Effect of Black Grape Juice against Heart Damage from Acute Gamma TBI in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phenolics, Flavonoids and, Condensed Tannins Contents and, HPLC-DAD Analysis in Black Grape Juice (BGJ)
| BGJ compounds | Composition mg/L | LOD mg/mL | LOQ mg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total phenolics (GE) | 223.14 ± 0.005 | - | - |
| Total flavonoids (Quer) | 180.45 ± 0.011 | - | - |
| Total tannin (Cat) | 154.09 ± 0.017 | - | - |
| Gallic acid | 8.43 ± 0.06a | 0.017 | 0.056 |
| Catechin | 5.17 ± 0.09b | 0.032 | 0.104 |
| Resveratrol | 31.28 ± 0.04c | 0.009 | 0.030 |
| Caffeic acid | 18.15 ± 0.03d | 0.013 | 0.041 |
| Ellagic acid | 8.03 ± 0.05a | 0.028 | 0.093 |
| Quercetin | 18.67 ± 0.12d | 0.015 | 0.049 |
| Kaempferol | 8.71 ± 0.03a | 0.008 | 0.026 |
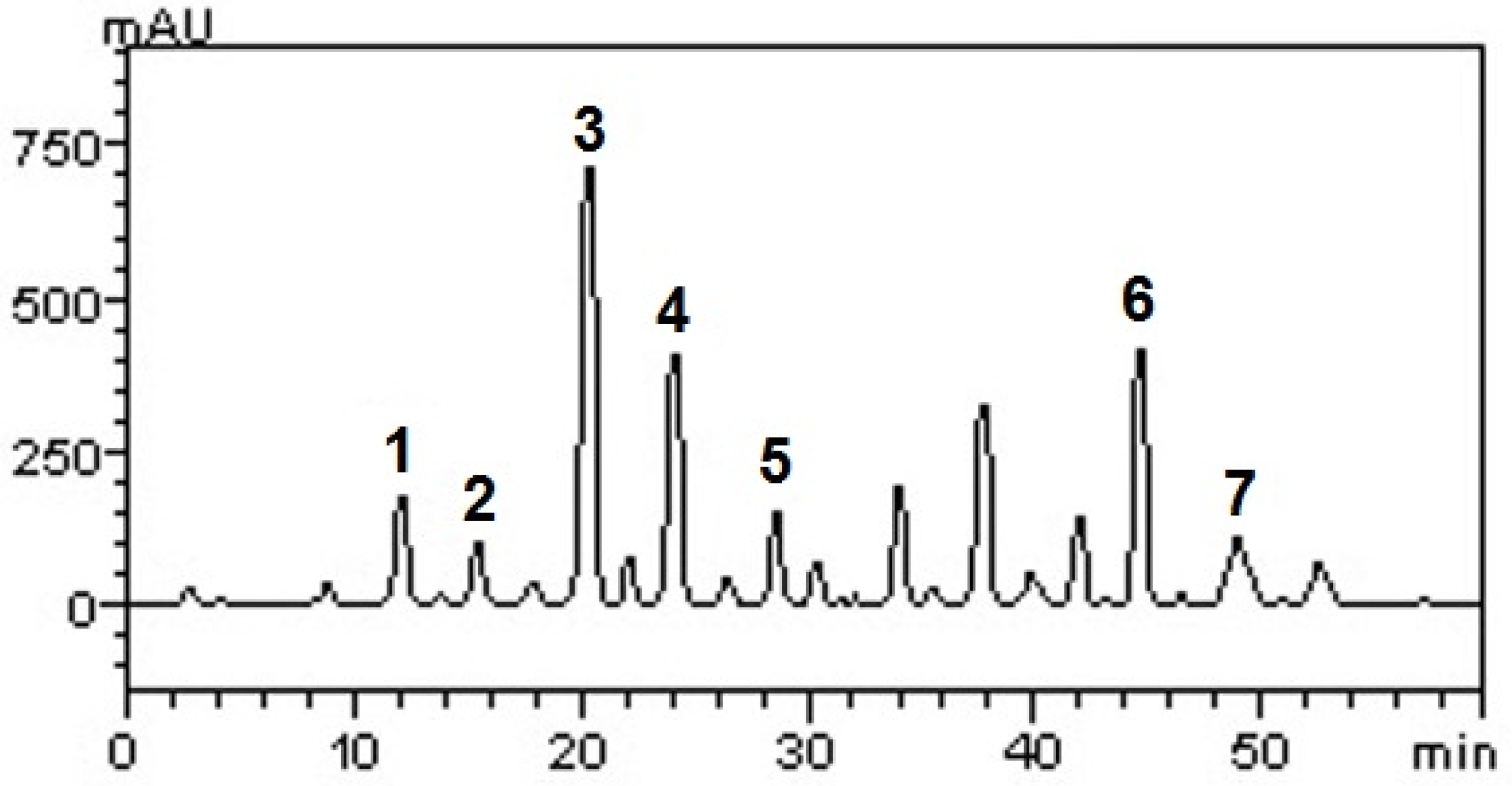
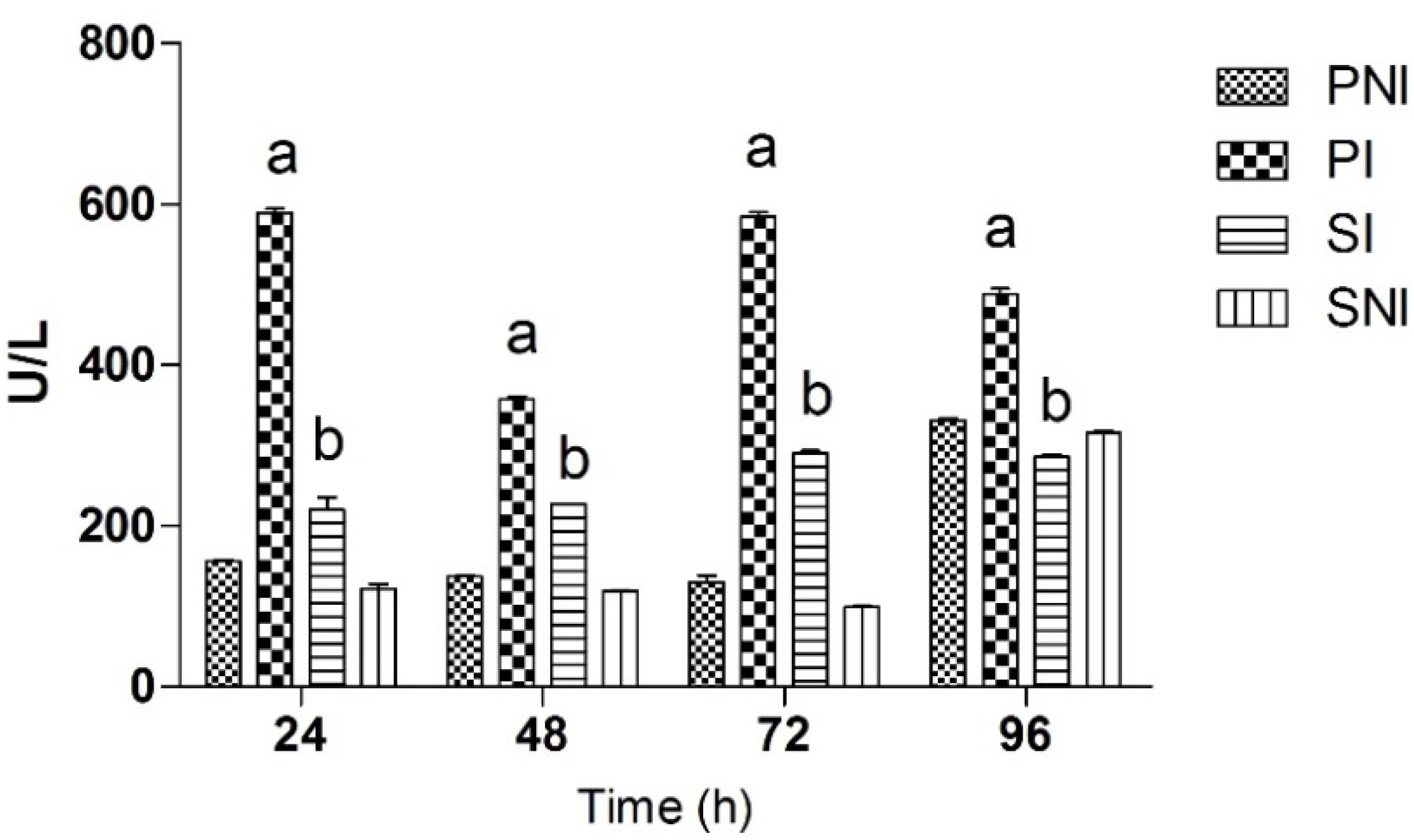
2.2. LDH Levels
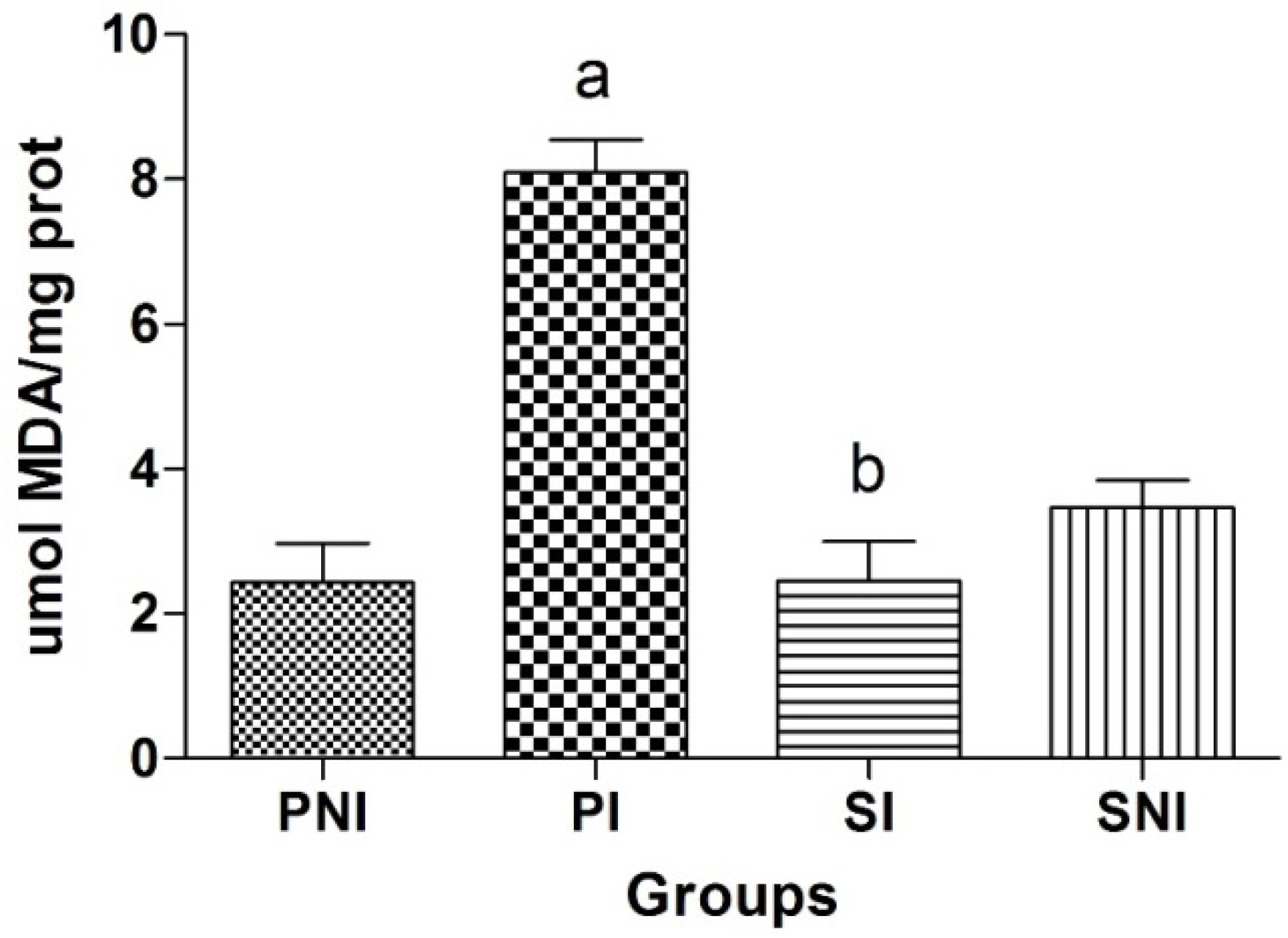
2.3. Lipid Peroxidation on Heart
3. Discussion
4. Experimental
4.1. Black Grape Juice (BGJ) and Placebo Solution
4.2. Colorimetric Assays
4.2.1. Determination of Total Phenolics
4.2.2. Determination of Total Flavonoids
4.2.3. Determination of Condensed Tannins
4.3. High Performance Liquid Chromatography
4.3.1. Chemicals, Apparatus and General Procedures
4.3.2. Quantification of Compounds by HPLC-DAD
4.3.3. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
4.4. Animals and Whole Body Irradiation
4.5. Food and Drink
4.6. Blood Samples Collection and LDH Measurement
4.7. Lipid Peroxidation of Heart Tissue
4.8. Quantification of Heart Protein
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ende, M. Management of the acute radiation syndrome. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 141, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, B.; Tadmor, B.; Har-Kedar, I. Biological effects of ionizing radiation and acute radiation syndrome. Harefuah 1988, 115, 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, K.P. Cell membrane oxidative damage induced by gamma-radiation and apoptotic sensitivity. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2004, 23, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, W.L., Jr.; Gallagher, C.; Myhand, R.C.; Waselenko, J.K. Medical management of patients with multiple organ dysfunction arising from acute radiation syndrome. BJR Suppl. 