Early Universe Thermodynamics and Evolution in Nonviscous and Viscous Strong and Electroweak Epochs: Possible Analytical Solutions
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geometry and Field Equations
3. Cosmic Evolution in Non-Viscous Approach
3.1. Hadronic Era
- At vanishing k, which is the case at , we have analytical solutions. Then, Equation (12) can be solved as,where and are integration constants which can be fixed at boundary and initial conditions. For instance, at , , Equation (14), then, . In general, has the dimension of the cosmic time t and therefore varies with the evolution of the Universe. Hence, is finite and the cosmological parameters of the hadron epoch (assuming that ) MeV), for instance Equation (14) can be estimated, numerically. On the other hand, for the scale factor, , we still need to estimate the other integration constant . Having an analytical expression for the scale factor, Equation (13), then the Hubble parameter can then be obtained,
- At non-vanishing k, there is no direct analytical solution for . When assuming that and substituting this into Equation (12),a solution for can be proposedThe physical solution is the one assuring that,Hence, the Hubble parameter can be deduced asBy solving the second-order differential Equation (16), an analytical expression for the scale factor can also be deduced,whose time dependence is given by the time dependence of the corresponding EoS, namely and , which are listed in Table 1. As discussed, they have an indirect time dependence through the coefficients of the corresponding EoS. Within one era, they are conjectured to remain constant. The latter might be the only way possible to gain an analytical solution. Then, , Equation (18), can be rewritten asApparently, all coefficients involved in it can be determined.
3.2. QCD and EW Era
3.3. Asymptotic Limit
4. Cosmic Evolution in Viscous Approaches
4.1. Viscous Equations of State
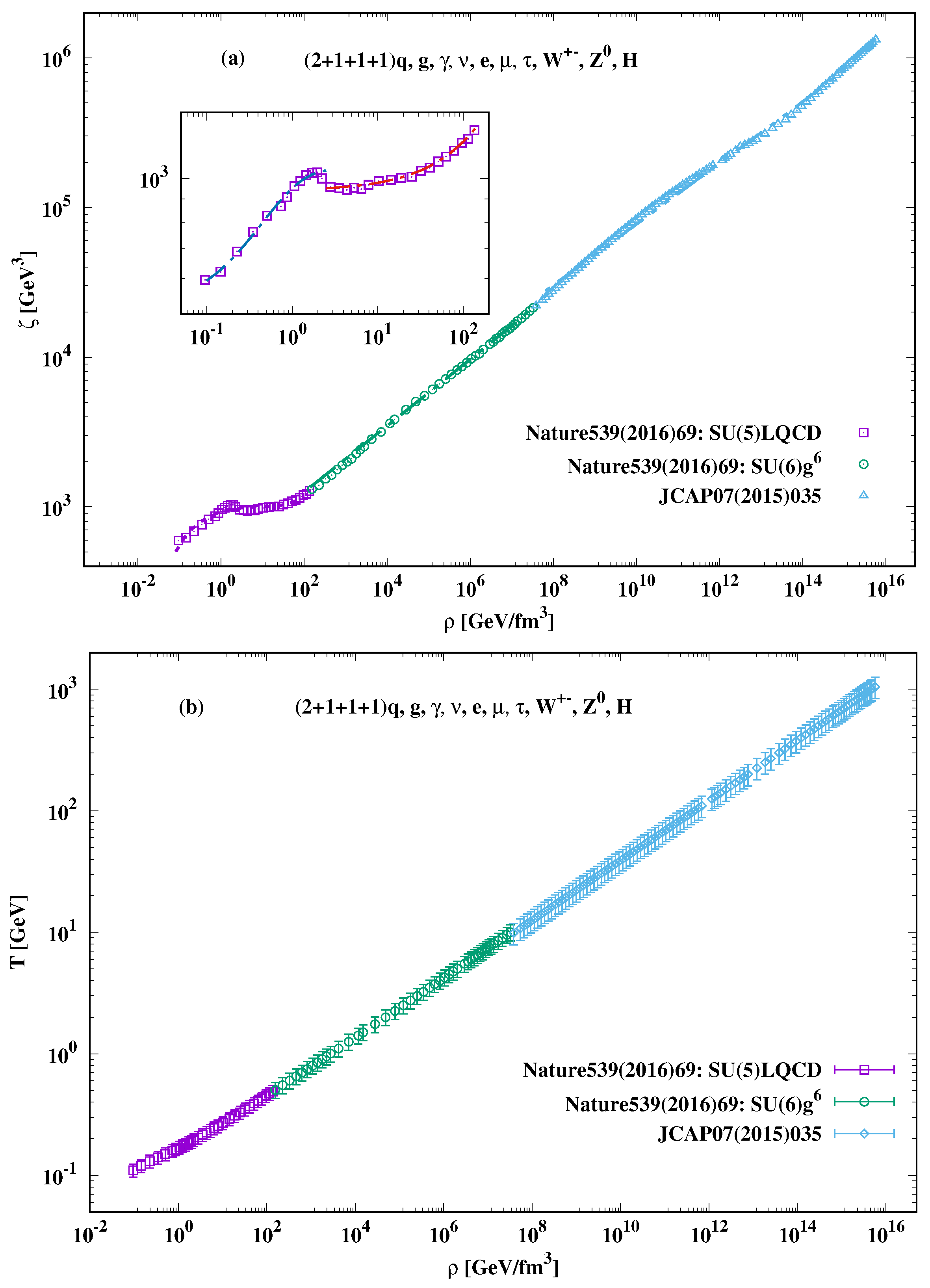
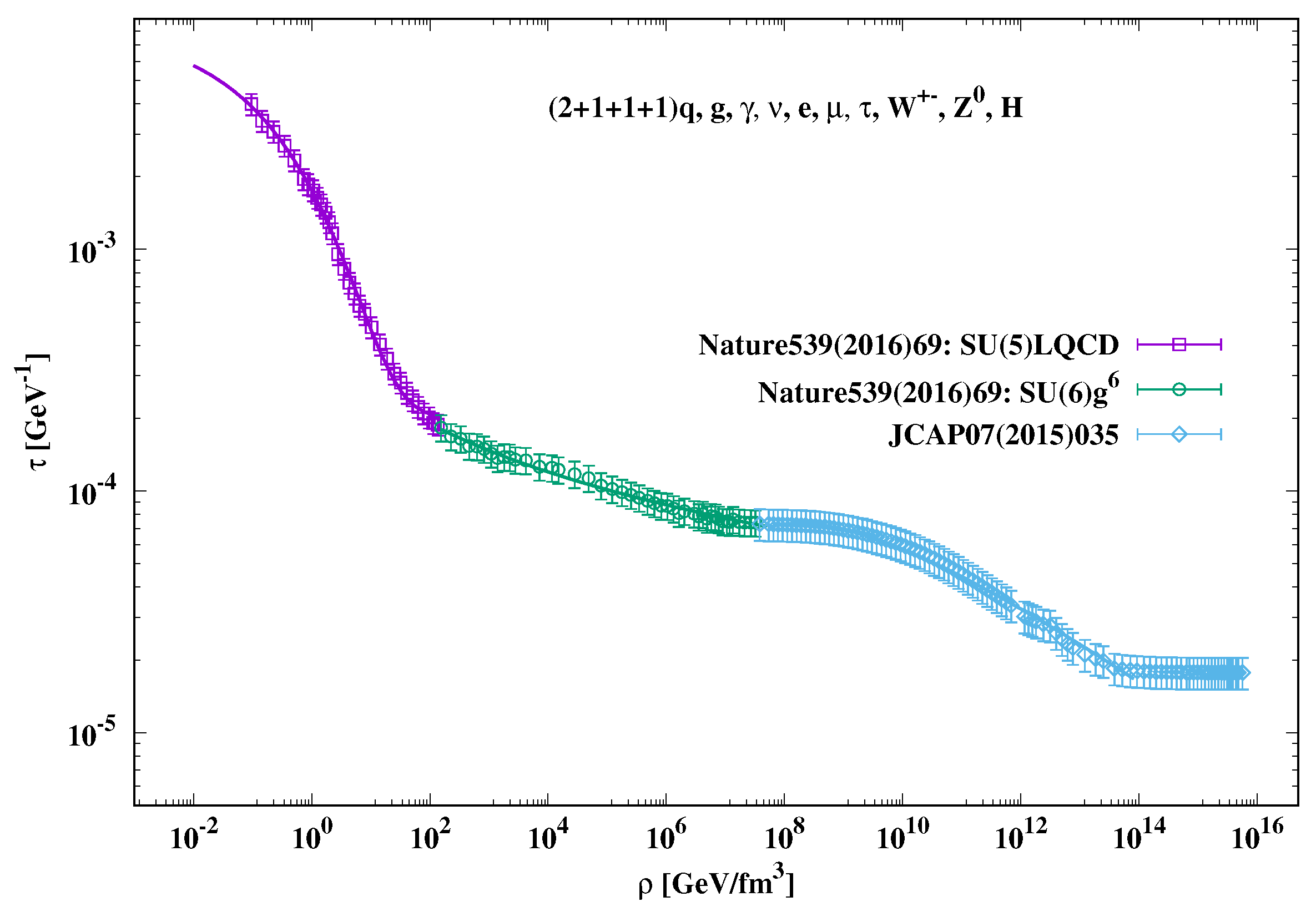
- The first one is the hadron-QGP domain (Hadron-QGP), which spans over GeV/fm. At the beginning, there is a rapid increase in , i.e., GeV, at GeV/fm, which is then followed by a slight increase in . For example, at GeV/fm, reaches ∼GeV. It is apparent that the hadron–parton phase transition seems to take place at GeV/fm[34,35]. At this value, GeV.
