Entropy-Regularized Attention for Explainable Histological Classification with Convolutional and Hybrid Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A modular explainable architecture combining attention mechanisms and entropy-based regularization, compatible with convolutional and hybrid models and capable of enhancing the quality and relevance of visual explanations in histological image classification;
- A systematic evaluation of attention and entropy mechanisms across six neural network backbones and five histological datasets;
- A quantitative evaluation framework based on well-defined metrics to objectively assess the quality of visual explanations generated by deep learning models.
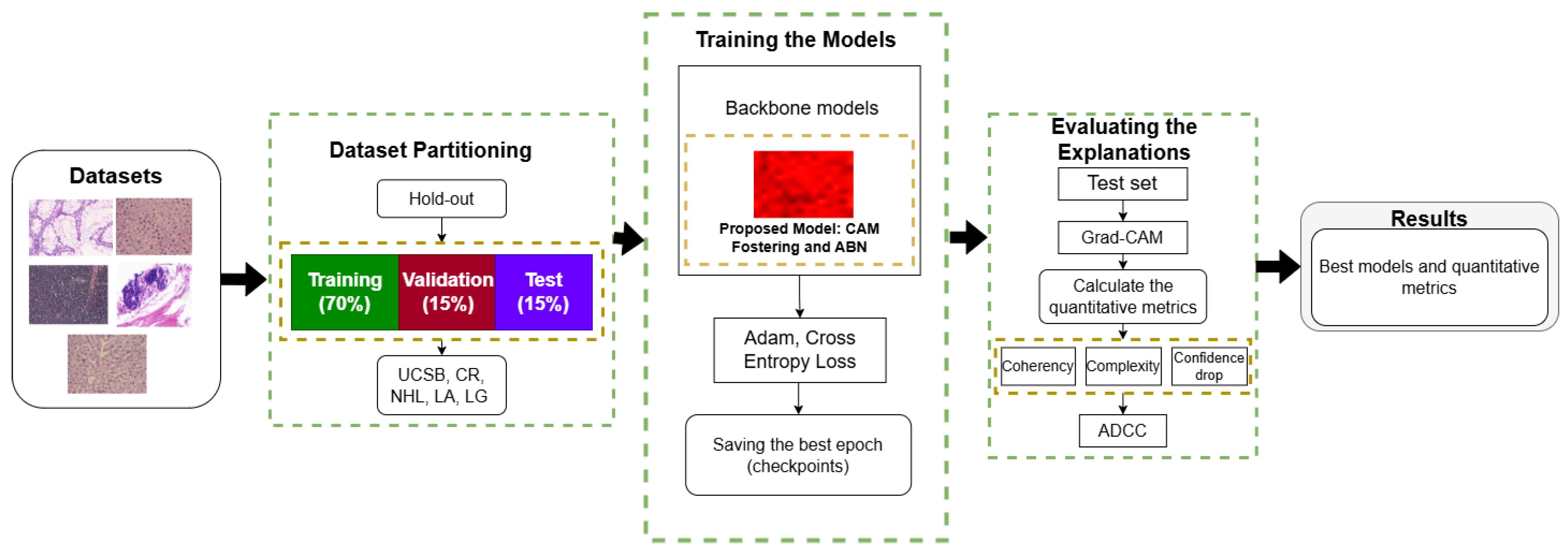
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Proposed Models
2.2.1. Feature Extractor
2.2.2. Attention Branch
2.2.3. Attention Mechanism
2.2.4. Perception Branch
2.2.5. CAM Fostering
2.3. Dataset Partitioning and Experimental Setup
2.4. Training Protocol and Optimization Strategy
2.5. Evaluation of Explanations
2.5.1. Coherence (CO)
2.5.2. Complexity (COM)
2.5.3. Confidence Drop (CD)
2.5.4. Average DCC (ADCC)
2.6. Software Packages and Execution Environment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Baseline Explainability Assessment
3.2. Evaluating Proposed Models
Summary of Explainability Results: Baseline Versus Proposed Models
3.3. Visual Explainability Analysis
3.4. Classification Performance: An Overview
4. Conclusions
Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| ViT | Vision Transformer |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| XAI | eXplainable Artificial Intelligence |
| ABN | Attention Branch Network |
| XCNN | eXplainable Neural Network |
| GAP | Global Average Pooling |
| CO | Coherency |
| COM | Complexity |
| CD | Confidence Drop |
| ADCC | Average DCC |
| Grad-CAM | Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping |
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Pereira, F., Burges, C., Bottou, L., Weinberger, K., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2023, arXiv:1706.03762. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Yue, W. An efficient medical image classification network based on multi-branch CNN, token grouping Transformer and mixer MLP. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 153, 111323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, K.; Dutta, M.K.; Pandey, J.P. EMViT-Net: A novel transformer-based network utilizing CNN and multilayer perceptron for the classification of environmental microorganisms using microscopic images. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, G.F.; Neves, L.A.; Lumini, A.; Martins, A.S.; Nascimento, M.Z.d. An ensemble of learned features and reshaping of fractal geometry-based descriptors for classification of histological images. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2024, 27, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenguam, J.J.; Longo, L.H.d.C.; Roberto, G.F.; Tosta, T.A.; de Faria, P.R.; Loyola, A.M.; Cardoso, S.V.; Silva, A.B.; do Nascimento, M.Z.; Neves, L.A. Ensemble learning-based solutions: An approach for evaluating multiple features in the context of H&E histological images. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1084. [Google Scholar]
- Rozendo, G.B.; do Nascimento, M.Z.; Roberto, G.F.; de Faria, P.R.; Silva, A.B.; Tosta, T.A.A.; Neves, L.A. Classification of non-Hodgkin lymphomas based on sample entropy signatures. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhn, J.; Krieghoff-Henning, E.; Jutzi, T.B.; von Kalle, C.; Utikal, J.S.; Meier, F.; Gellrich, F.F.; Hobelsberger, S.; Hauschild, A.; Schlager, J.G.; et al. Combining CNN-based histologic whole slide image analysis and patient data to improve skin cancer classification. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihabuddin, A.R.; Beevi, S. Multi CNN based automatic detection of mitotic nuclei in breast histopathological images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 158, 106815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, S.; Pramanik, P.; Sarkar, R. Gamma function based ensemble of CNN models for breast cancer detection in histopathology images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb-prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbs, J.L.; Mueller, J.L.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Shin, D.; Kuerer, H.; Yang, W.; Ramanujam, N.; Richards-Kortum, R. Micro-anatomical quantitative optical imaging: Toward automated assessment of breast tissues. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, C.I.; do Nascimento, M.Z.; Roberto, G.F.; Tosta, T.A.; Martins, A.S.; Neves, L.A. Hybrid models for classifying histological images: An association of deep features by transfer learning with ensemble classifier. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 21929–21952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.L.; Hua, B.; Tong, K.; Li, X.; Luo, J.L.; Yang, H.; Ding, J.R. EL-CNN: An enhanced lightweight classification method for colorectal cancer histopathological images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100, 106933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, M.; Chen, S.; Mu, B. An adaptive feature fusion framework of CNN and GNN for histopathology images classification. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 123, 110186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta Legorburu, A.; Bohoyo Bengoetxea, J.; Gracia, C.; Ferreres, J.C.; Bella-Cueto, M.R.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J. Automatic discrimination between neuroendocrine carcinomas and grade 3 neuroendocrine tumors by deep learning of H&E images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 184, 109443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, R.J.R.; Junior, G.B.; da Silva, I.F.S.; da Costa Oliveira, R.M.G. HistAttentionNAS: A CNN built via NAS for Penile Cancer Diagnosis using Histopathological Images. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2025, 256, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cen, M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.S. Improving feature extraction from histopathological images through a fine-tuning ImageNet model. J. Pathol. Inform. 2022, 13, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szandała, T. Unlocking the black box of CNNs: Visualising the decision-making process with PRISM. Inf. Sci. 2023, 642, 119162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, M.; Rahman, M.; Debnath, T. From black box to clarity: Strategies for effective AI informed consent in healthcare. Artif. Intell. Med. 2025, 167, 103169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Uszkoreit, H.; Du, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, J. Explainable AI: A Brief Survey on History, Research Areas, Approaches and Challenges. In Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing, Proceedings of the 8th CCF International Conference, NLPCC 2019, Dunhuang, China, 9–14 October 2019; Proceedings, Part II; Tang, J., Kan, M.Y., Zhao, D., Li, S., Zan, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 563–574. [Google Scholar]
- Rozendo, G.B.; Garcia, B.L.d.O.; Borgue, V.A.T.; Lumini, A.; Tosta, T.A.A.; Nascimento, M.Z.d.; Neves, L.A. Data Augmentation in Histopathological Classification: An Analysis Exploring GANs with XAI and Vision Transformers. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, L.; Brcic, M.; Cabitza, F.; Choi, J.; Confalonieri, R.; Ser, J.D.; Guidotti, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Herrera, F.; Holzinger, A.; et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) 2.0: A manifesto of open challenges and interdisciplinary research directions. Inf. Fusion 2024, 106, 102301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.M.C.; Neves, L.A.; Longo, L.H.d.C.; Rozendo, G.B.; Roberto, G.F.; Tosta, T.A.A.; de Faria, P.R.; Loyola, A.M.; Cardoso, S.V.; Silva, A.B.; et al. Exploring DeepDream and XAI representations for classifying histological images. SN Comput. Sci. 2024, 5, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abnar, S.; Zuidema, W. Quantifying Attention Flow in Transformers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.00928. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.00928 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Iglesias, G.; Menendez, H.; Talavera, E. Improving explanations for medical X-ray diagnosis combining variational autoencoders and adversarial machine learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 188, 109857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, H.; Oladimeji, O.; McLoughlin, I.; Tormey, D.; Booth, T.C.; Unnikrishnan, S. An eXplainable deep learning model for multi-modal MRI grading of IDH-mutant astrocytomas. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukahara, T.; Hirakawa, T.; Yamashita, T.; Fujiyoshi, H. Improving reliability of attention branch network by introducing uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1536–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, P.; Lumini, A.; Cardozo Medalha, G.; Freire Roberto, G.; Rozendo, G.; Cansian, A.; Tosta, T.; do Nascimento, M.Z.; Neves, L. Improving Explainability of the Attention Branch Network with CAM Fostering Techniques in the Context of Histological Images. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems—Volume 1: ICEIS, INSTICC, SciTePress, Angers, France, 28–30 April 2024; pp. 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Hirakawa, T.; Yamashita, T.; Fujiyoshi, H. Attention Branch Network: Learning of Attention Mechanism for Visual Explanation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10697–10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanaei, A. Embedded Encoder-Decoder in Convolutional Networks Towards Explainable AI. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.06712. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2007.06712 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Schöttl, A. Improving the Interpretability of GradCAMs in Deep Classification Networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashefi, R.; Barekatain, L.; Sabokrou, M.; Aghaeipoor, F. Explainability of Vision Transformers: A Comprehensive Review and New Perspectives. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.06786. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2311.06786 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Maniadis, Z. In defense of quantitative metrics in researcher assessments. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, J. Hybrid CNN-Transformer model for medical image segmentation with pyramid convolution and multi-layer perceptron. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 86, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Ali, M.S.; Mahim, S.; Miah, M.S. Enhancing lung abnormalities diagnosis using hybrid DCNN-ViT-GRU model with explainable AI: A deep learning approach. Image Vis. Comput. 2024, 142, 104918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud Kabir, S.; Imamul Hassan Bhuiyan, M. CWC-MP-MC Image-based breast tumor classification using an optimized Vision Transformer (ViT). Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100, 106941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Understanding Hold-Out Methods for Training Machine Learning Models. Comet. Available online: https://www.comet.com/site/blog/understanding-hold-out-methods-for-training-machine-learning-models (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Maaten, L.V.D.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated Residual Transformations for Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1611.05431. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1611.05431 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and Scaling ConvNets with Masked Autoencoder. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.00808. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00808 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Dai, Z.; Liu, H.; Le, Q.V.; Tan, M. CoAtNet: Marrying Convolution and Attention for All Data Sizes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.04803. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2106.04803 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Guo, D.; Lin, Y.; Ji, K.; Han, L.; Liao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Feng, J.; Tang, M. Classify breast cancer pathological tissue images using multi-scale bar convolution pooling structure with patch attention. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 96, 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek; Ranjan, A.; Srivastva, P.; Prabadevi, B.; Rajagopal, S.; Soangra, R.; Subramaniam, S.K. Classification of Colorectal Cancer using ResNet and EfficientNet Models. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2024, 18, e18741207280703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruk, I.; Pacal, I.; Toprak, A.N. A novel hybrid ConvNeXt-based approach for enhanced skin lesion classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 283, 127721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagaki, R.; Debsarkar, S.S.; Kawanaka, H.; Aronow, B.J.; Prasath, V.S. Deep learning-based IDH1 gene mutation prediction using histopathological imaging and clinical data. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 179, 108902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, F.B.; Alam, S.M.; Sakib, S.M. Enhancing breast cancer classification via histopathological image analysis: Leveraging self-supervised contrastive learning and transfer learning. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peta, J.; Koppu, S. Explainable Soft Attentive EfficientNet for breast cancer classification in histopathological images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 90, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppi, S.; Cornia, M.; Baraldi, L.; Cucchiara, R. Revisiting The Evaluation of Class Activation Mapping for Explainability: A Novel Metric and Experimental Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 2299–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvak, D. Visualizing CoAtNet Predictions for Aiding Melanoma Detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.10515. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2205.10515 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Drelie Gelasca, E.; Byun, J.; Obara, B.; Manjunath, B. Evaluation and benchmark for biological image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2008 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 October 2008; pp. 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirinukunwattana, K.; Pluim, J.P.; Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Heng, P.A.; Guo, Y.B.; Wang, L.Y.; Matuszewski, B.J.; Bruni, E.; Sanchez, U.; et al. Gland segmentation in colon histology images: The glas challenge contest. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 35, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, L.; Orlov, N.; Mark Eckley, D.; Macura, T.J.; Goldberg, I.G. IICBU 2008: A proposed benchmark suite for biological image analysis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2008, 46, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGEMAP—The Atlas of Gene Expression in Mouse Aging Project. Available online: https://ome.grc.nia.nih.gov/iicbu2008/agemap/index.html (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Tosta, T.A.A.; de Faria, P.R.; Neves, L.A.; Martins, A.S.; Kaushal, C.; do Nascimento, M.Z. Evaluation of sparsity metrics and evolutionary algorithms applied for normalization of H&E histological images. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2024, 27, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Tosta, T.A.A.; de Faria, P.R.; Servato, J.P.S.; Neves, L.A.; Roberto, G.F.; Martins, A.S.; do Nascimento, M.Z. Unsupervised method for normalization of hematoxylin-eosin stain in histological images. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 77, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, G.; Saygılı, A. Deep learning-based histopathological classification of breast tumors: A multi-magnification approach with state-of-the-art models. Signal Image Video Process. 2025, 19, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emegano, D.I.; Mustapha, M.T.; Ozsahin, I.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Uzun, B. Advancing Prostate Cancer Diagnostics: A ConvNeXt Approach to Multi-Class Classification in Underrepresented Populations. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudjelal, A.; Belkheiri, Y.; Elmoataz, A.; Goudjil, A.; Attallah, B. Two-Stage Hybrid Convolutional-Transformer Models for Breast Cancer Histopathology. In Proceedings of the 2024 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 July 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Saednia, K.; Tran, W.T.; Sadeghi-Naini, A. A hierarchical self-attention-guided deep learning framework to predict breast cancer response to chemotherapy using pre-treatment tumor biopsies. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 7852–7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, J.P.M.; Neves, L.A.; Martins, A.S.; do Nascimento, M.Z.; Tosta, T.A.A. Analysis of neural networks trained with evolutionary algorithms for the classification of breast cancer histological images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 231, 120609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, D.; Nalamada, T.; Arasanipalai, A.U.; Hou, Q. Rotate to Attend: Convolutional Triplet Attention Module. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 3138–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Object Detectors Emerge in Deep Scene CNNs. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1412.6856. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6856 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Mao, A.; Mohri, M.; Zhong, Y. Cross-entropy loss functions: Theoretical analysis and applications. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, JMLR.org, ICML’23, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, F.; Qi, Z.; Duan, K.; Xi, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, H.; He, Q. A Comprehensive Survey on Transfer Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.02685. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02685 (accessed on 23 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1409.0575. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0575 (accessed on 23 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Riche, N.; Duvinage, M.; Mancas, M.; Gosselin, B.; Dutoit, T. Saliency and Human Fixations: State-of-the-Art and Study of Comparison Metrics. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornia, M.; Baraldi, L.; Serra, G.; Cucchiara, R. Multi-level Net: A Visual Saliency Prediction Model. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–10 and 15–16 October 2016; Hua, G., Jégou, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 302–315. [Google Scholar]
- Cornia, M.; Baraldi, L.; Serra, G.; Cucchiara, R. Visual saliency for image captioning in new multimedia services. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, S.; Niaz, A.; Choi, K.N. Grad++ScoreCAM: Enhancing Visual Explanations of Deep Convolutional Networks Using Incremented Gradient and Score- Weighted Methods. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 61104–61112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.01703. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1912.01703 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Fomin, V.; Anmol, J.; Desroziers, S.; Kriss, J.; Tejani, A. High-Level Library to Help with Training Neural Networks in PyTorch. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/pytorch/ignite (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatov, A.; Yates, J.; Boeva, V. Histopathological Image Classification with Cell Morphology Aware Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.08625. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2407.08625 (accessed on 23 June 2025).



