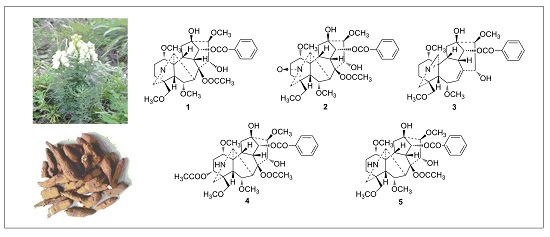
C19-Norditerpenoid Alkaloids from Aconitum szechenyianum and Their Effects on LPS-Activated NO Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Inhibitory Assay of NO Production
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, X.M.; Liu, H.J. Research and Application of "Qi-Medicines" in Taibai Mountains; People's Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.C.; Zhang, Z.Q. Crystal and molecular structure of songorine from the root of Aconitum szechenyianum Gay. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2008, 38, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, W.Y.; Zeng, C.J.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F. Diterpene alkaloids from the roots and processed products of Aconitum pendulum. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs 2010, 41, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.M.; Wang, H.C.; Zhu, Y.L. Studies on Chinese drug Aconitum spp. XIX. The alkaloids of Aconitum pendulum and their chemical structure. Yao Xue Xue Bao 1983, 18, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, C.J.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Three new C19-diterpenoid alkaloids from Aconitum pendulum. Phytochem. Lett. 2011, 4, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K.; Ohkoshi, E.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Bastow, K.F.; Lee, K.H. Cytotoxic esterified diterpenoid alkaloid derivatives with increased selectivity against a drug-resistant cancer cell line. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.F.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Kang, X.; Liu, J.L. LC-MS analysis for the components captured by ECV304 cell from extract of Aconitum szechenyianum Gay. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, J.; Yue, Z.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Mei, Q. Paris Saponin VII Inhibits the Migration and Invasion in Human A549 Lung Cancer Cells. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yue, Z.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, F.; Mei, Q. Paris saponin VII inhibits metastasis by modulating matrix metalloproteinases in colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fan, L.; Sun, Y.; Miao, X.; Zhang, F.; Meng, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, R.; Yue, Z.; et al. Paris saponin VII from trillium tschonoskii reverses multidrug resistance of adriamycin-resistant MCF-7/ADR cells via P-glycoprotein inhibition and apoptosis augmentation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Tang, Z.; Song, X.; Yue, Z. Steroidal Saponins from the Roots and Rhizomes of Tupistra chinensis. Molecules 2015, 20, 13659–13669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, D.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, C.; Tang, Z.; Cui, J.; Yue, Z. Steroidal glycosides from Reineckia carnea. Fitoterapia 2015, 105, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Qin, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, T.; Liu, L.; Wang, M.; Feng, F.; Mei, Q. Chemical constituents of the root of Jasminum giraldii. Molecules 2013, 18, 4766–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Mei, Q.; Li, Z.; Cui, J.; Tang, Z.; Yue, Z. Two new compounds from the roots and rhizomes of Trillium tschonoskii. Phytochem. Lett. 2014, 10, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, W.; Song, B.; Tang, Z.; Cui, J.; Yue, Z. Two new spirostanol saponins from the the roots and rhizomes of Tupistra chinensis. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 13, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Song, X.; Yue, Z. Two new pregnane glycosides from Reineckia carnea. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 15, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.G.; Wang, F.P.; Gao, F.; Yan, L.P.; Chen, D.L.; Liu, Y. A pharmacophylogenetic study of Aconitum L. (Ranunculaceae) from China. Acta Phytotaxon. Sin. 2006, 44, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Scott, M.J.; Fan, E.K.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiao, G.; Li, S.; Billiar, T.R.; Wilson, M.A.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Tissue damage negatively regulates LPS-induced macrophage necroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1428–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Xin, W.; Li, Y.; Ni, L.; Ma, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Du, G. Anti-inflammation effect of methyl salicylate 2-O-beta-d-lactoside on adjuvant induced-arthritis rats and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated murine macrophages RAW264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, F.; Cordova, L.A.; Pajarinen, J.; Lin, T.H.; Yao, Z.; Goodman, S.B. Inflammation, fracture and bone repair. Bone 2016, 86, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirsch, V.M.; Stuppner, H.; Vollmar, A.M. The Griess assay: Suitable for a bio-guided fractionation of anti-inflammatory plant extracts? Planta Med. 1998, 64, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 4–5 are available from the authors.
