Triterpenoids and diarylheptanoids from Alnus hirsuta inhibit HIF-1 in AGS cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, M.G.; Truong, T.T.C.; Phan, T.S.; Matsunami, K.; Otsuka, K. A new diarylheptanoid and a rare dammarane triterpenoid from Alnus nepalensis. Chem. Nat. Comp. 2011, 47, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Kushwaha, V.; Saxena, K.; Verma, R.; Murthy, P.K.; Gupta, M.M. Diarylheptanoid compounds from Alnus nepalensis express in vitro and in vivo antifilarial activity. Acta Trop. 2013, 218, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.Y.; Cai, X.F.; Na, M.K.; Lee, J.J.; Bae, K.W. Diarylheptanoids from Alnus hirsuta inhibit the NF-kB activation and NO and TNF-α production. Biol. Pharm. Bul. 2007, 30, 810–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeong, T.S.; Choi, S.G.; Ryu, Y.H.; Taeg Oh, G.; Baek, N.I.; Kwon, B.M. Cyclic diarylheptanoids inhibit cell mediated low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Tokoroyama, T.; Kubota, T. Biarylheptanoids and other constituents from wood of Alnus japonica. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.I.; Nishioka, I. Hirsunin, an ellagitannin with a diarylheptanoid moiety, from Alnus hirsuta var. microphylla. Phytochemistry 1992, 3, 967–970. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimatsu, M.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.I.; Nishioka, I. Alnusnins A and B from the leaves of Alnus sieboldiana. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.A.; Nomura, K.; Malfanova, I.L.; Ptitsyn, L.R. Glutinoin, a novel antioxidative ellagitannin from Alnus glutinosa cones with glutinoic acid dilactone moiety. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1806–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Yazaki, K.; Memon, M.U.; Maruyama, I.; Kurokawa, K.; Shingu, T.; Okuda, T. Structure of alnusiin and bicornin, new hydrolyzable tannins, having a monolactonized tergalloyl group. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 2655–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; She, G. Naturally occurring diarylheptanoids—A supplementary version. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2012, 6, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.A.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Sung, S.H. Chemical constituents of Alnus firma and their inhibitory activity on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in BV2 microglia. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novaković, M.; Stanković, M.; Vučković, I.; Todorović, N.; Trifunović, S.; Apostolović, D.; Mandić, B.; Veljić, M.; Marin, P.; Tešević, V.; et al. Diarylheptanoids from green alder bark and their potential for DNA protection. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, A.M. Anti-inflammatory activity of δ-amyrone and apigenin-4′,7-dimethylether isolated from Alnus acuminata. Rev. Col. Cienc. Quim. Farm. 2005, 34, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Fujinori, H.; Neil, T.G.H. Flavones from Alnus rubra Bong. seed coat. Bull. FFPRI 2003, 2, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Asakawa, Y.; Genjida, F.; Suga, T. Four new flavonoids isolated from Alnus sieboldiana. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1971, 44, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, T.; Nikaido, T. Constituents of Pollen. IX. Pollen of Alnus sieboldiana Matsum. Shoyakugaku Zasshi 1980, 34, 316–320. [Google Scholar]
- Kumarasamy, Y.; Cox, P.J.; Jaspars, M.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D. Bioactivity of hirsutanolol, oregonin and genkwanin isolated from the seeds of Alnus gultinosa (Betulaceae). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2006, 1, 641–644. [Google Scholar]
- Rashed, K.; Ćirić, A.; Glamočlija, J.; Calhelha, R.C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Soković, M. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of Alnus rugosa L. aerial parts and identification of the bioactive components. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 59, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, Y. Chemical constituents of Alnus sieboldiana (Betulaceae) II. The isolation and structure of flavonoids and stilbenes. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1971, 44, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, T.; Iwata, N.; Asakawa, Y. Chemical constituents of the male flower of Alnus pendula (Betulaceae). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 45, 2058–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klischies, M.; Zenk, M.H. Stereochemistry of C-methylation in the biosynthesis of rhododendrin in Alnus and Betula. Phytochemistry 1978, 17, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.B.; Miyashiro, H.; Nakamura, N.; Hattori, M.; Park, J.C. Effects of triterpenoids and flavonoids isolated from Alnus firma on HIV-1 viral enzymes. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tori, M.; Hashimoto, A.; Hirose, K.; Asakawa, Y. Diarylheptanoids, flavonoids, stilbenoids, sesquiterpenoids and a phenanthrene from Alnus maximowiczii. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 1263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenweber, E. Flavonoid compounds from Alnus virids. Phytochemistry 1974, 13, 2618–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Ohta, S.; Suga, T. Triterpenoids, diarylheptanoids and their glycosides in the flowers of Alnus species. Phytochemistry 1990, 11, 3611–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felföldi-Gáva, A.; Szarka, S.; Simándi, B.; Blazics, B.; Simon, B.; Kéry, A. Supercritical fluid extraction of Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 61, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.I.; Rovelo, R.; Verjan, J.G.; Illescas, O.; Baeza, A.E.; Fuente, M.D.L.; Avila, I.; Navarrete, A. Anti-inflammatory activities, triterpenoids, and diarylheptanoids of Alnus acuminata ssp. arguta. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suga, T.; Hirata, T. New C31-secodammarane-type triterpenoids, alnuseric acid and alnuselide, in the male flowers of Alnus serrulatoides. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1979, 52, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyukhina, L.G.; Ryabinin, A.A.; Saltykova, I.A.; Shakhvorostova, T.B. Triterpenes in plants from the Soviet Far East. Chem. Nat. Comp. 1968, 4, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.Y.; Rho, M.C.; Lee, S.W.; Park, H.R.; Kim, K.; Lee, I.A.; Kim, D.H.; Jeune, K.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y.K. Inhibition of diacylglycerol acyltransferase by betulinic acid from Alnus hisuta. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Sung, S.H. Antifibrotic constituents of Alnus firma on hepatic stellate cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 2906–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plattner, R.; Taylo, S.L.; Grove, M.D. Detection of brassinolide and castasterone in Alnus glutinosa (European Alder) pollen by mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry. J. Nat. Prod. 1986, 49, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Fouad, M.A.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Okino, T.; Mohamed, G.A. Alnuheptanoid A: A new diarylheptanoid derivative from Alnus japonica. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, L.J.; Zhang, J.G.; Wan, W.C.; Tu, X.F.; Lu, L.