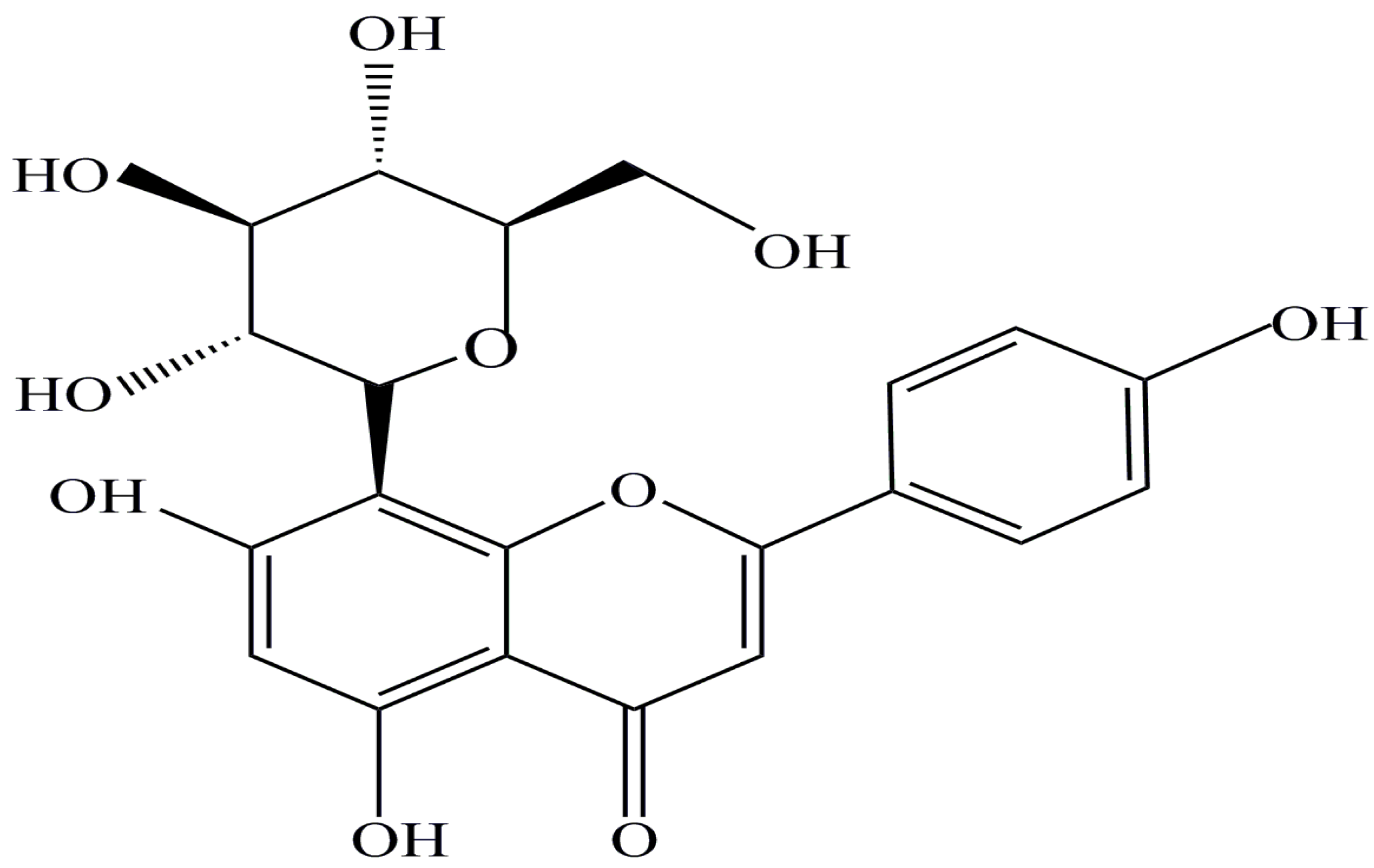
Preparation of Vitexin Nanoparticles by Combining the Antisolvent Precipitation and High Pressure Homogenization Approaches Followed by Lyophilization for Dissolution Rate Enhancement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of the ASP Process
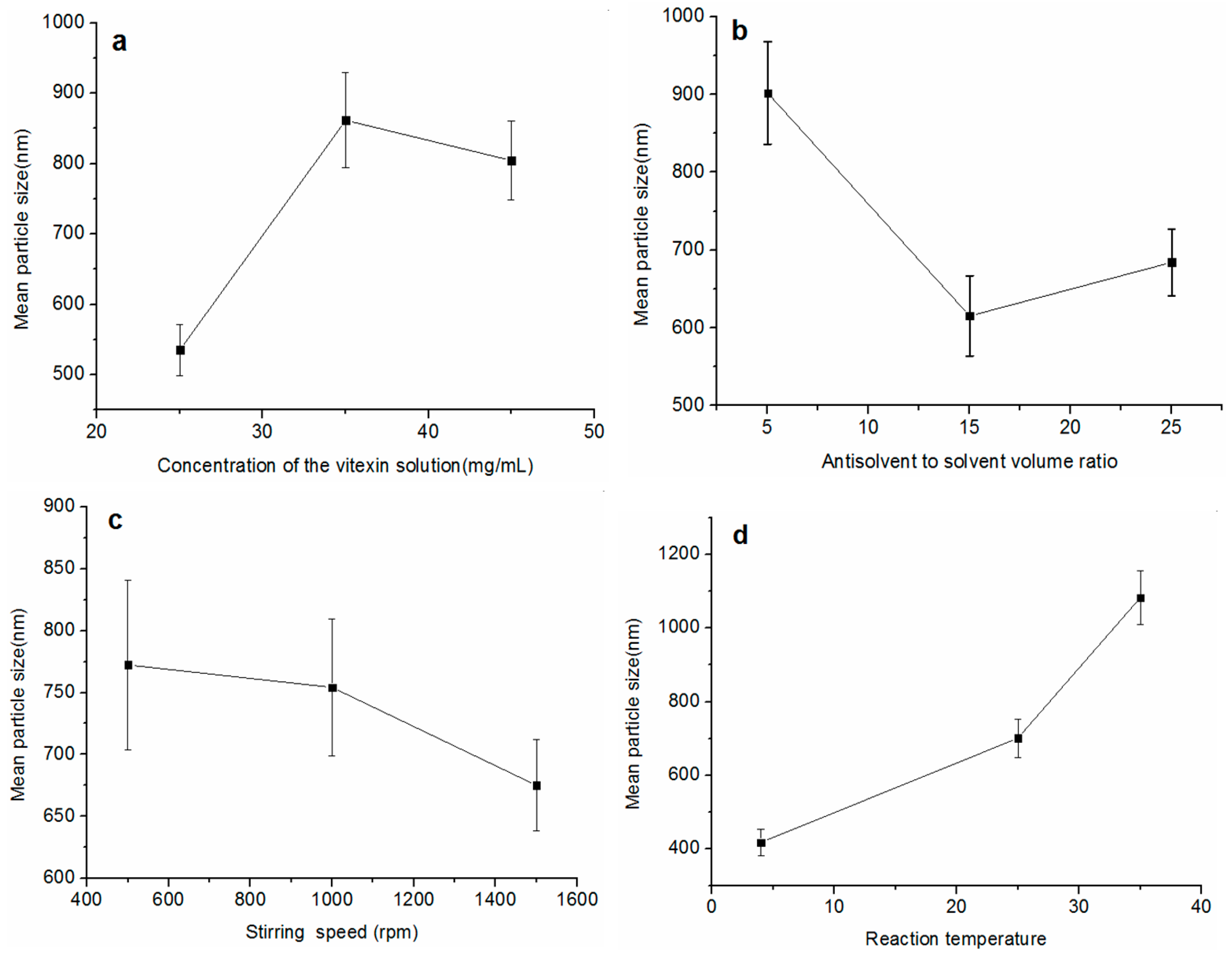
2.2. Effect of Different Influential Factors on the MPS of Vitexin Particles in the ASP Process
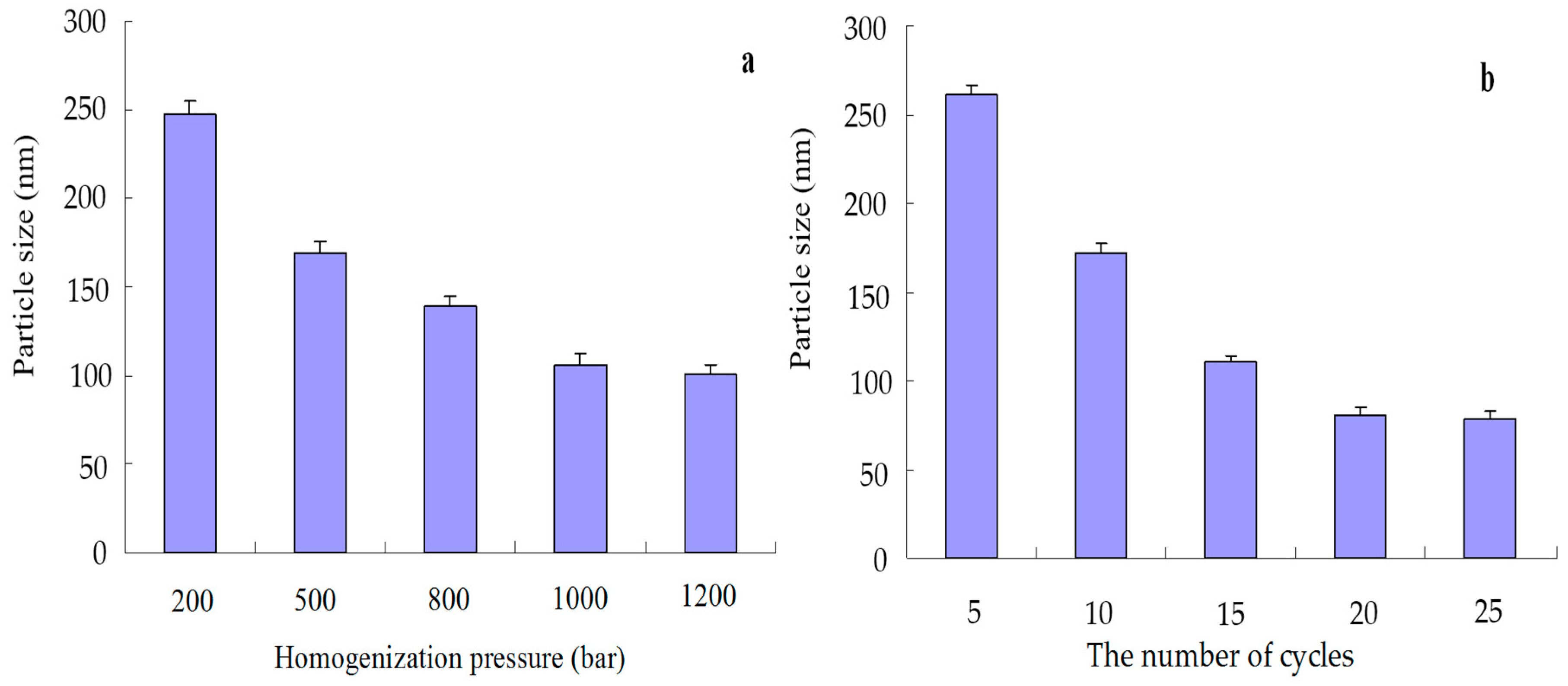
2.3. Optimization of HPH Process
2.4. Characterization of Vitexin Nanoparticles
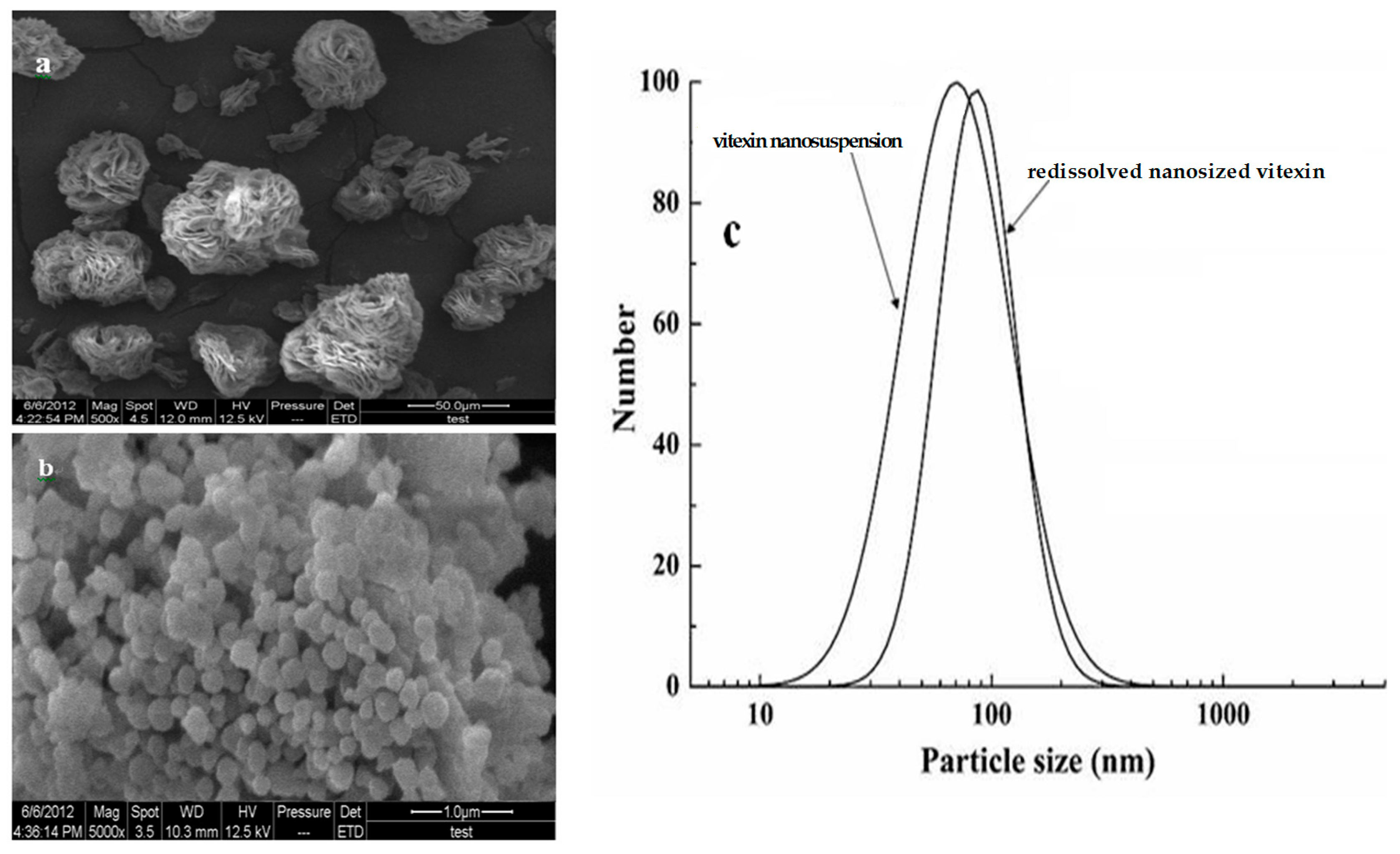
2.4.1. SEM and Particle Size Analysis
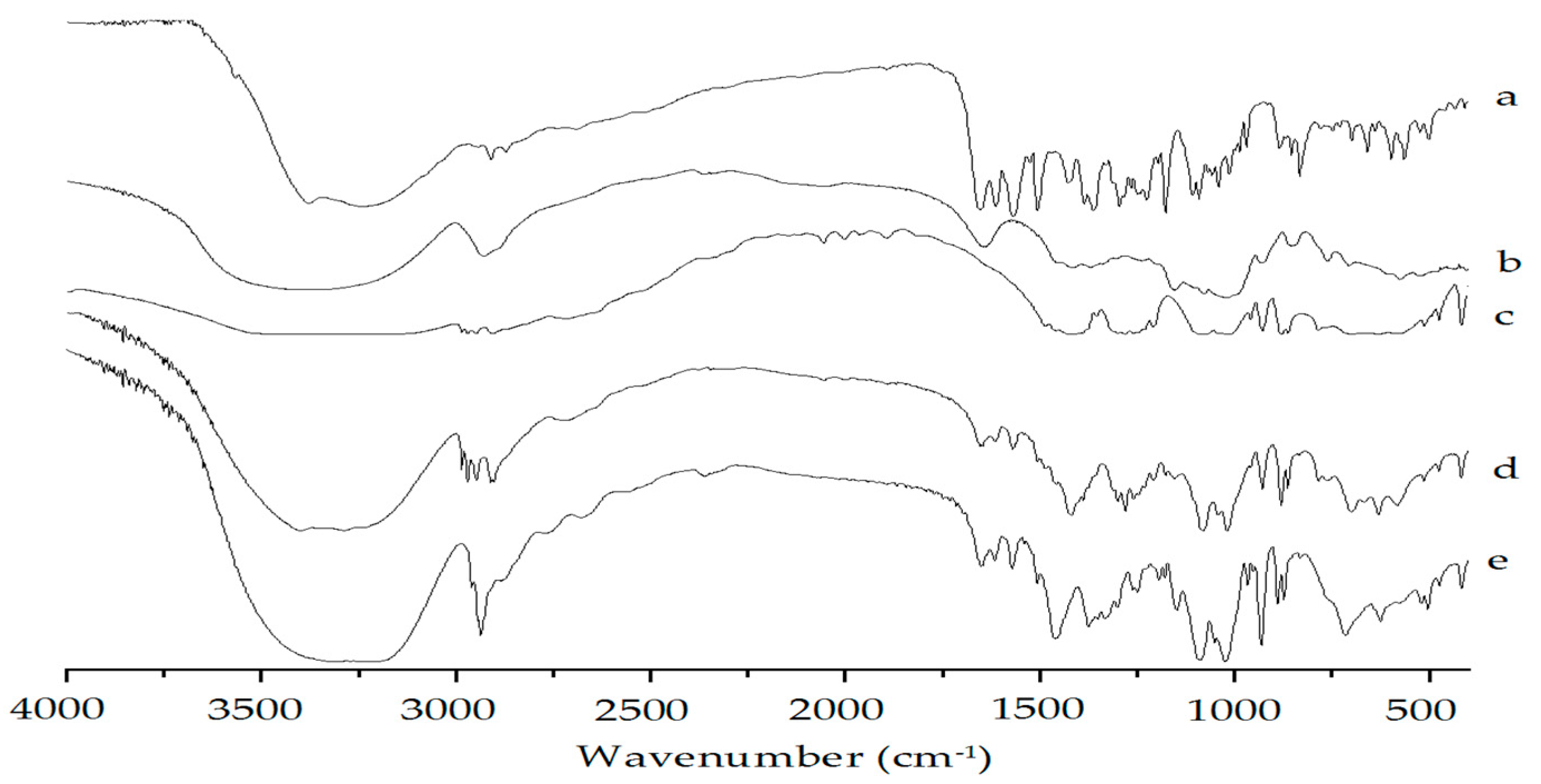
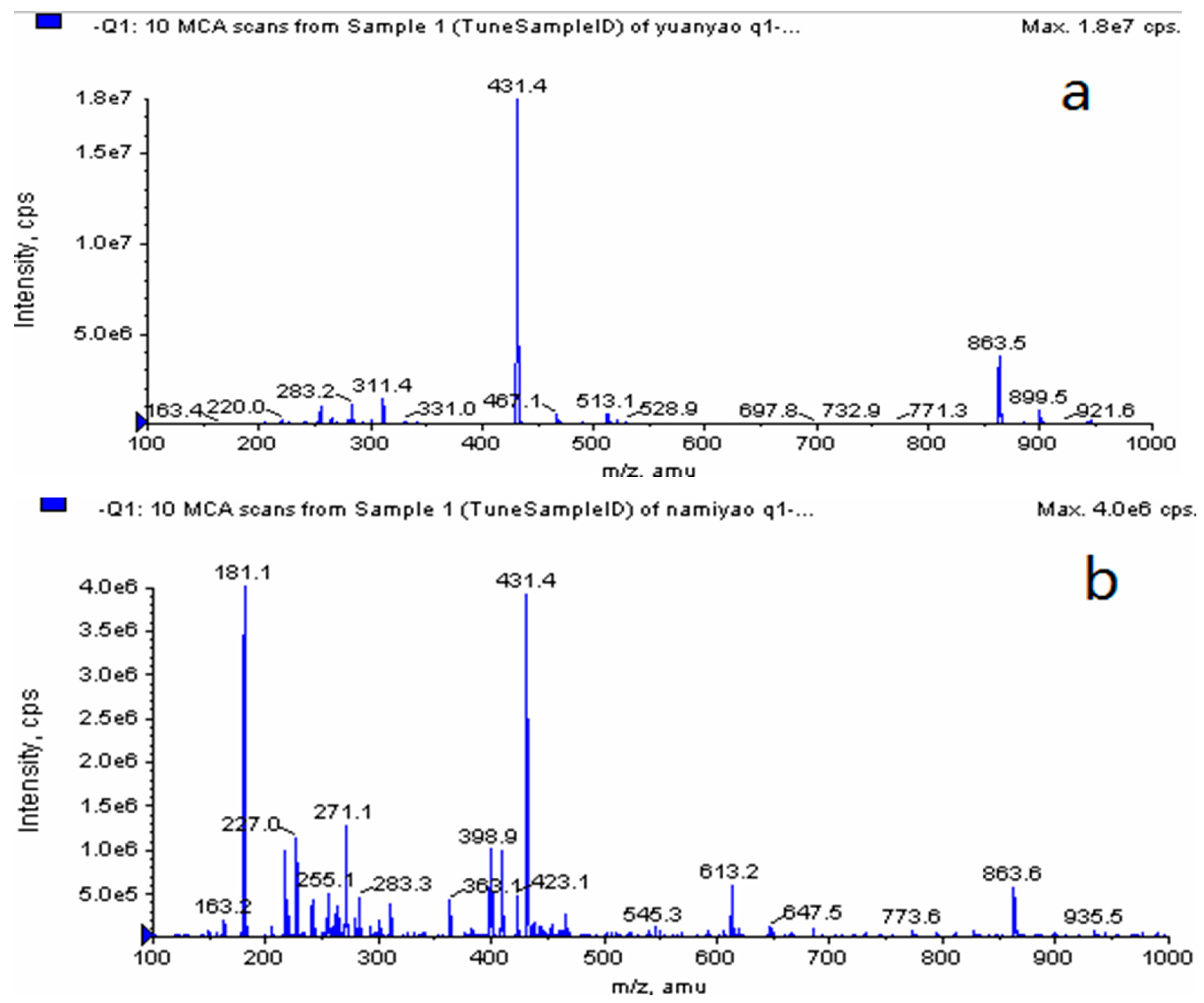
2.4.2. FTIR Assay and LC-MS Assay
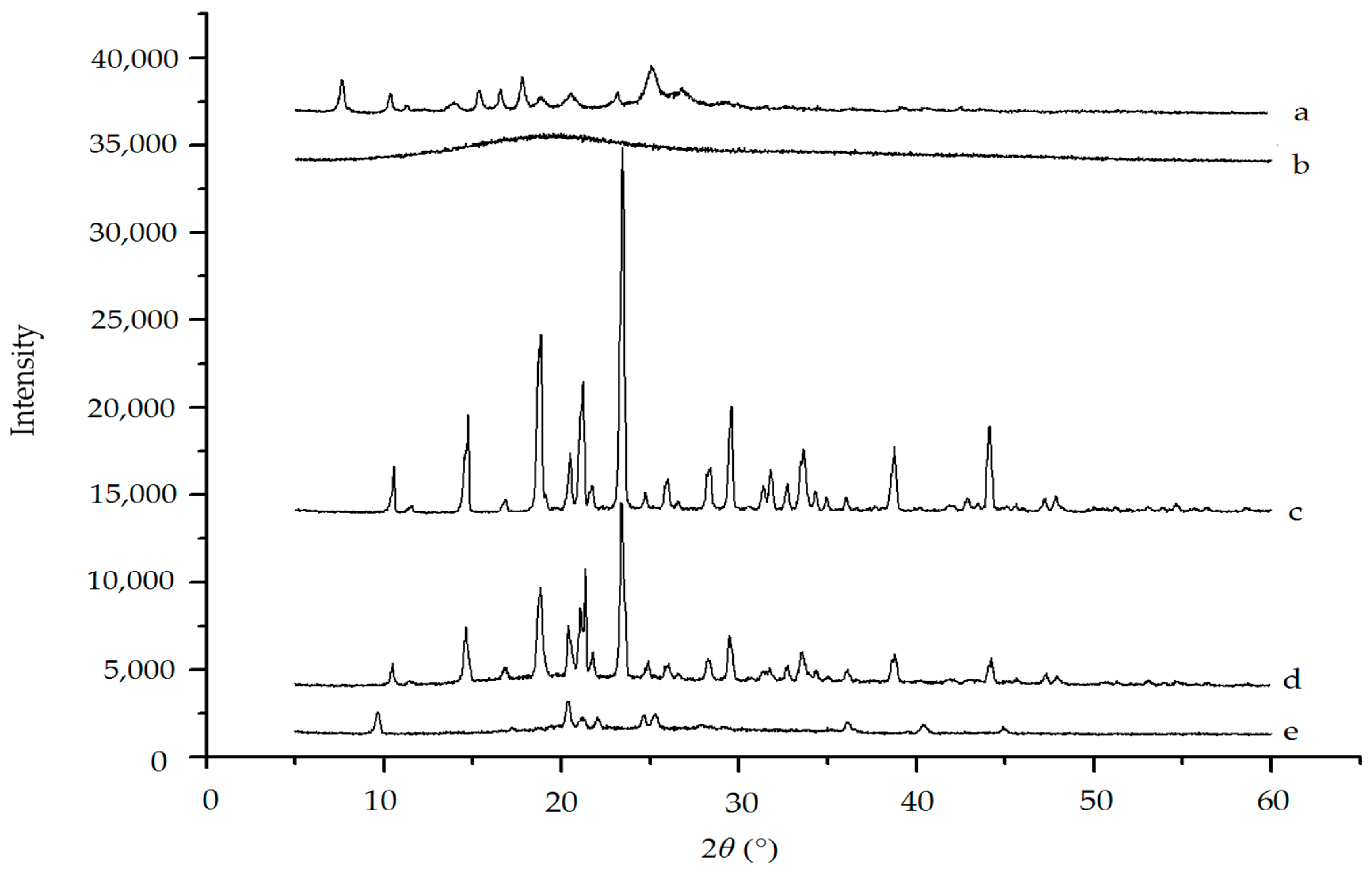
2.4.3. XRD Analysis
2.4.4. Residual Solvent Determination
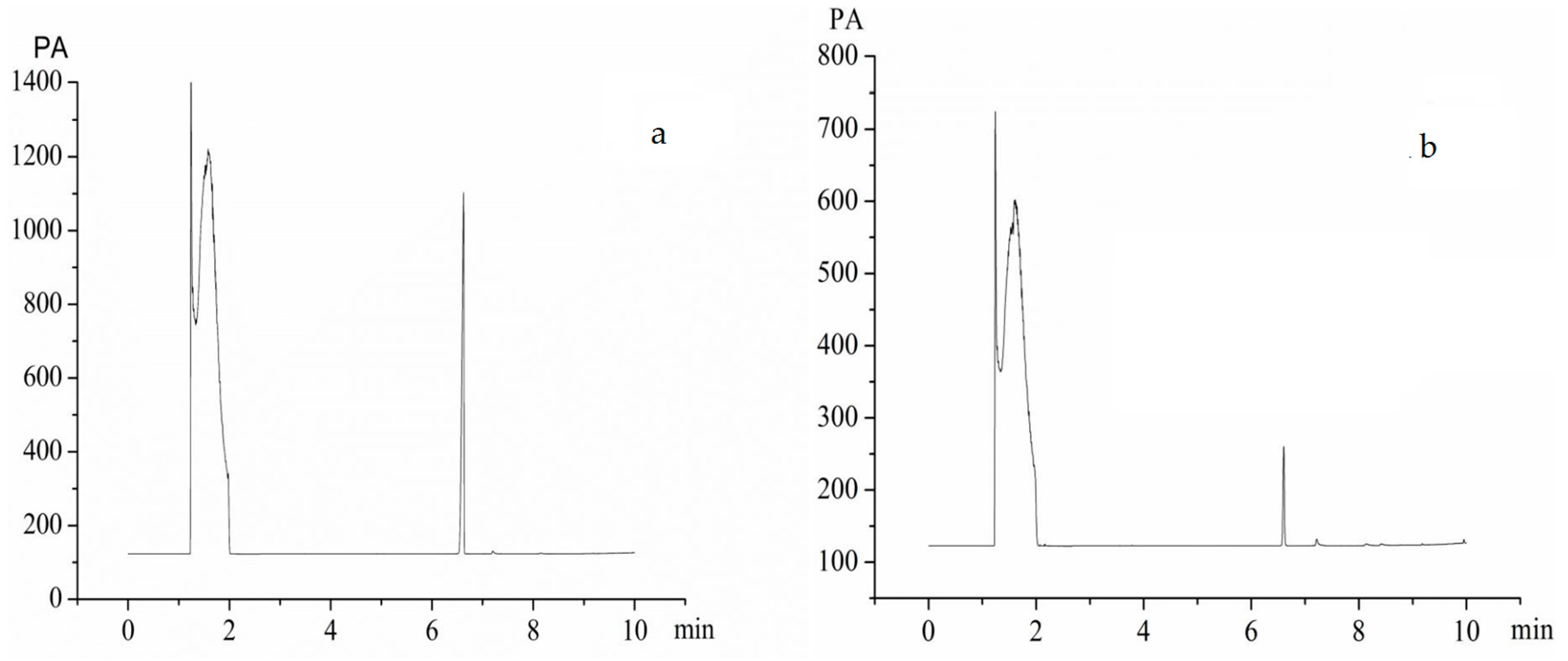
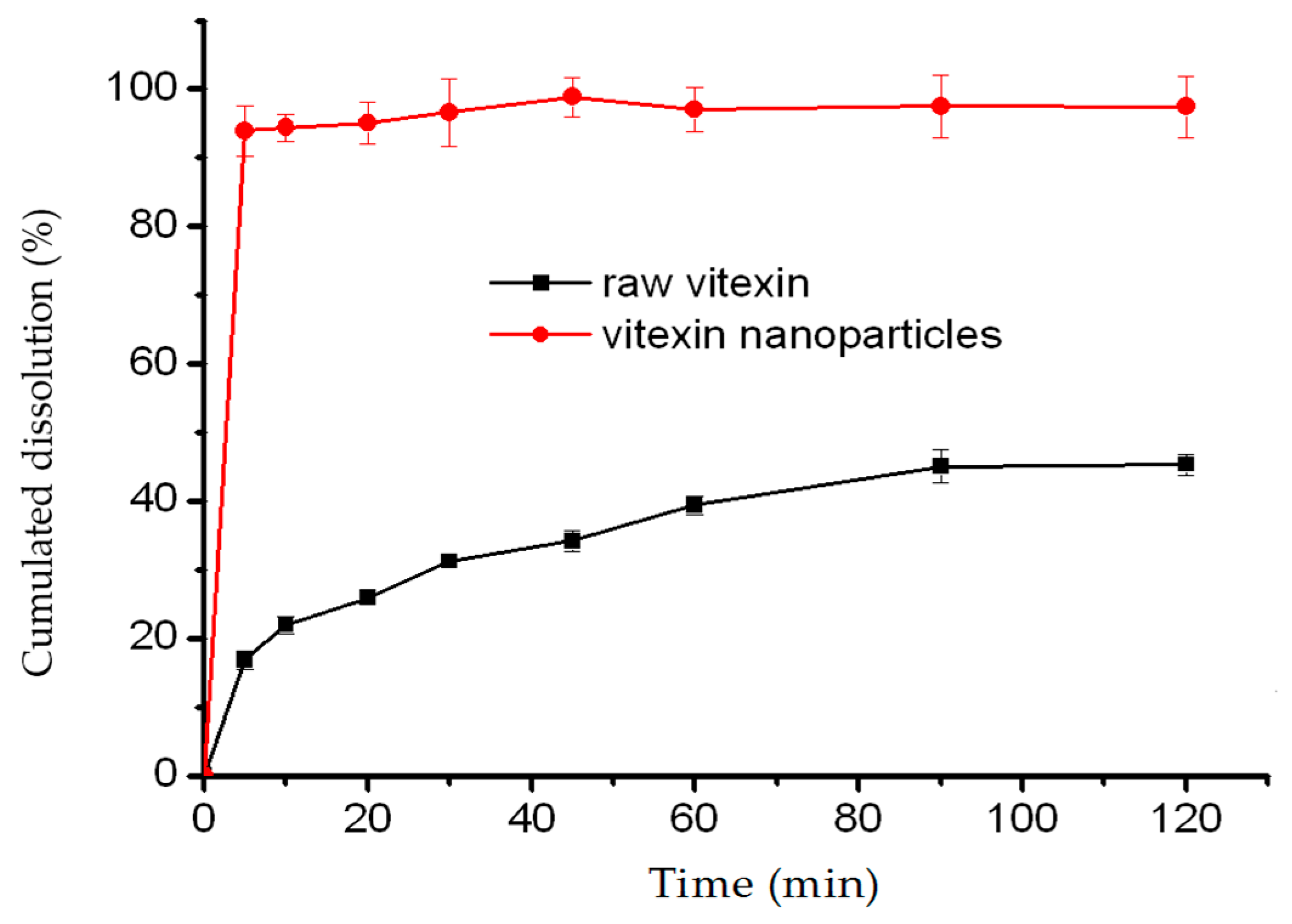
2.4.5. Dissolution Rate Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Vitexin Nanosuspensions by the ASP-HPH Approach
3.2.1. ASP Process
3.2.2. HPH Process
3.2.3. Lyophilization
3.3. Characterization Vitexin Nanoparticles
3.3.1. Morphology, MPS and Zeta Potential Measurement
3.3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3.3. LC-MS Analysis
3.3.4. XRPD Analysis
3.3.5. Residual DMSO Determination
3.3.6. Dissolution Test
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASP | antisolvent precipitation |