- The second domain, the QGP epoch, seems to be formed, at GeV/fm, i.e., a much wider than that of the hadron domain. Thus, we could conclude that over this wide range of , the bulk viscosity is obviously not only finite but rather largely supporting the RHIC discovery of strongly correlated viscous QGP [3,4,6]. At higher , we observe a tendency of a linear increase in with further increasing . Thus, the second domain is the one where GeV/fm and GeV. In light of this observation, we conclude that the phase transition from QCD to EW domain is very smooth.
- The third domain is also characterized by an almost linear increase in with increasing . For GeV/fm, there is a nearly steady increase in from to GeV.
4.2. Eckart Relativistic Viscous Fluid
4.2.1. Hadron-QGP Era
4.2.2. QCD-EW Era
4.2.3. EW (Asymptotic) Era
4.3. Israel–Stewart Relativistic Viscous Fluid
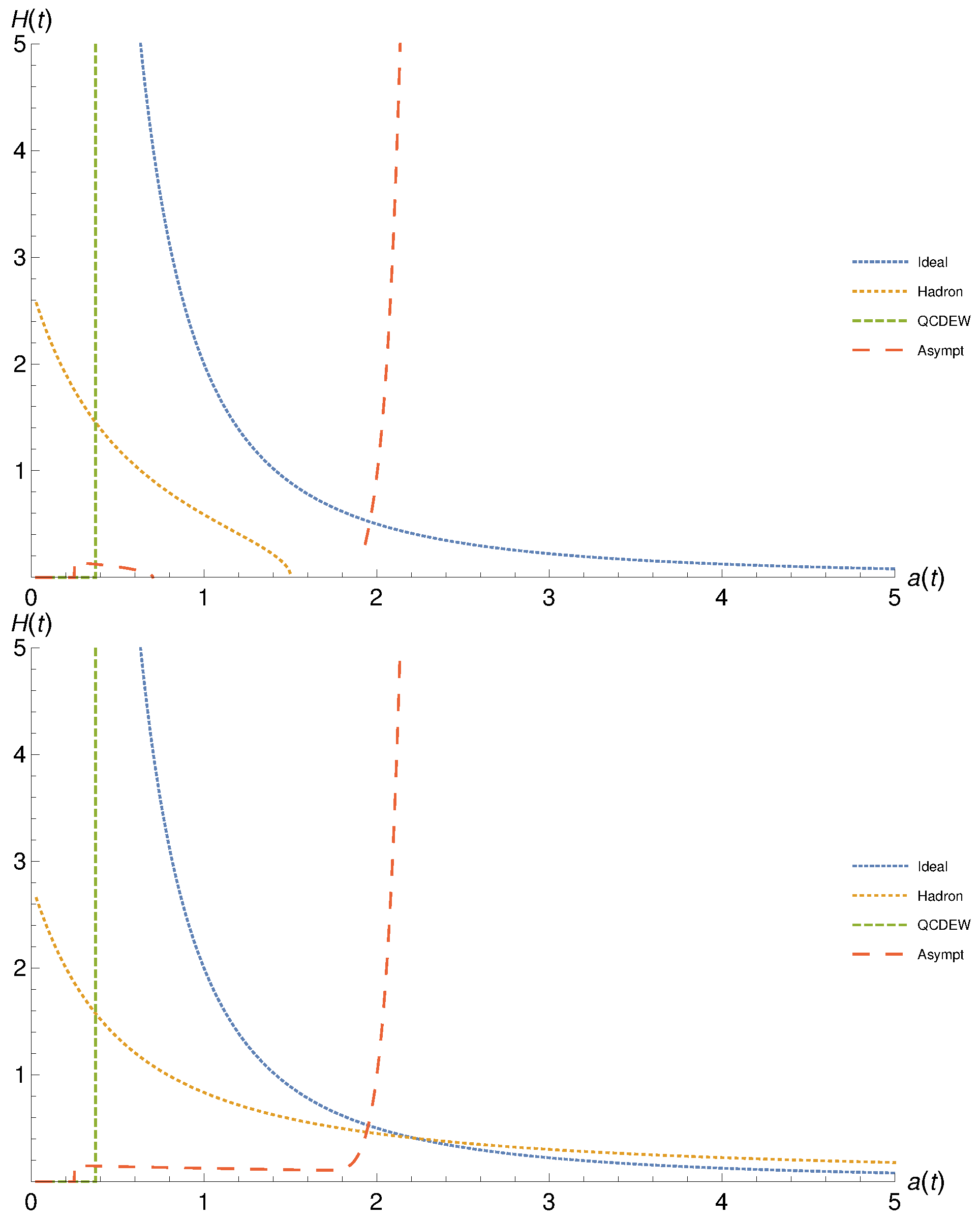
5. Results
5.1. Non-Viscous Fluid
5.2. Eckart-Type Viscous Fluid
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Relativistic Viscous Fluid in the Expanding Early Universe
Appendix A.1. Israel—Stewart Second-Order Theory
Appendix A.1.1. Hadron Epoch
Appendix A.1.2. QGP Epoch
Appendix A.1.3. QCD-EW Epoch
Appendix A.1.4. EW (Asymptotic) Epoch
References
- Heinz, U.W. The Little bang: Searching for quark gluon matter in relativistic heavy ion collisions. Nucl. Phys. 2001, 685, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.M.; Ganssauge, E. Levy stable law description of the intermittent behavior in Pb + Pb collisions at 158/A-GeV. Acta Phys. Hung. 2000, 12, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Gyulassy, M.; McLerran, L. New forms of QCD matter discovered at RHIC. Nucl. Phys. 2005, A750, 30–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, U.; Shen, C.; Song, H. The viscosity of quark-gluon plasma at RHIC and the LHC. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1441, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, L.; Adkins, J.K.; Agakishiev, G.; Aggarwal, M.M.; Ahammed, Z.; Alekseev, I.; Alford, J.; Anson, C.D.; Aparin, A.; Arkhipkin, D.; et al. Energy Dependence of Moments of Net-proton Multiplicity Distributions at RHIC. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 032302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.; Paquet, J.F.; Shen, C.; Denicol, G.; Schenke, B.; Jeon, S.; Gale, C. Effects of bulk viscosity and hadronic rescattering in heavy ion collisions at energies available at the BNL Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider and at the CERN Large Hadron Collider. Phys. Rev. 2018, C97, 034910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzdak, A.; Esumi, S.; Koch, V.; Liao, J.; Stephanov, M.; Xu, N. Mapping