Entropy Estimators for Markovian Sequences: A Comparative Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Maximum Likelihood Estimator
2.2. Miller–Madow Estimator
2.3. Nemenman–Shafee–Bialek Estimator
2.4. Chao–Shen Estimator
2.5. Grassberger Estimator
2.6. Bonachela–Hinrichsen–Muñoz Estimator
2.7. Shrinkage Estimator
2.8. Chao–Wang–Jost Estimator
2.9. Correlation Coverage-Adjusted Estimator
2.10. Corrected Miller–Madow Estimator
3. Results
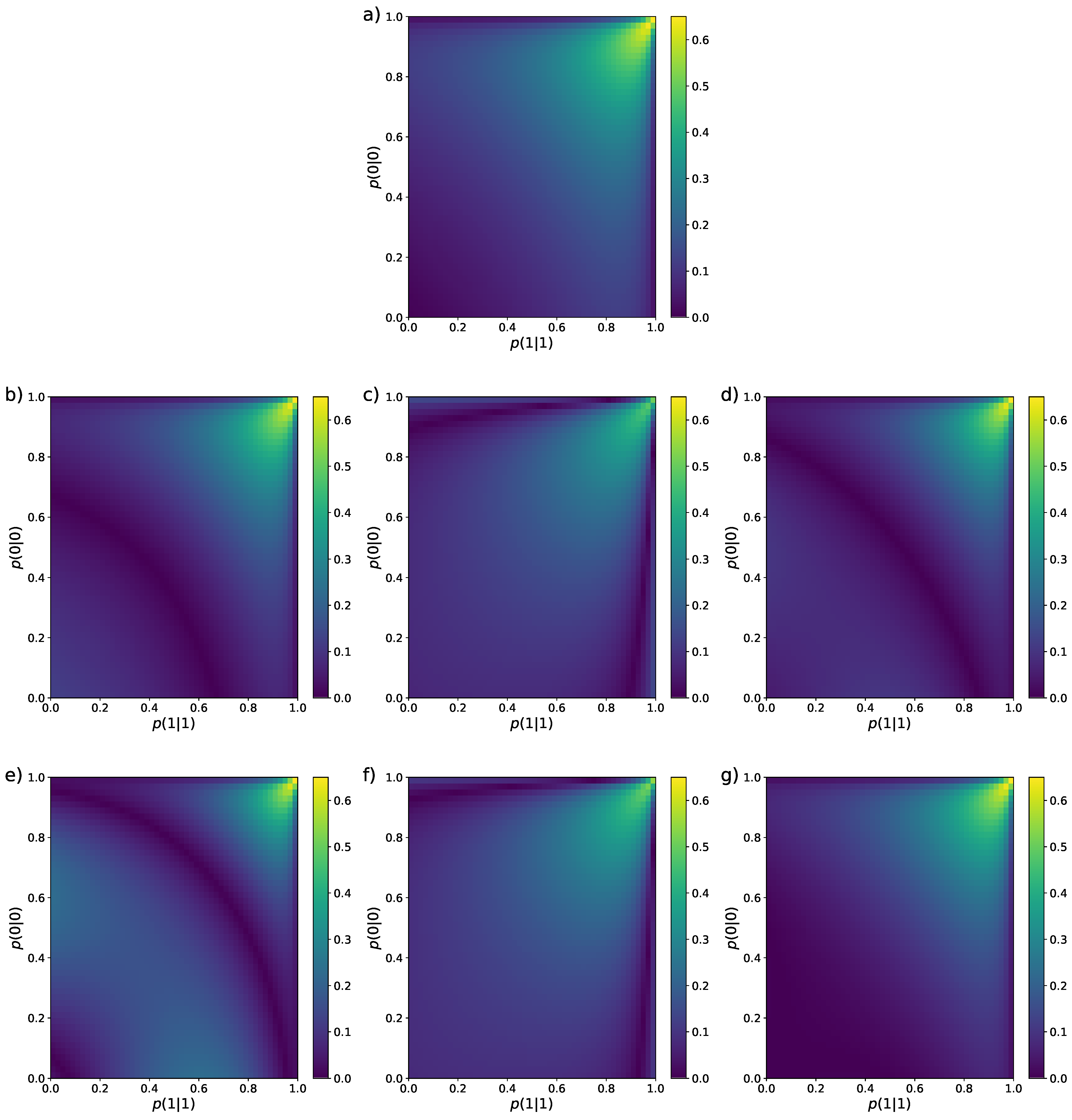
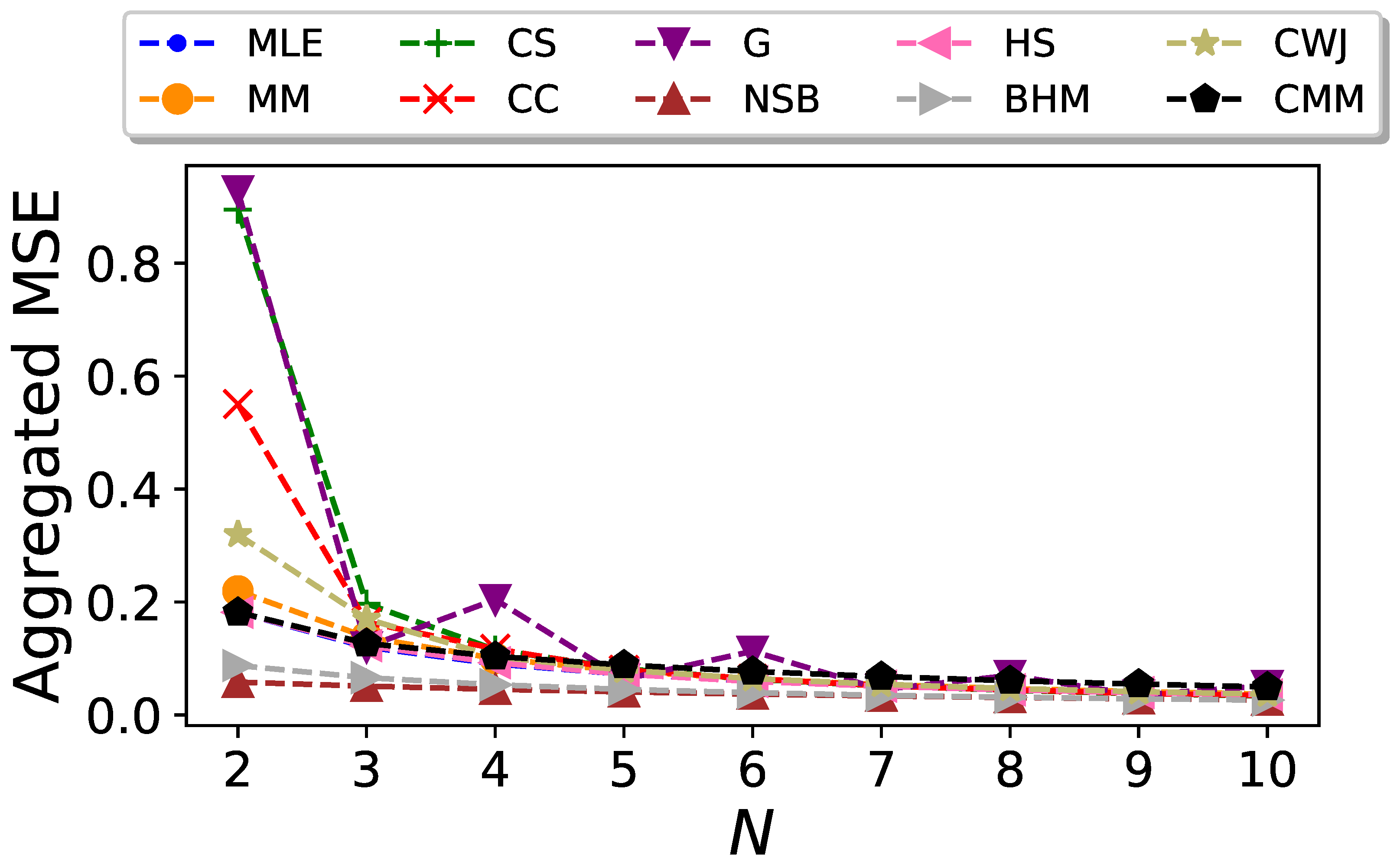
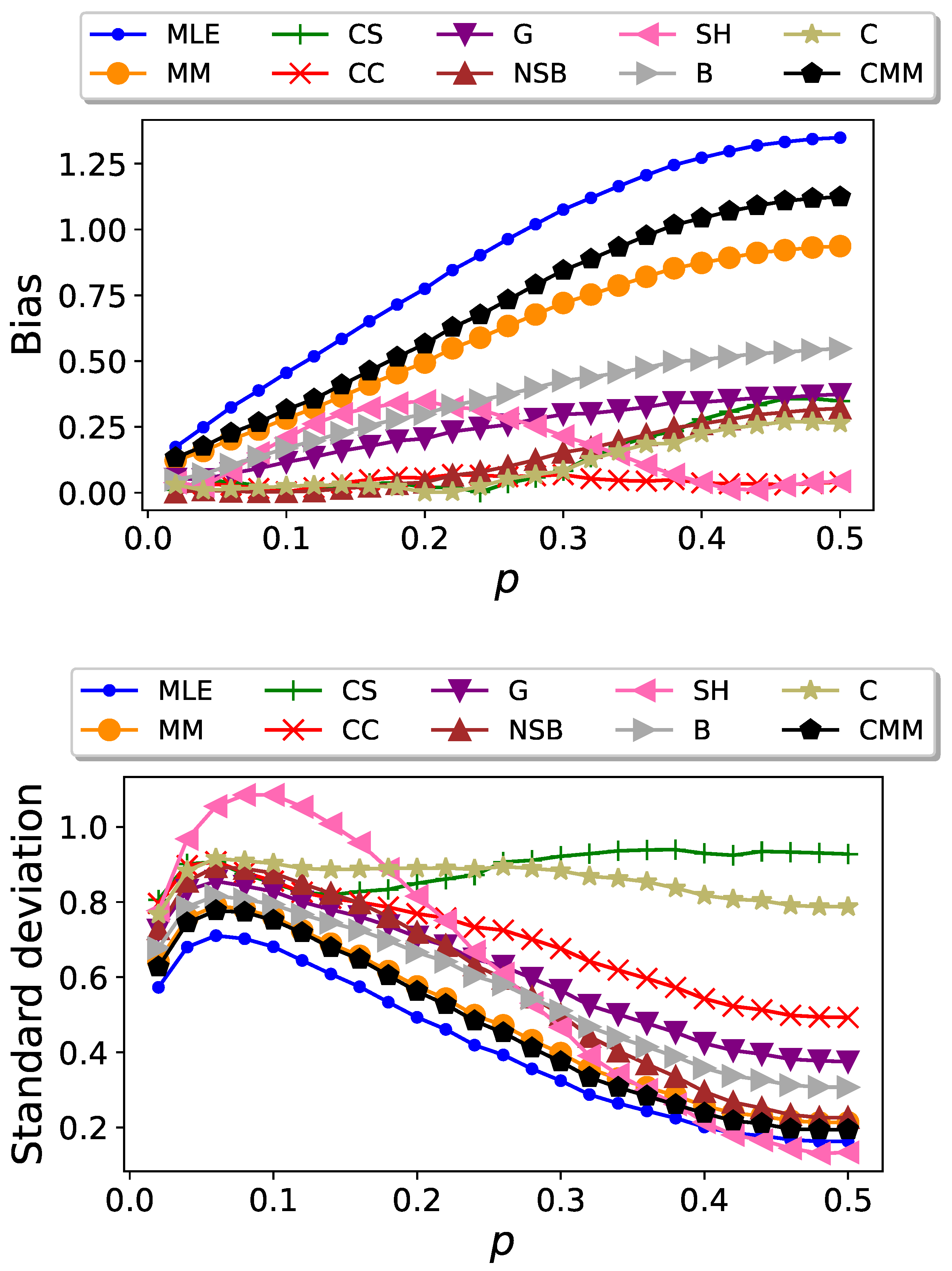
3.1. Binary Sequences
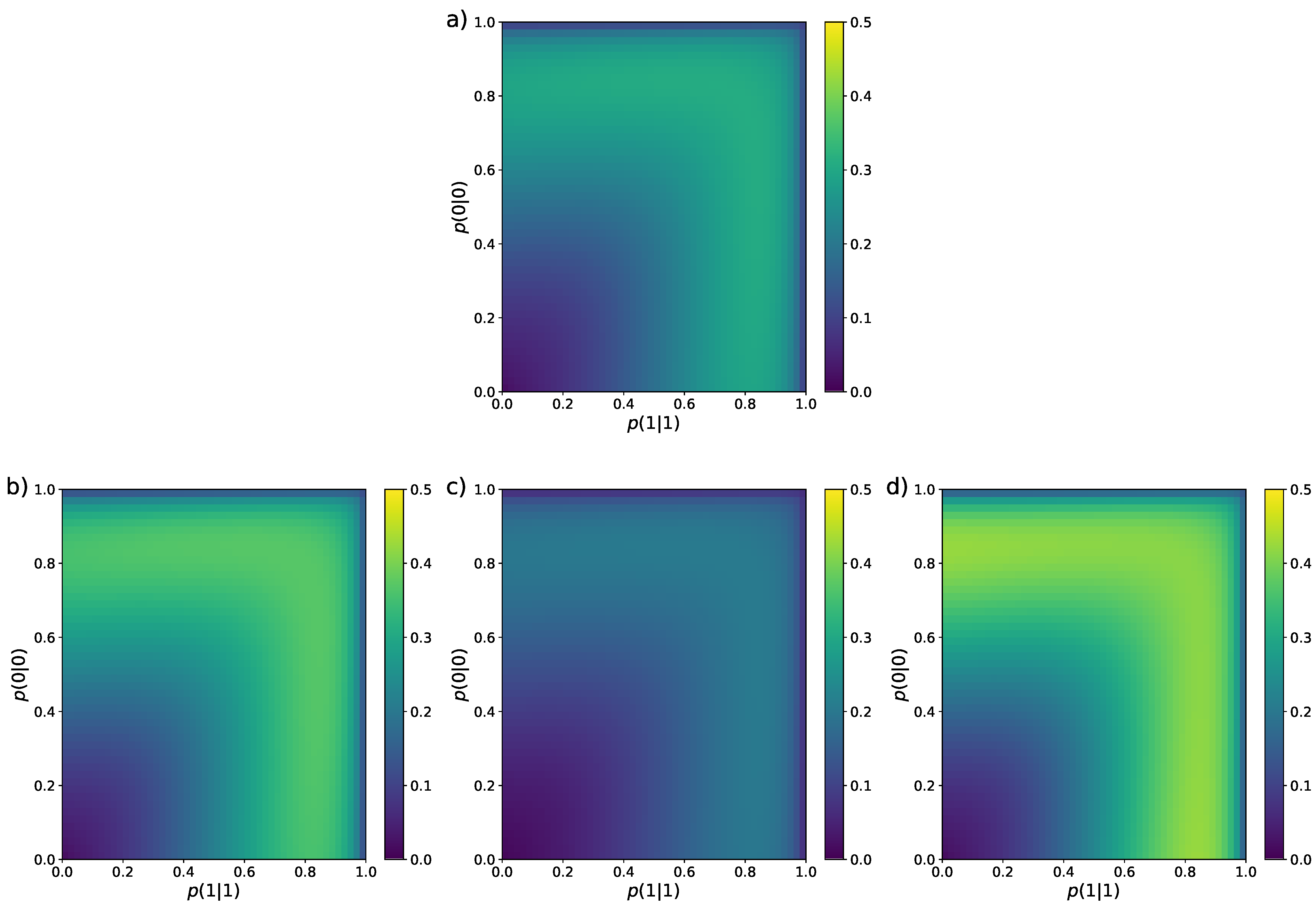
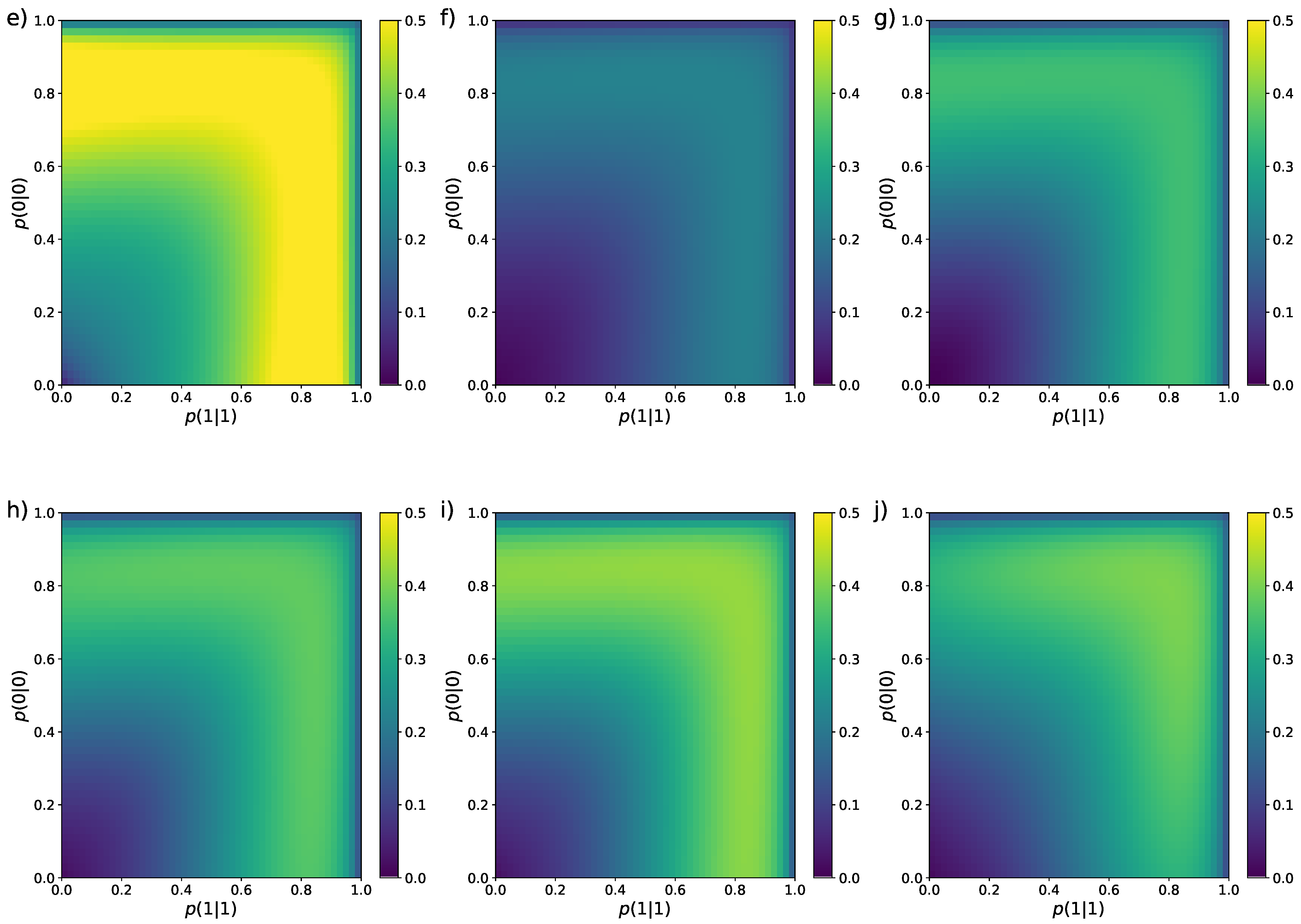
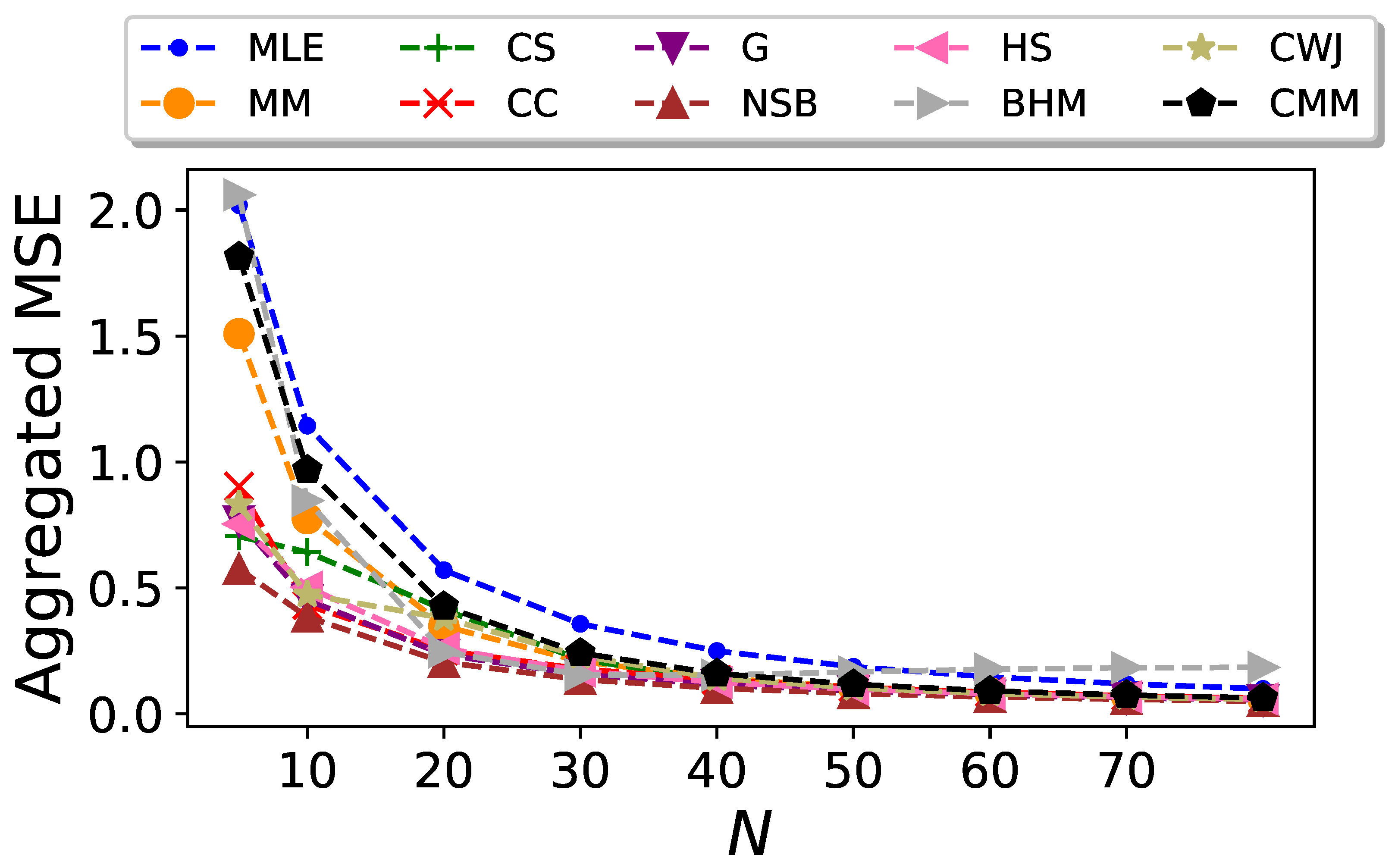
3.2. Undersampled Regime: Block Entropy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Proof of Equation (A7)
- Step 1:
- Note that not all permutations give a different set . There are, in fact, only permutations that differ in the value of the sequence , corresponding to the selection of the n locations of the x symbol in the sequence. Therefore, we can simplify the expression for the estimator aswhere the sum over i now runs over the permutations that give rise to a different set of numbers .
- Step 2:
- We prove this relation by mathematical induction. Consider the case . The N permutations that differ in the value of k correspond to the appearance of the symbol x in the first term of the series (), the second term of the series (), and so on up to the N-th term (). The sum in the left-hand-side of Equation (A14) iswhich coincides with , defined in Equation (A15).
- Step 3:
- We show that can finally be written aswhere is the digamma function.
Appendix A.2. Calculation of the Average 〈(S)〉
Appendix B
References
