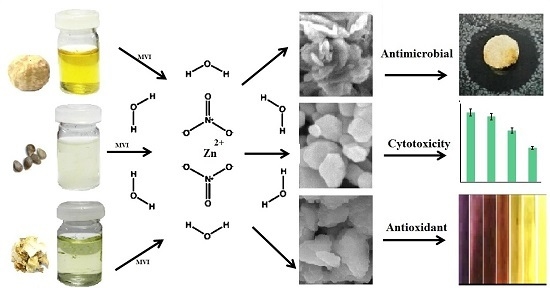
Green Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Characterization and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
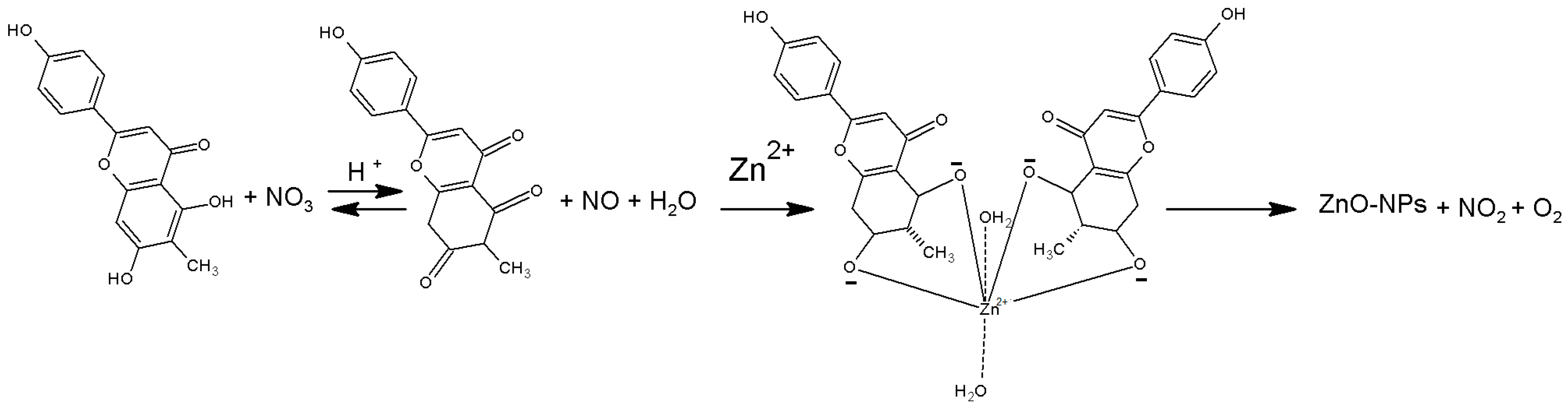
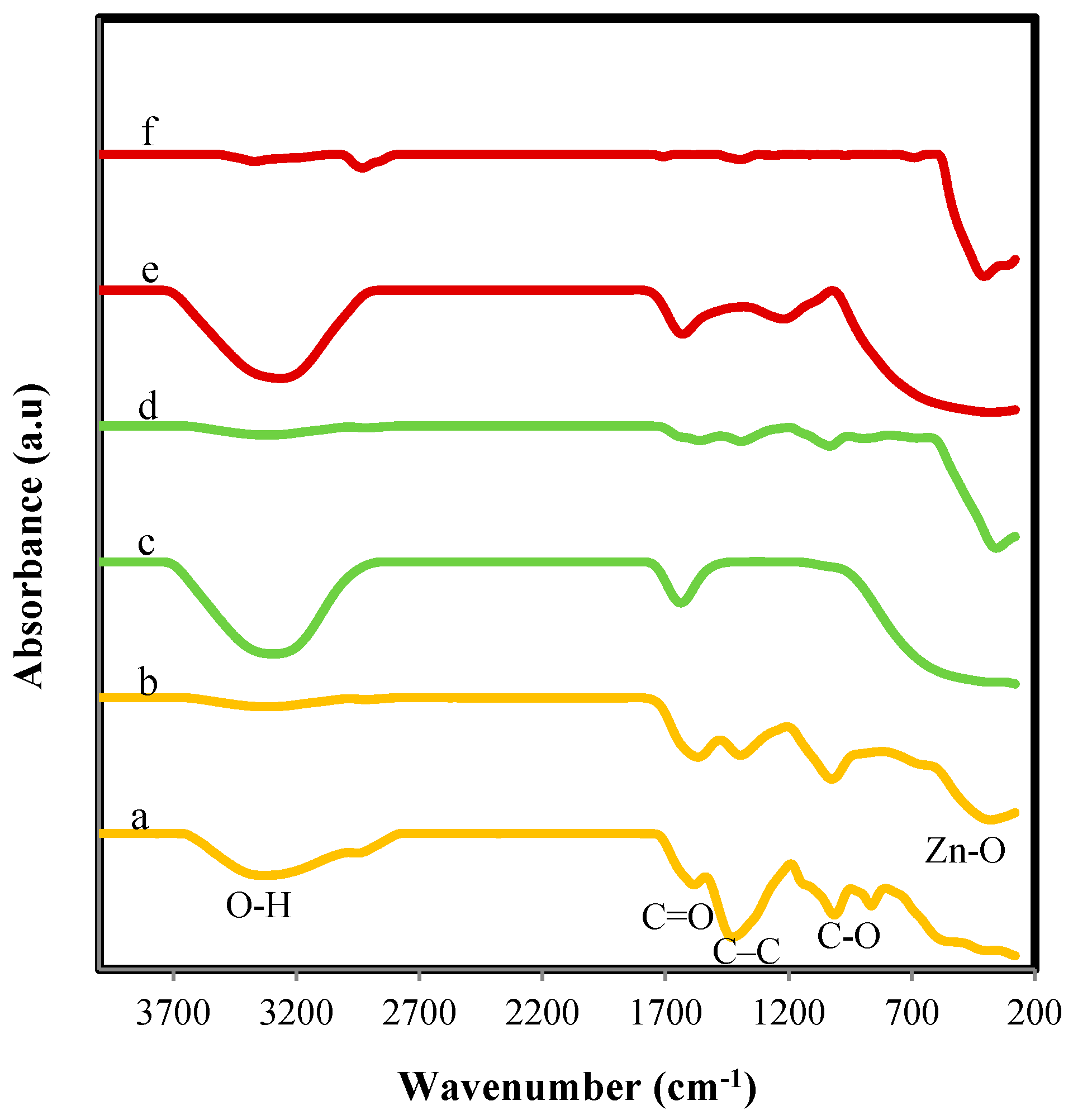
2.1. Structural and Morphology Characterization of ZnO-NPs
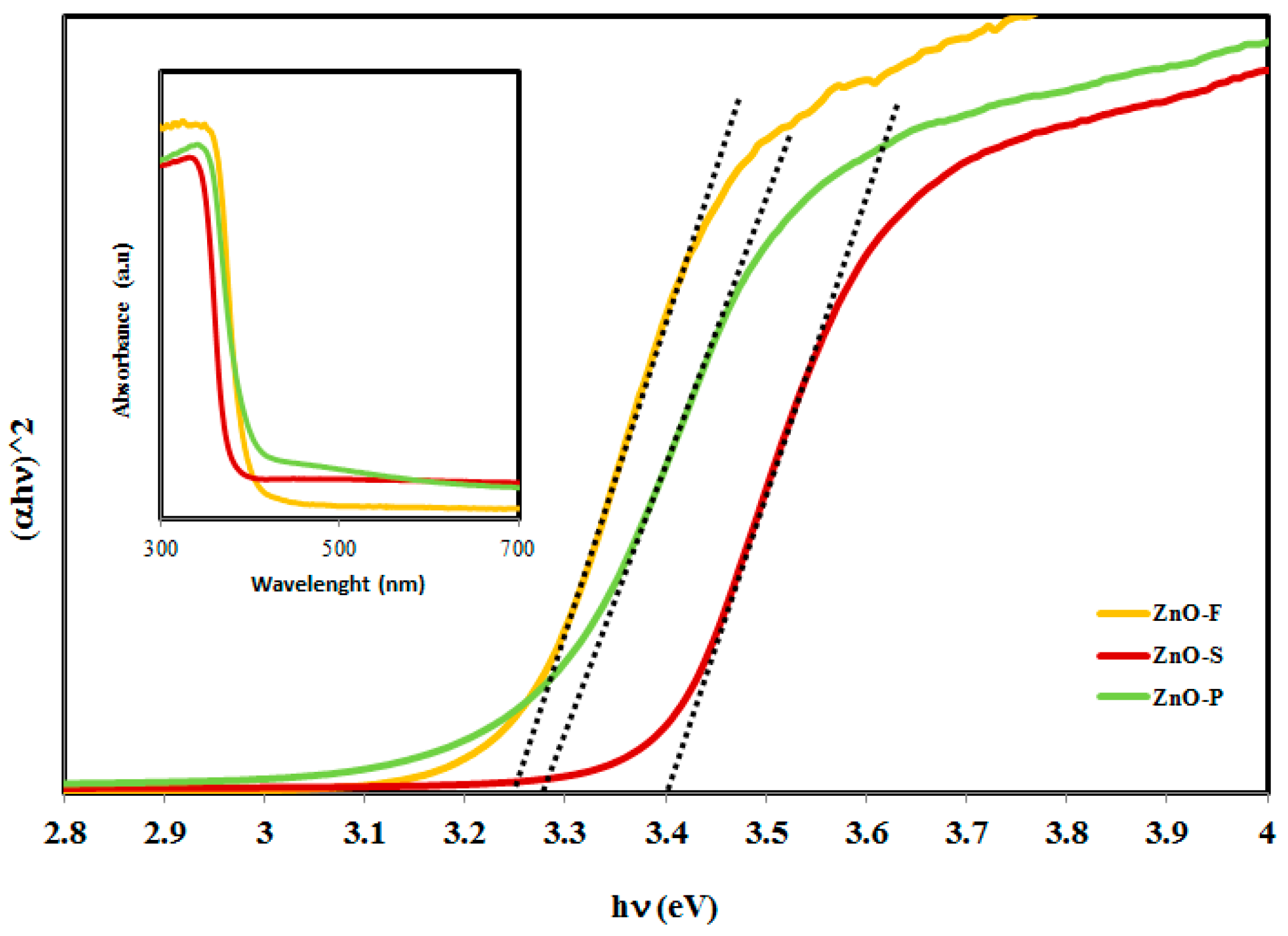
2.2. Analysis of Optical Properties
2.3. Analysis on Colloidal Properties
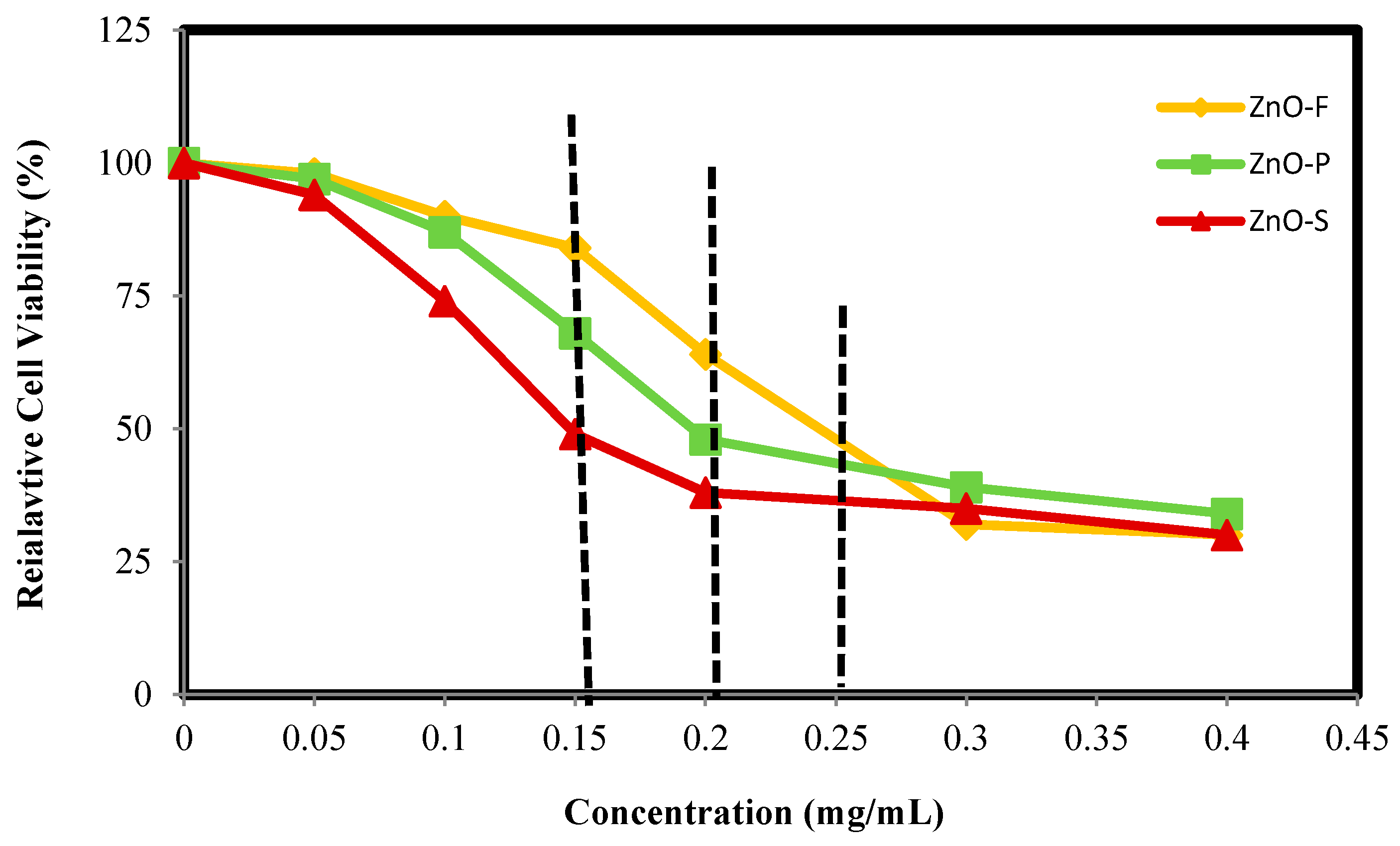
2.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
2.5. 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Radical Scavenging Activity
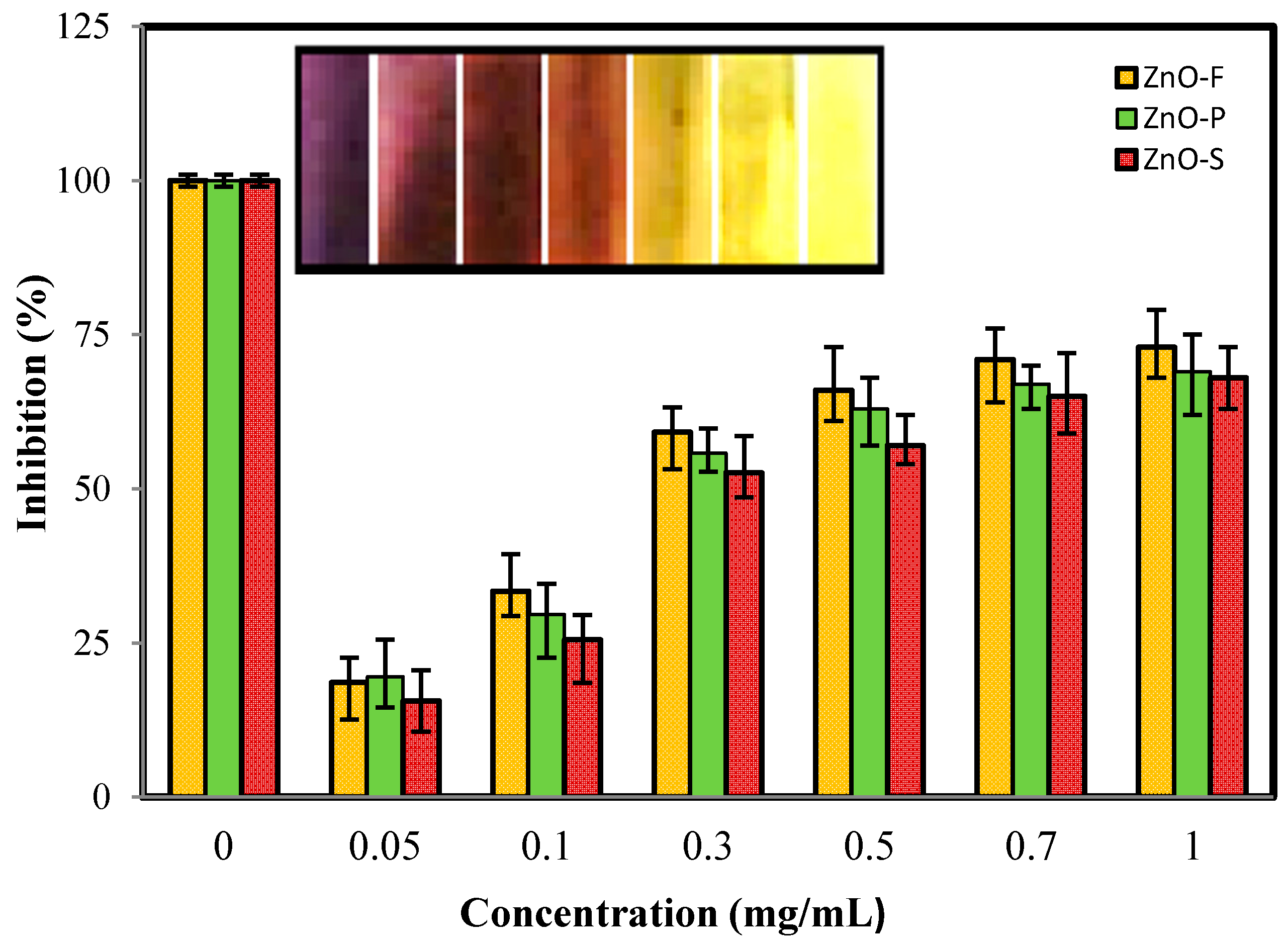
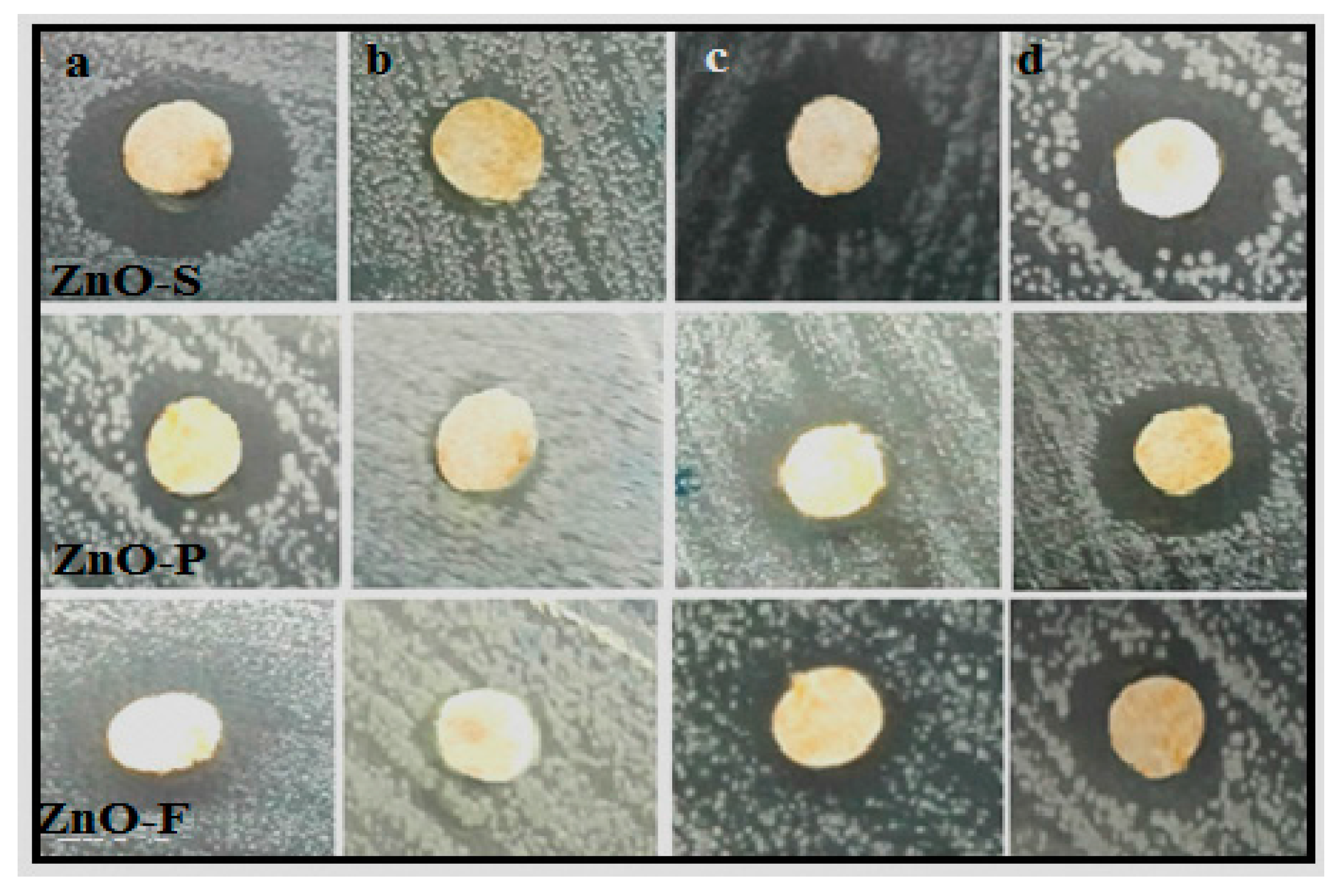
2.6. Antimicrobial Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of the C. colocynthis Extracts
3.2. Synthesis of ZnO-NPs
3.3. Characterization of ZnO-NPs
3.4. MTT Assay for Cell Viability
3.5. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
3.6. Antimicrobial Assessment
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, Z.; Chen, M.; Gu, G.; Wu, L. A facile method to fabricate ZnO hollow spheres and their photocatalytic property. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L. ZnO nanowire and nanobelt platform for nanotechnology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2009, 64, 33–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B.; Sharon, M. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of highly porous ZnO thin films prepared by sol-gel process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 76, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Waitz, T.; Roggenbuck, J.; Froba, M.; Kohl, C.-D.; Tiemann, M. Ordered mesoporous ZnO for gas sensing. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 8360–8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yamasaki, O.; Kanzaki, H.; Tadaa, J.; Arata, J. Effects of zinc oxide on the attachment of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1998, 17, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; He, J.H.; Tang, H.M.; Yan, C.X. Porous silica nanocapsules and nanospheres: Dynamic self-assembly synthesis and application in controlled release. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 5894–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.K.; Dutta, A.; Bhaumik, A. A self-assembled ultra small ZnO nanocrystals for dye- sensitized solar cell application. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 215, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Ahmad, M.B.; Mahdavi, M.; Abdolmohammadi, S. Preparation, characterization, and antimicrobial activities of ZnO nanoparticles/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites. Bioresources 2013, 8, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, R.; Zak, A.K.; Majid, W.H.A.; Darroudi, M. Solvothermal synthesis of microsphere ZnO nanostructures in DEA media. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 3657–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.C.; He, W.L.; Zhu, M.K.; Wang, B.; Yan, H. Hydrothermal synthesis of zinc oxide powders with controllable morphology. Ceram. Int. 2004, 30, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamiri, R.; Zakaria, A.; Ahangar, H.A.; Darroudi, M.; Zak, A.K.; Drummen, G.P.C. Aqueous starch as a stabilizer in zinc oxide nanoparticle synthesis via laser ablation. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 516, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Hu, H.; Shao, G.; Han, C. Facile template-free sonochemical fabrication of hollow ZnO spherical structures. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 852–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, A.K.; Majid, W.H.A.; Darroudi, M.; Yousefi, R. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles prepared in gelatin media. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, T.; Wegner, K.; Pratsinis, S.E. Towards carbon-free flame spray synthesis of homogeneous oxide nanoparticles from aqueous solutions. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, N.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Jacob, K.T. Glycol–nitrate combustion synthesis of fine sinter-active yttria. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 3, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalaraja, R.V.; Mouzon, J.; HedstrÖm, P.; Kero, I.; Ramam, K.V.S.; Camurri, C.P.; Odén, M. Combustion synthesis of Y2O3 and Yb–Y2O3: Part I. Nanopowders and their characterization. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2008, 208, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarong, W.; Toshiyuki, M.; Ji-Guang, L.; Yoshiyuki, Y. Low-temperature fabrication and electrical property of 10 mol % Sm2O3-doped CeO2 ceramics. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2003, 4, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Hasin, P.; Koonsaeng, N.; Laobuthee, A. Nickel-aluminium complex: A simple and effective precursor for nickel aluminate (NiAl2O4) spinel. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Mangalaraja, R.V.; Mouzon, J.; Hedström, P.; Camurri, C.P.; Ananthakumar, S.; Odén, M. Microwave assisted combustion synthesis of nanocrystalline yttria and its powder characteristics. Powder Technol. 2009, 191, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressel-Michel, E.; Chaumont, D.; Stuerga, D. From a microwave flash-synthesized TiO2 colloidal suspension to TiO2 thin films. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2005, 285, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.P.; Lin, C.H.; Hsu, C.S. Preparation of ultrafine CeO2 powders by microwave-induced combustion and precipitation. J. Alloy Compd. 2005, 391, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, B.; Huang, R.; Xia, Z.; Ge, S. Flash synthesis of flower-like ZnO nanostructures by microwave-assisted combustion process. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Bijanzada, K.; Mirsepah, A. Synthesis of graphene from natural and industrial carbonaceous wastes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 20441–20448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, W.N.; Daghir, N.J.; Khan, P. Chemical characterization and edibility of the oil extracted from Citrullus colocynthis seeds. J. Food Sci. 1983, 48, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafferman, D.; Behazav, A.; Shabelsky, E.; Yaniv, Z. Evaluation of Citrillus colocynthis a desert plant native in Israel as a potential source of edible oil. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 40, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, K.; Jahanbakhsh, T. Anticandidal screening and antibacterial of Citrullus colocynthis in South East of Iran. J. Hortic. For. 2011, 3, 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, D.; Saroha, K.; Singh, N.; Vashishta, B. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging potential of Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad. Methanolic fruit extract. Acta Pharm. 2008, 58, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delazar, A.; Gibbons, S.; Kosari, A.R.; Nazemiyeh, H.; Modarresi, M.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D. Flavone C-glycosides and cucurbitacin glycosides from Citrullus colocynthis. Daru 2006, 14, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.C.; Chiu, M.H.; Nie, R.L.; Cordell, G.A.; Qiu, S.X. Cucurbitacins and cucurbitane glycosides: structures and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, W.; Xia, S. Combustion synthesis and photoluminescence of nanocrystalline Y2O3: Eu phosphors. Mater. Res. Bull. 1997, 32, 501–506. [Google Scholar]