2005, 27, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Waselenko, J.K.; MacVittie, T.J.; Blakely, W.F.; Pesik, N.; Wiley, A.L.; Dickerson, W.E.; Tsu, H.; Confer, D.L.; Coleman, C.N.; Seed, T.; et al. Medical management of the acute radiation syndrome: recommendations of the strategic national stockpile radiation working group. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, B.; Sies, H.; Boveris, A. Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol. Rev. 1979, 59, 527–605. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, A.J.; Higgns, C.D.; Smith, P.; Cunninghan, D.; Hancock, B.W.; Horwich, A.; Hoskn, P.J.; Lister, A.; Radford, J.A.; Rohatiner, A.Z.; Linch, D.C. Myocardial infarction mortality risk after treatment for Hodgkin disease: a collaborative British cohort study. Nat. Cancer. Inst. 2007, 99, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifshits, R.I.; Slobodin, V.B.; Iakushev, V.S.; Bochina, T.V.; Popov, G.K. Lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in the heart, liver and kidneys in experimental ischemia. Biull. Eksp. Biol. Med. 1972, 73, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, P.J.; White, E.L.; Pruitt, K.M.; Vesell, E.S. Lactate dehydrogenase isozymes. Turnover in rat heart, skeletal muscle, and liver. Biochemistry 1973, 12, 4034–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Takamori, Y.; Nishio, K. The effects of X-irradiation on lactate dehydrogenase isozymes in plasma and in various organs of mice. Rad. Res. 1970, 43, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyagarajan, P.; Vakil, U.K.; Sreenivasan, A. Distribution of lactic dehydrogenase in X-irradiated tissues. Environ. Physiol. Biochem. 1975, 5, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, E.R.; Piccoli, J.C.E; Cruz, I.B.M.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Garzo, E.; Marina, R.; Mauriz, J.L.; González, P.; Barrio, J.P. Radiomodifying effect of organic grape juice supplementation on hematological parameters and organ weight in whole-body X-irradiation in rats. Nutr. Hosp. 2009, 24, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Saada, H.N.; Said, U.Z.; Meky, N.H.; Abd El Azime, A.S. ape seed extract Vitis vinifera protects against radiation-induced oxidative damage and metabolic disorders in rats. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Jain, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Nagpal, R.; Puniya, M.; Tomar, R.; Singh, V.; Parkash, O.; Prasad, G.B.; Marotta, F.; Yadav, H. Biological and medicinal properties of grapes and their bioactive constituents: an update. J. Med. Food. 2009, 12, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, E.R.; Piccoli, J.C.E; Cruz, I.B.M.