Action of Monomeric/Gemini Surfactants on Free Cells and Biofilm of Asaia lannensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
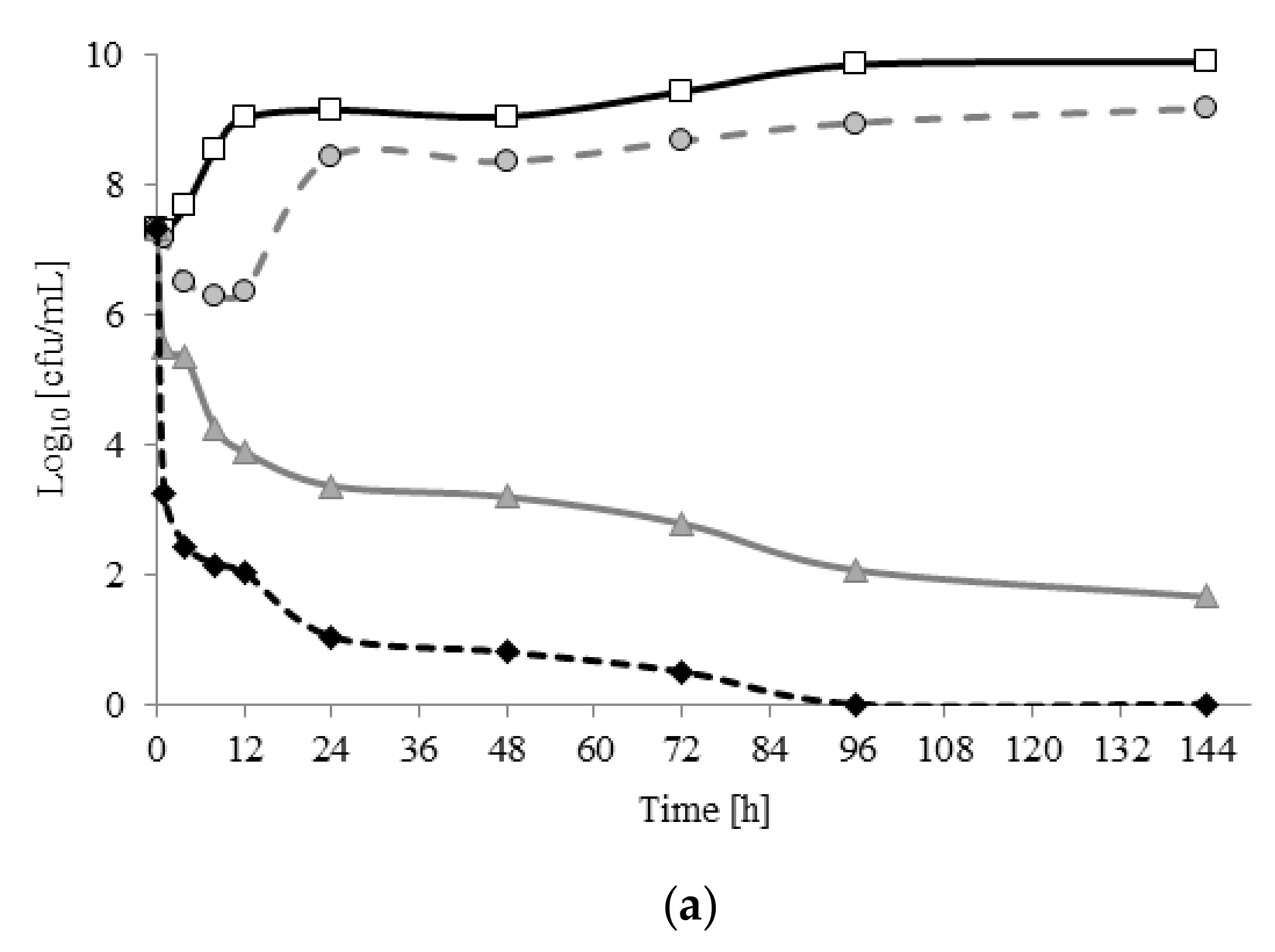
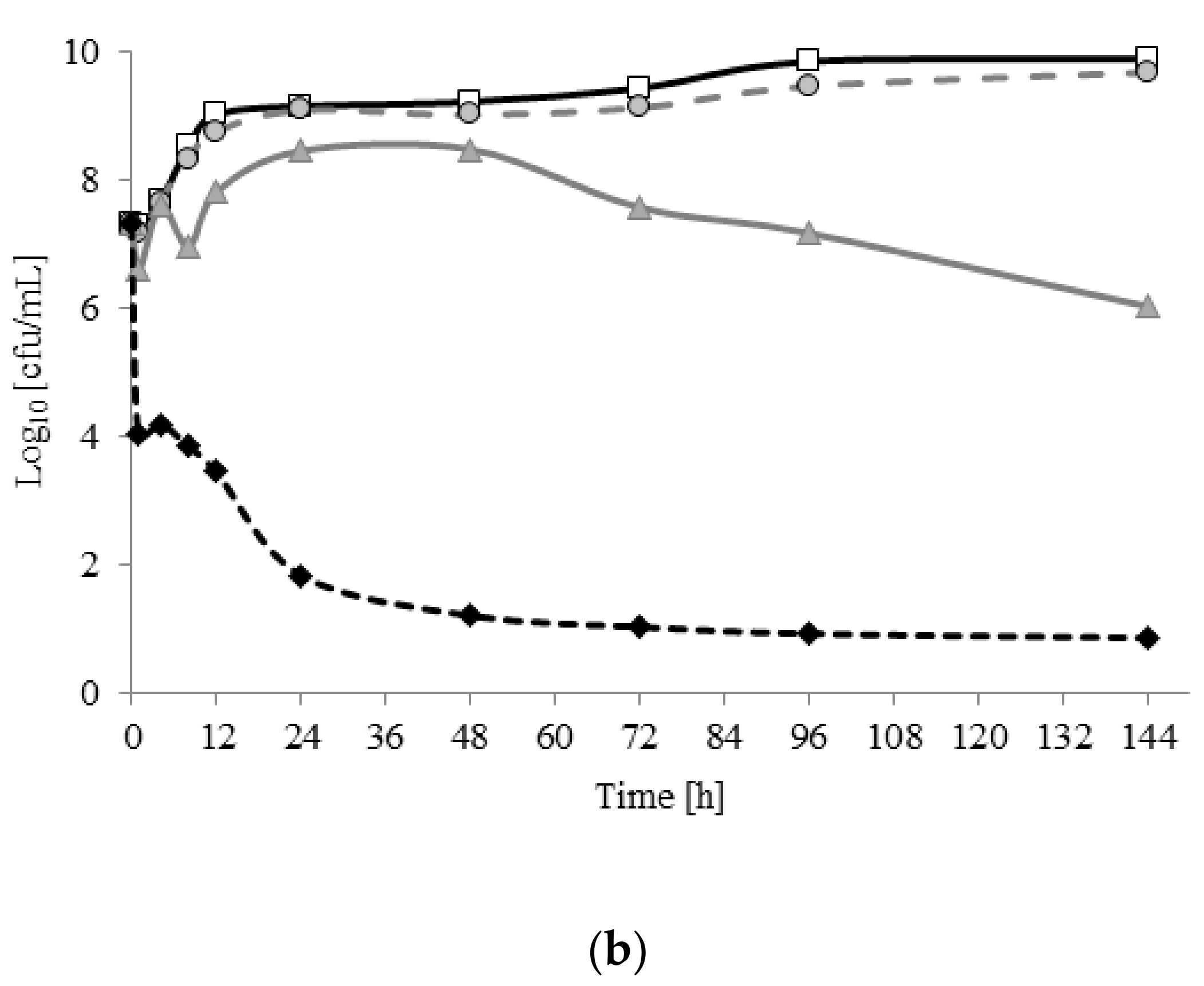
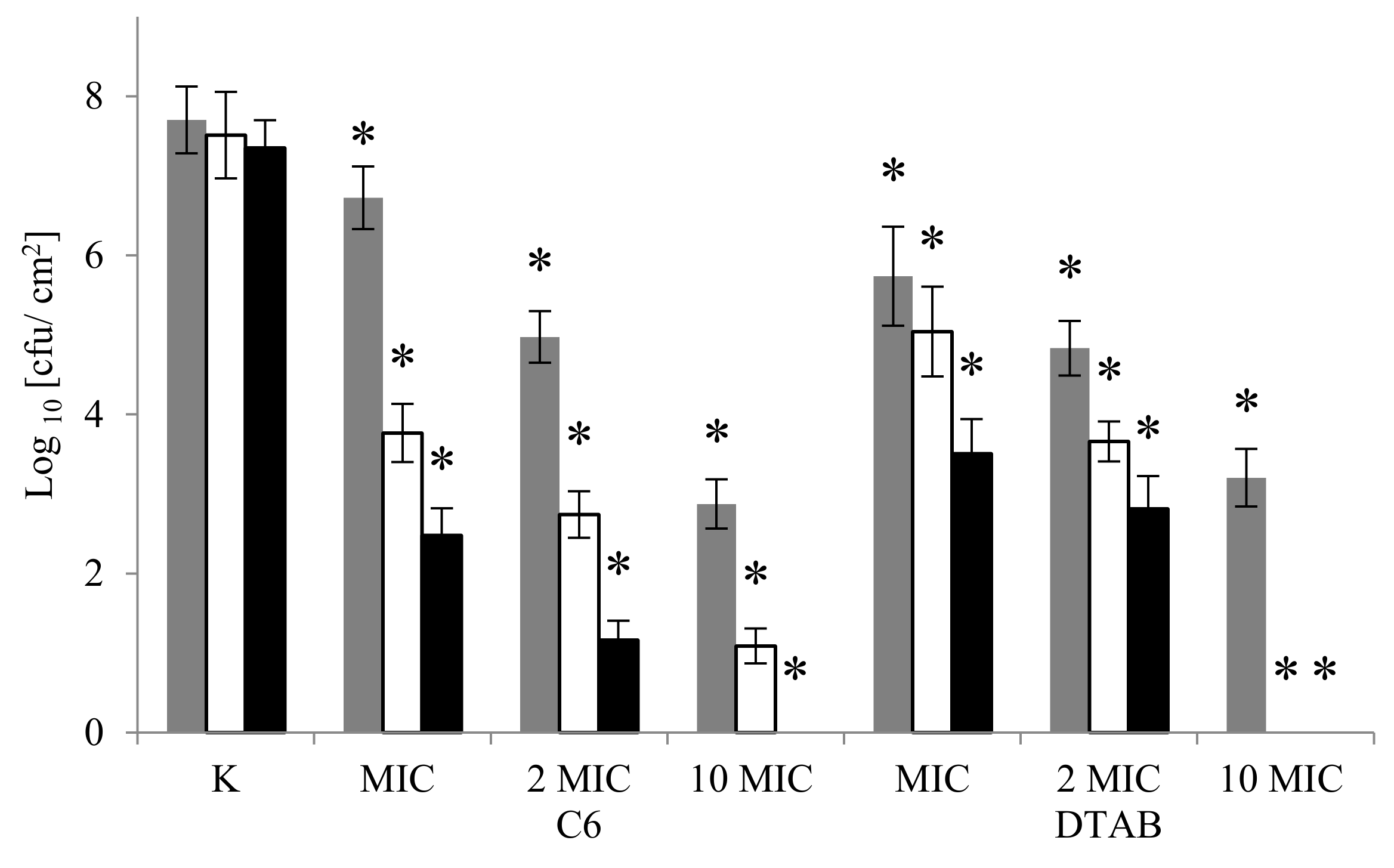
2.2. Viability of A. lannensis Cells in the Presence of Microbiocides
2.3. Planktonic Growth and Biofilm Formation
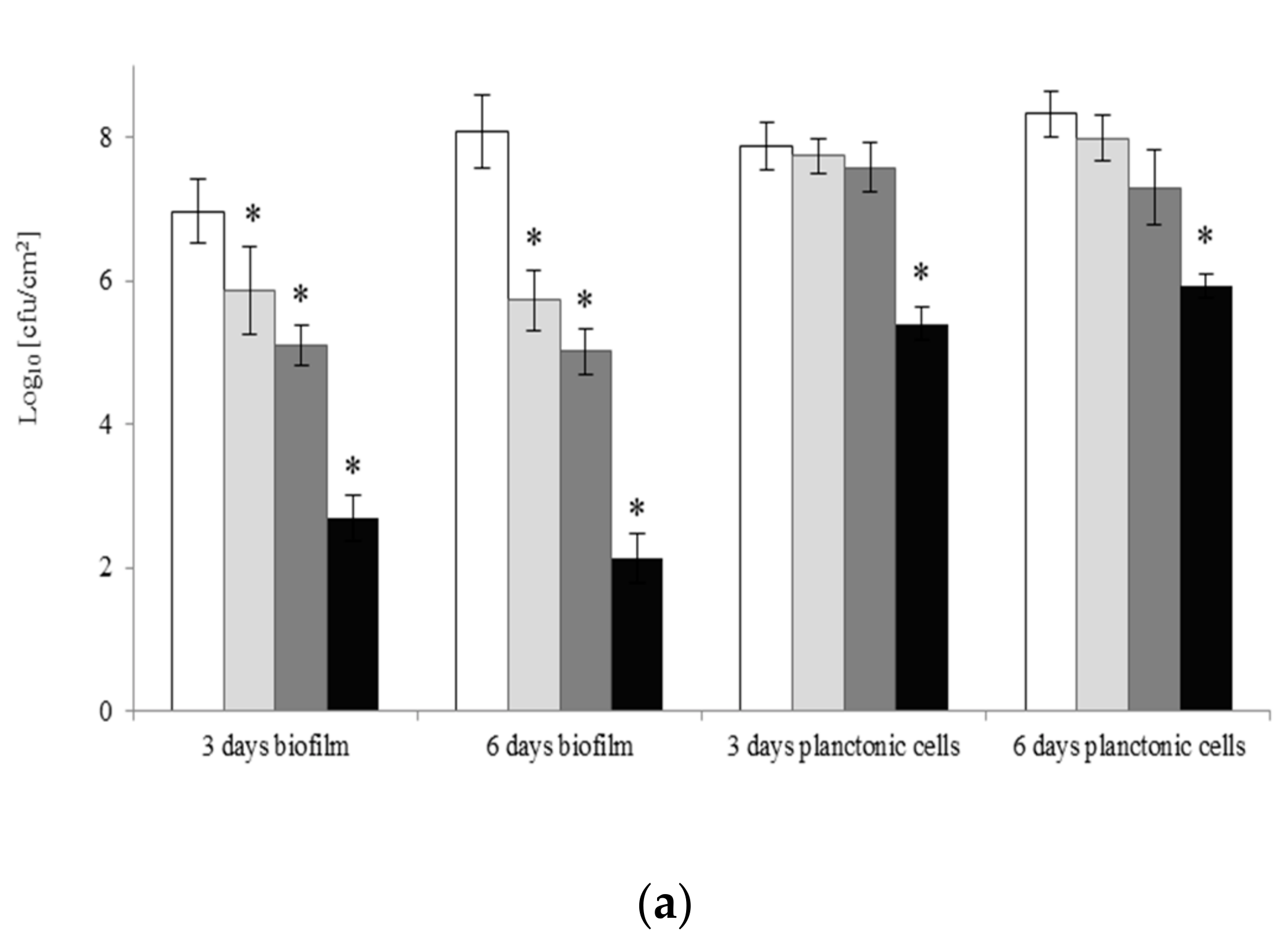
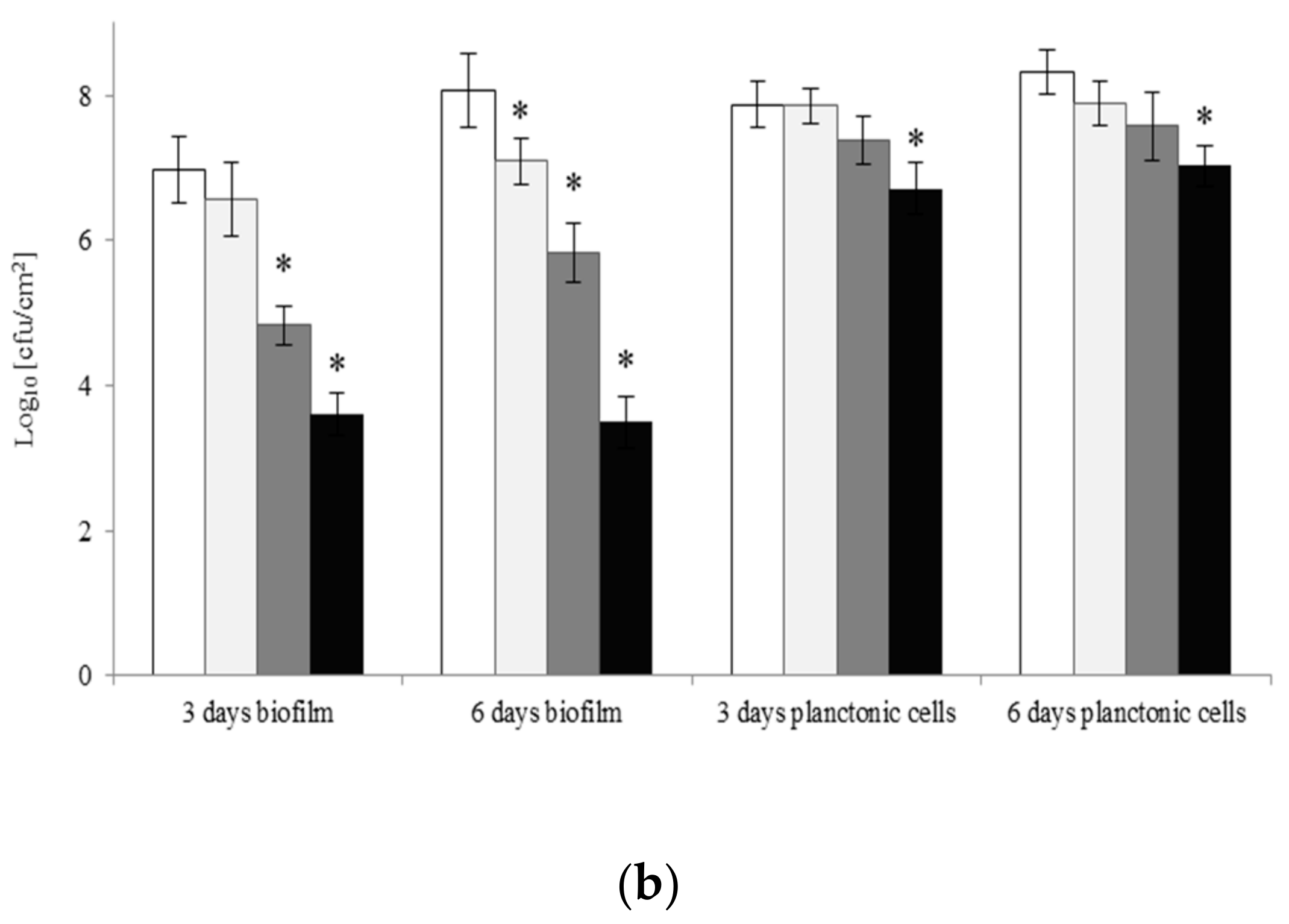
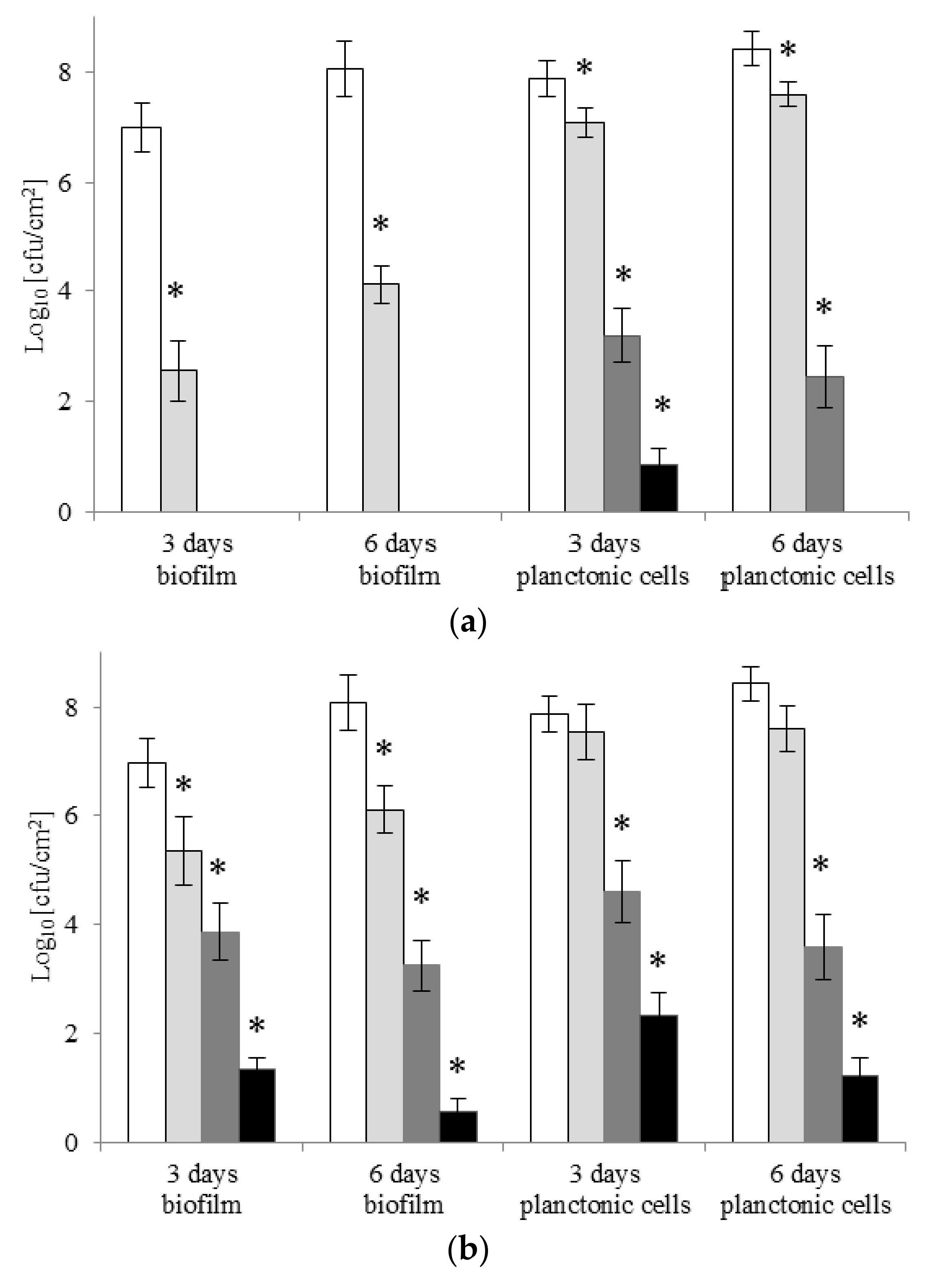
2.4. Eradication of Biofilm
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Microorganisms and Technical Materials
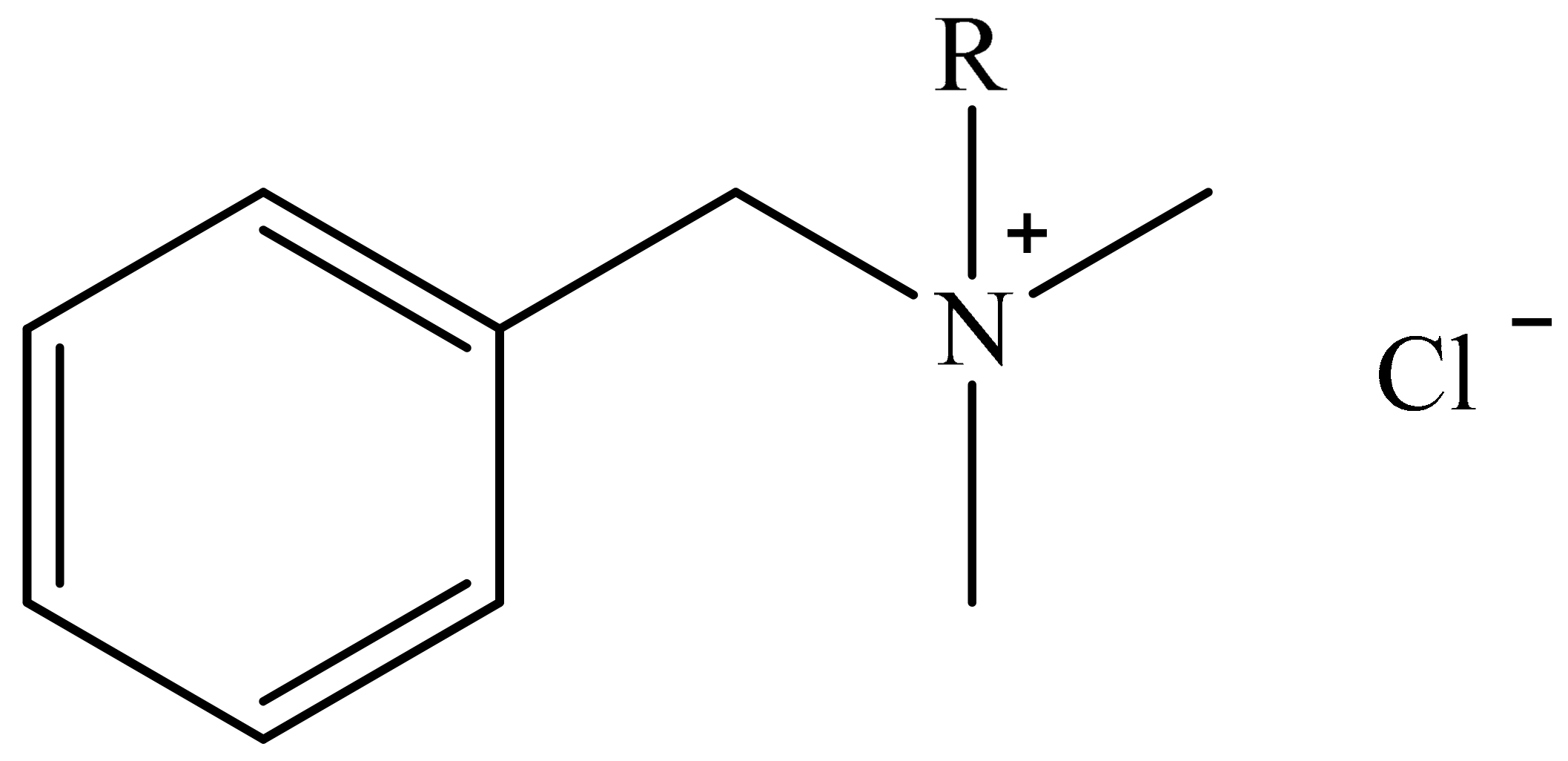
3.2. Antimicrobial Agents
3.3. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration
3.4. Viability of A. lannensis Cells in the Presence of Microbiocides
3.5. Adhesion Analysis
3.5.1. Short-Term Contact with Antimicrobial Agents
3.5.2. Adhesion in the Presence of Antimicrobial Agents
3.6. Biofilm Eradication
3.7. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horsáková, I.; Voldřich, M.; Čeřovský, M.; Sedláčková, P.; Šicnerová, P.; Ulbrich, P. Asaia sp. as a Bacterium Decaying the Packaged Still Fruit Beverages. Czech J. Food Sci. 2009, 27, S362–S365. [Google Scholar]
- Kręgiel, D.; Rygała, A.; Libudzisz, Z. Bakterie z rodzaju Asaia—Nowe zanieczyszczenie smakowych wód mineralnych. Żywność Nauka Technol. Jakość 2011, 75, 5–16. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.E.; McCalmont, M.; Xu, J.; Millar, B.Ch.; Heaney, N. Asaia sp., an usual spoilage organism of fruit-flavoured bottled water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4130–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedláčková, P.; Čeřovský, M.; Horsáková, I.; Voldřich, M. Cell surface characteristic of Asaia bogorensis- spoilage microorganism of bottled water. Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, 457–461. [Google Scholar]
