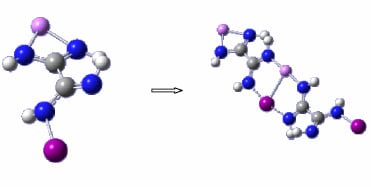
Concerted Halogen Bonding and Orthogonal Metal-Halogen Interactions in Dimers of Lithium Formamidinate and Halogenated Formamidines: An ab Initio Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
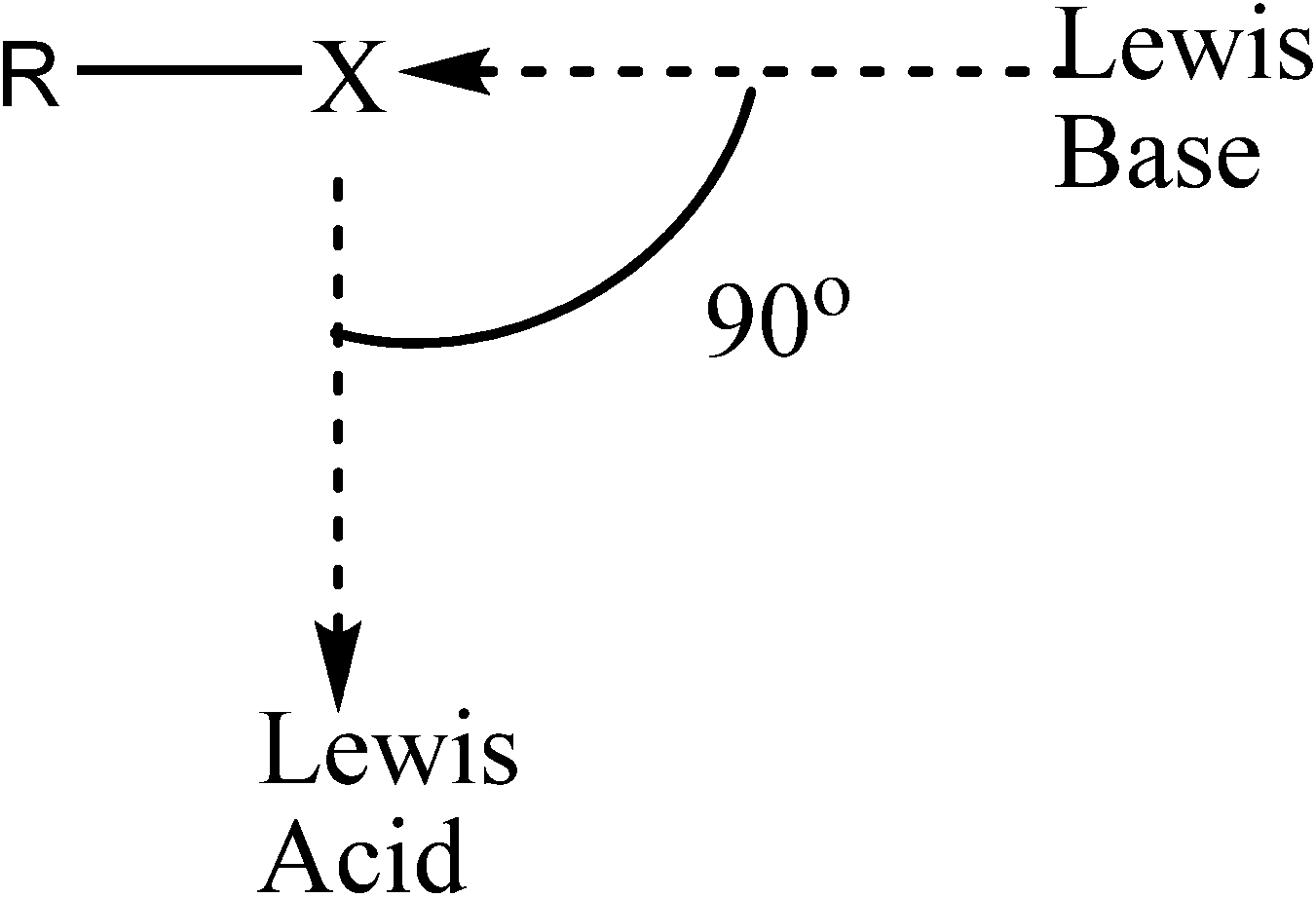
2. Computational Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geometries
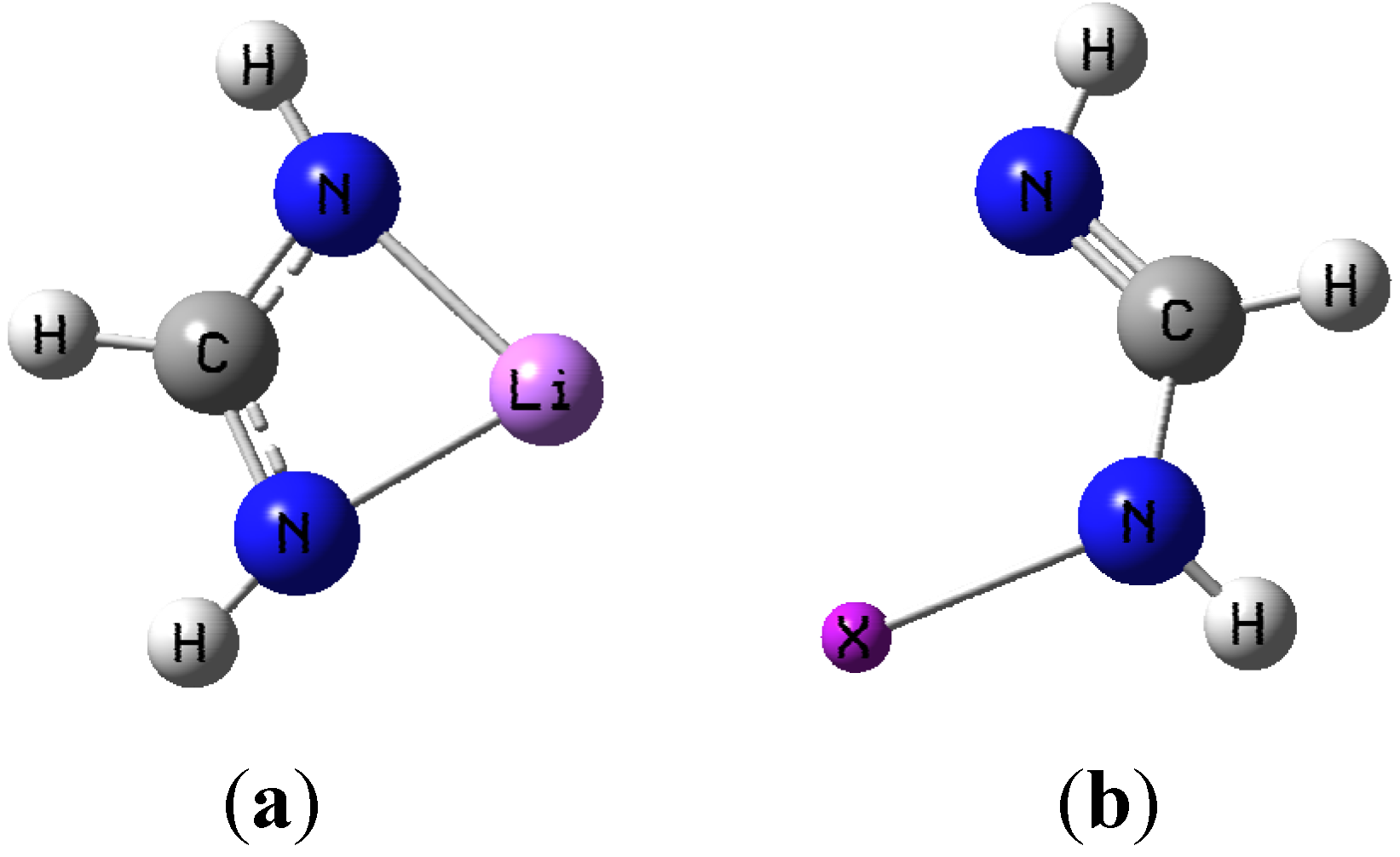
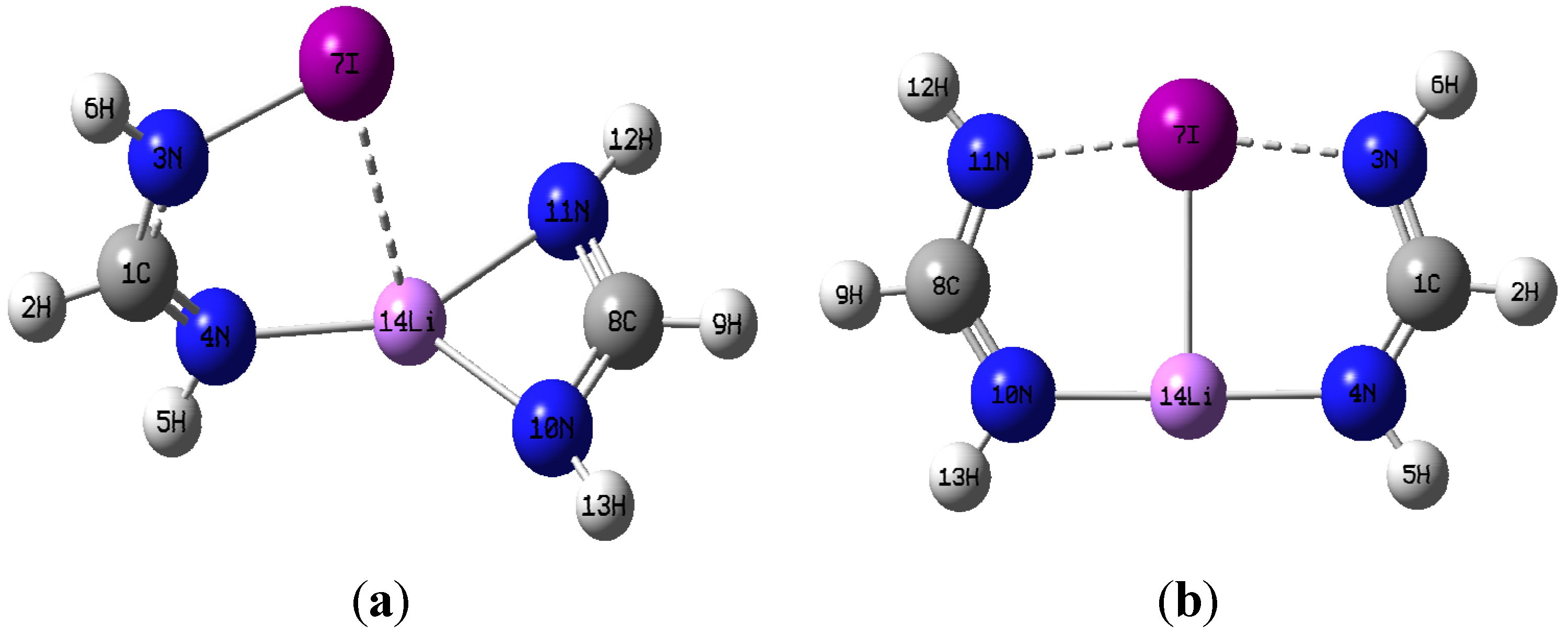
| HN=CHNHX | CH(NH2)Li | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4-C1 | C1-N3 | N3-X | τXN3H6C1 | N10-C8 | C8-N11 | N10-Li | N11-Li | |||
| Cl | 1.259 | 1.383 | 1.702 | 138.1 | 1.321 | 1.321 | 1.879 | 1.879 | ||
| Br | 1.260 | 1.380 | 1.848 | 140.2 | ||||||
| I | 1.263 | 1.373 | 2.032 | 145.5 | ||||||
| Dimers of C2v symmetry | ||||||||||
| N4-C1 | C1-N3 | N3-X | N10-C8 | C8-N11 | N10-Li | N11-Li | N11∙∙∙X | N4∙∙∙Li | Li∙∙∙X | |
| Cl | 1.305 | 1.318 | 1.964 | 1.305 | 1.318 | 1.933 | 2.979 | 1.933 | 1.964 | 2.323 |
| Br | 1.306 | 1.320 | 2.071 | 1.306 | 1.320 | 1.945 | 3.086 | 1.945 | 2.071 | 2.437 |