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Liu, W.Q.; Li, L. Analysis of chemical components from ethy acetate layer of Alnus nepalensis D. Don. Yunnan Chem. Tech. 2011, 38, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Favre-Bonvin, J.; Jay, M.; Wollenweber, E. A novel stilbene from bud excretion of Alnus viridis. Phytochemistry 1978, 17, 821–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Tokoroy, T. Further phenolic components from Alnus japonica Steud. JCS Chem. Comm. 1975, 131, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvarova, N.I.; Oshitok, G.I.; Suprunov, N.I.; Elyakov, G.B. Triterpenoids and other constituents from the far-Eastern species of Alnus. Phytoclmnistry 1972, 11, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Tori, M.; Asakawa, Y. Five new diarylheptanoids from the male flowers of Alnus sieboldiana. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 1846–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Song, J.Y.; Chin, Y.W.; Sung, S.H. Anti-adipogenic diarylheptanoids from Alnus hirsuta f. sibirica on 3T3-L1 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2069–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.C.; Chen, C.K.; Lin, W.W.; Lee, S.S. A comprehensive investigation of anti-inflammatory diarylheptanoids from the leaves of Alnus formosana. Phytochemistry 2012, 73, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashi, S. Diarylheptanoids of Alnus hirsuta Turcz. (Betulaceae); Research Bulletins of the College Experiment Forests Hokkaido University: Hokkaido, Japan, 1985; Volume 42, pp. 191–205. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Diarylheptanoid Glycosides from Red Alder Bark. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.E.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, M.W. Cytotoxic activities of diarylheptanoids from Alnus japonica. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 1287–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telysheva, G.; Dizhbite, T.; Bikovens, O.; Ponomarenko, J.; Janceva, S.; Krasilnikova, J. Structure and antioxidant activity of diarylheptanoids extracted from bark of grey alder (Alnus incana) and potential of biorefinery-based bark processing of European trees. Holzforschung 2011, 65, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.H.; Suzuki, M.; Uto, T.; Morinaga, O.; Kwofie, K.D.; Ammah, N.; Koram, K.A.; Aboagye, F.; Edoh, D.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Anti-trypanosomal activity of diarylheptanoids isolated from the bark of Alnus japonica. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 1245–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinić, J.; Novaković, M.; Renić, A.P.; Vajs, V.; Tešević, V.; Isaković, A.; Pešić, M. Structural differences in diarylheptanoids analogues from Alnus viridis and Alnus glutinosa influence their activity and selectivity towards cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 249, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.W.; Kim, N.Y.; Park, M.S.; Ahn, K.H.; Toh, S.H.; Hahn, D.R.; Kim, Y.C.; Chung, H.T. Diarylheptanoids with in vitro inducible nitric oxide synthesis inhibitory activity from Alnus hisuta. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Laredo, R.F.; Helm, R.F.; Helm, R.F.; Chen, J.; Karchesy, J.J. Two acylated diarylheptanoid glycosides from red alder bark. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1292–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, S.; Aoki, T.; Hirata, T.; Suga, T. The structures of four diarylheptanoid glycosides from the female flowers of Alnus serrulatoides. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1984, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunga, N.H.; Ra, J.C.; Sohnc, D.H.; Kima, Y.H. A new diarylheptanoid from the bark of Alnus japonica. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.M.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, J.R.; Son, J.; Nam, K.H.; Choi, S.C.; Lim, J.S.; Jeong, T.S. Effects of diarylheptanoids on the tumor necrosis factor-α-induced expression of adhesion molecules in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9457–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, L.C.; Hervé, J.; Muhammad, A.; Saleem, A.; Harris, C.S.; Arnsaon, J.T.; Haddad, P.S. Anti-adipogenic activities of Alnus incana and Populus balsamifera bark extracts, Part I: Sites and mechanisms of action. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, N.H.; Kwon, N.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ra, J.C.; Ding, Y.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, Y.H. Anti-influenza diarylheptanoids from the bark of Alnus japonica. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 10, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chena, J.; González-Laredo, R.F.; Karchesy, J.J. Minor diarylheptanoid glycosides of Alnus rubra bark. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.C.; Wang, M.H. Diarylheotanoid from Alnus hirsuta improves glucose metabolism via insulin signal transduction in human hepatocarcinoma (HepG2) cells. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2011, 16, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Yeom, S.H.; Kim, M.K.; Shim, J.G.; Lim, H.W.; Lee, M.W. New diarylheptanoid from the barks of Alnus japonica Steudel. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2005, 16, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.E.; Park, K.H.; Kim, M.H.; Song, J.H.; Jin, H.Y.; Lee, M.W. Diarylheptanoids from the bark of Alnus pendula Matsumura. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2012, 18, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, D.; Gupta, M.M. Simultaneous quantification of diarylheptanoids in Alnus nepalensis using a validated HPTLC method. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 52, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.K.; Choi, H. Oregonin from the stems and leaves of Korean Alnus species (Betulaceae). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Trouillas, P.; Martin, N.; Dizhbite, T.; Krasilnikova, J.; Telysheva, G. Elucidation of antioxidant properties of wood bark derived saturated diarylheptanoids: A comprehensive (DFT-supported) understanding. Phytochemistry 2014, 103, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, C.K.; Chen, C.K.; Kuo, C.M. Chemical constituents from Alnus formosana burk. II. Polar constituents from the leaves. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2006, 1, 461–464. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, H.; Tachibana, H.; Fuchino, H.; Takana, N. Three new diarylheptanoid glycosides from Alnus japonica. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 1054–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Karchesy, J.J.; González-Laredo, R.F. Phenolic diaryheptenones from Alnus rubra bark. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, I.N.; Ahmad, V.U.; Zahoor, A.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, S.S.; Khan, A.; Hassan, Z. The two diarylheptanoids from Alnus nitida. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1787–1788. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, Y. Chemical constituents of Alnus sieboldiana (Betulaceae). Ш. The synthesis and stereochemistry of yashabushiketols. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 45, 1794–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, Y. Chemical contituents of Alnus firma (Betuaceae). I. Phenyl propane derivatives isolated from Alnus firma. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1970, 43, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, K.; Ichizawa, H.; Kawai, S.; Nishida, T. α-Glucosidase inhibition activity by cyclic diarylheptanoids from Alnus sieboldiana. