New Cerebroside and Nucleoside Derivatives from a Red Sea Strain of the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea producens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Purification of Compounds 1–5
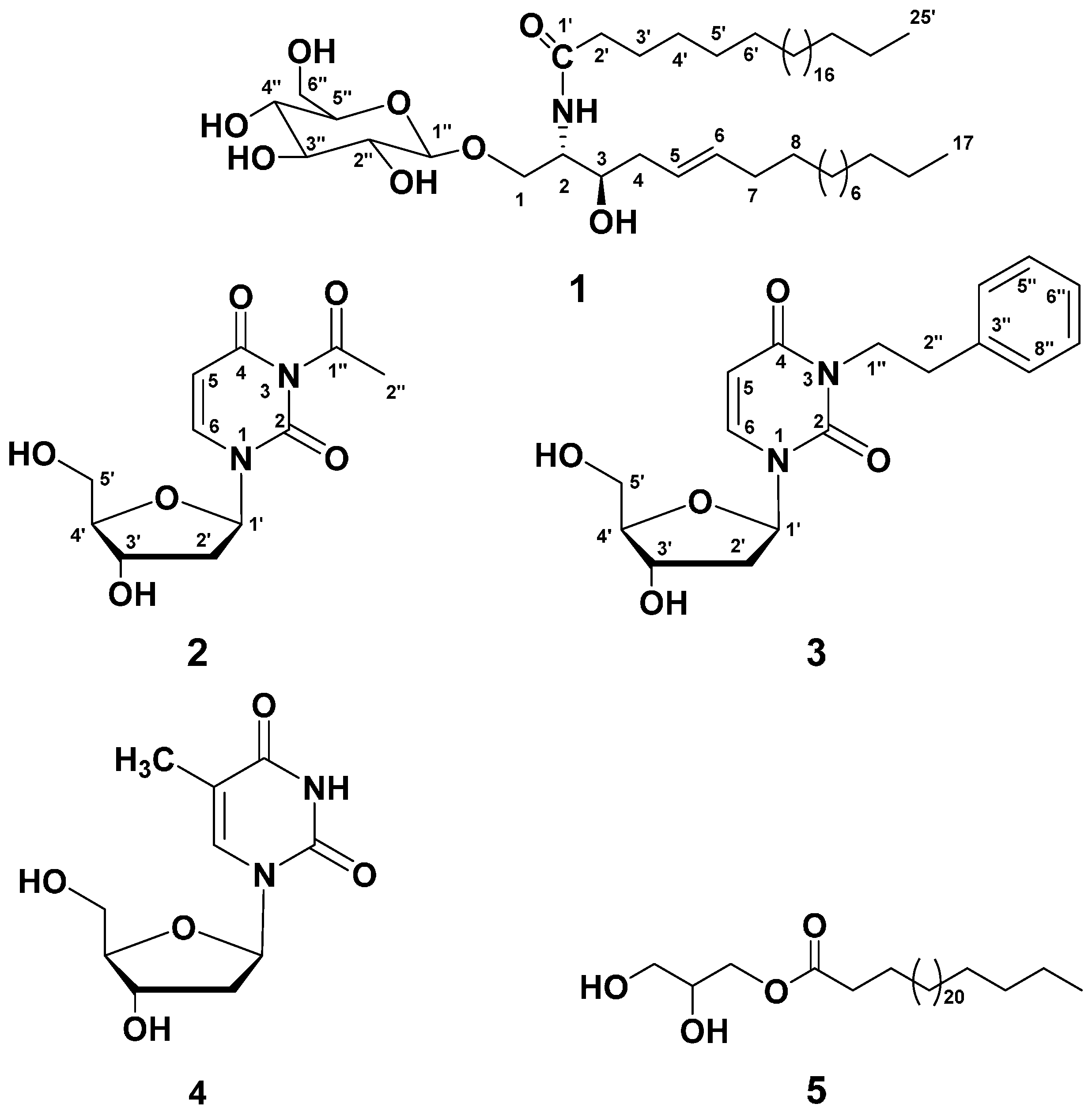
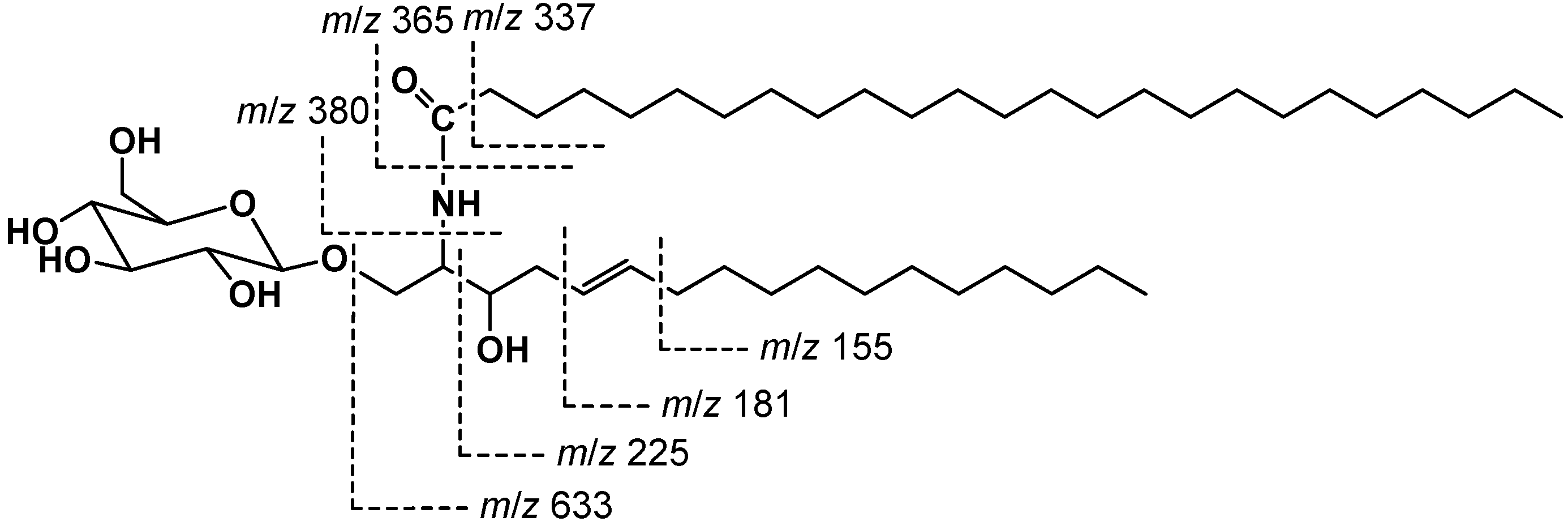
2.2. Structure Elucidation of Compound 1
2.3. Structure Elucidation of Compound 2
2.4. Structure Elucidation of Compound 3
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Materials
3.3. Extraction and Purifications of Compounds 1–5
3.4. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity of the Compounds
3.5. Methanolysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elkhayat, E.S.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Ceramides, activity and structure elucidation. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2013, 8, 370–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakomori, S. Structure and function of sphingoglycolipids in transmembrane signalling and cell-cell interactions. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 3, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, K.; Sanai, Y. Functional roles of glycosphingolipids in signal transduction via lipids rafts. Glycoconjugate J. 2000, 17, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Gao, C.; Su, X.; Peng, Y. Marine nucleosides: Structure, bioactivity, synthesis and biosynthesis. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5817–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sereda, M.J. Purines 2010: Adenine nucleosides and nucleotides in biomedicine. IDrugs 2010, 13, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cooperwood, J.S.; Gumina, G.; Boudinot, F.D.; Chu, C.K. Nucleoside and nucleotide prodrugs. In Recent Advances in Nucleosides: Chemistry and Chemotherapy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 91–147. [Google Scholar]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Coates, R.C.; Engene, N.; Gerwick, L.G.; Grindberg, R.; Jones, A.; Sorrels, C. Giant marine cyanobacteria produce exciting potential pharmaceuticals. Microbe 2008, 3, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Nunnery, J.K.; Mevers, E.; Gerwick, W.H. Biologically active secondary metabolites from marine cyanobacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidgewell, K.; Clark, B.R.; Gerwick, W.H. The natural products chemistry of cyanobacteria. In Comprehensive Natural Products II Chemistry and Biology; Mander, L., Lui, H.-W., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 141–188. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, L.T. Filamentous tropical marine cyanobacteria: A rich source of natural products for anticancer drug discovery. J. Appl. Phycol. 