Ferulaldehyde Improves the Effect of Methotrexate in Experimental Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of FRA and MTX Administered Alone or in Combination on Basic Parameters
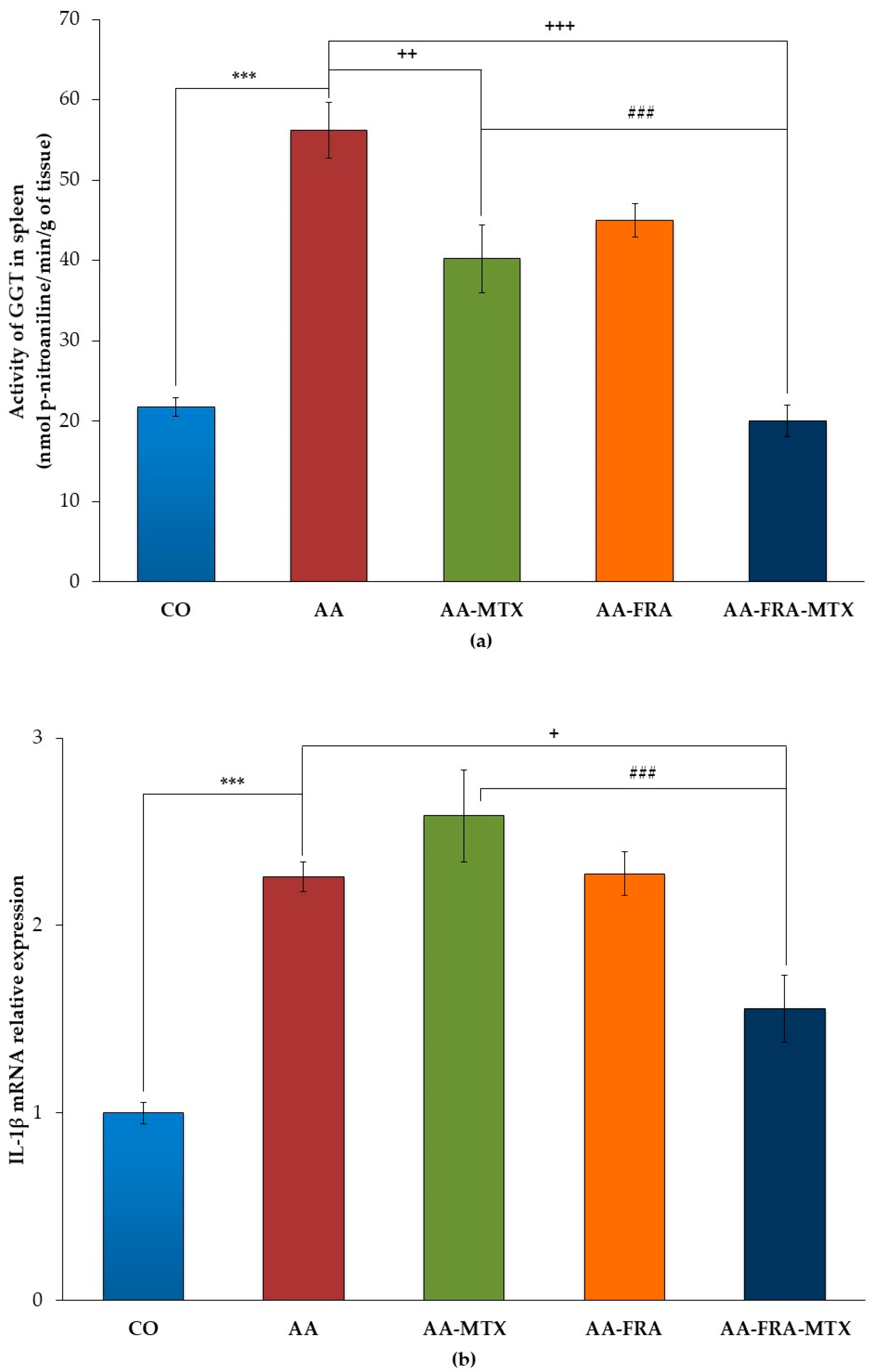
2.2. Effect of FRA and MTX Administered Alone or in Combination on the Activity of γ-Glutamyl Transferase and Interleukin-1β mRNA Relative Expression in Spleen
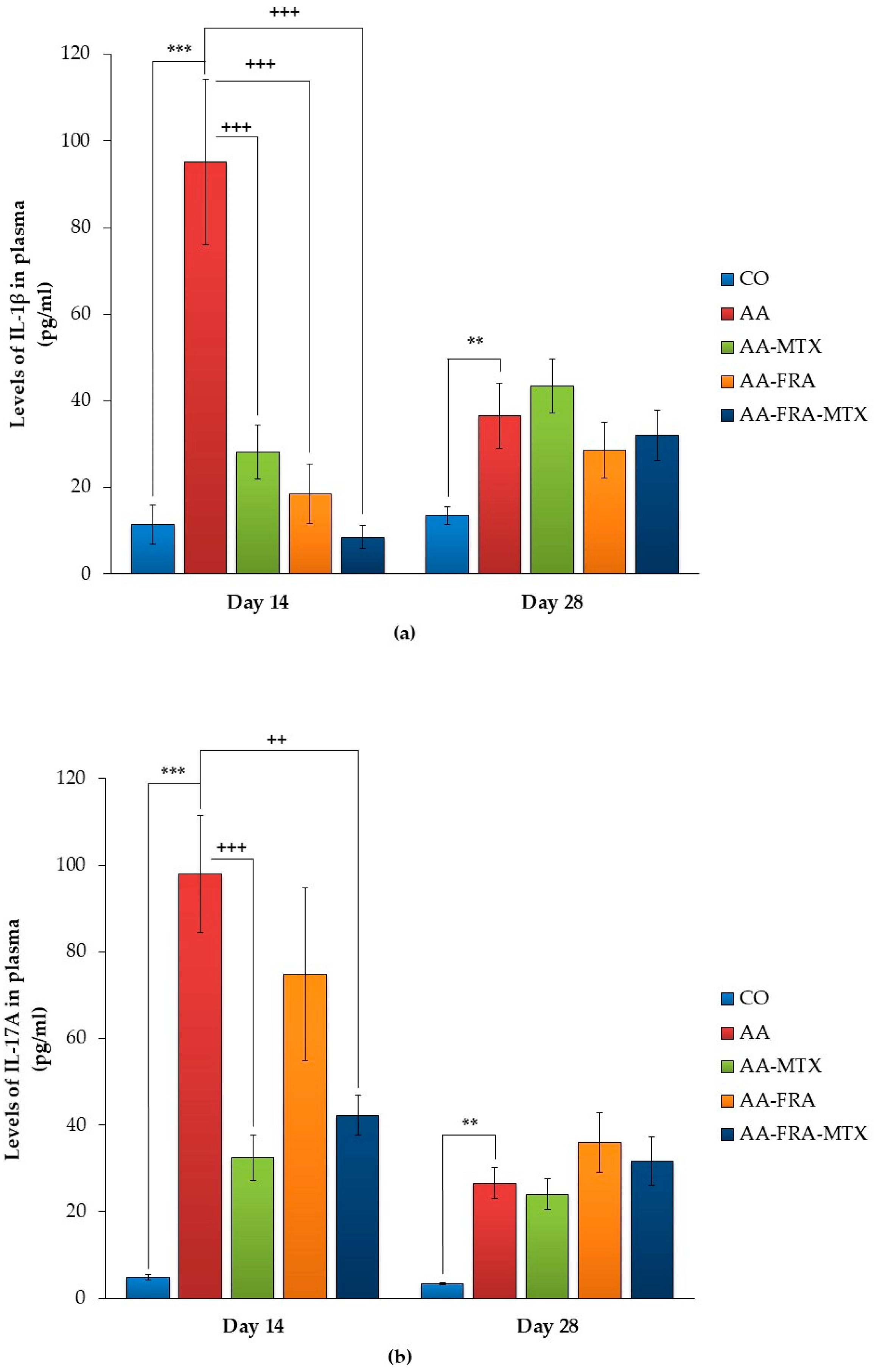
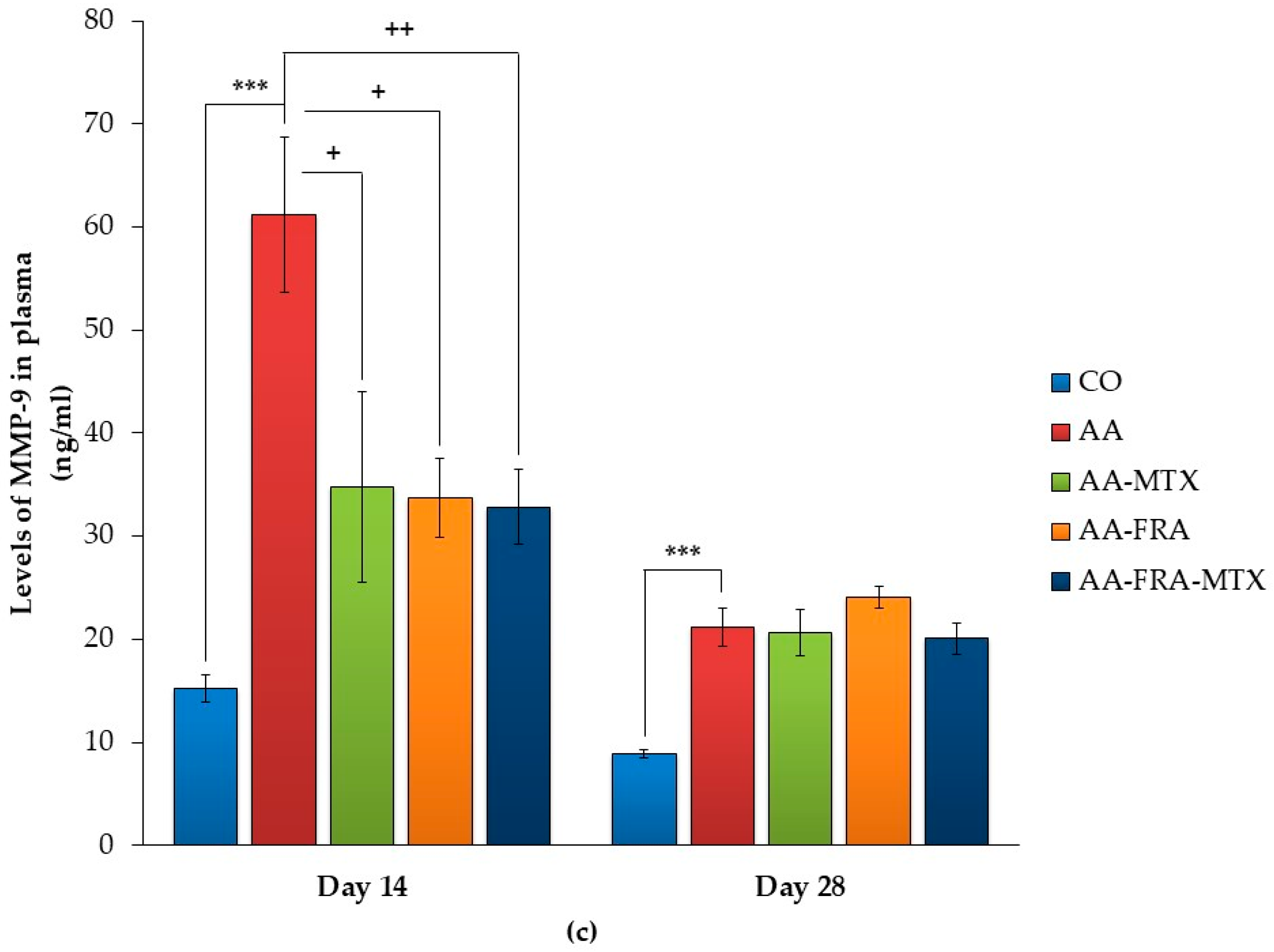
2.3. Effect of FRA and MTX Administered Alone or in Combination on the Levels of Interleukin-1β, Interleukin-17A, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Plasma
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Part of the Experiment
4.1.1. Animals
4.1.2. Induction of Adjuvant Arthritis
4.1.3. Experimental Design and Treatments
4.2. Experimental Assays
4.2.1. Basic Parameters
Change of Body Weight
Change of Hind Paw Volume
Arthritic Score
4.2.2. Parameters Assessed in Tissue
Measurement of Activity of γ-Glutamyltransferase in Spleen
Total RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.2.3. Parameters Assessed in Plasma
Measurement of Interleukin 1β, Interleukin 17A, and Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in Plasma
4.3. Statistical Analyses
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellucci, E.; Terenzi, R.; La Paglia, G.M.; Gentileschi, S.; Tripoli, A.; Tani, C.; Alunno, A. One year in review 2016: Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Picerno, V.; Ferro, F.; Adinolfi, A.; Valentini, E.; Tani, C.; Alunno, A. One year in review: The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angelotti, F.; Parma, A.; Cafaro, G.; Capecchi, R.; Alunno, A.; Puxeddu, I. One year in review 2017: Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brennan, F.M.; McInnes, I.B. Evidence that cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3537–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendele, A. Animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal. Interact. 2001, 1, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shinde, C.G.; Venkatesh, M.P.; Kumar, T.M.; Shivakumar, H.G. Methotrexate: A gold standard for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2014, 28, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salliot, C.; van der Heijde, D. Long-term safety of methotrexate monotherapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature research. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pubchem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5280536#section=Top (accessed on 25 September 2017).
