Numerical Assessment of the Hydrodynamic Behavior of a Volute Centrifugal Pump Handling Emulsion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Modeling
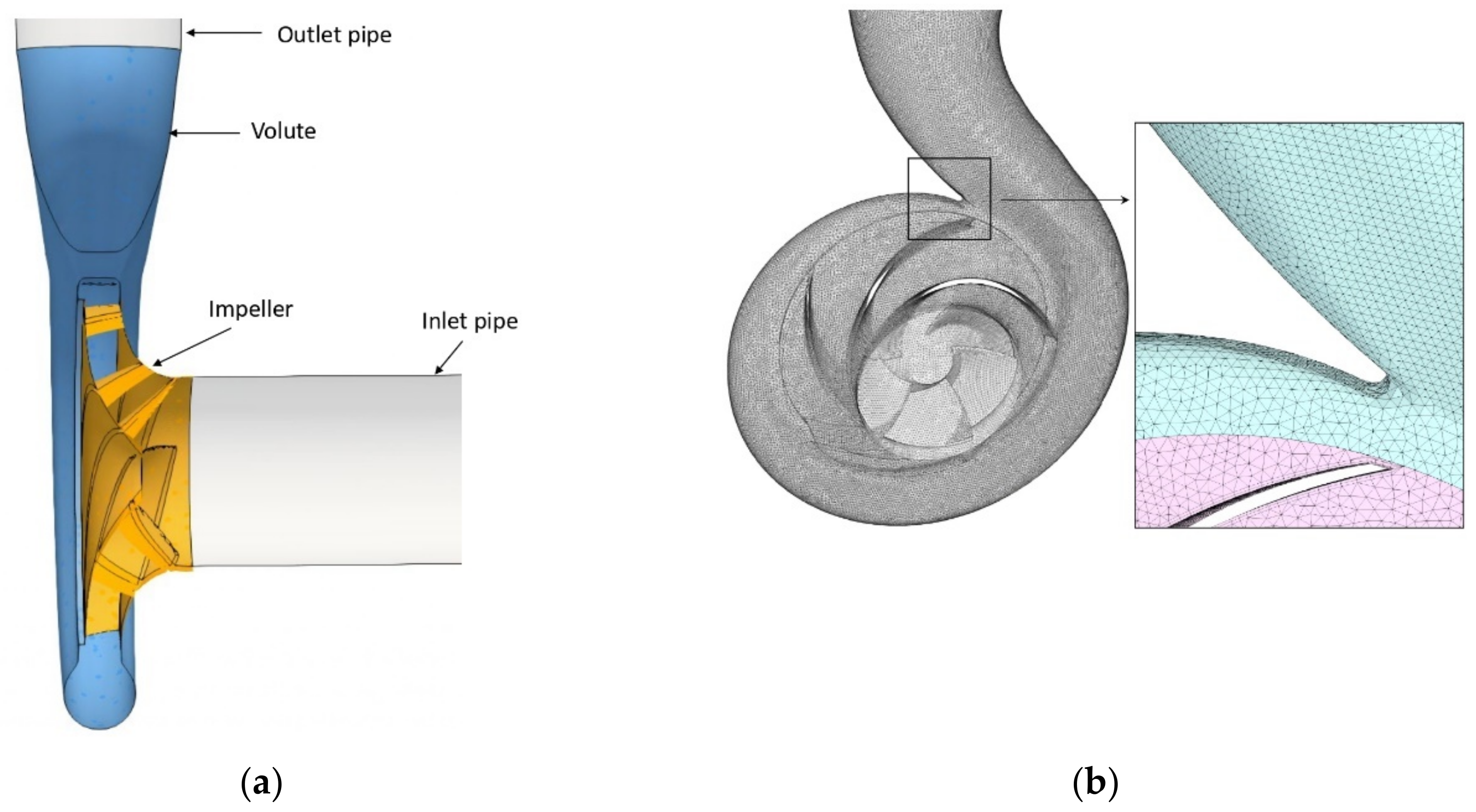
2.1. Geometry and Mesh
2.2. Physical Model Specification
2.3. Numerical Model Validation
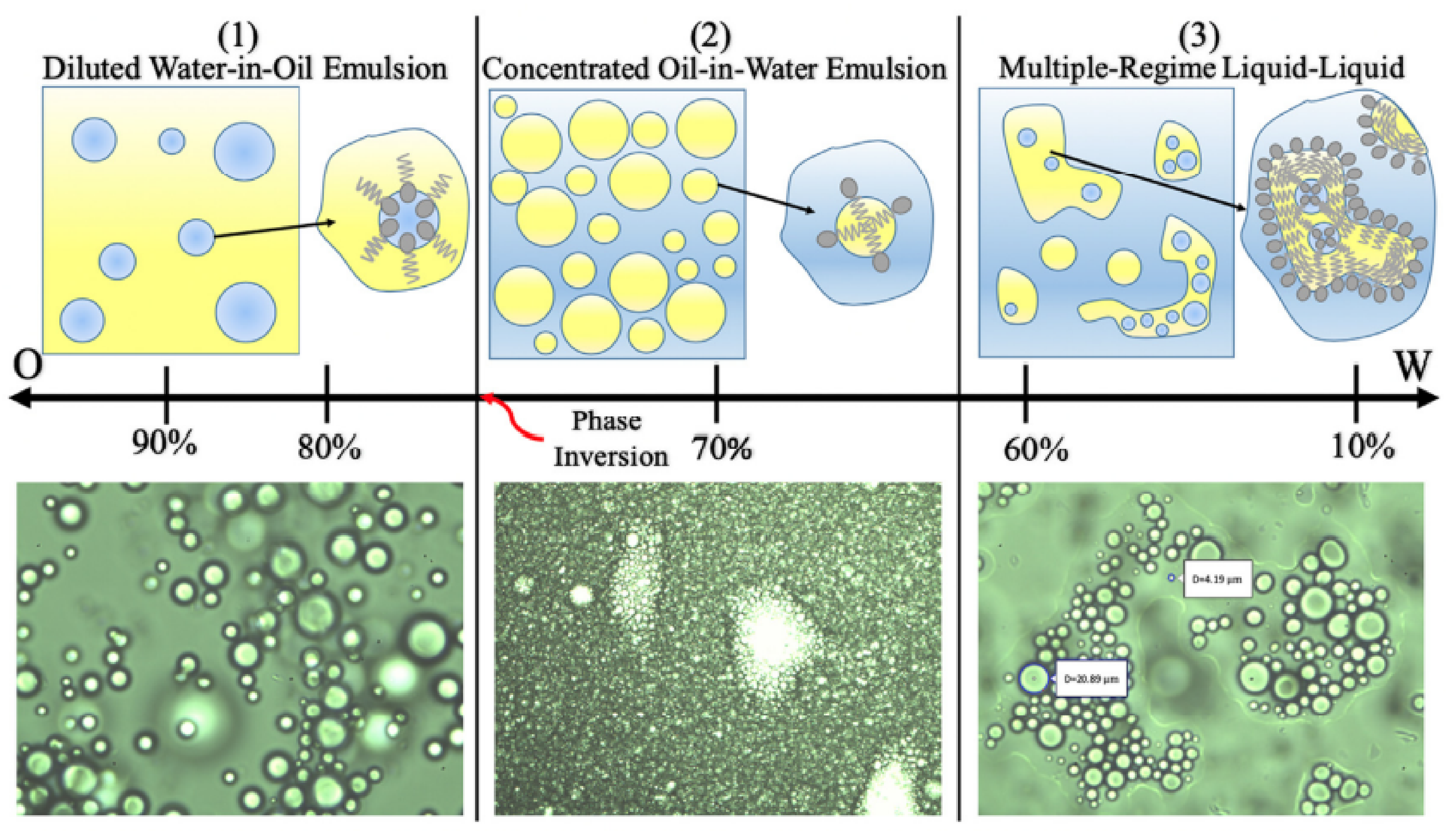
2.4. Emulsion Rheology
3. Results
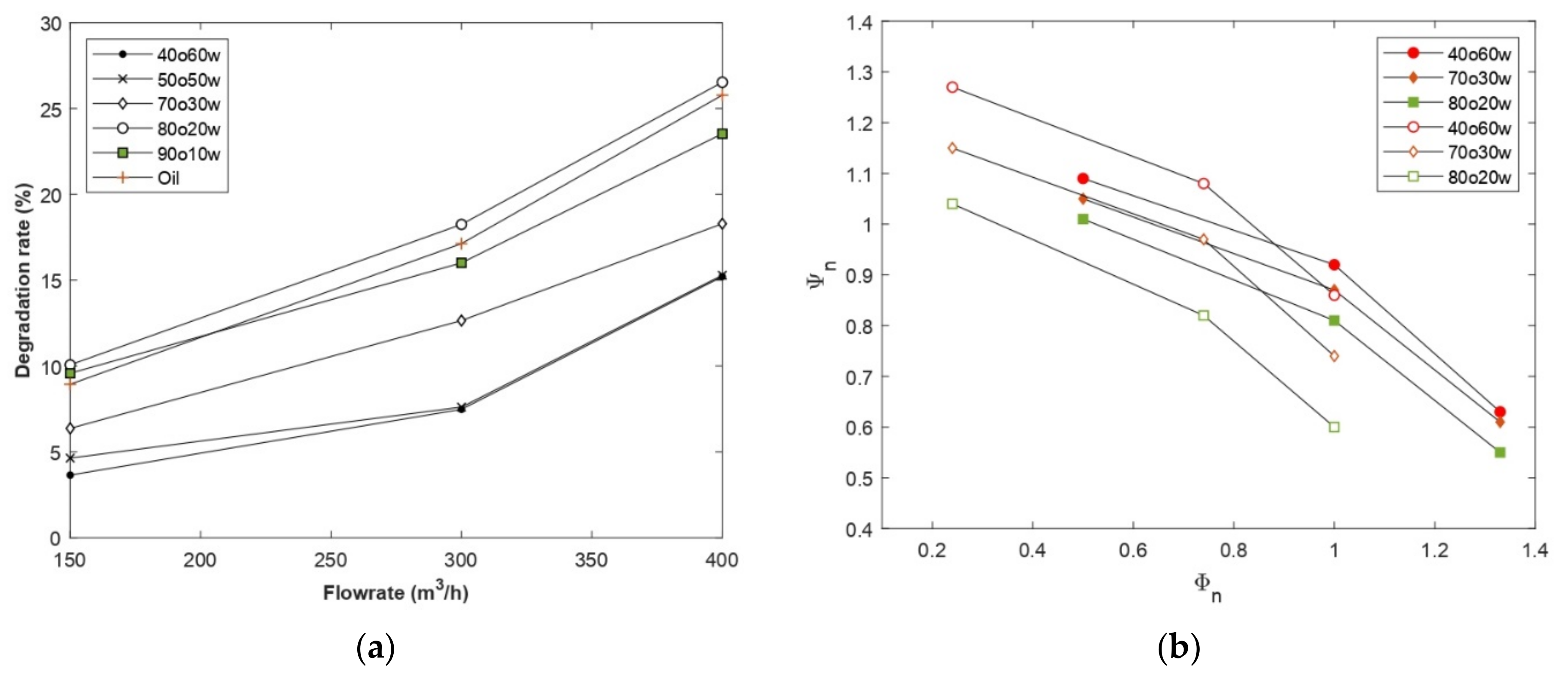
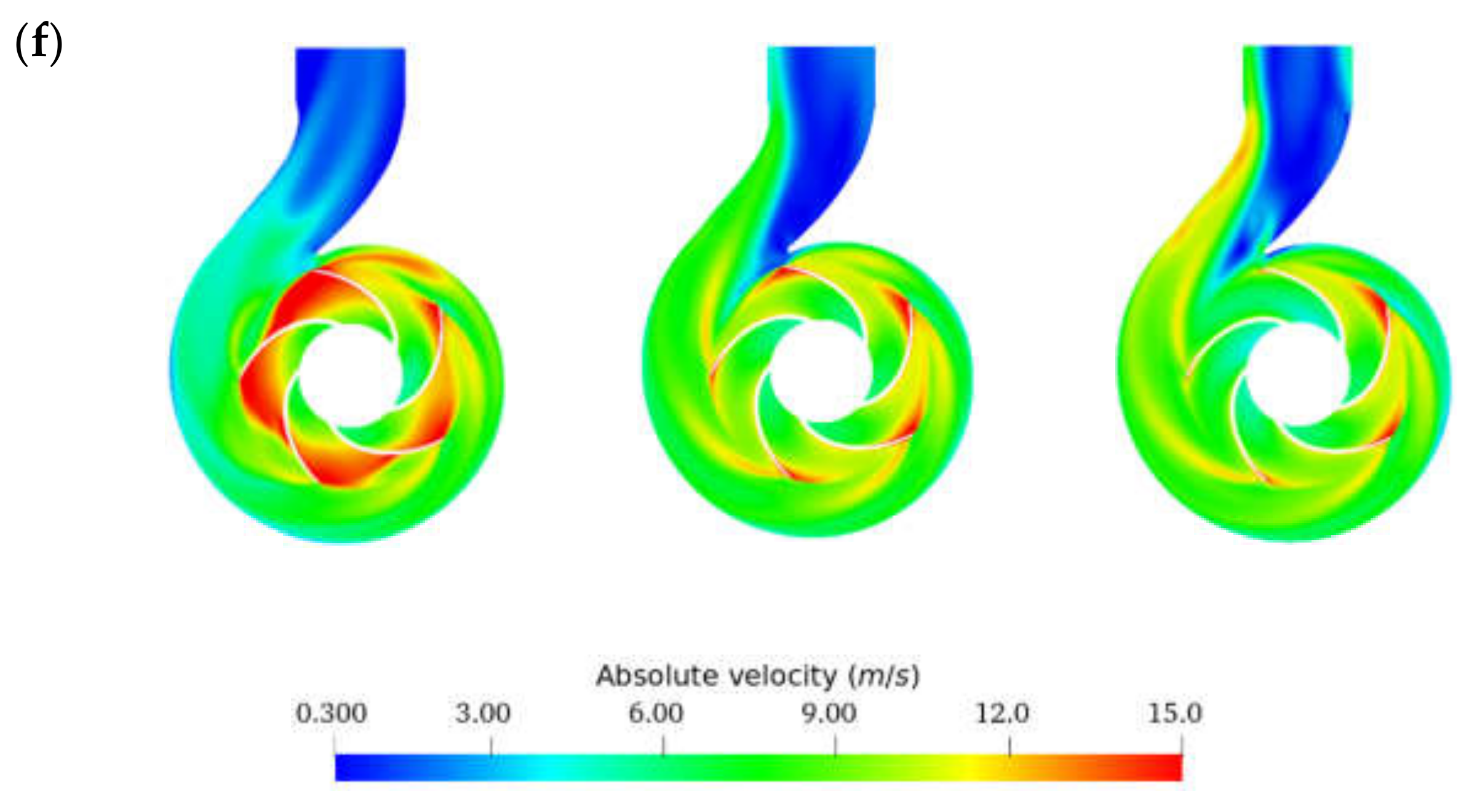
3.1. Centrifugal Pump Performance
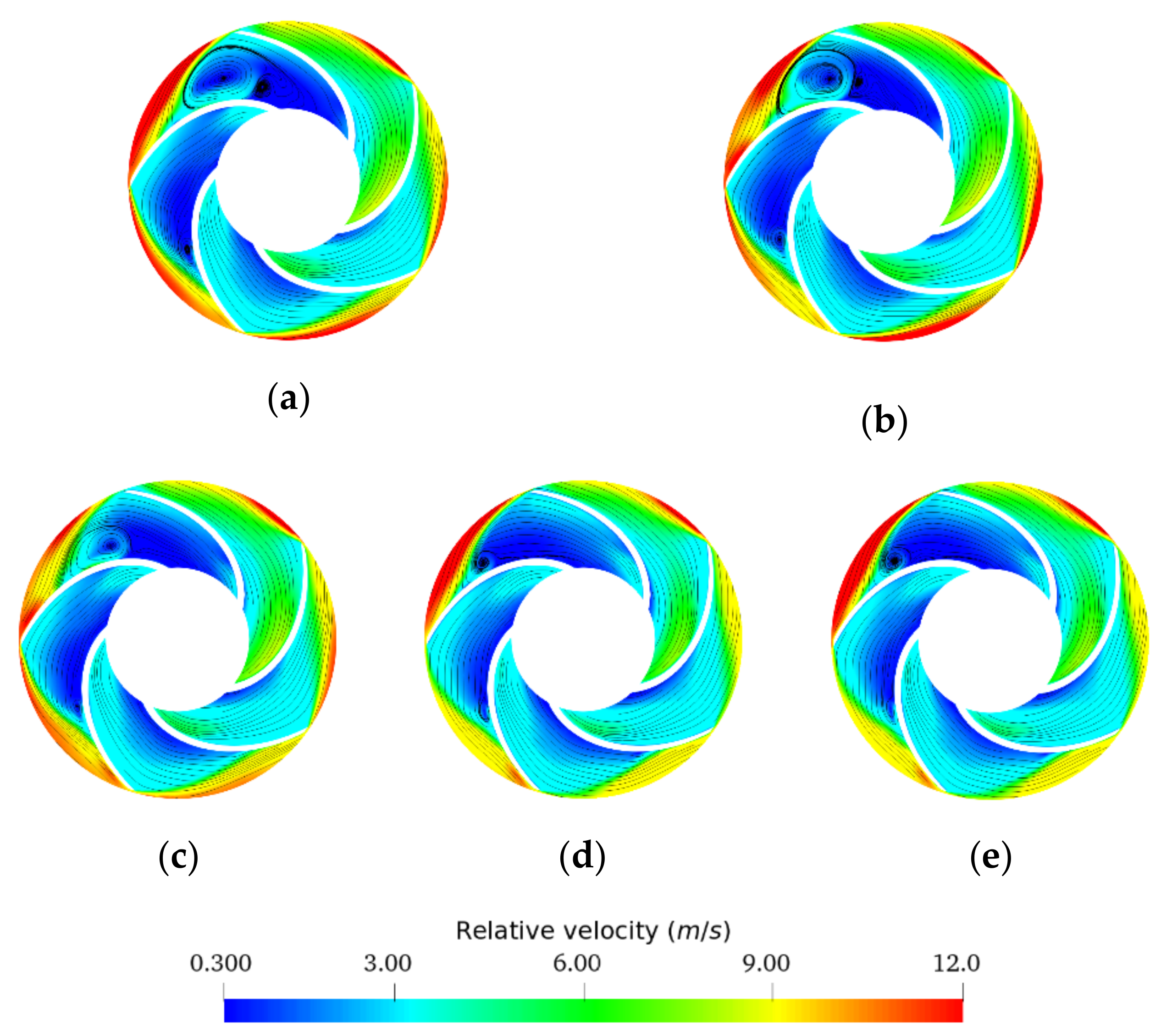
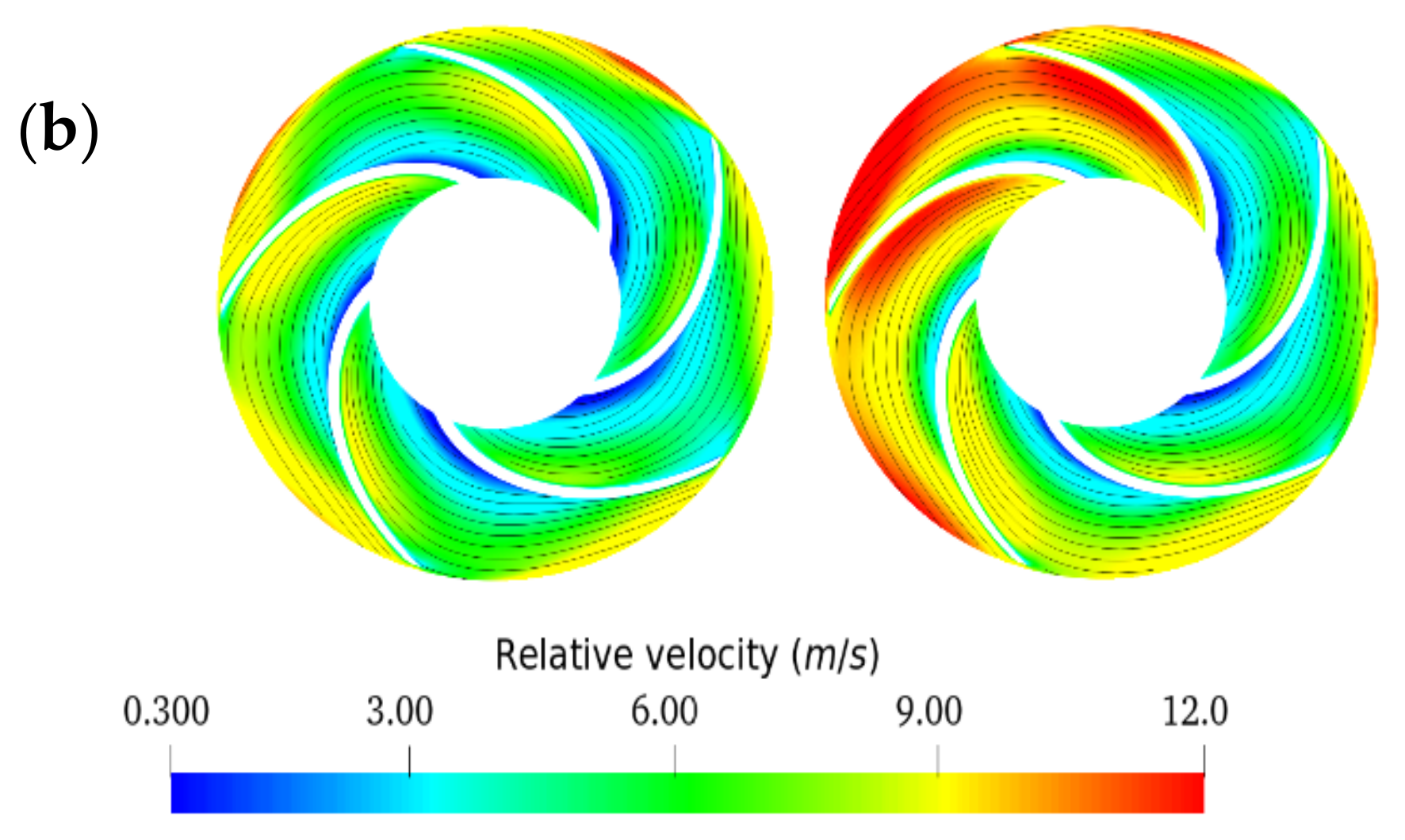
3.2. Internal Flow Analysis
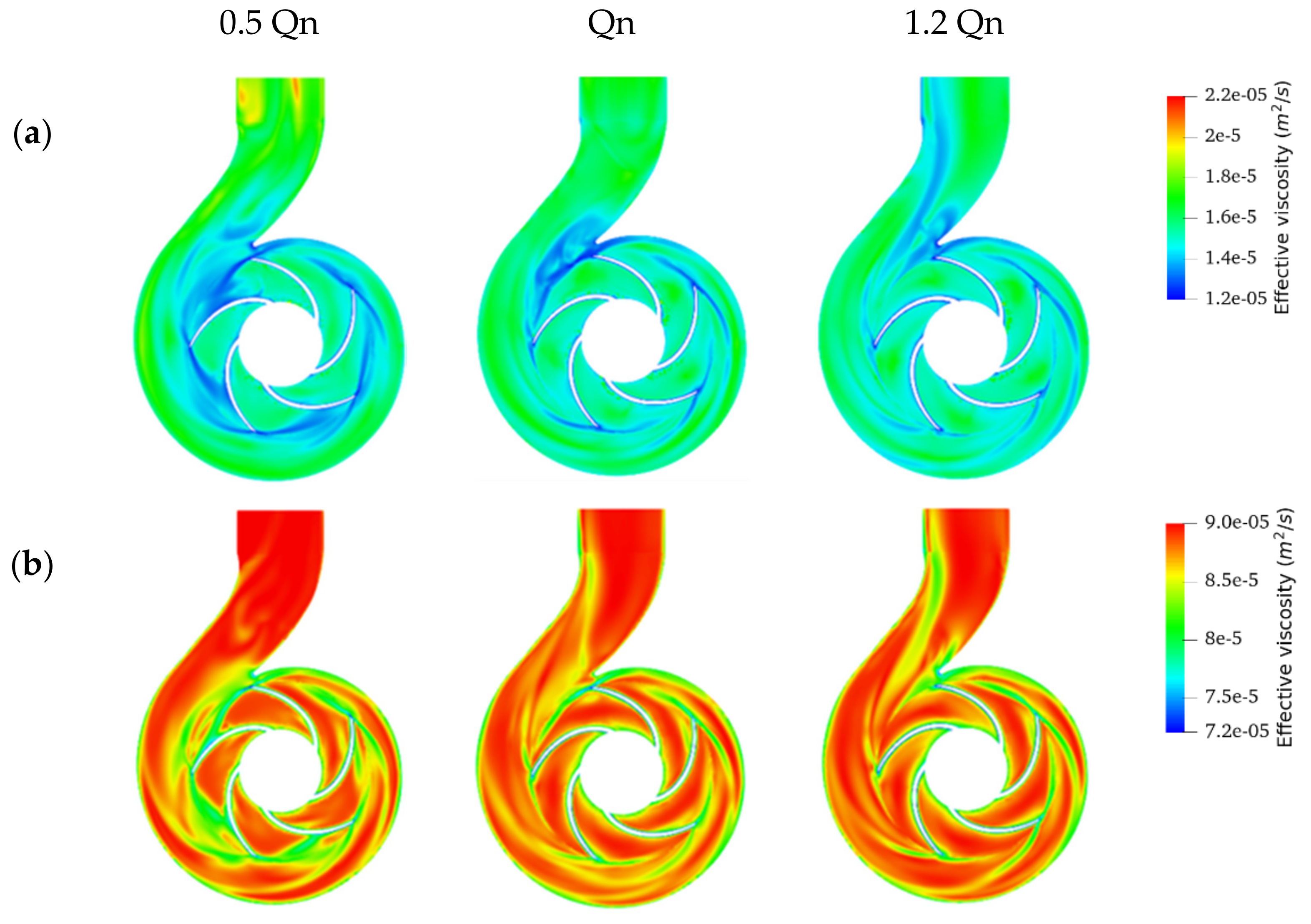
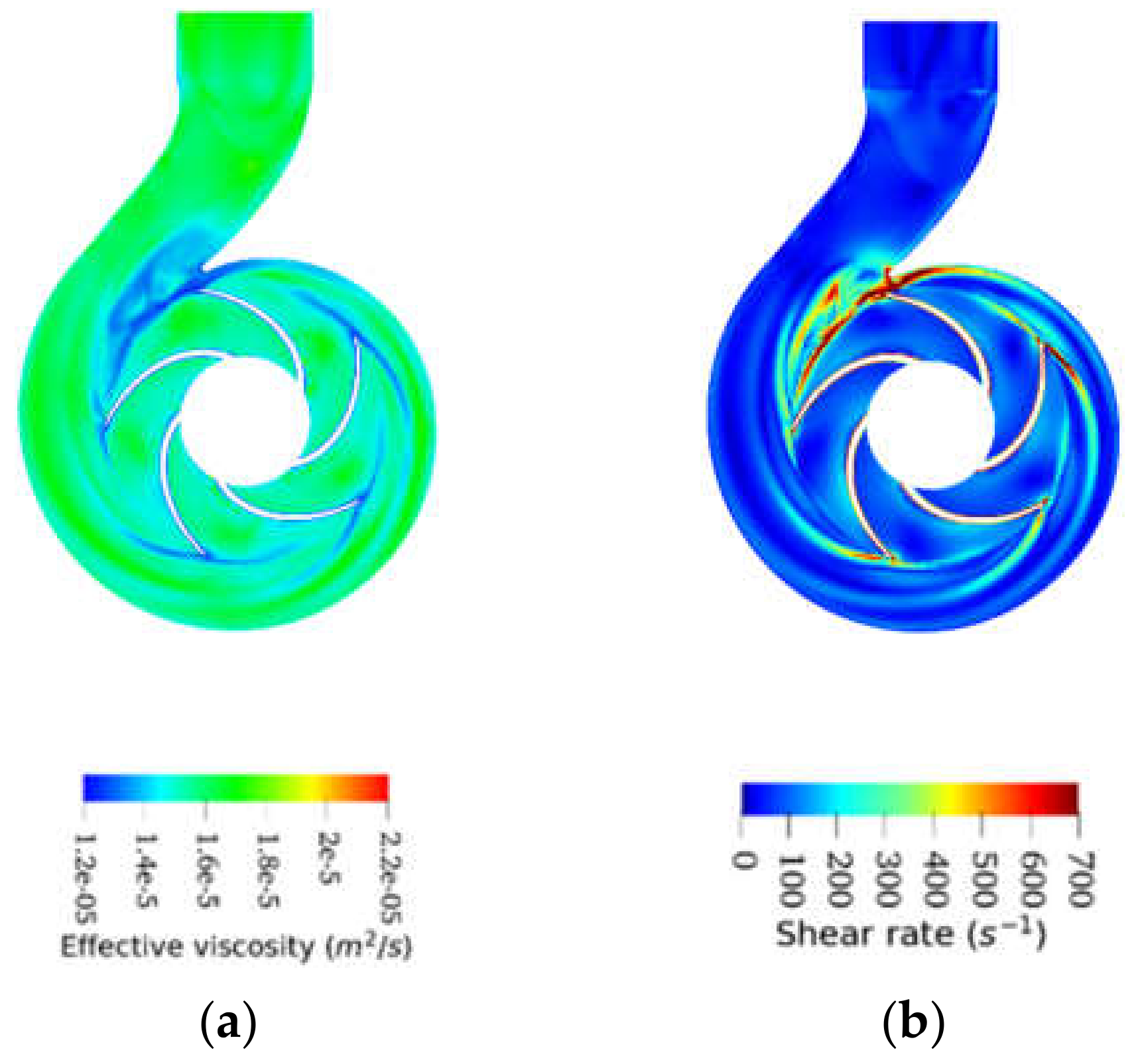
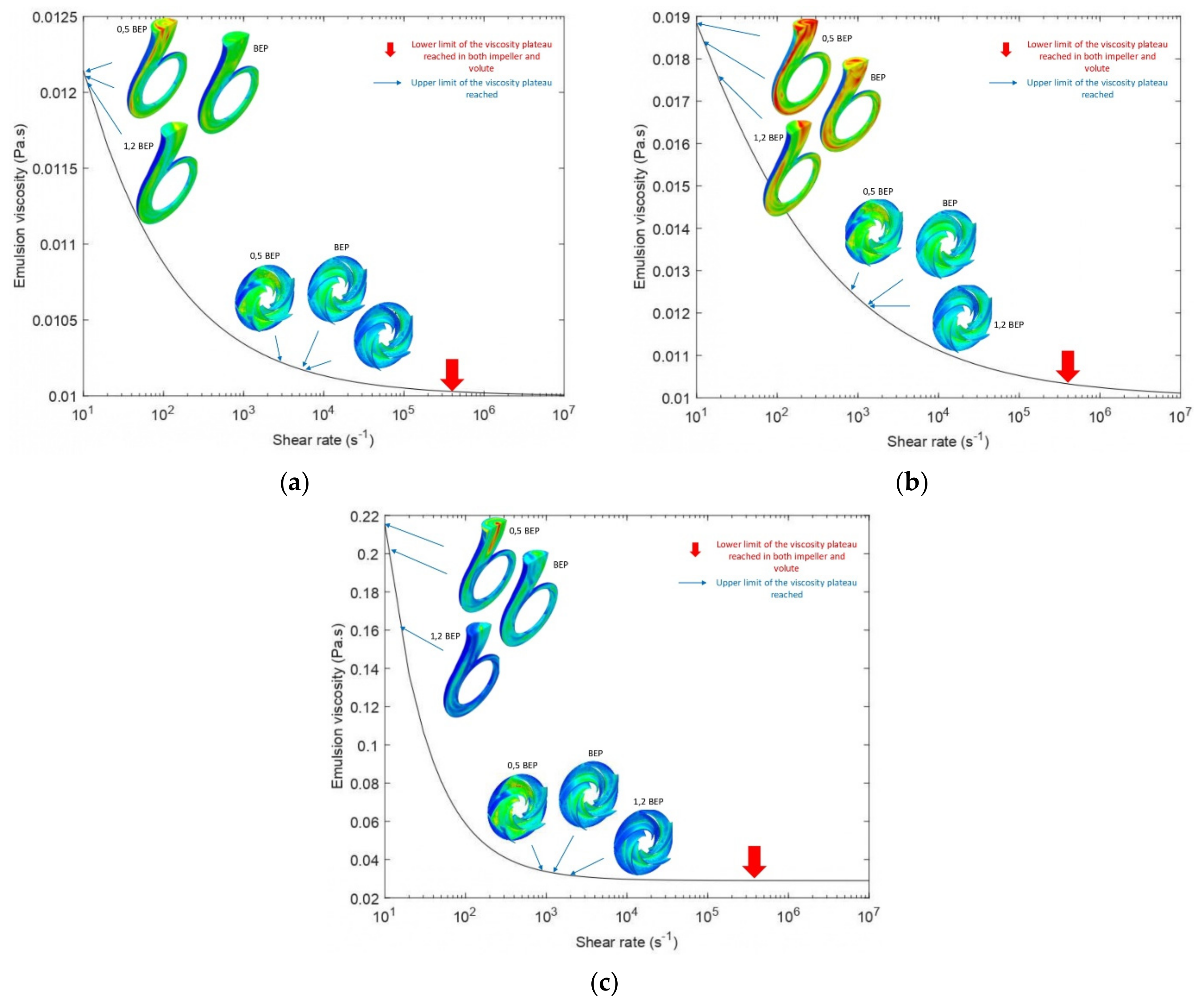
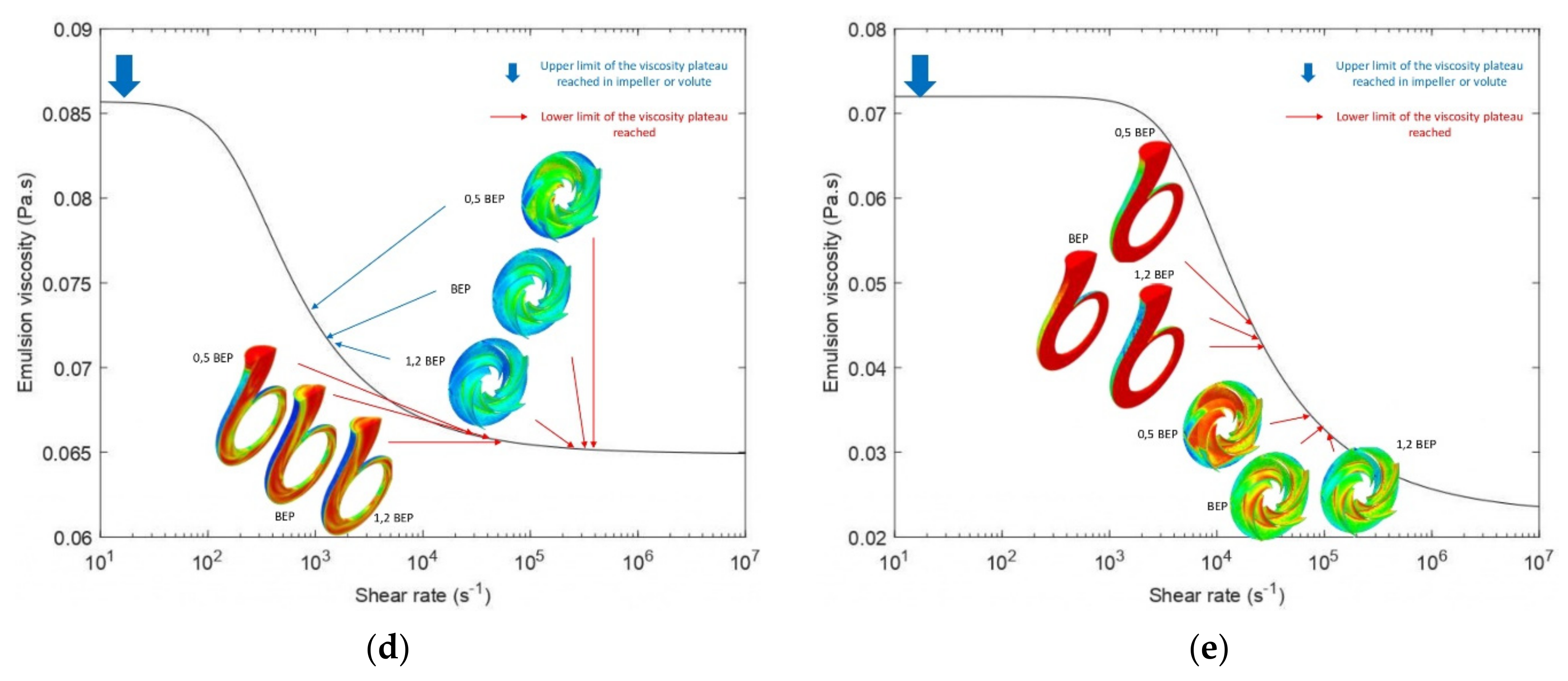
3.3. Effective Viscosity Variation and Shear Stress Profiles
4. Conclusions
- The pump head curves illustrated a general progressive deterioration in performance as the oil fraction increased, except for the composition at the inversion zone. Despite the high effective viscosity of this composition, the strong tendency of the fluid to shear-thinning and the high shear rates of the pump caused the viscosity to decrease sharply. Pointing out that the head developed by the pump at a low volume fraction of the dispersed phase (up to 20% WC) is almost identical to that developed by the continuous phase.
- The smaller the value of ν0, the less frictional losses the fluid will experience, and conversely, the larger the ν∞, the fewer recirculation losses the fluid will experience. As well as the recirculation and friction losses are related to the values of the upper and lower limits of the model; they are also related to the shear sensitivity reflected by the thinning behavior (value of k and n).