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Andrade, V.V.R.; González, P.; Bauermann, L.F.; Barrio, J.P. Effect of black grape juice intake on liver lipoperoxidation and body weight loss in whole body X-irradiated rats. J. Med. CBR Def. 2009, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, R.B.; Augusti, P.R.; Andrade, R.A.; Rother, F.C.; Rovani, B.T.; Quatrin, A.; Alves, N.M.; Emanuelli, T.; Bauermann, L.F. Black grape juice protects spleen from lipid oxidation induced by gamma radiation in rats. J. Food. Bichem. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y.; Weiss, J. Structural design principles for delivery of bioactive components in nutraceuticals and functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 577–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.; Andrade, E.R.; Soares, F.A.; Marina, R.; Barrio, J.P. Flavonoids como radioprotectores: evidencias y mecanismos de accíon. Fisiología 2011, 13, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Moon, C.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Jang, J.S.; Kee, S.; Kim, S.H. Modification of gamma-radiation response in mice by green tea polyphenols. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaput, J.; Ordovas, J.M.; Ferguson, L.; van Ommen, B.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Allen, L.; Ames, B.N.; Dawson, K.; German, B.; Krauss, R.; et al. The case for strategic international alliances to harness nutritional genomics for public and personal health. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Maliakal, P.; Lu, H.; Lee, M.J.; Yang, C.S. Urinary and plasma levels of resveratrol and quercetin in humans, mice, and rats after ingestion of pure compounds and grape juice. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2004, 52, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlachterman, A.; Valle, F.; Wall, K.M.; Azios, N.G.; Castillo, L.; Morell, L.; Washington, A.V.; Cubano, L.A.; Dharmawardhane, S.F. ombined resveratrol, quercetin, and catechin treatment reduces breast tumor growth in a nude mouse model. Transl. Oncol. 