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2013, 33, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altınyay, C.; Süntar, I.; Altun, L.; Keleş, H.; Akkol, E.K. Phytochemical and biological studies on Alnus glutinosa subsp. glutinosa, A. orientalis var. orientalis and A. orientalis var. pubescens leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 192, 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Sajida, M.; Khana, M.R.; Shah, S.A.; Majid, M.; Ismail, H.; Maryam, S.; Batool, R.; Younis, T. Investigations on anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of Alnus nitida Spach (Endl). stem bark in Sprague Dawley rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwiczuk, A.; Saha, A.; Kuzuhara, T.; Asakawa, Y. Bioactivity guided isolation of anticancer constituents from leaves of Alnus sieboldiana (Betulaceae). Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.B.; Park, J.S.; Lim, S.B. Antioxidant activity and cell toxicity of pressurised liquid extracts from 20 selected plant species in Jeju, Korea. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.K.; Choi, S.S.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, G.M.; Dong, M.S.; Na, C.S.; Chung, H.S. Diarylheptanoid and flavonoid with antioxidant activity from Alnus japonica Steud on DPPH free radical scavenging assay. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 11, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamura, F.; Ohta, S.; Aoki, T.; Suga, T. Triterpenoids from the female and male flowers of Alnus sieboldiana. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 2744–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, K.; Bianchi, E.; Wiedhopf, R.; Cole, J.R. Antitumor agents from Alnus oregona (Betulaceae). J. Pharm. Sci. 1973, 62, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Webster, D.; Johnson, J.A.; Gray, C.A. Anti-mycobacterial triterpenes from the Canadian medicinal plant Alnus incana. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 165, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felföldi-Gáva, A.; Simándi, B.; Plánder, S.; Szarka, É.; Kéry, Á. Betulaceae and Platanaceae plants as alternative sources of selected lupane-type triterpenes. Their composition profile and betulin content. Acta Chromatogr. 2009, 21, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, V.C. The Dictionary of Vietnamese Medicinal Plants; Publishing House Medicine: Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.K. Curcuminoids from Curcuma longa L. (Zingiberaceae) that protect PC12 rat pheochromocytoma and normal human umbilical vein endothelial cells from betaA(1–42) insult. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 303, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, L.X. Advances in understanding mechanisms underlying the antitumor activity of curcumin analogue EF24. World Chin. J. Digesto. 2012, 20, 1853–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, H.J.; Kimd, S.H.; Surha, Y.J. Hirsutenone inhibits phorbol ester-induced upregulation of COX-2 and MMP-9 in cultured human mammary epithelial cells: NF-κB as a potential molecular target. FEBS. Lett. 2006, 580, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Jang, E.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Myung, S.C.; Kim, W.; Lee, M.W. Diarylheptanoid hirsutenone enhances apoptotic effect of TRAIL on epithelial ovarian carcinoma cell lines via activation of death receptor and mitochondrial pathway. Investig. New Drugs. 2012, 30, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Kim, J.E.; Li, Y.; Jung, S.K.; Song, N.Y.; Thimmegowda, N.R.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z.; et al. Hirsutenone in Alnus extract inhibits Akt activity and suppresses prostate cancer cell proliferation. Mol. Carcinogen. 2015, 54, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.W.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, D.W.; Ahn, K.H.; Toh, S.H.; Surh, Y.J. Inhibition of clycooxygenase-2 expression by diarylheptanoids from the bark of Alnus hisuta var. sibirica. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 517–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.S.; Kim, M.S.; Oh, W.S.; Lee, D.I. Enhancement of NK cytotoxicity, antimetastasis and elongation effect of survival time in B16-F10 melanoma cells by oregonin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2002, 25, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, H.S.; Lee, D.I. Augmentation of macrophage antitumor activities and nitric oxide production by oregonin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2002, 25, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stević, T.; Šavikin, K.; Zdunić, G.; Stanojković, T.; Juranić, Z.; Janković, T.; Menković, N. Antioxidant, cytotoxic, and antimicrobial activity of Alnus incana (L.) ssp. incana Moench and A. viridis (Chaix) DC ssp. viridis extracts. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 700–704. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, K.P.; Lee, M.W.; Han, S.S.; Lee, D.I. Antitumor activity of pedunculagin, one of the ellagitannin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1995, 18, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljsak, B.; Šuput, D.; Milisav, I. Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: When to use the synthetic antioxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 956792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Khan, M.R.; Shah, N.A.; Shah, S.A.; Ismail, H.; Younis, T.; Zahra, Z. Phytochemical, antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects of Alnus nitida bark in carbon tetrachloride challenged Sprague Dawley rats. BMC Complem. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; kim, J.Y.; Im, K.R.; Cho, K.H.; Sok, D.E.; Jeong, T.S. Antioxidant effects of diarylheptanoid derivatives from Alnus japonica on human LDL oxidation. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Yeom, S.H.; Kim, M.K.; Paek, I.N.; Lee, M.W. Nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 synthesis inhibitory activities of diarylheptanoids from the barks of Alnus japonica Steudel. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Yadav, D.; Maurya, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Mohanty, S.; Gupta, M.M.; Lingaraju, M.C.; Yatoo, M.I.; Thakur, U.S.; Bawankule, D.U. Diarylheptanoids from Alnus nepalensis attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages and endotoxic shock in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 30, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Lee, S.S.; Chen, S.C.; Ho, F.M.; Lin, W.W. Oregonin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS gene transcription and upregulates HO-1 expression in macrophages and microglia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, A.; Magnusson, L.U.; Ullstrom, C.; Krasilnikova, J.; Telysheva, T.; Dizhbite, T.; Hulten, L.M. Oregonin reduces lipid accumulation and proinflammatory responses in primary human macrophages. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Ko, H.H.; Seo, S.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, M.W.; Myung, S.C.; Bang, H. Diarylheptanoid hirsutenone prevents tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated production of inflammatory mediators in human keratinocytes through NF-κB inhibition. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.G.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, S.E.; Kim, M.H.; Kang, O.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Chae, H.S.; Obiang-Obounou, B.; OH, Y.C.; Kim, M.R.; et al. Antibacterial activity of bark of Alnus pendula against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 853–859. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, T.K.; Jung, D.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Ahn, G.S.; Lee, Y.I.; Jeong, Y.S. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Alnus japonica extracts on acetaminophen induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 971–975. [Google Scholar]