| I | 1.308 | 1.323 | 2.228 | 1.308 | 1.323 | 1.963 | 3.220 | 1.963 | 2.228 | 2.594 |
| X | ΘN3XN11 | ΘN20LiN4 | ΘXLiN10 | τXN3H6C1 | ||||||
| Cl | 175.2 | 175.8 | 92.1 | 180.0 | ||||||
| Br | 171.9 | 178.6 | 90.7 | 180.0 | ||||||
| I | 166.9 | 178.7 | 89.3 | 180.0 | ||||||
| Dimer of C1 symmetry | ||||||||||
| N4-C1 | C1-N3 | N3-X | N10-C8 | C8-N11 | N10-Li | N11-Li | N11∙∙∙X | N4∙∙∙Li | Li∙∙∙X | |
| Cl | 1.270 | 1.361 | 1.696 | 1.318 | 1.321 | 1.934 | 1.964 | 2.040 | 3.229 | 2.606 |
| Br | 1.272 | 1.356 | 1.839 | 1.318 | 1.321 | 1.934 | 1.966 | 2.036 | 3.368 | 2.769 |
| I | 1.277 | 1.347 | 2.025 | 1.318 | 1.321 | 1.940 | 1.971 | 2.033 | 3.530 | 2.961 |
| X | ΘN3XN11 | ΘN10LiN4 | ΘXLiN10 | τXN3H6C1 | ||||||
| Cl | 131.5 | 134.8 | 109.0 | 147.0 | ||||||
| Br | 124.5 | 135.2 | 107.3 | 153.1 | ||||||
| I | 117.0 | 134.6 | 104.7 | 172.7 | ||||||
3.2. Vibrational Frequency Shifts
| HN=CHNHX | CH(NH2)Li | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4-C1 | C1-N3 | 3-X | τXN3H6C1 | N10-C8 | C8-N11 | N10-Li | N11-Li | |||
| Cl | 1.273 | 1.386 | 1.711 | 133.8 | 1.329 | 1.329 | 1.916 | 1.916 | ||