the Phases of Quantum Chromodynamics with Beam Energy Scan. Phys. Rep. 2020, 853, 1–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, E.; Smith, K.M.; Dunkley, J.; Bennett, C.L.; Gold, B.; Hinshaw, G.; Jarosik, N.; Larson, D.; Nolta, M.R.; Page, L.; et al. Seven-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Cosmological Interpretation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2011, 192, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ade, P.A.R.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartlett, J.G.; Bartolo, N.; et al. Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; et al. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parametersAstron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar]
- Akrami, Y.; Arroja, F.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; et al. Planck 2018 results. X. Constraints on inflation. Astron. Astrophys. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; et al. Planck 2018 results. V. CMB power spectra and likelihoods. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A5. [Google Scholar]
- Akrami, Y.; Arroja, Y.; Ashdown, M.; Aumont, J.; Baccigalupi, C.; Ballardini, M.; Banday, A.J.; Barreiro, R.B.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; et al. Planck 2018 results. VII. Isotropy and Statistics of the CMB. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A7. [Google Scholar]
- Misner, C.W. The isotropy of the universe. Astrophys. J. 1968, 151, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B.; Novikov, I.D. Relativistic Astrophysics. Vol. 2: The Structure and Evolution of the Universe; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik, A.N.; Mishustin, I. Equation of State for Cosmological Matter at and beyond QCD and Electroweak Eras. J. Phys. 2019, G46, 125201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gron, O. Viscous inflationary universe models. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1990, 173, 191–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maartens, R. Dissipative cosmology. Class. Quant. Grav. 1995, 12, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.; Harko, T.; Mansour, H.; Wahba, M. Dissipative Processes in the Early Universe: Bulk Viscosity. Uzb. J. Phys. 2010, 12, 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik, A.; Wahba, M.; Mansour, H.; Harko, T. Hubble Parameter in QCD Universe for finite Bulk Viscosity. Ann. Phys. 2010, 522, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.; Harko, T. Quark-Hadron Phase Transitions in Viscous Early Universe. Phys. Rev. 2012, D85, 084032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A. The Hubble parameter in the