- Kręgiel, D. Attachment of Asaia lannensis to materials commonly used in beverage industry. Food Control 2013, 32, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.S. Biocide resistance mechanisms. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 51, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.H.; Chen, J.H.; Fang, M.; Xing, X.D.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, F. Antibacterial effects of three experimental quaternary ammonium salt (QAS) monomers on bacteria associated with oral infections. J. Oral. Sci. 2008, 50, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegstad, K.; Langsrud, S.; Lunestad, B.T.; Scheie, A.A.; Sunde, M.; Yazdankhah, S.P. Does the wide use of quaternary ammonium compounds enhance the selection and spread of antimicrobial resistance and thus threaten our health? Microb. Drug Resist. 2010, 16, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, R.J.W.; Joynson, J.; Forbes, B. The relationships and susceptibilities of some industrial, laboratory and clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to some antibiotics and biocides. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, M.; Kalhhapure, R.S.; Rambharose, S.; Mocktar, C.; Govender, T. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of novel heterocyclic quaternary ammonium surfactants. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 47, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhanafi, D.; Dutta, V.; Kathariou, S. Genetic characterization of plasmid-associated benzalkonium chloride resistance determinants in a Listeria monocytogenes strain from the 1998–1999 outbreak. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 8231–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.; Pereira, A.M.; Pereira, M.C.; Melo, L.F.; Simŏes, M. Physiological changes induced by the quaternary ammonium compound benzyldimethyldodecylammonium chloride on Pseudomonas fluorescens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakic-Martinez, M.; Drevetes, M.; Dutta, V.; Katic, V.; Kathariou, S. Listeria monocytogenes strains selected on ciprofloxacin or the disinfectant benzalkonium chloride exhibit reduced susceptibility to ciprofloxacin, gentamicicn, benzalkonium chloride and other toxic compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8714–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, S.; Ingmer, H. Modes