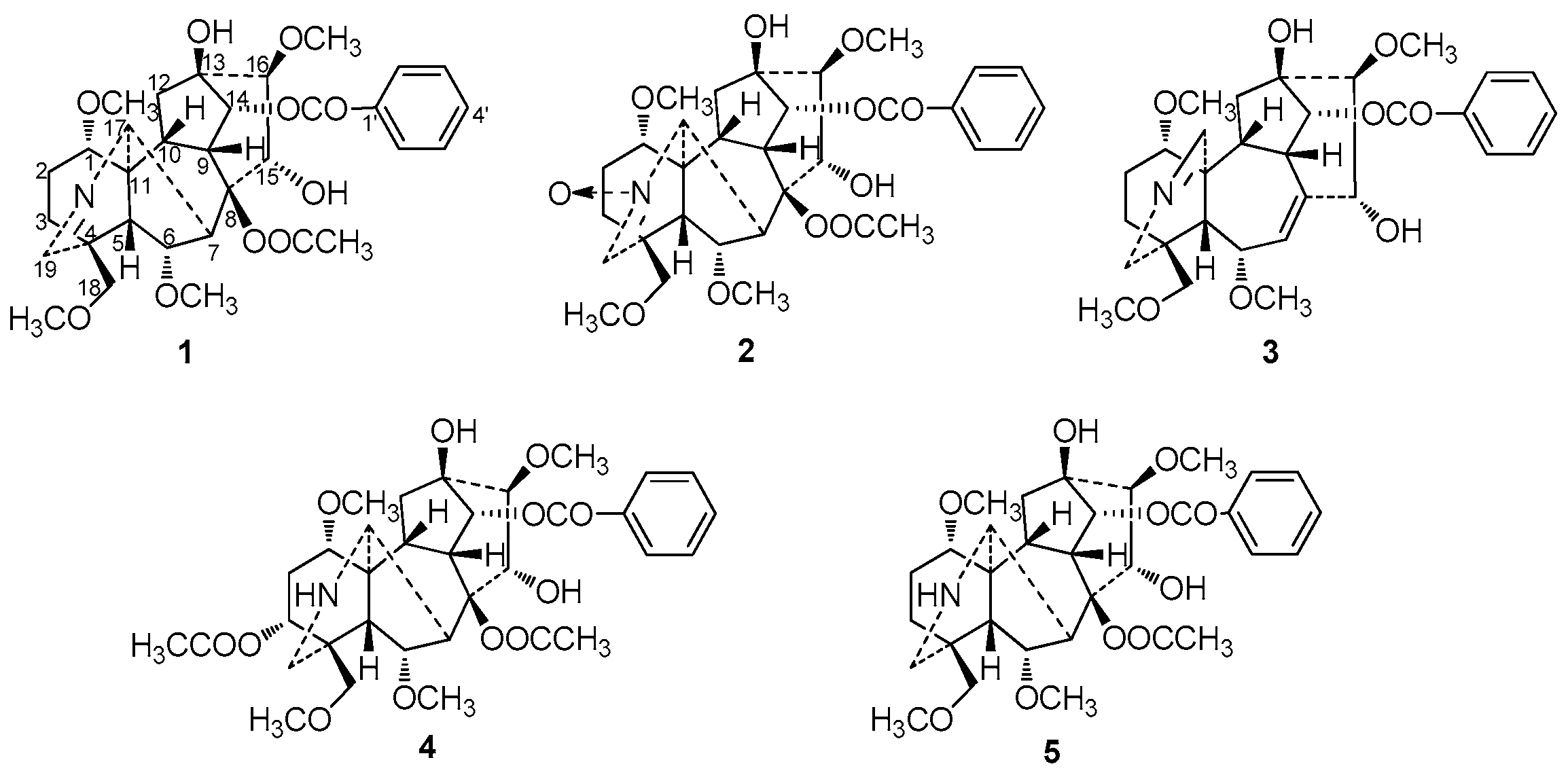
 H), HMBC (H→C) and ROESY (H↔H) correlations of compound 1.