2010, 5, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engene, N.; Choi, H.; Esquenazi, E.; Rottacker, E.C.; Ellisman, M.H.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Gerwick, W.H. Underestimated biodiversity as a major explanation for the perceived rich secondary metabolite capacity of the cyanobacterial genus Lyngbya. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 116–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burja, A.M.; Banaigs, B.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Burgess, J.G.; Wright, P.C. Marine cyanobacteria—A prolific source of natural products. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9347–9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.A.; Gerwick, L. Marine natural product drug discovery: Leads for treatment of inflammation, cancer, infections, and neurological disorders. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2010, 32, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.C.; Monroe, E.A.; Podell, S.; Hess, W.R.; Klages, S.; Esquenazi, E.; Niessen, S.; Hoover, H.; Rothmann, M.; Lasken, R.S.; et al. Genomic insights into the physiology and ecology of the marine filamentous cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8815–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; McPhail, K.L.; Elbandy, M. Malyngamide 4, a new lipopeptide from the Red Sea marine cyanobacterium Moorea producens (formerly Lyngbya majuscula). Phytochem. Lett. 2013, 6, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Shaala, L.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Banjar, Z.M.; Badr, J.M.; McPhail, K.L.; Risinger, A.L.; Mooberry, S.L. 2,3-Seco-2,3-dioxo-lyngbyatoxin A from a Red Sea strain of the marine cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 29, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, C.C.; Cowley, E.S.; Sikorska, J.; Shaala, L.A.; Ismael, J.E.; Youssef, D.T.A.; McPhail, K.L. Apratoxin H and apratoxin A sulfoxide from the Red Sea cyanobacterium Moorea producens. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, C.C.; Thimmaiah, M.; Shaala, L.A.; Hau, A.M.; Malmo, J.M.; Ishmael, J.E.; Youssef, D.T.A.; McPhail, K.L. Cyclic depsipeptides, grassypeptolides D and E and Ibu-epidemethoxylyngbyastatin 3, from a Red Sea Leptolyngbya cyanobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Fouad, M.A.; Elkhayat, E.S.; Proksch, P. Iotrochotamides I and II new ceramides from the Indonesian sponge Iotrochota purpurea. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Elkhayat, E.S.; Gouda, Y.G.; Proksch, P. Strepsiamide A–C, new ceramides from the marine sponge Strepsichordaia lendenfeldi. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Murshid, S.S.A.; Badr, J.M.; Youssef, D.T.A. Penicillosides A and B: New cerebrosides from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium species. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Abd-Elrazek, A.E.E.; Hassanean, H.A.; van Soest, R.M.; Youssef, D.T.A. New compounds from the Red Sea marine sponge Echinoclathria gibbosa. Phytochem. Lett. 2014, 9, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, H.; Kawashima, K.; Sakagami, M.; Kawanishi, H.; Shimomura, M.; Ohashi, K.; Kitagawa, I. Sphingolipids and glycerolipids. I. Chemical structures and ionophoretic activities of soyacerebrosides I and II from soybean. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2933–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitrin, R.D.; Chan, G.; Dingerdissen, J.; DeBrosse, C.; Mehta, R.; Roberts, G.; Rottschaefer, S.; Staiger, D.; Valenta, J.; Snader, K.M. Isolation and structure determination of Pachybasium cerebrosides which potentiate the antifungal activity of aculeacin. J. Antibiot. 1988, 41, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawatake, S.; Nakamura, K.; Inagaki, M.; Higuchi, R. Isolation and structure determination of six glucocerebrosides from the starfish Luidia maculata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.S.; Kim, J.S.; Xu, Y.N.; Kim, Y.H. Isolation of a new cerebroside from the root bark of Aralia elata. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1059–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, D. Structure determination and synthesis of a new cerebroside isolated from the traditional Chinese medicine Typhonium giganteum Engl. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 3529–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, C.O.; Kim, Y.C.; Kang, S.S. New bioactive cerebrosides from Arisaema amurense. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmientos, F.; Schwarzmann, G.; Sandhoff, K. Direct evidence by carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy for the erythro configuration of the sphingoid moiety in Gaucher cerebroside and other natural sphingolipids. Eur. J. Bichem. 1985, 146, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodato, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Hino, T. Synthesis of cerebroside B1b with antiulcerogenic activity II. Total synthesis and determination of absolute configuration of cerebroside B1b and its stereoisomers. Tetrahedron 1989, 45, 7263–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, S.; Guilliaume, D.; Sun, C. New cerebrosides from Euryale ferox. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 7, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Gomes, J.D.; Byrn, S.R. Chemical modification of deoxyribonucleic acids: A direct study by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Org. Chem. 1983, 48, 5151–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, Q.; Ji, N.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Cao, X. Deoxyuridines from the marine sponge associated Actinomycete Streptomyces microflavus. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Li, Z.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y. Neobacillamide A, a novel thiazole-containing alkaloid from the marine bacterium Bacillus vallismortis C89, associated with South China Sea sponge Dysidea avara. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Gao, S.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Wang, B. Chemical constituents of a marine-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium commune G2M. Molecules 2010, 15, 3270–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinsen, P.; Gutiérrez, A.; Faulds, C.B.; del Río, J.C. Lipophilic extractives from the cortex and pith of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schumach.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6408–6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinsen, P.; Gutiérrez, A.; Faulds, C.B.; del Río, J.C. Comprehensive study of valuable lipophilic phytochemicals in Wheat Bran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.

| No. | δH [mult., J (Hz)] | δC (mult.) | HMBC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.91 m, 3.74 m | 68.5 CH2 | 2, 3, 1′′ |
| 2 | 3.97 m | 59.3 CH | 1, 3, 4, 1′ |
| 3 | 3.61 m | 73.4 CH | 1, 2 |
| 4 | 2.08 m | 32.2 CH2 | 2, 5, 6 |
| 5 | 5.35 dt (15.3, 7.6) | 129.9 CH | 3, 4, 7 |
| 6 | 5.37 dt (15.3, 7.1) | 128.8 CH | 4, 5, 7 |
| 7 | 2.01 m | 32.0 CH2 | 5, 6 |
| 8–15 | 1.27–1.23 | 30.3–29.0 CH2 | - |
| 16 | 1.29 m | 22.6 CH2 | 15, 17 |
| 17 | 0.87 t (6.7) | 14.1 CH3 | 14, 16 |
| 1′ | - | 173.8 C | - |
| 2′ | 2.33 t (7.6) | 34.4 CH2 | 1′, 4′ |
| 3′ | 1.61 m | 24.8 CH2 | 1′, 2′, 4′ |
| 4′ | 1.28 m | 28.7 CH2 | - |
| 5′–17′ | 1.27–1.23 m | 30.3–29.0 CH2 | - |
| 18′ | 1.30 m | 22.7 CH2 | 17′, 19′ |
| 19′ | 0.89 t (6.8) | 14.1 CH3 | 16′, 18′ |
| 1′′ | 4.28 d (7.7) | 104.0 CH | 1, 2′′, 3′′ |
| 2′′ | 3.65 m | 70.2 CH | 3′′, 4′′ |
| 3′′ | 3.63 m | 71.7 CH | 1′′, 2′′, 4′′ |
| 4′′ | 4.02 m | 69.5 CH | 5′′, 6′′ |
| 5′′ | 3.56 m | 74.6 CH | 4′′, 6′′ |
| 6′′ | 4.38 m, 4.22 m | 62.7 CH2 | 1′′, 5′′ |
| 2-NH | 7.52 d (8.5) | - | 2, 3, 1′ |
| 2 | 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | δH [mult., J Hz)] | δC (mult.) | HMBC | No. | δH [mult., J (Hz)] | δC (mult.) | HMBC |