| Br | 1.274 | 1.383 | 1.847 | 135.8 | ||||||
| I | 1.276 | 1.375 | 2.022 | 142.2 | ||||||
| Dimers of C2v symmetry | ||||||||||
| N4-C1 | C1-N3 | N3-X | N10-C8 | C8-N11 | N10-Li | N11-Li | N11∙∙∙X | N4∙∙∙Li | Li∙∙∙X | |
| Cl | 1.314 | 1.324 | 1.969 | 1.314 | 1.324 | 1.957 | 3.029 | 1.969 | 1.957 | 2.374 |
| Br | 1.315 | 1.326 | 2.064 | 1.315 | 1.326 | 1.966 | 3.123 | 2.064 | 1.966 | 2.473 |
| I | 1.317 | 1.330 | 2.204 | 1.317 | 1.330 | 1.985 | 3.250 | 2.204 | 1.985 | 2.619 |
| X | ΘN3XN11 | ΘN10LiN4 | ΘXLiN10 | τXN3H6C1 | ||||||
| Cl | 175.8 | 178.9 | 90.6 | 180.0 | ||||||
| Br | 173.0 | 178.7 | 86.5 | 180.0 | ||||||
| I | 168.5 | 175.9 | 87.9 | 180.0 | ||||||
| Dimer of C1 symmetry | ||||||||||
| N4-C1 | C1-N3 | N3-X | N10-C8 | C8-N11 | N10-Li | N11-Li | N11∙∙∙X | N4∙∙∙Li | Li∙∙∙X | |
| Cl | 1.282 | 1.366 | 1.705 | 1.327 | 1.330 | 1.967 | 2.000 | 3.195 | 2.081 | 2.618 |
| X | ΘN3XN11 | ΘN10LiN4 | ΘXLiN10 | τXNH6C1 | ||||||
| Cl | 134.8 | 136.5 | 111.0 | 140.8 | ||||||