H), HMBC (H→C) and ROESY (H↔H) correlations of compound 1.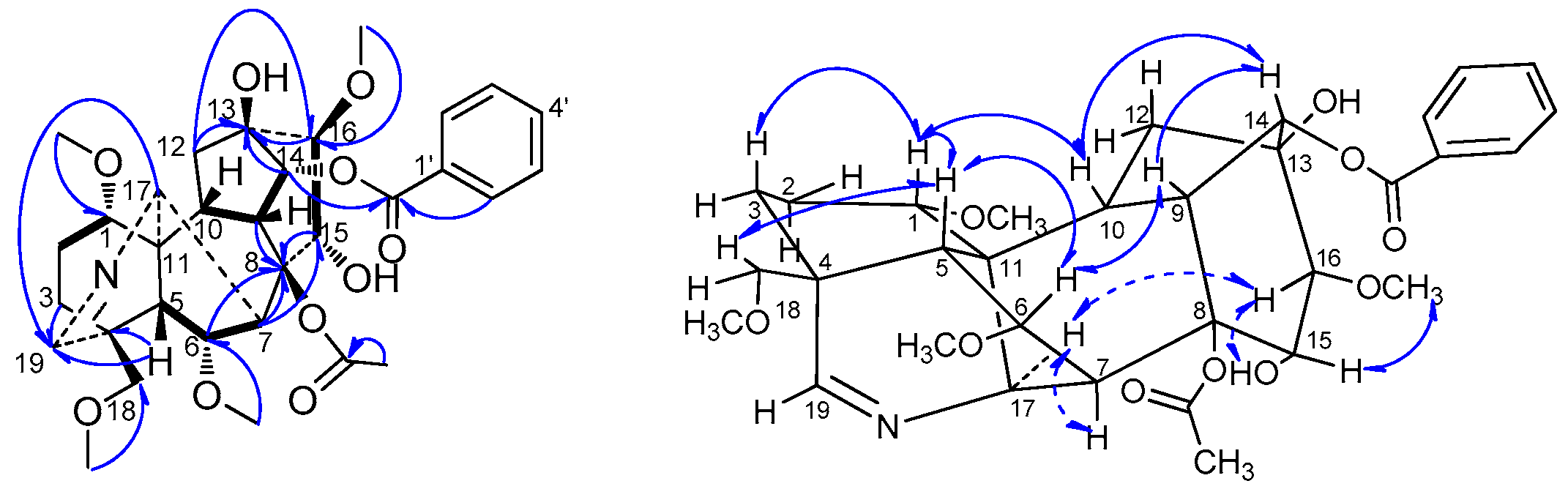
 H), HMBC (H→C) and ROESY (H↔H) correlations of compound 2.