of action of three disinfectant active substances: A review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2013, 67, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragg, R.; Jansen, A.; Coetzee, M.; van der Westhuizen, W.; Boucher, C. Bacterial resistance to quaternary ammonium compounds (QAC) disinfectants. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 808, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhon, B.S. Gemini (dimeric) surfactants. Resonance 2004, 9, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obłąk, E.; Piecuch, A.; Guz-Regner, K.; Dworniczek, E. Antibacterial activity of gemini quaternary ammonium salts. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 350, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziróg, A.; Brycki, B. Monomeric and gemini surfactants as antimicrobial agents—Influence on environmental and reference strains. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 62, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziróg, A.; Brycki, B.; Nowak, A. Influence of surfactants on environmental and collection bacterial strains. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2015, 2 (Suppl.), 132. [Google Scholar]
- Hait, S.K.; Moulik, S.P. Gemini surfactants: A distinct class of self-assembling molecules. Curr. Sci. India 2002, 82, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, D.; Tyagi, V.K. Cationic gemini surfactants: A review. J. Oleo Sci. 2006, 55, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brycki, B.; Kowalczyk, I.; Szulc, A.; Kaczerewska, O.; Pakiet, M. Multifunctional gemini surfactants: Structure, synthesis, properties and application. In Application and Characterization of Surfactants, 1st ed.; Najjae, R., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3326-1. [Google Scholar]
