Biodegradable Polymers for Microencapsulation of Drugs
Abstract
:Introduction
Techniques of Microparticle Preparation
Emulsion-solvent evaporation/extraction methods
Single emulsion method
Double emulsion method
Phase separation
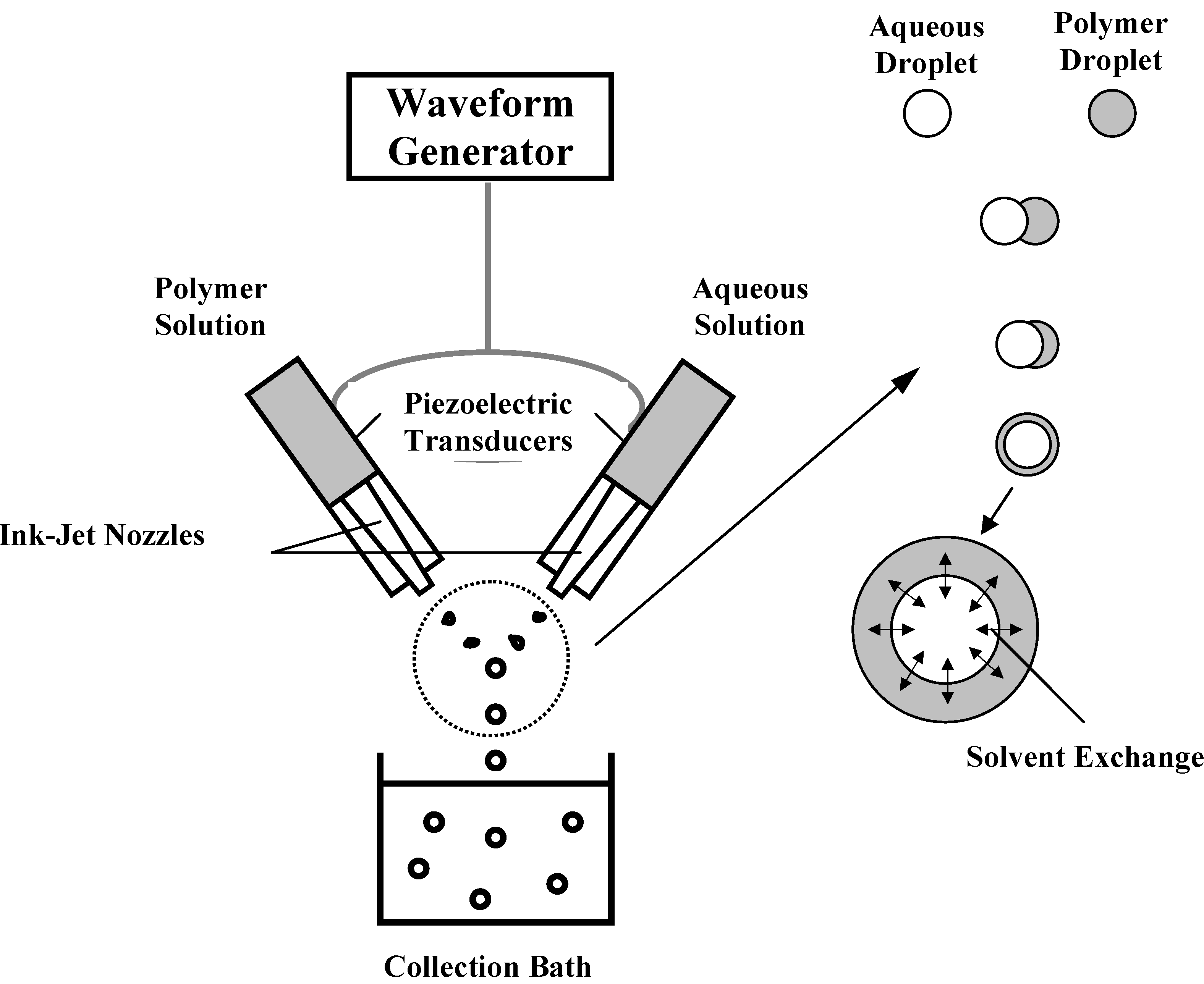
Spray drying
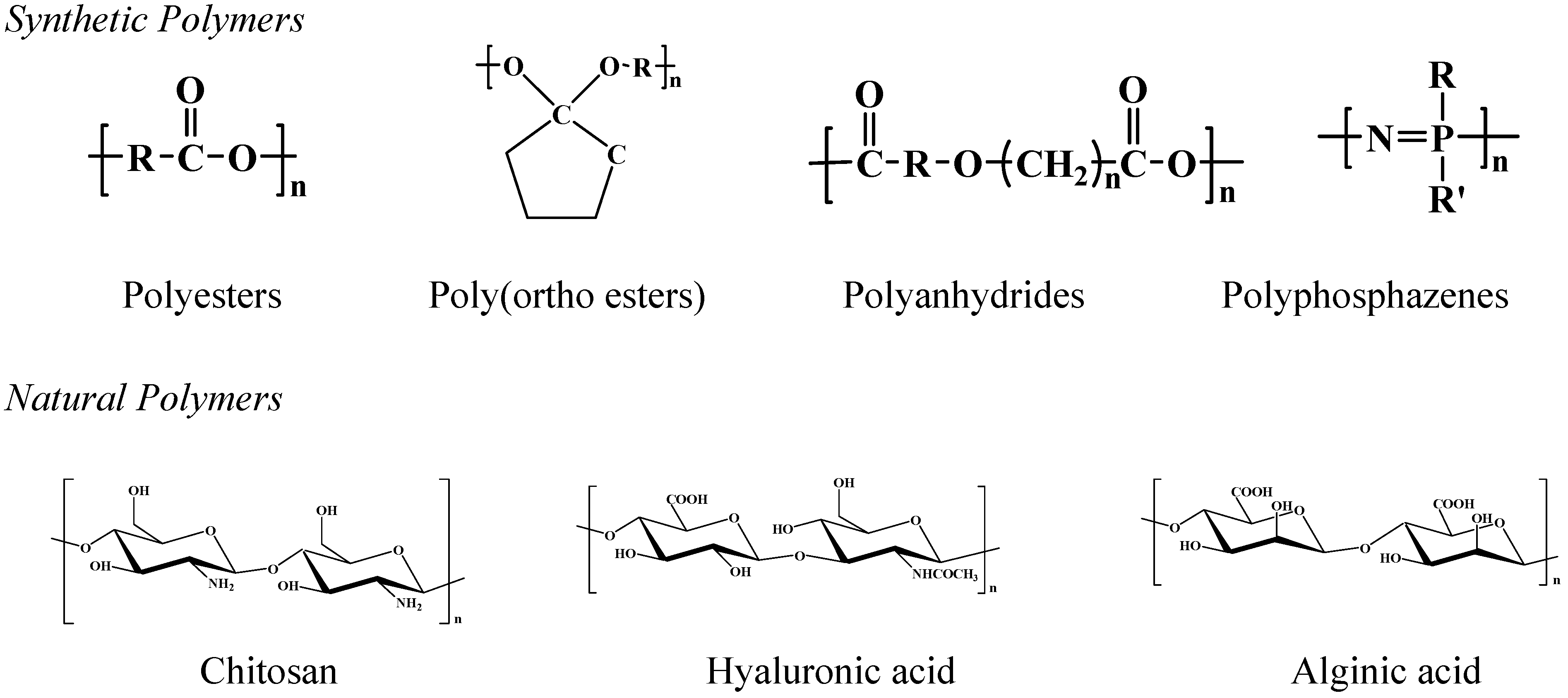
Biodegradable Polymers for Microparticles
Polyesters
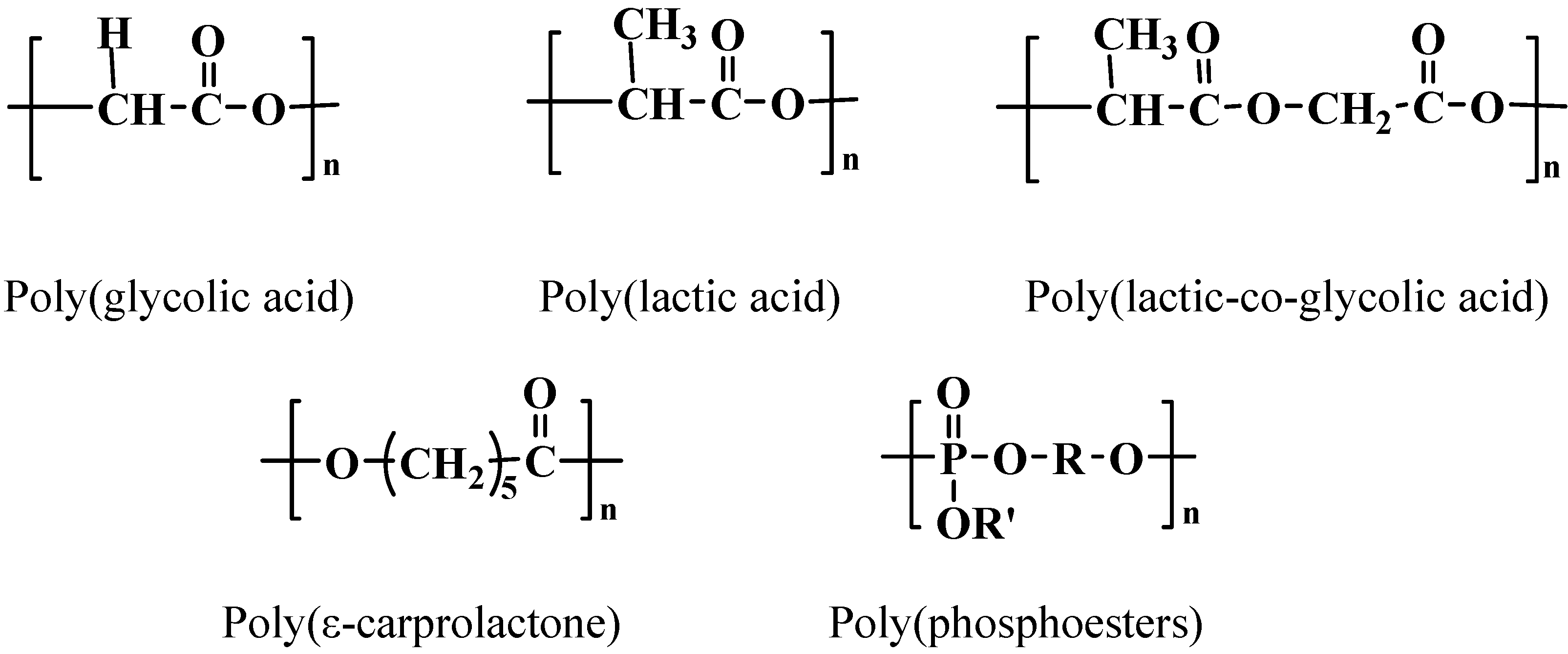
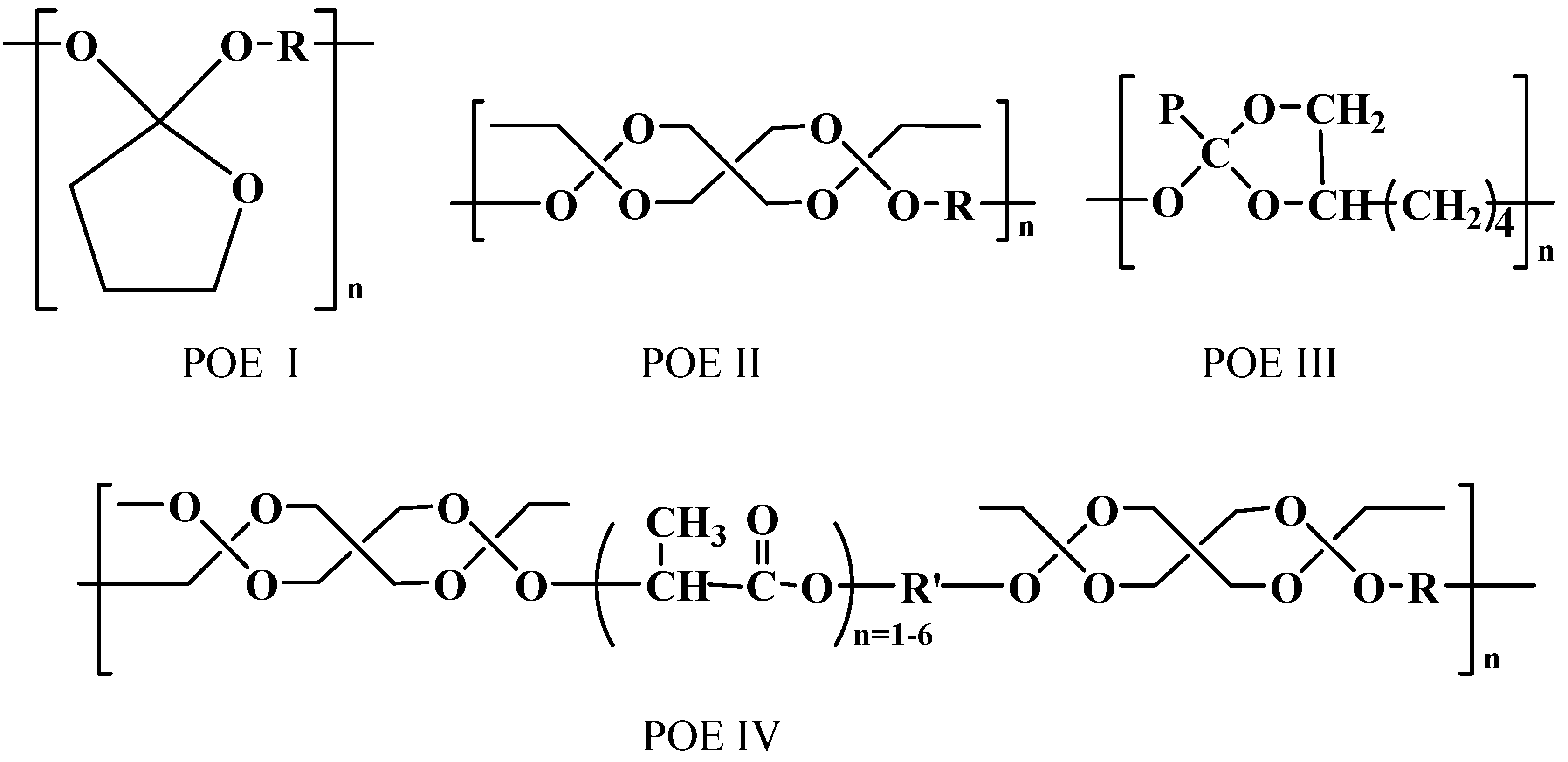
Poly(ortho esters)
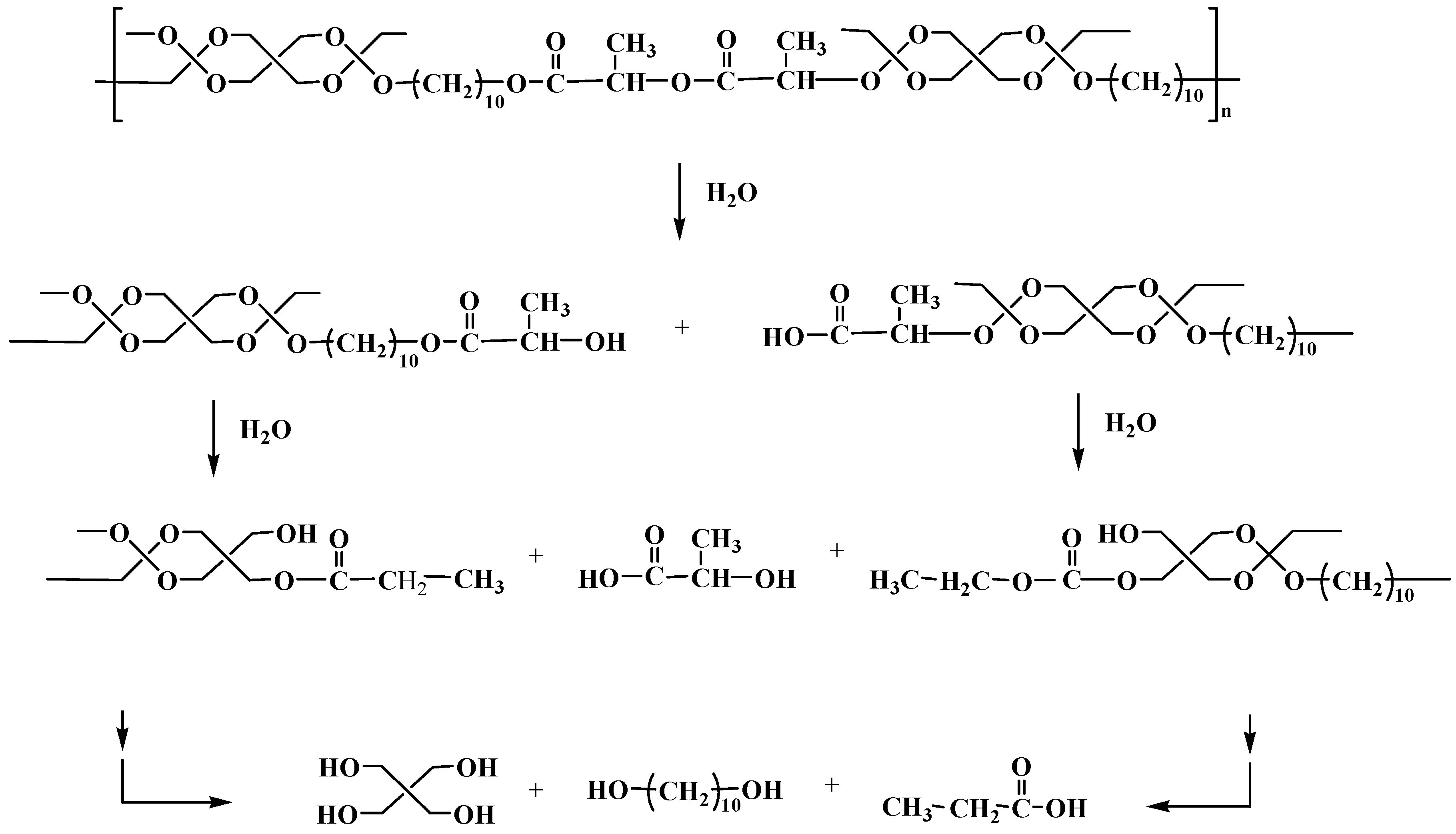
Polyanhydrides
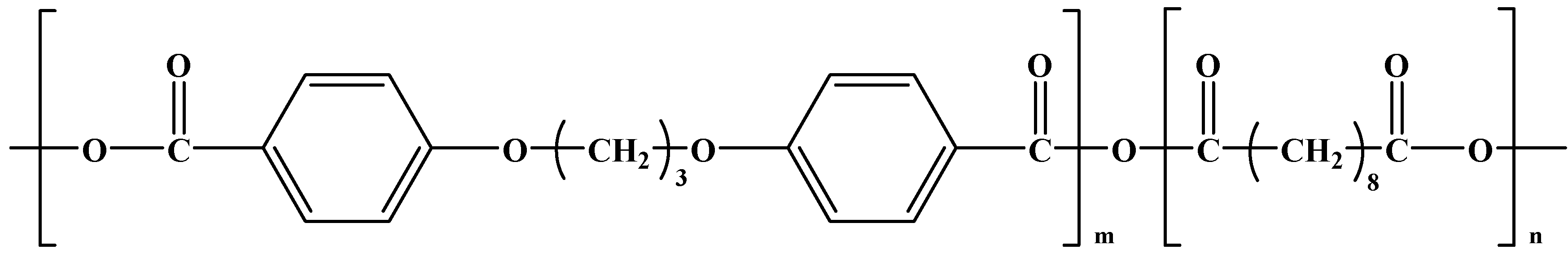
Polyphosphazenes
Natural polymers
Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Pekarek, K. J.; Jacob, J. S.; Mathiowitz, E. Double-walled polymer microspheres for controlled drug release. Nature 1994, 367, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.; Bae, Y. H.; Lee, D. S.; Kim, S. W. Biodegradable block copolymers as injectable drug-delivery systems. Nature 1997, 388, 860–862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulbrich, K.; Pechar, M.; Strohalm, J.; Subr, V.; Rihova, B. Synthesis of biodegradable polymers for controlled drug release. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 831, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hejazi, R.; Amiji, M. Chitosan-based gastrointestinal delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Mao, H. Q.; Leong, K. W. Polyphosphoesters in drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicek, H.; Tuncel, A.; Tuncel, M.; Piskin, E. Degradation and drug release characteristics of monosize polyethylcyanoacrylate microspheres. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1995, 6, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, F. L.; Lin, Y. M.; Wu, Y. B.; Shyu, S. S.; Tsai, Y. H. Chitin/PLGA blend microspheres as a biodegradable drug-delivery system: phase-separation, degradation and release behavior. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3257–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chu, C. C. In vitro release behavior of insulin from biodegradable hybrid hydrogel networks of polysaccharide and synthetic biodegradable polyester. J. Biomater. Appl. 2002, 16, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abraham, G. A.; Gallardo, A.; San Roman, J.; Fernandez-Mayoralas, A.; Zurita, M.; Vaquero, J. Polymeric matrices based on graft copolymers of PCL onto acrylic backbones for releasing antitumoral drugs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 64A, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandrelli, L.; De Rosa, G.; Errico, M. E.; La Rotonda, M. I.; Laurienzo, P.; Malinconico, M.; Oliva, A.; Quaglia, F. Novel graft PLLA-based copolymers: potential of their application to particle technology. J Biomed Mater Res 2002, 62, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Allen, C. Polymer-drug compatibility: a guide to the development of delivery systems for the anticancer agent, ellipticine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, B. H.; Lee, D. J. Slow release of drug through deformed coating film: effects of morphology and drug diffusivity in the coating film. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 1478–1496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tunon, A.; Grasjo, J.; Alderborn, G. Effect of intragranular porosity on compression behaviour of and drug release from reservoir pellets. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 19, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulzele, S. V.; Satturwar, P. M.; Kasliwal, R. H.; Dorle, A. K. Preparation and evaluation of microcapsules using polymerized rosin as a novel wall forming material. J. Microencapsul. 2004, 21, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, R. A. The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2475–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkland, C.; King, M.; Cox, A.; Kim, K.; Pack, D. W. Precise control of PLG microsphere size provides enhanced control of drug release rate. J. Control. Release 2002, 82, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felder Ch, B.; Blanco-Prieto, M. J.; Heizmann, J.; Merkle, H. P.; Gander, B. Ultrasonic atomization and subsequent polymer desolvation for peptide and protein microencapsulation into biodegradable polyesters. J. Microencapsul. 2003, 20, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyoyama, S.; Shiomori, K.; Kawano, Y.; Hatate, Y. Preparation of microcapsules and control of their morphology. J. Microencapsul. 2003, 20, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V. R.; Trehan, A. Biodegradable microspheres for protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2003, 90, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V. R.; Goyal, V.; Bhinge, J. R.; Mittal, B. R.; Trehan, A. Diagnostic microspheres: an overview. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 2003, 20, 431–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chua, K. M.; Wang, C. H. Stabilization and encapsulation of human immunoglobulin G into biodegradable microspheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 271, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kissel, T.; Li, Y.; Unger, F. ABA-triblock copolymers from biodegradable polyester A-blocks and hydrophilic poly(ethylene oxide) B-blocks as a candidate for in situ forming hydrogel delivery systems for proteins. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 99–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tabata, Y.; Gutta, S.; Langer, R. Controlled delivery systems for proteins using polyanhydride microspheres. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipper, M. J.; Shen, E.; Determan, A.; Narasimhan, B. Design of an injectable system based on bioerodible polyanhydride microspheres for sustained drug delivery. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4405–4412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y. H.; Vasavada, R. C. Studies on microencapsulation of 5-fluorouracil with poly(ortho ester) polymers. J. Microencapsul. 2000, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, J. S.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Ginsburg, E.; Widman, M.; Myers, A. In vitro characterization of polyorthoester microparticles containing bupivacaine. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2003, 8, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ge, Q.; Ting, D.; Nguyen, D.; Shen, H. R.; Chen, J.; Eisen, H. N.; Heller, J.; Langer, R.; Putnam, D. Molecularly engineered poly(ortho ester) microspheres for enhanced delivery of DNA vaccines. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Veronese, F. M.; Marsilio, F.; Lora, S.; Caliceti, P.; Passi, P.; Orsolini, P. Polyphosphazene membranes and microspheres in periodontal diseases and implant surgery. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, S.; Katti, D. S.; Laurencin, C. T. Biodegradable polyphosphazenes for drug delivery applications. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kas, H. S. Chitosan: properties, preparations and application to microparticulate systems. J. Microencapsul. 1997, 14, 689–711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felt, O.; Buri, P.; Gurny, R. Chitosan: a unique polysaccharide for drug delivery. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1998, 24, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, S.; Kishimoto, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Fukushima, M. Preparation and evaluation of o/w type emulsions containing antitumor prostaglandin. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2000, 45, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Toguchi, H. Biodegradable microspheres in drug delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 1995, 12, 1–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hombreiro Perez, M.; Zinutti, C.; Lamprecht, A.; Ubrich, N.; Astier, A.; Hoffman, M.; Bodmeier, R.; Maincent, P. The preparation and evaluation of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microparticles containing both a lipophilic and a hydrophilic drug. J. Control. Release. 2000, 65, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Passerini, N.; Craig, D. Q. Characterization of ciclosporin A loaded poly (D,L lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres using modulated temperature differential scanning calorimetry. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshady, R. Preparation of biodegradable microspheres and microcapsules: 2. Polylactides and related polyesters. J. Control. Release 1991, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasquillo, K. G.; Stanley, A. M.; Aponte-Carro, J. C.; De Jesus, P.; Costantino, H. R.; Bosques, C. J.; Griebenow, K. Non-aqueous encapsulation of excipient-stabilized spray-freeze dried BSA into poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres results in release of native protein. J. Control. Release 2001, 76, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Schwendeman, S. P. Stabilization of a model formalinized protein antigen encapsulated in poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-based microspheres. J Pharm Sci 2001, 90, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Schwendeman, S. P. Stabilization and controlled release of bovine serum albumin encapsulated in poly(D, L-lactide) and poly(ethylene glycol) microsphere blends. Pharm Res 2001, 18, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crotts, G.; Park, T. G. Protein delivery from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) biodegradable microspheres: release kinetics and stability issues. J. Microencapsul. 1998, 15, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okochi, H.; Nakano, M. Preparation and evaluation of w/o/w type emulsions containing vancomycin. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2000, 45, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mallarde, D.; Boutignon, F.; Moine, F.; Barre, E.; David, S.; Touchet, H.; Ferruti, P.; Deghenghi, R. PLGA-PEG microspheres of teverelix: influence of polymer type on microsphere characteristics and on teverelix in vitro release. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 261, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansen, P.; Moon, L.; Tamber, H.; Merkle, H. P.; Gander, B.; Sesardic, D. Immunogenicity of single-dose diphtheria vaccines based on PLA/PLGA microspheres in guinea pigs. Vaccine 1999, 18, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J. P.; Tissier, B.; Benoit, J. P. Microencapsulation of peptide: a study of the phase separation of poly(D,L-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) copolymers 50/50 by silicone oil. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 49, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, J. M.; Busnel, J. P.; Benoit, J. P. Influence of average molecular weights of poly(DL-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) copolymers 50/50 on phase separation and in vitro drug release from microspheres. Pharm. Res. 1990, 7, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.; Basaran, O. A.; Park, K. A new process for making reservoir-type microcapsules using ink-jet technology and interfacial phase separation. J. Control. Release 2003, 93, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.; Chen, A. U.; Basaran, O. A.; Park, K. Solvent exchange method: a novel microencapsulation technique using dual microdispensers. In Pharm. Res.; 2004. (In press) [Google Scholar]