- Lewontin, R.C. The Apportionment of Human Diversity. In Evolutionary Biology: Volume 6; Dobzhansky, T., Hecht, M.K., Steere, W.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, D.R. Cryptography: Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Strong, S.P.; Koberle, R.; de Ruyter van Steveninck, R.R.; Bialek, W. Entropy and Information in Neural Spike Trains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, G.; Burge, C. Maximum Entropy Modeling of Short Sequence Motifs with Applications to RNA Splicing Signals. J. Comput. Biol. J. Comput. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 11, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cover, T.; Thomas, J. Elements of Information Theory; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Letellier, C. Estimating the Shannon Entropy: Recurrence Plots versus Symbolic Dynamics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 254102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, J. Approaches to Information-Theoretic Analysis of Neural Activity. Biol. Theory 2006, 1, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlaváčková-Schindler, K.; Paluš, M.; Vejmelka, M.; Bhattacharya, J. Causality detection based on information-theoretic approaches in time series analysis. Phys. Rep. 2007, 441, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, O.A.; Larrondo, H.A.; Martin, M.T.; Plastino, A.; Fuentes, M.A. Distinguishing Noise from Chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 154102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, W.B. Entropy and Information Approaches to Genetic Diversity and its Expression: Genomic Geography. Entropy 2010, 12, 1765–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, M.; Zunino, L.; Rosso, O.A.; Papo, D. Permutation Entropy and Its Main Biomedical and Econophysics Applications: A Review. Entropy 2012, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, C.; Alikaniotis, D.; Cysouw, M.; Ferrer-i Cancho, R. The Entropy of Words—Learnability and Expressivity across More than 1000 Languages. Entropy 2017, 19, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetti, J.; Delgadino, D.; Rey, A.; Frery, A.C. Entropy Estimators in SAR Image Classification. Entropy 2022, 24, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paninski, L. Estimation of Entropy and Mutual Information. Neural Comput. 