- Non-Newtonian behavior of the emulsions was observed with a wide range of effective viscosity in the volute. In contrast, the emulsions exhibited minor non-Newtonian characteristics and/or a small effective viscosity range in the impeller due to the high shear rate generated by rotation in this region.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalil, M.; Kassab, S.; Ismail, A.; Elazab, I. Centrifugal pump performance under stable and unstable oil-water emulsions flow. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Water Technology Conference, Alexandria, Egypt, 27–30 March 2008; pp. 687–702. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgarelli, N.A.V.; Biazussi, J.L.; Monte Verde, W.; Perles, C.E.; de Castro, M.S.; Bannwart, A.C. Experimental investigation on the performance of Electrical Submersible Pump (ESP) operating with unstable water/oil emulsions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 197, 107900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokal, S.; Aramco, S. Crude-Oil Emulsions: A State-of-the-Art Review. SPE Prod. Facil. 2005, 20, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yin, D.; Chen, W.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X. A comprehensive review of emulsion and its field application for enhanced oil recovery. Energy Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.F.; Lim, J.S.; Dol, S.S. Crude oil emulsion: A review on formation, classi fi cation and stability of water-in-oil emulsions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 135, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasencia, J.; Pettersen, B.; Jørgen, O. Pipe flow of water-in-crude oil emulsions: Effective viscosity, inversion point and droplet size distribution. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 101, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, A.H.; Khalil, M.F. Characteristics of centrifugal pump handling stable oil-in-water emulsions. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2006, 15, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Barrios, L.; Rojas, M.; Monteiro, G.; Sleight, N. Brazil field experience of ESP performance with viscous emulsions and high gas using multi-vane pump MVP and high power ESPs. In Proceedings of the SPE Electric Submersible Pump Symposium, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 24–28 April 2017; pp. 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, A.; Yassine, K.; Khalil, M. Effect of Oil-in-Water Concentration on the Performance of Centrifugal Pump. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress of Fluid Dynamics, Ain Soukhna, Egypt, 16–19 December 2010; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, P.; Hlawitschka, M.W.; Bart, H.J. Centrifugal Pumps as Extractors. Chem.-Ing.