Abstract
Titan’s haze is strongly suspected to be an HCN-derived polymer, but despite the first in situ measurements by the ESA-Huygens space probe, its chemical composition and formation process remain largely unknown. To investigate this question, we simulated the atmospheric haze formation process, experimentally. We synthesized analogues of Titan’s haze, named Titan tholins, in an irradiated N2–CH4 gas mixture, mimicking Titan’s upper atmosphere chemistry. HCN was monitored in situ in the gas phase simultaneously with the formation and evolution of the haze particles. We show that HCN is produced as long as the particles are absent, and is then progressively consumed when the particles appear and grow. This work highlights HCN as an effective precursor of Titan’s haze and confirms the HCN-derived polymer nature of the haze.
1. Introduction
Hydrogen cyanide, HCN, is acknowledged as a key-starting ingredient for RNA synthesis [,]. The complexity of RNA constrains its synthesis to a multi-step abiotic process [], where HCN is a central molecule in the synthesis of all of the different sub-systems composing RNA, except phosphates. Additionally, for molecules closer in size, HCN also participates in the formation of α-amino acids and hydroxy acids, through Strecker-cyanohydrin reactions [,], enabling the synthesis of nucleobases and amino acids for protein. These have been observed in irradiated interstellar analogue ices, by hydrogenation of HCN (reaction 1), as well as in meteorites, notably that of Murchison, by photochemical processes (reaction 2).
Reaction 1—Hydrogenation of HCN:
HCN + 2H2 → CNH3 (Methanimine)
CNH3 + HCN + 2H2O → C2NH5O2 (Glycine) + NH3
CNH3 + HCN + 2H2O → C2NH5O2 (Glycine) + NH3
Reaction 2:
CNH5 (Methylamine) + HCN → C2N2H4 (α-amino acids)
C2N2H4 + 2H2O → C2NH5O2 (Glycine) + NH3
C2N2H4 + 2H2O → C2NH5O2 (Glycine) + NH3
HCN is therefore of primary importance in prebiotic processes. An important question points towards the synthesis of this specific central prebiotic molecule. It requires harsh conditions involving extreme UV radiation or shocks []. An exogenous scenario, with HCN originating from meteoric impacts, is often considered because HCN is abundantly observed and produced in the interstellar medium. However, Titan, the largest moon of Saturn, hosts a thick nitrogen-based atmosphere, where HCN is also efficiently produced by endogenous atmospheric photochemistry. During its flyby close to Titan, the infrared spectrometer IRIS on board the Voyager 1 space probe detected nitriles, among them HCN, within Titan’s atmosphere [].
In Titan’s upper atmosphere, EUV photochemistry based on methane (CH4) and molecular nitrogen (N2) produces large amounts of atmospheric HCN in the upper atmosphere of Titan, with a mixing ratio of about ~10−3 between altitudes 700 and 1000 km [,] (and references therein). Production processes in reducing atmospheric conditions have been studied in detail. They involve the following reactions with contributions depending on the considered altitude:
with H2CN produced by the reaction between N(4S) and CH3, and N(4S) and CH3 directly produced by photolysis of N2 and CH4.
H2CN + H → HCN + H2
N(4S) + CH3 → HCN + H + H
Titan is moreover surrounded by an organic photochemical haze, which was probed by the DISR (Descent Imager/Spectral Radiomater), ISS (Imaging Science Subsystem), and UVIS (Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph) instruments onboard the Cassini/Huygens space mission [,]. The production of the first nanoparticles was found to begin in the upper atmosphere at ~1000 km of altitude []. Haze particles sediment slowly towards Titan’s surface over several years [] and are suspected to undergo chemical and microphysical evolution processes during their descent []. Their chemical composition has been studied by the Huygens space probe during its descent in Titan’s atmosphere in January 2005 []. HCN was found to be one of the main chemical signatures extracted from the aerosols after their pyrolysis and analysis by mass spectrometry. Laboratory experiments confirmed HCN’s possible contribution to Titan’s aerosols. Pyrolysis of Titan’s aerosol analogues, named Titan tholins, combined with GC-MS analyses identified HCN as a systematic pyrolytic fragment [,,]. Plasma erosion experiments studied in [] showed a release of HCN when tholins are exposed to N2–H2 plasma. High-resolution mass spectrometry similarly highlighted HCN as a repetitive unit in Titan tholins [,], but Titan tholins were also found to be more complex than pure HCN polymers [,]. This converging evidence points to a likely HCN polymer derivative structure for Titan’s aerosols, including a random production factor consistent with extra-terrestrial environments.