early universe with viscous QCD matter and finite cosmological constant. Ann. Phys. 2011, 523, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.; Magdy, H. Thermodynamics of viscous Matter and Radiation in the Early Universe. Can. J. Phys. 2012, 90, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.; Wahba, M.; Mansour, H.; Harko, T. Viscous Quark-Gluon Plasma in the Early Universe. Ann. Phys. 2011, 523, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A. Thermodynamics in the Viscous Early Universe. Can. J. Phys. 2010, 88, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.N.; Greiner, C. Bulk viscosity at high temperatures and energy densities. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.02797. [Google Scholar]
- Laine, M.; Schroder, Y. Quark mass thresholds in QCD thermodynamics. Phys. Rev. 2006, D73, 085009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, M.; Meyer, M. Standard Model thermodynamics across the electroweak crossover. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 1507, 035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, M.; Rummukainen, K. Standard model cross-over on the lattice. Phys. Rev. 2016, D93, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsanyi, S.; Fodor, Z.; Guenther, J.; Kampert, K.-H.; Katz, S.D.; Kawanai, T.; Kovacs, T.G.; Mages, S.W.; Pasztor, A.; Pittler, F.; et al. Calculation of the axion mass based on high-temperature lattice quantum chromodynamics. Nature 2016, 539, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrea, W.H.; Milne, E.A. A Newtonian expanding universe. Q. J. Math. 1934, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrea, W.H.; Milne, E.A. Newtonian Universes and the Curvature of Space. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2000, 32, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, P.J.E. Principles of Physical Cosmology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik, A. QCD phase diagram: A Comparison of lattice and hadron resonance gas model calculations. Phys. Rev. 2005, D71, 054502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A. The Influence of strange quarks on QCD phase diagram and chemical freeze-out: Results from the hadron resonance gas model. J. Phys. 2005, G31, S1105–S1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pun, C.S.J.; Gergely, L.A.; Mak, M.K.; Kovacs, Z.; Szabo, G.M.; Harko, T. Viscous dissipative Chaplygin gas dominated homogenous and isotropic cosmological models. Phys. Rev. 2008, D77, 063528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckart, C. The Thermodynamics of Irreversible Processes. 