Variability Identification and Uncertainty Evolution Characteristic Analysis of Hydrological Variables in Anhui Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Research Framework
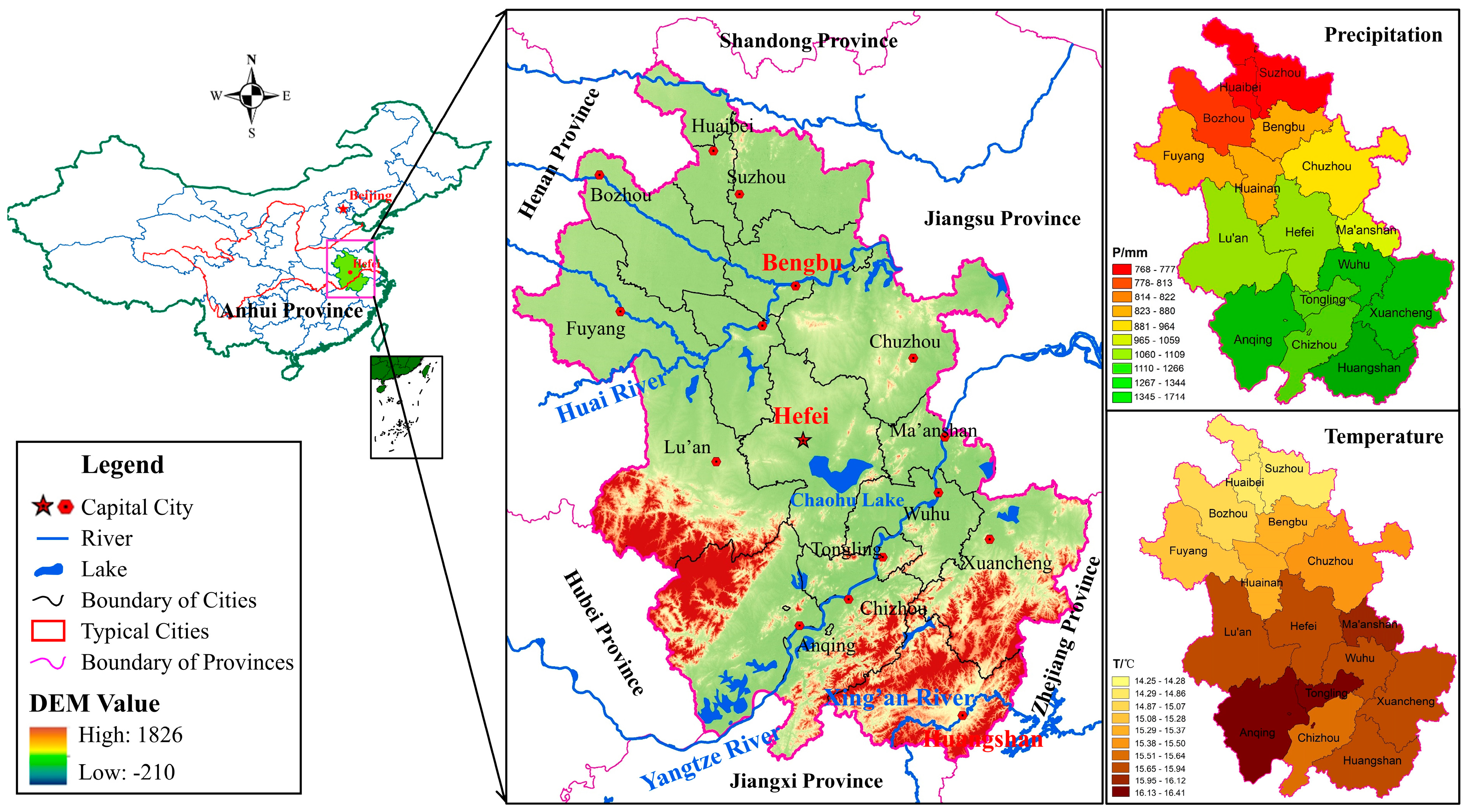
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
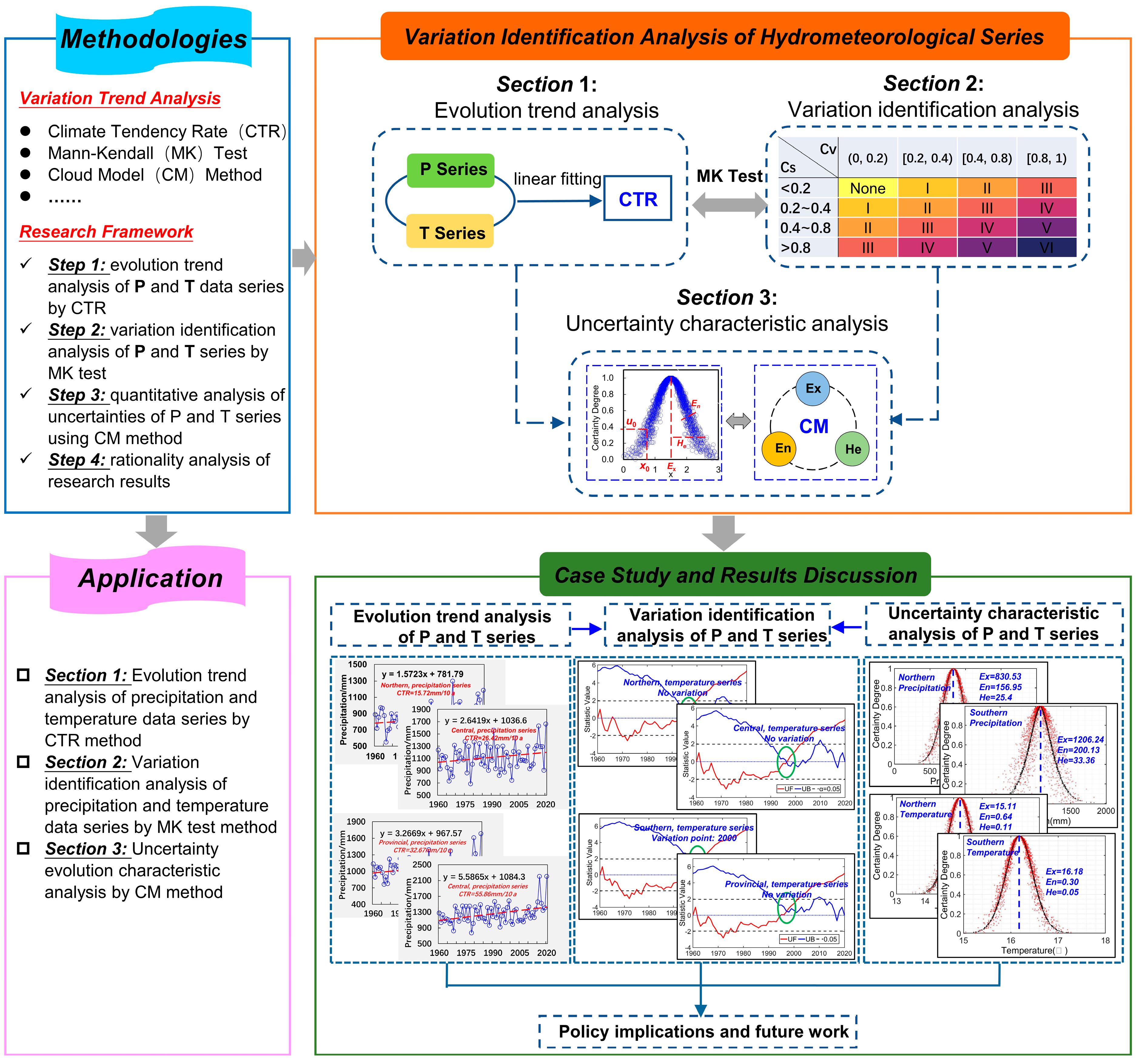
2.2. Research Framework
3. Methodologies
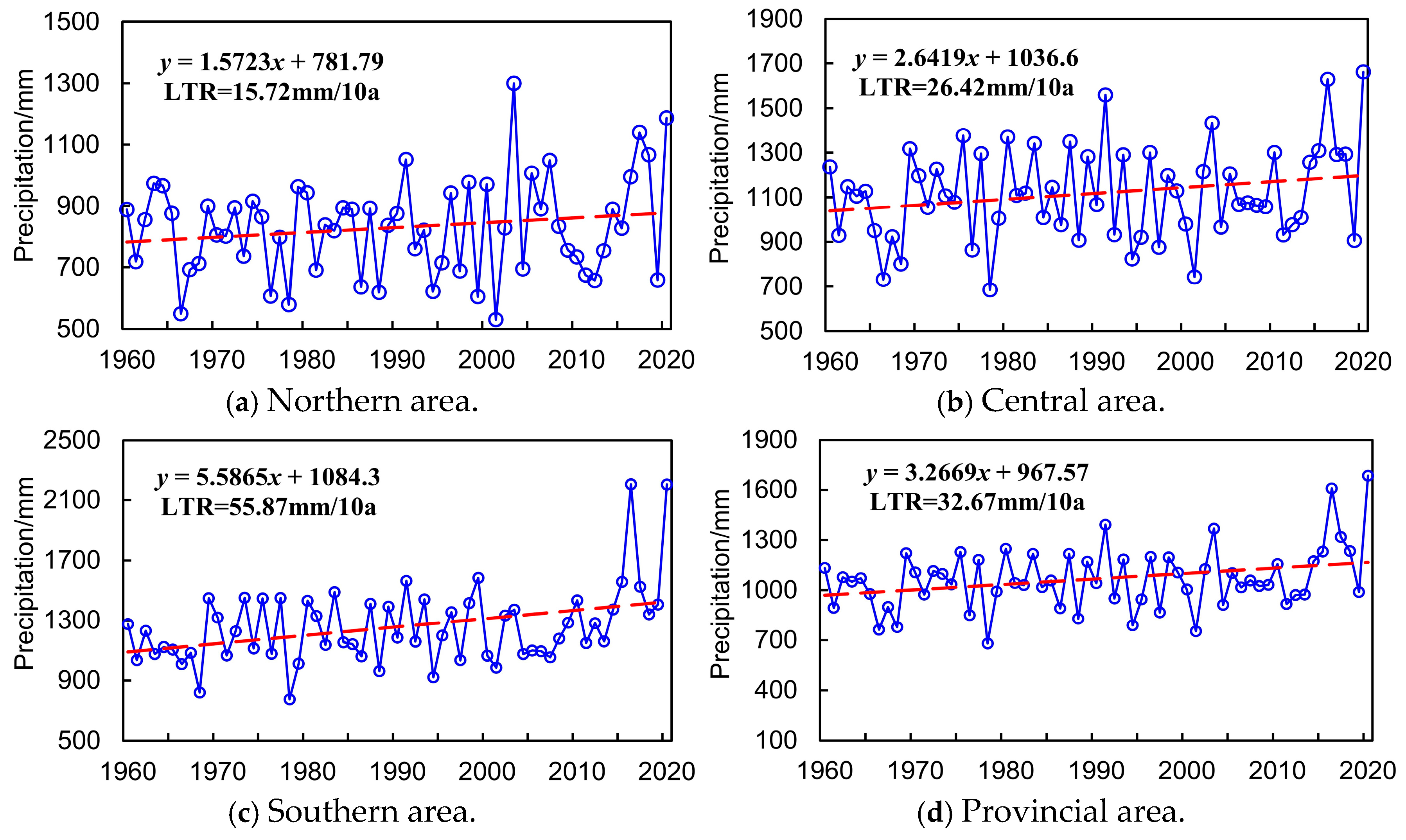
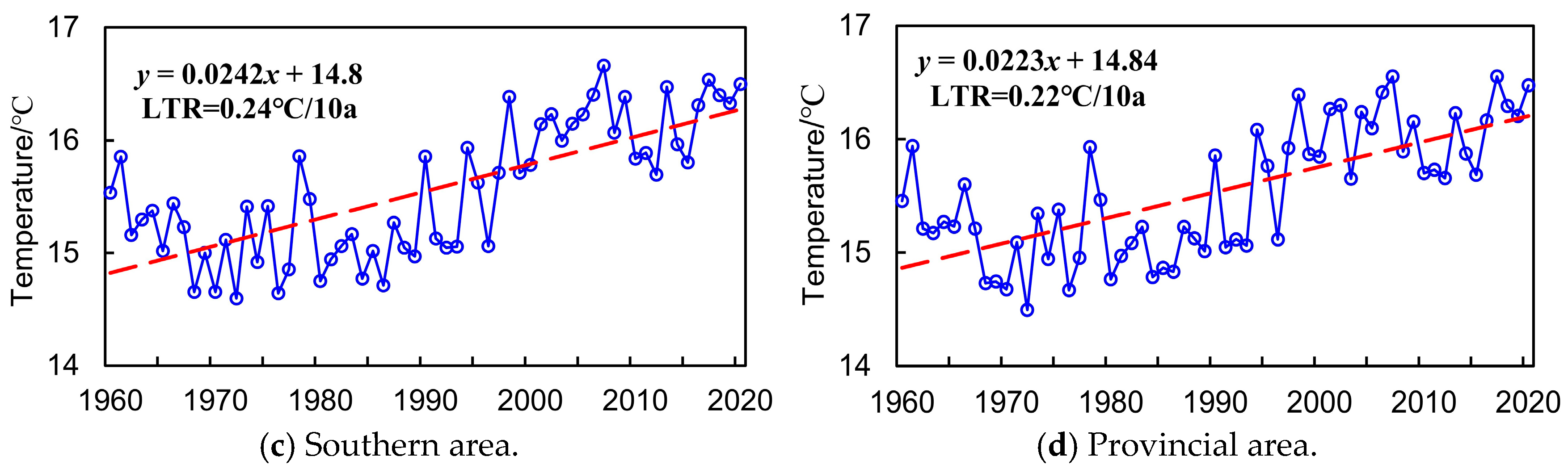
3.1. Linear Tendency Rate (LTR)
3.2. Mann–Kendall (M–K) Test Method
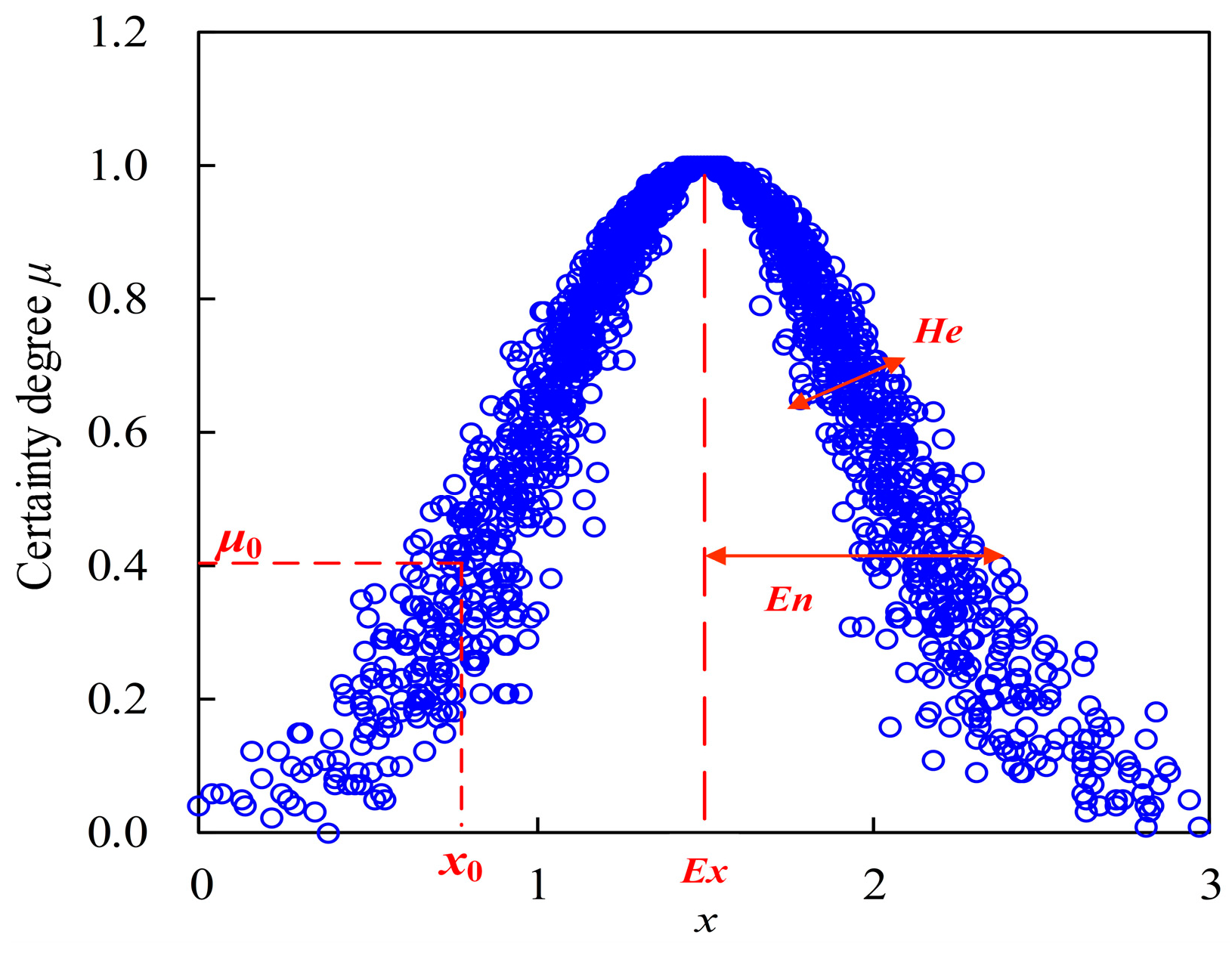
3.3. Cloud Model (CM)
3.4. Calculation Procedures
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Evolution Trend Analysis of Historical Precipitation and Temperature Series
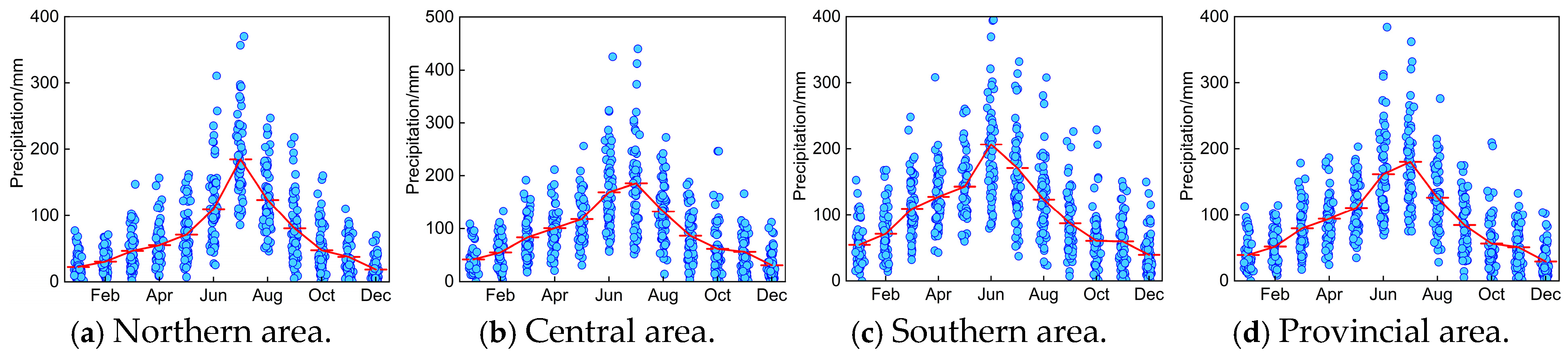
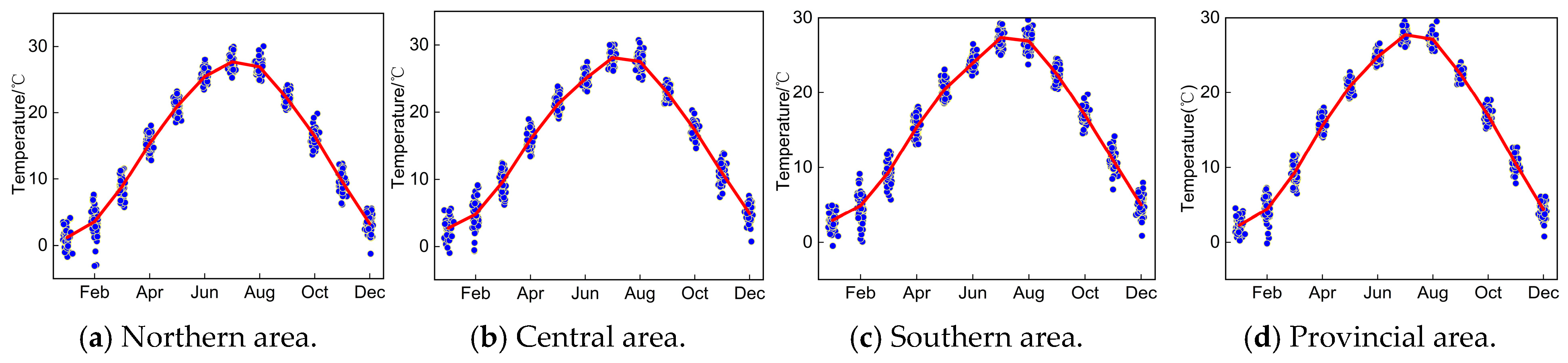
4.1.1. Monthly Variation Trend Analysis
4.1.2. Annual Variation Features Analysis
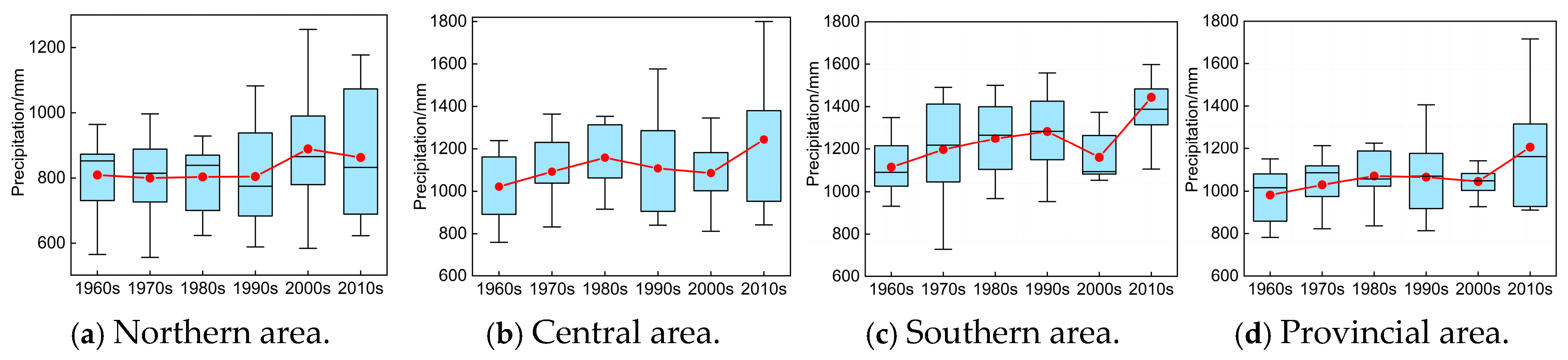
4.1.3. Interdecadal Variation Characteristics Analysis
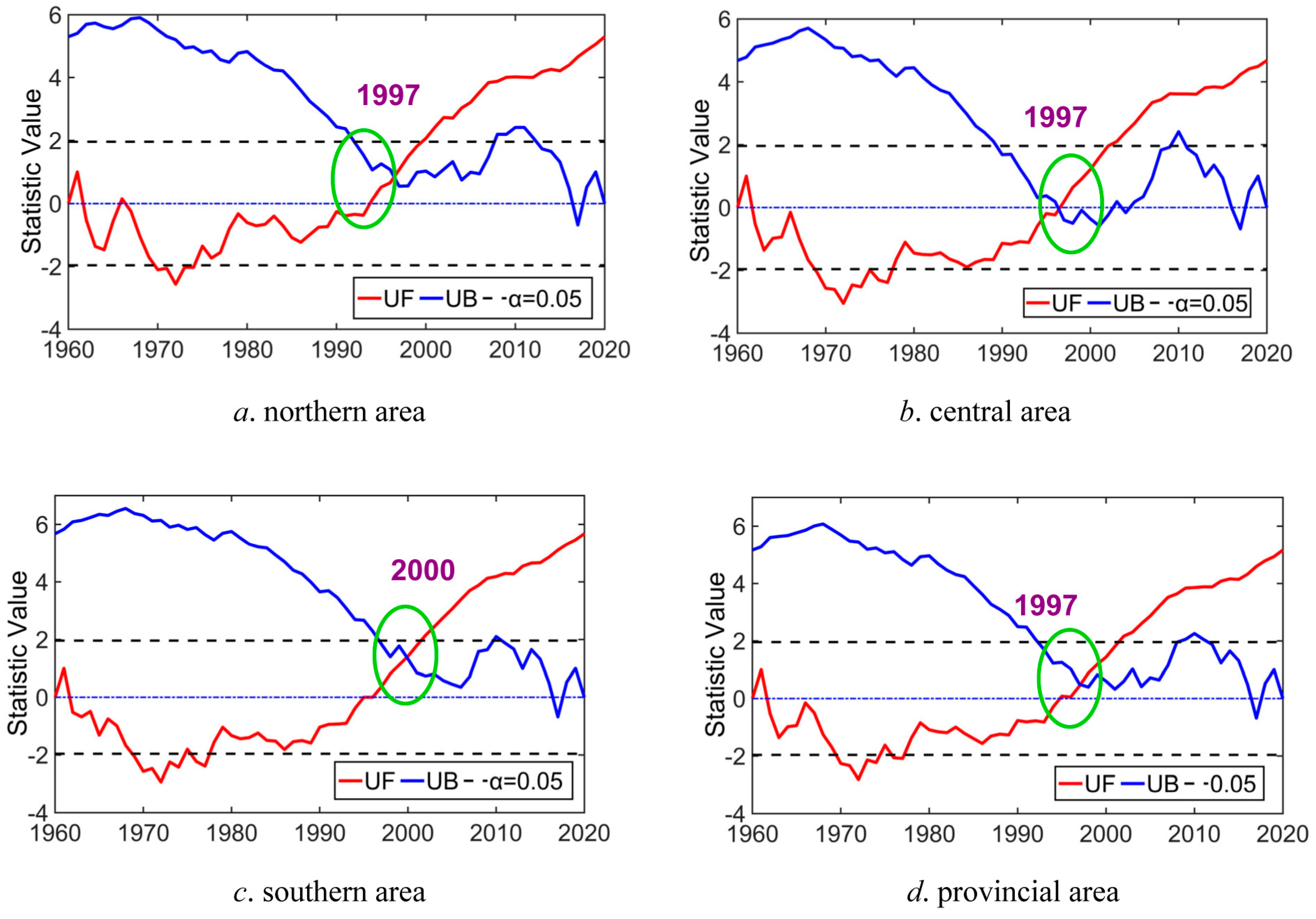
4.2. Variability Recognition Analysis According to M–K Trend Test Method
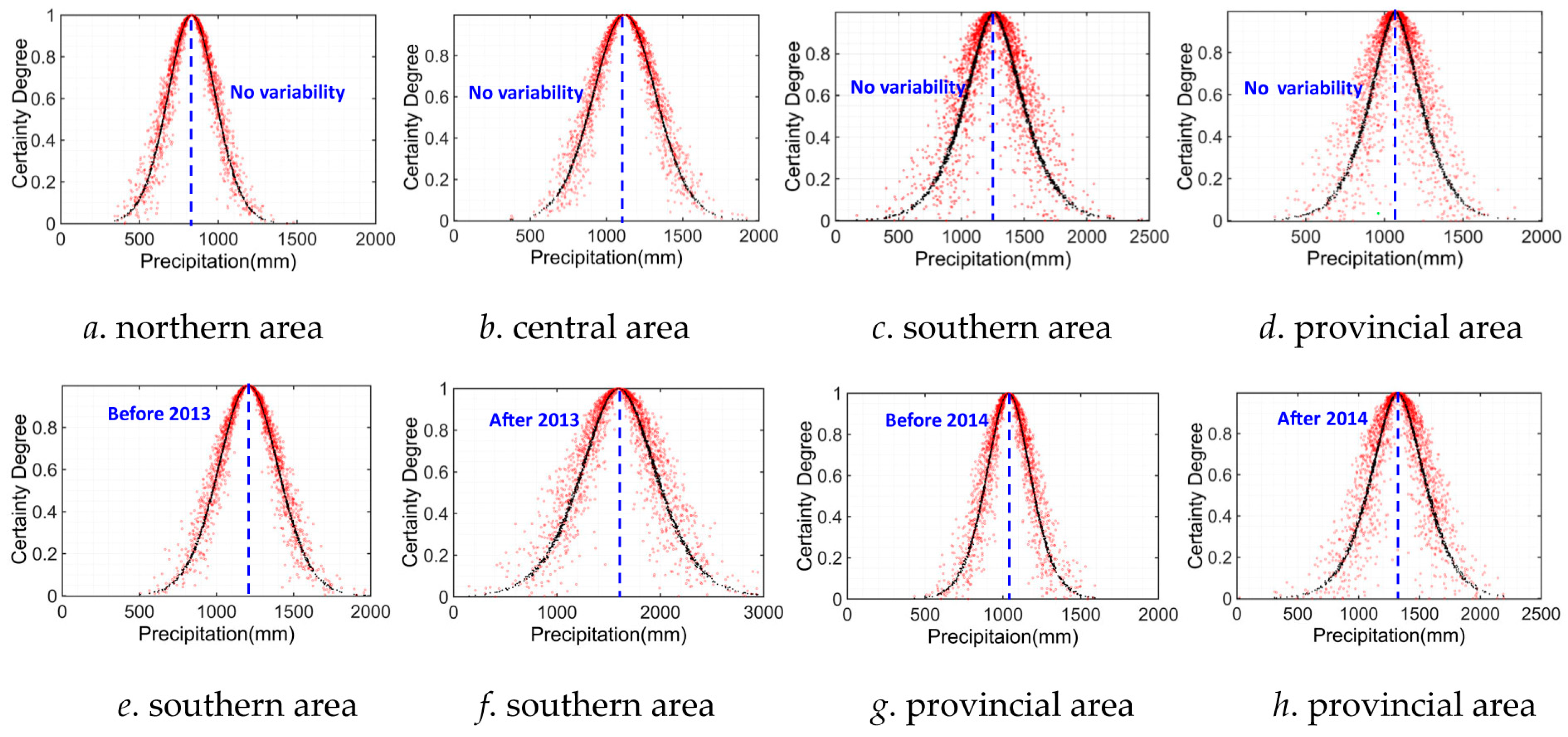
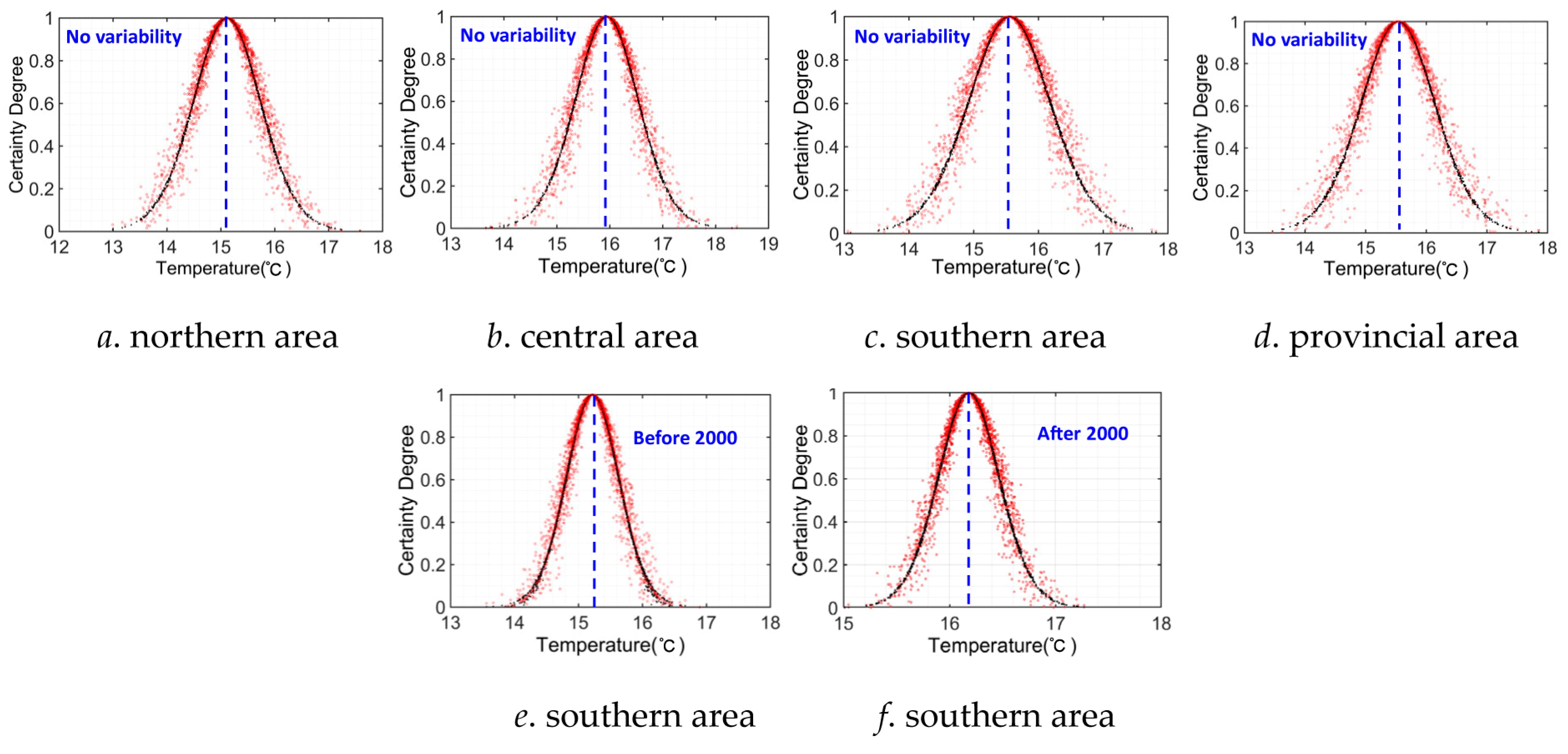
4.3. Uncertainty Characteristic Analysis by CM Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ning, Z.R.; Jia, Y.; Sun, G.; Wang, G. Impact of environmental changes on variability of outlet hydrological process of the Lancang River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2024, 35, 313–324. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhan, C.S.; Liu, C.Z. Review for impacts of climate change and human activities on water cycle. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 44, 779–790. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Group to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Huang, Q.; Chang, J.; Sun, D.; Cui, S. Detecting abrupt change of streamflow at lintong station of Wei river. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 211–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Song, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Ren, C.; Li, Y. Changes in global air temperature from 1981 to 2019. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2660–2672. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cook, B.I.; Smerdon, J.E.; Seager, R.; Coats, S. Global warming and 21st century drying. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 2607–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, H.; Feng, Q. Characterizing the spatiotemporal variations of evapotranspiration and aridity index in mid-western China from 2001 to 2016. J. Arid. Land 2021, 13, 1230–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, L.; Bernier, J.; Bobée, B.; Parent, E. Bayesian change-point analysis in hydrometeorological time series. Part I. The Normal Model Revisited. J. Hydrol. 2000, 235, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.D.; Jiang, J. Abrupt behaviors of the streamflow of the Pearl River basin and implications for hydrological alterations across the Pearl River Delta, China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal variations and abrupt changes of potential evapotranspiration and its sensitivity to key meteorological variables in the Wei River basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakken, M. Wavelet analysis of rainfall-runoff variability isolating climatic from anthropogenic patterns. Environ. Model. Softw. 1999, 14, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, T. Evaluation of the ecological instream flow in the Yellow River basin with hydrological alterations. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 4826–4834. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, A.J.; Chang, J.X.; Huang, Q.; Sun, J.N. Quantitative analysis of the impacts of climate change and human activities of runoff change in Weihe Basin. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 42, 212–220. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kong, B.; Fang, J.J.; Huang, Q. Diagnosis of runoff variation in different periods in Beiluo River Basin and its causes analysis. Water Resour. Prot. 2019, 35, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.L.; Wang, Z.L.; Lyu, H.