- Martineau, L.C.; Muhammad, A.; Saleem, A.; Hervé, J.; Harris, C.S.; Arnsaon, J.T.; Haddad, P.S. Anti-adipogenic activities of Alnus incana and Populus balsamifera bark extracts, Part II: bioassay-guided identification of actives salicortin and oregonin. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.E.; Jeong, M.S.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, D.I.; Joo, S.S.; Lee, C.S.; Bang, H.; Lee, M.K.; Myung, S.C.; Choi, Y.W.; et al. Effect of topical application and intraperitoneal injection of oregonin on atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, M.S.; Choi, S.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, E.J.; Park, K.H.; Lee, D.I.; Joo, S.S.; Lee, C.S.; Bang, H.; et al. Atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions reduced by topical application and intraperitoneal injection of hirsutenone in NC/Nga mice. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2010, 2010, 618517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.E.; Park, K.H.; Jeong, M.S.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, D.I.; Joo, S.S.; Lee, C.S.; Bang, H.B.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, M.K.; et al. Effect of Alnus japonica extract on a model of atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 136, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.S.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, S.E.; Kim, Y.B.; Park, H.Y.; Seo, S.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, M.W.; Lee, D.I. Suppression of T cell activation by hirsutenone, isolated from the bark of Alnus japonica, and its therapeutic advantages for atopic dermatitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 614, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Eum, J.Y.; Jeong, M.S.; Park, S.H.; Moon, K.Y.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, S.E.; Lee, MW.; Lee, D.I.; et al. Tat peptide-admixed elastic liposomal formulation of hirsutenone for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2459–2467. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.J.; Eum, J.Y.; Jeong, M.S.; Choi, S.E.; Park, S.H.; Cho, H.I.; Cho, C.S.; Seo, S.J.; Lee, M.W.; Choi, Y.W. Facilitated skin permeation of oregonin by elastic liposomal formulations and suppression of atopic dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, D.; Singh, S.C.; Verma, R.K.; Saxena, K.; Verma, R.; Murthy, P.K.; Gupta, M.M. Antifilarial diarylheptanoids from Alnus nepalensis leaves growing in high altitude areas of Uttarakhand, India. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.M.; Kwon, Y.M.; Cho, S.M.; Kwon, Y.M.; Lee, J.H.; Yon, K.H.; Lee, M.W. Melanogenesis inhibitory activities of diarylheptanoids from Alnus hirsuta Turcz in B16 mouse melanoma cell. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2002, 25, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, H.; Choi, S.J.; Jung, S.H. Protective effects of a compound isolated from Alnus japonica on oxidative stress-induced death in transformed retinal ganglion cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashed, K.; Sucupira, A.C.C.; Neto, J.M.M.; Feitosa, C.M. Evaluation of acetylcholinesterase inhibition by Alnus rugosa L. stems methanol extract and phytochemical content. IJBAR 2013, 4, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
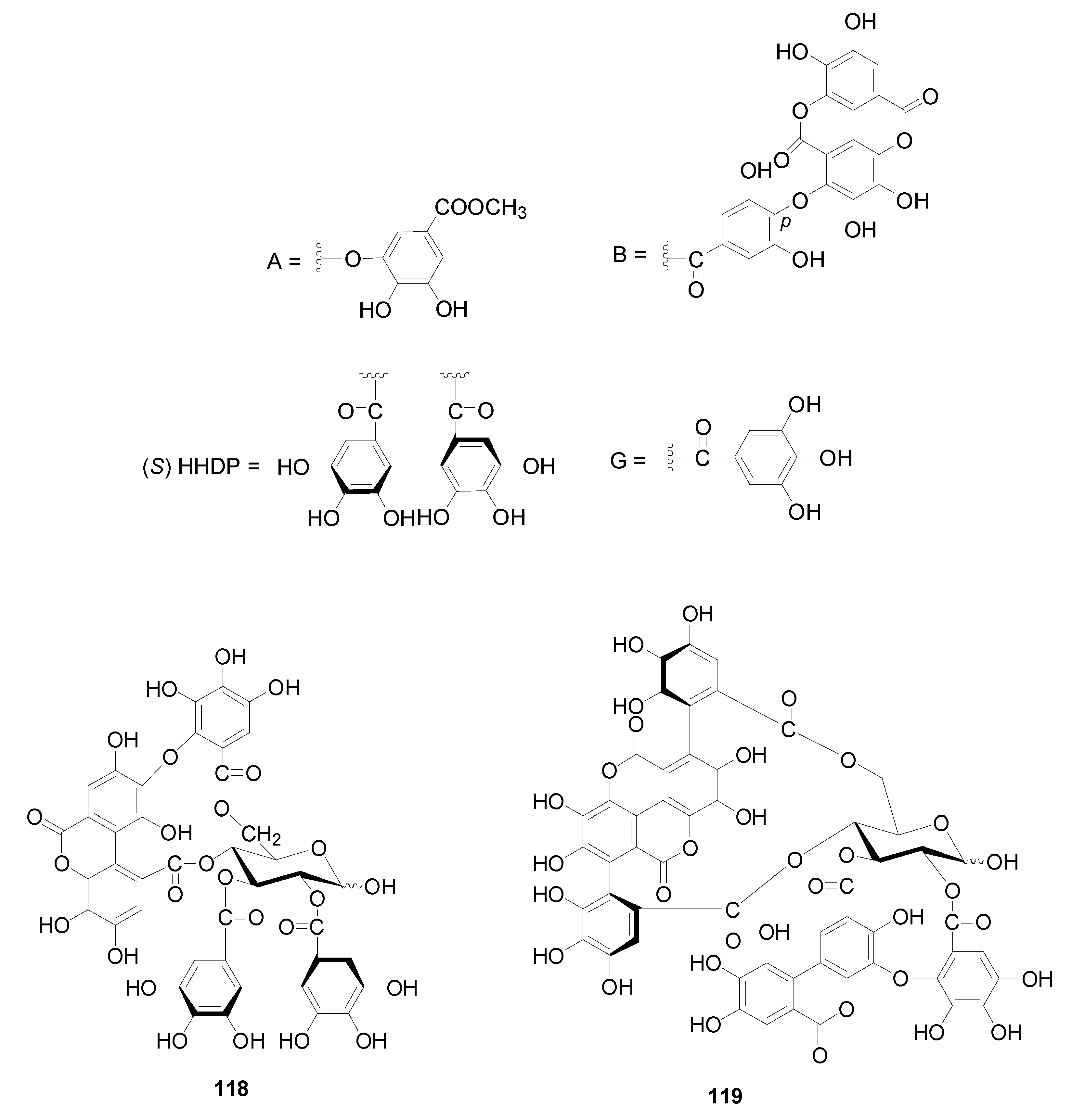
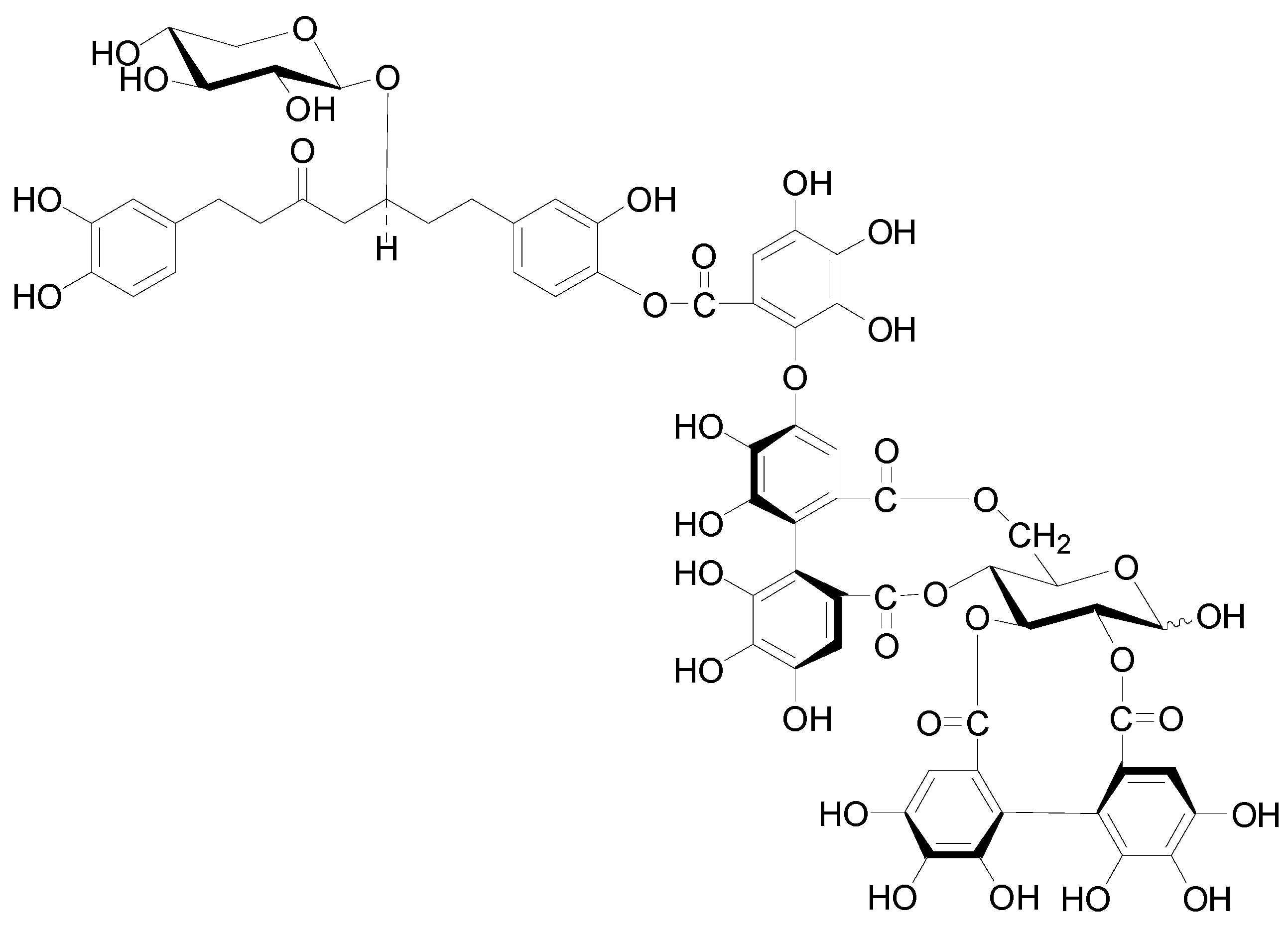
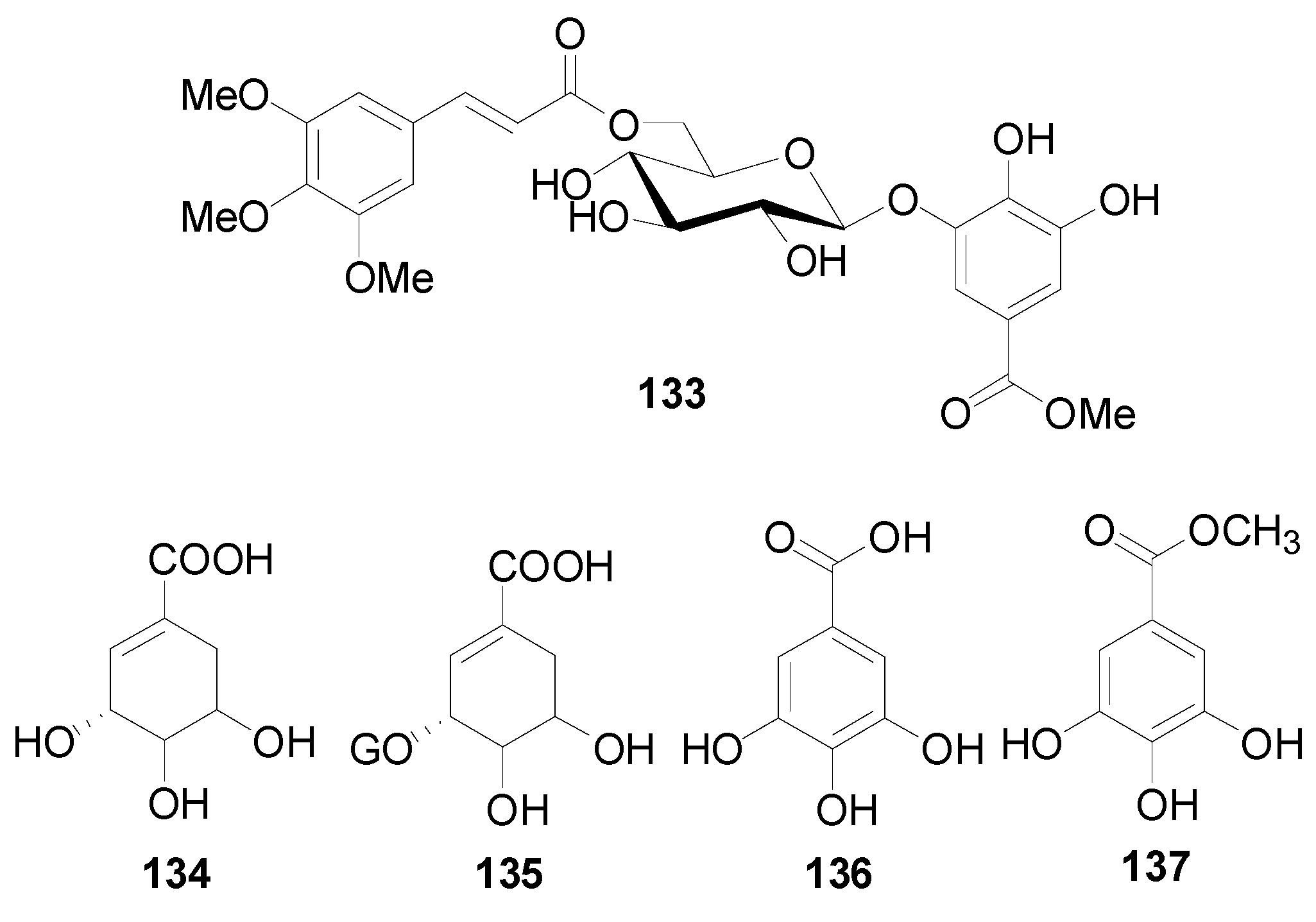

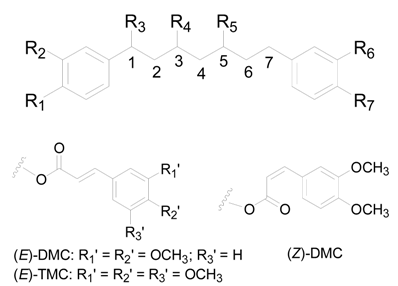
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | H | H | OH (R) | OH (S) | H | H |
| 2 | H | H | H | OH (R) | OH (R) | H | H |
| 3 | H | H | OH (R) | OH (R) | OH (S) | H | H |
| 4 | OH | H | H | OH (R) | OH (R) | H | OH |
| 5 | OH | H | H | OH (R) | H | H | OH |
| 6 | OH | H | H | OH (R) | H | OH | OH |
| 7 | OH | OH | H | OH (R) | H | OH | OH |
| 8 | OH | OH | H | OH (R) | H | H | OH |
| 9 | OH | OH | H | OH (R) | O-xylp (S) | OH | OH |
| 10 | OH | H | H | OH (R) | O-apif(1→6)glcp | H | OH |
| 11 | OH | H | H | O-xylp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 12 | OH | OH | H | O-xylp (R) | H | OH | OH |
| 13 | OH | OH | H | O-xylp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 14 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp (R) | H | OH | OH |
| 15 | OH | H | H | O-glcp (R) | H | OH | OH |
| 16 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 17 | OH | H | H | O-glcp (R) | OH | H | OH |
| 18 | OH | H | H | O-glcp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 19 | OH | H | H | O-apif(1→6)glcp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 20 | OH | H | H | O-araf(1→6)glcp (S) | H | H | OH |
| 21 | OH | H | H | O-araf(1→6)glcp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 22 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp(1→3)xylp (R) | H | OH | OH |
| 23 | OH | OH | H | O-apip(1→6)glcp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 24 | OH | OH | H | O-rhap(1→6)glcp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 25 | OH | H | H | O-glcp(1→3)xylp (R) | H | H | OH |
| 26 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-(E)-DMC (R) | H | OH | OH |
| 27 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-(Z)-DMC (R) | H | OH | OH |
| 28 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-(E)-TMC (R) | H | OH | OH |
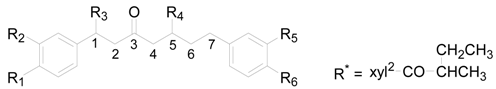
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
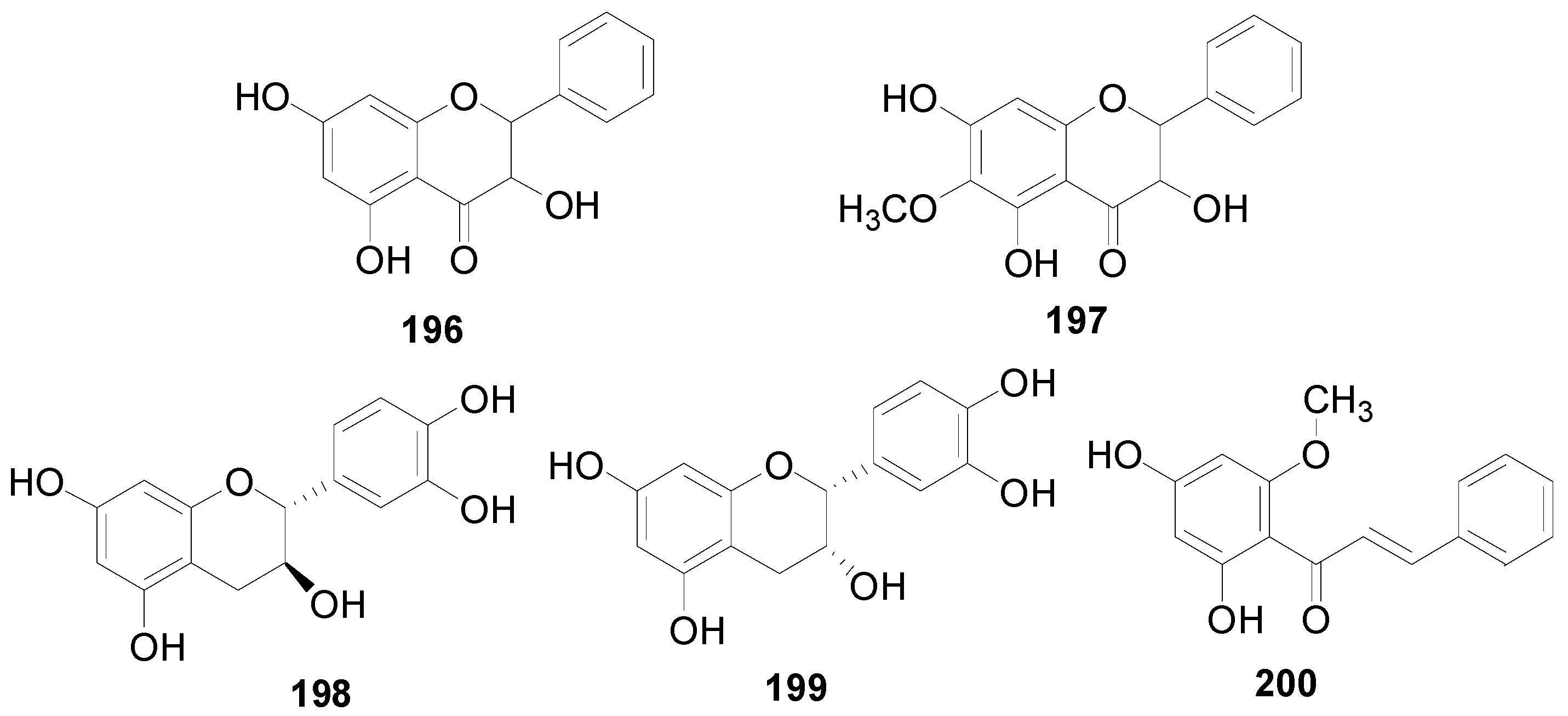
| 29 | OH | H | H | H | H | OH |
| 30 | H | H | OH (S) | OH (S) | H | H |
| 31 | H | H | OH (R) | OH (S) | H | H |
| 32 | H | H | H | OH (S) | H | H |
| 33 | OH | OH | H | OH (S) | OH | OH |
| 34 | OH | OH | H | OH (S) | H | OH |
| 35 | OH | H | H | OH (S) | OH | OH |
| 36 | OH | H | H | OH (S) | H | OH |
| 37 | OH | OH | H | OH (R) | OH | OH |
| 38 | OH | OH | H | OCH3 (S) | OH | OH |
| 39 | OH | H | H | OCH3 (S) | OH | OH |
| 40 | OH | H | H | OCH3 (S) | H | OH |
| 41 | OH | OH | H | OCH3 (R) | OH | OH |
| 42 | OH | OH | H | O-nBu (S) | OH | OH |
| 43 | OH | OH | H | O-nBu (S) | OH | OH, △1(E) |
| 44 | OH | H | H | O-nBu (S) | H | OH |
| 45 | OH | H | H | O-xyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 46 | OH | OH | H | O-xyl (S) | H | OH |
| 47 | OH | H | H | O-xyl (S) | H | OH |
| 48 | OH | OH | H | O-xyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 49 | OH | OH | H | O-glc (S) | OH | OH |
| 50 | OH | H | H | O-glc (S) | H | OH |
| 51 | OH | H | H | O-glc (S) | OH | OH |
| 52 | OH | OH | H | O-glc (S) | H | OH |
| 53 | OH | H | H | O-apif(1→6)glcp (S) | H | OH |
| 54 | OH | H | H | O-galloyl-glcp (S) | H | OH |
| 55 | OH | OH | H | O-xylp-p-coumaroyl | OH | OH |
| 56 | OH | OH | H | O-xylp-feruloyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 57 | OH | OH | H | O-galloyl-glcp (S) | OH | OH |
| 58 | OH | OH | H | O-xylp-benzoyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 59 | OH | OH | H | O-xylp-cinnamoyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 60 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-benzoyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 61 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-vanilloyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 62 | OH | H | H | O-glcp-coumaroyl (S) | H | OH |
