Design, Synthesis, Characterization of Novel Ruthenium(II) Catalysts: Highly Efficient and Selective Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde to (E)-3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-ol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthetic Investigation of Ruthenium(II) Complex 1 and Xerogel X1
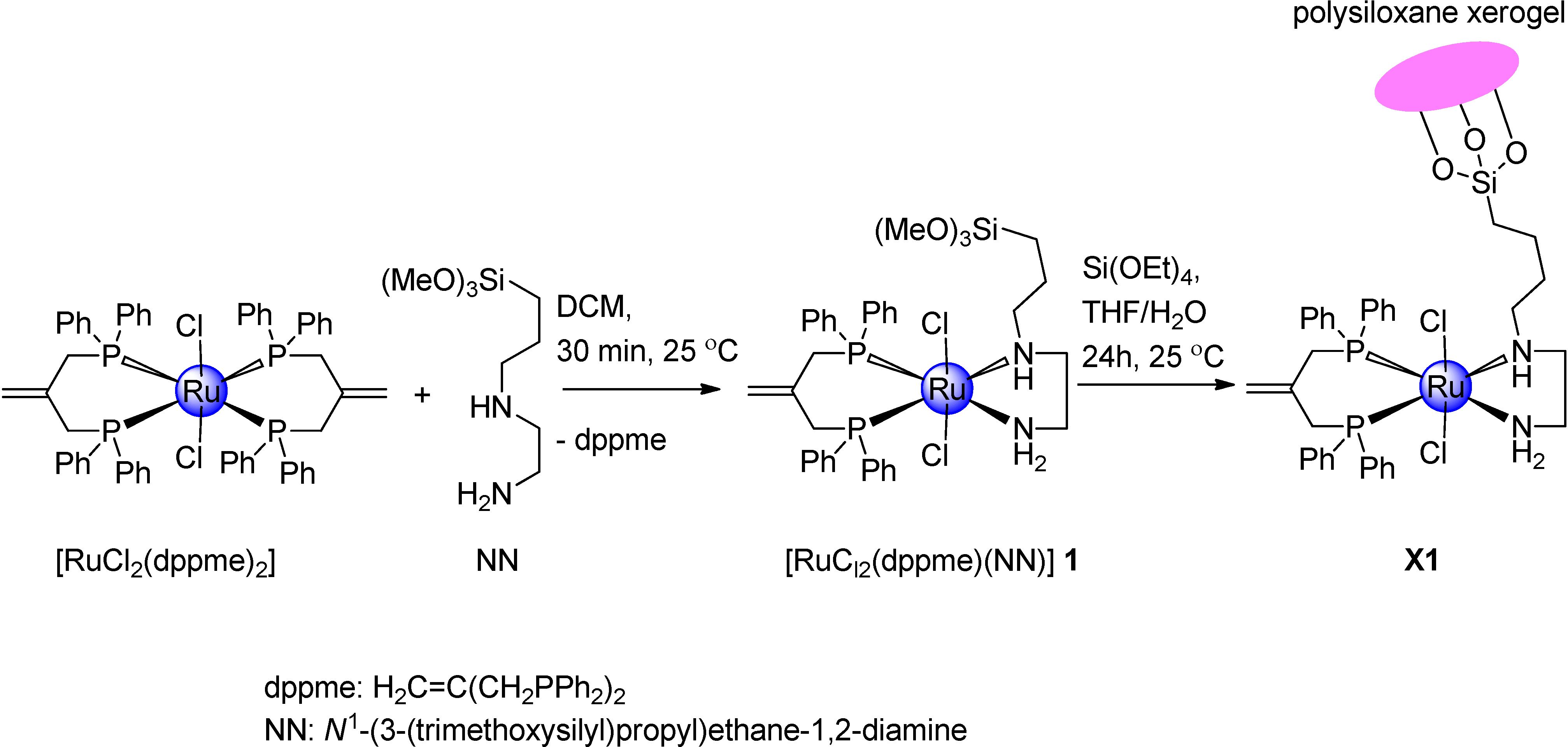
2.2. Spectral Data
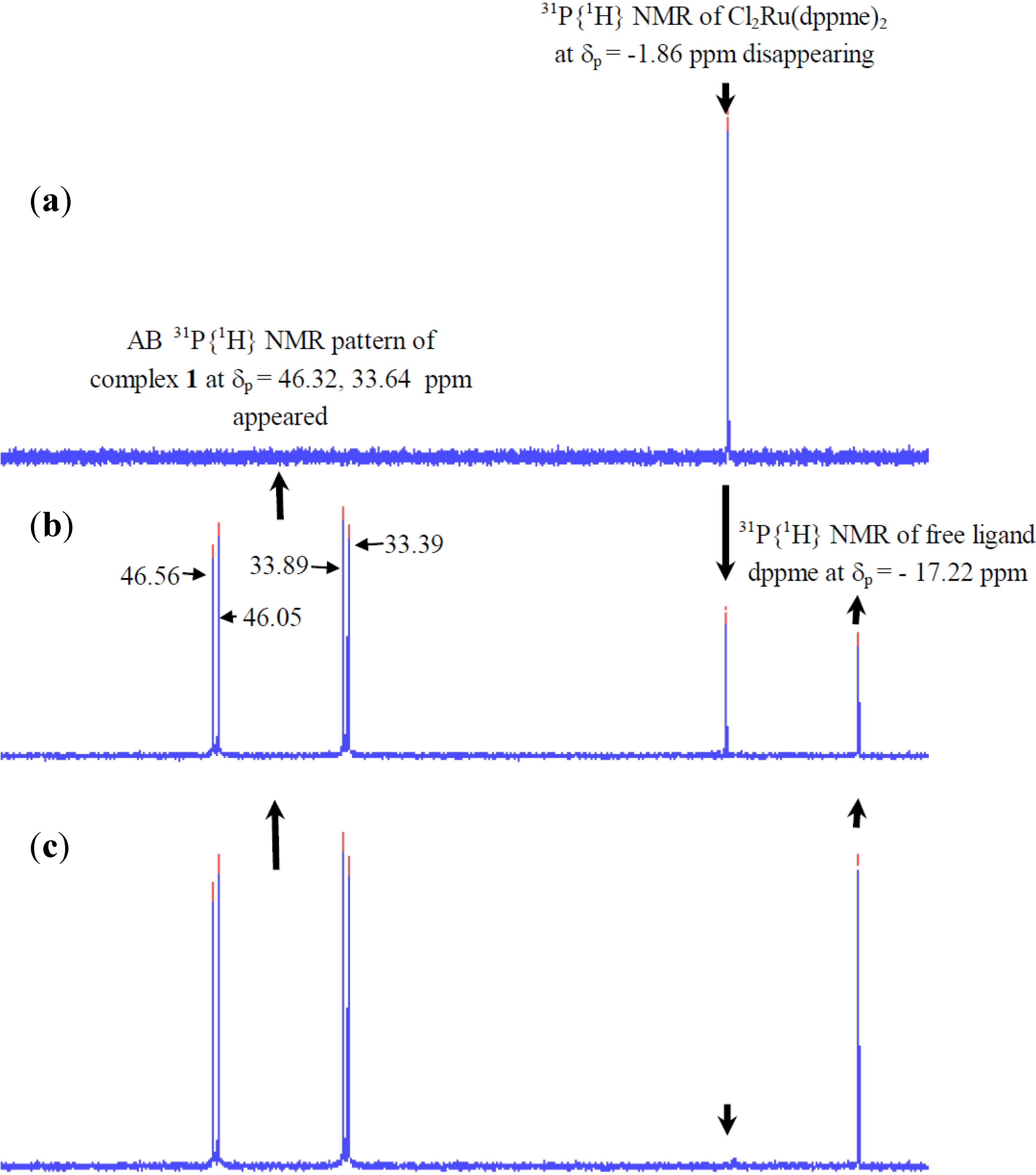
2.2.1. 31P-NMR Spectrum of Complex 1
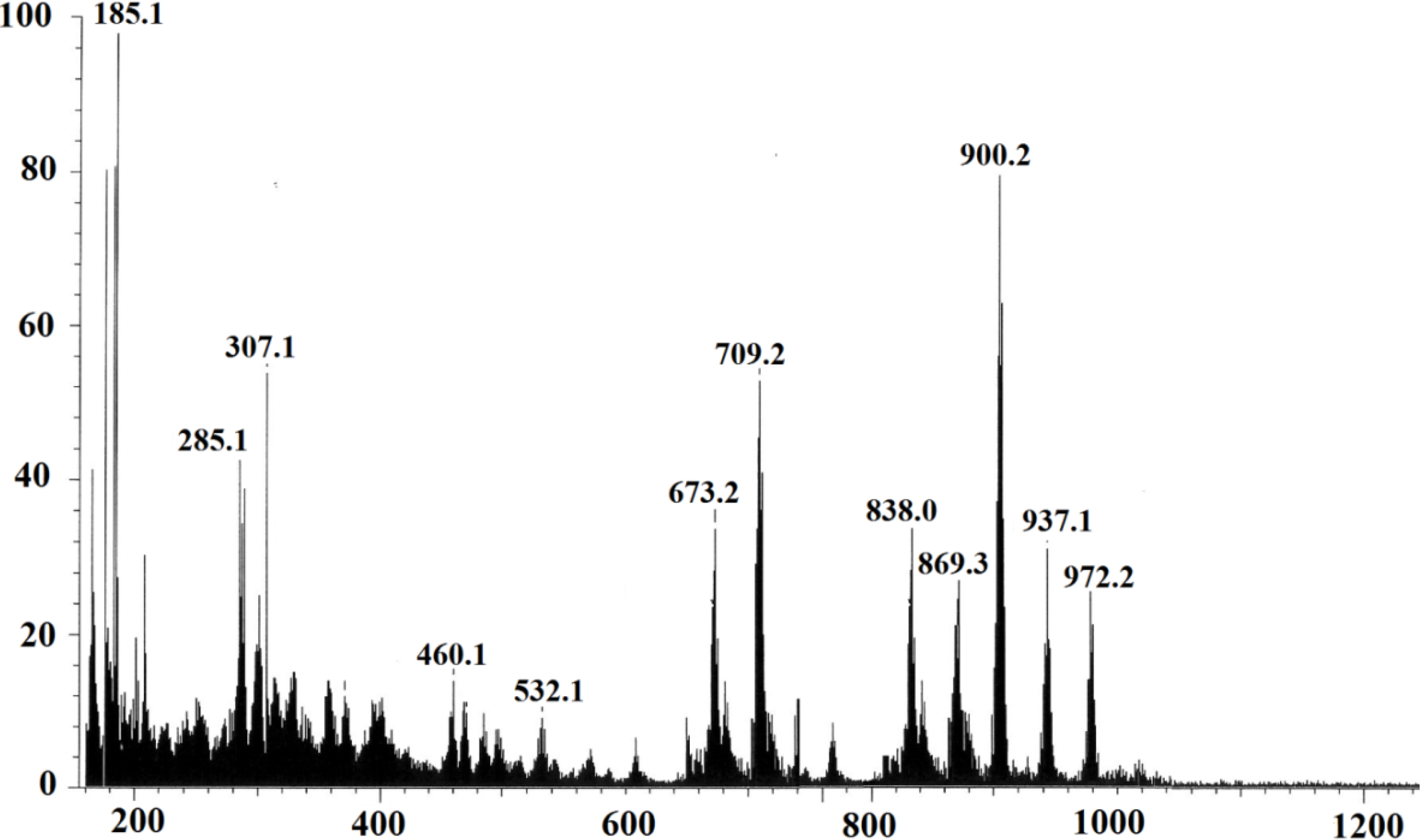
2.2.2. Elemental Analysis and FAB-Mass Spectrum of Complex 1
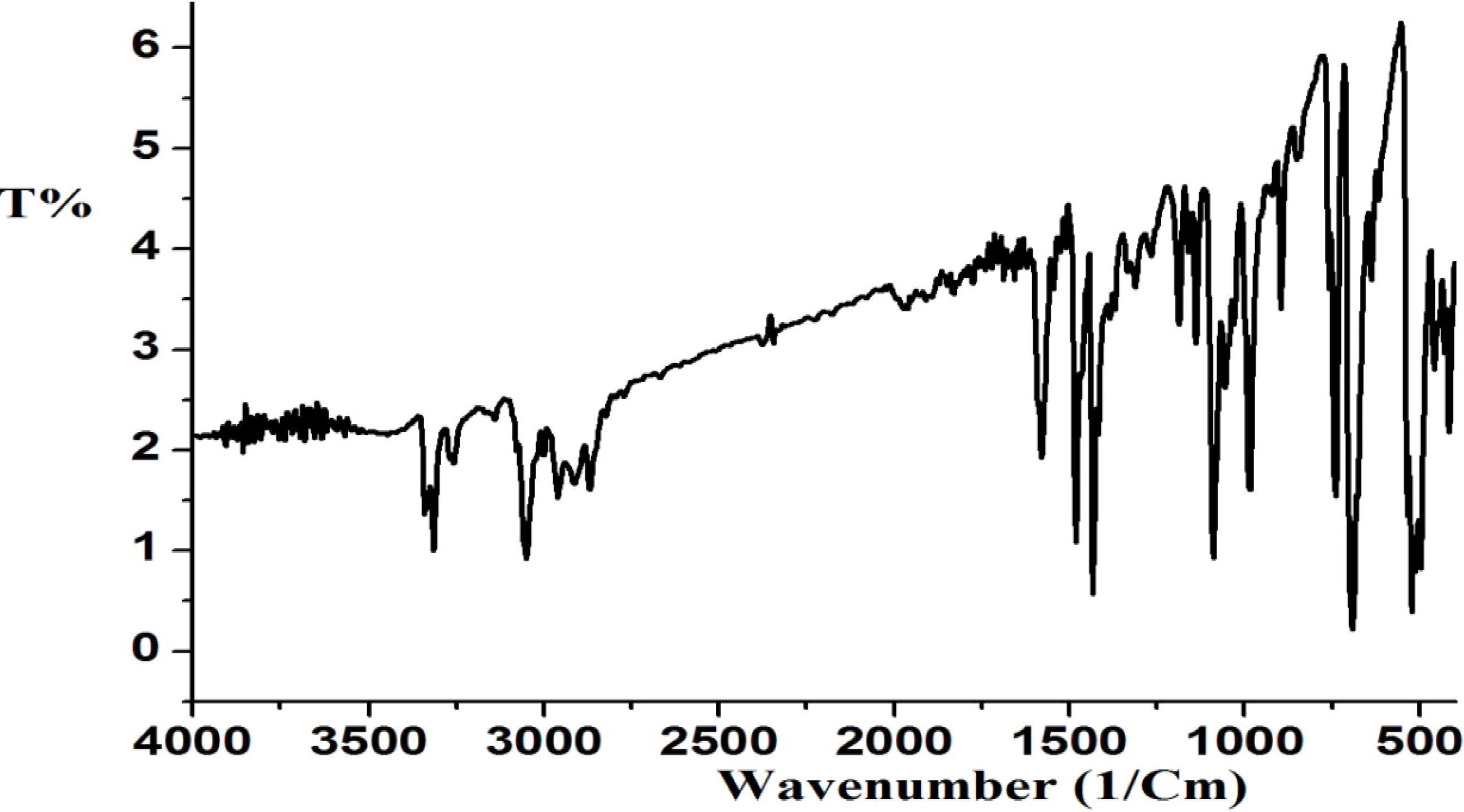
2.2.3. IR Spectrum of Complex 1
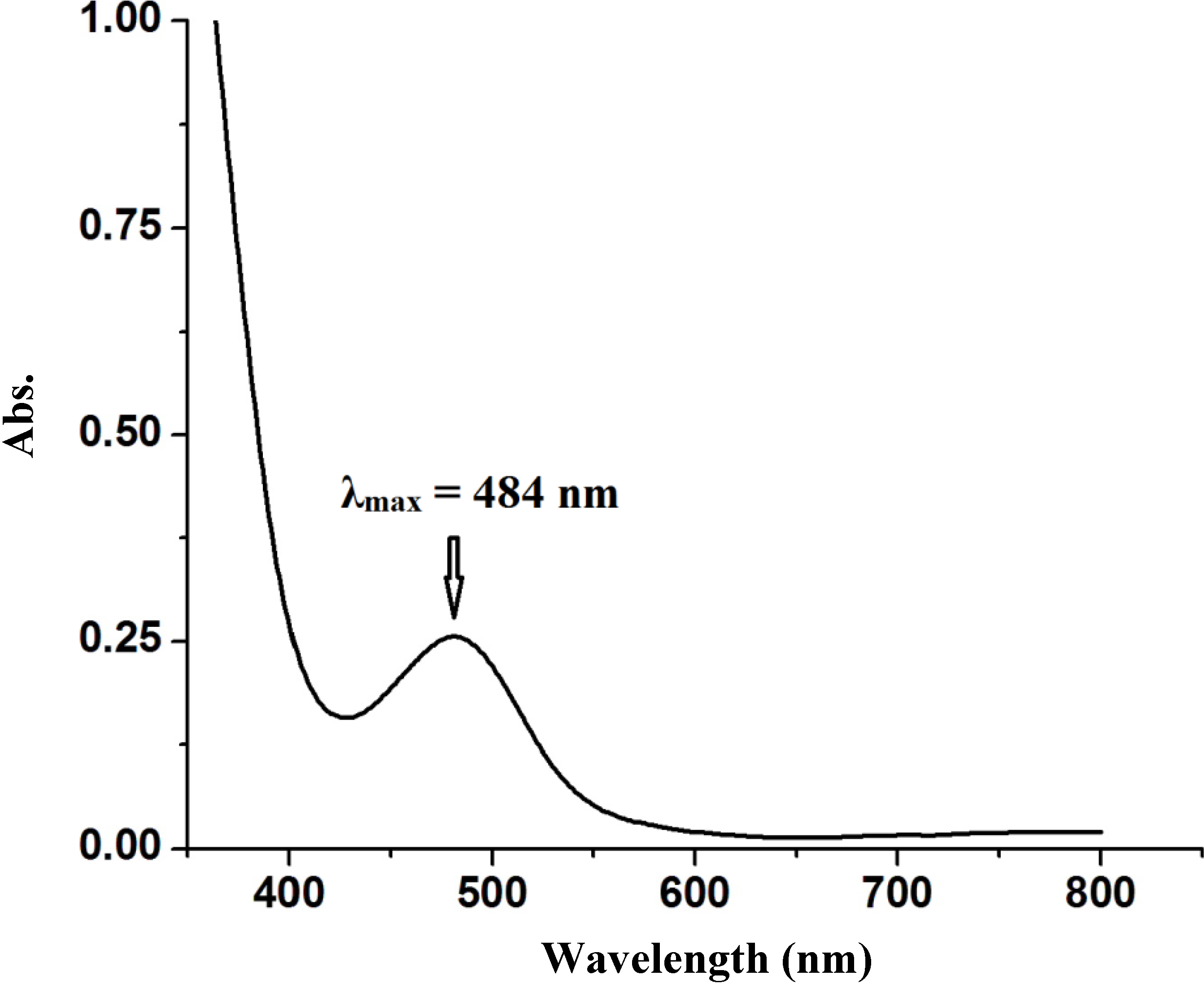
2.2.4. Electronic Absorption Spectral Study
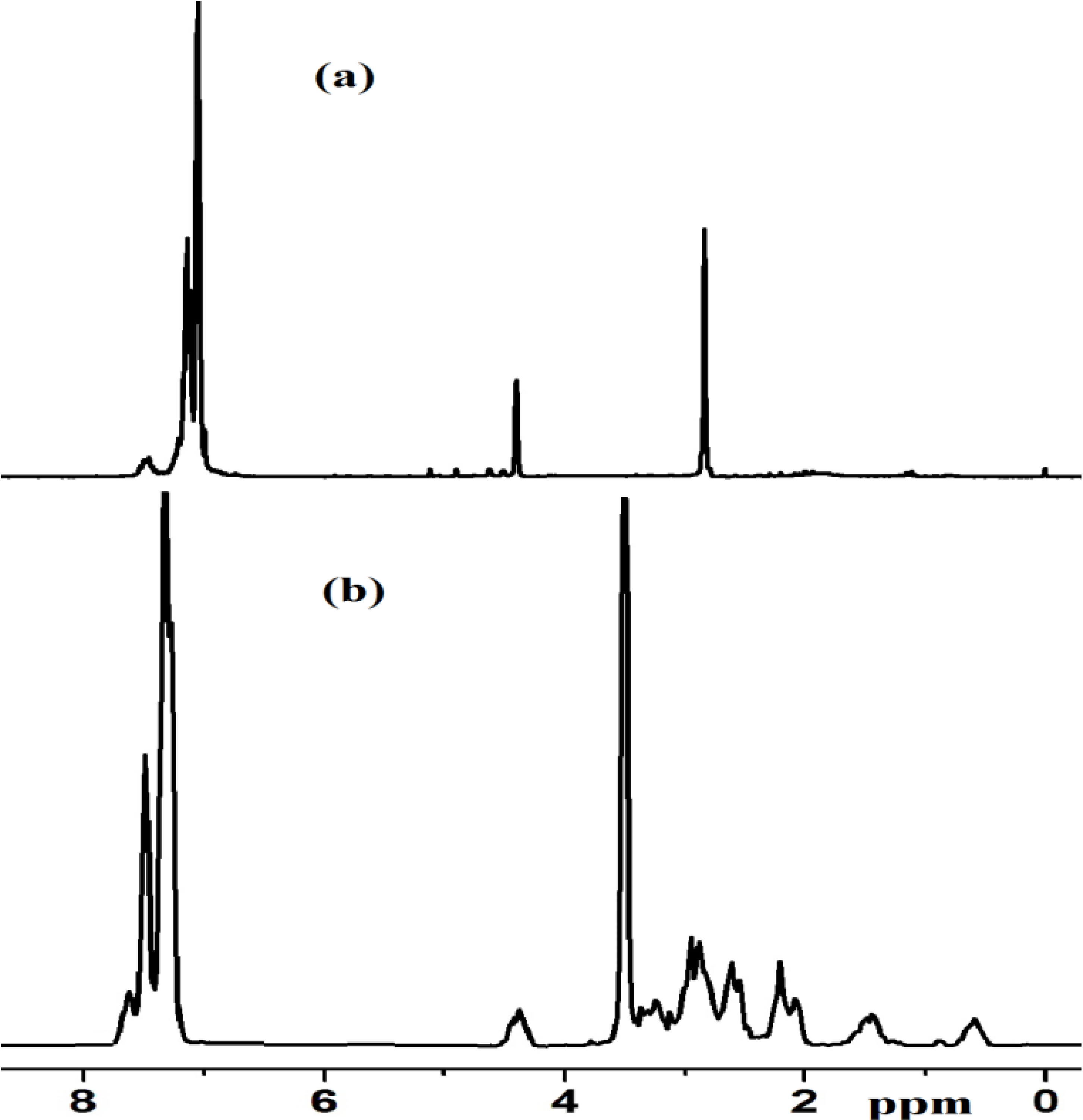
2.2.5. NMR Spectra of Complex 1 and Xerogel X1
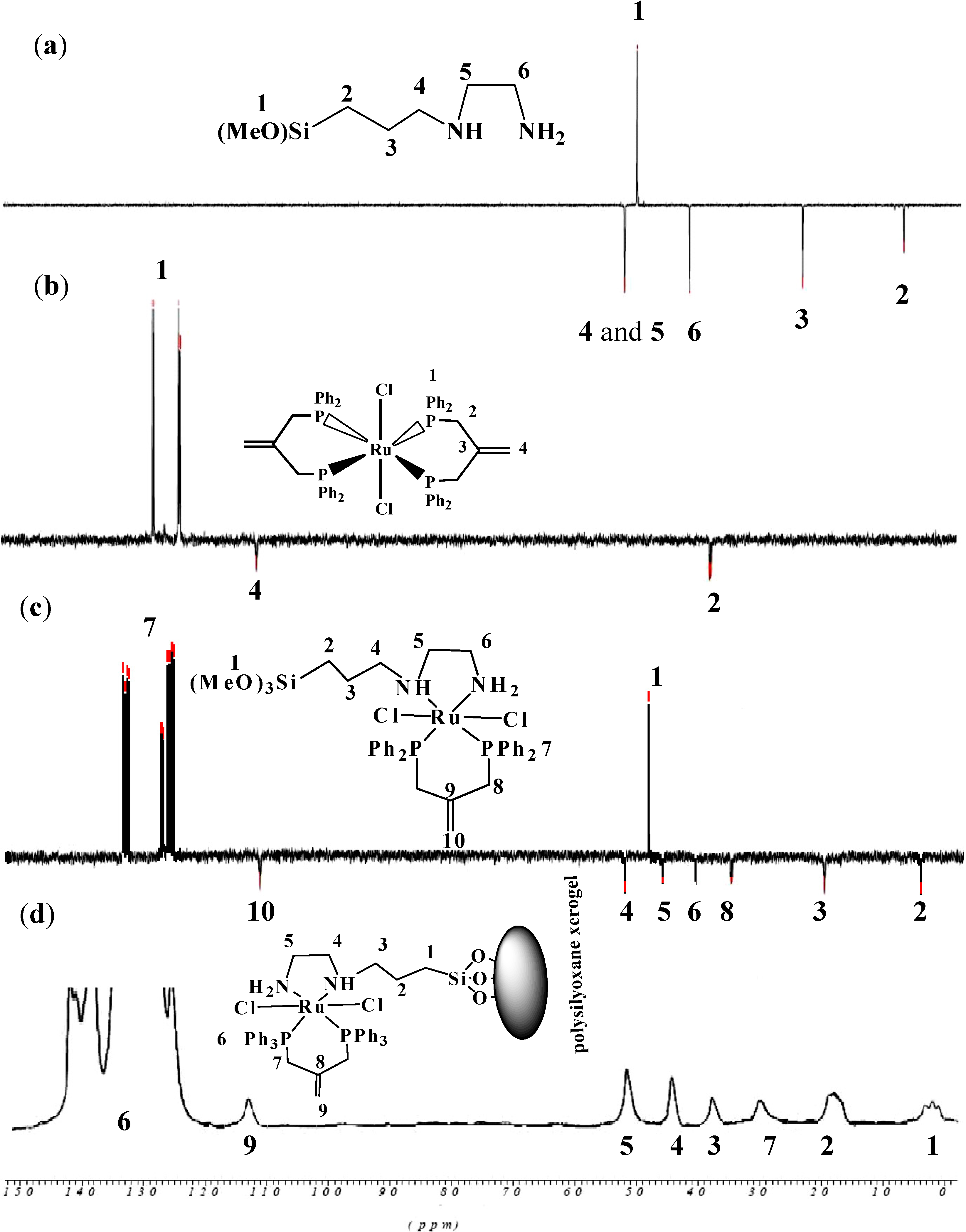
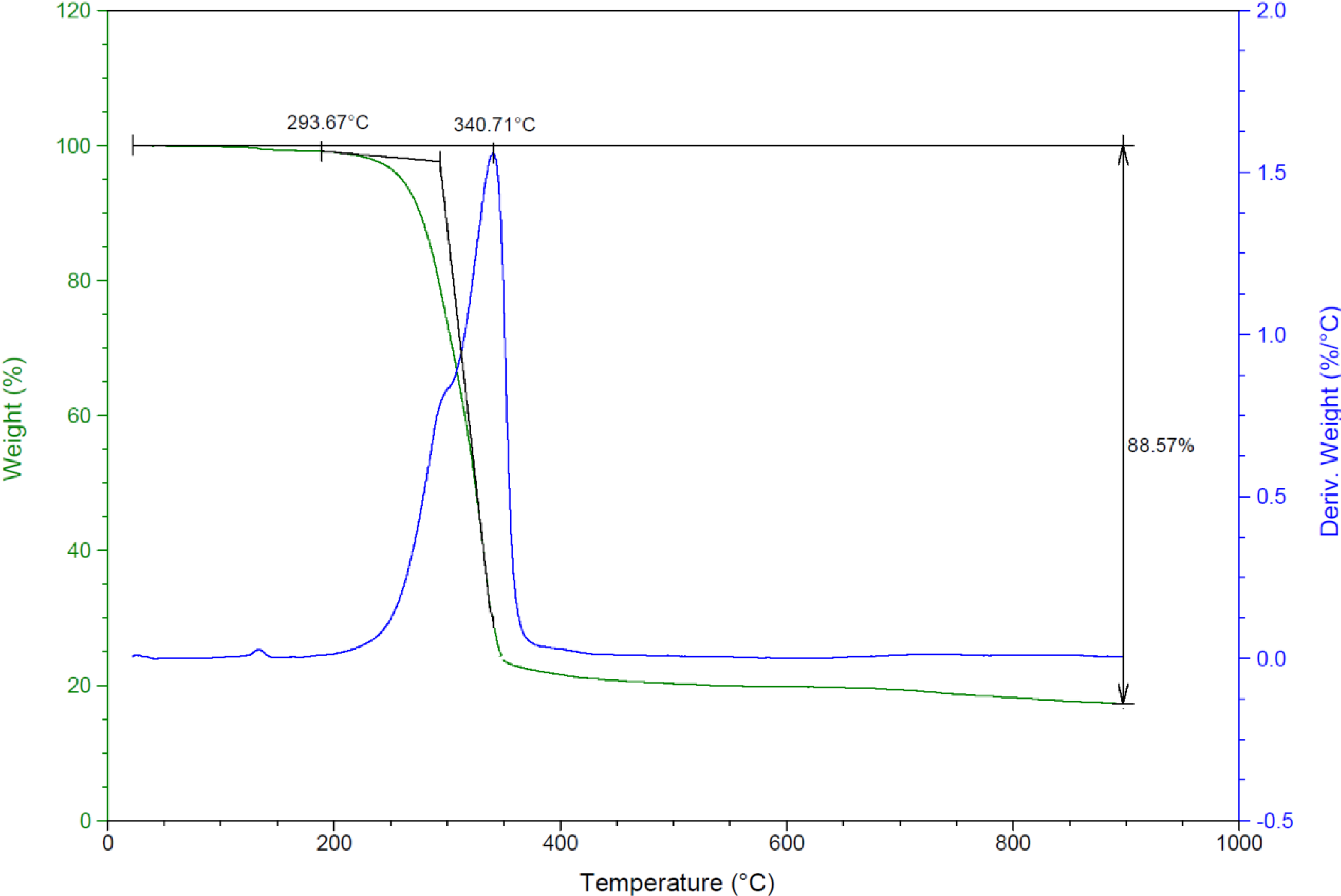
2.2.6. Thermal Studies
2.2.7. Electrochemistry
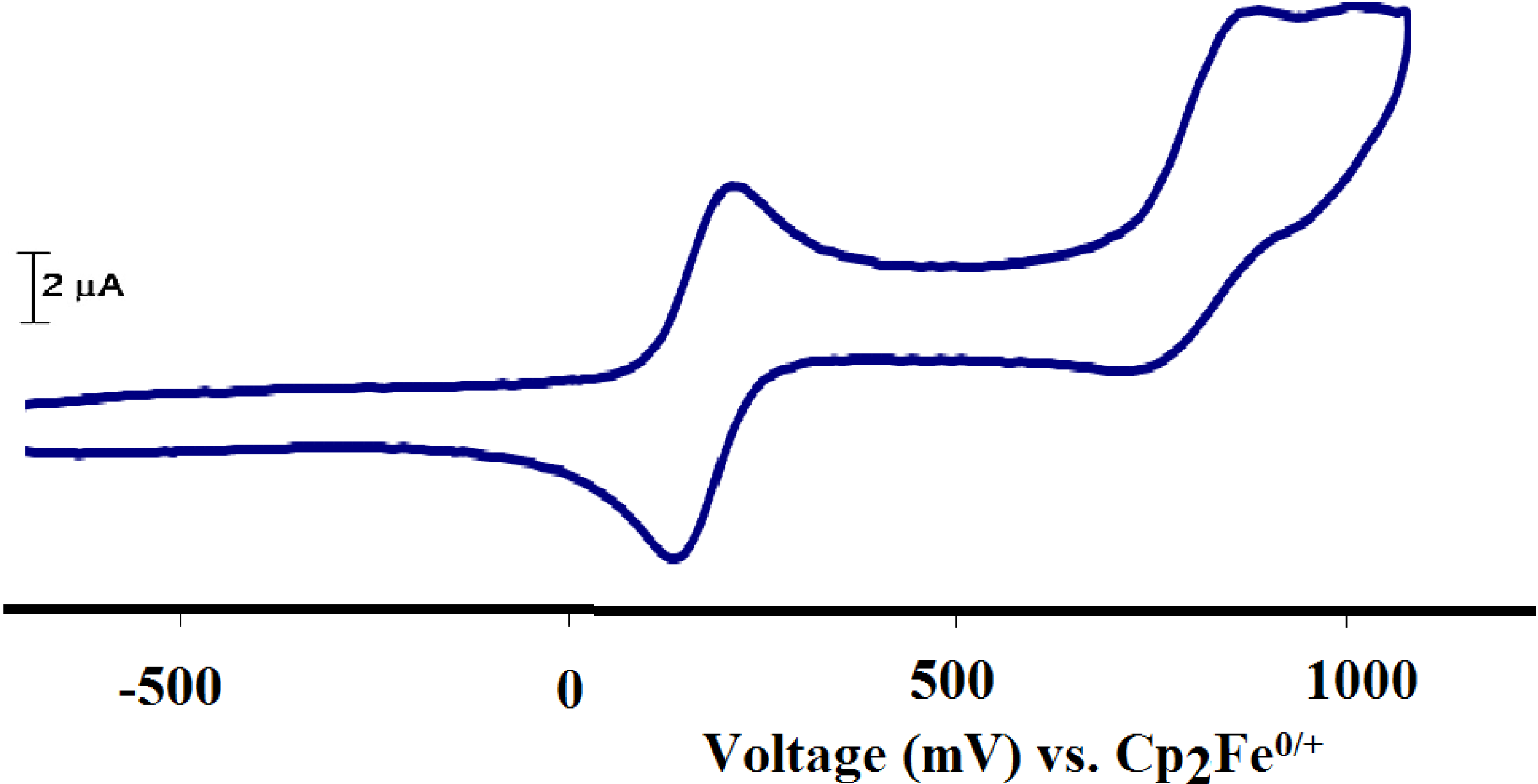
2.3. Complexes 1 and X1 as Catalysts in the Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde
| Trial | Catalyst a | Co-catalyst | Conversion (%) a | Selectivity (%) b | TOF c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | t-BuOK | >99 | >99 | 1380 |
| 2 | 1' | t-BuOK | >99 | >99 | 1160 |
| 3 | 1 | KOH | >99 | >99 | 1460 |
| 4 | 1' | KOH | >99 | >99 | 1210 |
| 5 | 1, 1', X1', X1' | K2CO3 | 0 d | - | - |
| 6 | X1 | t-BuOK | 95 d | 93 | |
| 7 | X1 | t-BuOK | 90 d | 90 | |
| 8 | X1 | KOH | 94 d | 92 | |
| 9 | X1 | KOH | 88 d | 92 |
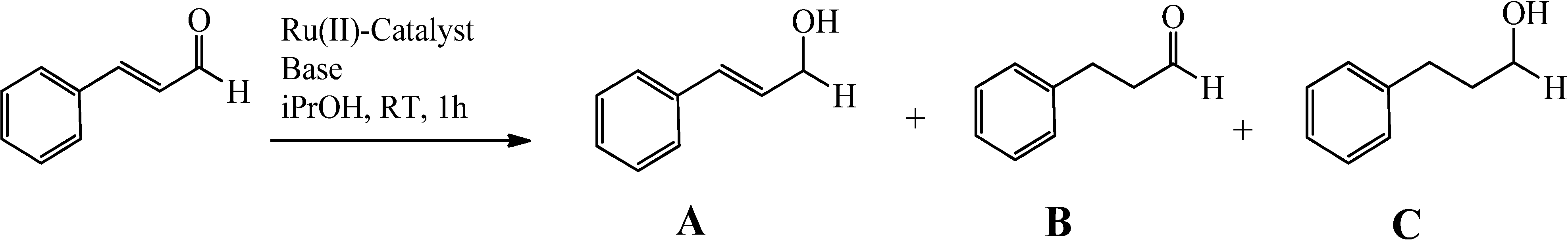
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Instrumentation