| M06-2X/aug-cc-pVDZ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN=CHNHX | Dimer of C1 symmetry | Dimers of C2v symmetry | |||||
| X | ν(N-X) | ν(N-X) | νas(N-Li-N) | ν(N∙∙∙X∙∙∙N) | νas(N∙∙∙Li∙∙∙N) | ν(Li∙∙∙X) | |
| Cl | 659 | 688 | 608 | 236 | 663 | 294 | |
| Br | 586 | 607 | 602 | 286 | 640 | 307 | |
| I | 540 | 550 | 596 | 327 | 607 | 326 | |
| MP2/aug-cc-pVDZ | |||||||
| HN=CHNHX | Dimer of C1 symmetry | Dimers of C2v symmetry | |||||
| X | ν(N-X) | ν(N-X) | νas(N-Li-N) | ν(N∙∙∙X∙∙∙N) | νas(N∙∙∙Li∙∙∙N) | ν(Li∙∙∙X) | |
| Cl | 637 | 664 | 589 | 304 | 647 | 342 | |
| Br | 576 | 313 | 633 | 338 | |||
| I | 539 | 337 | 604 | 356 | |||
3.3. Energetics
| C2v-Dimers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M06-2X | MP2 | ||||
| ΔEint | ΔEcomp | ΔEint | ΔEcomp | ||
| Cl | −62.02 | −19.88 | −62.77 | −22.17 | |
| Br | −67.97 | −29.88 | −66.84 | −30.56 | |
| I | −72.76 | −37.48 | −69.32 | −36.37 | |
| C1-Dimers | |||||
| M06-2X | MP2 | ||||
| ΔEint | ΔEcomp | ΔEint | ΔEcomp | ||
| Cl | −20.72 | −19.57 | −19.79 | −18.79 | |
| Br | −21.03 | −19.83 | |||
| I | −21.58 | −20.23 | |||
3.4. AIM Analysis