- Sah, H. Protein behavior at the water/methylene chloride interface. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H. K.; Park, T. G. Microencapsulation of human growth hormone within biodegradable polyester microspheres: protein aggregation stability and incomplete release mechanism. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 65, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murillo, M.; Gamazo, C.; Goni, M.; Irache, J.; Blanco-Prieto, M. Development of microparticles prepared by spray-drying as a vaccine delivery system against brucellosis. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Prieto, M. J.; Campanero, M. A.; Besseghir, K.; Heimgatner, F.; Gander, B. Importance of single or blended polymer types for controlled in vitro release and plasma levels of a somatostatin analogue entrapped in PLA/PLGA microspheres. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, P. A.; Klumb, L. A.; Herberger, J. D.; Nguyen, X. C.; Harrell, R. A.; Zordich, M. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microsphere formulations of darbepoetin alfa: spray drying is an alternative to encapsulation by spray-freeze drying. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, S.; Uda, Y.; Toguchi, H.; Ogawa, Y. Application of a spray drying technique in the production of TRH-containing injectable sustained-release microparticles of biodegradable polymers. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 1995, 49, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnson, O. L.; Jaworowicz, W.; Cleland, J. L.; Bailey, L.; Charnis, M.; Duenas, E.; Wu, C.; Shepard, D.; Magil, S.; Last, T.; Jones, A. J.; Putney, S. D. The stabilization and encapsulation of human growth hormone into biodegradable microspheres. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnson, O. L.; Cleland, J. L.; Lee, H. J.; Charnis, M.; Duenas, E.; Jaworowicz, W.; Shepard, D.; Shahzamani, A.; Jones, A. J.; Putney, S. D. A month-long effect from a single injection of microencapsulated human growth hormone. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bittner, B.; Morlock, M.; Koll, H.; Winter, G.; Kissel, T. Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres: influence of the encapsulation technique and polymer purity on microsphere characteristics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morlock, M.; Kissel, T.; Li, Y. X.; Koll, H.; Winter, G. Erythropoietin loaded microspheres prepared from biodegradable LPLG-PEO-LPLG triblock copolymers: protein stabilization and in-vitro release properties. J. Control. Release. 1998, 56, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Witschi, C.; Doelker, E. Influence of the microencapsulation method and peptide loading on poly(lactic acid) and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation during in vitro testing. J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jalil, R.; Nixon, J. R. Biodegradable poly(lactic acid) and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microcapsules: problems associated with preparative techniques and release properties. J. Microencapsul. 