2003, 15, 1191–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras Rodríguez, L.; Madarro-Capó, E.J.; Legón-Pérez, C.M.; Rojas, O.; Sosa-Gómez, G. Selecting an Effective Entropy Estimator for Short Sequences of Bits and Bytes with Maximum Entropy. Entropy 2021, 23, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, A.; Priesemann, V.; Zierenberg, J. Tackling the subsampling problem to infer collective properties from limited data. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2022, 4, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Shen, T.J. Nonparametric estimation of Shannon’s diversity index when there are unseen species in sample. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2003, 10, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.Q.; Yu, B.; Kass, R.E. Coverage-adjusted entropy estimation. In Statistics in Medicine; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 26, pp. 4039–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausser, J.; Strimmer, K. Entropy Inference and the James-Stein Estimator, with Application to Nonlinear Gene Association Networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, A.; Meister, C.; Cotterell, R. Estimating the Entropy of Linguistic Distributions. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; Association for Computational Linguistics: Cedarville, OH, USA, 2022; pp. 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.W. Handbook of Stochastic Methods for Physics, Chemistry and the Natural Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Churchill, G.A. Stochastic models for heterogeneous DNA sequences. Bull. Math. Biol. 1989, 51, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S.; Wilby, R.L. The weather generation game: A review of stochastic weather models. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 1999, 23, 329–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanter, I.; Kessler, D.A. Markov Processes: Linguistics and Zipf’s Law. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 4559–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchfield, J.P.; Feldman, D.P. Regularities unseen, randomness observed: Levels of entropy convergence. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2003, 13, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gregorio, J.; Sánchez, D.; Toral, R. An improved estimator of Shannon entropy with applications to systems with memory. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 165, 112797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulmetyev, R.M.; Demin, S.A.; Panischev, O.Y.; Hänggi, P.; Timashev, S.F.; Vstovsky, G.V. Regular and stochastic behavior of Parkinsonian pathological tremor signals. Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 2006, 369, 655–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ho, D.T.; Cao, T.H. A high-order hidden Markov model for emotion detection from textual data. In Pacific Rim Knowledge Acquisition Workshop; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, M.; Gohr, A.; Strickert, M.; Grosse, I. Parsimonious higher-order hidden Markov models for improved array-CGH analysis with applications to Arabidopsis Thaliana. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, P.; Helic, D.; Taraghi, B.; Strohmaier, M. Detecting memory and structure in human navigation patterns using Markov chain models of varying order. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.; Rieger, H. Optimal Non-Markovian Search Strategies with n-Step Memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 127, 070601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson Kemsley, S.; Osborn, T.J.; Dorling, S.R.; Wallace, C.; Parker, J. Selecting Markov chain orders for generating daily precipitation series across different Köppen climate regimes. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 6223–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiß, C.H. Measures of Dispersion and Serial Dependence in Categorical Time Series. Econometrics 2019, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z. On a Markov multinomial distribution. Math. Sci. 1995, 20, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Grassberger, P. Entropy Estimates from Insufficient Samplings. arXiv 2008, arXiv:2301.13647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonachela, J.A.; Hinrichsen, H.; Muñoz, M.A. Entropy estimates of small data sets. J. Phys. Math. Theor. 2008, 41, 202001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, U.N.; Lal, R. Number of successes in Markov trials. Adv. Appl. Probab. 1988, 20, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Overton, W.S. Estimation of the size of a closed population when capture probabilities vary among animals. Biometrika 1978, 65, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Wolf, D.R. Estimating functions of probability distributions from a finite set of samples. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 52, 6841–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinck, M.; Battaglia, F.P.; Balakirsky, V.B.; Vinck, A.J.H.; Pennartz, C.M.A. Estimation of the entropy based on its polynomial representation. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 051139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Entropy Estimation in Turing’s Perspective. Neural Comput. 2012, 24, 1368–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, E.W.; Park, I.M.; Pillow, J.W. Bayesian entropy estimation for binary spike train data using parametric prior knowledge. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Burges, C., Bottou, L., Welling, M., Ghahramani, Z., Weinberger, K., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert, D.H.; DeDeo, S. Estimating Functions of Distributions Defined over Spaces of Unknown Size. Entropy 2013, 15, 4668–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiant, G.; Valiant, P. Estimating the Unseen: Improved Estimators for Entropy and Other Properties. Assoc. Comput. Mach. 2017, 64, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P. On Generalized Schürmann Entropy