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, W.J. Change in temperature over the past 50 years at Wudaogou and its influence on soil temperature at different depths. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 41, 83–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Strupczewski, W.G.; Singh, V.P.; Feluch, W. Non-stationary approach to at-site flood frequency modelling I. Maximum likelihood estimation. J. Hydrol. 2001, 248, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, B.; Thieken, A.H. Separating natural and epistemic uncertainty in flood frequency analysis. J. Hydrol. 2005, 309, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.B.; Li, Y.; Cai, M.K. Methods of frequency analysis for hydrologic data with jump up components. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 43, 734–739. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.X. Flood Frequency Analysis Considering Uncertainties Under Changing Environments. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, China, 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y. Characteristics of precipitation days and intensity of Anhui province in summer during recent 38 years. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 157–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Yan, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y. Climatic change and drought-flood regional responses in Anhui. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2016, 55, 127–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.T.; Xu, G.L.; Yin, Z.X.; Hu, C.Q.; Wang, Y.; Liao, F.Q. Spatio-temporal change of surface air temperature in Anhui Province in the context of global warming from 1960 to 2014. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 680–691. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Dong, X.H.; Yu, D.; Hu, C.Q.; Wang, Y.; Liao, F.Q. Spatio-temporal variations of rainfall erosivity, correlation of climatic indices and influence on human activities in the Huaihe River Basin, China. Catena 2022, 217, 106486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y. Modern Climate Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Technology, 2nd ed.; Meteorological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Jin, Y.T.; Guo, Z.C.; Liu, N.; Su, H.M. Study on the summer precipitation spatial-temporal variation and influencing factors in Anhui Province in 1959–2017. J. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 39, 99–106. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, K. Trend detection in hydrologic data: The Mann–Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Zou, S.B.; Jin, J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yu, L.; Kang, S.M. Analysis of changes in water use in Gansu section of the Yellow River in recent 20 years. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2024, 60, 450–455. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Huang, Q.; Bai, T.; Zhou, S.; Lin, M. Temporal and spatial variation of hydrological condition in the Ziwu River Basin of the Han River in China. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2018, 379, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.Y.; Gan, W.Y. A new cognitive model: Cloud model. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Shen, F.; Jin, J. A novel multi-dimensional cloud model coupled with connection numbers theory for evaluation of slope stability. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 77, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ning, S.; Jin, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Bai, X.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y. Construction and application of comprehensive drought index based on uncertainty cloud reasoning algorithm. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variability Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 0.2 | ≤ 0.4 | ≤ 0.8 | > 0.8 | |
| < 0.2 | Level 0 (no variability) | Level 1 (weak) | Level 2 (light) | Level 3 (moderate) |
| 0.2 < ≤ 0.4 | Level 1 (weak) | Level 2 (light) | Level 3 (moderate) | Level 4 (strong) |
| 0.4 < ≤ 0.8 | Level 2 (light) | Level 3 (moderate) | Level 4 (strong) | Level 5 (severe) |
| > 0.8 | Level 3 (moderate) | Level 4 (strong) | Level 5 (severe) | Level 6 (extreme) |
| Area | Variability Point | Variability Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern area | 2017 | 0.1954 | 0.2587 | level 1 (weak variability) |