The aim of this work is to question this assumption and to investigate, in the laboratory, whether HCN is actually a gas phase precursor contributing to Titan’s aerosol formation. During the synthesis of Titan tholins, HCN was found as an abundant gas phase product [,]. In the present work, we simultaneously investigate the time evolution of HCN and the formation and growth of Titan tholins.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Simulation of Titan’s Upper Atmospheric Chemistry
The atmospheric chemistry occurring in Titan’s upper atmosphere was simulated with the PAMPRE experiment [,]. The reactor was composed of a cylindrical stainless-steel chamber measuring 40 cm in height and 30 cm in diameter. Before each experiment, the reactor was pumped down to 10−6 mbar. The reactor was then flowed at room temperature and at a total gas pressure of 0.9 ± 0.1 mbar, ensured by the addition of the 95–5% N2–CH4 reactive gas mixture flux at 10 sccm (standard cubic centimetres per minute). The gas mixture was permanently extracted from the chamber by a primary vane pump ensuring the experiments were conducted in an open system, similar to photochemistry occurring in natural atmospheres.
The energy was provided by a Radio-Frequency Capacitively Coupled Plasma generated in a gas mixture by a 13.56 MHz generator, with a 30 W incidence power. The electrons, going from one electrode to the other, induced a cascade of reactions involving the molecules of the reactive gas mixture. The energy distribution of the electrons was similar at first order to the energy distribution of solar photons, with a maximum at ~1–2 eV [,].
The electrodes were shaped as a cylindrical box, 13.7 cm in diameter and 5 cm in height. The top electode is a polarized grid, when de side and the bottom of the box are grounded. Both electrodes were grids: the top one in order to let a laminar shower-like gas flow pass through the “plasma box”, and the bottom one to let the tholins produced in the plasma be ejected from the plasma. The tholins were then deposited onto a glass vessel (or crystallizer) for further collection and ex situ analysis. After 54 h of plasma duration, 1.2 g of Titan’s tholins was collected.
A comparison between the experimental conditions and the environmental conditions in Titan’s ionosphere are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of the environmental conditions encountered in our experiment and in Titan’s ionosphere.
Since ion–molecule reaction rates are relatively insensitive to low temperatures [,], the lower temperature of Titan’s upper atmosphere (200 K instead of 293 K in the presented experiment) was not an issue in our case. Moreover, the choice to perform the experiment at room temperature avoided heterogeneous chemistry due to condensation effects, as pointed out by [].
The pressure of Titan’s upper atmosphere is not reproducible in the PAMPRE experiment. The higher pressure during the experiment induced a shorter mean free path for the molecules, whose main implication is faster kinetics, favouring termolecular reactions, which are not very present in Titan’s upper atmosphere. However, at a pressure lower than a few mbar, termolecular reactions are minimized and limited, and then taken into account in the interpretations.
The initial gas mixture injected was composed of 95% nitrogen and 5% methane. After consumption by methane reaction, the stationary CH4 rate decreased to 0.4% in the experiment (about 2% of N2 is dissociated).
The radiofrequency discharge, with a power of about 12 W coupled to the plasma (incident power of 30 W), induced electrons whose energy distribution is similar to the first-order Maxwellian energy distribution of solar photons, with a maximum at about 1.2 eV [].
2.2. Gas Phase Diagnosis with Mass Spectrometry
Neutrals produced by irradiation of the N2–CH4 gas mixture were detected in situ in the 1–200 u mass range with a mass resolution of 1 u by quadrupole mass spectrometry. A EQP 200 quadrupole mass spectrometer (Hiden Analytical, Warrington, United Kingdom) was thus coupled to the reactor through a 100 µm pinhole. A turbomolecular pump (Pfeiffer vacuum, Annecy, France) enabled a secondary vacuum of 10−9 mbar inside the MS chamber, and 10–8 mbar during neutrals extraction, avoiding secondary reactions in the ionization chamber of the mass spectrometer. Neutrals were ionized in the ionization chamber by electron impact at 70 eV. In all the spectra presented below, counts <10 cps correspond to background noise. Thus, the presented mass spectra show the direct signal registered without background subtraction. The experiments were performed three times to ensure repeatability.
2.3. Size and Morphology of Titan’s Tholins: SEM Analysis
The size and morphology of Titan’s tholins were analysed by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The instruments used were an environment SEM Quanta 200 from the FEI Company (Hillsboro, OR, USA) (×25 to ×10,000, with a LFD detector (Large Field Detector), a high voltage of 12.5 kV, and at 0.5 mbar) and a Field Emission Gun SEM LEO1530 from the GEMINI Company (New York City, NY, USA) (×1000 to ×40,000, with a high voltage of 2 kV, at 0.6 mbar). Scanning electron microscopy provides information on the structure of sample surfaces. Especially when secondary electrons are detected it provides a map of the surface according to the different electronic properties of the materials.