3.2. Synthesis of Complex 1
3.3. General Procedure for Sol–gel Processing of Xerogel X1
3.4. General Procedure for the Catalytic Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ojima, I. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 420–545. [Google Scholar]
- Noyori, R. Asymmetric Catalysis in Organic Synthesis; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 16–47. [Google Scholar]
- Noyori, R. Asymmetric Catalysis: Science and Opportunities (Nobel Lecture). Adv. Synth. Catal. 2003, 345, 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma, T.; Koizumi, M.; Muniz, K.; Hilt, G.; Kabuta, C.; Noyori, R. Trans-RuH(η1-BH4)(binap)(1,2-diamine): A Catalyst for asymmetric hydrogenation of simple ketones under base-Free conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6508–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuma, T.; Takeno, H.; Honda, Y.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric hydrogenation of ketones with polymer-bound BINAP diamine ruthenium catalysts. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2001, 343, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warad, I.; Siddiqui, M.; Al-Resayes, S.; Al-Warthan, A.; Mahfouz, R. Synthesis, characterization, crystal structure and chemical behavior of [1,1-bis(diphenylphosphinomethyl)ethene]ruthenium-(II) complex toward primary alkylamine addition. Transit. Met. Chem. 2009, 34, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warad, I.; Al-Noaimi, M.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; Awwadi, F.; Hammouti, B.; Hadda, T.B. Trans/cisisomerization of [RuCl2{H2C=C(CH2PPh2)2)}(diamine)] complexes: Synthesis, spectral, crystal structure and DFT calculations and catalytic activity in the hydrogenation of a,b-unsaturated ketones. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2014, 117, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Noaimi, M.; Nafady, A.; Warad, I.; Alshwafy, R.; Husein, A.; Talib, W.; Hadda, T.B. Heterotrimetallic Ru(II)/Pd(II)/Ru(II) complexes: Synthesis, crystalstructure, spectral Characterization, DFT calculation and antimicrobial study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2014, 122, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warad, I.; Al-Noaimi, M.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; AlDamen, M.; Hammouti, B.; Hadda, T.B. New catalysts for the chemoselective reduction of a,b-unsaturated ketones: Synthesis, spectral, structural and DFT characterizations of mixed ruthenium(II) complexes containing 2-ethene-1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane and diamine ligands. Polyhedron 2013, 63, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Noaimi, M.; Warad, I.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; Awwadi, F.; Haddad, S.; Hadda, T.B. Synthesis, structure, spectroscopic properties, electrochemistry, and DFT correlative studies of trans-[Ru(P-P)2Cl2] complexes. Polyhedron 2013, 62, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Haack, K.J.; Matsumura, K.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Kinetic resolution of racemis secondary alcohols by Ru(II)-catalyzed hydrogen transfer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, K.J.; Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. The catalyst precursor, catalyst, and intermediate in the Ru-II-promoted asymmetric hydrogen transfer between alcohols and ketones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdur-Rashid, K.; Faatz, M.; Lough, A.J.; Morris, H.R. Catalytic Cycle for the asymmetric hydrogenation of prochiral ketones to chiral alcohols: Direct hydride and proton transfer from chiral catalysts trans-Ru(H)2(diphosphine)(diamine) to ketones and direct Addition of Dihydrogen to the Resulting Hydridoamido Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7473–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, E.; Mayer, H.A.; Warad, I.; Eichele, K. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic application of a new family of diamine(diphosphine)ruthenium(II) complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2003, 665, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, E.; Lu, Z.L.; Mayer, A.H.; Speiser, B.; Tittel, C.; Warad, I. Cyclic voltammetric redox screening of homogeneous ruthenium(II) hydrogenation catalysts. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, E.; Warad, I.; Eichele, K.; Mayer, H.A. Synthesis and structures of an array of diamine(ether-phosphine)ruthenium(II) complexes and their application in the catalytic hydrogenation of trans-4-phenyl-3-butene-2-one. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2003, 350, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.L.; Eichele, K.; Warad, I.; Mayer, H.A.; Lindner, E.; Jiang, Z.; Schurig, V. Bis(methoxyethyldimethylphosphine)ruthenium(II) complexes as transfer hydrogenation catalysts. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2003, 629, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warad, I.; Lindner, E.; Eichele, K.; Mayer, A.H. Cationic diamine(ether–phosphine)ruthenium(II) complexes as precursors for the hydrogenation of trans-4-phenyl-3-butene-2-one. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2004, 357, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warad, I. Synthesis and crystal structure of cis-dichloro-1,2-ethylenediamine-bis[1,4-(diphenylphosphino)butane]ruthenium(II) dichloromethane disolvate, RuCl2(C2H8N2) (C28H28P2)-2CH2Cl2. Z. Kristallogr. 2007, 222, 415–417. [Google Scholar]
- Jakob, A.; Ecorchard, P.; Linseis, M.; Winter, R. Synthesis, solid state structure and spectro-electrochemistry of ferrocene-ethynyl phosphine and phosphine oxide transition metal complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2010, 694, 655–666. [Google Scholar]
- Lindner, E.; Ghanem, A.; Warad, I.; Eichele, K.; Mayer, H.A.; Schurig, V. Asymmetric hydrogenation of an unsaturated ketone by diamine(ether–phosphine)ruthenium(II) complexes and lipase-catalyzed kinetic resolution: A consecutive approach. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2003, 14, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warad, I. Supported and nons supported ruthenium(II)/phosphine/[3-(2-aminoethyl)-aminopropyl]trimethoxysilane complexes and their activities in the chemoselective hydrogenation of trans-4-Phenyl-3-butene-2-al. Molecules 2010, 15, 4652–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warad, I.; Al-Othman, Z.; Al-Resayes, S.; Al-Deyab, S.; Kenawy, E. Synthesis and characterization of novel