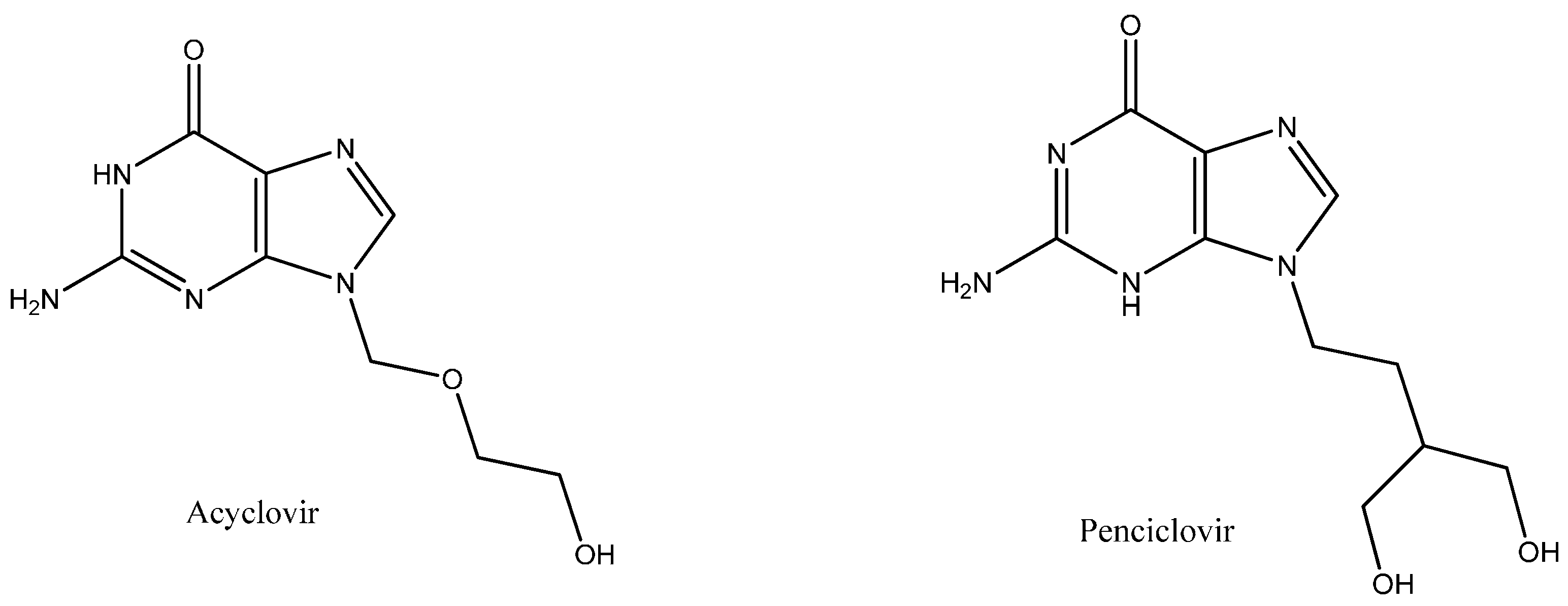
Biophysical and In Silico Studies of the Interaction between the Anti-Viral Agents Acyclovir and Penciclovir, and Human Serum Albumin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
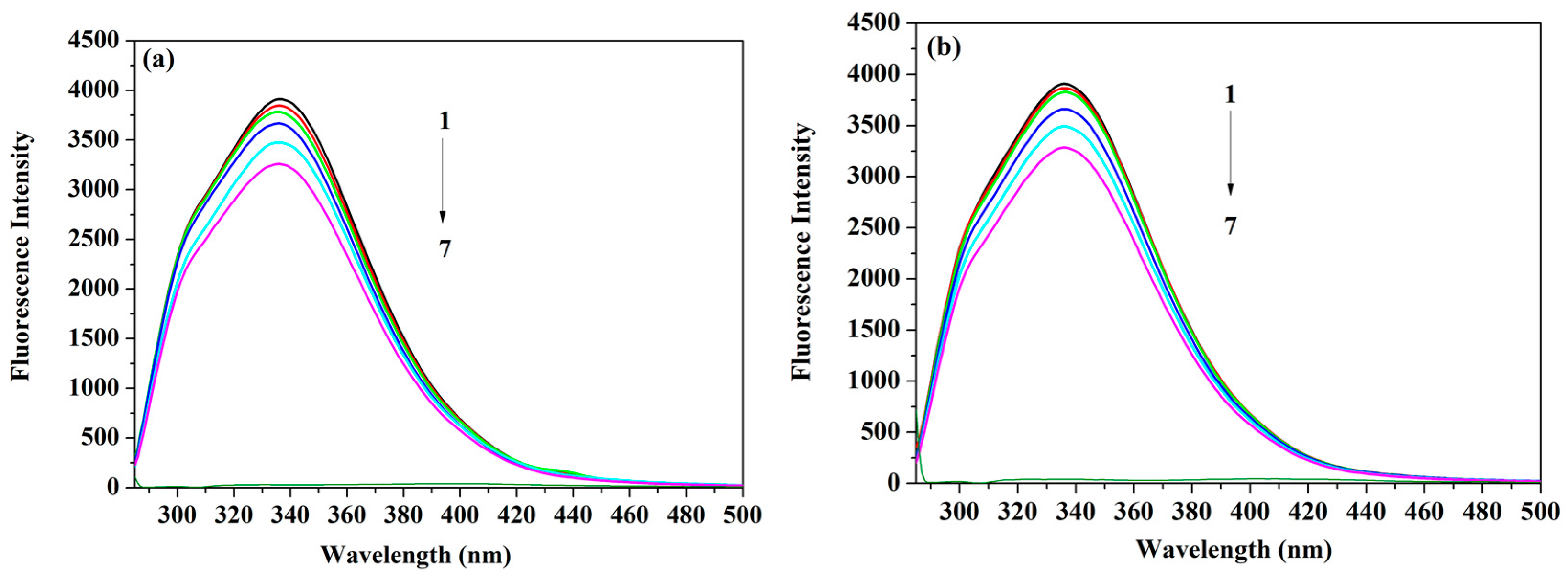
2.1. Measurements of the Fluorescence Emission Intensity
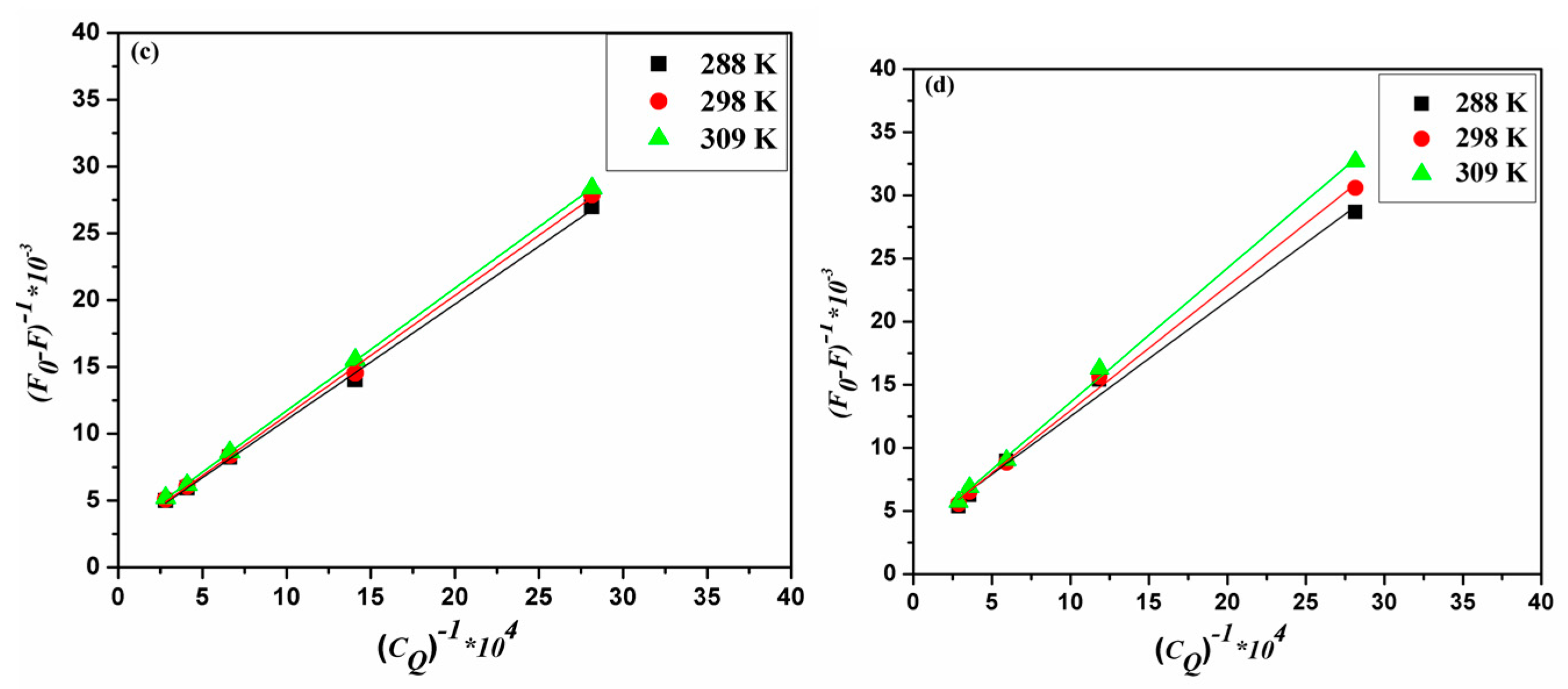
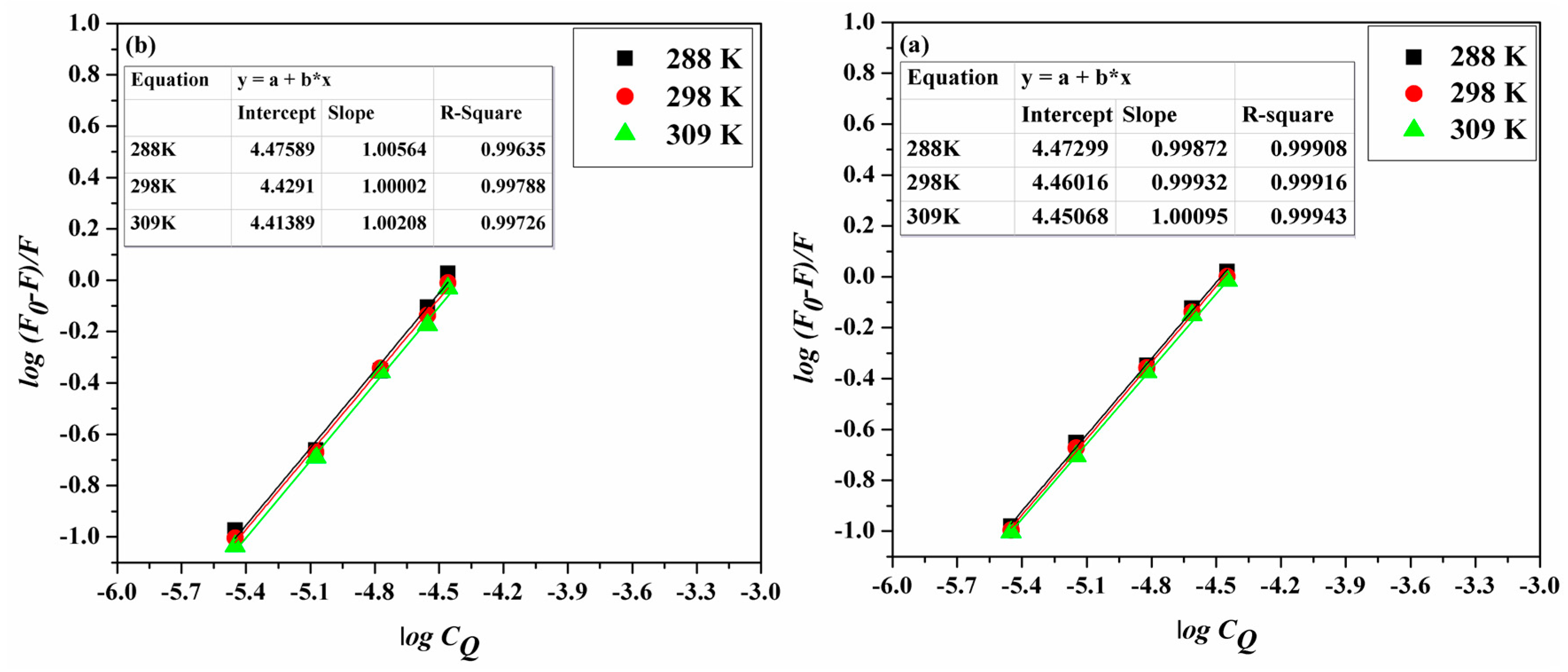
2.2. Binding Mode and Binding Sites
2.3. Thermodynamic Parameters and Nature of the Binding Forces
2.4. UV-Vis Absorption Spectra
2.5. ACV/PNV Effect on HSA Conformation
2.5.1. Synchronous Fluorescence
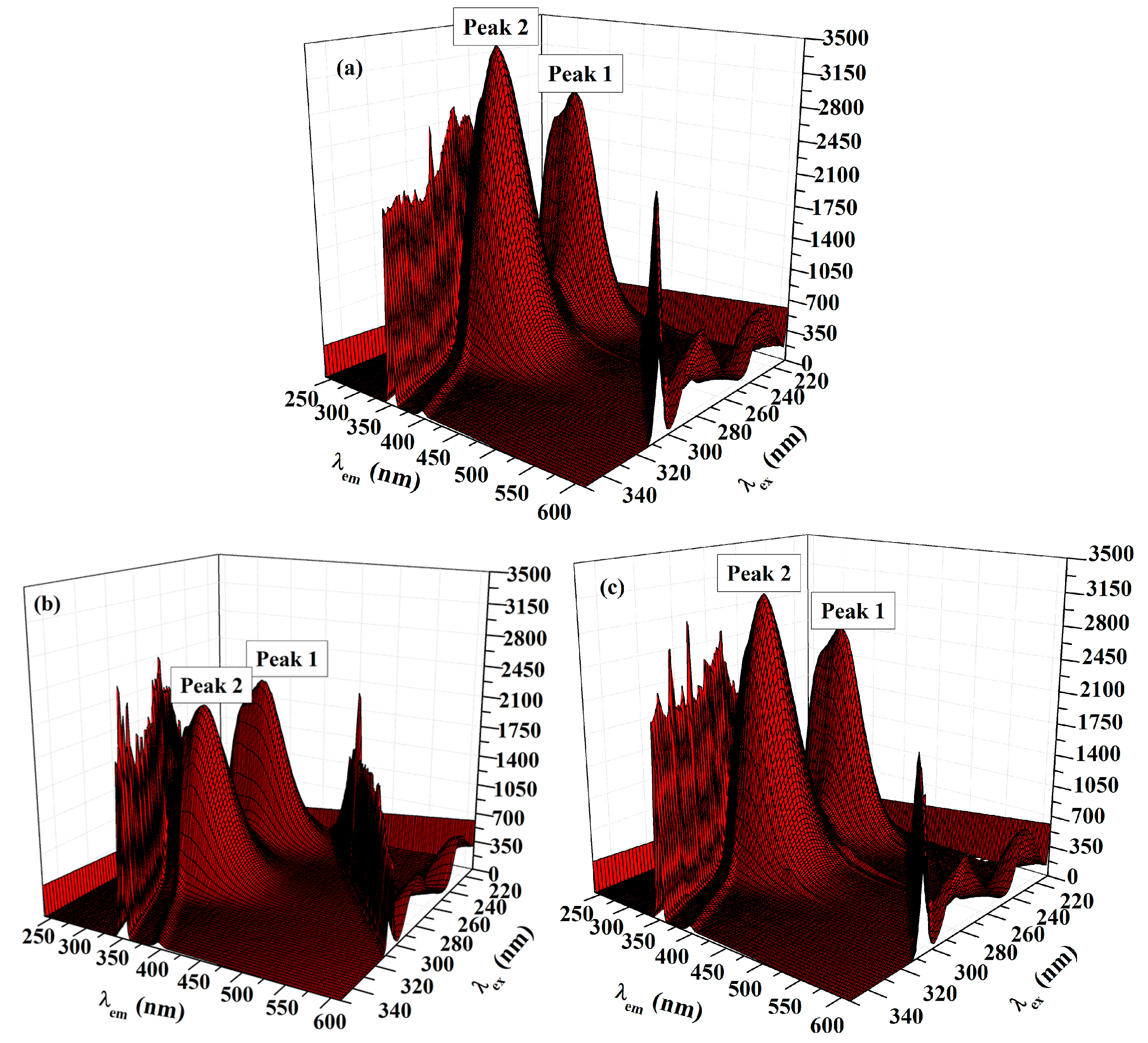
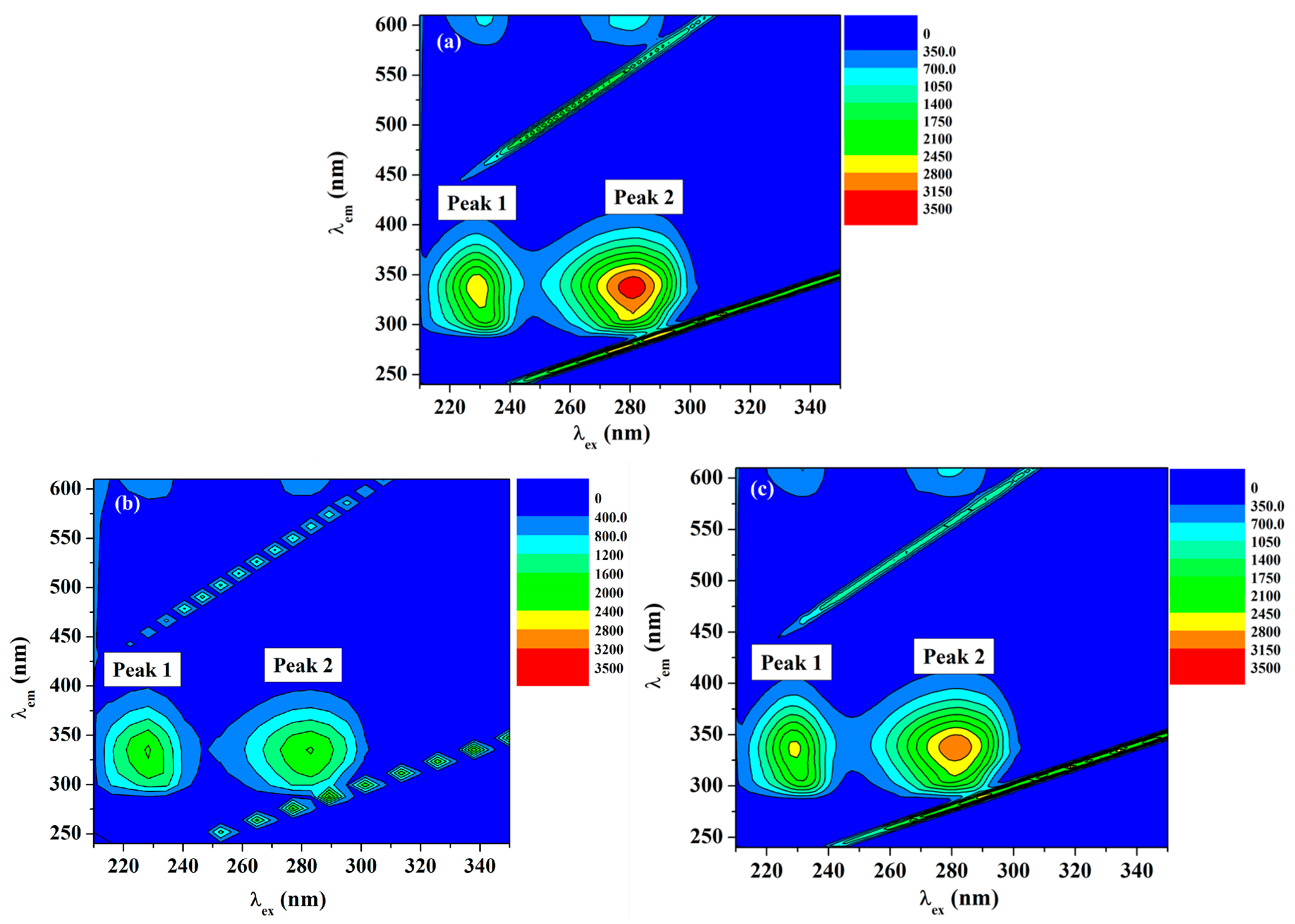
2.5.2. Three-Dimensional (3D) Fluorescence Measurements
2.6. Site Markers Competitive Binding
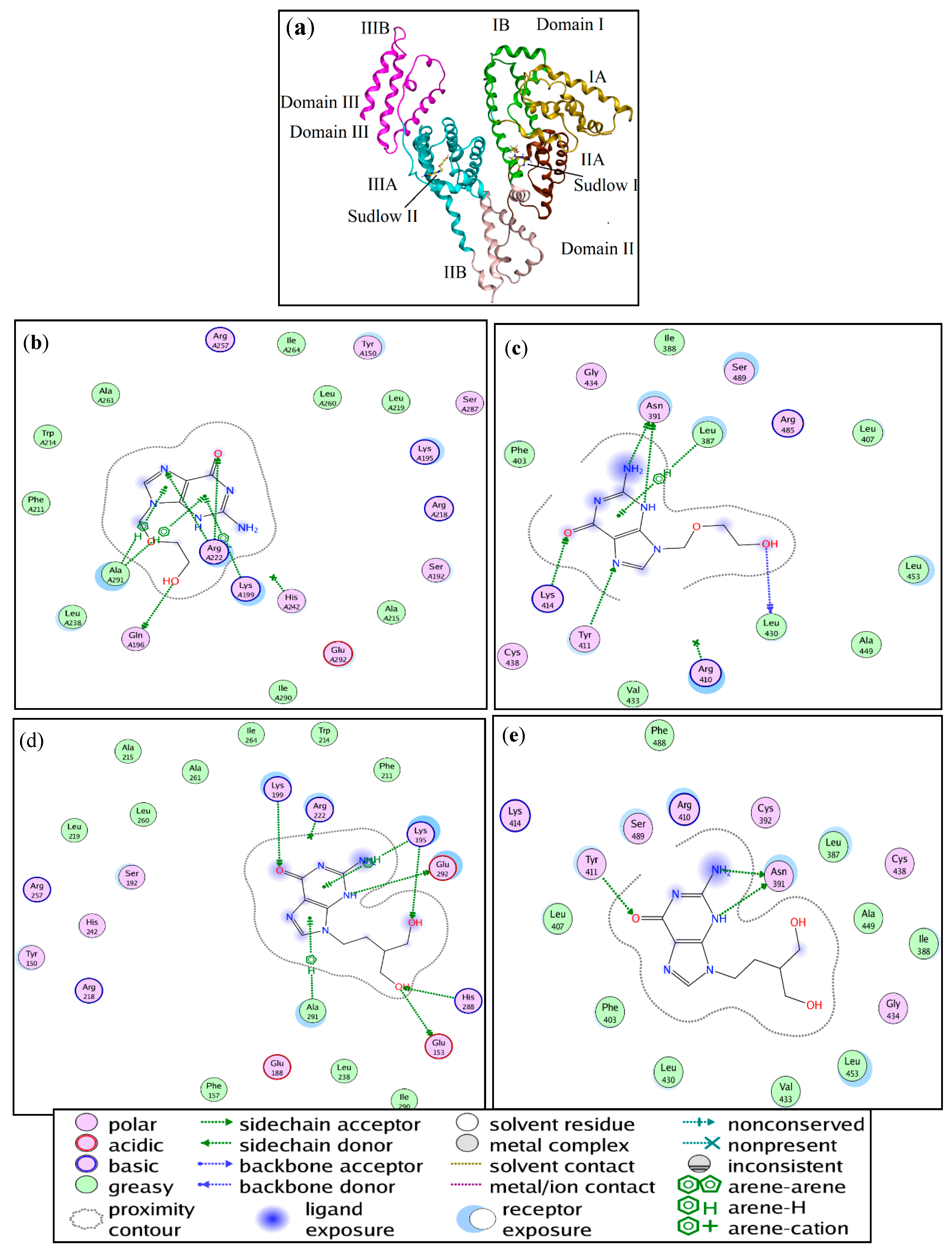
2.7. Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Standards and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Experimental Solutions
3.3. Ligand-Induced Fluorescence Quenching of HSA
3.4. Synchronous and 3D Fluorescence Measurements
3.5. Competitive Binding Studies
3.6. UV-Vis Spectral Determinations
3.7. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaeffer, H.J.; Beauchamp, L.; de Miranda, P.; Elion, G.B. 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine activity against viruses of the herpes group. Nature 1978, 272, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elion, G.B.; Furman, P.A.; Fyfe, J.A.; De Miranda, P.; Beauchamp, L.; Schaeffer, H.J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5716–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E. Antivirals for the treatment of herpesvirus infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1993, 