| Central area | 1983 | 0.0654 | 0.0787 | level 0 (no variability) |
| 2014 | 0.1876 | 0.1693 | level 0 (no variability) | |
| Southern area | 2013 | 0.2492 | 0.3787 | level 2 (light variability) |
| Provincial area | 2014 | 0.2237 | 0.2176 | level 2 (light variability) |
| Area | Variability Point | Variability Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern area | 1997 | 0.0571 | 0.2934 | level 1 (weak variability) |
| Central area | 1997 | 0.0502 | 0.1789 | level 0 (no variability) |
| Southern area | 2000 | 0.0595 | 0.5852 | level 2 (light variability) |
| Provincial area | 1997 | 0.0570 | 0.1913 | level 0 (no variability) |
| Area | Variability Point | Ex | En | He |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern area | No variability | 830.53 | 156.95 | 25.42 |
| Central area | No variability | 1118.54 | 212.22 | 35.37 |
| Southern area | Before variability point (2013) | 1206.24 | 200.13 | 33.36 |
| After variability point (2013) | 1596.79 | 380.89 | 101.34 | |
| No variability | 1257.50 | 243.36 | 86.62 | |
| Provincial area | Before variability point (2014) | 1036.26 | 148.58 | 34.62 |
| After variability point (2014) | 1320.19 | 233.86 | 74.93 | |
| No variability | 1068.82 | 174.57 | 66.64 |
| Area | Variability Point | Ex | En | He |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern area | No variability | 15.11 | 0.64 | 0.11 |