inorganic-organic hybrid Ru(II) complexes and their application in selective hydrogenation. Molecules 2010, 15, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warad, I.; Al-Resayes, S.; Al-Othman, Z.; Al-Deyab, S.; Kenawy, E. Synthesis and spectrosopic identification of hybrid 3-(triethoxysilyl)propylamine phosphine ruthenium(II) complexes. Molecules 2010, 15, 3618–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, E.; Al-Gharabli, S.; Warad, I.; Mayer, H.A.; Steinbrecher, S.; Plies, E.; Seiler, M.; Bertagnolli, H. Diaminediphosphineruthenium(II) interphase catalysts for the hydrogenation of α,ß-unsaturated ketones. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2003, 629, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.L.; Eichele, K.; Warad, I.; Mayer, H.A.; Lindner, E.; Jiang, Z.; Schurig, V. Bis(methoxyethyldimethylphosphine)ruthenium(II) complexes as transfer hydrogenation catalysts. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2003, 629, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tfouni, E.; Doro, F.; Gomes, A.; Silva, R.; Metzker, G.; Grac, P.; Benini, Z.; Franco, D. Immobilized ruthenium complexes and aspects of their reactivity. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraczynska, D.; Serwicka, E.M.; Drelinkiewicz, A.; Olejniczak, Z. Ruthenium(II) phosphine/mesoporous silica catalysts: The impact of active phase loading and active site density on catalytic activity in hydrogenation of phenylacetylene. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 371, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, E.; Salesch, T.; Brugger, S.; Steinbrecher, S.; Plies, E.; Seiler, M.; Bertagnolli, H.; Mayer, A.M. Accessibility studies of sol-gel processed phosphane-substituted iridium(I) complexes in the interphase. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 2002, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayah, R.; Flochc, M.; Framery, E.; Dufaud, V. Immobilization of chiral cationic diphosphine rhodium complexes in nanopores of mesoporous silica and application in asymmetric hydrogenation. J. Mol. Cat. A-Chem. 2010, 315, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.L.; Lindner, E.; Mayer, H.A. Applications of sol-gel-processed interphase catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3543–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.T.; Wang, W.W.; Wang, Q.R.; Tao, Q.R. Asymmetric hydrogenation of aromatic ketones with MeO-PEG supported BIOHEP/DPEN ruthenium catalysts. J. Mol. Cat. A-Chem. 2007, 270, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergbreiter, D. Using soluble polymers to recover catalysts and ligands. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3345–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Lee, S. Supported chiral catalysts on inorganic materials. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3495–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from authors.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Darwish, H.W.; Barakat, A.; Nafady, A.; Suleiman, M.; Al-Noaimi, M.; Hammouti, B.; Radi, S.; Hadda, T.B.; Abu-Obaid, A.; Mubarak, M.S.; et al. Design, Synthesis, Characterization of Novel Ruthenium(II) Catalysts: Highly Efficient and Selective Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde to (E)-3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-ol. Molecules 2014, 19, 5965-5980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19055965
Darwish HW, Barakat A, Nafady A, Suleiman M, Al-Noaimi M, Hammouti B, Radi S, Hadda TB, Abu-Obaid A, Mubarak MS, et al. Design, Synthesis, Characterization of Novel Ruthenium(II) Catalysts: Highly Efficient and Selective Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde to (E)-3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-ol. Molecules. 2014; 19(5):5965-5980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19055965
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarwish, Hany W., Assem Barakat, Ayman Nafady, Mohammed Suleiman, Mousa Al-Noaimi, Belkheir Hammouti, Smaail Radi, Taibi Ben Hadda, Ahmad Abu-Obaid, Mohammad S. Mubarak, and et al. 2014. "Design, Synthesis, Characterization of Novel Ruthenium(II) Catalysts: Highly Efficient and Selective Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde to (E)-3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-ol" Molecules 19, no. 5: 5965-5980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19055965
APA StyleDarwish, H. W., Barakat, A., Nafady, A., Suleiman, M., Al-Noaimi, M., Hammouti, B., Radi, S., Hadda, T. B., Abu-Obaid, A., Mubarak, M. S., & Warad, I. (2014). Design, Synthesis, Characterization of Novel Ruthenium(II) Catalysts: Highly Efficient and Selective Hydrogenation of Cinnamaldehyde to (E)-3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-ol. Molecules, 19(5), 5965-5980. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19055965