| 63 | OH | H | H | O-glcp-(E)-DMC (S) | H | OH |
| 64 | OH | H | H | O-glcp-(E)-DMC (S) | OH | OH |
| 65 | OH | H | H | O-glcp-(Z)-DMC (S) | H | OH |
| 66 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-coumaroyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 67 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-(Z)-DMC (S) | OH | OH |
| 68 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-(E)-TMC (S) | OH | OH |
| 69 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-(E)-DMC (S) | OH | OH |
| 70 | OH | OH | H | O-xylp-2-methyl-butanoyl (S) | OH | OH |
| 71 | OH | OH | H | O-R* (S) | OH | OH |
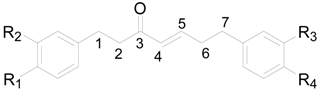
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72 | H | H | H | H |
| 73 | OH | OH | OH | OH |
| 74 | OH | H | H | OH |
| 75 | OH | H | OCH3 | OH |
| 76 | OH | OH | H | OH |
| 77 | OH | H | OH | OH |
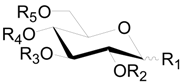
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | OH | H | H | G | G |
| 101 | OG | H | H | G | H |
| 102 | OG | H | H | G | H |
| 103 | OG | G | H | H | H |
| 104 | A | H | H | H | H |
| 105 | OH | H | G | (S) HHDP | |
| 106 | OH | G | G | (S) HHDP | |
| 107 | OG | H | H | (S) HHDP | |
| 108 | OH | (S) HHDP | H | H | |
| 109 | OH | (S) HHDP | (S) HHDP | ||
| 110 | β-OG | (S) HHDP | (S) HHDP | ||
| 111 | OB | (S) HHDP | (S) HHDP | ||
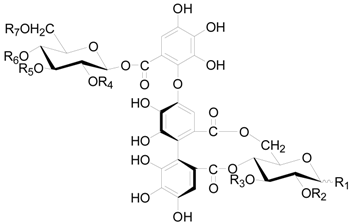
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | OH | (S) HHDP | G | G | (S) HHDP | ||
| 122 | β-OG | (S) HHDP | G | G | (S) HHDP | ||
| 123 | OH | (S) HHDP | H | H | (S) HHDP | ||
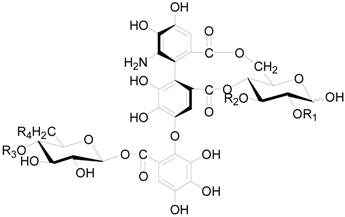
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 124 | (S) HHDP | (S) HHDP | ||
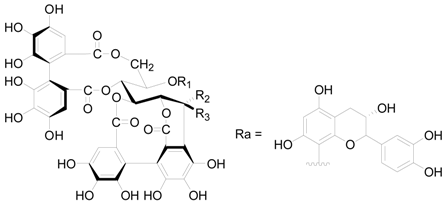
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | H | H | OH |
| 126 | G | H | OH |
| 127 | G | OH | H |
| 128 | G | Ra | H |
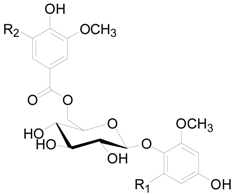
| Compound | R1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 129 | OCH3 | OCH3 |
| 130 | OCH3 | H |
| 131 | H | OCH3 |
| 132 | H | H |
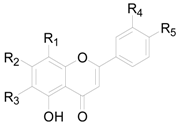
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 138 | H | OH | H | H | H |
| 149 | H | OH | H | H | OH |
| 140 | H | OH | H | OH | OCH3 |
| 141 | H | OH | H | H | OCH3 |
| 142 | H | OCH3 | H | H | H |
| 143 | H | OCH3 | H | H | OH |
| 144 | H | OCH3 | H | OH | OCH3 |
| 145 | H | OCH3 | H | OCH3 | OH |
| 146 | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | H |
| 147 | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | OCH3 |
| 148 | H | O-glcp-glcp | H | H | OH |
| 149 | H | OH | H | H | O-glcp-glcp |
| 150 | H | OCH3 | H | H | OCH3 |
| 151 | H | OH | OCH3 | H | OCH3 |
| 152 | H | OH | H | OH | OH |
| 153 | H | O-glc | H | OH | OH |
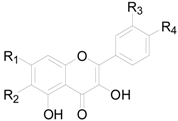
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 154 | OH | H | H | H |
| 155 | OH | H | H | OH |
| 156 | OH | H | H | OCH3 |
| 157 | OH | H | OH | OH |
| 158 | OH | H | OCH3 | OH |
| 159 | OH | OCH3 | H | H |
| 160 | OH | OCH3 | H | OCH3 |
| 161 | OCH3 | H | H | H |
| 162 | OCH3 | H | OH | OH |
| 163 | OCH3 | H | OCH3 | OCH3 |
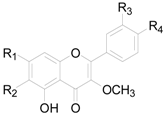
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 164 | OH | H | H | H |
| 165 | OH | H | OCH3 | OH |
| 166 | OH | OCH3 | H | OH |
| 167 | OH | OCH3 | H | OCH3 |
| 168 | OH | OCH3 | OH | OCH3 |
| 169 | OCH3 | H | H | OH |
| 170 | OCH3 | H | OH | OH |
| 171 | OCH3 | H | OH | OCH3 |
| 172 | OCH3 | OCH3 | H | H |
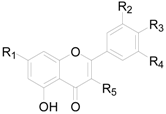
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 173 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-araf |
| 174 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-glcp |
| 175 | OH | H | OH | OH | O-glcp |
| 176 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-rhap |
| 177 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-glucuronide |
| 178 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-rhap(1→6)glcp |
| 179 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-cel |
| 180 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-mal |
| 181 | OH | H | OH | H | O-rha |
| 182 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-galf |
| 183 | OH | H | OH | H | O-rha-rha |
| 184 | OH | OH | OH | H | O-sop |
| 185 | OH | OH | OH | OH | O-galp |
| 186 | OCH3 | OH | OH | H | O-glcp-glcp |
| 187 | OH | OCH3 | OH | H | O-glc |
| 188 | O-rha | OCH3 | OH | H | O-glc |
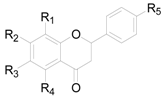
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 189 | H | OH | H | OH | H |
| 190 | H | OH | H | OH | OH |
| 191 | H | OH | H | OCH3 | H |
| 192 | H | OH | CH3 | OH | H |
| 193 | H | OCH3 | H | OH | H |
| 194 | H | OH | OH | OH | OH |
| 195 | CH3 | OH | CH3 | OH | OH |
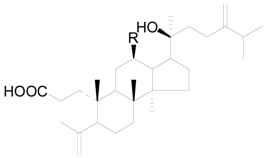
| Compound | R |
|---|---|
| 216 | H |
| 217 | OH |
| 218 | O-xylp |
| 219 | O-glcp |
| 220 | O-arap |
| 221 | O-(2′-OAc)-araf |
| 222 | O-(2′-OAc)-xylp |
| 223 | O-(2′-OAc)-glcp |
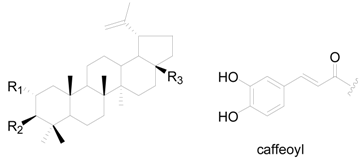
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 236 | H | OH | CH3 |
| 237 | H | OH | CH2OH |
| 238 | H | O | CH2OH |
| 239 | H | OH | COOH |
| 240 | H | OH | OH |
| 241 | H | OH | CHO |
| 242 | H | OCOCH3 | CHO |
| 243 | H | OCOCH3 | CH3 |
| 244 | H | O | CH3 |
| 245 | OH | O-caffeoyl | CH2OH |
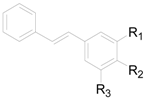
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 255 | OH | H | OH |
| 256 | OH | H | OCH3 |
| 257 | OCH3 | OH | OH |
| 258 | H | H | H |
| 259 | OCH3 | H | OCH3 |
| No. | Compound Class and Name | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diarylheptanoids | |||
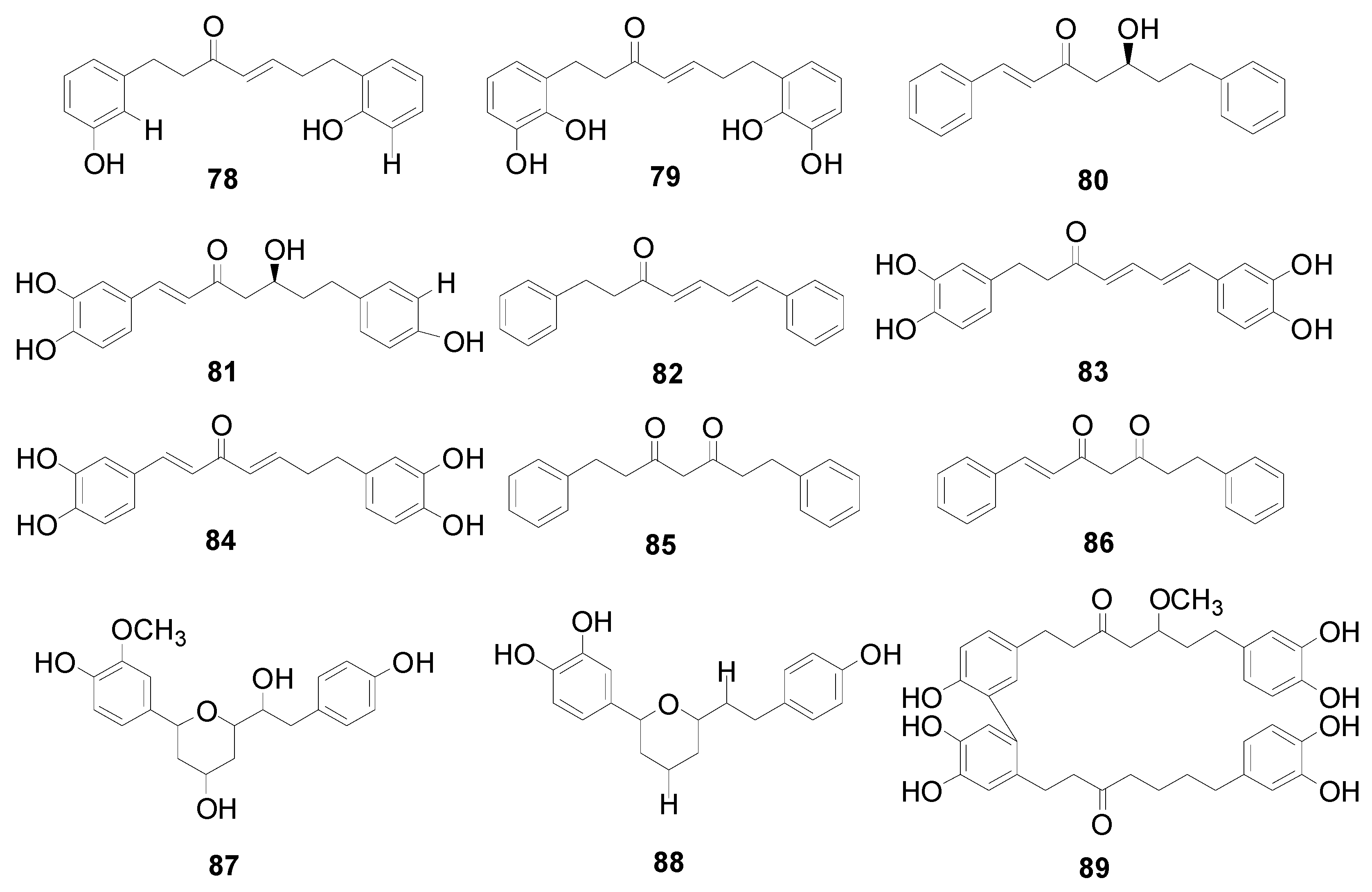
| 1 | yashabushidiol A | A. sieboldiana, Alnus fruticosa Rupr., Alnus mandshurica (Callier) Hand.-Mazz | [2,67,68] |
| 2 | yashabushidiol B | A. sieboldiana, A. fruticosa, A. mandshurica | [2,67,68] |
| 3 | yashabushitriol | A. sieboldiana | [2,68] |
| 4 | (+)-hannokinol | A. hirsuta, A. japonica | [35,69] |
| 5 | (−)-centrolobol | Alnus formosana Burk., A. nepalensis, A. acuminata, A. hirsuta | [31,57,70,71] |
| 6 | (±)-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-heptanol | A. formosana | [70] |
| 7 | rubranol | A. hirsuta, A. japonica, A. rubra, A. formosana | [2,23,69,70,72] |
| 8 | 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3 (R)-heptanol | A. formosana | [70] |
| 9 | (3R,5S)-1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxylheptane-5-O-β-d-xylopyranoside | A. japonica, A. glutinosa, A. incana | [11,73,74] |
| 10 | 5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptan-3-yl β-d-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. viridis | [42] |
| 11 | 1,7-di(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3(R)-β-d-xylosyloxyheptane. | A. formosana | [70] |
| 12 | rubranoside B | A. hirsuta, A. rubra, A. japonica, A. formosana, A. glutinosa | [2,4,69,70] |
| 13 | alnuside C | A. japonica | [75] |
| 14 | rubranoside A | A. hirsuta, A. japonica, A. rubra, A. incana, A. formosana, A. glutinosa | [2,3,4,70,73,74] |
| 15 | 7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3(R)-β-d-glucosyloxyheptane | A. formosana | [70] |
| 16 | 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3(R)-β-d-glucosyloxyheptane | A. formosana, A. japonica | [70,75] |
| 17 | (1S,3R)-3-hydroxy-5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]pentyl β-d-glucopyranoside | A. viridis | [76] |