- Paniak, T.J.; Jennings, M.C.; Shanahan, P.C.; Joyce, M.D.; Santiago, C.N.; Wuest, W.M.; Minbiole, K.P.C. The antimicrobial activity of mono-, bis-, tris-, and tetracationic amphiphiles derived from simple polyamine platforms. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5824–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Sun, X.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ni, H. Antibacterial activities of five cationic gemini surfactants with ethylene glycol bisacetyl spacers. J. Surf. Deterg. 2014, 17, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ding, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Lei, Q.; Fang, W. Antibacterial activity, in vitro cytotoxicity, and cell cycle arrest of gemini quaternary ammonium surfactants. Langmuir 2015, 10, 12161–12169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banno, T.; Toshima, K.; Kawada, K.; Matsumura, S. Synthesis and properties of gemini-type cationic surfactants containing carbonate linkages in the linker moiety directed toward green and sustainable chemistry. J. Surf. Deterg. 2009, 12, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brycki, B.; Kowalczyk, I.; Koziróg, A. Synthesis, molecular structure, spectral properties and antifungal activity of polymethylene-α,ω-bis(N,N-dimethyl-N-dodecyloammonium bromides). Molecules 2011, 16, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obłak, E.; Piecuch, A.; Dworniczek, E.; Olejniczak, T. The influence of biodegradable gemini surfactants, N,N′-bis(1-decyloxy-1-oxopronan-2-yl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylpropane-1,3-diammonium dibromide and N,N′-bis(1-decyloxy-1-oxopronan-2-yl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethane-1,2-diammonium dibromide, on fungal biofilm and adhesion. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Chakraborty, S.; Liu, R.; Gellman, S.H.; Weisshaar, J.C. Medium effects on minimum inhibitory concentrations of Nylon-3 polymers against E. coli. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houari, A.; Di Martino, P. Effect of chlorhexidine and benzalkonium chloride on bacterial biofilm formation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, S.; Lopez, V.; Martinez-Suárez, J.V. The influence of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of benzalkonium chloride on biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 189, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolak, H.; Czyżowska, A.; Sakač, M.; Mišan, A.; Đuragić, O.; Kręgiel, D. Phenolic compounds contained in little-known wild fruits as antiadhesive agents against the beverage-spoiling bacteria Asaia spp. Molecules 2017, 22, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolak, H.; Czyżowska, A.; Kręgiel, D. Antibacterial and antiadhesive activities of extracts from edible plants against soft drink spoilage by Asaia spp. J. Food Protect. 2017, 80, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aka, S.T.; Haji, S.H. Sub-MIC of antibiotics induced biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the presence of chlorhexidine. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2015, 46, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kręgiel, D.; Rygała, A.; Libudzisz, Z.; Walczak, P.; Oltuszak-Walczak, E. Asaia lannensis—The spoilage acetic acid bacteria isolated from strawberry-flavored bottled water in Poland. Food Control 2012, 26, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolak, H.; Kręgiel, D.; Czyżowska, A. Adhesion of Asaia bogorensis to glass and polystyrene in the presence of cranberry juice. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolak, H.; Czyżowska, A.; Kręgiel, D. Black currant (Ribes nigrum L.) and bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) fruit juices inhibit adhesion of Asaia spp. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3671306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.; Shah, R.; Bhave, M.; Palombo, E.A. Inhibitory activity of yarrow essential oil on Listeria planktonic cells and biofilms. Food Control 2013, 29, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkana, E.N.; Doulgeraki, A.I.; Kathariou, S.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Biofilm formation by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus on stainless steel under either mono- or dual-species multi-strain conditions and resistance of sessile communities to sub-lethal chemical disinfection. Food Control 2017, 73, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, K.K. What drives bacteria to produce a biofilm? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srey, S.; Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.-D. Biofilm formation in food industries: A food safety concern. Food Control 2013, 31, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houdt, R.; Michiels, C.W. Biofilm formation and the food industry, a focus on the bacterial outer surface. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1117–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabo, M.L.; Herrera, J.J.; Crespo, M.D.; Pastoriza, L. Comparison among the effectiveness of ozone, nisin and benzalkonium chloride for the elimination of planktonic cells and biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus CECT4459 on polypropylene. Food Control 2009, 20, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanac, C.; Pineau, L.; Payard, A.; Baziard-Mouysset, G.; Roques, C. Interaction between biocide cationic agents and bacterial biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chick, H. An investigation of the laws of disinfection. J. Hyg. 1908, 8, 92–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.E. A note on the variation of the rate of disinfection with change in the concentration of the disinfectant. J. Hyg. 1908, 8, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, R.J.W.; Johnston, M.D. Disinfection kinetics: A new hypothesis and model for the tailing of log-survivor/time curves. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Hemati, M.; Shabanpour, Z.; Dehkordi, S.H.; Bahadoran, S.; Lotfalian, S.; Khubani, S. Effects of benzalkonium chloride on planktonic growth and biofilm formation by animal bacterial pathogens. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toté, K.; Berghe, D.V.; Deschacht, M.; de Wit, K.; Maes, L.; Cos, P. Inhibitory efficacy of various antibiotics on matrix and viable mass of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toté, K.; Horemans, T.; Berghe, D.V.; Maes, L.; Cos, P. Inhibitory effect of biocides on the viable masses and matrices of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3135–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saá Ibusquiza, P.; Herrera, J.J.R.; Cabo, M.L. Resistance to benzalkonium chloride, peracetic acid and nisin during formation of mature biofilms by Listeria monocytogenes. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, P.S. Antimicrobial Tolerance in Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacheus, O.M.; Ivanainen, E.K.; Nissinen, T.K.; Markku, J.; Lehtola, M.J.; Martikainen, P.J. Bacterial biofilm formation on polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene and stainless steel exposed to ozonated water. Water Res. 2000, 34, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, B.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M. Effects of nutritional and environmental conditions on Salmonella sp. biofilm formation. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, M12–M16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsteinsson, T.; Másson, M.; Kristinsson, K.G.; Hjálmarsdóttir, M.A.; Hilmarsson, H.; Loftsson, T. Soft antimicrobial agents: Synthesis and activity of labile environmentally friendly long chain quaternary ammonium compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4173–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.S.; Townsend, K.M.; Fenwick, S.G.; Trengove, R.D.; O’Handley, R.M. Comparative susceptibility of planktonic and 3-day-old Salmonella typhimurium biofilms to disinfectants. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 2222–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, M.; Morris, D.; De Lappe, N.; O’Connor, J.; Lalor, P.; Dockery, P.; Cormican, M. Commonly used disinfectants fail to eradicate Salmonella enterica biofilms from food contact surface materials. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hage, S.; Lajoie, B.; Stigliani, J.-L.; Furiga-Chusseau, A.; Roques, C.; Baziard, G. Synthesis, antimicrobial activity and physico-chemical properties of some n-alkyldimethylbenzylammonium halides. J. Appl. Biomed. 2014, 12, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massi, L; Guittard, F.; Levy, R.; Géribaldi, S. Enhanced activity of fluorinated quaternary ammonium surfactants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balgavy, P.; Devinsky, F. Cutt-off effects in biological activities of surfactants. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci 1996, 66, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, C.R.; Malamud, D.; Schnaare, R.L. Antimicrobial evaluation of N-alkyl betaines and N-alkyl-N,N-dimethylamine oxides with variations in chain length. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2514–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joondan, N.; Jhaumeer-Laulloo, S.; Caumul, P. A study of the antibacterial activity of L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine esters in relation to their CMCs and their interactions with 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycer- 3-phosphocholine, DPPC as model membrane. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds C6 and DTAB are available from the authors. |
| Type of Culture Medium | MIC [μM] | |
|---|---|---|
| DTAB | C6 | |
| Minimal medium + 2% glucose | 0.1267 | 0.0073 |
| Minimal medium + 2% saccharose | 0.2534 | 0.0073 |
| Minimal medium + 2% fructose | 1.0134 | 0.0073 |
| Minimal medium + 2% maltose | 2.0268 | 0.0073 |
| TSB + 2% glucose | 2.0268 | 0.0036 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koziróg, A.; Kręgiel, D.; Brycki, B. Action of Monomeric/Gemini Surfactants on Free Cells and Biofilm of Asaia lannensis. Molecules 2017, 22, 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112036
Koziróg A, Kręgiel D, Brycki B. Action of Monomeric/Gemini Surfactants on Free Cells and Biofilm of Asaia lannensis. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112036
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoziróg, Anna, Dorota Kręgiel, and Bogumił Brycki. 2017. "Action of Monomeric/Gemini Surfactants on Free Cells and Biofilm of Asaia lannensis" Molecules 22, no. 11: 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112036
APA StyleKoziróg, A., Kręgiel, D., & Brycki, B. (2017). Action of Monomeric/Gemini Surfactants on Free Cells and Biofilm of Asaia lannensis. Molecules, 22(11), 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22112036







