Designing Bivariate Auto-Regressive Timeseries with Controlled Granger Causality
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Vector Auto-Regressive Model, Granger Causality, and Transfer Entropy
2. Vector Auto-Regression (VAR)
2.1. Marginal Distribution of the VAR at Each Step
2.2. Stability of VAR: Lyapunov Equation
3. Transfer Entropy and Granger Causality
4. Stability and Constraints of VAR
- Stability
- Any stable VAR model has both of the eigenvalues of its coefficient matrix A meeting .
- Properness
- To have a proper (non-degenerated) bivariate normal distribution in a VAR model, its base covariance matrix and stationary covariance matrix need to satisfy . The set of positive-definite matrices is equivalently written with the entries of the following matrix:
4.1. Stability of VAR
- If is real, this stability condition is equivalent to
- If is not real, this stability condition is equivalent with
4.2. Stability and Existence of the Solution for the Lyapunov Equation
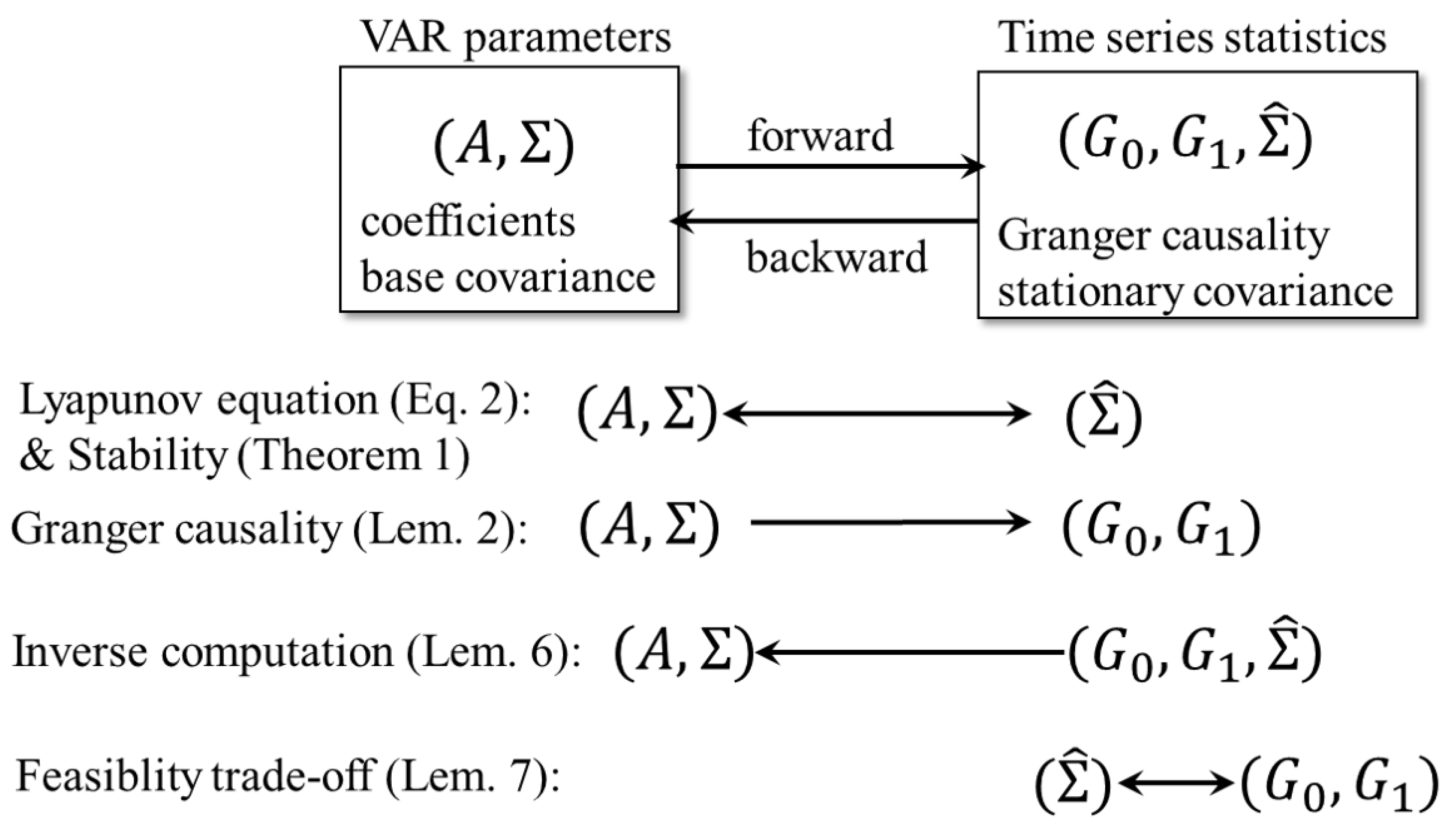
5. Design of Bivariate Timeseries Given GCs
- The coefficient matrix A;
- The base covariance matrix ;
- The stationary covariance matrix ; and
- The two types of Granger causality .