2.4. Chemical Analysis of Titan’s Tholins: Mid-infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared transmission spectroscopy was used to obtain information on the chemical composition of the sample, with a similar technique as in []. Titan’s tholins were conditioned for IR measurement as pressed pellets with a KBr matrix. A pressure of 5 tons was applied to form pellets of 0.17 g, 1.3 cm in diameter and about 0.5 mm in thickness. A mass-mixing ratio of 0.4% tholins–99.6% KBr thin grains is considered optimal for both mechanical solidity and IR transmission. KBr is completely transparent at IR wavelengths.
The sample pellet was put inside a reactor under vacuum with CaF2 windows and was inserted in the sample compartment of a Nicolet 6700 FTIR from Thermo Company (Waltham, MA, USA) The reactor including the sample pellet was then degassed at 80–100 °C under vacuum during 40 min to remove possible water traces adsorbed on the sample. The spectra were acquired by a DTGS detector (Thermo Company, Waltham, MA, USA) between 900 and 4000 cm−1, this range being limited by the CaF2 windows used on the FTIR and the reactor. We chose a spectral resolution of 2 cm−1, and averaged 250 scans. The width of the IR beam at the focal point was a few millimetres.
Transmission spectra were converted into absorption spectra by dividing by a reference spectrum obtained with a pure KBr pellet. The spectra were corrected from water and CO2 atmospheric contributions with the OMNIC software. Baseline was corrected with an adjusted polynomial function using two reference wavelength ranges where tholins do not absorb: 1990–2030 cm−1 and 3700–4000 cm−1.
3. Results
Titan tholins were synthesized, as nanometre to micrometre-size solid organic particles, in a gas phase, mimicking Titan’s upper atmospheric composition, with a 95–5% N2–CH4 initial gas mixture, consistent with Cassini-INMS (Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer) in situ measurements in the ionosphere of Titan []. Compared to previous work with this experiment in [] and [], the gas flow is decreased from 55 down to 10 standard cubic centimetres per minute (sccm) in order to increase the residence time of the reactive gas mixture by a factor of 5.5 (residence time of 28 s at 55 sccm, and 154 s at 10 sccm). The chemical growth of the solid particles is thus favoured, enabling to track simultaneously the formation and evolution of the particles and the co-evolution of the gas mixture composition.
3.1. Size and Morphology of Titan’s Tholins
To determine their morphology, in particular their growth (size), the tholins produced were analysed by scanning electron microscopy (Figure 1). The particles presented on the SEM pictures were formed with a longer residence time than those collected in previous studies performed at 55 sccm. At 55 sccm, [] observed only primary nanometer monomers, while we also observed agglomerates of these nanoparticles.. The longer residence time used in the present work therefore enables simulation of a higher growth stage, involving microphysics of the particles.
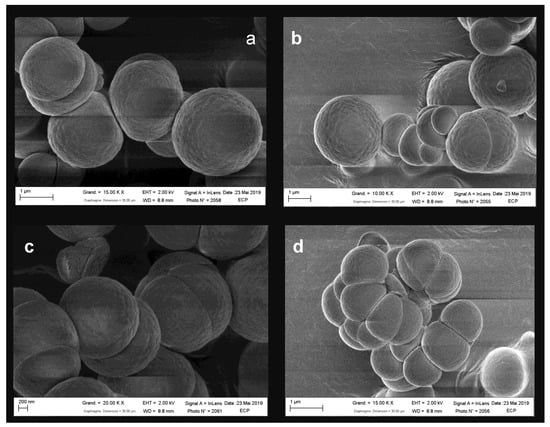
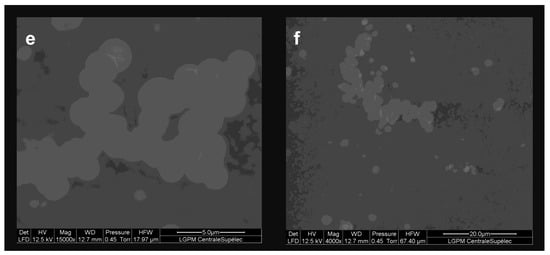
Figure 1.
Morphologies of Titan’s tholins obtained with a FEG SEM for the images (a–d), and an environment SEM for the images (e,f), at different magnifications. (a,b) show spherical monomers formed from the coagulation of primary monomers (evolution of aggregate). (c,d) present aggregated monomers. (e,f) show agglomerates of spherical grains and aggregates.
The obtained images were processed to determine the size distribution of the observed monomers (Figure 2a), as well as that of the formed agglomerates (lengths) of monomers and monomer aggregates (Figure 2b). Primary monomers, of a few hundred nanometres, coagulated and formed aggregates (Figure 1c,d). While continuing their growth in the plasma, these aggregates evolved until they formed spherical grains (Figure 1a,b) with diameters up to a few microns (Figure 2a). The monomers and aggregates residing in the plasma associated to form agglomerates (Figure 1e,f), with an average length of 5 to 10 μm (Figure 2b). The higher the residence time of tholins in the plasma, the more monomers composed the agglomerates, which can reach lengths up to about 60 μm (Figure 2b).