| HPH | high pressure homogenization |
| OAD | orthogonal array design |
| MPS | mean particle size |
| ICH | International Conference on Harmonization |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| XRPD | X-ray powder diffraction |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
References
- Pan, H.F.; Wang, X.; Du, Y.L.; Li, Y.R.; Zhao, S.N.; Pan, W.D. A simple and sensitive method for the simultaneous determination of six constituents in hawthorn leaves. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7475–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Tong, M.H.; Efferth, T.; Kong, Y.; Hou, C.L.; Chen, L.Y. Determination of vitexin and isovitexin in pigeonpea using ultrasonic extraction followed by LC-MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, P.Y.; Hu, J.; Li, S.G.; Huang, L.Y.; Lin, J.H.; Lin, X.H. Screening and quantitative analysis of antioxidants in the fruits of Livistona chinensis R. Br using HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS coupled with pre-column DPPH assay. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2802–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, K.; Zhou, W.L.; Zhou, J.A.; Yang, P. Studies on the active components and antioxidant activities of the extracts of Mimosa pudica Linn. from southern China. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2011, 7, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.J.; Meng, Z.F.; Guo, X.F.; Yue, Y.D.; Tang, F.; Yu, J.; Chen, C. Simultaneous Determination of Four Flavone C-Glycosides in Phyllostachys edulis Leaves by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Ultraviolet Spectrometry. Spectrosc. Spect. Anal. 2014, 34, 2568–2572. [Google Scholar]
- An, F.; Yang, G.D.; Tian, J.M.; Wang, S.H. Antioxidant effects of the orientin and vitexin in Trollius chinensis Bunge in d-galactose-aged mice. Neural Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, M.C.; Bano, H.; Kumar, I.; Shamsi, M.A.; Khan, M.S.Y. Pharmacological Investigations on Vitexin. Planta Med. 1981, 43, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Min, J.W.; Kong, W.L.; He, X.H.; Li, J.X.; Peng, B.W. A review on the pharmacological effects of vitexin and isovitexin. Fitoterapia 2016, 115, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Li, W.; Sui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.G.; Wang, Q.; Gu, C. Preparation and characterization of vitexin powder micronized by a supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Powder Technol. 2012, 228, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Pini, E.; Corrias, F.; Perricci, J.; Manconi, M.; Fadda, A.M.; Sinico, C. Formulation strategy and evaluation of nanocrystal piroxicam orally disintegrating tablets manufacturing by freeze-drying. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 467, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Suresh, P.K. Nanosuspension: A new vehicle for the improvement of the delivery of drugs to the ocular surface. Application to amphotericin B. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keck, C.M.; Muller, R.H. Drug nanocrystals of poorly soluble drugs produced by high pressure homogenisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 62, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Peters, K. Nanosuspensions for the formulation of poorly soluble drugs: I. Preparation by a size-reduction technique. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 160, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patravale, V.B.; Date, A.A.; Kulkarni, R.M. Nanosuspensions: A promising drug delivery strategy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.M.; Dong, W.J.; Li, Y.H.; Xia, X.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Hao, H.Z.; Jiang, L.M.; Liu, Y.L. Purification of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Essential Oil Using Macroporous Resin Followed by Microemulsion Encapsulation to Improve Its Safety and Antiviral Activity. Molecules 2017, 22, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Huang, Y.B.; Cheng, Y. Structure Evolution of Curcumin Nanoprecipitation from a Micromixer. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.P.; Kayser, O.; Mader, K.; Gust, R.; Muller, R.H. Heavy metal contamination of nanosuspensions produced by high-pressure homogenisation. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 196, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaculikova, E.; Cernikova, A.; Placha, D.; Pisarcik, M.; Peikertova, P.; Dedkova, K.; Devinsky, F.; Jampilek, J. Preparation of Hydrochlorothiazide Nanoparticles for Solubility Enhancement. Molecules 2016, 21, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorat, A.A.; Dalvi, S.V. Particle formation pathways and polymorphism of curcumin induced by ultrasound and additives during liquid antisolvent precipitation. Crystengcomm 2014, 16, 11102–11114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Kumar, N. Nanonization of curcumin by antisolvent precipitation: Process development, characterization, freeze drying and stability performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, B.; Muller, R.H.; Moschwitzer, J.P. Bottom-up approaches for preparing drug nanocrystals: Formulations and factors affecting particle size. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Second generation of drug nanocrystals for delivery of poorly soluble drugs: SmartCrystal technology. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, S20–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shegokar, R.; Muller, R.H. Nanocrystals: Industrially feasible multifunctional formulation technology for poorly soluble actives. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 399, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalvakuntla, S.; Deshpande, M.; Attari, Z.; Kunnatur, B.K. Preparation and Characterization of Nanosuspension of Aprepitant by H96 Process. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavatur, R.K.; Suryanarayanan, R. Characterization of phase transitions during freeze-drying by in situ X-ray powder diffractometry. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 1998, 3, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möschwitzer, J.; Lemke, A. Method for Carefully Producing Ultrafine Particle Suspensions and Ultrafine Particles and Use Thereof. WO/2006/108637, 19 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Noyes, A.A.; Whitney, W.R. The rate of solution of solid substances in their own solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1897, 19, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesisoglou, F.; Panmai, S.; Wu, Y.H. Nanosizing—Oral formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |
| Trial No. | A | B | C | D | MPS (nm) ± SD (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1(25) | 1(5) | 1 (500) | 1(4) | 425.8 ± 45.22 |
| 2 | 1(25) | 2(15) | 2(1000) | 2(25) | 404.4 ± 34.83 |
| 3 | 1(25) | 3(25) | 3(1500) | 3(35) | 775.8 ± 29.12 |
| 4 | 2(35) | 1(5) | 2(1000) | 3(35) | 1129.2 ± 95.25 |
| 5 | 2(35) | 2(15) | 3(1500) | 1(4) | 368.4 ± 31.23 |
| 6 | 2(35) | 3(25) | 1(500) | 2(25) | 817.6 ± 70.69 |
| 7 | 3(45) | 1(5) | 3(1500) | 2(25) | 880.9 ± 50.18 |
| 8 | 3(45) | 2(15) | 1(500) | 3(35) | 1073.6 ± 88.90 |
| 9 | 3(45) | 3(25) | 2(1000) | 1(4) | 459.0 ± 28.92 |
| K1 (a) | 535.33 ± 36.39 | 901.967 ± 65.81 | 772.333 ± 68.27 | 417.733 ± 35.12 | |
| K2 | 861.73 ± 67.98 | 615.467 ± 51.65 | 754.2 ± 55.26 | 700.967 ± 51.90 | |
| K3 | 804.50 ± 56.00 | 684.133 ± 42.91 | 675.033 ± 36.84 | 1082.867 ± 73.35 | |
| R (b) | 326.40 | 286.50 | 97.30 | 665.13 | |
| Optimal level | A1 | B2 | C2 | D1 |
| Factor | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | F Ratio | F0.05 | Type of Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: Concentration of vitexin solution (mg/mL) | 182,263.31 | 2 | 11.35 | 19.00 | |
| B: Antisolvent to solvent volume ratio | 134,248.72 | 2 | 8.36 | 19.00 | |
| C: Stirring speed (rpm) | 16,063.47 | 2 | 1.00 | 19.00 | |
| D: Reaction temperature | 668,471.08 | 2 | 41.61 | 19.00 | significant |
| Error | 16,063.47 | 2 |
| Factor/Level | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of Vitexin Solution (mg/mL) | Antisolvent to Solvent Volume Ratio | Stirring Speed (rpm) | Precipitation Temperature (°C) | |
| 1 | 25 | 5 | 500 | 4 |
| 2 | 35 | 15 | 1000 | 25 |