- The variables need to satisfy the Lyapunov Equation (4).
- Granger causality () is the function of , , and (Lemma 2).
5.1. Solution A of the Lyapunov Equality Given , , and
5.2. Sufficiency of the Solution
6. Concluding Remarks
6.1. Summary and Potential Usage of the Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Compute a VAR parameter set for the desired statistics |
| Data: Desired timeseries statistics in the feasible range satisfy both inequalities (56) in Lemma 6 and (60) in Lemma 7. 1 Derive four sets of VAR parameters for the given timeseries statistics by Lemma 5 2 Choose one of the four sets of VAR parameters . Result: The VAR parameters . |
6.2. Validity of Granger Causality Estimated on Empirical Timeseries
6.3. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heider, F.; Simmel, M. An experimental study of apparent behavior. Am. J. Psychol. 1944, 57, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassili, J.N. Temporal and spatial contingencies in the perception of social events. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1976, 33, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, W.H.; Lea, S.E. Visual perception of intentional motion. Perception 1994, 23, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremoulet, P.D.; Feldman, J. Perception of animacy from the motion of a single object. Perception 2000, 29, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholl, B.J.; Tremoulet, P.D. Perceptual causality and animacy. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2000, 4, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, K. Synchronous motion modulates animacy perception. J. Vis. 2015, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, C.W. Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 1969, 37, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, T. Measuring information transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, L.; Barrett, A.B.; Seth, A.K. Granger causality and transfer entropy are equivalent for Gaussian variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 238701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, M. Granger causality and path diagrams for multivariate time series. J. Econom. 2007, 137, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.R. Granger causality and the times series analysis of political relationships. Am. J. Political Sci. 1983, 27, 327–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerding, W. Economic growth and defense spending: Granger causality. J. Dev. Econ. 1986, 21, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.K. Measuring autonomy and emergence via Granger causality. Artif. Life 2010, 16, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, S.; Hirotani, M.; Koike, T.; Bosch-Bayard, J.; Takahashi, H.K.; Hashiguchi, M.; Sadato, N. Unintentional interpersonal synchronization represented as a reciprocal visuo-postural feedback system: A multivariate autoregressive modeling approach. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressler, S.L.; Seth, A.K. Wiener–Granger causality: A well established methodology. Neuroimage 2011, 58, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Chen, Y.; Bressler, S.L. 17 Granger causality: Basic theory and application to neuroscience. In Handbook of Time Series Analysis: Recent Theoretical Developments and Applications; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 437. [Google Scholar]
- Porta, A.; Faes, L. Wiener–Granger causality in network physiology with applications to cardiovascular control and neuroscience. Proc. IEEE 2015, 104, 282–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.K.; Barrett, A.B.; Barnett, L. Granger causality analysis in neuroscience and neuroimaging. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 3293–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prichard, D.; Theiler, J. Generating surrogate data for time series with several simultaneously measured variables. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 73, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hidaka, S.; Torii, T. Designing Bivariate Auto-Regressive Timeseries with Controlled Granger Causality. Entropy 2021, 23, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23060742
Hidaka S, Torii T. Designing Bivariate Auto-Regressive Timeseries with Controlled Granger Causality. Entropy. 2021; 23(6):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23060742
Chicago/Turabian StyleHidaka, Shohei, and Takuma Torii. 2021. "Designing Bivariate Auto-Regressive Timeseries with Controlled Granger Causality" Entropy 23, no. 6: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23060742
APA StyleHidaka, S., & Torii, T. (2021). Designing Bivariate Auto-Regressive Timeseries with Controlled Granger Causality. Entropy, 23(6), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23060742