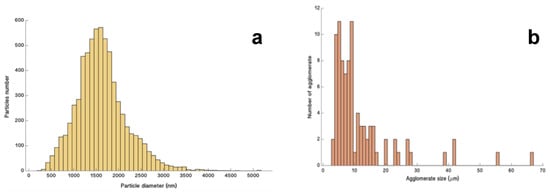
Figure 2.
Size distributions of Titan’s tholins made from 19 images captured with SEM, then processed using a semi-automated code written for this study, detecting circular shapes using the Hough transform, and thus determining the diameter of spherical particles (with a visual check). Distribution (a) accounts for 6692 monomers in total. The distribution (b) takes into account 90 agglomerates.
The micrometre-sized monomers observed in this study exhibited growth/formation by coagulation of nanometre primary monomers. The interaction between these formed monomers and the aggregates of primary monomers can lead to the formation of agglomerates. These experimental results are in agreement with the model presented by [], simulating the production and evolution of aerosols residing in Titan’s atmosphere. They predict the presence of an aggregated growth region below a spherical production and growth region in the upper atmosphere. In Titan’s atmosphere, the primary particles are first expected to be initiated from the collision of aromatics, formed by reactions between benzene (C6H6) and other radicals present in the gas phase. Then, they coagulate to form aggregates. These aggregates evolve by chemical interaction at their surface, with radical species in the gas phase, grow, and thus form spherical particles of larger size. One of the possible radical species cited was H2CN, a major precursor of HCN by reaction with atomic hydrogen, but no in situ measurement in Titan’s atmosphere can sustain this assertion yet.
3.2. Chemical Composition of Titan’s Tholins
An absorption spectrum in the range of mid-IR (1000–4000 cm−1) corresponding to Titan’s tholins is shown in Figure 3.
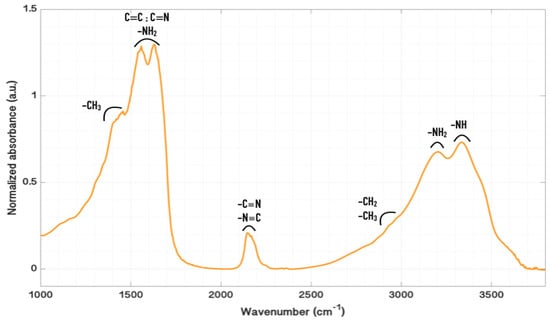
Figure 3.
Absorption spectrum in the mid-IR range (1000–4000 cm−1) corresponding to Titan’s tholins, realized with infrared transmission spectroscopy. The analysed tholin sample was pressed into a pellet with a KBr matrix.
Three absorption bands stand out on the mid-infrared absorption spectrum corresponding to Titan’s tholins. In the high wavenumbers from 2900 to 3500 cm−1, the intense bands at 3330 cm−1 and 3200 cm−1 correspond to the N–H stretching of secondary amines (R–NH–R) and primary amines (R–NH2) []. The 2970 cm−1 and 2930 cm−1 bands is attributed to the asymmetric stretching of –CH2 and –CH3 [].
The bands at 2240, 2170, and 2140 cm−1 are attributed to saturated aliphatic nitriles, conjugated nitriles stretching, unsaturated nitriles, and isocyanides. In the range from 1350 to 1650 cm−1, the different bands observed correspond to the aromatic, heteroaromatic, and aliphatic groups [,,]. The bands at 1560 cm−1 and 1630 cm−1 correspond to different functional groups, as aromatic or aliphatic –NH2, C=N, C=C, aromatics, or heteroaromatics, which are difficult to distinguish from each other. The band at 1450 cm−1 is attributed to the asymmetric bending of –CH3, included in the aliphatic groups.
The significance of N-containing bonds suggests an efficient incorporation of nitrogen in the organic particles. The nitrile and imine functions show multiple bonds between carbon and nitrogen, which would also agree with HCN as a possible precursor.
Other studies on Titan-type tholins show that these particles are structured from nitrogenous polycyclic aromatics in a matrix of carbon and nitrogen branched chain arrays, tightly linked to each other by N–H hydrogen bonds []. The prediction that HCN could promote the incorporation of nitrogen into particles, forming nitrogenous polycyclic aromatic compounds, is made by []. Aromatic groups could remove highly reactive hydrogen atoms in the form of hydrogen molecules through catalytic reactions on the aerosol surface [,,,]. The strong hydrogen bonding, caused by nitrogen-containing heteroaromatics, could be an important HCN gas adsorption site on the surface of tholins from the upper to the lower atmosphere [].