| 18 | aceroside VII | A. hirsuta, A. formosana, A. glutinosa, A. viridis | [2,3,4,42,70] |
| 19 | aceroside VIII | A. hirsuta, A. viridis | [42,69] |
| 20 | (1S)-5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]pentyl 6-O-α-L-arabinofuranosyl-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. viridis | [76] |
| 21 | (3R)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptan-3-yl α-L-arabinofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. viridis | [42] |
| 22 | rubranoside C | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. rubra | [2,3,73] |
| 23 | rubranoside D | A. japonica. A. rubra | [2,73] |
| 24 | alnuside D | A. japonica | [75] |
| 25 | (3R)-1,7-bis-(4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-heptanol-3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl(1→3)-β-d-xylopyranoside | A. hirsuta | [2,3] |
| 26 | 3(R)-1,7-di(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-O-β-d-[6-(E-3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)] heptane | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 27 | 3(R)-1,7-di(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(Z-3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)] heptane | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 28 | 3(R)-1,7-di(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(E-3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)] heptane | A. glutinosa | [11] |
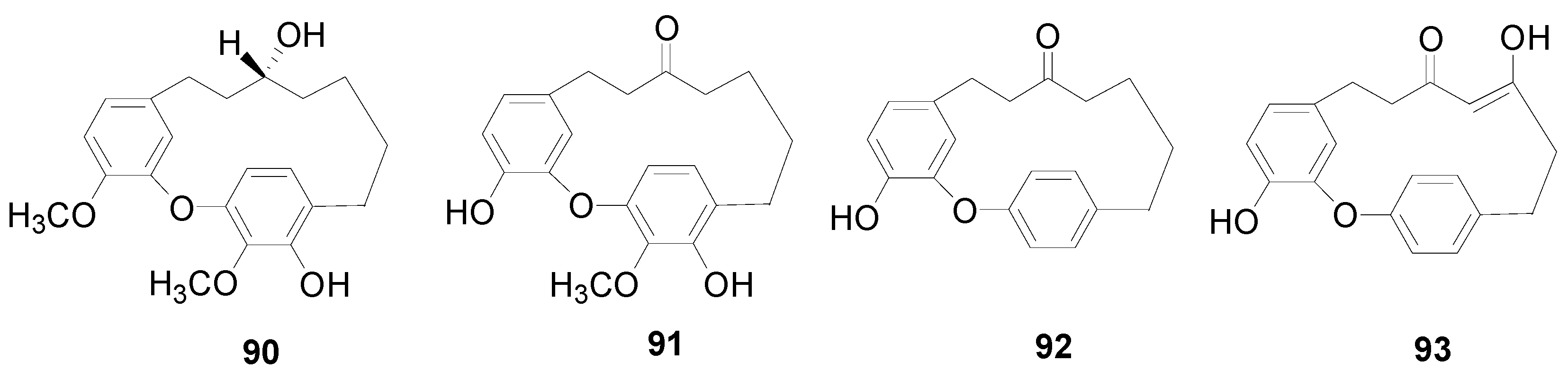
| 29 | 1,7-bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-3-heptanone | A. nepalensis | [11] |
| 30 | yashabushiketodiol B | A. sieboldiana | [2,68] |
| 31 | yashabushiketodiol A | A. sieboldiana | [2,68] |
| 32 | dihydroyashabushiketol | A. firma, A. sieboldiana, A. maximowiczii | [2,54] |
| 33 | hirsutanonol | A. hirsuta, A. japonica, A. rubra, A. glutinosa, A. formosana, A. acuminata, A. serrulatoides | [11,13,57,70,77,78,79] |
| 34 | 5(S)-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptane-3-one | A. japonica | [80] |
| 35 | 5(S)-1-(4-dihydroxyphenyl )-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptane-3-one | A. japonica, A. nepalensis, A. hirsuta | [32,69,80] |
| 36 | hannokinin | A. japonica, A. nepalensis, A. hirsuta, A. firma | [16,32,41,69] |
| 37 | epihirsutanonol | A. japonica | [80] |
| 38 | 5(S)-O-methylhirsutanonol | A. japonica, A. glutinosa, A. formosana, A. nepalensis | [11,32,70,81] |
| 39 | alunheptanoid A | A. japonica | [63] |
| 40 | 5(S)-O-methylplatyphyllonol | A. japonica | [63] |
| 41 | 5(R)-O-methylhirsutanonol | A. japonica | [63] |
| 42 | 5-O-butylhirusutanonol | A. formosana | [70] |
| 43 | 5(S)-butyloxy-1,7-di(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1(E)-hepten-3-one | A. formosana | [70] |
| 44 | 5(S)-butyloxy-1,7-di(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-heptanone | A. formosana | [70] |
| 45 | alnuside A | A. japonica, A. serrulatoides, A. hirsuta, A. formosana, A. glutinosa, A. incana | [2,11,28,70,79,82] |
| 46 | alnuside B | A. japonica, A. serrulatoides, A. hirsuta, A. formosana, A. glutinosa, A. incana | [2,11,28,70,79,82] |
| 47 | platyphyllonol-5-O-β-d-xylopyranoside | A. rubra, A. hirsuta, A. japonica, A. glutinosa | [11,69,83,84] |
| 48 | oregonin | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. rubra, A. nepalensis, A. glutinosa, A. firma, A. formosana, A. incana, A. serrulatoides, A. pendula, A. tinctoria Sarg. | [2,4,41,70,74,79,85,86,87,88,89] |
| 49 | 5(S)-hirsutanonol-5-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. hirsuta, A. japonica, A. rubra, A. incana, A. formosana, A. serrulatoides, A. acuminata, A. nepalensis, A. glutinosa | [2,3,11,57,70,74,79,84,86,88] |
| 50 | platyphylloside | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. glutinosa, A. formosana, A. pendula, A. firma, A. incana, A. nepalensis, A. rubra, A. viridis | [2,3,11,24,41,73,84,87,88,90,91] |
| 51 | (5S)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(3,4-dihydroxy-phenyl)-5-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-heptan-3-one | A. glutinosa | [4] |
| 52 | 1-(3′,4′-dihydroxypheny1)-7-(4′′-hydroxypheny1)-5-O-β-d-glucopyranosylheptan-3-one | A. rubra | [72] |
| 53 | (5S)-5-hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-heptanone-5-O-β-d-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. hirsuta, A. viridis | [42,69] |
| 54 | (3S)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-oxoheptan-3-yl 6-O-galloyl-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. viridis | [42] |
| 55 | oregonoyl A | A. japonica, A. formosana | [2,70,83] |
| 56 | oregonoyl B | A. japonica | [2,83] |
| 57 | hirsutanonol 5-O-(6-O-galloyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. japonica | [2,92] |
| 58 | 2′′′-O-benzoyl-oregonin | A. formosana | [70] |
| 59 | 2′′′-O-cinnamoyl-oregonin | A. formosana | [70] |
| 60 | oregonoside A | A. rubra | [78] |
| 61 | oregonoside B | A. rubra | [78] |
| 62 | 5(S)-1,7-di(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(E-p-coumaroyl glucopyranosyl)]heptane-3-one | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 63 | 5(S)-1,7-di(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(E-3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)]heptane-3-one | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 64 | 5(S)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(E-3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)]heptane-3-one | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 65 | 5(S)-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(Z-3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)]heptane-3-one | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 66 | 5(S)-1,7-di(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(E-p-coumaroyl glucopyranosyl)]heptane-3-one | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 67 | 5(S)-1,7-di(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(Z-3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)] heptane-3-one | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 68 | 5(S)-1,7-di(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(E-3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)] heptane-3-one | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 69 | 5(S)-1,7-di(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-O-β-d-[6-(E-3,4-dimethoxycinnamoyl glucopyranosyl)] heptane-3-one | A. glutinosa | [11] |
| 70 | 2′′′-O-(2-methylbutanoyl)-oregonin | A. formosana | [70] |
| 71 | 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-3-heptanone-5-O-[2-(2-methylbutenoyl)]-β-d-xylopyranoside | A. japonica | [2,28] |
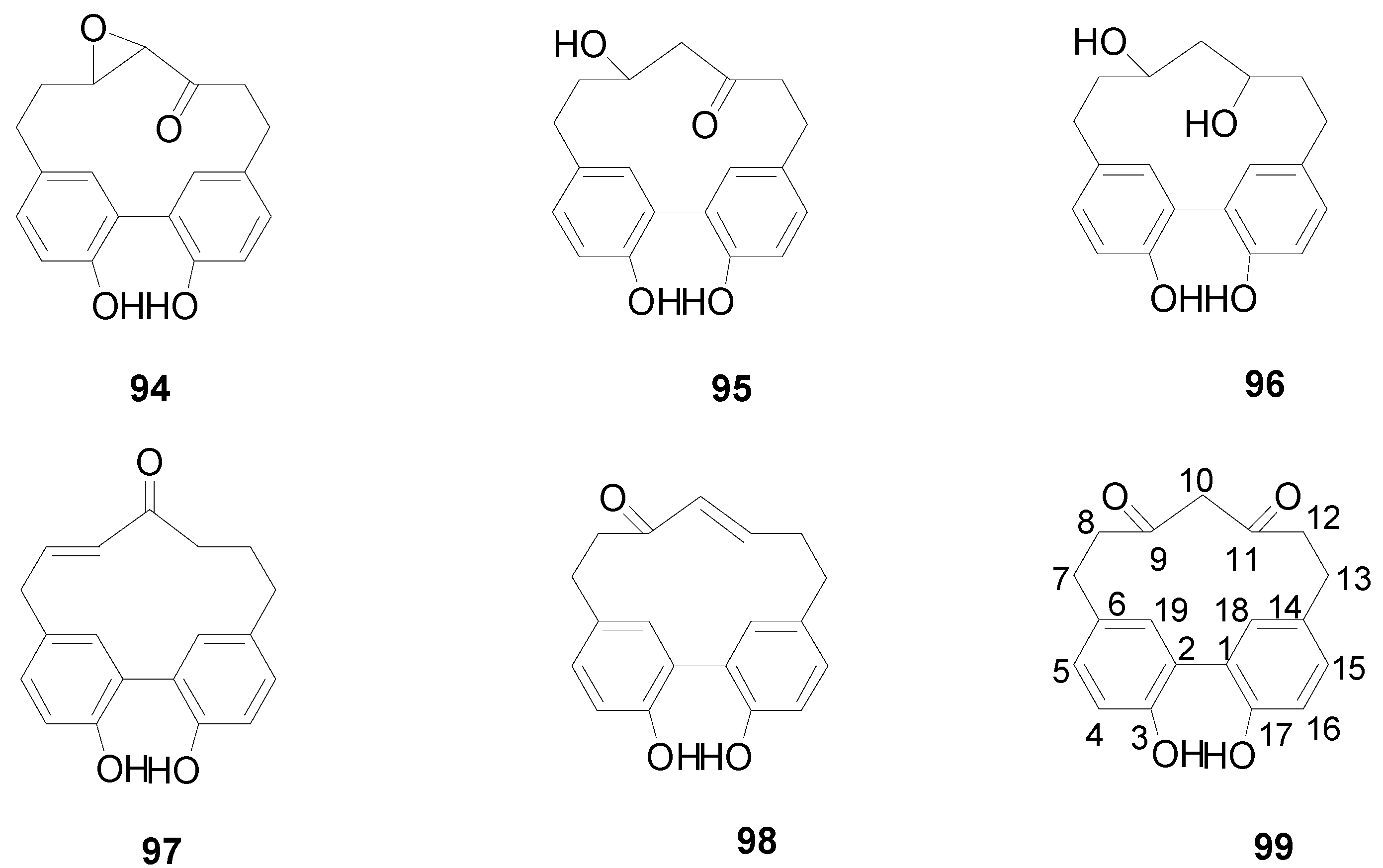
| 72 | 1,7-diphenylhept-3-en-5-one | A. maximowiczii | [2] |
| 73 | hirsutenone | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. pendula, A. nepalensis, A. glutinosa, A. firma, A. formosana, A. acuminata | [2,8,11,28,41,57,69,70,87] |
| 74 | platyphyllenone | A. hirsuta, A. japonica, A. formosana, A. rubra A. acuminata, A. viridis | [2,3,16,42,57,70,93] |
| 75 | 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-4-hepten-3-one | A. hirsuta | [2,30] |
| 76 | 1-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4′′-hydroxyphenyl)-4-hepten-3-one | A. japonica, A. rubra | [2,16,93] |
| 77 | alusenone | A. japonica | [2,13] |
| 78 | nitidone A | Alnus nitida Endl. | [94] |
| 79 | nitidone B | Alnus nitida Endl. | [94] |
| 80 | yashabushiketol | A. firma, A. sieboldiana, A. hirsuta | [2,71,95,96] |
| 81 | (5S)-hydroxy-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-hepta-1E-en-3-one | A. hirsuta | [69] |
| 82 | alnustone | A. pendula, A. japonica | [2,35] |
