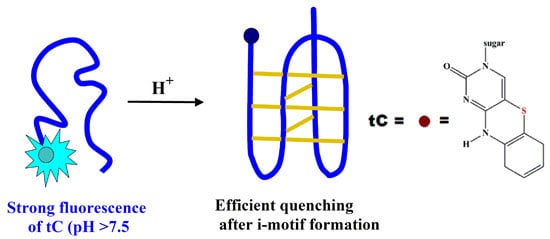
Fluorescent Sensor for PH Monitoring Based on an i-Motif- – Switching Aptamer Containing a Tricyclic Cytosine Analogue (tC)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
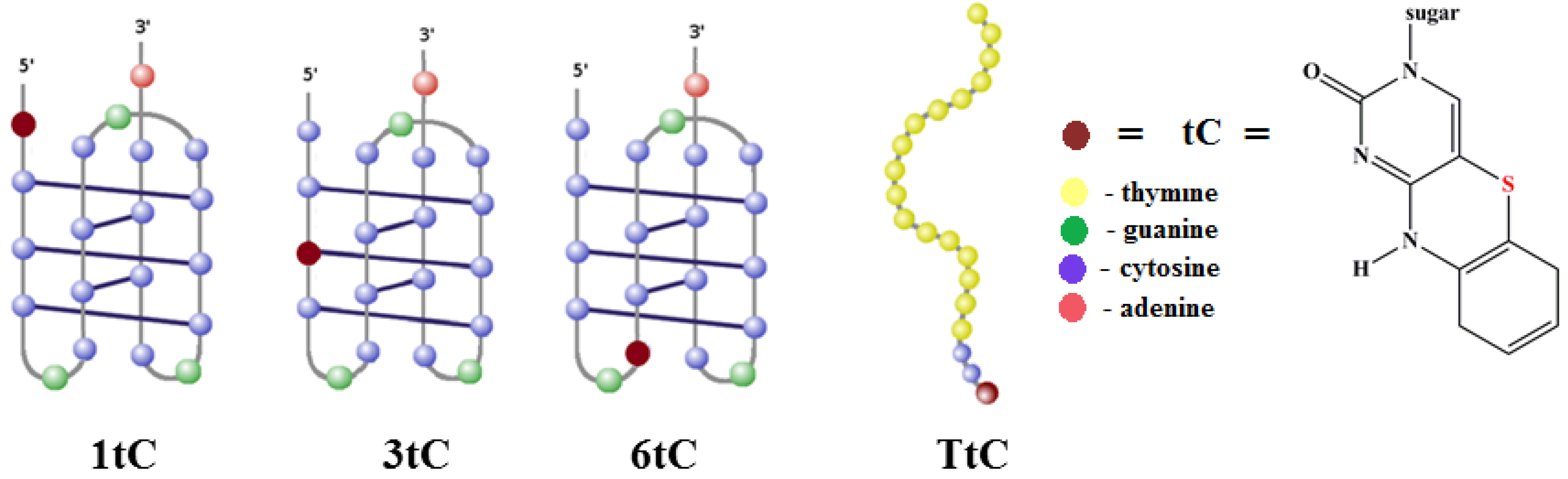
2.1. Design of tC-Modified i-Motifs
| Name | Sequence 5′-3′ | Position of tC Analogue |
|---|---|---|
| 1tC | tCCC CGC CCC GCC CCG CCC CA | 1 |
| 3tC | CCtC CGC CCC GCC CCG CCC CA | 3 |
| 6tC | CCC CGtC CCC GCC CCG CCC CA | 6 |
| TtC | tCCC TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TT | 1 |
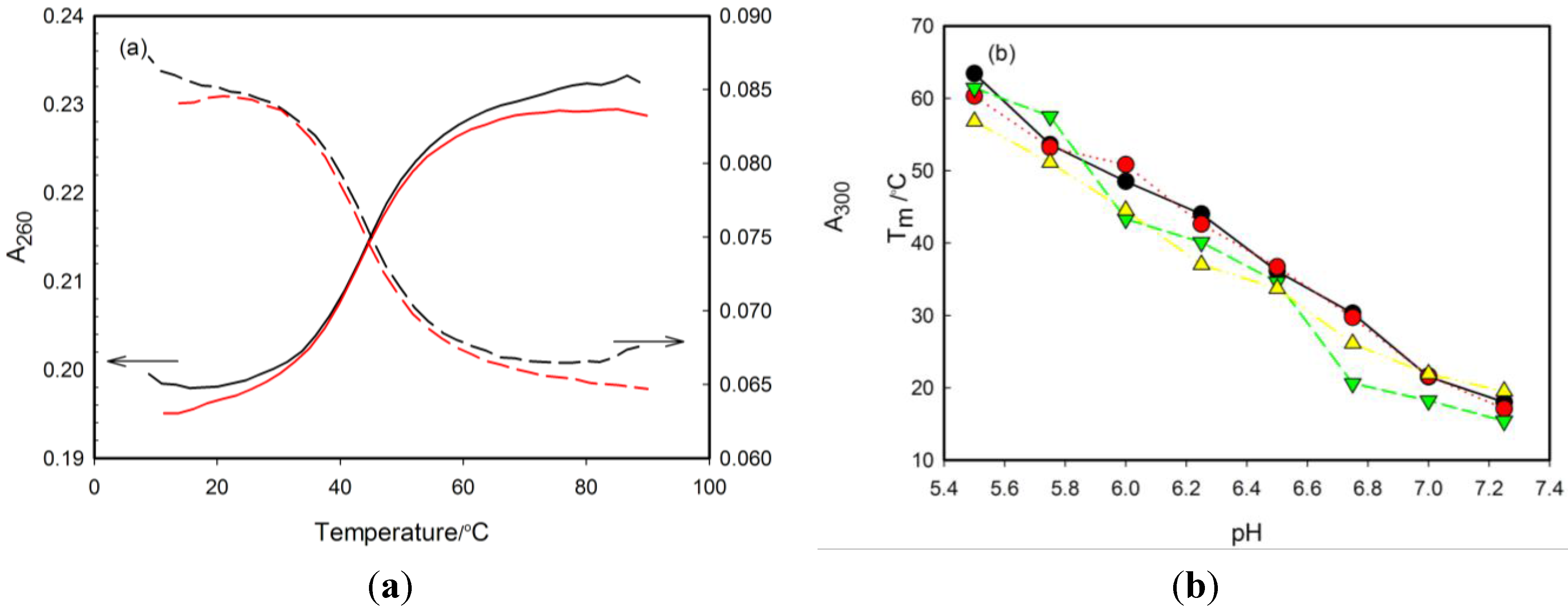
2.2. Thermal Stability of i-Motifs
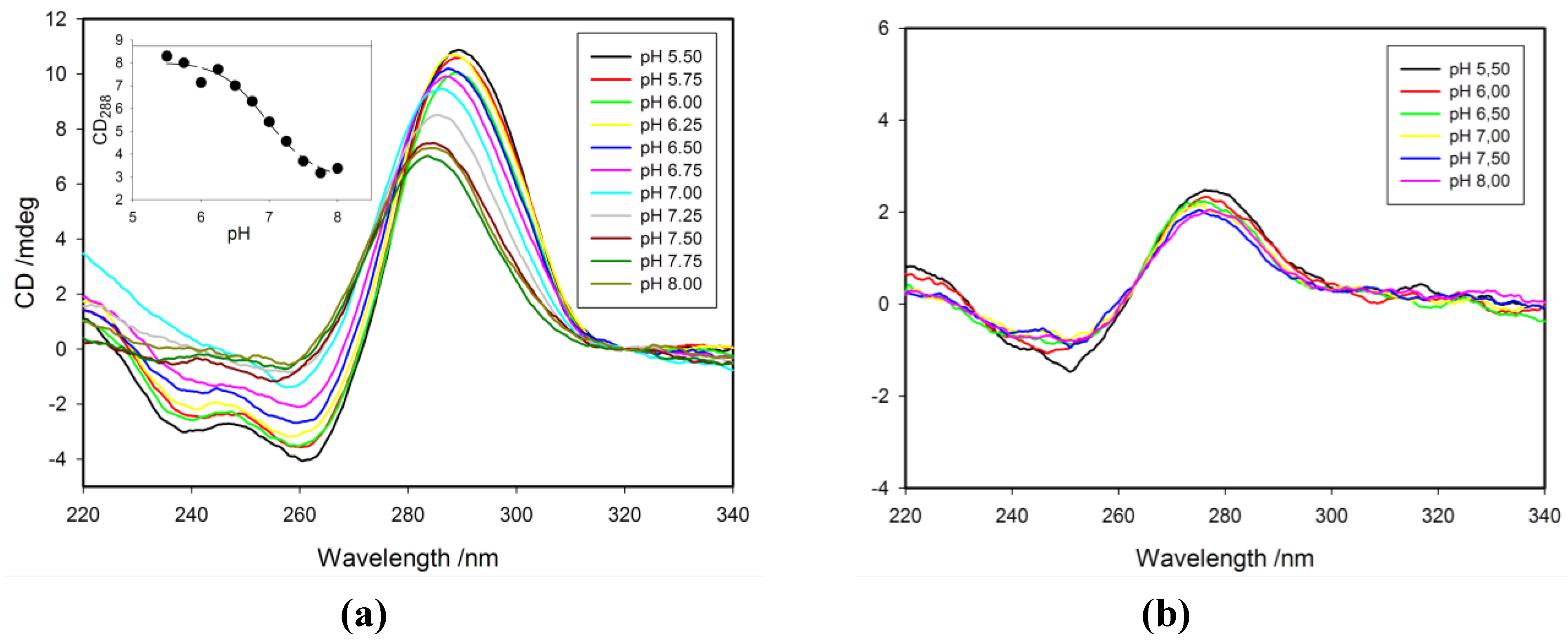
2.3. Effect of pH on CD Spectra
| pH 5.50 | pH 5.75 | pH 6.00 | pH 6.25 | pH 6.50 | pH 6.75 | pH 7.00 | pH 7.25 | pH 7.50 | pH 7.75 | pH 8.00 | pHT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RET20 | 63.4 ± 1.5 | 53.6 ± 1.3 | 48.5 ± 1.5 | 44.0 ± 1.4 | 36.1 ± 1.2 | 30.3 ± 1.1 | 21.5 ± 1.2 | 18.0 ± 0.8 | <15 | <15 | <15 | 7.1 ± 0.2 |
| 1tC | 60.3 ± 1.8 | 53.2 ± 1.5 | 50.8 ± 1.4 | 42.6 ± 1.1 | 36.7 ± 1.0 | 29.7 ± 0.8 | 21.6 ± 0.8 | 17.1 ± 0.7 | <15 | <15 | <15 | 6.9 ± 0.2 |
| ΔTm,R20-1tC | 3.1 | 0.4 | −2.3 | 1.4 | −0.6 | 0.6 | −0.1 | 0.9 | - | - | - | - |
| 3tC | 61.4 ± 1.5 | 57.5 ± 1.9 | 43.3 ± 1.3 | 40.1 ± 1.4 | 34.6 ± 1.5 | 20.6 ± 1.2 | 18.2 ± 0.7 | 15.4 ± 0.8 | <15 | <15 | <15 | 6.9 ± 0.2 |
| ΔTm,R20-3tC | 2.0 | −3.9 | 5.2 | 3.9 | 1.5 | 9.4 | 3.3 | 2.6 | - | - | - | - |
| 6tC | 59.1 ± 1.9 | 57.3 ± 1.7 | 47.0 ± 1.2 | 42.9 ± 1.1 | 36.1 ± 1.1 | 26.7 ± 1.4 | 21.3 ± 0.6 | 19.6 ± 0.7 | <15 | <15 | <15 | 7.1 ± 0.2 |
| ΔTm,R20-6tC | 4.3 | −3.7 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 3.6 | 0.2 | −1.6 | - | - | - | - |