| Dataset | Tissue Type | Classes | Samples | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCSB [54] | Breast cancer | 2 | 58 | 896 × 768 |
| CR [55] | Colorectal tumors | 2 | 165 | Between 567 × 430 and 775 × 522 |
| NHL [56] | Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas | 3 | 173 | Between 86 × 65 and 1388 × 1040 |
| LG [57] | Liver tissue | 2 | 265 | 417 × 312 |
| LA [57] | Liver tissue | 4 | 529 | 417 × 312 |
| Dataset: UCSB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 25.94 | 0.11 | 13.92 | 51.26 |
| DenseNet-201 | 35.08 | 0.11 | 15.92 | 63.70 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 27.40 | 0.11 | 38.91 | 54.33 |
| ResNext-50 | 29.11 | 0.11 | 14.36 | 55.57 |
| ConvNext | 25.93 | 0.11 | 11.14 | 50.99 |
| CoatNet-small | 28.65 | 0.11 | 24.64 | 56.49 |
| Dataset: NHL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 20.53 | 0.07 | 71.13 | 43.35 |
| DenseNet-201 | 21.42 | 0.07 | 57.95 | 42.86 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 29.14 | 0.07 | 64.34 | 60.22 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 22.74 | 0.07 | 62.49 | 46.45 |
| ConvNeXt | 24.99 | 0.07 | 33.87 | 50.99 |
| CoatNet-small | 34.14 | 0.07 | 69.19 | 70.74 |
| Dataset: CR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 25.39 | 0.13 | 8.19 | 50.72 |
| DenseNet-201 | 26.38 | 0.13 | 5.38 | 50.09 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 27.70 | 0.14 | 19.83 | 54.07 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 38.11 | 0.14 | 8.27 | 65.39 |
| ConvNeXt | 28.38 | 0.13 | 5.34 | 53.68 |
| CoatNet-small | 34.38 | 0.14 | 5.19 | 60.81 |
| Dataset: LG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 28.85 | 0.24 | 42.51 | 53.25 |
| DenseNet-201 | 26.19 | 0.24 | 31.08 | 50.90 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 32.14 | 0.24 | 41.66 | 62.33 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 27.18 | 0.24 | 22.81 | 52.54 |
| ConvNeXt | 29.07 | 0.24 | 6.27 | 54.60 |
| CoatNet-small | 32.43 | 0.24 | 53.97 | 65.44 |
| Dataset: LA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 19.92 | 0.24 | 71.24 | 40.03 |
| DenseNet-201 | 26.50 | 0.24 | 60.51 | 52.59 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 32.36 | 0.24 | 67.82 | 66.84 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 24.60 | 0.24 | 52.43 | 52.49 |
| ConvNeXt | 25.31 | 0.24 | 51.39 | 53.75 |
| CoatNet-small | 34.98 | 0.23 | 72.33 | 71.60 |
| Dataset: UCSB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 28.56 | 0.10 | 55.56 | 56.36 |
| DenseNet-201 | 14.67 | 0.09 | 28.96 | 28.18 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 32.28 | 0.11 | 31.50 | 61.86 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 29.03 | 0.11 | 55.56 | 58.12 |
| ConvNeXt | 35.42 | 0.11 | 7.00 | 62.69 |
| CoatNet-small | 27.89 | 0.11 | 22.04 | 55.80 |
| Dataset: NHL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 35.96 | 0.07 | 71.43 | 73.06 |
| DenseNet-201 | 27.30 | 0.07 | 65.86 | 57.97 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 24.63 | 0.07 | 64.48 | 50.94 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 31.00 | 0.07 | 64.36 | 64.46 |
| ConvNeXt | 34.62 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 60.74 |
| CoatNet-small | 40.05 | 0.07 | 60.36 | 77.90 |
| Dataset: CR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 31.74 | 0.13 | 5.74 | 58.11 |
| DenseNet-201 | 31.05 | 0.13 | 17.44 | 58.33 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 23.05 | 0.14 | 20.54 | 47.40 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 34.12 | 0.13 | 14.13 | 62.77 |
| ConvNeXt | 32.41 | 0.13 | 9.98 | 58.03 |
| CoatNet-small | 32.20 | 0.13 | 20.73 | 60.59 |