-Tech. 2020, 92, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales, R.; Pereyra, E.; Wang, S.; Shoham, O. Droplet formation through centrifugal pumps for oil-in-water dispersions. SPE J. 2013, 18, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotto, R.M.; Monte Verde, W.; Perles, C.E.; Biazussi, J.L.; de Castro, M.S.; Bannwart, A.C. Experimental analysis on the behavior of water drops dispersed in oil within a centrifugal pump impeller. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2020, 112, 109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotto, R.M.; Monte Verde, W.; Gallassi, M.; Gonçalves, G.F.N.; de Castro, M.S.; Carneiro, J.; Biazussi, J.L.; Bannwart, A.C. Experimental and numerical study of oil drop motion within an ESP impeller. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 175, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotto, R.M.; Monte Verde, W.; de Castro, M.S.; Biazussi, J.L.; Estevam, V.; Bannwart, A.C. Experimental investigation of oil drops behavior in dispersed oil-water two-phase flow within a centrifugal pump impeller. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2019, 105, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotto, R.M.; Verde, W.M.; Biazussi, J.L.; de Castro, M.S.; Bannwart, A.C. Experimental analysis on the velocity of oil drops in oil-water two-phase flows in electrical submersible pump impellers. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 2019, 141, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellary, S.A.; Siddique, M.H.; Samad, A.; Sangwai, J.S.; Chon, B. Effects of crude oil-water emulsions at various water-cut on the performance of the centrifugal pump. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2017, 16, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, D.; Pereyra, E. Study of oil/water flow and emulsion formation in electrical submersible pumps. SPE Prod. Oper. 2019, 35, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dabirian, R.; Mohan, R.S.; Shoham, O. Effect of Shear and Water Cut on Phase Inversion and Droplet Size Distribution in Oil-Water Flow. J. Energy Resour. Technol. Trans. ASME 2019, 141, 032905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqob, B. Experimentally Investigation the Effect of Oil-Water Phase. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computational Heat and Mass Transfer, Istanbul, Turkey, 18–22 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.G. A method for analyzing the performance of centrifugal oil pumps. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2004, 126, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülich, J.F. Pumping highly viscous fluids with centrifugal pumps—Part 1. World Pumps 1999, 1999, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülich, J.F. Centrifugal Pumps; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.A. A one-dimensional flow analysis for the prediction of centrifugal pump performance characteristics. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2013, 2013, 473512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Cao, G.; Zhang, J.; Peng, J.; Banjar, H.; Zhang, H.Q. A new mechanistic model to predict boosting pressure of electrical submersible pumps ESPs under high-viscosity fluid flow with validations by experimental data. In Proceedings of the SPE Gulf Coast Section Electric Submersible Pumps Symposium, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 13–17 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Cao, G.; Banjar, H.; Peng, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.Q. A new mechanistic model for oil-water emulsion rheology and boosting pressure prediction in electrical submersible pumps ESP. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Calgary, AB, Canada, 30 September–2 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjar, H.; Zhang, H.Q. Experiments and emulsion rheology modeling in an electric submersible pump. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Beijing, China, 26–28 March 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, D.; Rozo, D.; Valdés, J.P.; Asuaje, M.; Ratkovich, N. Experimental and CFD study of an Electrical Submersible Pump’s (ESP) operating under Two-Phase Liquid-Liquid Flow and Water-Oil emulsions. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Multiphase Flow, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 19–24 May 2019; p. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Valdés, J.P.; Asuaje, M.; Ratkovich, N. Study of an ESP’s performance handling liquid-liquid flow and unstable O-W emulsions part II: Coupled CFD-PBM modelling. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 198, 108227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achour, L.; Specklin, M.; Belaidi, I.; Kouidri, S. Numerical Study of the Performance Loss of A Centrifugal Pump Carrying Emulsion. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 321, 01010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuaje, M.; Bakir, F.; Kouidri, S.; Kenyery, F.; Rey, R. Numerical Modelization of the Flow in Centrifugal Pump: Volute Influence in Velocity and Pressure Fields. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2005, 2005, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdés, J.P.; Asuaje, M.; Ratkovich, N. Study of an ESP’s performance handling liquid-liquid flow and unstable O-W emulsions Part I: Experimental. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 223, 115726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Impeller | ||
| Inlet diameter (mm) | 150 | |
| Outlet Diameter (mm) | 408.4 | |
| Inlet blade width (mm) | 85.9 | |
| Outlet blade width (mm) | 42 | |
| Inlet blade angle (°) | 70 | |
| Outlet blade angle (°) | 63 | |
| Number of Blades | 5 | |
| Blade thickness (mm) | e | 8 |
| Volute | ||
| Diameter (mm) | 436 | |
| Base width of the volute | 50 | |
| Pompe NS32 | ||
| Nominal Head (m) | 49 | |
| Rotational speed (rpm) | 1470 | |
| Nominal Flowrate ( /h) | 590 | |
| Specific Speed | 32 |
| Characteristics | Number of Cells |
|---|---|
| M1 | 1,230,000, |
| M2 | 2,750,000, |
| M3 | 4,091,000, |
| M4 | 7,900,000, |
| Parameter | Max Aspect Ratio | Max Non-Orthogonality | Max Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 349 | 7.95 | 3.13 |
| Phase Composition (% v/v oil) | Viscosity Model | ρ (kg/m3) | (-) | ν (m2/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | Newtonian | 922.0 | - | - | - | - | 6.29 × 10−5 |