- Rios, L.Y.; Gonthier, M.P.; Rémésy, C.; Mila, I.; Lapierre, C.; Lazarus, S.A.; Williamson, G.; Scalbert, A. Chocolate intake increases urinary excretion of polyphenol-derived phenolic acids in healthy human subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonthier, M.P.; Cheynier, V.; Donovan, J.L.; Manach, C.; Morand, C.; Mila, I.; Lapierre, C.; Remesy, C.; Scalbert, A. Microbial aromatic acid metabolites formed in the gut account for a major fraction of the polyphenols excreted in urine of rats fed red wine polyphenols. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Moghadasian, M.H. Chemistry, natural sources, dietary intake and pharmacokinetic properties of ferulic acid: A review. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamać, M.; Koleva, L.; Kancheva, V.D.; Amarowicz, R. The Structure-Antioxidant Activity Relationship of Ferulates. Molecules 2017, 22, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alañón, M.E.; Díaz-Maroto, M.C.; Díaz-Maroto, I.J.; Vila-Lameiro, P.; Pérez-Coello, M.S. Cyclic polyalcohols: Fingerprints to identify the botanical origin of natural woods used in wine aging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.Y.; Pae, H.O.; Ko, Y.S.; Yoo, J.C.; Choi, B.M.; Jun, C.D.; Chung, H.T.; Inagaki, M.; Higuchi, R.; Kim, Y.C. In vitro inducible nitric oxide synthesis inhibitory active constituents from Fraxinus rhynchophylla. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 656–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radnai, B.; Tucsek, Z.; Bognar, Z.; Antus, C.; Mark, L.; Berente, Z.; Gallyas, F., Jr.; Sumegi, B.; Veres, B. Ferulaldehyde, a water-soluble degradation product of polyphenols, inhibits the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in mice. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucsek, Z.; Radnai, B.; Racz, B.; Debreceni, B.; Priber, J.K.; Dolowschiak, T.; Palkovics, T.; Gallyas, F., Jr.; Sumegi, B.; Veres, B. Suppressing LPS-induced early signal transduction in macrophages by a polyphenol degradation product: A critical role of MKP-1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 89, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Heo, D.R.; Kim, Y.A.; Lee, J.; Kim, N.S.; Bang, O.S. Coniferaldehyde inhibits LPS-induced apoptosis through the PKC α/β II/Nrf-2/HO-1 dependent pathway in RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuncirova, V.; Ponist, S.; Mihalova, D.; Drafi, F.; Nosal, R.; Acquaviva, A.; Gardi, C.; Harmatha, J.; Hradkova, I.; Bauerova, K. N-feruloylserotonin in preventive combination therapy with methotrexate reduced inflammation in adjuvant arthritis. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 28, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauerova, K.; Paulovicova, E.; Mihalova, D.; Drafi, F.; Strosova, M.; Mascia, C.; Biasi, F.; Rovensky, J.; Kucharska, J.; Gvozdjakova, A.; et al. Combined methotrexate and coenzyme Q10 therapy in adjuvant-induced arthritis evaluated using parameters of inflammation and oxidative stress. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2010, 57, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pigott, E.; DuHadaway, J.B.; Muller, A.J.; Gilmour, S.; Prendergast, G.C.; Mandik-Nayak, L. 1-Methyl-tryptophan synergizes with methotrexate to alleviate arthritis in a mouse model of arthritis. Autoimmunity 2014, 47, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovenský, J.; Stancíková, M.; Rovenská, E.; Stvrtina, S.; Stvrtinová, V.; Svík, K. Treatment of rat adjuvant arthritis with flavonoid (Detralex), methotrexate, and their combination. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pašková, Ľ.; Kuncírová, V.; Poništ, S.; Mihálová, D.; Nosáľ, R.; Harmatha, J.; Hrádková, I.; Čavojský, T.; Bilka, F.; Šišková, K.; et al. Effect of N-Feruloylserotonin and Methotrexate on Severity of Experimental Arthritis and on Messenger RNA Expression of Key Proinflammatory Markers in Liver. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 7509653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, D.; Gogarty, M.; O’leary, J.; Silva, I.; Bermingham, N.; Bresnihan, B.; Fitzgerald, O. Reduction of synovial sublining layer inflammation and proinflammatory cytokine expression in psoriatic arthritis treated with methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3286–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häupl, T.; Yahyawi, M.; Lübke, C.; Ringe, J.; Rohrlach, T.; Burmester, G.R.; Sittinger, M.; Kaps, C. Gene expression profiling of rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells treated with antirheumatic drugs. J. Biomol. Screen. 2007, 12, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, O.; Fujikawa, Y.; Itonaga, I.; Sabokbar, A.; Torisu, T.; Athanasou, N.A. Proinflammatory cytokine (TNFalpha/IL-1alpha) induction of human osteoclast formation. J. Pathol. 2002, 198, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayer, J.M. The pivotal role of interleukin-1 in the clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2003, 42 (Suppl. 2), ii3–ii10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraccioli, G.; Bracci-Laudiero, L.; Alivernini, S.; Gremese, E.; Tolusso, B.; De Benedetti, F. Interleukin-1β and interleukin-6 in arthritis animal models: Roles in the early phase of transition from acute to chronic inflammation and relevance for human rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med. 2010, 16, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.L.; Dyer, R.; Hupe, D.J. Matrix metalloproteinases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1998, 2, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, R.; Rasool, M. Interleukin 17 regulates SHP-2 and IL-17RA/STAT-3 dependent Cyr61, IL-23 and GM-CSF expression and RANKL mediated osteoclastogenesis by fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. 2017, 9, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, K.A.; Walker, J.S.; Lee, C.S.; Kirkham, B.W. Cytokine expression and synovial pathology in the initiation and spontaneous resolution phases of adjuvant arthritis: Interleukin-17 expression is upregulated in early disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2001, 123, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolina, M.; Bolon, B.; Middleton, S.; Dwyer, D.; Brown, H.; Duryea, D.; Zhu, L.; Rohner, A.; Pretorius, J.; Kostenuik, P.; et al. The evolving systemic and local biomarker milieu at different stages of disease progression in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenders, M.I.; Lubberts, E.; Oppers-Walgreen, B.; van den Bersselaar, L.; Helsen, M.M.; Di Padova, F.E.; Boots, A.M.; Gram, H.; Joosten, L.A.; van den Berg, W.B. Blocking of interleukin-17 during reactivation of experimental arthritis prevents joint inflammation and bone erosion by decreasing RANKL and interleukin-1. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, J.A.; Huizinga, T.W.; Guchelaar, H.J. Recent insights in the pharmacological actions of methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunnane, G.; Fitzgerald, O.; Beeton, C.; Cawston, T.E.; Bresnihan, B. Early joint erosions and serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase 1, matrix metalloproteinase 3, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charni-Ben Tabassi, N.; Desmarais, S.