| 3 | 45 | 25 | 1500 | 35 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, C.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Li, W.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y. Preparation of Vitexin Nanoparticles by Combining the Antisolvent Precipitation and High Pressure Homogenization Approaches Followed by Lyophilization for Dissolution Rate Enhancement. Molecules 2017, 22, 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112038
Gu C, Liu Z, Yuan X, Li W, Zu Y, Fu Y. Preparation of Vitexin Nanoparticles by Combining the Antisolvent Precipitation and High Pressure Homogenization Approaches Followed by Lyophilization for Dissolution Rate Enhancement. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112038
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Chengbo, Ziwei Liu, Xiaohan Yuan, Wang Li, Yuangang Zu, and Yujie Fu. 2017. "Preparation of Vitexin Nanoparticles by Combining the Antisolvent Precipitation and High Pressure Homogenization Approaches Followed by Lyophilization for Dissolution Rate Enhancement" Molecules 22, no. 11: 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112038
APA StyleGu, C., Liu, Z., Yuan, X., Li, W., Zu, Y., & Fu, Y. (2017). Preparation of Vitexin Nanoparticles by Combining the Antisolvent Precipitation and High Pressure Homogenization Approaches Followed by Lyophilization for Dissolution Rate Enhancement. Molecules, 22(11), 2038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112038