H), HMBC (H→C) and ROESY (H↔H) correlations of compound 2.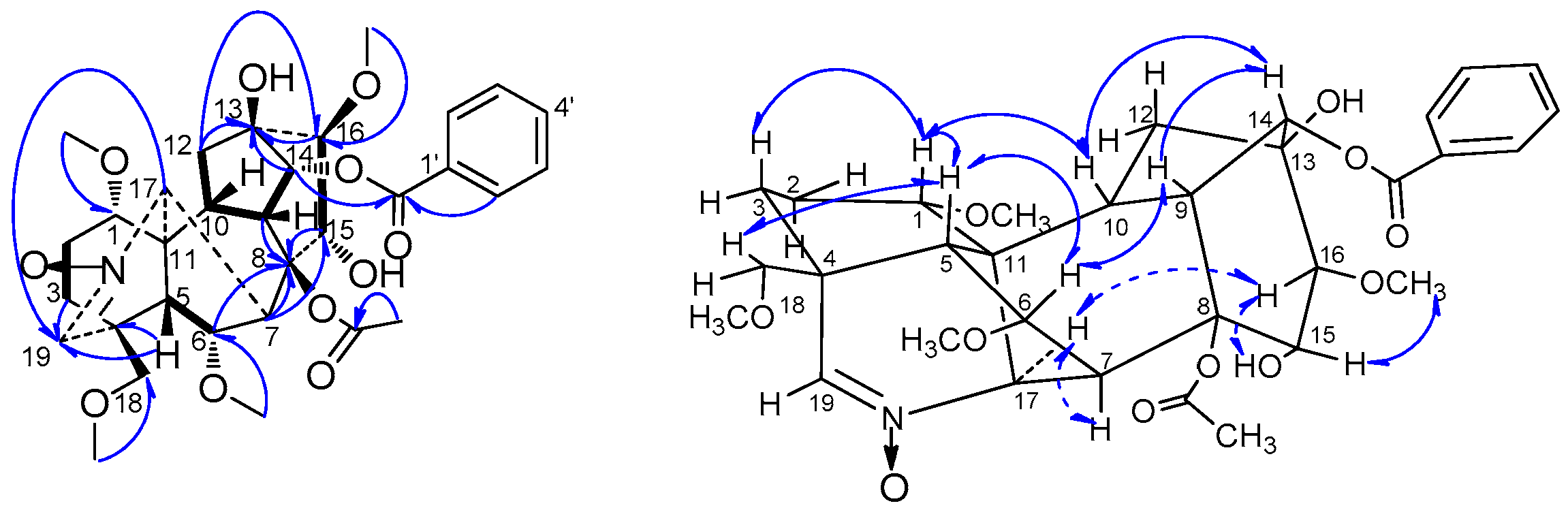
 H), HMBC (H→C) and ROESY (H↔H) correlations of compound 3.
H), HMBC (H→C) and ROESY (H↔H) correlations of compound 3.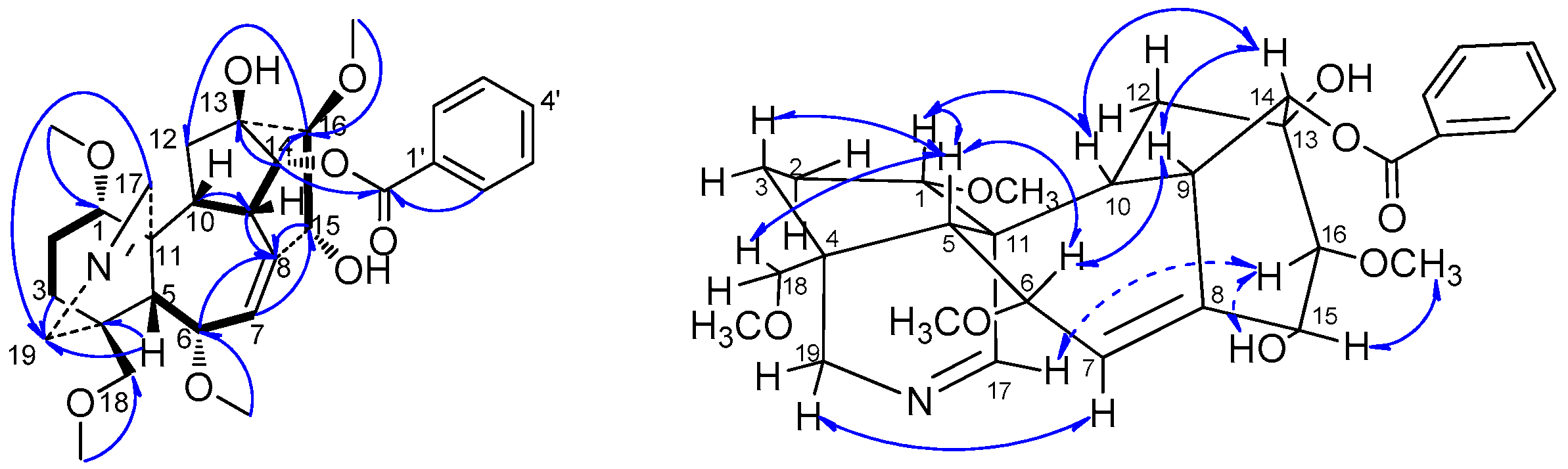
| NO. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δC | |
| 1 | 82.3 | 3.20 (d, 4.1) | 80.5 | 3.32 (m) | 89.6 | 2.99 (dd, 4.4, 11.3) | 81.0 | 82.3 |
| 2 | 22.9 | 1.66 (m, H-2a) | 22.0 | 1.45 (m, H-2a) | 24.7 | 1.10 (m) | 31.8 | 23.5 |
| 1.57 (m, H-2b) | 1.81 (m, H-2b) | 1.86 (m) | ||||||
| 3 | 28.2 | 1.63 (m, H-3a) | 29.5 | 1.70 (m, H-3a) | 37.4 | 1.55 (m) | 72.3 | 29.0 |
| 1.64 (m, H-3b) | 1.79 (m, H-3b) | 1.69 (m) | ||||||
| 4 | 46.8 | 42.1 | 39.7 | 43.2 | 39.0 | |||
| 5 | 45.8 | 2.23 (d, 7.1) | 44.7 | 2.35 (d, 7.0) | 46.2 | 2.32 (d, 8.9) | 51.2 | 48.7 |
| 6 | 84.1 | 3.92 (d, 7.1) | 82.7 | 4.00 (d, 7.0) | 80.1 | 4.45 (m) | 83.8 | 83.2 |
| 7 | 49.6 | 2.87 (s) | 49.7 | 3.30 (s) | 132.1 | 5.62 (d, 5.5) | 45.2 | 43.6 |
| 8 | 90.6 | 89.3 | 137.5 | 91.7 | 91.5 | |||
| 9 | 42.6 | 2.70 (t, 6.1) | 41.9 | 2.74 (m) | 43.0 | 3.18 (s) | 43.9 | 43.2 |