| M06-2X | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρc (N∙∙∙X) | ρc (N∙∙∙Li) | Hc (N∙∙∙X) | Hc (N∙∙∙Li) | ρrcp1 |
| 0.0107 | 0.0275 | 0.0012 | 0.0058 | 0.0228 |
| 0.0102 | 0.0278 | 0.0009 | 0.0058 | 0.0227 |
| 0.0100 | 0.0281 | 0.0007 | 0.0058 | 0.0225 |
| MP2 | ||||
| ρc (N∙∙∙X) | ρc (N∙∙∙Li) | Hc (N∙∙∙X) | Hc (N∙∙∙Li) | ρrcp1 |
| 0.0112 | 0.0248 | 0.0012 | 0.0057 | 0.0210 |
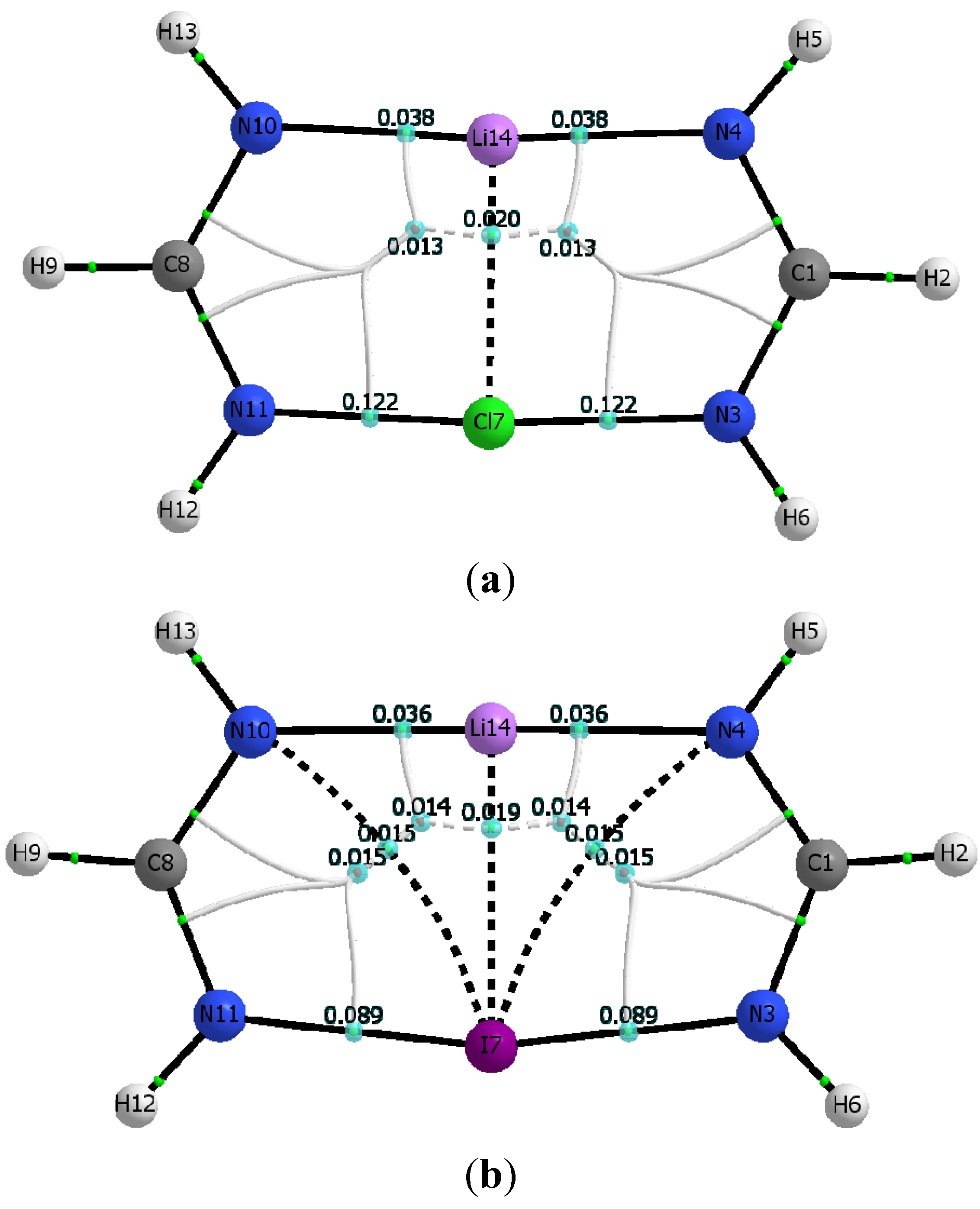
| M06-2x | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ρc (N∙∙∙X) | ρc (N∙∙∙Li) | ρc (Li∙∙∙X) | Hc (N∙∙∙X) | Hc (N∙∙∙Li) | Hc (Li∙∙∙X) | ρrcp1 | ρrcp2 | |
| Cl | 0.1222 | 0.0377 | 0.0202 | −0.0500 | 0.0054 | 0.0046 | 0.0133 | 0.0133 |
| Br | 0.1066 | 0.0351 | 0.0197 | −0.0472 | 0.0052 | 0.0036 | 0.0139 | 0.0139 |
| I | 0.0888 | 0.0355 | 0.0188 | −0.0346 | 0.0052 | 0.0026 | 0.0145 | 0.0145 |
| 0.0150 | 0.0008 | 0.0143 | 0.0143 | |||||
| MP2 | ||||||||
| X | ρc (N∙∙∙X) | ρc (N∙∙∙Li) | ρc (Li∙∙∙X) | Hc (N∙∙∙X) | Hc (N∙∙∙Li) | Hc (Li∙∙∙X) | ρrcp1 | ρrcp2 |
| Cl | 0.1211 | 0.0358 | 0.0177 | −0.0471 | 0.0052 | 0.0044 | 0.0123 | 0.0123 |