| 2 | - | 151.7 C | 2 | - | 151.7 C | - | |
| 4 | - | 162.8 C | 4 | - | 162.8 C | - | |
| 5 | 5.69 d (8.5) | 102.6 CH | 4, 6 | 5 | 5.69 d (8.5) | 102.6 CH | 6 |
| 6 | 7.98 d (8.5) | 142.5 CH | 2, 4, 5, 1′ | 6 | 7.98 d (8.5) | 142.5 CH | 2, 4, 5 |
| 1′ | 6.27 t (6.8) | 86.6 CH | 2, 6, 2′ | 1′ | 6.26 t (6.8) | 86.2 CH | 2′, 3′ |
| 2′ | 2.28 m | 41.4 CH2 | 1′, 3′ | 2′ | 2.21 m | 41.2 CH2 | 1′, 3′ |
| 3′ | 4.38 m | 72.2 CH | 3′ | 4.36 m | 72.3 CH | ||
| 4′ | 3.89 m | 89.0 CH | 4′ | 3.91 m | 88.8 CH | ||
| 5′ | 3.75 m, 3.71 m | 62.8 CH2 | 5′ | 3.75 m, 3.71 m | 62.8 CH2 | ||
| 1′′ | - | 183.4 C | 1′′ | 3.16 t (7.6) | 42.0 CH2 | 2, 4, 2′′, 3′′ | |
| 2′′ | 1.95 s | 23.5 CH3 | 1′′ | 2′′ | 2.95 t (7.6) | 34.7 CH2 | 3′′, 4′′, 8′′ |
| 3′′ | - | 137.9 C | - | ||||
| 4′′, 8′′ | 7.27 brd (6.8) | 129.8 CH | 2′′, 6′′ | ||||
| 5′′, 7′′ | 7.35 m | 130.0 CH | 3′′, 4′′, 8′′ | ||||
| 6′′ | 7.27 m | 128.3 CH | |||||
| Compound | IC50 (μg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal Carcinoma (HCT-116) | Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HepG2) | Breast Cancer (MCF-7) | |
| 1 | >50 | >50 | 20.5 |
| 2 | >50 | >50 | 18.2 |
| 3 | >50 | >50 | 22.8 |
| 4 | NT | NT | NT |
| 5 | NT | NT | NT |
| Doxorubicin | 0.789 | 0.621 | 0.415 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youssef, D.T.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Shaala, L.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Banjar, Z.M. New Cerebroside and Nucleoside Derivatives from a Red Sea Strain of the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Molecules 2016, 21, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030324
Youssef DTA, Ibrahim SRM, Shaala LA, Mohamed GA, Banjar ZM. New Cerebroside and Nucleoside Derivatives from a Red Sea Strain of the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Molecules. 2016; 21(3):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030324
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoussef, Diaa T.A., Sabrin R.M. Ibrahim, Lamiaa A. Shaala, Gamal A. Mohamed, and Zainy M. Banjar. 2016. "New Cerebroside and Nucleoside Derivatives from a Red Sea Strain of the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea producens" Molecules 21, no. 3: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030324
APA StyleYoussef, D. T. A., Ibrahim, S. R. M., Shaala, L. A., Mohamed, G. A., & Banjar, Z. M. (2016). New Cerebroside and Nucleoside Derivatives from a Red Sea Strain of the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Molecules, 21(3), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21030324