| 10 | 40.6 | 2.17 (m) | 39.1 | 2.26 (m) | 41.7 | 2.43 (s) | 40.9 | 40.3 |
| 11 | 51.4 | 51.9 | 48.5 | 49.4 | 49.7 | |||
| 12 | 36.4 | 2.20 (m, H-12a) | 36.5 | 2.27 (m, H-12a) | 38.9 | 2.45 (m) | 35.2 | 35.4 |
| 2.21 (m, H-12b) | 1.98 (m, H-12b) | |||||||
| 13 | 74.3 | 74.1 | 75.6 | 74.4 | 74.0 | |||
| 14 | 79.3 | 4.90 (d, 4.9) | 78.8 | 4.89 (d, 4.8) | 79.4 | 5.08 (d, 4.2) | 79.1 | 78.9 |
| 15 | 78.9 | 4.48 (dd, 2.9, 5.3) | 78.7 | 4.48 (dd, 3.0, 4.9) | 74.1 | 4.80 (dd, 3.0, 5.8) | 79.2 | 79.0 |
| 16 | 89.9 | 3.42 (d, 5.3) | 89.6 | 3.45 (d, 5.0) | 92.2 | 3.30 (d, 6.0) | 90.0 | 89.5 |
| 17 | 60.6 | 3.97 (s) | 72.9 | 4.02 (s) | 166.4 | 7.86 (br s) | 55.8 | 56.7 |
| 18 | 78.2 | 3.78 (d, 8.5, H-18a) | 77.9 | 3.79 (d, 8.5, H-18a) | 80.6 | 3.16 (d, 8.4) | 73.8 | 79.8 |
| 3.42 (d, 8.5, H-18b) | 3.33 (d, 8.5, H-18b) | 3.86 (d, 8.4) | ||||||
| 19 | 165.9 | 7.31 (s) | 138.9 | 6.70 (d, 1.2) | 58.3 | 3.53 (m) | 41.6 | 49.0 |
| 3.45 (m) | ||||||||
| 8-OAc | 172.6 | 172.1 | 172.3 | 172.0 | ||||
| 21.5 | 1.32 (s) | 21.4 | 1.32 (s) | 21.5 | 21.3 | |||