Estimators. Entropy 2022, 24, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, A.; Font-Pomarol, L.; Sales-Pardo, M.; Guimerà, R. Bayesian estimation of information-theoretic metrics for sparsely sampled distributions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.13647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G. Note on the bias of information estimates. Inf. Theory Psychol. Probl. Methods 1955, 71, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Schürmann, T. Bias analysis in entropy estimation. J. Phys. Math. Gen. 2004, 37, L295–L301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trybula, S. Some Problems of Simultaneous Minimax Estimation. Ann. Math. Stat. 1958, 29, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krichevsky, R.; Trofimov, V. The performance of universal encoding. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1981, 27, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürmann, T.; Grassberger, P. Entropy estimation of symbol sequences. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 1996, 6, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holste, D.; Große, I.; Herzel, H. Bayes’ estimators of generalized entropies. J. Phys. Math. Gen. 1998, 31, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemenman, I.; Shafee, F.; Bialek, W. Entropy and Inference, Revisited. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Dietterich, T., Becker, S., Ghahramani, Z., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Nemenman, I.; Bialek, W.; de Ruyter van Steveninck, R. Entropy and information in neural spike trains: Progress on the sampling problem. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 056111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemenman, I. Coincidences and Estimation of Entropies of Random Variables with Large Cardinalities. Entropy 2011, 13, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simomarsili. ndd—Bayesian Entropy Estimation from Discrete Data. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/simomarsili/ndd (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Horvitz, D.G.; Thompson, D.J. A Generalization of Sampling without Replacement from a Finite Universe. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 663–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rényi, A. On measures of entropy and information. In Proceedings of the Fourth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics Probability, Oakland, CA, USA, 20–30 July 1961; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 1961; Volume 1, pp. 547–561. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, M.H.J. Improving Efficiency by Shrinkage: The James-Stein and Ridge Regression Estimators; Routledge: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer, J.; Strimmer, K. A Shrinkage Approach to Large-Scale Covariance Matrix Estimation and Implications for Functional Genomics. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Wang, Y.T.; Jost, L. Entropy and the species accumulation curve: A novel entropy estimator via discovery rates of new species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raftery, A.E. A model for high-order Markov chains. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. Stat. Methodol. 1985, 47, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelioff, C.C.; Crutchfield, J.P.; Hübler, A.W. Inferring Markov chains: Bayesian estimation, model comparison, entropy rate, and out-of-class modeling. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 011106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bercher, J.F.; Vignat, C. Estimating the entropy of a signal with applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 48, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feutrill, A.; Roughan, M. A review of Shannon and differential entropy rate estimation. Entropy 2021, 23, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C. Generalised information and entropy measures in physics. Contemp. Phys. 2009, 50, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraskov, A.; Stögbauer, H.; Grassberger, P. Estimating mutual information. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 066138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters-Williams, J.; Li, Y. Estimation of mutual information: A survey. In Proceedings of the Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology: 4th International Conference, RSKT 2009, Gold Coast, Australia, 14–16 July 2009; Proceedings 4. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Minculete, N.; Savin, D. Some properties of a type of the entropy of an ideal and the divergence of two ideals. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.07975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaglia, F.; Nemenman, I.; Mora, T.; Walczak, A.M. Bayesian estimation of the Kullback-Leibler divergence for categorical sytems using mixtures of Dirichlet priors. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.04201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery-Smith, S.; Schürmann, T. Unbiased Estimators for Entropy and Class Number. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1410.5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, I. The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 1953, 40, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Gregorio, J.; Sánchez, D.; Toral, R. Entropy Estimators for Markovian Sequences: A Comparative Analysis. Entropy 2024, 26, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26010079
De Gregorio J, Sánchez D, Toral R. Entropy Estimators for Markovian Sequences: A Comparative Analysis. Entropy. 2024; 26(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Gregorio, Juan, David Sánchez, and Raúl Toral. 2024. "Entropy Estimators for Markovian Sequences: A Comparative Analysis" Entropy 26, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26010079
APA StyleDe Gregorio, J., Sánchez, D., & Toral, R. (2024). Entropy Estimators for Markovian Sequences: A Comparative Analysis. Entropy, 26(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/e26010079