3.3. Time Evolution of the Gas Phase and Formation and Growth of Titan’s Tholins
The evolution of the gas phase N2–CH4, allowing the production of tholins, is observed by mass spectrometry, particularly for the masses corresponding to methane (m/z = 16) and hydrogen cyanide (m/z = 27). Their monitoring is shown in Figure 4. Four phases are highlighted in the experiment.
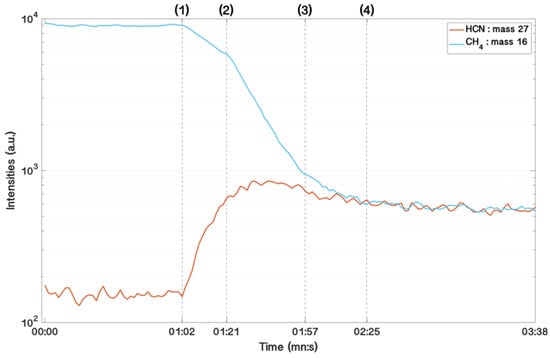
Figure 4.
Time evolution of the masses m/z 16 (CH4), 27 (HCN), obtained with a mass spectrometer. These species are formed from an initial gas mixture of N2–CH4 injected in the PAMPRE reactor. (1) At one minute, a plasma discharge is triggered, ionizes the injected gas mixture, and dissociates, in particular, the methane (first slope of decrease CH4). (2) Apparition of primary monomers in the plasma (second decay slope of CH4). Between (2) and (3), the primary monomers grow spherically down to a few hundred nanometres. (3) Formation of aggregates of primary monomers (third decay slope of CH4). Between (3) and (4): The aggregates evolve into micrometric monomers. After (4), the formed tholins exit the plasma and sediment at the bottom of the reactor.
Phase 1: During the ignition of the plasma discharge, the energy brought by the electrons of the plasma ionized and dissociated the methane, as well as the molecular nitrogen. The radicals and products formed from these two major species of Titan’s atmosphere combined, by a high number of reaction pathways, to form more complex organic compounds and nitriles, such as hydrogen cyanide. Indeed, the curve representing the temporal evolution of CH4 (Figure 4, blue curve) shows a decrease in intensity associated with the ignition of the plasma discharge, and this is represented by a decreasing linear slope in logarithmic scale for the curve of mass 16. In parallel, the curve corresponding to HCN (Figure 4, orange curve) shows a clear increase in its intensity.
Phase 2: 20 s after plasma ignition, a change in the methane slope (log-scale) was observed, with a more rapid consumption of methane. This change is an indicator of the appearance of the first nanoparticles in the discharge []. The appearance of these nanoparticles in the plasma is shown in Figure 5. Radicals and products formed behaved as nucleation sites, to allow the formation of nanoparticles (tholins). Wattieaux et al. [] showed that the formation of solid particles in the plasma induced an increase in the electron temperature, which consequently implies an acceleration of CH4 consumption. Simultaneously, with the methane’s larger consumption, HCN formation slowed down. At any time, the HCN concentration results from a competition between its source and its loss. As the source of HCN increased (coming from the methane consumption), the decline in HCN indicates that HCN began to be consumed in phase 2, when the nanoparticles were formed. This correlation between the HCN consumption and the aerosols appearance shows that HCN participates in the aerosol formation and growth.
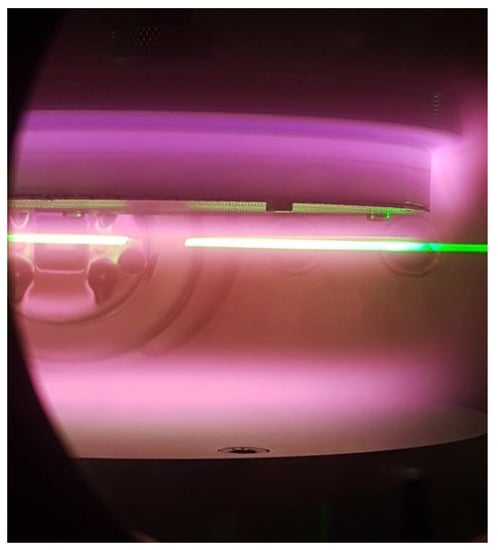
Figure 5.
Appearance of tholins in the N2–CH4 plasma, diffusing a laser light of wavelength 532 nm, during experiments carried out with the PAMPRE reactor.
Phase 3: A second change was observed in the methane’s slope (log scale). Methane consumption slowed down, indicating that the number of particles decreased in the discharge, and the agglomeration process occurred. During this step, the formation of HCN was even more decreased, in agreement with either the lower consumption of methane (decrease in the source) and/or a larger contribution of HCN to the particle growth during this step.