32 (Suppl. A), 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, A.; Faulds, D. Ganciclovir: An update of its therapeutic use in cytomegalovirus infection. Drugs 1994, 48, 455–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korba, B.E.; Boyd, M.R. Penciclovir is a selective inhibitor of hepatitis B virus replication in cultured human hepatoblastoma cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1996, 40, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyd, M.R.; Bacon, T.H.; Sutton, D.; Cole, M. Antiherpesvirus activity of 9-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxy-methylbut-1-yl) guanine (BRL 39123) in cell culture. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnann, J.W.; Barton, N.H.; Whitley, R.J. Acyclovir: Mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, safety and clinical applications. Pharmacotherapy 1983, 3, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, R.V.; Cheng, Y.-C. The mode of action of penciclovir. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 1993, 4(Issue 6_suppl), 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, S.E.; Smith, H.A.; Brickman, C.; de Miranda, P.; Mclaren, C.; Keeney, R.E. Acyclovir for chronic mucocutaneous herpes simplex virus infection in immunosuppressed patients. Ann. Intern. Med. 1982, 96, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straus, S.E.; Tariff, H.E.; Seidlin, M.; Bachrach, S.; Lininger, L.; DiGiovanna, J.J.; Western, K.A.; Smith, H.A.; Lehrman, S.N.; Creagh-Kirk, T. Suppression of frequently recurring genital herpes: A placebo-controlled double-blind trial of oral acyclovir. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenkel, F.; Csajka, C.; Baglivo, E.; Kondo-Oestreicher, M.; Dayer, P.; Gex-Fabry, M.; Daali, Y. Intraocular penetration of penciclovir after oral administration of famciclovir: A population pharmacokinetic model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.H.; Cocchetto, D.M.; Duggan, D.E. Protein binding as a primary determinant of the clinical pharmacokinetic properties of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1987, 12, 402–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugio, S.; Kashima, A.; Mochizuki, S.; Noda, M.; Kobayashi, K. Crystal structure of human serum albumin at 2.5 Å resolution. Protein Eng. 1999, 12, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sułkowska, A. Interaction of drugs with bovine and human serum albumin. J. Mol. Struct. 2002, 614, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.-L.; Hu, X.-G.; Fang, G.-Y.; Zhang, H.-J. Experimental and molecular simulation investigation of interaction between acyclovir and bovine serum albumin. Mol. Simul. 2011, 37, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Hou, B.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Aodeng, G. Fluorescence Spectrometry of Interaction of Acyclovir and Bovine Serum Albumin in Presence of Carbon Nanotubes. Asian J. Chem. 2015, 27, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.M.; Abdelhameed, A.S. A Spectroscopic Approach to Investigate the Molecular Interactions between the Newly Approved Irreversible ErbB blocker “Afatinib” and Bovine Serum Albumin. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhameed, A.S. Insight into the Interaction between the HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitor Elvitegravir and Bovine Serum Albumin: A Spectroscopic Study. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 435674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Weber, G. Quenching of fluorescence by oxygen. Probe for structural fluctuations in macromolecules. Biochemistry 1973, 12, 4161–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Zheng, W.; Shi, S.; Chen, L.; Ji, L. Differences in structure, physiological stability, electrochemistry, cytotoxicity, DNA and protein binding properties between two Ru(III) complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatchi, T.S.; Kalaivani, P.; Poornima, P.; Padma, V.V.; Fronczek, F.R.; Natarajan, K. New organometallic ruthenium(II) complexes containing chelidonic acid (4-oxo-4H-pyran-2, 6-dicarboxylic acid): Synthesis, structure and in vitro biological activity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2004–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, O.; Volmer, M. The extinction period of fluorescence. Phys. Z. 1919, 20, 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Lineweaver, H.; Burk, D. The Determination of Enzyme Dissociation Constants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T. Serum albumin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1985, 37, 161–245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carter, D.C.; Ho, J.X. Structure of serum albumin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1994, 45, 153–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eftink, M.R. Fluorescence methods for studying equilibrium macromolecule-ligand interactions. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 278, 221–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forster, T.; Sinanoglu, O. Modern Quantum Chemistry; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 3, p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, P.D.; Subramanian, S. Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: Forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 3096–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhameed, A.S.; Alanazi, A.M.; Bakheit, A.H.; Darwish, H.W.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Darwish, I.A. Fluorescence spectroscopic and molecular docking studies of the binding interaction between the new anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor crizotinib and bovine serum albumin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 171, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhu, J.; Jin, J.; Yao, X. Studies on the binding of nevadensin to human serum albumin by molecular spectroscopy and modeling. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 846, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.-L.; Wang, J.-L.; Cui, Y.-R.; Li, J.-P. Fluorescent investigation of the interactions between N-(p-chlorophenyl)-N′-(1-naphthyl) thiourea and serum albumin: Synchronous fluorescence determination of serum albumin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 571, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhameed, A.S.; Alam, P.; Khan, R.H. Binding of janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib with human serum albumin: Multi-technique approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekshin, I. Separation of the tyrosine and tryptophan components of fluorescence using synchronous scanning method. Biofizika 1995, 41, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Ghuman, J.; Zunszain, P.A.; Petitpas, I.