In Vivo and In Vitro Activities and ADME-Tox Profile of a Quinolizidine-Modified 4-Aminoquinoline: A Potent Anti-P. falciparum and Anti-P. vivax Blood-Stage Antimalarial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Vitro Antimalarial Activity against P. falciparum and P. vivax
2.2. In Vivo Oral Efficacy Studies
2.3. In Vivo Transmission-Blocking and Prophylactic Effects
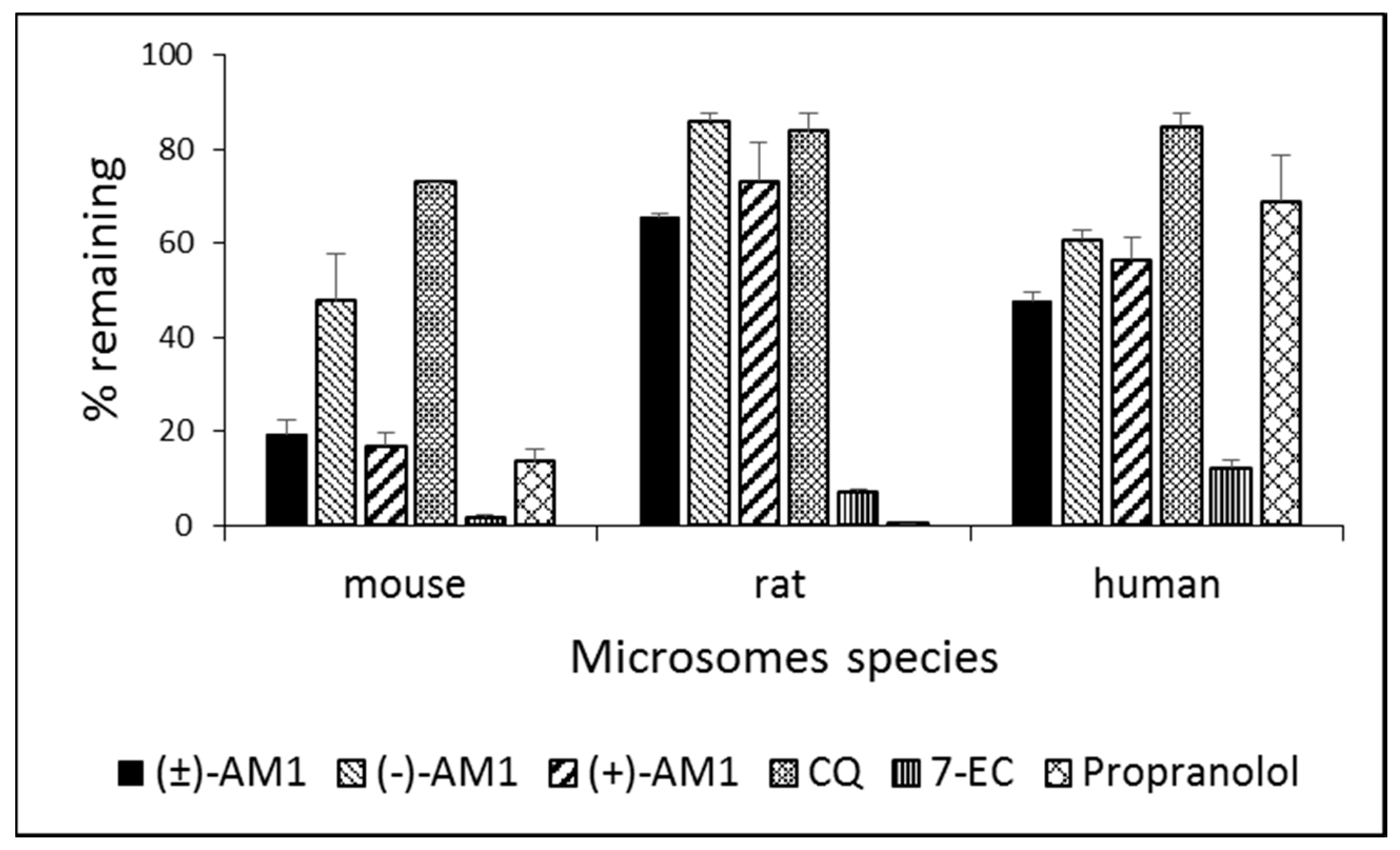
2.4. Metabolic Stability and Biotransformation Studies in Rat, Mouse, and Human Microsomes
2.5. P450 and hERG Interaction
2.6. Pharmacokinetics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compounds
4.2. Cultures of P. falciparum and In Vitro Chemosensitivity Assays
4.3. In Vitro Assays against P. vivax Field Isolates
4.4. In Vivo Efficacy Tests and Transmission-Blocking/Prophylactic Activities
4.5. LC–MS/MS Analytical Methods
4.6. In Vitro Microsome Stability and Metabolism Studies
4.7. Pharmacokinetics
4.8. P450 Assay
4.9. hERG Binding Assay
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO World Malaria Report, 2016; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Imwong, M.; Hien, T.T.; Thuy-Nhien, N.T.; Dondorp, A.M.; White, N.J. Spread of a single multidrug resistant malaria parasite lineage (PfPailin) to Vietnam. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, B.; Leroy, D.; Fidock, D.A. Antimalarial drug resistance: Linking Plasmodium falciparum parasite biology to the clinic. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takala-Harrison, S.; Jacob, C.G.; Arze, C.; Cummings, M.P.; Silva, J.C.; Dondorp, A.M.; Fukuda, M.M.; Hien, T.T.; Mayxay, M.; Noedl, H.; et al. Independent emergence of artemisinin resistance mutations among Plasmodium falciparum in Southeast Asia. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, D.; Khim, N.; Beghain, J.; Adegnika, A.A.; Shafiul-Alam, M.; Amodu, O.; Rahim-Awab, G.; Barnadas, C.; Berry, A.; Boum, Y.; et al. A worldwide map of Plasmodium falciparum K13-propeller polymorphisms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar]
- Mendis, K.; Sina, B.J.; Marchesini, P.; Carter, R. The neglected burden of Plasmodium vivax malaria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 64, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, R.E.; Battle, K.E.; Mendis, K.N.; Smith, D.L.; Cibulskis, R.E.; Baird, J.K.; Hay, S.I. Global epidemiology of Plasmodium vivax. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, J.K. Evidence and implications of mortality associated with acute Plasmodium vivax malaria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Jain, M.; Reddy, R.P.; Jain, R. Quinolines and structurally related heterocycles as antimalarials. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3245–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiarie, W.C.; Wangai, L.; Agola, E.; Kimani, F.T.; Hungu, C. Chloroquine sensitivity: Diminished prevalence of chloroquine-resistant gene marker Pfcrt-76 13 years after cessation of chloroquine use in Msambweni, Kenya. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaque, M.; Shahjahan. Reemergence of chloroquine (CQ) analogs as multi-targeting antimalarial agents: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 90, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, A.; McMahon, B.; Daughton, A.R.; Abeyta, E.L.; Hodge, D.; Anderson, K.; Pillai, S. Surveillance for emerging diseases with multiplexed point-of-care diagnostics. Health Secur. 2016, 14, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparatore, A.; Basilico, N.; Casagrande, M.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Brun, R.; Wittlin, S.; Sparatore, F. Antimalarial activity of novel pyrrolizidinyl derivatives of 4-aminoquinoline. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 3737–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, P.M.; Park, B.K.; Shone, A.E.; Maggs, J.L.; Roberts, P.; Stocks, P.A.; Biagini, G.A.; Bray, P.G.; Gibbons, P.; Berry, N.; et al. Candidate selection and preclinical evaluation of n-tert-butyl isoquine (GSK369796), an affordable and effective 4-aminoquinoline antimalarial for the 21st century. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Ongarora, D.S.; Strydom, N.; Wicht, K.; Njoroge, M.; Wiesner, L.; Egan, T.J.; Wittlin, S.; Jurva, U.; Masimirembwa, C.M.; Chibale, K. Antimalarial benzoheterocyclic 4-aminoquinolines: Structure-activity relationship, in vivo evaluation, mechanistic and bioactivation studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 5419–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biot, C.; Nosten, F.; Fraisse, L.; Ter-Minassian, D.; Khalife, J.; Dive, D. The antimalarial ferroquine: From bench to clinic. Parasite 2011, 18, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, W.A.; Jameel, E.; Baig, U.; Mumtazuddin, S.; Hun, L.T. Ferroquine and its derivatives: New generation of antimalarial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.S.; Rückle, T.; Djeriou, E.; Cantalloube, C.; Ter-Minassian, D.; Baker, M.; O’Rourke, P.; Griffin, P.; Marquart, L.; van Huijsduijnen, R.H.; et al. A phase II pilot trial to evaluate safety and efficacy of ferroquine against early Plasmodium falciparum in an induced blood-stage malaria infection study. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mzayek, F.; Deng, H.; Mather, F.J.; Wasilevich, E.C.; Liu, H.; Hadi, C.M.; Chansolme, D.H.; Murphy, H.A.; Melek, B.H.; Tenaglia, A.N.; et al. Randomized dose-ranging controlled trial of AQ-13, a candidate antimalarial, and chloroquine in healthy volunteers. PLoS Clin. Trials 2007, 2, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koita, O.A.; Sangaré, L.; Miller, H.D.; Sissako, A.; Coulibaly, M.; Thompson, T.A.; Fongoro, S.; Diarra, Y.; Ba, M.; Maiga, A.; et al. AQ-13, an investigational antimalarial, versus artemether plus lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria: A randomised, phase 2, non-inferiority clinical trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, J.N.; Duparc, S.; Gutteridge, W.E.; van Huijsduijnen, R.H.; Kaszubska, W.; Macintyre, F.; Mazzuri, S.; Möhrle, J.J.; Wells, T.N.C. New developments in anti-malarial target candidate and product profiles. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparatore, A.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Romeo, S.; Novelli, F.; Sparatore, F.; Taramelli, D. 4-aminoquinoline quinolizidinyl- and quinolizidinylalkyl-derivatives with antimalarial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5338–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omodeo-Salè, F.; Cortelezzi, L.; Basilico, N.; Casagrande, M.; Sparatore, A.; Taramelli, D. Novel antimalarial aminoquinolines: Heme binding and effects on normal or Plasmodium falciparum-parasitized human erythrocytes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4339–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, T.J.; Chen, J.Y.; de Villiers, K.A.; Mabotha, T.E.; Naidoo, K.J.; Ncokazi, K.K.; Langford, S.J.; McNaughton, D.; Pandiancherri, S.; Wood, B.R. Haemozoin (beta-haematin) biomineralization occurs by self-assembly near the lipid/water interface. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 5105–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusconi, C.; Vaiana, N.; Casagrande, M.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Romeo, S.; Sparatore, A. Synthesis and comparison of antiplasmodial activity of (+), (−) and racemic 7-chloro-4-(N-lupinyl)aminoquinoline. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 5980–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, W. Drug resistance in Plasmodium berghei vincke and lips, 1948. I. Chloroquine resistance. Exp. Parasitol. 1965, 17, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, D.; Damre, A.; Varghese, A.; Addepalli, V. In vitro evaluation of hepatic and extra-hepatic metabolism of coumarins using rat subcellular fractions: Correlation of in vitro clearance with in vivo data. Drug Metabol. Drug Interact. 2008, 23, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedoyin, A.; Frye, R.F.; Mauro, K.; Branch, R.A. Chloroquine modulation of specific metabolizing enzymes activities: Investigation with selective five drug cocktail. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 46, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, D.; Krogstad, F.M.; Cogswell, F.B.; Krogstad, D.J. Aminoquinolines that circumvent resistance in Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 55, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, D.; Krogstad, F.M.; Byers, L.D.; Krogstad, D.J. Structure-activity relationships for antiplasmodial activity among 7-substituted 4-aminoquinolines. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 4918–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelièvre, J.; Almela, M.J.; Lozano, S.; Miguel, C.; Franco, V.; Leroy, D.; Herreros, E. Activity of clinically relevant antimalarial drugs on Plasmodium falciparum mature gametocytes in an ATP bioluminescence “Transmission blocking” Assay. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz, F.E.; Mutka, T.; Udenze, K.; Oduola, A.M.; Kyle, D.E. Novel 4-aminoquinoline analogs highly active against the blood and sexual stages of Plasmodium in vivo and in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4685–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. The cardiotoxicity of antimalarials. In Report of the WHO Evidence Review Group Meeting on 13–14 October; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aderounmu, A.F. In vitro assessment of the antimalarial activity of chloroquine and its major metabolites. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1984, 78, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan-Girish, S.; Catz, P.; Creek, M.R.; Wu, B.; Thomas, D.; Krogstad, D.J.; De, D.; Mirsalis, J.C.; Green, C.E. Pharmacokinetics of the antimalarial drug, AQ-13, in rats and Cynomolgus macaques. Int. J. Toxicol. 2004, 23, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boido, C.C.; Boido, V.; Sparatore, F. Preparation and antileukemic activity of quinolizidinylalkyl-derivatives of 4-aminoquinoline and 9-aminoacridine. Boll. Chim. Farm. 1989, 128, 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- Trager, W.; Jensen, J.B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science 1976, 193, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makler, M.T.; Hinrichs, D.J. Measurement of the lactate dehydrogenase activity of Plasmodium falciparum as an assessment of parasitemia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 48, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit-Vical, F.; Robert, A.; Meunier, B. In vitro and in vivo potentiation of artemisinin and synthetic endoperoxide antimalarial drugs by metalloporphyrins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2836–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, A. Antimalarial drug synergism and antagonism: Mechanistic and clinical significance. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 253, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriprawat, K.; Kaewpongsri, S.; Suwanarusk, R.; Leimanis, M.L.; Lek-Uthai, U.; Phyo, A.P.; Snounou, G.; Russell, B.; Renia, L.; Nosten, F. Effective and cheap removal of leukocytes and platelets from Plasmodium vivax infected blood. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, B.; Chalfein, F.; Prasetyorini, B.; Kenangalem, E.; Piera, K.; Suwanarusk, R.; Brockman, A.; Prayoga, P.; Sugiarto, P.; Cheng, Q.; et al. Determinants of in vitro drug susceptibility testing of Plasmodium vivax. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1040–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, B.M.; Udomsangpetch, R.; Rieckmann, K.H.; Kotecka, B.M.; Coleman, R.E.; Sattabongkot, J. Simple in vitro assay for determining the sensitivity of Plasmodium vivax isolates from fresh human blood to antimalarials in areas where P. vivax is endemic. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucantoni, L.; Yerbanga, R.S.; Lupidi, G.; Pasqualini, L.; Esposito, F.; Habluetzel, A. Transmission blocking activity of a standardized neem (Azadirachta indica) seed extract on the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei in its vector Anopheles stephensi. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stresser, D.M.; Blanchard, A.P.; Turner, S.D.; Erve, J.C.; Dandeneau, A.A.; Miller, V.P.; Crespi, C.L. Substrate-dependent modulation of CYP3a4 catalytic activity: Analysis of 27 test compounds with four fluorometric substrates. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2000, 28, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peretto, I.; Radaelli, S.; Parini, C.; Zandi, M.; Raveglia, L.F.; Dondio, G.; Fontanella, L.; Misiano, P.; Bigogno, C.; Rizzi, A.; et al. Synthesis and biological activity of flurbiprofen analogues as selective inhibitors of beta-amyloid(1)(−)(42) secretion. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5705–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, P.J.; Marcoe, K.F.; Bounds, S.E.; Lin, C.H.; Feng, J.J.; Lin, A.; Cheng, F.C.; Crumb, W.J.; Mitchell, R. Validation of a [3H]astemizole binding assay in HEK293 cells expressing hERG K+ channels. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 95, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (−)-AM-1are available from the authors, samples of (±)-AM1 and (+)-AM1 are not available. |
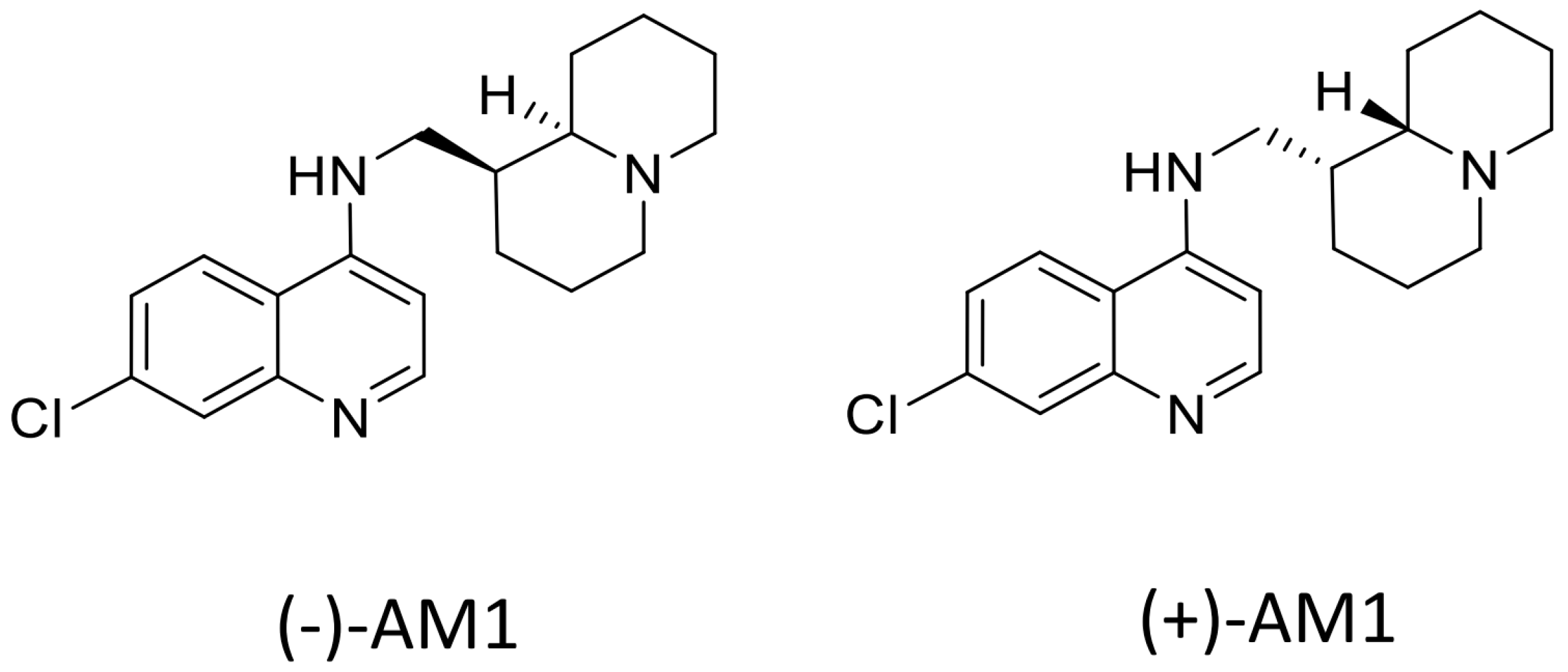

| Compounds | P. falciparum IC50 (nM) a | P. vivax IC50 (nM) b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D10 c (CQ-S) | W-2 c (CQ-R) | TM91C235 | FCR1 | FCR3 | Field Isolates | |
| (±)-AM1 | 16.15 | 35.44 | - | - | - | 29.72 |
| (−)-AM1 | 23.98 | 53.67 | 16.74 | 32.87 | 23.28 | - |
| (+)-AM1 | 17.49 | 35.77 | - | - | - | - |
| CQ | 23.72 | 437.62 | 199.46 | 181.93 | 112.56 | 86.66 |
| Compounds | P. berghei a | P. yoelii a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED50 (95% CI) (mg/kg) | ED90 (95% CI) (mg/kg) | ED50 (95% CI) (mg/kg) | ED90 (95% CI) (mg/kg) | |
| (±)-AM1 | 2.77 (1.26–4.29) | 12.58 (7.69–17.46) | ||
| (−)-AM1 | 2.05 (1.31–2.79) | 8.65 (7.06–10.23) | 1.55 (1.25–1.92) | 4.95 (3.08–7.94) |
| (+)-AM1 | 1.60 (1.08–2.11) | 2.03 (1.46–2.60) | ||
| Chloroquine | 1.12 (0.98–1.26) | 2.93 (2.64–3.22) | <3 | 58.5 (5.38–6.42) |
| MH+ (rt, min) | Proposed Structure | Metabolic Products Detected In Vitro and In Vivo | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vitro Microsomes (−)-AM1 1 μM | In Vivo Plasma Levels after 50 mg/kg Oral Gavage | ||||