| 90 | Carreau | 947.8 | 0.471 | 2.03 × 10−4 | 7.59 × 10−5 | 2.40 × 10−5 | - |
| 80 | Carreau | 952.2 | 0.421 | 5.30 × 10−3 | 9.01 × 10−5 | 6.82 × 10−5 | - |
| 70 | Carreau Cross | 953.0 | 0.339 0.801 | 45.88 23.39 | 1.57 × 10−2 | 3.14 × 10−5 | - |
| 50 | Cross | 966.9 | 0.339 | 1.94 | 4.44 × 10−5 | 1.03 × 10−5 | - |
| 40 | Cross | 978.3 | 0.416 | 21.06 | 3.27 × 10−5 | 1.02 × 10−5 | - |
| 0 | Newtonian | 1000.0 | - | - | - | - | 1.00 × 10−6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achour, L.; Specklin, M.; Belaidi, I.; Kouidri, S. Numerical Assessment of the Hydrodynamic Behavior of a Volute Centrifugal Pump Handling Emulsion. Entropy 2022, 24, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020221
Achour L, Specklin M, Belaidi I, Kouidri S. Numerical Assessment of the Hydrodynamic Behavior of a Volute Centrifugal Pump Handling Emulsion. Entropy. 2022; 24(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020221
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchour, Lila, Mathieu Specklin, Idir Belaidi, and Smaine Kouidri. 2022. "Numerical Assessment of the Hydrodynamic Behavior of a Volute Centrifugal Pump Handling Emulsion" Entropy 24, no. 2: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020221
APA StyleAchour, L., Specklin, M., Belaidi, I., & Kouidri, S. (2022). Numerical Assessment of the Hydrodynamic Behavior of a Volute Centrifugal Pump Handling Emulsion. Entropy, 24(2), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/e24020221