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Otagiri, M.; Curry, S. Structural Basis of the Drug-binding Specificity of Human Serum Albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, S.K.; Ahmad, E.; Khan, J.M.; Alam, P.; Ishtikhar, M.; Khan, R.H. Elucidating the interaction of limonene with bovine serum albumin: A multi-technique approach. Mol. BioSyst. 2015, 11, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D.; Wade, D. Further characterization of specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1976, 12, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |





| Ligand | Measured Parameters | Temperature (K) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 | 298 | 309 | |||
| ACV | Stern-Volmer parameters: | KSV × 104 (M−1) | 2.96 ± 0.06 | 2.84 ± 0.07 | 2.75 ± 0.07 |
| Kq × 1013 (M−1 ·s−1) | 1.10 | 1.05 | 1.02 | ||
| R2 | 0.9987 | 0.9984 | 0.9978 | ||
| Lineweaver–Burk parameters: | KLB × 104 (M−1) | 2.76 ± 0.11 | 2.64 ± 0.14 | 2.56 ± 0.06 | |
| R2 | 0.9988 | 0.9991 | 0.9999 | ||
| PNV | Stern-Volmer parameters: | KSV × 104 (M−1) | 3.04 ± 0.15 | 2.77 ± 0.09 | 2.60 ± 0.13 |
| Kq × 1013 (M−1· s−1) | 1.13 | 1.03 | 0.96 | ||
| R2 | 0.9922 | 0.9964 | 0.9918 | ||
| Lineweaver–Burk parameters: | KLB × 104 (M−1) | 3.64 ± 0.18 | 3.13 ± 0.16 | 2.80 ± 0.14 | |
| R2 | 0.9941 | 0.9978 | 0.9986 | ||
| Temp. (K) | ∆G0(kJ·mol−1) | ∆H0 (kJ·mol−1) | ∆S0 (J·mol−1·K−1) | K × 104 (L·mol−1) | n * | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACV | 288 | −24.66 ± 0.02 | −1.79 ± 0.29 | 79.40 ± 0.95 | 2.97 ± 0.02 | 1.00 ± 0.04 | 0.9991 |
| 298 | −25.45 ± 0.01 | 2.89 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.02 | 0.9992 | |||
| 309 | −26.33 ± 0.01 | 2.82 ± 0.01 | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 0.9994 | |||