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Delaissé, J.M.; Percival, M.D.; Garnero, P. The type II collagen fragments Helix-II and CTX-II reveal different enzymatic pathways of human cartilage collagen degradation. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, H.; Visse, R.; Murphy, G. Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 15, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Shi, H.J.; Wang, Q.M.; Chen, B.R.; Khurwolah, M.R.; Long, Q.Q.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, Z.M.; et al. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 Expression Through the 67-κDa Laminin Receptor and the TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB Signalling Pathway in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Macrophages. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlowski, M.; Meister, A. The gamma-glutamyl cycle: A possible transport system for amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 67, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondrejickova, O.; Ziegelhoeffer, A.; Gabauer, I.; Sotnikova, R.; Styk, J.; Gibala, P.; Sedlak, J.; Horakova, L. Evaluation of ischemia-reperfusion injury by malondialdehyde, glutathione and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: Lack of specific local effects in diverse parts of the dog heart following acute coronary occlusion. Cardioscience 1993, 4, 225–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Basic Parameters | Group | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | AA | AA-MTX | AA-FRA | AA-FRA-MTX | |
| Change of body weight (g) | |||||
| Day 14 | 68.6 ± 5.9 | 38.8 ± 6.0 * | 67.3 ± 5.0 + | 36.2 ± 8.0 | 56.8 ± 6.4 |
| Day 21 | 86.0 ± 7.0 | 31.0 ± 5.3 *** | 52.4 ± 7.5 | 22.9 ± 4.6 | 64.2 ± 10.5 + |
| Day 28 | 98.1 ± 8.3 | 48.1 ± 6.6 *** | 51.1 ± 6.0 | 42.8 ± 4.3 | 67.0 ± 13.4 |
| Change of hind paw volume (%) | |||||
| Day 14 | 8.3 ± 0.9 | 47.1 ± 6.4 *** | 18.5 ± 5.2 ++ | 30.5 ± 8.7 | 13.1 ± 1.4 ++ |
| Day 21 | 13.4 ± 2.0 | 80.2 ± 9.0 *** | 44.9 ± 9.2 + | 65.0 ± 12.3 | 24.1 ± 7.8 +++ |
| Day 28 | 12.8 ± 1.8 | 60.7 ± 7.4 ** | 56.6 ± 11.2 | 50.3 ± 8.6 | 36.9 ± 10.5 |
| Arthritic score (points) | |||||
| Day 14 | 16.3 ± 0.9 | 14.4 ± 0.7 | 13.6 ± 0.9 | 10.9 ± 0.6 +++/# | |
| Day 21 | 21.3 ± 1.2 | 19.3 ± 0.9 | 18.0 ± 1.3 | 14.1 ± 1.3 ++/# | |
| Day 28 | 21.3 ± 1.1 | 20.5 ± 1.1 | 19.4 ± 1.2 | 15.9 ± 1.6 + | |
| Product | Sense Primer (5′-3′) | Antisense Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β [22] | CCTCTGTGACTCGTGGGATG | GGGTGTGCCGTCTTTCATCA |
| β-actin | TCAAGATCATTGCTCCTCCTG | AGGGTGTAAAACGCAGCTCA |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Slovák, L.; Švík, K.; Mihalová, D.; Tóth, J.; Czigle, S.; Pašková, Ľ.; Bilka, F.; Bauerová, K. Ferulaldehyde Improves the Effect of Methotrexate in Experimental Arthritis. Molecules 2017, 22, 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111911
Slovák L, Švík K, Mihalová D, Tóth J, Czigle S, Pašková Ľ, Bilka F, Bauerová K. Ferulaldehyde Improves the Effect of Methotrexate in Experimental Arthritis. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111911
Chicago/Turabian StyleSlovák, Lukáš, Karol Švík, Danica Mihalová, Jaroslav Tóth, Szilvia Czigle, Ľudmila Pašková, František Bilka, and Katarína Bauerová. 2017. "Ferulaldehyde Improves the Effect of Methotrexate in Experimental Arthritis" Molecules 22, no. 11: 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111911
APA StyleSlovák, L., Švík, K., Mihalová, D., Tóth, J., Czigle, S., Pašková, Ľ., Bilka, F., & Bauerová, K. (2017). Ferulaldehyde Improves the Effect of Methotrexate in Experimental Arthritis. Molecules, 22(11), 1911. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111911