| 83 | 1,7-bis-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-hepta-4E,6E-dien-3-one | A. hirsuta | [69] |
| 84 | 1,4-hepta-dien-3-one-1,7-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-(1E,4E) | A. hirsuta | [69] |
| 85 | 1,7-diphenylheptane-3,5-dione | A. maximowiczii | [2,53] |
| 86 | 1,7-diphenylhept-1-ene-3,5-dione | A. maximowiczii | [2,53] |
| 87 | rhoiptelol B | A. hirsuta | [2,30] |
| 88 | 1,5-epoxy-1-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4′′-hydroxyphenyl)heptane | A. nepalensis | [31] |
| 89 | alnus dimer | A. nepalensis | [32] |
| 90 | trans-rhoiptelol | A. hirsuta | [2,9,30] |
| 91 | myricatomentogenin | A. hirsuta | [2,9,30] |
| 92 | acerogenin L | A. japonica | [2,34] |
| 93 | garugamblin-3 | A. japonica | [2,34] |
| 94 | alnusoxide | A. japonica | [35] |
| 95 | alnusonol | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. sieboldiana | [35,71,97] |
| 96 | alnusdiol | A. japonica, A. hirsuta | [35,71] |
| 97 | trideoxysasadanin-8-ene | A. hirsuta | [71] |
| 98 | alnusone | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. sieboldiana | [35,71,90,97] |
| 99 | 3,17-dihydroxy-tricyclo[12.3.1.1 2,6]-nonadeca-1(18),2,4,6(19),14, 16-hexaen-9,11-dione | A. sieboldiana | [97] |
| Polyphenols | |||
| 100 | 4,6-di-O-galloyl-d-glucose | A. japonica | [2,5] |
| 101 | 1,4-di-O-galloyl-β-d-glucose | A. japonica | [2,5] |
| 102 | 1,4,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-d-glucose | A. hirsuta | [2,36] |
| 103 | 1,2,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-d-glucose | A. hirsuta, A. sieboldiana | [2,36,37] |
| 104 | gentisic acid 5-O-β-d-(6′-O-galloyl) glucopyranoside | A. hirsuta | [2,36] |
| 105 | gemin D | A. japonica | [2,5] |
| 106 | tellimagrandin I | A. hirsuta, A. sieboldiana | [2,36,37] |
| 107 | strictinin | A. japonica, A. sieboldiana | [5,37] |
| 108 | 2,3-O-(S)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-d-glucose | A. japonica, A. sieboldiana | [2,5] |
| 109 | pedunculagin | A. japonica, A. sieboldiana, A. hirsuta, A. glutinosa | [2,5,36,38,39] |
| 110 | 1(β)-O-galloylpendunculagin | A. japonica, A. sieboldiana | [2,37] |
| 111 | glutinoin | A. glutinosa | [38] |
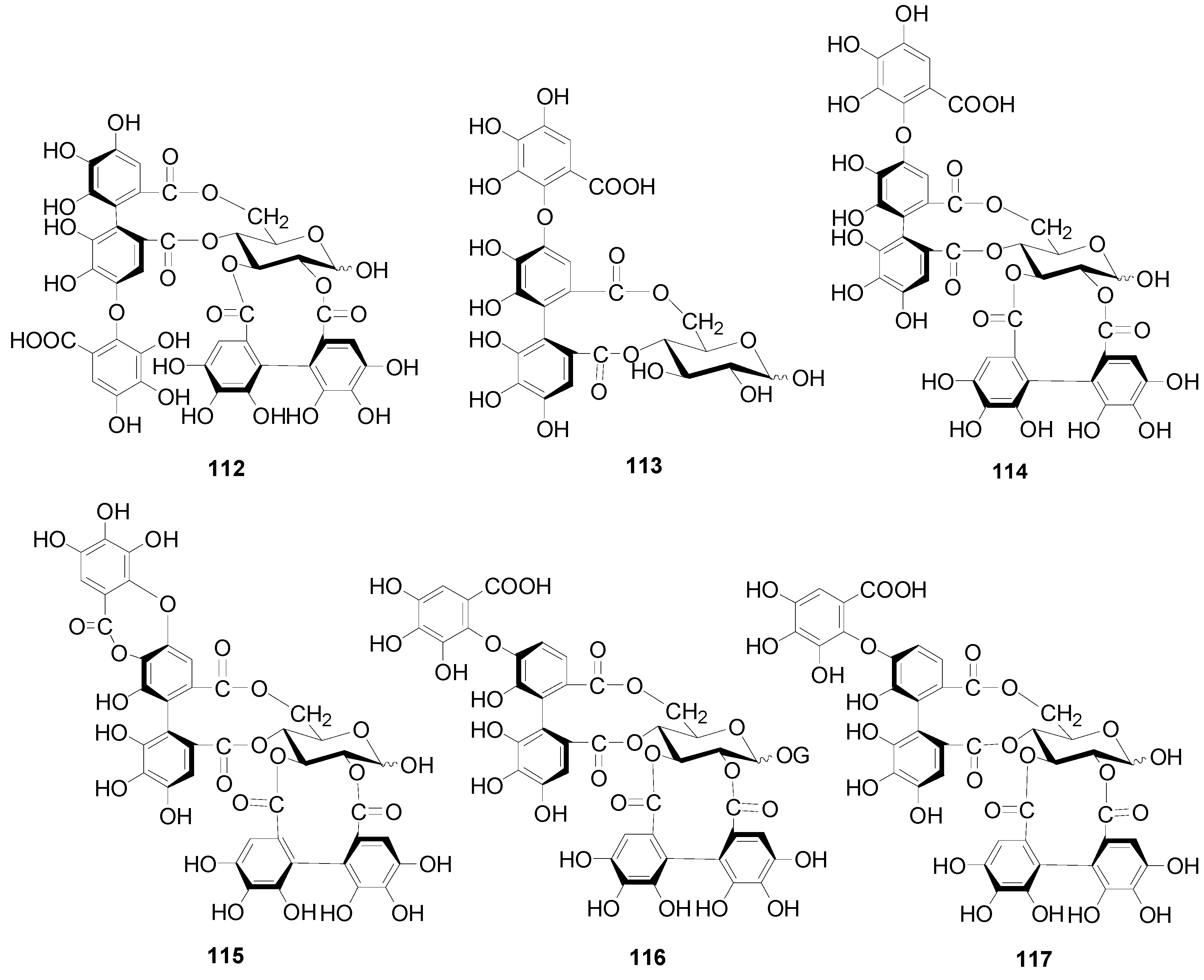
| 112 | flosin A | A. japonica | [2,5] |
| 113 | 4,6-(S)-valoneoyl-d-glucose | A. japonica | [2,5] |
| 114 | praecoxin A | A. japonica, A. hirsuta | [2,5,36] |
| 115 | praecoxin D | A. glutinosa | [38] |
| 116 | alnusnins A | A. sieboldiana | [2,37] |
| 117 | alnusnins B | A. sieboldiana | [2,37] |
| 118 | alnusiin | A. sieboldiana | [2,39] |
| 119 | tergallin | A. sieboldiana | [37] |
| 120 | hirsunin | A. hirsuta | [2,36] |
| 121 | 1-desgalloylrugosin F | A. hirsuta | [2,36] |
| 122 | rugosin F | A. hirsuta | [2,36] |
| 123 | alnusjaponins A | A. japonica | [2,5] |
| 124 | alnusjaponins B | A. japonica | [2,5] |
| 125 | casuariin | A. sieboldiana | [2,39] |
| 126 | casuarinin | A. japonica, A. sieboldiana | [2,5,39] |
| 127 | stachyurin | A. japonica, A. sieboldiana | [2,5,37] |
| 128 | stenophyllanin A | A. sieboldiana | [2,37] |
| 129 | 4-hydroxy-2,6-dimethoxyphenyl-6′-O-syringoyl-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. firma | [2,41] |
| 130 | 4-hydroxy-2,6-dimethoxyphenyl-6′-O-vanilloyl-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. firma | [2,41] |
| 131 | 4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl-6′-O-syringoyl-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. firma | [41] |
| 132 | 6′-O-vanilloylisotachioside | A. firma | [41] |
| 133 | methyl 3,4-dihydroxy-5-{[6-O-(3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamoyl) -β-d-glucopyranosyl]oxy}benzoate | A. viridis | [42] |
| 134 | shikimic acid | A. japonica | [98] |
| 135 | 5-O-galloyl-(−)-shikimic acid | A. japonica | [2,5] |
| 136 | gallic acid | A. nepalensis, A. nitida | [8,99] |
| 137 | methyl gallate | A. sieboldiana | [100] |
| Flavonoids | |||
| 138 | chrysin | A. sieboldiana | [2,49] |
| 139 | apigenin | A. rubra, A. sieboldiana, A. rugosa | [2,44,46,48] |
| 140 | diosmetin | A. rugosa | [48] |
| 141 | acacetin | A. japonica, A. rubra, Alnus koehnei Call. | [2,6,44] |
| 142 | tectochrysin | A. sieboldiana | [2,49] |
| 143 | genkwanin | A. sinuata, A. glutinosa | [2,6,47] |
| 144 | 5,3′-dihydroxy-7,4′-dimethoxyflavone | A. japonica | [2,6] |
| 145 | rhamnazin | A. japonica | [2,6] |
| 146 | 5-hydroxy-6,7,8-tritmethoxyflavone | A. sieboldiana | [2,45,49] |
| 147 | salvigenin | A. japonica, A. rubra, A. koehnei | [2,6,44] |
| 148 | apigenin 7-β-cellobioside | A. sieboldiana | [46] |
| 149 | apigenin 4′-β-cellobioside | A. sieboldiana | [46] |
| 150 | 5-hydroxy-4′,7-dimethoxyflavone | A. japonica, A. acuminata, A. rubra | [2,6,43,44] |
| 151 | scutellarein-6,4′-dimethyl ether | A. japonica, A. rubra | [2,6,44] |
| 152 | luteolin | A. rugosa | [48] |
| 153 | luteolin 7-O-β-glucside | A. rugosa | [48] |
| 154 | galangin | A. sieboldiana, A. pendula, A. viridis | [2,50,54,100] |
| 155 | kaempferol | A. koehnei, A. sieboldiana | [6,46] |
| 156 | kaempferide | A. japonica, A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 157 | quercetin | A. japonica, A. nepalensis, A. firma, A. formosana, A. sieboldiana | [2,8,91,100,101,102] |
| 158 | isorhamnetin | A. japonica, A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 159 | alnusin | A. sieboldiana, A. pendula | [2,49,50] |
| 160 | the 6,4′-dimethyl ether of 6-hydroxykaempferol | A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 161 | izalpinin | A. sieboldiana | [2,50] |
| 162 | rhamnetin | A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 163 | quercetin-7,3′,4′-trimethyl ether | A. japonica, A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 164 | galangin 3-methyl ether | A. viridis | [54] |
| 165 | quercetin-3,3′-dimethyl ether | A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 166 | 3,6-dimethyl ether of 6-hydroxykaempferol | A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 167 | 3,6,4′-trimethyl ether of 6-hydroxy-kaempferol | A. japonica, A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 168 | quercetagetin-3,6,4′-trimethyl ether | A. koehnei | [2,6] |
| 169 | kumatakenin | Alnus crispa Pursh., Alnus sinuate Rydbg. | [2,6] |
| 170 | quercetin 3,7-dimethyl ether | A. crispa, A. koehnei, A. sinuata | [2,6] |
| 171 | quercetin-3,7,4′-trimethyl ether (ayanin) | A. crispa | [2,6] |
| 172 | 5-hydroxy-3,6,7-trimethoxyflavone | A. sieboldiana | [2,49] |
| 173 | quercetin-3-O-α-l-arabinofuranoside | A. firma | [2,52] |
| 174 | isoquercitrin | A. firma | [2,52,53] |
| 175 | quercetin-3-O-glucoside | A. formosana, A. nepalensis | [32,91] |
| 176 | quercitrin | A. firma, A. formosana, A. nepalensis, A. japonica | [2,8,28,52,91] |
| 177 | quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucuronide | A. sieboldiana | [2,37] |
| 178 | rutin | A. nitida | [99] |
| 179 | quercetin-3-β-cellobioside | A. sieboldiana | [46] |
| 180 | quercetin-3-β-maltoside | A, sieboldiana | [46] |
| 181 | kaempferol 3-O-rhamnoside | A. japonica, A. formosana | [28,91] |
| 182 | quercetin-3-O-galactoside | A. japonica, A. nepalensis | [8,28] |
| 183 | kaempferol-3-dirhamnoside | A. sieboldiana | [46] |
| 184 | quercetin-3-sophoroside | A. gultinosa, Alnus cordata Loisel. | [2,32] |
| 185 | myricetin-3-O-β-d-galactopyranoside | A. firma | [2] |
| 186 | rhamnetin-3-O-rhamnoside | A. formosana | [91] |
| 187 | isorhamnetin 3-O-β-glucoside | A. rugosa | [48] |
| 188 | isorhamnetin 3-β-O-glucoside-7-O-α-rhamnoside | A. rugosa | [48] |
| 189 | pinocembrin | A. sieboldiana, A. pendula, A. maximowiczii, A. firma | [50,52,53,100] |