| PNV | 288 | −24.62 ± 0.03 | −4.47 ± 0.51 | 69.95 ± 1.69 | 2.99 ± 0.03 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | 0.9936 |
| 298 | −25.32 ± 0.02 | 2.68 ± 0.02 | 1.00 ± 0.03 | 0.9979 | |||
| 309 | −26.08 ± 0.02 | 2.59 ± 0.03 | 1.00 ± 0.03 | 0.9973 |
| Relative Intensity (IF) | Relative Intensity (IF) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Peak 228/340 (λex/λem) nm | 2nd Peak 280/340 (λex/λem) nm | |
| HSA | 2726.96 | 3370.78 |
| ACV-HSA | 2063.92 (↓663.04; 24.31%) | 2042.05 (↓1328.73; 39.42%) |
| PNV-HSA | 2551.82 (↓175.14; 6.42%) | 3079.69 (↓291.09; 8.64%) |
| Systems | KSV × 104 (L·mol−1) | R2 | K × 104 (L·mol−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACV-HSA | 2.84 ± 0.07 | 0.9984 | 2.89 ± 0.01 | 0.9992 |
| ACV-HSA + IBP | 0.58 ± 0.03 | 0.9947 | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 0.9988 |
| ACV-HSA + WAR | 0.63 ± 0.06 | 0.9863 | 0.48 ± 0.03 | 0.9989 |
| PNV-HSA | 2.77 ± 0.09 | 0.9964 | 2.68 ± 0.02 | 0.9979 |
| PNV-HSA + IBP | 0.42 ± 0.08 | 0.9463 | 0.35 ± 0.06 | 0.9457 |
| PNV-HSA + WAR | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 0.9972 | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 0.9938 |
| Ligand | Binding Site | Amino Acid Residues | Interaction Type | Distance (Å) | Total Binding Energy (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACV | Site I | Gln196 | H-donor | 2.87 | −25.61 |
| Lys199 | cation-π | 3.80 | |||
| Arg222 | H-acceptor | 3.15 | |||
| Arg222 | H-acceptor | 3.06 | |||
| Ala291 | H-π | 4.19 | |||
| Ala291 | H-π | 4.37 | |||
| Site II | Leu387 | H-π | 4.43 | −22.01 | |
| Asn391 | H-donor | 3.01 | |||
| Tyr411 | H-acceptor | 3.36 | |||