2008, 1, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dani, C.; Oliboni, L.S.; Vanderlinde, R.; Pra, D.; Dias, J.F.; Yoneama, M.L.; Bonatto, D.; Salvador, M.; Henriques, J.A. Antioxidant activity and phenolic and mineral content of rose grape juice. J. Med. Food. 2009, 12, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Mandair, R.; Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, C. Grape seed extract induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells. Nutr. Cancer 2008, 60, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Anticancer and cancer chemopreventive potential of grape seed extract and other grape-based products. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1806S–1812S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Ramprasath, V.R.; Aluko, R.E.; Jones, P.J. Potential of resveratrol in anticancer and anti-inflammatory therapy. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llópiz, N.; Puiggròs, F.; Céspedes, E.; Arola, L.; Ardévol, A.; Bladé, C.; Salvadó, M.J. Antigenotoxic effect of grape seed procyanidin extract in Fao cells submitted to oxidative stress. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2004, 52, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, C.O.L.; Pasquali, M.A.; Oliveira, M.R.; Umezu, F.; Salvador, M.; Moreira, J.C.; Henriques, J.A. Intake of purple grape juice as a hepatoprotective agent in Wistar rats. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifert, W.R.; Abeywardena, M.Y. Cardioprotective actions of grape polyphenols. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, S. Principles of cancer treatment by radiotherapy. Suergery 2006, 24, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, H.H.; Tawfik, S.S. Early treatment of radiation-induced heart damage in rats by caffeic acid phenethyl ester. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 692, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messarah, M.; Saoudi, M.; Boumendjel, A.; Boulakoud, M.S.; Feki, A.E. Oxidative stress induced by thyroid dysfunction in rat erythrocytes and heart. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 31, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Milochevitch, C. Study of the antioxidant effect of a-tocopherolon low-density lipoprotein peroxidation induced at low and high g-radiation dose rates. Rad. Phys. Chem. 2005, 72, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.J.; Bakker, J. Basic taste, stimulant and other constituents of wines. In Wine Favour Chemistry; Blackwell Publishing Ltd: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 66–99. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, M.M.; Montagner, G.F.F.S.; Boligon, A.A.; Athayde, M.L.; Rocha, M.I.U.M.; Lera, J.P.B.; Belló, C.; da Cruz, I.B.M. Determination of polyphenol contents and antioxidant capacity of no-alcoholic red grape products (Vitis labrusca) from conventional and organics crops. Quim. Nova 2011, 34, 798–803. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, K.; Ji, C.-B.; Lu, X.-W.; Ni, Y.-H.; Gao, C.-L.; Chen, X.-H.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Gu, G.-X.; Guo, X.-R. Resveratrol attenuates radiation damage in Caenorhabditis elegans by preventing oxidative stress. J. Radiat. Res. 2010, 51, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.W.; Dieter, R.S.; Stone, C.K. A review of clinical relevant cardiac biochemical markers. WMJ 2002, 101, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, H.H.; Abo Nour, S. Biochemical and histopatological study of the protective effect of propionyl-L-carnitine against cardiotoxicity in rats. Egypt. J. Radiat. Sci. Appl. 2009, 22, 99–128. [Google Scholar]
- Carini, R.; Parola, M.; Dianzani, M.U.; Albano, E. Lipid peroxidation and hepatocyte death investigation of a possible mechanism of oxidative cell injur. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 663, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheij, M.; Ruiter, G.A.; Zerp, S.F.; van Blitterswijk, W.J.; Fuks, Z.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Bartelink, H. The role of the stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK/JNK) signaling pathway in radiation-induced apoptosis. Radiother. Oncol. 1998, 47, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, G.R.; Angeli, J.P.; Serpeloni, J.M.; Grotto, D.; Rocha, B.A.; Bastos, J.K.; Knasmüller, S.; Júnior, F.B. Quercetin protects human-derived liver cells against mercury-induced DNA-damage and alterations of the redox status. Mutat. Res. 2011, 726, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boligon, A.A.; Pereira, R.P.; Feltrin, A.C.; Machado, M.M.; Janovik, V.; Rocha, J.B.; Athayde, M.L. Antioxidant activities of flavonol derivatives from the leaves and stem bark of Scutia buxifolia Reiss. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6592–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woisky, R.G.; Salatino, A. Analysis of própolis: Some parameters and procedures for chemical quality control. J. Apic. Res. 1998, 37, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, M.; Asiedu, E.A.; Stuchbury, T.; Powell, A.A. Determination of lignin and tannin contents of cowpea seeds coats. Ann. Bot. 1995, 76, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdem, J.P.; Stefanello, S.T.; Boligon, A.A.; Wagner, C.; Kade, I.J.; Pereira, R.P.; Preste, A.S.; Roos, D.H.; Waczuk, E.P.; Appel, A.S.; Athayde, M.L.; Souza, D.O.; Rocha, J.B.T. In vitro antioxidant activity of stem bark of Trichilia catigua Adr. Juss. Acta Pharm. 2012, 62, 371–382. [Google Scholar]
- Boligon, A.A.; Sagrillo, M.R.; Machado, L.F.; Filho, O.S.; Machado, M.M.; da Cruz, I.B.M.; Athayde, M.L. Potective effects of extracts and flavonoids isolated from Scutia buxifolia Reissek against chromosome damage in human lymphocytes exposed to hydrogen peroxide. Molecules 2012, 17, 5757–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the black grape juice are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
De Freitas, R.B.; Boligon, A.A.; Rovani, B.T.; Piana, M.; De Brum, T.F.; Da Silva Jesus, R.; Rother, F.C.; Alves, N.M.; Teixeira da Rocha, J.B.; Athayde, M.L.; et al. Effect of Black Grape Juice against Heart Damage from Acute Gamma TBI in Rats. Molecules 2013, 18, 12154-12167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012154
De Freitas RB, Boligon AA, Rovani BT, Piana M, De Brum TF, Da Silva Jesus R, Rother FC, Alves NM, Teixeira da Rocha JB, Athayde ML, et al. Effect of Black Grape Juice against Heart Damage from Acute Gamma TBI in Rats. Molecules. 2013; 18(10):12154-12167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012154
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Freitas, Robson Borba, Aline Augusti Boligon, Bruno Tomazele Rovani, Mariana Piana, Thiele Faccim De Brum, Roberta Da Silva Jesus, Fagner Chagas Rother, Nelson Mendes Alves, João Batista Teixeira da Rocha, Margareth Linde Athayde, and et al. 2013. "Effect of Black Grape Juice against Heart Damage from Acute Gamma TBI in Rats" Molecules 18, no. 10: 12154-12167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012154
APA StyleDe Freitas, R. B., Boligon, A. A., Rovani, B. T., Piana, M., De Brum, T. F., Da Silva Jesus, R., Rother, F. C., Alves, N. M., Teixeira da Rocha, J. B., Athayde, M. L., Barrio, J. P., De Andrade, E. R., & De Freitas Bauerman, L. (2013). Effect of Black Grape Juice against Heart Damage from Acute Gamma TBI in Rats. Molecules, 18(10), 12154-12167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules181012154