| Central area | No variability | 15.94 | 0.61 | 0.10 |
| Southern area | Before variability point (2000) | 15.22 | 0.42 | 0.07 |
| After variability point (2000) | 16.18 | 0.30 | 0.05 | |
| No variability | 15.55 | 0.65 | 0.11 | |
| Provincial area | No variability | 15.53 | 0.63 | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Wu, C.; Zhou, R. Variability Identification and Uncertainty Evolution Characteristic Analysis of Hydrological Variables in Anhui Province, China. Entropy 2025, 27, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030305
Bai X, Yu J, Li Y, Jin J, Wu C, Zhou R. Variability Identification and Uncertainty Evolution Characteristic Analysis of Hydrological Variables in Anhui Province, China. Entropy. 2025; 27(3):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030305
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Xia, Jinhuang Yu, Yule Li, Juliang Jin, Chengguo Wu, and Rongxing Zhou. 2025. "Variability Identification and Uncertainty Evolution Characteristic Analysis of Hydrological Variables in Anhui Province, China" Entropy 27, no. 3: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030305
APA StyleBai, X., Yu, J., Li, Y., Jin, J., Wu, C., & Zhou, R. (2025). Variability Identification and Uncertainty Evolution Characteristic Analysis of Hydrological Variables in Anhui Province, China. Entropy, 27(3), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/e27030305