Phase 4: Finally, methane and hydrogen cyanide reached a plateau and remained stationary for the duration of tholin production.
4. Discussion
Analysis of the gas phase of the experiment, simulating Titan’s upper atmosphere (95% N2–5% CH4), using the PAMPRE dusty plasma reactor, shows a consumption of methane, as well as a net production of hydrogen cyanide HCN, after the ignition of the plasma discharge. As soon as the aerosols appeared and grew in the plasma (Figure 4 and Figure 5), a consumption of HCN present in the gas phase was observed. During this growth, the morphology of Titan tholins evolved (Figure 1). SEM images showed primary monomers coagulating to form aggregates, then continuing to grow to larger spherical grains. The micrometric aggregates and spherical grains formed can also coalesce to form even larger agglomerates. This growth may be due to a chemical reaction on their surface with gas phase radicals. In addition, the aggregates formed provide a larger reaction surface. The spectrum in the mid-infrared range (Figure 3) revealed the presence of bonds linked to cyanide, isocyanide, aromatic, heteroaromatic, and aliphatic moieties, in the organic polymers produced in this study. This nitrogenous structure may be due to the incorporation of HCN chemistry during the growth of tholins.
Our experimental work confirms the model’s predictions suggesting that aerosols are formed by HCN chemistry in Titan’s atmosphere, while undergoing a chemical-morphological evolution in different steps, and are partly realized by a reaction with hydrogen cyanide. In the case of Titan’s atmosphere, photochemical models have had difficulties reproducing the observed vertical distribution of HCN [,,] involving the stratospheric layer, where a decrease in the HCN ratio is measured. The reduction of this nitrile may be due to its transformation into complex nitrogen-containing molecules []. To represent the lower atmosphere, the photochemical model of [] took into account a loss of HCN induced by aerosol haze, present in large quantities in this atmospheric layer (main layer). In this lower atmosphere, the aerosol morphology predicted by the models in [] undergoes an evolution. The primary particles formed in the upper atmosphere coagulate into aggregates. These aggregates continue their growth towards larger spherical particles.
This formation of atmospheric HCN on Titan, and its efficient incorporation in Titan’s haze to produce large organic polymers can be interestingly compared to the sequential chemistry, synthesizing different subsystems of RNA, presented in the experiments of [,]. During the different stages of chemical growth of tholins, HCN interacts differently with the surfaces of increasingly complex molecules, such as its intervention in some ribose or amino acid synthesis for RNA (in abiotic environment). This work highlighted various phenomena involving the contribution of HCN in both steps of evolution of the nanoparticles: one, during the generation and growth of the first nanoparticles in the discharge, and two, when the nanoparticles begin to agglomerate. These processes depend on multiple parameters coupling dynamics, microphysics, and heterogeneous chemistry, which will need to be carefully decoupled in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.C. and Z.P.; methodology, Z.P., N.C., L.V., N.R., A.C., L.J., G.C.; formal analysis, Z.P.; investigation, Z.P.; data curation, Z.P.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.P. and N.C.; writing—review and editing, Z.P., N.C., A.C., L.J., G.C.; visualization, Z.P.; supervision, N.C.; project administration, N.C.; funding acquisition, N.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Research Council, grant number No. 636829.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
NC thanks the European Research Council for funding via the ERC PrimChem project (grant agreement No. 636829). We thank CNES for their financial support of the Besafe/stratopart project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Patel, B.H.; Percivalle, C.; Ritson, D.J.; Duffy, C.D.; Sutherland, J.D. Common origins of RNA, protein and lipid precursors in a cyanosulfidic protometabolism. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saladino, R.; Crestini, C.; Pino, S.; Costanzo, G.; Di Mauro, E. Formamide and the origin of life. Phys. Life Rev. 2012, 9, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powner, M.; Gerland, B.; Sutherland, J.D. Synthesis of activated pyrimidine ribonucleotides in prebiotically plausible conditions. Nature 2009, 459, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.L. The mechanism of synthesis of amino acids by electric discharges. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1957, 23, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, E.; Bada, J.; Schlesinger, G.; Miller, S. The chemical conditions on the parent body of the murchison meteorite: Some conclusions based on amino, hydroxy and dicarboxylic acids. Adv. Space Res. 1984, 4, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, R.; Conrath, B.; Flasar, F.M.; Kunde, V.; Maguire, W.; Pearl, J.; Pirraglia, J.; Samuelson, R.; Herath, L.; Allison, M.; et al. Infrared Observations of the Saturnian System from Voyager 1. Science 1981, 212, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebrard, E.; Dobrijevic, M.; Loison, J.; Bergeat, A.; Hickson, K.M. Neutral production of hydrogen isocyanide (HNC) and hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in Titan’s upper atmosphere. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 541, A21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, L.M.; Lellouch, E.; López-Moreno, J.J.; Rodrigo, R. Vertical distribution of Titan’s atmospheric neutral constituents. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 23261–23283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasko, M.; Doose, L.; Engel, S.; Dafoe, L.; West, R.; Lemmon, M.; Karkoschka, E.; See, C. A model of Titan’s aerosols based on measurements made inside the atmosphere. Planet. Space Sci. 2008, 56, 669–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.-C.; Yung, Y.L.; Shemansky, D.E. Photolytically Generated Aerosols in the Mesosphere and Thermosphere of Titan. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, L199–L202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H., Jr.; Young, D.T.; Cravens, T.E.; Coates, A.J.; Crary, F.J.; Magee, B.; Westlake, J. The Process of Tholin Formation in Titan’s Upper Atmosphere. Science 2007, 316, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavvas, P.; Sander, M.; Kraft, M.; Imanaka, H. Surface chemistry and particle shape: Processes for the evolution of aerosols in titan’s atmosphere. Astrophys. J. 2011, 728, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavvas, P.; Yelle, R.V.; Koskinen, T.; Bazin, A.; Vuitton, V.; Vigren, E.; Galand, M.; Wellbrock, A.; Coates, A.; Wahlund, J.-E.; et al. Aerosol growth in Titan’s ionosphere. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2729–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israël, G.; Szopa, C.; Raulin, F.; Cabane, M.; Niemann, H.B.; Atreya, S.K.; Bauer, S.; Brun, J.-F.; Chassefière, E.; Coll, P.; et al. Complex organic matter in Titan’s atmospheric aerosols from in situ pyrolysis and analysis. Nature 2005, 438, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisson, M.; Szopa, C.; Carrasco, N.; Buch, A.; Gautier, T. Titan’s organic aerosols: Molecular composition and structure of laboratory analogues inferred from pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry analysis. Icarus 2016, 277, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, B.; Sagan, C.; Thompson, W.; Arakawa, E.; Suits, F.; Callcott, T.; Williams, M.; Shrader, S.; Ogino, H.; Willingham, T.; et al. The organic aerosols of Titan. Adv. Space Res. 1984, 4, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, P.; Navarro-González, R.; Szopa, C.; Poch, O.; Ramírez, S.; Coscia, D.; Raulin, F.; Cabané, M.; Buch, A.; Israel, G. Can laboratory tholins mimic the chemistry producing Titan’s aerosols? A review in light of ACP experimental results. Planet. Space Sci. 2013, 77, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatain, A.; Carrasco, N.; Ruscassier, N.; Gautier, T.; Vettier, L.; Guaitella, O. Interaction dust–plasma in Titan’s ionosphere: An experimental simulation of aerosols erosion. Icarus 2020, 345, 113741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, J.; Carrasco, N.; Schmitz-Afonso, I.; Gautier, T.; Afonso, C. Comparison of soluble and insoluble organic matter in analogues of Titan’s aerosols. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 495, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernot, P.; Carrasco, N.; Thissen, R.; Schmitz-Afonso, I. Tholinomics—Chemical Analysis of Nitrogen-Rich Polymers. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, J.-Y.; Thissen, R.; Frisari, M.; Vuitton, V.; Quirico, É.; Orthous-Daunay, F.-R.; Dutuit, O.; Le Roy, L.; Fray, N.; Cottin, H.; et al. Compositional and structural investigation of HCN polymer through high resolution mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 354–355, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuitton, V.; Bonnet, J.-Y.; Frisari, M.; Thissen, R.; Quirico, E.; Dutuit, O.; Schmitt, B.; Le Roy, L.; Fray, N.; Cottin, H.; et al. Very high resolution mass spectrometry of HCN polymers and tholins. Faraday Discuss. 2010, 147, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, T.; Carrasco, N.; Buch, A.; Szopa, C.; Sciamma-O’Brien, E.; Cernogora, G. Nitrile gas chemistry in Titan’s atmosphere. Icarus 2011, 213, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, C.; Cernogora, G.; Boufendi, L.; Correia, J.J.; Coll, P. PAMPRE: A dusty plasma experiment for Titan’s tholins production and study. Planet. Space Sci. 2006, 54, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcouffe, G.; Cavarroc, M.; Cernogora, G.; Ouni, F.; Jolly, A.; Boufendi, L.; Szopa, C. Capacitively coupled plasma used to simulate Titan’s atmospheric chemistry. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.L.; Marques, L.; Pintassilgo, C.; Wattieaux, G.; Es-Sebbar, E.; Berndt, J.; Kovačević, E.; Carrasco, N.; Boufendi, L.; Cernogora, G. Capacitively coupled radio-frequency discharges in nitrogen at low pressures. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2012, 21, 045008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulchignoni, M.; Ferri, F.; Angrilli, F.; Ball, A.; Bar-Nun, A.; Barucci, M.A.; Bettanini, C.; Bianchini, G.; Borucki, W.; Colombatti, G.; et al. In situ measurements of the physical characteristics of Titan’s environment. Nature 2005, 438, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H.W., Jr.; Niemann, H.; Yelle, R.V.; Kasprzak, W.T.; Cravens, T.E.; Luhmann, J.G.; McNutt, R.L.; Ip, W.-H.; Gell, D.; De La Haye, V.; et al. Ion Neutral Mass Spectrometer Results from the First Flyby of Titan. Science 2005, 308, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anicich, V. An Index of the Literature for Bimolecular Gas Phase Cation-Molecule Reaction Kinetics; JPL Publication: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka, H.; Smith, M.A. EUV Photochemical Production of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Implications to EUV Photochemistry in Titan and Jovian Planets. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 11187–11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, A.; Carrasco, N.; Dahoo, P.-R.; Fleury, B.; Gautier, T.; Cernogora, G. Effect of the Synthesis Temperature on the Optical Indices of Organic Materials Produced by N2-CH4RF Plasma. Plasma Process. Polymers 2014, 11, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciamma-O’Brien, E.; Carrasco, N.; Szopa, C.; Buch, A.; Cernogora, G. Titan’s atmosphere: An optimal gas mixture for aerosol production? Icarus 2010, 209, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadamcik, E.; Renard, J.B.; Alcouffe, G.; Cernogora, G.; Levasseur-Regourd, A.C.; Szopa, C. Light scattering measurements on Titan’s aerosols analogues produced by a dusty plasma. Planet. Space Sci. 2009, 57, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanaka, H.; Khare, B.N.; Elsila, J.E.; Bakes, E.L.; McKay, C.P.; Cruikshank, D.P.; Sugita, S.; Matsui, T.; Zare, R.N. Laboratory experiments of Titan tholin formed in cold plasma at various pressures: Implications for nitrogen-containing polycyclic aromatic compounds in Titan haze. Icarus 2004, 168, 344–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, T.; Carrasco, N.; Mahjoub, A.; Vinatier, S.; Giuliani, A.; Szopa, C.; Anderson, C.M.; Correia, J.-J.; Dumas, P.; Cernogora, G. Mid- and far-infrared absorption spectroscopy of Titan’s aerosols analogues. Icarus 2012, 221, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yung, Y.L.; Allen, M.; Pinto, J.P. Photochemistry of the atmosphere of Titan—Comparison between model and observations. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1984, 55, 465–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtin, R.; Wagener, R.; McKay, C.P.; Caldwell, J.; Fricke, K.-H.; Raulin, F.; Bruston, P. UV spectroscopy of Titan’s atmosphere, planetary organic chemistry and prebiological synthesis: II. Interpretation of new IUE observations in the 220–335 nm Range. Icarus 1991, 90, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakes, E.L.O.; Lebonnois, S.; Bauschlicher, C.W.; McKay, C.P. The role of submicrometer aerosols and macromolecules in H2 formation in the titan haze. Icarus 2003, 161, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebonnois, S.; Bakes, E.; McKay, C.P. Atomic and molecular hydrogen budget in Titan’s atmosphere. Icarus 2003, 161, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattieaux, G.; Carrasco, N.; Henault, M.; Boufendi, L.; Cernogora, G. Transient phenomena during dust formation in a N2–CH4capacitively coupled plasma. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 015028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, L.; Bézard, B.; Marten, A.; Gautier, D.; Gérard, E.; Paubert, G.; Lecacheux, A. Stratospheric profile of HCN on Titan from millimeter observations. Icarus 1990, 85, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayata, T.; Arten, A.M.; Ezard, B.B.; Gautiera, D.; Owenb, T.; Matthews, H.E.; Paubertd, G. Millimeter and Submillimeter Heterodyne Observations of Titan: Retrieval of the Vertical Profile of HCN and the12C/13C Ratio. Icarus 1997, 126, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marten, A. New Millimeter Heterodyne Observations of Titan: Vertical Distributions of Nitriles HCN, HC3N, CH3CN, and the Isotopic Ratio 15N/14N in Its Atmosphere. Icarus 2002, 158, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, Y.; Imanaka, H.; Matsui, T.; Khare, B.N.; Bakes, E.L.; McKay, C.P.; Sugita, S. The role of organic haze in Titan’s atmospheric chemistry: I. Laboratory investigation on heterogeneous reaction of atomic hydrogen with Titan tholin. Icarus 2008, 194, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).