| Br | 0.1084 | 0.0351 | 0.0180 | −0.0460 | 0.0052 | 0.0034 | 0.0132 | 0.0132 |
| I | 0.0926 | 0.0336 | 0.0178 | −0.0346 | 0.0052 | 0.0025 | 0.0145 | 0.0145 |
| 0.0149 | 0.0008 | 0.0139 | 0.0139 | |||||
3.5. Polymer Synthons
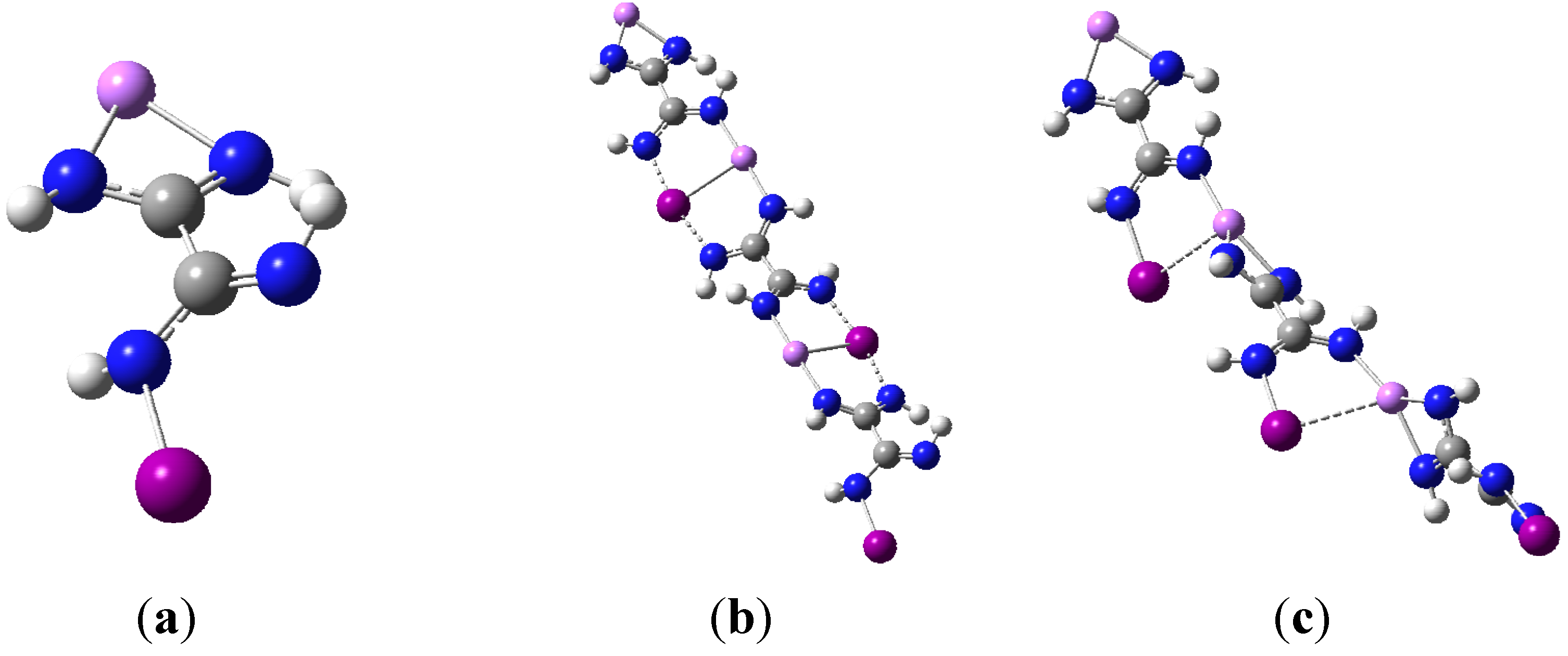
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. Halogen bonding: A paradigm in supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metrangolo, P.; Neukirch, H.; Pilati, T.; Resnati, G. Halogen bonding based recognition processes: A world parallel to hydrogen bonding. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Clark, T. Halogen bonding: An electrostatically driven highly directional noncovalent interaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7748–7757. [Google Scholar]
- Legon, A.C. The halogen bond: An interim perspective. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7736–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.M.; Scanlon, J.D.; Jimenez-Izal, E.; Ugalde, J.M.; Infante, I. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 10350–10357.