| Lys414 | H-acceptor | 2.85 | |||
| Leu430 | H-donor | 3.12 | |||
| PNV | Site I | Glu153 | H-donor | 3.14 | −22.97 |
| Lys195 | H-π | 4.05 | |||
| Lys195 | H-acceptor | 3.22 | |||
| Lys199 | H-acceptor | 3.18 | |||
| His288 | H-acceptor | 3.12 | |||
| Ala291 | H-π+ | 4.26 | |||
| Glu292 | H-donor | 2.82 | |||
| Site II | Asn391 | H-donor | 3.22 | −26.53 | |
| Asn391 | H-donor | 2.96 | |||
| Tyr411 | H-acceptor | 2.87 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelhameed, A.S.; Bakheit, A.H.; Almutairi, F.M.; AlRabiah, H.; Kadi, A.A. Biophysical and In Silico Studies of the Interaction between the Anti-Viral Agents Acyclovir and Penciclovir, and Human Serum Albumin. Molecules 2017, 22, 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111906
Abdelhameed AS, Bakheit AH, Almutairi FM, AlRabiah H, Kadi AA. Biophysical and In Silico Studies of the Interaction between the Anti-Viral Agents Acyclovir and Penciclovir, and Human Serum Albumin. Molecules. 2017; 22(11):1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111906
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelhameed, Ali S., Ahmed H. Bakheit, Fahad M. Almutairi, Haitham AlRabiah, and Adnan A. Kadi. 2017. "Biophysical and In Silico Studies of the Interaction between the Anti-Viral Agents Acyclovir and Penciclovir, and Human Serum Albumin" Molecules 22, no. 11: 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111906
APA StyleAbdelhameed, A. S., Bakheit, A. H., Almutairi, F. M., AlRabiah, H., & Kadi, A. A. (2017). Biophysical and In Silico Studies of the Interaction between the Anti-Viral Agents Acyclovir and Penciclovir, and Human Serum Albumin. Molecules, 22(11), 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111906