| Human | Rat | Mouse | Mouse | ||
| At 30 Min | At 120 Min | ||||
| 330 (6.1) | 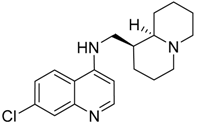 | + | + | + | + |
| 344 (5.9) |  | + | + | + | ND |
| 346 (4.7) | 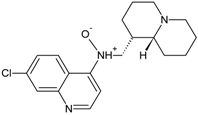 | + | + | + | + |
| Compounds | P450 Interaction—Gentest Kit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP1A2 | CYP2C9 | CYP2C19 | CYP2D6 | CYP3A4 | |
| CEC a | MFC | CEC | AMMC | BFC | |
| Mean % Inhibition at 3 µM b | |||||
| (±)-AM1 | <5 | 5.7 ± 0.2 | 6.0 ± 1.6 | 61.4 ± 2.0 | 11.6 ± 0.4 |
| (+)-AM1 | 8.3 ± 0.8 | 11.1 ± 0.5 | 9.0 ± 1.1 | 62.2 ± 1.0 | 14.3 ± 1.9 |
| (−)-AM1 | <5 | <5 | 5.0 ± 1.3 | 74.4 ± 3.5 | 8.4 ± 0.8 |
| CQ | <5 | <5 | <5 | 20.4 ± 1.1 | 6.8 ± 1.7 |
| Parameters a | (±)-AM1 | (+)-AM1 | (−)-AM1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/kg | |||
| Cmax (µM) | 0.0996 | 0.108 | 0.084 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 32.78 | 35.48 | 27.60 |
| Tmax (min) | 30 | 120 | 15 |
| MRT last (min) | 196 | 162 | 200 |
| AUC last (min·µM) | 19.5 | 22.9 | 18.8 |
| AUC last (min·ng/mL) | 6421 | 7551 | 6179 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Sparatore, A.; Romeo, S.; Misiano, P.; Vivas, L.; Yardley, V.; Croft, S.L.; Habluetzel, A.; Lucantoni, L.; et al. In Vivo and In Vitro Activities and ADME-Tox Profile of a Quinolizidine-Modified 4-Aminoquinoline: A Potent Anti-P. falciparum and Anti-P. vivax Blood-Stage Antimalarial. Molecules 2017, 22, 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122102
Basilico N, Parapini S, Sparatore A, Romeo S, Misiano P, Vivas L, Yardley V, Croft SL, Habluetzel A, Lucantoni L, et al. In Vivo and In Vitro Activities and ADME-Tox Profile of a Quinolizidine-Modified 4-Aminoquinoline: A Potent Anti-P. falciparum and Anti-P. vivax Blood-Stage Antimalarial. Molecules. 2017; 22(12):2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122102
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasilico, Nicoletta, Silvia Parapini, Anna Sparatore, Sergio Romeo, Paola Misiano, Livia Vivas, Vanessa Yardley, Simon L. Croft, Annette Habluetzel, Leonardo Lucantoni, and et al. 2017. "In Vivo and In Vitro Activities and ADME-Tox Profile of a Quinolizidine-Modified 4-Aminoquinoline: A Potent Anti-P. falciparum and Anti-P. vivax Blood-Stage Antimalarial" Molecules 22, no. 12: 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122102
APA StyleBasilico, N., Parapini, S., Sparatore, A., Romeo, S., Misiano, P., Vivas, L., Yardley, V., Croft, S. L., Habluetzel, A., Lucantoni, L., Renia, L., Russell, B., Suwanarusk, R., Nosten, F., Dondio, G., Bigogno, C., Jabes, D., & Taramelli, D. (2017). In Vivo and In Vitro Activities and ADME-Tox Profile of a Quinolizidine-Modified 4-Aminoquinoline: A Potent Anti-P. falciparum and Anti-P. vivax Blood-Stage Antimalarial. Molecules, 22(12), 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122102