| Dataset: LG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 28.54 | 0.24 | 42.50 | 55.08 |
| DenseNet-201 | 28.96 | 0.24 | 40.88 | 59.81 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 32.20 | 0.24 | 43.38 | 63.22 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 31.59 | 0.24 | 40.00 | 58.00 |
| ConvNeXt | 30.89 | 0.24 | 8.53 | 57.69 |
| CoatNet-small | 37.71 | 0.24 | 32.25 | 69.14 |
| Dataset: LA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ |
| ResNet-50 | 36.22 | 0.24 | 79.75 | 74.22 |
| DenseNet-201 | 26.74 | 0.24 | 62.54 | 53.47 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 32.07 | 0.24 | 69.30 | 66.30 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 30.02 | 0.24 | 70.89 | 64.37 |
| ConvNeXt | 31.61 | 0.24 | 15.79 | 59.33 |
| CoatNet-small | 36.57 | 0.24 | 75.70 | 75.11 |
| Model | CO ↑ | COM ↓ | CD ↓ | ADCC ↑ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Proposed | Baseline | Proposed | Baseline | Proposed | Baseline | Proposed | |
| ResNet-50 | 24.13 | 32.20 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 41.40 | 51.00 | 47.72 | 63.37 |
| DenseNet-201 | 27.11 | 25.74 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 34.17 | 43.14 | 52.03 | 51.55 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 29.75 | 28.85 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 46.51 | 45.84 | 59.56 | 57.94 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 28.35 | 31.15 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 32.07 | 48.99 | 54.49 | 61.54 |
| ConvNeXt | 26.74 | 32.99 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 21.60 | 8.36 | 52.80 | 59.70 |
| CoatNet-small | 32.92 | 34.88 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 45.06 | 42.22 | 65.02 | 67.71 |
| Model | F1-Score | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Proposed | Baseline | Proposed | |
| ResNet-50 | 92.71 | 85.03 | 91.89 | 82.06 |
| DenseNet-201 | 94.95 | 96.20 | 93.36 | 95.45 |
| EfficientNet-b0 | 95.67 | 95.69 | 95.01 | 95.05 |
| ResNeXt-50 | 97.70 | 93.27 | 97.09 | 91.69 |
| ConvNeXt | 93.76 | 97.35 | 92.10 | 96.68 |
| CoatNet-small | 94.78 | 96.10 | 93.86 | 94.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miguel, P.L.; Neves, L.A.; Lumini, A.; Medalha, G.C.; Roberto, G.F.; Rozendo, G.B.; Cansian, A.M.; Tosta, T.A.A.; do Nascimento, M.Z. Entropy-Regularized Attention for Explainable Histological Classification with Convolutional and Hybrid Models. Entropy 2025, 27, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070722
Miguel PL, Neves LA, Lumini A, Medalha GC, Roberto GF, Rozendo GB, Cansian AM, Tosta TAA, do Nascimento MZ. Entropy-Regularized Attention for Explainable Histological Classification with Convolutional and Hybrid Models. Entropy. 2025; 27(7):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070722
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiguel, Pedro L., Leandro A. Neves, Alessandra Lumini, Giuliano C. Medalha, Guilherme F. Roberto, Guilherme B. Rozendo, Adriano M. Cansian, Thaína A. A. Tosta, and Marcelo Z. do Nascimento. 2025. "Entropy-Regularized Attention for Explainable Histological Classification with Convolutional and Hybrid Models" Entropy 27, no. 7: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070722
APA StyleMiguel, P. L., Neves, L. A., Lumini, A., Medalha, G. C., Roberto, G. F., Rozendo, G. B., Cansian, A. M., Tosta, T. A. A., & do Nascimento, M. Z. (2025). Entropy-Regularized Attention for Explainable Histological Classification with Convolutional and Hybrid Models. Entropy, 27(7), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27070722