1. The Simple Fluid. Phys. Rev. 1940, 58, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.; Lifshitz, E. Fluid Mechanics; Number v. 6; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Osada, T. Modification of Eckart theory of relativistic dissipative fluid by introducing extended matching conditions. Phys. Rev. 2012, C85, 014906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piattella, O.F.; Fabris, J.C.; Zimdahl, W. Bulk viscous cosmology with causal transport theory. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 1105, 029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, W. Thermo field dynamics of black holes. Phys. Lett. 1976, A57, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, A.A.; van den Hoogen, R.J. Qualitative analysis of viscous fluid cosmological models satisfying the Israel-Stewart theory of irreversible thermodynamics. Class. Quant. Grav. 1995, 12, 1977–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Israel, W. Nonstationary irreversible thermodynamics: A Causal relativistic theory. Ann. Phys. 1976, 100, 310–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, W.; Stewart, J.M. Thermodynamics of nonstationary and transient effects in a relativistic gas. Phys. Lett. A 1976, 58, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, W.A.; Lindblom, L. Stability and causality in dissipative relativistic fluids. Ann. Phys. 1983, 151, 466–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S. Israel-Stewart approach to viscous dissipative extended holographic Ricci dark energy dominated universe. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2016, 2016, 8515967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

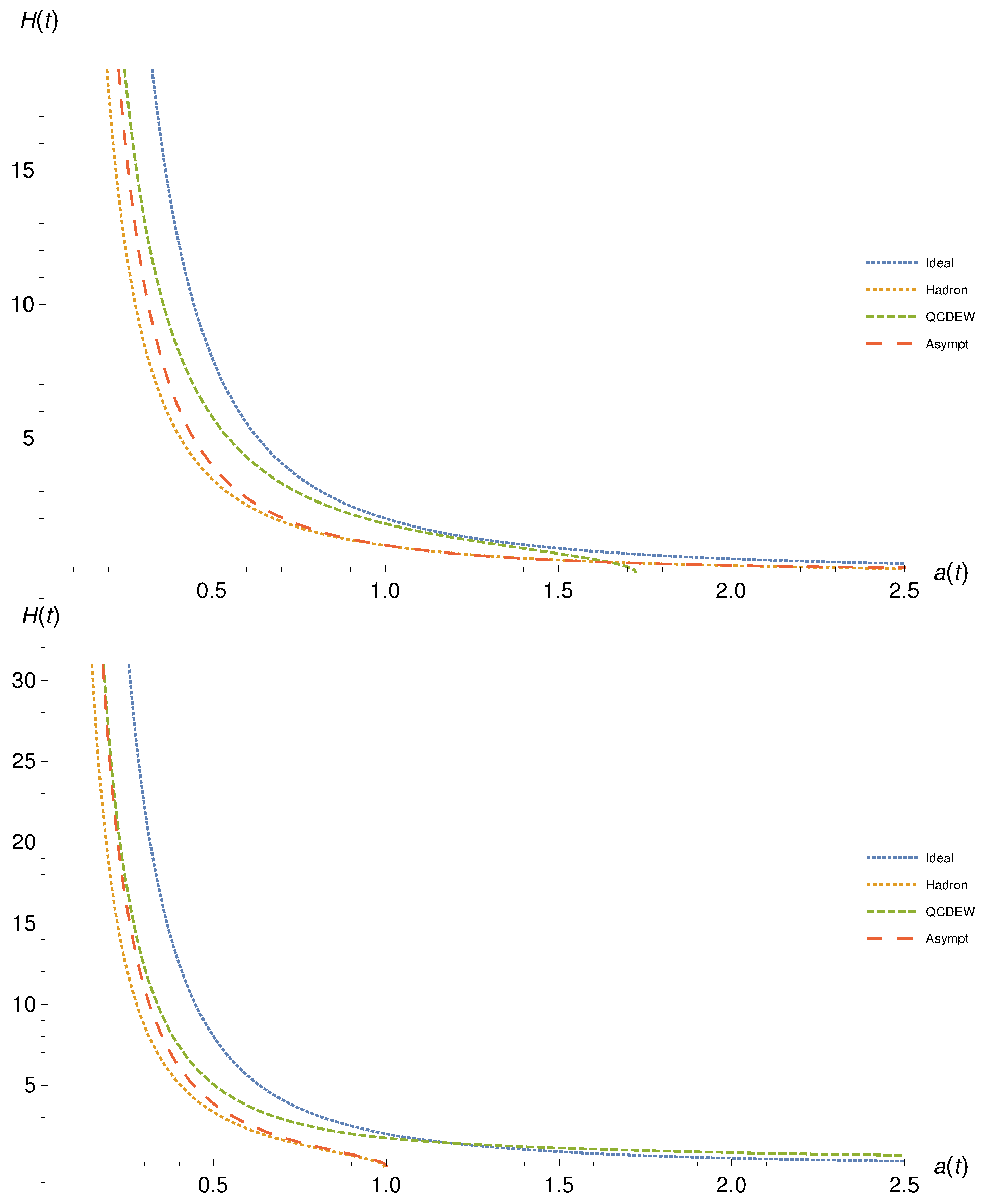
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tawfik, A.N.; Greiner, C. Early Universe Thermodynamics and Evolution in Nonviscous and Viscous Strong and Electroweak Epochs: Possible Analytical Solutions. Entropy 2021, 23, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030295
Tawfik AN, Greiner C. Early Universe Thermodynamics and Evolution in Nonviscous and Viscous Strong and Electroweak Epochs: Possible Analytical Solutions. Entropy. 2021; 23(3):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030295
Chicago/Turabian StyleTawfik, Abdel Nasser, and Carsten Greiner. 2021. "Early Universe Thermodynamics and Evolution in Nonviscous and Viscous Strong and Electroweak Epochs: Possible Analytical Solutions" Entropy 23, no. 3: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030295
APA StyleTawfik, A. N., & Greiner, C. (2021). Early Universe Thermodynamics and Evolution in Nonviscous and Viscous Strong and Electroweak Epochs: Possible Analytical Solutions. Entropy, 23(3), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/e23030295