- Nagappa, B.; Chandrappa, G.T. Mesoporous nanocrystalline magnesium oxide for environmental remediation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 106, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.C.; Hegde, M.S.; Rattan, T.; Aruna, H.T. Chemistry of Nanocrystalline Oxide Materials: Combustion Synthesis, Properties and Applications; World Scientific Publishing Pvt., Ltd.: Singapore, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of X-ray Diffraction: A Practical Approach; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Hosokawa, M.; Nogi, K.; Naito, M.; Yokoyama, T. Nanoparticle Technology Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, A.; Bergmann, C.P.; Berutti, F.A. Novel synthesis And Characterization of Nanostructured Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yu, J.; Cheng, B.; Zhou, M. Effects of hydrothermal post-treatment on microstructures and morphology of titanate nanoribbons. J. Solid State Chem. 2006, 179, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namvar, F.; Azizi, S.; Ahmad, M.B.; Shameli, K.; Mohamad, R.; Mahdavi, M.; Md Tahir, P. Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using the marine macroalgae Sargassum muticum. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 5723–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punnoose, A.; Dodge, K.; Rasmussen, J.W.; Chess, J.; Wingett, D.; Anders, C. Cytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles can be tailored by modifying their surface structure: A green chemistry approach for safer nanomaterials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Boroumand Moghaddam, A.; Moniri, M.; Ariff, A.; Saad, W.Z.; Namvar, F. ZnO-Ag core shell nanocomposite formed by green method using essential oil of wild ginger and their bactericidal and cytotoxic effects. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 384, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, C.; Thurber, A.; Hanna, C.; Punnoose, A.; Zhang, J.; Wingett, D.G. The influences of cell type and ZnO nanoparticle size on immune cell cytotoxicity and cytokine induction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, M.; Kim, M.K.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, J.A.; Yu, J.; Chung, H.E.; Choi, S.J. Factors influencing the cytotoxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: particle size and surface charge. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 304, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, K.; Velmurugan, S. Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Azadirachta indica (L.). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R.; Bahadoran, A.; Bayat, S.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Ariff, A.; Zuhainis Saad, W. Effect of annealing temperature on antimicrobial and structural properties of bio-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Anchusa italic. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 161, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Mehrabian, M.; Mirabbaszadeh, K.; Azimirad, R. Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanorod arrays for photocatalytic inactivation of bacteria. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 225305–225314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, M.S. Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 1958, 181, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.