- Desiraju, G.R.; Ho, P.S.; Kloo, L.; Legon, A.C.; Marquardt, R.; Metrangolo, P.; Politzer, P.; Resnati, G.; Rissanen, K. Definition of the halogen bond (IUPAC Recommendations 2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1711–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.; Hennemann, M.; Murray, J.S.; Politzer, P. Halogen bonding: The σ-hole. J. Mol. Model. 2007, 13, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Clark, T. Halogen bonding and other σ-hole interactions: A perspective. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11178–11189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, K.; Zariny, H. Halogen bonding: A lump-hole interaction. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 492, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuch, S.; Martin, J.M.L. Halogen bonds: Benchmarks and theoretical analysis. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 1918–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauzá, A.; Alkorta, I.; Frontera, A.; Elguero, J. On the reliability of pure and hybrid DFT methods for the evaluation of halogen, chalcogen, and pnicogen bonds involving anionic and neutral electron donors. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 5201–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halogen Bonding: Fundamentals and Applications; Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. (Eds.) Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008.
- Erdelyi, M. Halogen bonding in solution. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3547–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, T.M.; Chudzinski, M.G.; Sarwar, M.G.; Taylor, M.S. Halogen bonding in solution: Thermodynamics and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Priimagi, A.; Cavallo, G.; Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. The halogen bond in the design of functional supramolecular materials: Recent advances. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2686–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parisini, E.; Metrangolo, P.; Pilati, T.; Resnati, G.; Terraneo, G. Halogen bonding in halocarbon–protein complexes: A structural survey. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2267–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcken, R.; Liu, X.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Rutherford, T.J.; Fersht, A.R.; Joerger, A.C.; Boeckler, F.M. Halogen-Enriched fragment libraries as leads for drug rescue of mutant p53. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6810–6818. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcken, R.; Zimmernmann, M.O.; Lange, A.; Joerger, A.C.; Boeckler, F.M. Principles and applications of halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1363–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Kolar, M.; Hobza, P.; Bronowska, A.K. Plugging the explicit σ-holes in molecular docking. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politzer, P.; Murray, J.S.; Lane, P. σ-Hole bonding and hydrogen bonding: Competitive interactions. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2007, 107, 3046–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooibroek, T.J.; Gamez, P. Halogen bonding versus hydrogen bonding: What does the Cambridge Database reveal? CrystEngComm. 2013, 15, 4565–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, E.; Meille, S.V.; Messina, M.T.; Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. Halogen bonding versus hydrogen bonding in driving self-assembly processes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xing, C.; Xu, W.; Jin, G.; Li, Z. Halogen bonding and hydrogen bonding coexist in driving self-assembly process. Cryst. Growth Des. 2004, 4, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metrangolo, P.; Resnati, G. Halogens versus hydrogen. Science 2008, 321, 918–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esrafili, M.D.; Hadipour, N.L. Characteristics and nature of halogen bonds in linear clusters of NCX (X=Cl, and Br): An ab initio, NBO, and QTAIM study. Mol. Phys. 2011, 109, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Blanco, F.; Elguero, J. A computational study of the cooperativity in clusters of interhalogen derivatives. Struct. Chem. 2009, 20, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabowski, S.J.; Bilewicz, E. Cooperativity halogen bonding effect–Ab initio calculations on H2CO···(ClF)n complexes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 427, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkorta, I.; Blanco, F.; Deya, P.M.; Elguero, J.; Estarellas, C.; Frontera, A.; Quinorero, D. Cooperativity in multiple unusual weak bonds. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2010, 126, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankau, T.M.; Wu, Y.C.; Zou, J.W.; Yu, C.H. The cooperativity between hydrogen and halogen bonds. J. Theoret. Comput. Chem. 2008, 7, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, A.-C.C.; Gräfenstein, J.; Laurilla, J.L.; Bergquist, J.; Erdélyi, M. Symmetry of [N-X-N]+ halogen bonds in solution. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, A.-C.C.; Gräfenstein, J.; Budnjo, A.; Laurilla, J.L.; Bergquist, J.; Karim, A.; Kleinmaier, R.; Brath, U.; Erdélyi, M. Symmetric halogen bonding is preferred in solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5706–5715. [Google Scholar]