1990, 7, 297–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andrianov, A. K.; Payne, L. G. Polymeric carriers for oral uptake of microparticulates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 34, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sluzky, V.; Tamada, J. A.; Klibanov, A. M.; Langer, R. Kinetics of insulin aggregation in aqueous solutions upon agitation in the presence of hydrophobic surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1991, 88, 9377–9381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Youan, B. B.; Benoit, M. A.; Baras, B.; Gillard, J. Protein-loaded poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microparticles. I. Optimization of the preparation by (water-in-oil)-in water emulsion solvent evaporation. J. Microencapsul. 1999, 16, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V. R.; Bansal, K.; Kaushik, R.; Kumria, R.; Trehan, A. Poly-epsilon-caprolactone microspheres and nanospheres: an overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 278, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mao, H. Q.; Leong, K. W. A novel biodegradable gene carrier based on polyphosphoester. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9480–9481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yu, H.; Gao, S.; Ma, H. Q.; Leong, K. W.; Wang, S. Polyphosphoester microspheres for sustained release of biologically active nerve growth factor. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3765–3772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wan, A. C.; Xu, X.; Gao, S.; Mao, H. Q.; Leong, K. W.; Yu, H. A new nerve guide conduit material composed of a biodegradable poly(phosphoester). Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yee, W. C.; Hwang, P. Y.; Yu, H.; Wan, A. C.; Gao, S.; Boon, K. L.; Mao, H. Q.; Leong, K. W.; Wang, S. Peripheral nerve regeneration with sustained release of poly(phosphoester) microencapsulated nerve growth factor within nerve guide conduits. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2405–2412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heller, J. Poly(ortho esters). Adv. Polym. Sci. 1993, 107, 41–92. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, J.; Barr, J.; Ng, S. Y.; Shen, H. R.; Schwach-Abdellaoui, K.; Einmahl, S.; Rothen-Weinhold, A.; Gurny, R.; Emmahl, S. Poly(ortho esters) - their development and some recent applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heller, J.; Barr, J.; Ng, S. Y.; Abdellauoi, K. S.; Gurny, R. Poly(ortho esters): synthesis, characterization, properties and uses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 1015–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S. Y.; Heller, J. Synthesis and erosion studies of self-catalyzed poly(orthoester)s. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 770–772. [Google Scholar]
