Novel Biological Activities of Allosamidins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
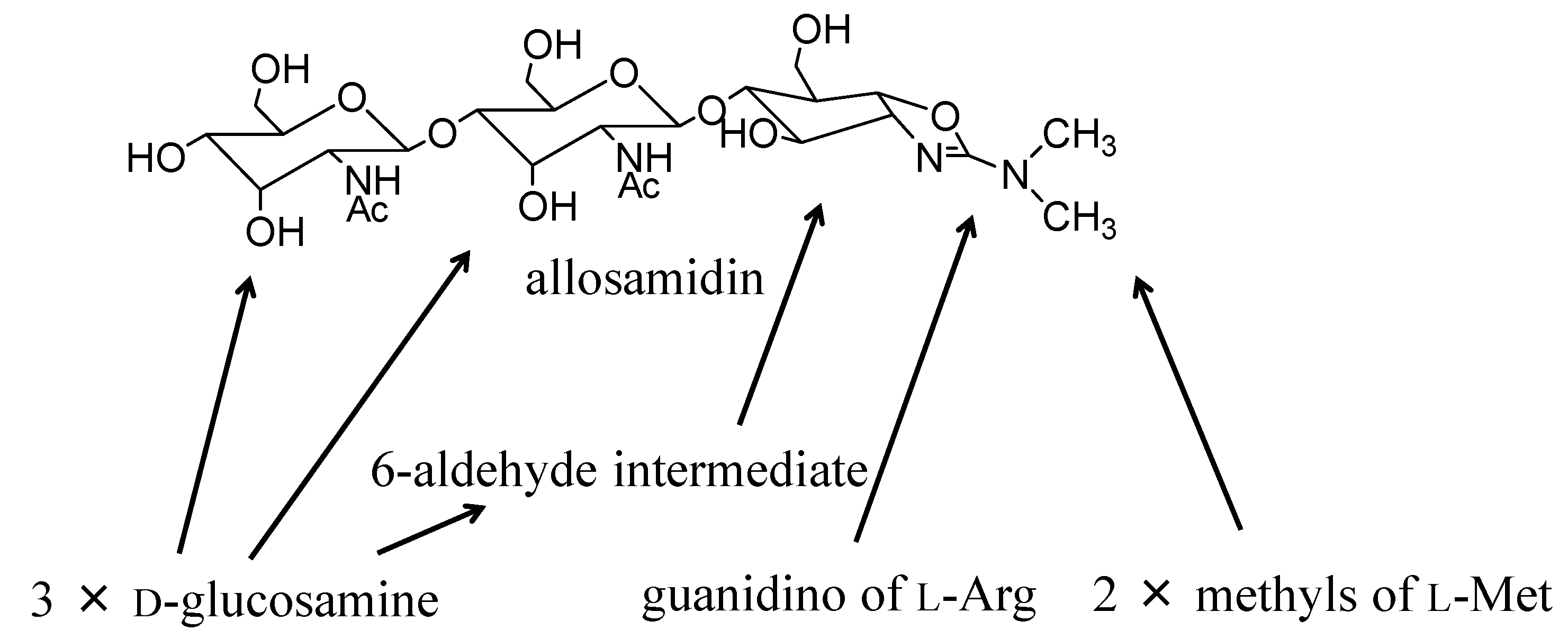
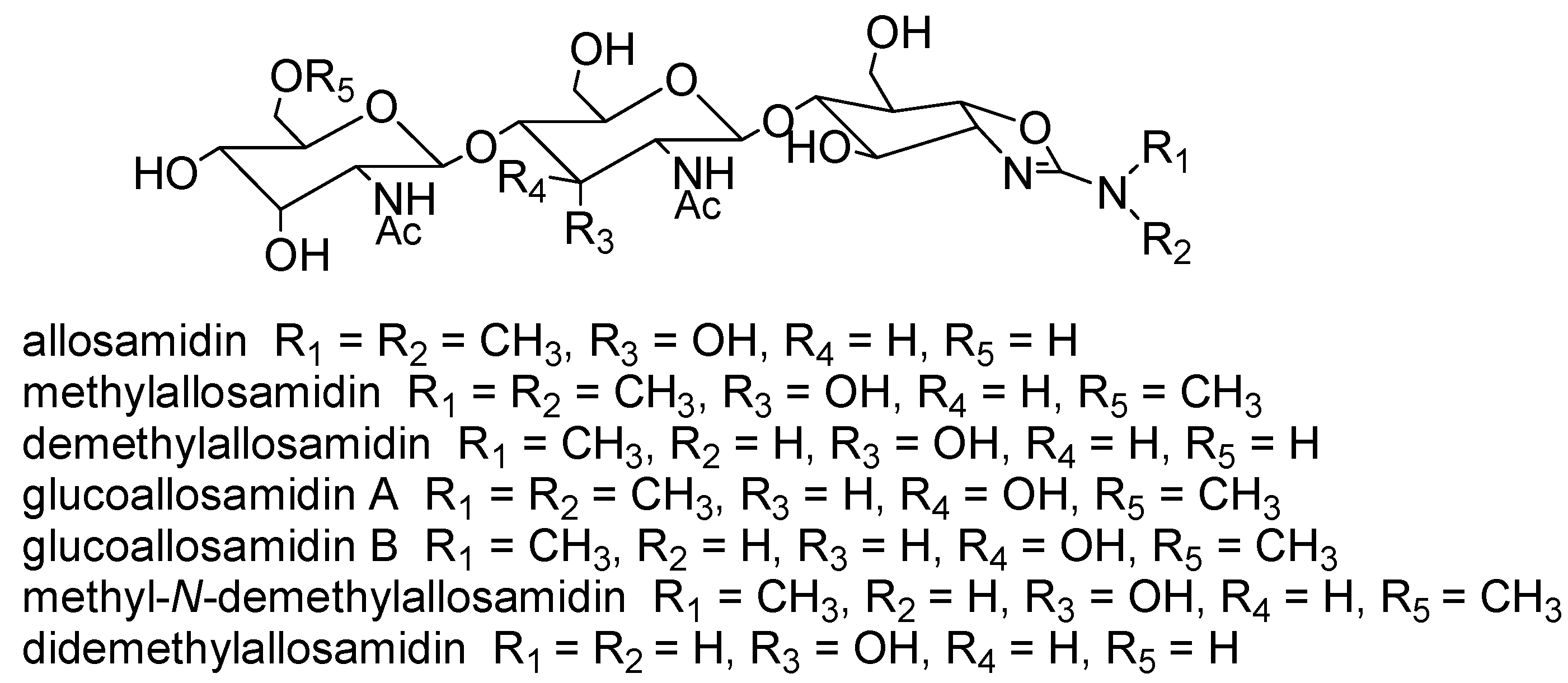
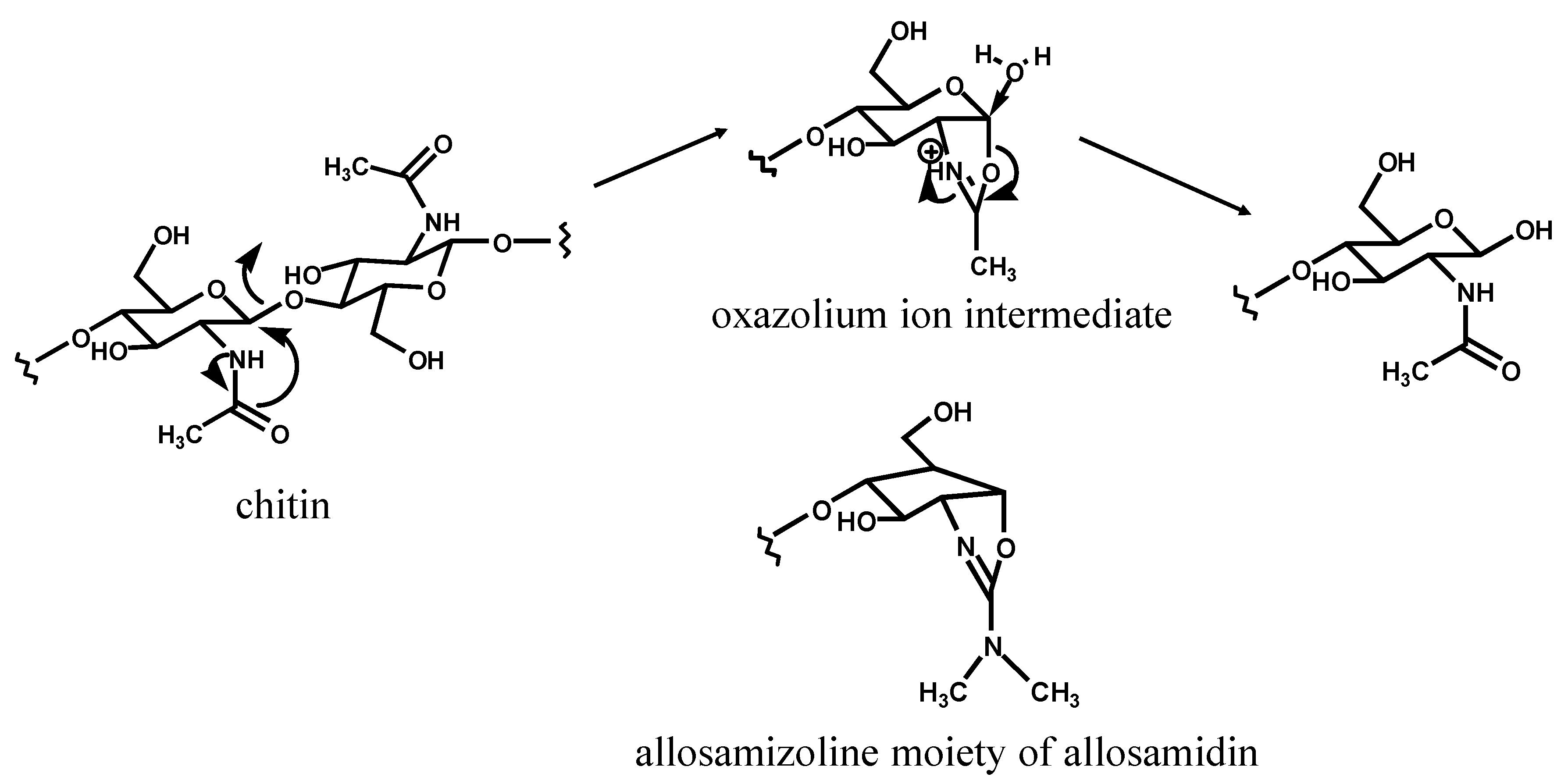
| Organisms | Roles of Chitinases | Allosamidin’s Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| insects | degradation of old culticle | inhibition of moulting | [7,32,33,34] |
| yeasts | fission of septum | inhibition of cell separation | [35,36] |
| fungi | (hyphal growth and branching) a | no significant effect | |
| parasites | degradation of peritrophic matrix | inhibition of transmission of | [42,43,44,45] |
| malaria ookinetes | |||
| inhibition of encystment | [41] | ||
| plants | (defensive function) a | enhancement of stress tolerance | [46] |
| bacteria | obtaining nutrient | promotion of chitinase production of Streptomyces | [49,50,51] |
| mammals | (defensive function) a | anti-asthmatic activity | [52,68] |
2. Physiological Roles of Allosamidin in its Producing Streptomyces
2.1. Microbial Secondary Metabolites
2.2. Streptomyces Chitinases
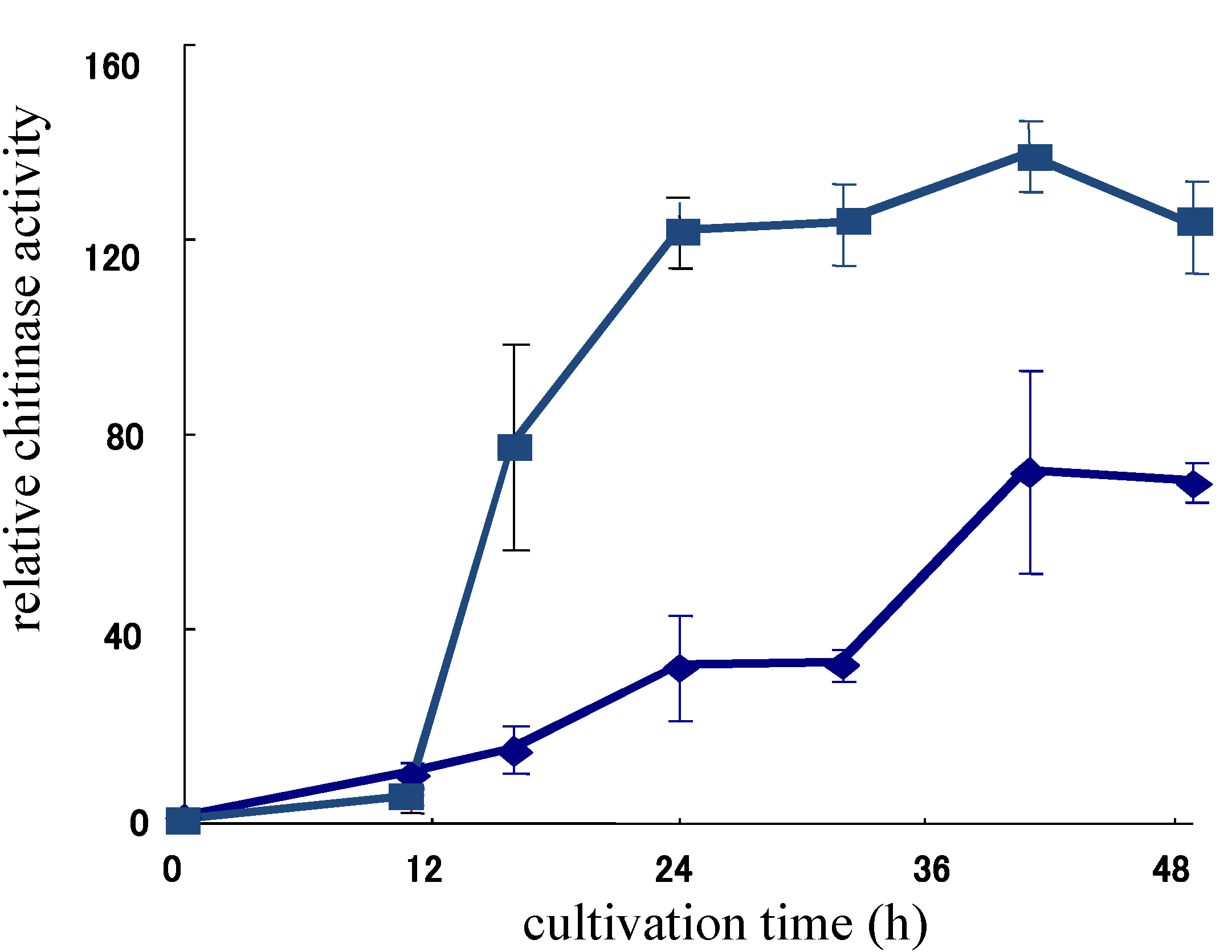
2.3. Chitinase Production Promoting Activity of Allosamidin in an Allosamidin-Producing Strain
2.4. Molecular Mechanism of Allosamidin’s Function on Chitinase Production

2.5. Localization of Allosamidin
2.6. Generality of the Action of Allosamidin in Streptomyces
2.7. Role of Allosamidin in Nature

3. Anti-Asthmatic Activity of Allosamidins
3.1. Asthma and Acidic Mammalian Chitinase
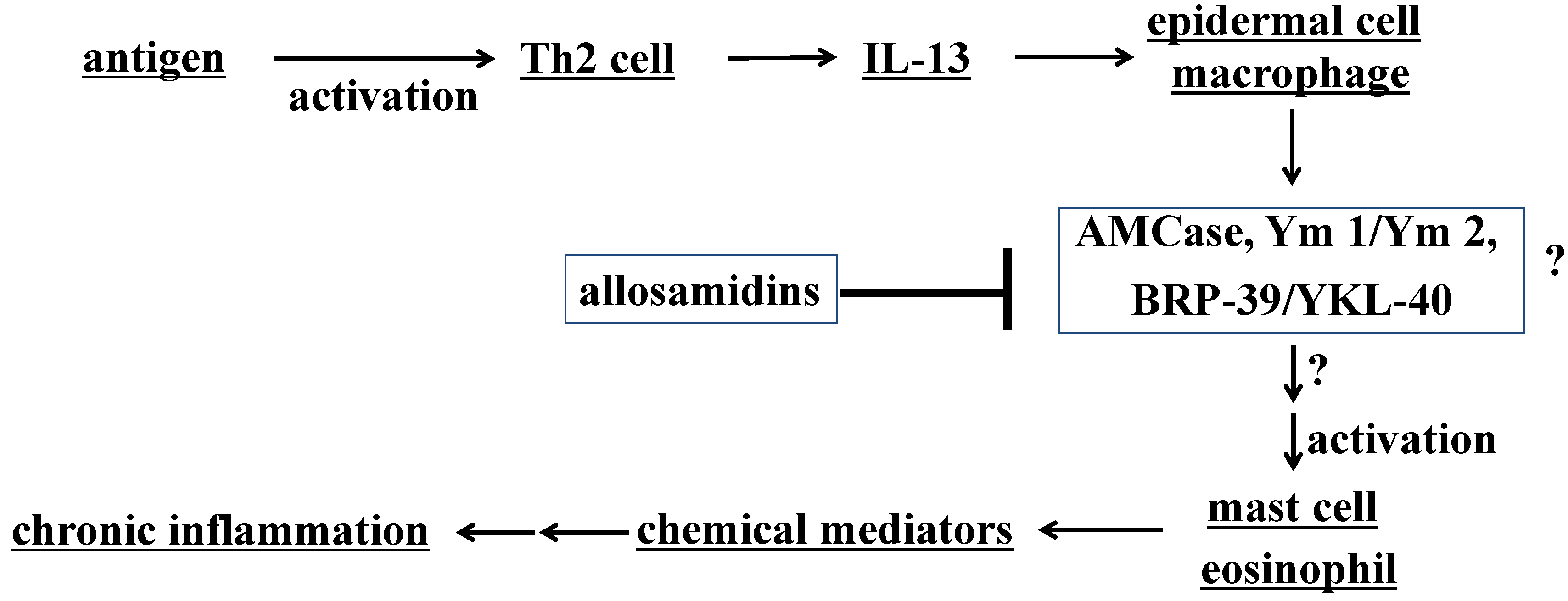
3.2. Activities of Allosamidin and Demethylallosamidin on AMCase and Asthma
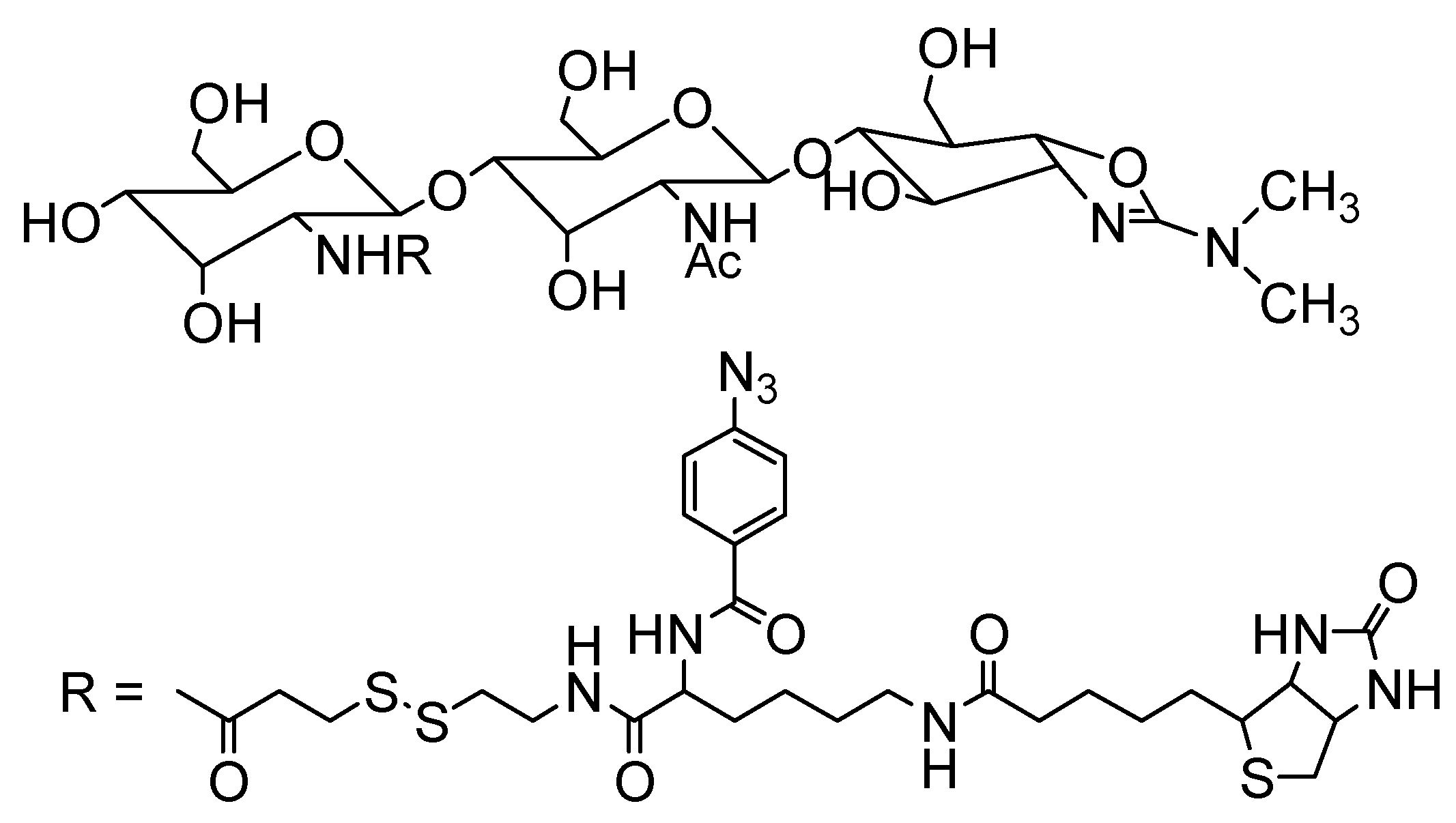
3.3. Targets of Allosamidins for Their Anti-asthmatic Activity
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A. Chitin; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, K.J.; Koga, D. Insect chitin; physical state, synthesis, degradation and metabolic regulation. Insect biochem. 1986, 16, 851–877. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, E. Chitin biochemistry; Synthesis and inhibition. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1987, 32, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.; Casida, J.E. Properties and inhibition of insect integumental chitin synthase. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 1982, 17, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuda, S. The biochemical significance of allosamidins as chitinase inhibitors. In Binomium Chitin-Chitinase: Resent Issues; Musumeci, S., Paoletti, M.G., Eds.; Nova Science: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuda, S.; Isogai, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Suzuki, A.; Koseki, K. Structure of allosamidin, a novel insect chitinase inhibitor, Produced by Streptomyces sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 2475–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuda, S.; Isogai, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Suzuki, A. Search for microbial insect growth regulators II. Allosamidin. A novel insect chitinase inhibitor. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuda, S.; Isogai, A.; Makita, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Koseki, K.; Kodama, H.; Suzuki, A. Structures of allosamidins, Novel insect chitinase inhibitors, Produced by actinomycetes. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1987, 51, 3251–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakuda, S.; Isogai, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Suzuki, A.; Koseki, K.; Kodama, H.; Yamada, Y. Absolute configuration of allosamizoline, an aminocyclitol derivative of the chitinase inhibitor allosamidin. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1988, 52, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Sakuda, S.; Yamada, Y. Biosynthetic studies on the chitinase inhibitor, allosamidin. Origin of the carbon and nitrogen atoms. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1992, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Sakuda, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Yamada, Y. Biosynthetic studies of allosamidin 2. Isolation of didemethylallosamidin, and conversion experiments of 14C-labeled demethylallosamidin, didemethylallosamidin and their related compounds. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuda, S.; Sugiyama, Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Takao, H.; Ikeda, H.; Kakinuma, K.; Yamada, Y.; Nagasawa, H. Biosynthetic studies on the cyclopentane ring formation of allosamizoline, an aminocyclitol component of the chitinase inhibitor allosamidin. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 3356–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, Y.; Sakuda, S.; Takayama, S.; Yamada, Y. Isolation and characterization of new allosamidins. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berecibar, A.; Grandjean, C.; Siriwardena, A. Synthesis and biological activity of natural aminocyclopentitol glycosidase inhibitors: Mannostatins, Trehazoline, Allosamidins, And their analogues. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 779–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderses, O.A.; Dixon, M.J.; Eggleston, I.M.; van Aalten, D.M.F. Natural product family 18 chitinase inhibitors. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1005, 22, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangliang, H. Recent progress on synthesis and activities of allosamidin and its analogues. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 665–670. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuda, S.; Isogai, A.; Suzuki, A.; Yamada, Y. Chemistry and biochemistry of the chitinase inhibitors, allosamidins. Actinomycetologica 1993, 7, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrissat, B.A. Classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J. 1991, 280, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spindler, K.D.; Spindler-Barth, M. Inhibitor of chitinases. In Chitin and Chitinases; Jolles, P., Muzzarelli, R.A.A., Eds.; Birkhauser Verlag.: Basel, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Tews, I.; van Scheltinga, A.C.T.; Perrakis, A.; Wilson, K.S.; Dijkstra, B.W. Substrate-assisted catalysis unifies two families of chitinolytic enzymes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 7954–7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Scheltinga, A.C.T.; Armand, S.; Kalk, K.H.; Isogai, A.; Henrissat, B.; Dijkstra, B.W. Stereochemistry of chitin hydrolysis by a plant chitinase/lysozyme and X-ray structure of a complex with allosamidin: Evidence for substrate assisted catalysis. Biochemstry 1995, 34, 15619–15623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brameld, K.A.; Shrader, W.D.; Imperiali, B.; Gddard, W.A., III. Substrate assistance in the mechanism of family 18 chitinases: Theoretical studies of potential intermediates and inhibitors. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 280, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germer, A.; Klod, S.; Peter, M.G.; Kleinpeter, E. NMR spectroscopic and theoretical study of the complexation of the inhibitor allosamidin in the binding pocket of the plant chitinase hevamine. Mol. Model. 2002, 8, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolau, Y.; Tavlas, G.; Vorgias, C.E.; Petratos, K. De novo purification scheme and crystallization conditions yield high-resolution structures of chitinase A and its complex with the inhibitor allosamidin. Acta Cryst. 2003, D59, 400–403. [Google Scholar]
- van Aalten, D.M.F.; Komander, D.; Synstad, B.; Gaseidnes, S.; Peter, M.G.; Eijsink, V.G.H. Structural insights into the catalytic mechanism of a family 18 exo-chitinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8979–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortone, K.; Monzingo, A.F.; Ernst, S.; Robertus, J.D. The structure of an allosamidin complex with the Coccidioides immitis chtinase defines a role for a second acid residue in substrate-assisted mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 320, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, F.V.; Houston, D.R.; Boot, R.G.; Aerts, J.M.F.; Sakuda, S.; van Aalten, M.F. Crystal structures of allosamidin derivatives in complex with human macrophage chitinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20110–20116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Zheng, Q.C.; Zhang, H.X.; Chu, H.Y.; Sun, C.C. Analysis of a three-dimensional structure of human acidic mammalian chitinase obtained by homology modeling and ligand binding studies. J. Mol. Model. 2009, 15, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederkvist, F.H.; Saua, S.F.; Karlsen, V.; Sakuda, S.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Sorlie, M. Thermodynamic analysis of allosamidin binding to a family 18 chitinase. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 12347–12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakariassen, H.; Klemetsen, L.; Sakuda, S.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G.; Varum, KM.; Sorlie, M.; Eijsink, V.G.H. Effect of enzyme processivity on the efficacy of a competitive chitinase inhibitor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baban, J.; Fjeld, S.; Sakuda, S.; Eijsink, V.G.H.; Sorlie, M. The roles of three Serratia marcescens chitinases in chitin conversion are reflected in different thermodynamic signatures of allosamidin binding. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 6144–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blattner, R.; Gerard, P.J.; Spindler-Barth, M. Synthesis and biological activity of allosamidin and allosamidin analogues. Pestic. Sci. 1997, 50, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, P.J.B.; Yao, R.C.; Doolin, L.E.; McGowan, M.J.; Fukuda, D.S.; Mynderse, J.S. Methods for detection and quantitation of chitinase inhibitors in fermentation broths; isolation and insect life cycle effect of A82516. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, B.P.D.; Lemos, F.J.A.; Secundino, N.F.C.; Pascoa, V.; Pereira, S.T.; Pimenta, P.F.P. Presence of chitinase and beta-N-acetyl glucosaminidase in the Aedes aegypti a chitinolytic system involving peritrophic matrix formation and degradation. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuda, S.; Nishimoto, Y.; Ohi, M.; Watanabe, M.; Takayama, S.; Isogai, A.; Yamada, Y. Effects of demethylallosamidin, a potent yeast chitinase inhibitor, on the cell division of yeast. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 1333–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S.; Tsuyoshi, N.; Kikuchi, R.; Takayama, S.; Sakuda, S.; Yamada, Y. Effect of demethylallosamidin, a chitinase inhibitor, on morphology of fungus Geotrichum candidum. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 40, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J. Fungal cell wall chitinases and glucanases. Microbiology 2004, 150, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, K.; Keer, V.; Hitchcock, C.A.; Adams, D.J. Chtinase activity from Candida albicans and its inhibition by allosamidin. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1989, 135, 1417–1421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Yamazaki, D.; Takaya, N.; Takagi, M.; Ohta, M.; Horiuchi, H. A chitinase gene, chiB, involved in the autolysis process of Aspergillus nidulans. Curr. Genet. 2007, 51, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami, L.; Pusztahelyi, T.; Emri, T.; Varecza, Z.; Fekete, A.; Grallert, A.; Karanyi, Z.; Kiss, L.; Pocsi, I. Autolysis and aging of Penicillium chrysogenum cultures under carbon starvation: Chitinase production and antifungal effect of allosamidin. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 47, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villagomez-Castro, J.C.; Calvo-Mendez, C.; Lopez-Romero, E. Chtinase activity in encysting Entamoeba invadens and its inhibition by allosamidin. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 52, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabuddin, M.; Toyoshima, T.; Aikawa, M.; Kaslow, D.C. Transmission-blocking activity of a chitinase inhibitor and activation of malarial parasite chitinase by mosquito protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 4266–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinetz, J.M.; Dave, S.K.; Specht, C.A.; Brameld, K.A.; Xu, B.; Hayward, R.; Fidock, D.A. The chitinase PfCHT1 from the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum lacks proenzyme and chitin-binding domains and displays unique substrate preferences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14061–14066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeo, S.; Hisamori, D.; Matsuda, S.; Vinetz, J.; Sattabongkot, J.; Tsuboi, T. Enzymatic characterization of the Plasmodium vivax chitinase, a potential malaria transmission-blocking target. Parasitol. Int. 2009, 58, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Egerton, G.; Underwood, A.P.; Sakuda, S.; Bianco, A.E. Expression and secretion of a larval-specific chtinase (family 18 glycosyl hydrolase) by the infective stages of the parasitic nematode, Onchocerca volvulus. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42557–42564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, Y.; Nakano, S.; Tamoi, M.; Sakuda, S.; Fukamizo, T. Chitinase gene expression in response to environmental stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana: Chitinase inhibitor allosamidin enhances the stress. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, M.N.; Gooday, G.W. Involvement of chitinases of Bacillus thuringiensis during pathogenesis in insects. Microbiology 1998, 144, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boer, W.D.; Gunnewiek, P.J.A.K.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; van Veen, J.A. Growth of chitinolytic dune soil β-subclass Proteobacteria in response to invading fungal hyphae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3358–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Nakanishi, E.; Ohira, T.; Kawachi, R.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Chitinase inhibitor allosamidin is a signal molecule for chitinase production in its producing Streptomyces. I. Analysis of the chitinase whose production is promoted by allosamidin and growth accelerating activity of allosamidin. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Nakanishi, E.; Ohira, T.; Kawachi, R.; Ohnishi, Y.; Horinouchi, S.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Chitinase inhibitor allosamidin is a signal molecule for chitinase production in its producing Streptomyces. II. Mechanism for regulation of chitinase production by allosamidin through a two-component regulatory system. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Nakanishi, E.; Furihata, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Tsujibo, H.; Watanabe, T.; Ohnishi, Y.; Horinouchi, S.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Chtinase inhibitor allosamidin promotes chitinase production of Streptomyces generally. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 43, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, T.; Homer, R.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Chen, N.Y.; Cohn, L.; Hamid, Q.; Elias, J.A. Acidic mammalian chitinase in asthmatic Th2 inflammation and IL-13 pathway activation. Science 2004, 304, 1678–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucolo, C.; Musumeci, M.; Maltese, A.; Drago, F.; Musumeci, S. Effect of chitinase inhibitors on endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) in rabbits. Pharmacol. Res. 2008, 57, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamoto, S.; Egashira, K.; Ichiki, T.; Han, X.; McCurdy, S.; Sakuda, S.; Sunagawa, K.; Boisvert, W.A. Chitinase inhibition promotes atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingappa, Y.; Lockwood, J.L. A chitin medium for isolation, growth and maintenance of actinomycetes. Nature 1961, 189, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, S.D.; Chater, K.F.; Cerdeño-Tárraga, A.M.; Challis, G.L.; Thomson, N.R.; James, K.D.; Harris, D.E.; Quail, M.A.; Kieser, H.; Harper, D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 2002, 417, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Westpheling, J. Direct repeat sequences in the Streptomyces chitinase-63 promoter direct both glucose repression and chitin induction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 13116–13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Ishizaka, M.; Francisco, P.B., Jr.; Fujii, T.; Miyashita, K. Transcriptional co-regulation of five chitinase genes scattered on the Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) chromosome. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2937–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Schrempf, H. Mutational analysis of the binding affinity and transport activity for N-acetylglucosamine of the novel ABC transporter Ngc in the chitin-degrader Streptomyces olivaceoviridis. Mol. Genet. Gen. 2004, 271, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Sakuda, S.; Yamada, Y. Purification of allosamidin-sensitive and -insensitive chitinases produced by allosamidin-producing Streptomyces. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1993, 57, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, T.; Armand, S.; Hara, T.; Nikaidou, N.; Henrissat, B.; Mitsutomi, M.; Watanabe, T. A modular family 19 chitinase found in the prokaryotic organism Streptomyces griseus HUT 6037. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5065–5070. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, H.; Okamoto, S.; Anamnart, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Nihira, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kuzuyama, T.; Seto, H.; Nakayama, J.; Suzuki, A.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Nucleotide sequences of genes encoding allosamidin-sensitive and -insensitive chitinases produced by allosamidin-producing Streptomyces. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 2003, 67, 2002–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, E.; Okamoto, S.; Matsuura, H.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Allosamidin, a chitinase inhibitor produced by Streptomyces, acts as an inducer of chitinase production in its producing strain. Proc. Japan Academy Ser. B 2001, 77, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills-Karp, M.; Luyimbazi, J.; Xu, X.; Schofield, B.; Neben, T.Y.; Karp, C.L.; Donaldson, D.D. Interleukin-13: Central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 1998, 282, 2258–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boot, R.G.; Blommaart, E.F.C.; Swart, E.; Ghauharali-van der Vlugt, K.; Bijl, N.; Moe, C.; Place, A.; Aerts, M.F. Identification of a novel acidic mammalian chitinase distinct from chitotriosodase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 6770–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boot, R.G.; Bussink, A.P.; Verhoek, M.; de Boer, P.A.J.; Moorman, A.F.M.; Aerts, J.M.F.G. Marked diffrences in tissue-specific expression of chitinases in mouse and man. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2005, 53, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homer, R.J.; Zhu, Z.; Cohn, L.; Lee, C.G.; White, W.I.; Chen, S.; Elias, J.A. Differential expression of chitinases identify subsets of murine airway epithelial cells in allergic inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L502–L511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Inoue, H.; Sato, Y.; Kita, Y.; Nakano, T.; Noda, N.; Eguchi-Tsuda, M.; Moriwaki, A.; Kan-o, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimizu, T.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S.; Nakanishi, Y. demethylallosamidin, a chitinase inhibitor, suppresses airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasuda, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Kono, M.; Sakuda, S.; Koga, D. Kinetics analysis of a chitinase from red sea bream, Pagrus major. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 2004, 68, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Muraoka, S.; Kikuchi, N.; Noda, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Inoue, H.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Preparation of allosamidin and demethylallosamidin photoaffinity probes and analysis of allosamidin-binding proteins in asthmatic mice. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 3054–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ober, C.; Chupp, G.L. The chitinase and chitinase-like proteins: A review of genetic and functional stidies in asthma and immune-mediated diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 9, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, T.E.; Maizels, R.M.; Allen, J.E. Chitinases and chitinase-like proteins: Potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of T-helper type 2 allergies. Clin. Experi. Allergy 2009, 39, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owashi, M.; Arita, H.; Hayai, N. Identification of a novel eosinophil chemotactic cytokine (ECF-L) as a chitinase family protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, D.R.; Recklies, A.D.; Krupa, J.C.; van Aalten, D.M.F. Structure and ligand-induced conformational change of the 39-kDa glycoprotein from human articular chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30206–30212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimpl, M.; Rush, C.L.; Betou, M.; Eggleston, I.M.; Recklies, A.D.; van Aalten, D.M.F. Human YKL-39 is apseudo-chitinase with retained chitooligosaccharide-binding properties. Biochem. J. 2012, 146, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.G.; Elias, J.A. Role of breast regression protein-39/YKL-40 in asthma and allergic responses. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2010, 2, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashita, H.; Morita, S.; Sagiya, Y.; Nakanishi, A. Role of eosinophil chemotactic factor by T lymphocytes on airway hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of allergic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.G.; Hartl, D.; Lee, G.R.; Koller, B.; Matsuura, H.; Da Silva, C.A.; Sohn, M.H.; Cohn, L.; Homer, R.J.; Kozhich, A.A.; et al. Role of breast regression protein 39 (BRP-39)/chitinase 3-like-1 in Th2 and IL-13-induced tissue responses and apoptosis. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1149–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Kumar, R.K.; Zhou, J.; Foster, P.S.; Webb, D.C. Ym1/2 promotes Th2 cytokine expression by inhibiting 12/15(S)-lipoxygenase: Identification of a novel pathway for regulating allergic inflammation. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5393–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakuda, S.; Inoue, H.; Nagasawa, H. Novel Biological Activities of Allosamidins. Molecules 2013, 18, 6952-6968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066952
Sakuda S, Inoue H, Nagasawa H. Novel Biological Activities of Allosamidins. Molecules. 2013; 18(6):6952-6968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066952
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakuda, Shohei, Hiromasa Inoue, and Hiromichi Nagasawa. 2013. "Novel Biological Activities of Allosamidins" Molecules 18, no. 6: 6952-6968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066952
APA StyleSakuda, S., Inoue, H., & Nagasawa, H. (2013). Novel Biological Activities of Allosamidins. Molecules, 18(6), 6952-6968. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18066952