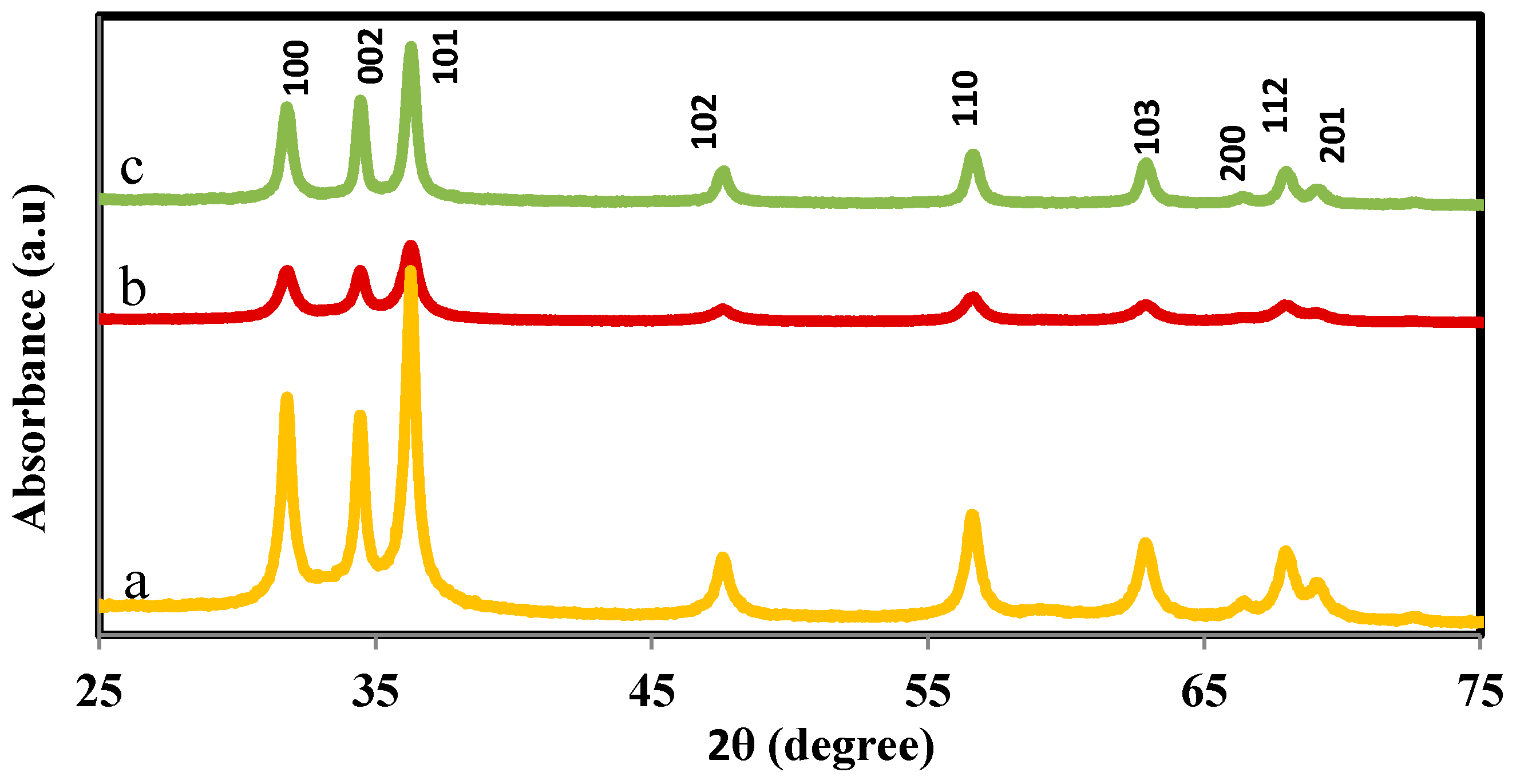

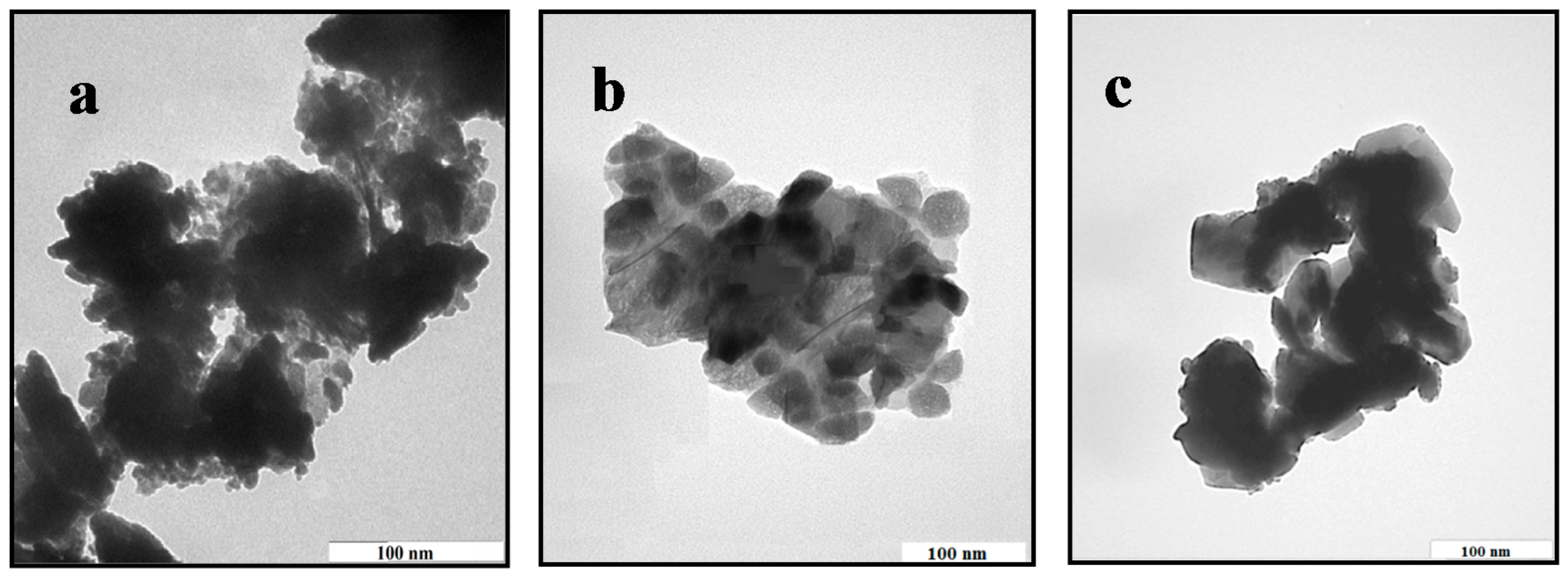

| Sample | 2θ ± 0.1 | h k l | Structure | Lattice Parameter (nm) | V (A°)3 | cosφ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO-F | 67.96 | 1 1 2 | wurtzite | a = 0.3222, c/a = 1.599 | 48.17 | 0.8480 |
| 69.10 | 2 0 1 | |||||
| ZnO-S | 68.08 | 1 1 2 | wurtzite | a = 0.3248, c/a = 1.592 | 47.88 | 0.7193 |
| 69.18 | 2 0 1 | |||||
| ZnO-P | 67.92 | 1 1 2 | wurtzite | a = 0.3249, c/a = 1.601 | 47.62 | 0.7180 |
| 69.15 | 2 0 1 |
| Sample | Zeta Potential (mV) | Hydrodynamic Size (nm) | Polydispersity Indices (μ2/Г2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO-S | −15.3 ± 2 | 1050 ± 80 | 0.369 |
| ZnO-P | −19.5 ± 2 | 860 ± 80 | 0.385 |
| ZnO-F | −25.60 ± 2 | 750 ± 80 | 0.407 |
| Pathogens | ZnO-S | ZnO-P | ZnO-F |
|---|---|---|---|
| B. subtilis | 14.3 ± 0.51 | 11.2 ± 0.25 | 12.2 ± 0.24 |
| MRSA | 6.8 ± 0.36 | 6.9 ± 0.12 | 6.8 ± 0.39 |
| P. aeruginosa | 12.2 ± 0.27 | 10.7 ± 0.49 | 10.4 ± 0.49 |
| E. coli | 13.4 ± 0.47 | 11.8 ± 0.28 | 10.8 ± 0.10 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R.; Mahdavi Shahri, M. Green Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Characterization and Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2017, 22, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020301
Azizi S, Mohamad R, Mahdavi Shahri M. Green Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Characterization and Biomedical Applications. Molecules. 2017; 22(2):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020301
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzizi, Susan, Rosfarizan Mohamad, and Mahnaz Mahdavi Shahri. 2017. "Green Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Characterization and Biomedical Applications" Molecules 22, no. 2: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020301
APA StyleAzizi, S., Mohamad, R., & Mahdavi Shahri, M. (2017). Green Microwave-Assisted Combustion Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: Characterization and Biomedical Applications. Molecules, 22(2), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22020301