| 1-OCH3 | 56.3 | 3.18 (s) | 56.6 | 3.21 (s) | 58.2 | 3.20 (s) | 56.0 | 55.4 |
| 6-OCH3 | 57.4 | 3.03 (s) | 57.3 | 3.05 (s) | 56.9 | 3.19 (s) | 58.3 | 57.9 |
| 16-OCH3 | 61.3 | 3.75 (s) | 61.4 | 3.77 (s) | 61.8 | 3.75 (s) | 61.4 | 61.1 |
| 18-OCH3 | 59.3 | 3.29 (s) | 59.3 | 3.27 (s) | 59.1 | 3.27 (s) | 59.1 | 59.1 |
| ArC=O | 166.2 | 166.2 | 166.4 | 166.2 | 165.9 | |||
| ArC-1′ | 130.0 | 129.9 | 130.0 | 130.0 | 130.7 | |||
| 3′, 5′ | 128.9 | 7.43 (t, 7.6) | 129.0 | 7.44 (t, 7.3) | 128.7 | 7.42 (t, 7.5) | 128.9 | 128.6 |
| 2′, 6′ | 129.8 | 8.02 (d, 7.6) | 129.9 | 8.01 (d, 7.3) | 130.1 | 8.03 (d, 7.5) | 129.8 | 129.6 |
| 4′ | 133.6 | 7.55 (t, 7.6) | 133.8 | 7.57 (t, 7.3) | 133.5 | 7.53 (t, 7.5) | 133.5 | 133.3 |
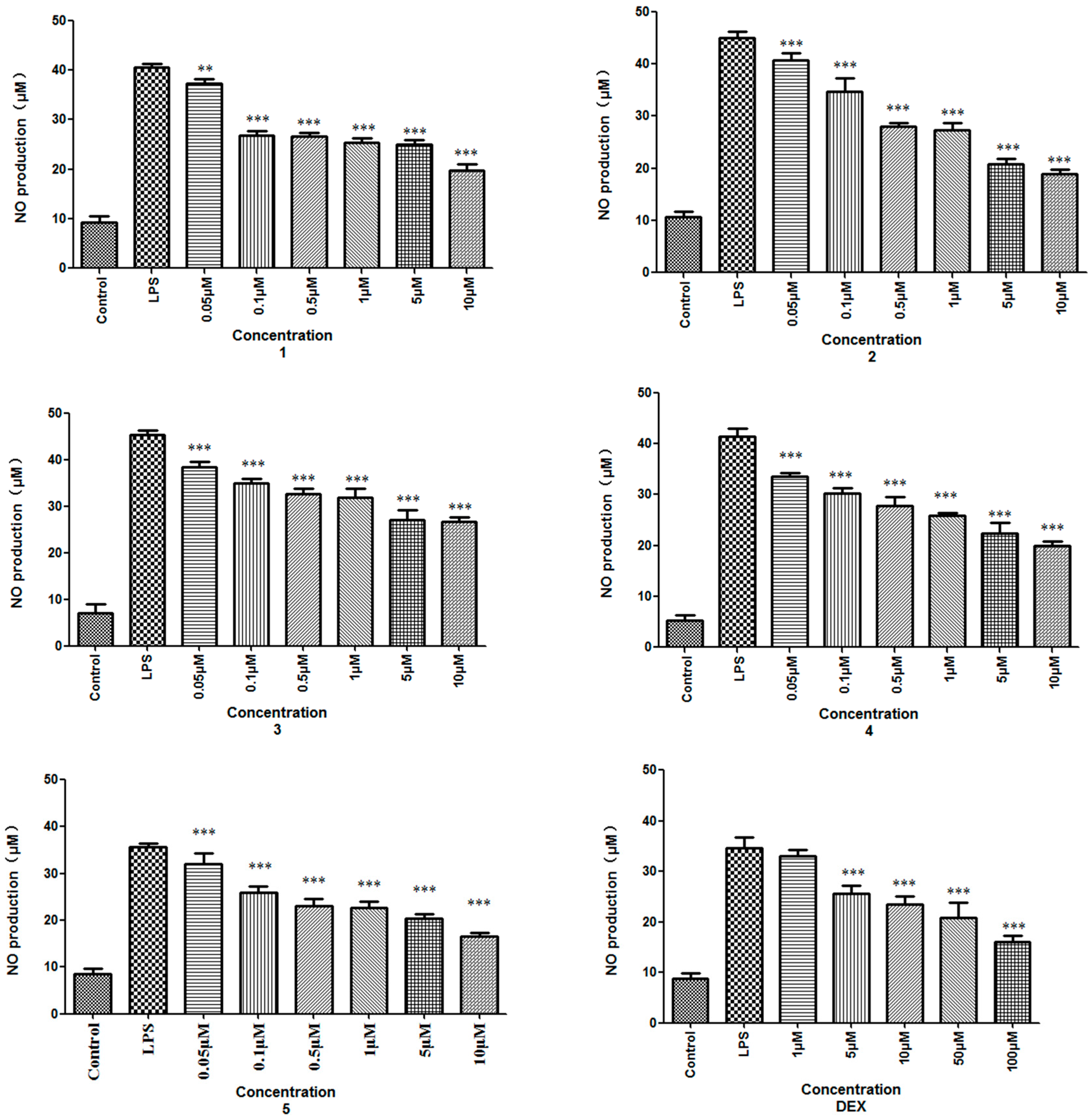
| Compound | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Dexamethasone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) | 36.62 ± 6.86 | 3.30 ± 0.11 | 7.46 ± 0.89 | 8.09 ± 1.31 | 11.73 ± 1.94 | 8.32 ± 1.45 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Yue, Z.; Xie, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Song, B.; Tang, Z.; Song, X. C19-Norditerpenoid Alkaloids from Aconitum szechenyianum and Their Effects on LPS-Activated NO Production. Molecules 2016, 21, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091175
Wang F, Yue Z, Xie P, Zhang L, Li Z, Song B, Tang Z, Song X. C19-Norditerpenoid Alkaloids from Aconitum szechenyianum and Their Effects on LPS-Activated NO Production. Molecules. 2016; 21(9):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091175
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fei, Zhenggang Yue, Pei Xie, Li Zhang, Zhen Li, Bei Song, Zhishu Tang, and Xiaomei Song. 2016. "C19-Norditerpenoid Alkaloids from Aconitum szechenyianum and Their Effects on LPS-Activated NO Production" Molecules 21, no. 9: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091175
APA StyleWang, F., Yue, Z., Xie, P., Zhang, L., Li, Z., Song, B., Tang, Z., & Song, X. (2016). C19-Norditerpenoid Alkaloids from Aconitum szechenyianum and Their Effects on LPS-Activated NO Production. Molecules, 21(9), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21091175