- Uhrich, K. E.; Cannizzaro, S. M.; Langer, R.; Shakesheff, K. M. Polymeric systems for controlled drug release. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 3181–3198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leong, K. W.; Kost, J.; Mathiowitz, E.; Langer, R. Polyanhydrides for controlled release of bioactive agents. Biomaterials 1986, 7, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leong, K. W.; D'Amore, P. D.; Marletta, M.; Langer, R. Bioerodible polyanhydrides as drug-carrier matrices. II. Biocompatibility and chemical reactivity. J Biomed Mater Res 1986, 20, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Langer, R. S.; Domb, A. J. Polyanhydrides: an overview. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 889–910. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katti, D. S.; Lakshmi, S.; Langer, R.; Laurencin, C. T. Toxicity, biodegradation and elimination of polyanhydrides. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dang, W.; Daviau, T.; Brem, H. Morphological characterization of polyanhydride biodegradable implant gliadel during in vitro and in vivo erosion using scanning electron microscopy. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allcock, H. R.; Kugel, R. L.; Valan, K. J. Synthesis of high polymeric alkoxy and aryloxy phosphonitriles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87, 4216–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crommen, J. H.; Schacht, E. H.; Mense, E. H. Biodegradable polymers. I. Synthesis of hydrolysis-sensitive poly[(organo)phosphazenes]. Biomaterials 1992, 13, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laurencin, C. T.; Koh, H. J.; Neenan, T. X.; Allcock, H. R.; Langer, R. Controlled release using a new bioerodible polyphosphazene matrix system. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1987, 21, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allcock, H. R.; Pucher, A. G. Polyphosphazenes with glucosyl and methyl amino, trifluoroethoxy, phenoxy, or (methoxyethoxy)ethoxy side groups. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Allcock, H. R.; Pucher, A. G.; Scopelianos, A. G. Synthesis of poly(organophosphazenes) with glycolic acid ester and lactic acid ester side groups: prototypes for new bioerodible polymers. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, S. Chitin and chitosan as novel biotechnological materials. Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 732–734. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J. H.; Cho, Y. W.; Chung, H.; Kwon, I. C.; Jeong, S. Y. Synthesis and characterization of sugar-bearing chitosan derivatives: aqueous solubility and biodegradability. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sashiwa, H.; Saimoto, H.; Shigemasa, Y.; Ogawa, R.; Tokura, S. Lysozyme susceptibility of partially deacetylated chitin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1990, 12, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, S.; Tsuchida, H.; Nagao, N. N-acetylation in chitosan and the rate of its enzymic hydrolysis. Biomaterials 1989, 10, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. E.; Park, J. H.; Cho, Y. W.; Chung, H.; Jeong, S. Y.; Lee, E. B.; Kwon, I. C. Porous chitosan scaffold containing microspheres loaded with transforming growth factor-beta1: implications for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2003, 91, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinha, V. R.; Singla, A. K.; Wadhawan, S.; Kaushik, R.; Kumria, R.; Bansal, K.; Dhawan, S. Chitosan microspheres as a potential carrier for drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 274, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jameela, S. R.; Kumary, T. V.; Lal, A. V.; Jayakrishnan, A. Progesterone-loaded chitosan microspheres: a long acting biodegradable controlled delivery system. J. Control. Release 1998, 52, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chandy, T.; Rao, G. H.; Wilson, R. F.; Das, G. S. Development of poly(Lactic acid)/chitosan co-matrix microspheres: controlled release of taxol-heparin for preventing restenosis. Drug. Deliv. 2001, 8, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J. E.; Kim, K. E.; Kwon, I. C.; Ahn, H. J.; Lee, S. H.; Cho, H.; Kim, H. J.; Seong, S. C.; Lee, M. C. Effects of the controlled-released TGF-beta 1 from chitosan microspheres on chondrocytes cultured in a collagen/chitosan/glycosaminoglycan scaffold. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4163–4173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, B. C.; Kim, J. Y.; Lee, J. H.; Chung, H. Y.; Park, J. W.; Roh, K. H.; Kim, G. U.; Kwon, I. C.; Jang, K. H.; Lee, D. S.; Park, N. W.; Kim, I. S. The bone regenerative effect of chitosan microsphere-encapsulated growth hormone on bony consolidation in mandibular distraction osteogenesis in a dog model. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2004, 15, 299–311, discussion 312-293. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J. H.; Kwon, S.; Nam, J. O.; Park, R. W.; Chung, H.; Seo, S. B.; Kim, I. S.; Kwon, I. C.; Jeong, S. Y. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on glycol chitosan bearing 5-beta-cholanic acid for RGD peptide delivery. J. Control. Release. 2004, 95, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2005 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Ye, M.; Park, K. Biodegradable Polymers for Microencapsulation of Drugs. Molecules 2005, 10, 146-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/10010146
Park J, Ye M, Park K. Biodegradable Polymers for Microencapsulation of Drugs. Molecules. 2005; 10(1):146-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/10010146
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, J., M. Ye, and K. Park. 2005. "Biodegradable Polymers for Microencapsulation of Drugs" Molecules 10, no. 1: 146-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/10010146
APA StylePark, J., Ye, M., & Park, K. (2005). Biodegradable Polymers for Microencapsulation of Drugs. Molecules, 10(1), 146-161. https://doi.org/10.3390/10010146