2.4. Fluorescence Properties of tC Modified Probes

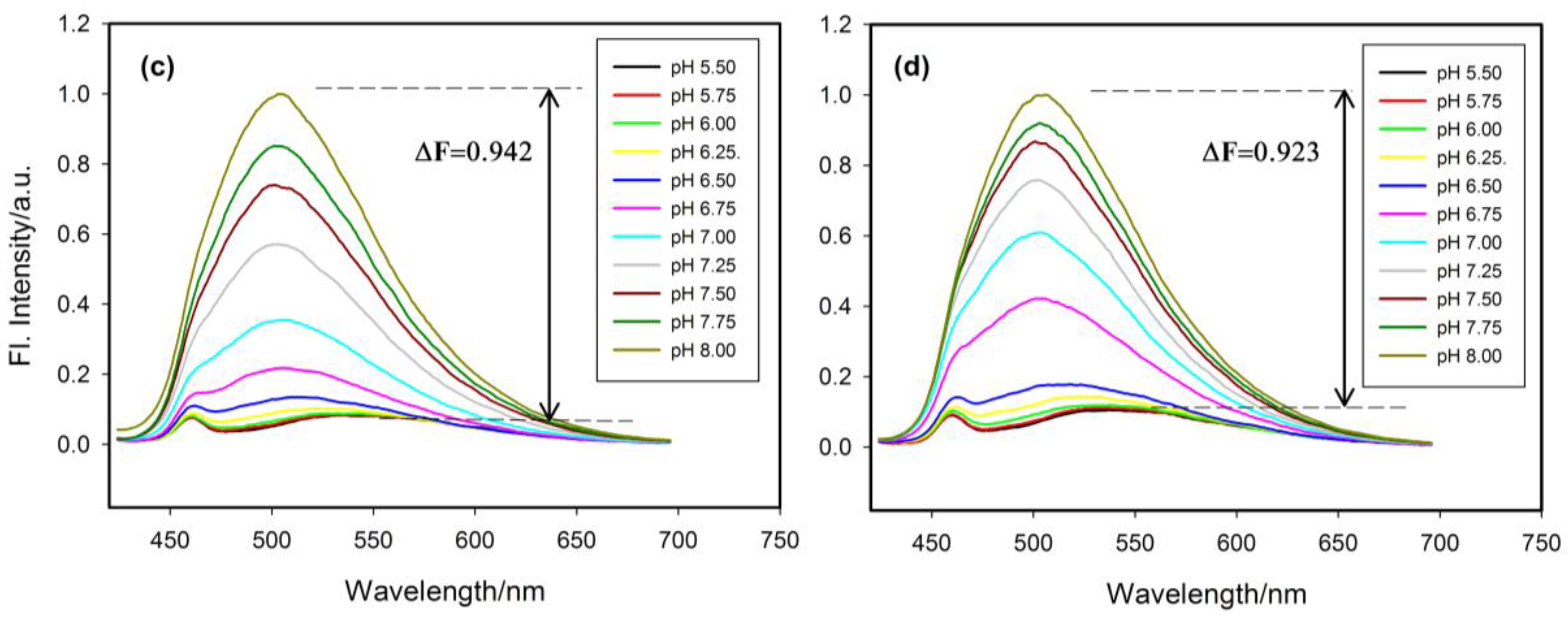


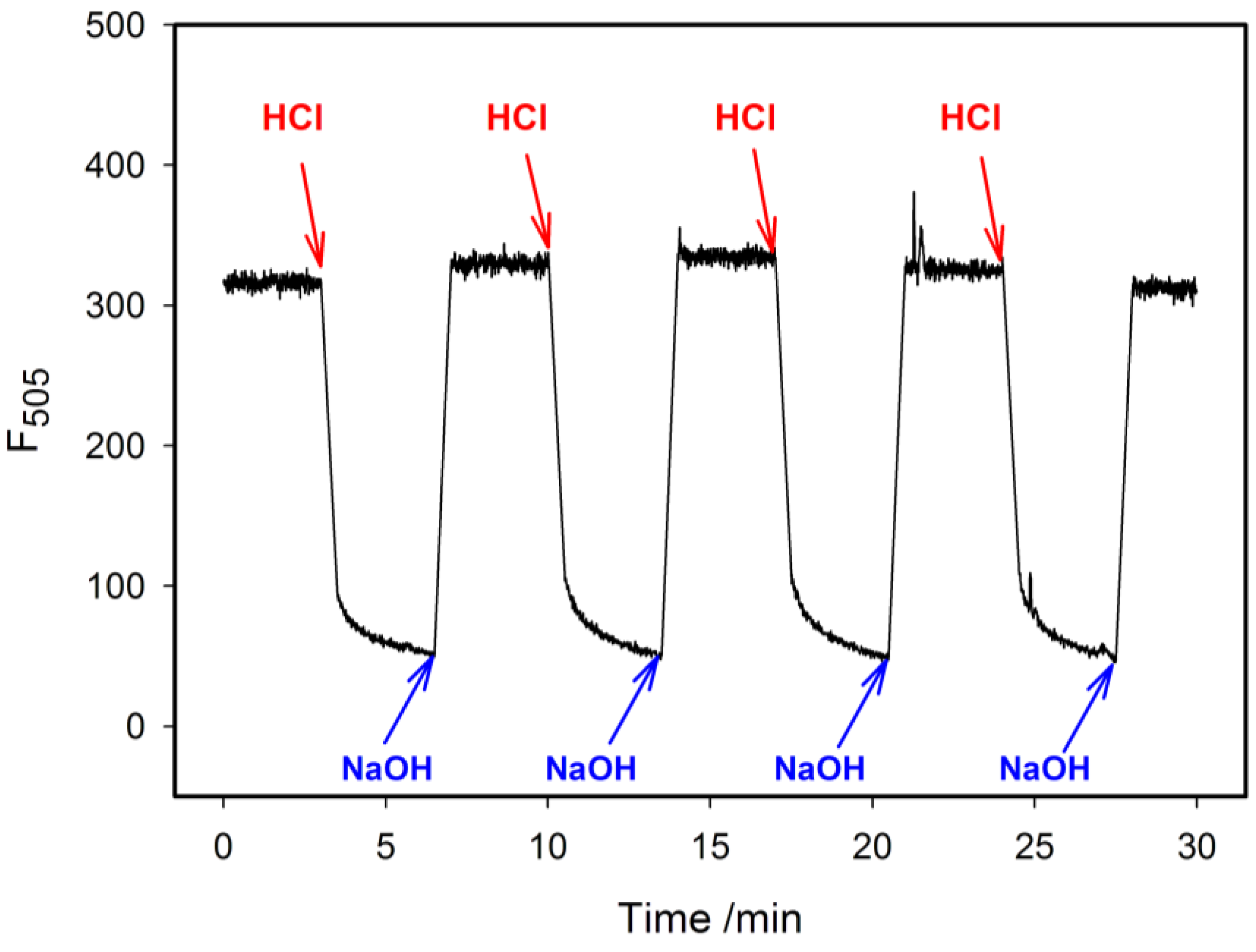
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Oligonucleotides
3.2. UV Melting Experiments
3.3. Circular Dichroism (CD)
3.4. Fluorescence Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, S.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Fan, C. Aptamer-based biosensors. Trends. Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltenburg, R.; Reinemann, C.; Strehlitz, B. SELEX-A (r)evolutionarymethod to generate high-affinity nucleic acid ligands. Biomol. Eng. 2007, 24, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, K.; Leroy, J.L.; Guéron, M. A tetrameric DNA structure with protonated cytosine-cytosine base pairs. Nature 1993, 363, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, J.L.; Gehring, K.; Kettani, A.; Gudron, M. Acid multimers of oligodeoxycytidine strands: Stoichiometry, base-pair characterization, and proton exchange properties. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 6019–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, J.L.; Gueron, M.; Mergny, J.L.; Helene, C. Intramolecular folding of a fragment of the cytosine-rich strand of telomeric DNA into an i-motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.L.; Lacroix, L.; Han, X.; Leroy, J.L.; Helene, C. Intramolecular folding of pyrimidine oligodeoxynucleotides into an i-DNA motif. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8887–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kintanar, A.; Henderson, E. Human telomeric C-strand tetraplexes. Nature Struct. Biol. 1994, 1, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsson, T.; Pribylova, M.; Vorlickova, M. A nuclease hypersensitive element in the human c-myc promoter adopts several distincti-tetraplex structures. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 278, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Sugiyama, H. Formation of the G-quadruplex and i-motif structures in retinoblastoma susceptibility genes (Rb). Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Pourpak, A.; Beetz-Rogers, K.; Gokhale, V.; Sun, D.; Hurley, L.H. Formation of pseudosymmetrical G-quadruplex and i-motif structures in the proximal promoter region of the RET oncogene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10220–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Gokhale, V.; Hurley, L.H.; Sun, D. Intramolecularly folded G-quadruplex and i-motif structures in the proximal promoter of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 4598–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendrick, S.; Akiyama, Y.; Hecht, S.M.; Hurley, L.H. The i-Motif in the bcl-2P1 promoter forms an unexpectedly stable structure with a unique 8:5:7 loop folding pattern. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17667–17676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volker, J.; Klump, H.H.; Breslauer, K.J. The energetics of i-DNA tetraplex structures formed intermolecularly by d(TC5) and intramolecularly by d[(C5T3)(3)C-5]. Biopolymers 2007, 86, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar-Jog, Y.P.; Dornshuld, E.V.; Brooks, T.A.; Tschumper, G.S.; Wadkins, R.M. Epigenetic modification, dehydration, and molecular crowding effects on the thermodynamics of i-Motif structure formation from C-Rich DNA. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.J.; Rytting, J.H.; Izattl, R.M. Thermodynamics of proton dissociation in dilute aqueous solution. VIII. pK, ΔH°, and ΔS° Values for proton ionization from several pyrimidines and Their nucleosides at 25 °C. Journal of Physical Chemistry 1967, 71, 2700–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.L.; Lacroix, L. Kinetics and thermodynamics of i-DNA formation: Phosphodiester versus modified oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 4797–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, S.; Eritja, R.; Avinó, A.; Jaumot, J.; Gargallo, R. Influence of pH, temperature and the cationic porphyrin TMPyP4 on the stability of the i-motif formed by the 5′-(C3TA2)4-3′ sequence of the human telomere. Int. J. Biol. Macromolec. 2011, 49, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, S.M.; Morgan, R.K.; Brooks, T.A.; Wadkins, R.M. Effect of interior loop length on the thermal stability and pKa of i-motif DNA. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, S.P.; Schwarz, C.; Hall, J.P.; Cardin, C.J.; Brazier, J.A. The importance of loop length on the stability of i-motif structures. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 5630–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wei, C.; Jia, G.; Wang, X.; Feng, Z.; Li, C. Formation of i-motif structure at neutral and slightly alkaline pH. Mol. BioSyst. 2010, 6, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Waltman, P.; Le, V.H.; Lewis, E.A. The effect of molecular crowding on the stability of human c-MYC promoter sequence i-motif at neutral pH. Molecules 2013, 18, 12751–12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Majima, T. Reversible conformational switching of i-motif DNA studied by fluorescence spectroscopy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2013, 89, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Wu, X.; Yeow, E.K.L.; Shao, F. A single thiazole orange molecule forms an exciplex in a DNA i-motif. Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 6402–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proudnikov, D.; Mirzabekov, A. Chemical methods of DNA and RNA fluorescent labeling. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 4535–4532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Juskowiak, B. Nucleic acid-based fluorescent probes and their analytical potential. Anal Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 3157–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembska, A.; Rzepecka, P.; Juskowiak, B. Spectroscopic characterization of i-motif forming c-myc derived sequences double-labeled with pyrene. J. Fluoresc. 2013, 23, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katilius, E.; Katiliene, Z.; Woodbury, N.W. Signaling aptamers created using fluorescent nucleotide analogues. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6484–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmsson, L.M.; Sandim, P.; Holmen, A.; Albinsson, B.; Lincoln, P.; Nielsen, P.E.; Norden, B. Photophysical characterization of fluorescent DNA base analogue, tC. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 9094–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmsson, L.M.; Holmen, A.; Lincoln, P.; Nielsen, P.E.; Norden, B. A highly fluorescent DNA base analogue that forms Watson-Crick base pairs with guanine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2434–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandin, P.; Wilhelmsson, L.M.; Lincoln, P.; Powers, V.E.C.; Brown, T.; Albinsson, B. Fluorescent properties of DNA base analogue tC upon incorporation into DNA—negligible influence of neighbouring bases on fluorescence quantum yield. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5019–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preus, S.; Kilsa, K.; Wilhelmsson, L.M.; Albinsson, B. Photophysical and structural properties of the fluorescent nucleobase analogues of the tricyclic cytosine (tC) family. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 8881–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preus, S.; Borjesson, K.; Kilsa, K.; Albinsson, B.; Wilhelmsson, L.M. Characterization of nucleobase analogue FRET acceptor tCnitro. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engman, K.C.; Sandin, P.; Osborne, S.; Brown, T.; Billeter, M.; Lincoln, P.; Norden, B.; Albinsson, B.; Wilhelmsson, L.M. DNA adopts normal B-form upon incorporation of highly fluorescent DNA base analogue tC: NMR structure and UV-Vis spectroscopy characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 5087–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, S.M.; Lyons, D.F.; Wingate, S.E.; Wright, R.T.; Correia, J.J.; Jameson, D.M.; Wadkins, R.M. Folding and hydrodynamics of a DNA i-Motif from the c-MYC promoter determined by fluorescent cytidine analogs. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzini, G.; Yathindra, N.; Xodo, L.E. Evidence for intramolecularly folded i-DNA structures in biologically relevant CC-repeat sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4634–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardarsson, H.; Kale, A.S.; Sigurdsson, S. Th. Structure-function relationships of phenoxazine nucleosides for identification of mismatches in duplex DNA by fluorescence spectroscopy. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, M.; Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; Joedecke, C.-C.; Jin, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D. Study of pH-Induced Folding and Unfolding Kinetics of the DNA i-Motif by Stopped-Flow Circular Dichroism. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17743–17748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds not available from the authors, but can be synthesized by Future Synthesis, Poznan, Poland.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bielecka, P.; Juskowiak, B. Fluorescent Sensor for PH Monitoring Based on an i-Motif- – Switching Aptamer Containing a Tricyclic Cytosine Analogue (tC). Molecules 2015, 20, 18511-18525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201018511
Bielecka P, Juskowiak B. Fluorescent Sensor for PH Monitoring Based on an i-Motif- – Switching Aptamer Containing a Tricyclic Cytosine Analogue (tC). Molecules. 2015; 20(10):18511-18525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201018511
Chicago/Turabian StyleBielecka, Patrycja, and Bernard Juskowiak. 2015. "Fluorescent Sensor for PH Monitoring Based on an i-Motif- – Switching Aptamer Containing a Tricyclic Cytosine Analogue (tC)" Molecules 20, no. 10: 18511-18525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201018511
APA StyleBielecka, P., & Juskowiak, B. (2015). Fluorescent Sensor for PH Monitoring Based on an i-Motif- – Switching Aptamer Containing a Tricyclic Cytosine Analogue (tC). Molecules, 20(10), 18511-18525. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201018511