- Parra, R.D. Dimers and trimers of formamidine and its mono-halogenated analogues HNCHNHX, (X = H, Cl, Br, or I): A comparative study of resonance-assisted hydrogen and halogen bonds. Comp. Theor. Chem. 2012, 998, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, D.C.; Butler, P.; Browne, E.C.; Wilson, D.J.D.; Dutton, J.L. On the bonding in bis-pyridine iodonium cations. Aust. J. Chem. 2013, 66, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Voth, A.R.; Khuu, P.; Oishi, K.; Ho, P.S. Halogen bonds as orthogonal molecular interactions to hydrogen bonds. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelyubina, Y.V.; Antipin, M.Y.; Dunin, D.S.; Kotov, V.Y.; Lyssenko, K.A. Unexpected “amphoteric” character of the halogen bond: The charge density study of the co-crystal of N-methylpyrazine iodide with I2. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5325–5327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.-P.; Qiu, W.-Y.; Liu, S.; Jinc, N.-Z. Halogen as halogen-bonding donor and hydrogen-bonding acceptor simultaneously in ring-shaped H3N.X(Y).HF (X = Cl, Br and Y = F, Cl, Br) Complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 7408–7418. [Google Scholar]
- Dikundwar, A.G.; Row, T.N.G. Evidence for the “Amphoteric” nature of fluorine in halogen bonds: An instance of Cl···F contact. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 1713–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dunning, T.H. A road map for the calculation of molecular binding energies. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 9062–9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, T.H. Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. I. The atoms boron through neon and hydrogen. J. Phys. Chem. A 1989, 90, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, K.A.; Figgen, D.; Dolg, M.; Stoll, H. Energy-consistent relativistic pseudopotentials and correlation consistent basis sets for the 4d elements Y-Pd. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 124101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boys, S.F.; Bernardi, F. Calculation of small molecular interactions by differences of separate total energies—some procedures with reduced errors. Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.F.W. Atoms in Molecules: A Quantum Theory; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Biegler-König, F.; Schönbohm, J.; Bayles, D. AIM2000—A program to analyze and visualize atoms in molecules. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, T.A. AIMAll (Version 13.11.04), TK Gristmill Software; Overland Park, KS, USA, 2013.
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, S.J. QTAIM Characteristics of halogen bond and related interactions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, S.J. What is the covalency of hydrogen bonding? Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2597–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-X.; Zou, J.-W.; Wang, Y.-H.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Yu, Q.-S. Ab initio investigation of the complexes between bromobenzene and several electron donors: Some insights into the magnitude and nature of halogen bonding interactions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 10781–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-L.; Xiao, T.; Lin, C.; Wang, L. Advanced supramolecular polymers constructed by orthogonal self-assembly. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5950–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Gasparini, G.; Matile, S. Functional systems with orthogonal dynamic covalent bonds. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014. advanced article. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Parra, R.D. Concerted Halogen Bonding and Orthogonal Metal-Halogen Interactions in Dimers of Lithium Formamidinate and Halogenated Formamidines: An ab Initio Study. Molecules 2014, 19, 1069-1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19011069
Parra RD. Concerted Halogen Bonding and Orthogonal Metal-Halogen Interactions in Dimers of Lithium Formamidinate and Halogenated Formamidines: An ab Initio Study. Molecules. 2014; 19(1):1069-1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19011069
Chicago/Turabian StyleParra, Ruben D. 2014. "Concerted Halogen Bonding and Orthogonal Metal-Halogen Interactions in Dimers of Lithium Formamidinate and Halogenated Formamidines: An ab Initio Study" Molecules 19, no. 1: 1069-1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19011069
APA StyleParra, R. D. (2014). Concerted Halogen Bonding and Orthogonal Metal-Halogen Interactions in Dimers of Lithium Formamidinate and Halogenated Formamidines: An ab Initio Study. Molecules, 19(1), 1069-1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19011069