| 190 | naringenin | A. sieboldiana | [2,49] |
| 191 | alpinetin | A. pendula, A. firma, A. sieboldiana | [2,49,50] |
| 192 | strobopinin | A. sieboldiana | [2,49] |
| 193 | pinostrobin | A. pendula, A. firma, A. sieboldiana | [2,49,50] |
| 194 | rhododendrin | A. glutinosa | [2,51] |
| 195 | pinobanksin | A. sieboldiana | [2,49] |
| 196 | alnustinol | A. maximowiczii, A. firma, A. sieboldiana, A. pendula | [2,49,50,53] |
| 197 | 3,5,8-trihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone | A. sieboldiana | [45] |
| 198 | (+)-catechin | A. firma, A. viridis | [2,42,52] |
| 199 | (−)-epicatechin | A. firma | [2,52] |
| 200 | 2′,4′-dihydroxy-6′-methoxychalcone | A. viridis | [54] |
| Terpenoids | |||
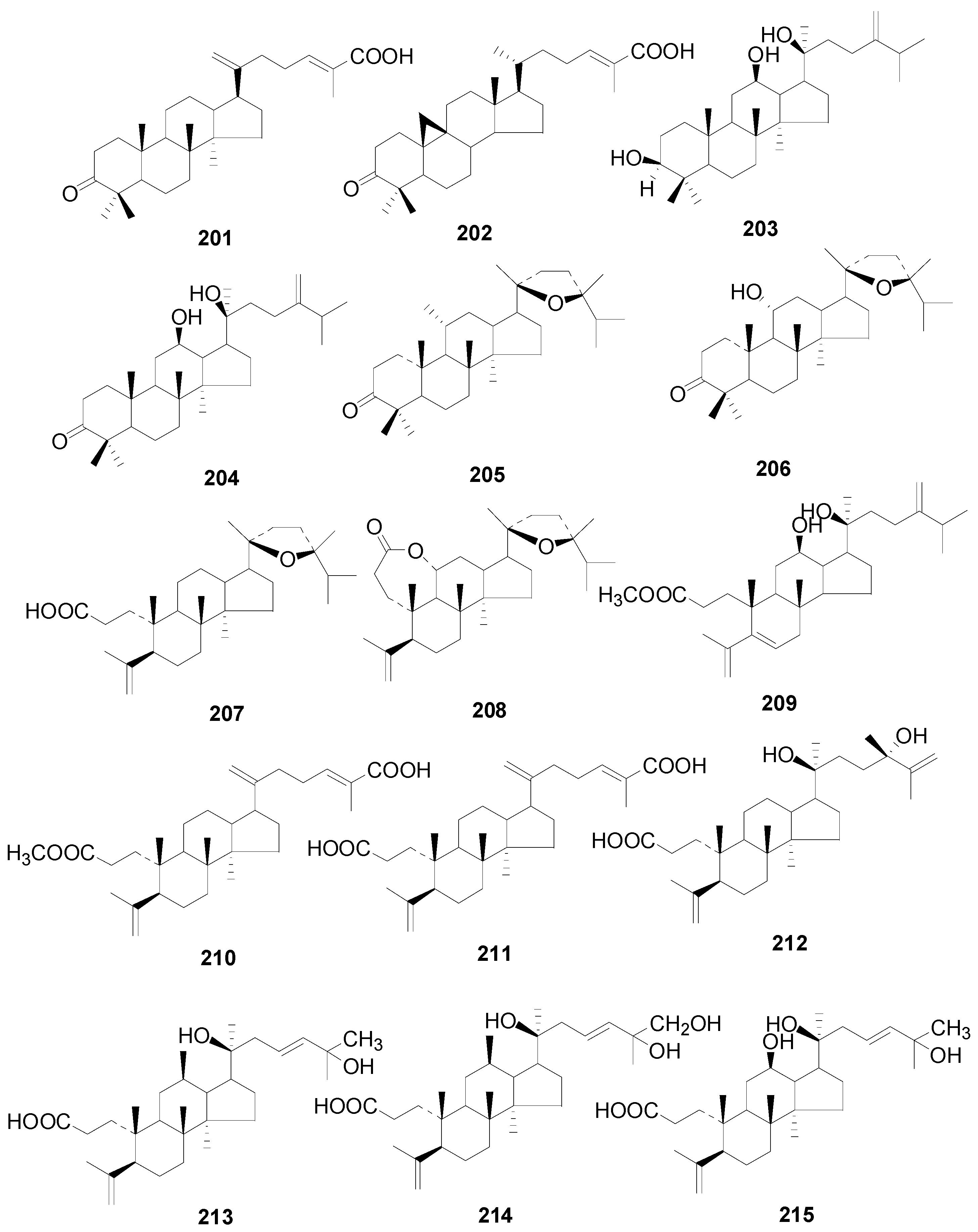
| 201 | 24-(E)-3-oxodammara-20 (21),24-dien-27-oic acid | A. nepalensis | [32] |
| 202 | mangiferonic acid | A. nepalensis | [8] |
| 203 | alnuserrutriol | A. serrulatoides | [2,55] |
| 204 | alnuserrudiolone | A. sieboldiana, A. serrulatoides | [2,55,103] |
| 205 | alnincanone | A. serrulatoides | [2,55] |
| 206 | alnuserol | A. serrulatoides | [2,55] |
| 207 | alnuseric acid | A. serrulatoides, A. pendula | [2,55,58,104] |
| 208 | alnuselide | A. serrulatoides | [2,55,58] |
| 209 | alnustic acid methyl ester | A. firma | [2,52] |
| 210 | methyl(24E)-3,4-secodammara-4(28),20,24-trien-26-oic acid-3-oate | A. japonica | [2,55] |
| 211 | (24E)-3,4-secodammara-4 (28),20,24-trien-3,26-dioic acid | A. japonica | [2,55] |
| 212 | (20S,24S)-20,24-dihydroxy-3,4-secodammara-4 (28),25-dien-3-oic acid | A. japonica | [2,55] |
| 213 | (23E)-(20S)-20,25-dihydroxy-3,4-secodammara-4 (28),23-dien-3-oic acid | A. japonica | [2,55] |
| 214 | (23E)-(20S)-20,25,26-trihydroxy-3,4-secodammara-4 (28),23-dien-3-oic acid | A. japonica | [2,55] |
| 215 | (23E)-(12R,20S)-12,20,25-trihydroxy-3,4-secodammara-4 (28),23-dien-3-oic acid | A. japonica | [2,55] |
| 216 | (20S)-20-hydroxy-24-methylene-3,4-secodammar-4 (28)-en-3-oic acid | A. pendula | [2,55] |
| 217 | alnustic acid | A. serrulatoides, A. pendula, A. sieboldiana | [2,7,55,103] |
| 218 | alnustic acid-12-O-β-d-xylopyranoside | A. serrulatoides, A. pendula, A. sieboldiana | [2,7,55,103] |
| 219 | alnustic acid-12-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. serrulatoides, A. pendula, A. sieboldiana | [2,7,55,103]] |
| 220 | alnustic acid-12-O-α-l-arabinofuranoside | A. serrulatoides, A. pendula, A. sieboldiana | [2,7,55,103] |
| 221 | alnustic acid-12-O-(2′-O-acetyl)-α-l-arabinofuranoside | A. serrulatoides, A. pendula | [2,7,55] |
| 222 | alnustic acid-12-O-(2′-O-acetyl)-β-d-xylopyranoside | A. serrulatoides, A. pendula | [2,7,55] |
| 223 | alnustic acid-12-O-(2′-O-acetyl)-β-d-glucopyranosid | A. serrulatoides, A. pendula | [2,7,55] |
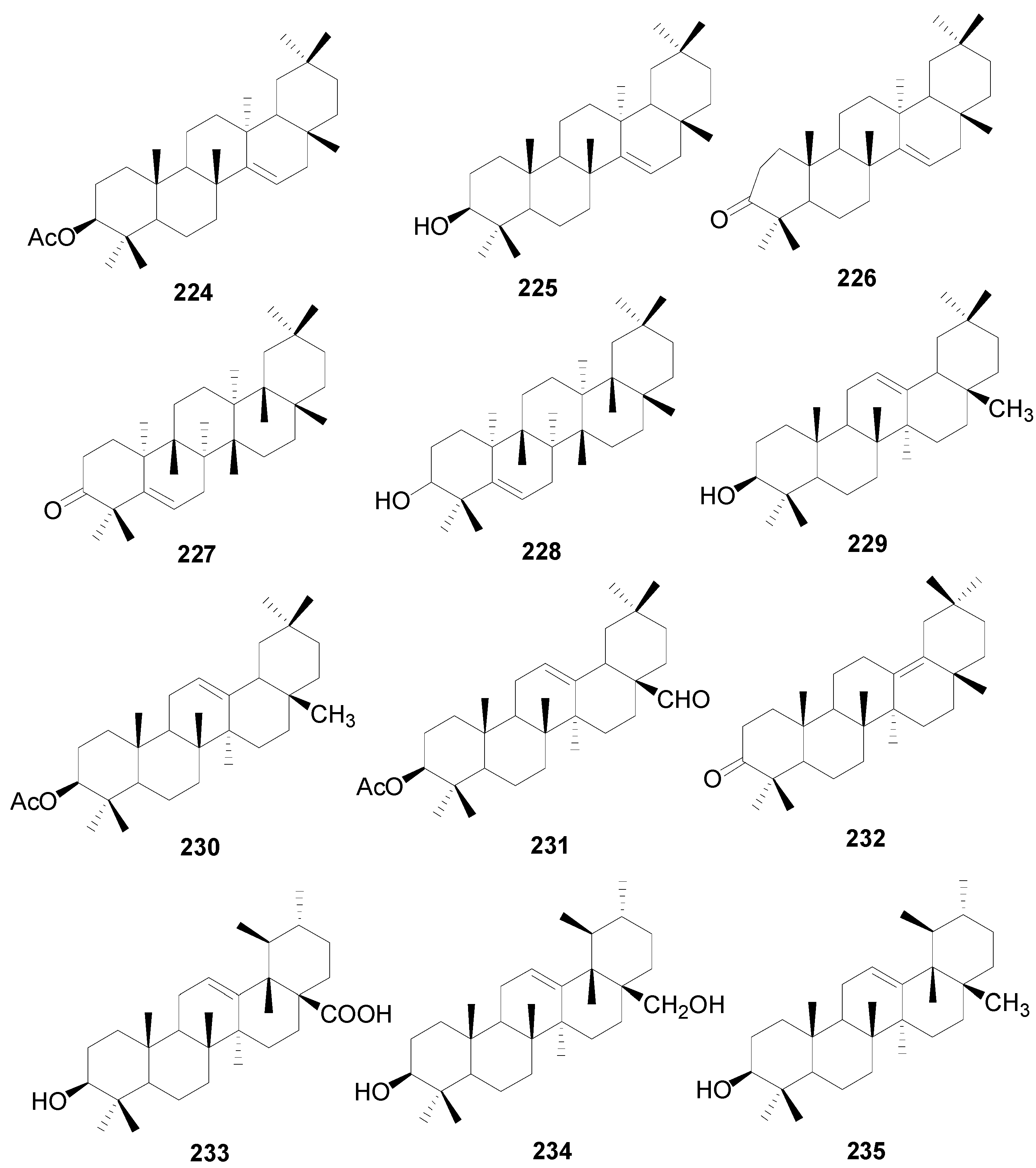
| 224 | taraxeryl acetate | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. nepalensis, A. acuminata | [2,8,30,57,92] |
| 225 | taraxerol | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. nepalensis, A. maximowiczii, A. acuminata, A. rubra | [2,8,30,57,59] |
| 226 | taraxerone | A. japonica, A. rubra, A. nepalensis, A. glutinosa, A. acuminata | [2,56,57] |
| 227 | glutenone | A. japonica, A. rubra, A. fruticosa, A. kamtschatica | [2,72] |
| 228 | glutinol | A. japonica | [2,92] |
| 229 | β-amyrin | A. japonica, A. fruticosa, A. kamtschatica, A. firma, A. glutinosa | [2,52,56] |
| 230 | 3-O-acetyl-β-amyrin | A. japonica, A. firma | [2,52] |
| 231 | 3β-acetoxy-olean-12-ene-28-al | A. acuminata | [57] |
| 232 | δ-amyrone | A. acuminata | [43] |
| 233 | ursolic acid | A. glutinosa | [56] |
| 234 | uvaol | A. glutinosa | [56] |
| 235 | α-amyrin | A. fruticosa, A. kamtschatica | [2] |
| 236 | lupeol | A. japonica, A. rubra, A. nepalensis, A. glutinosa, Alnus oregona Nutt., A. acuminata | [2,12,56,57,104] |
| 237 | betulin | A. hirsuta, A. rubra, A. nepalensis, A. japonica, A. glutinosa, A. maximowiczii, A. oregona | [2,7,8,12,30,56,59,104] |
| 238 | betulone | A. incana | [105] |
| 239 | betulinic acid | A. japonica, A. hirsuta, A. nepalensis | [2,8,30,63] |
| 240 | 3β,28-dihydroxy-lup-20(29)-ene | A. acuminata | [57] |
| 241 | betulinic aldehyde | A. japonica, A. glutinosa, A. acuminata | [12,56,57] |
| 242 | 3-acetoxybetulinic aldehyde | A. japonica | [12] |
| 243 | lupenylacetate | A. glutinosa | [56] |
| 244 | lupenone | A. japonica, A. rubra, A. fruticosa, A. kamtschatica, A. glutinosa | [2,56] |
| 245 | lup-20(29)en-2,28-diol-3-yl caffeate | A. firma | [61] |
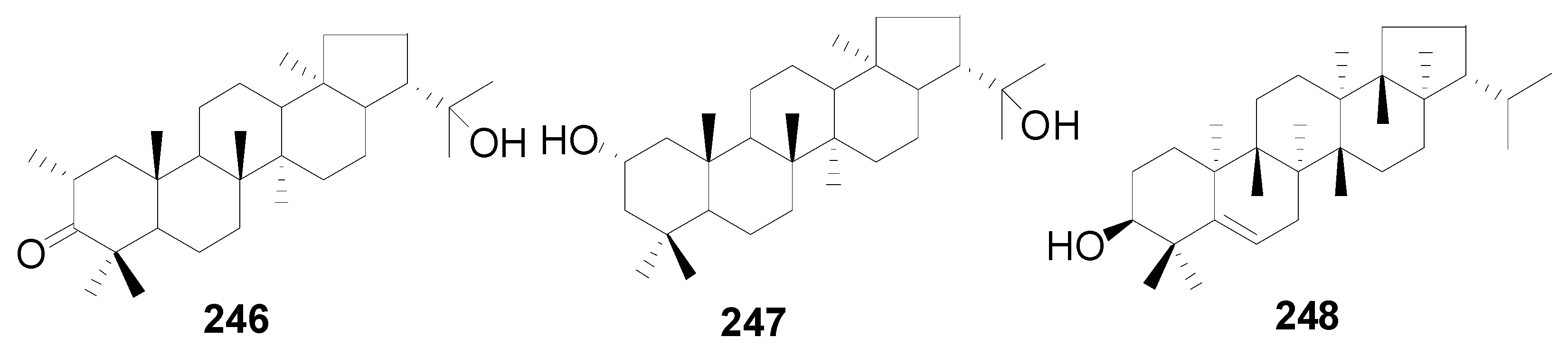
| 246 | 22-hydroxyhopan-3-one | A. nepalensis | [8] |
| 247 | 2-hydroxydiploterol | A. nepalensis | [8] |
| 248 | simiarenol | A. glutinosa | [56] |
| Steroids | |||
| 249 | β-sitosterol | A. japonica, A. fruticosa, A. rubra, A. nepalensis, A. kamtschatica, A. firma, A. glutinosa, A. acuminata, A. rugosa | [2,8,48,52,57,63,64,106] |
| 250 | β-sitosterol 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | A. japonica, A. nepalensis, A. acuminata, A. rugosa | [2,8,48,57,63,64] |
| 251 | β-rosasterol | A. nepalensis | [64] |
| 252 | stigmasterol | A. nepalensis | [64] |
| 253 | brassinolide | A. glutinosa | [62] |
| 254 | castasterone | A. glutinosa | [62] |
| Others | |||
| 255 | pinosylvin | A. sieboldiana, A. pendula | [2,49,50] |
| 256 | pinosylvin monomethyl ether | A. sieboldiana, A. pendula, A. maximowiczii | [2,49,50,53] |
| 257 | 4′,5′-dihydroxy-3′-methoxy stilbene | A. viridis | [65] |
| 258 | trans-stilbene | A. firma, A. sieboldiana | [2,49,96] |
| 259 | pinosylvin dimethyl ether | A. sieboldiana, A. maximowiczii | [2,49,53] |
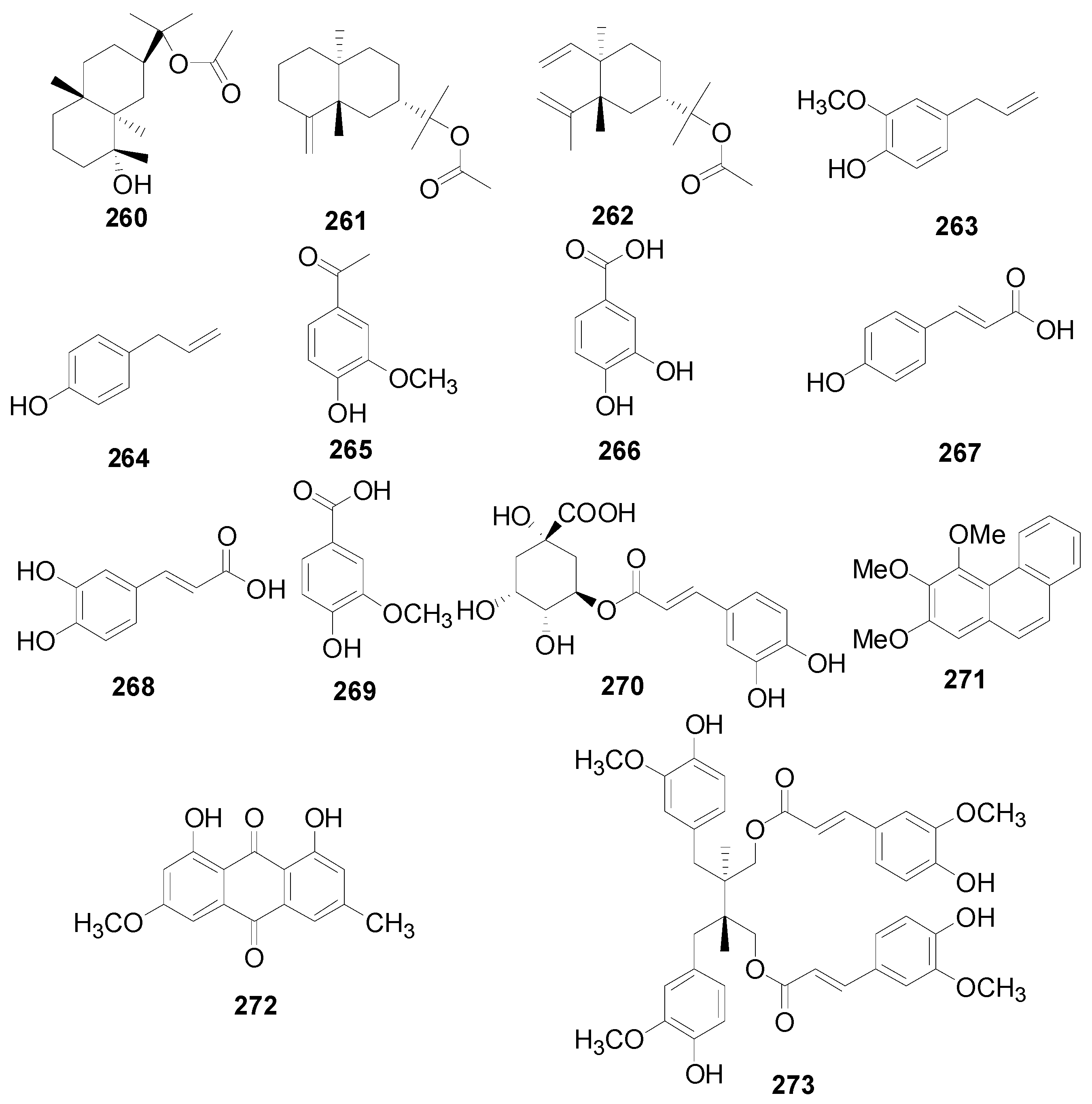
| 260 | cryptomeridiol 11-O-monoacetate | A. maximowiczii | [2,53] |
| 261 | β-eudesmol acetate | A. maximowiczii | [2,53] |
| 262 | elemol acetate | A. maximowiczii | [2,53] |
| 263 | eugenol | A. pendula | [2,50] |
| 264 | chavicol | A. pendula | [2,50] |
| 265 | vanillin | A. nepalensis | [64] |
| 266 | protocatechuic acid | A. firma, A. formosana | [91,101] |
| 267 | p-coumaric acid | A. firma | [101] |
| 268 | caffeic acid | A. firma | [101] |
| 269 | vanilic acid | A. japonica | [66] |
| 270 | chlorogenic acid | A. firma | [101] |
| 271 | 2,3,4-trimethoxyphenanthrene | A. maximowiczii | [2,53] |
| 272 | physcion | A. nepalensis | [8] |
| 273 | secoisolariciresinol diferulate | A. japonica | [66] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; He, T.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Bai, S.; Wang, L.; Shen, M.; She, G. The Genus Alnus, A Comprehensive Outline of Its Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities. Molecules 2017, 22, 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081383
Ren X, He T, Chang Y, Zhao Y, Chen X, Bai S, Wang L, Shen M, She G. The Genus Alnus, A Comprehensive Outline of Its Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities. Molecules. 2017; 22(8):1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081383
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xueyang, Ting He, Yanli Chang, Yicheng Zhao, Xiaoyi Chen, Shaojuan Bai, Le Wang, Meng Shen, and Gaimei She. 2017. "The Genus Alnus, A Comprehensive Outline of Its Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities" Molecules 22, no. 8: 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081383
APA StyleRen, X., He, T., Chang, Y., Zhao, Y., Chen, X., Bai, S., Wang, L., Shen, M., & She, G. (2017). The Genus Alnus, A Comprehensive Outline of Its Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities. Molecules, 22(8), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081383




