Abstract
In this work, the production of biologically synthesized silica nanoparticles was proposed to prepare a nanosuspension as a thermal fluid in parabolic solar panels at the laboratory level. Silica nanoparticles were produced from construction sand in two stages. Biosynthesis broth was produced by Aspergillus niger aerated fermentation in a 1 L bioreactor for 9 days. Each supernatant was contacted with 18% construction sand in a 500 L reactor with mechanical agitation, at a temperature of 25 °C, and a contact time of 30 min. Subsequently, the separation process was carried out. For day 9, a pH value of 1.71 was obtained as well as acid concentrations of 15.78 g/L for citrus and 4.16 g/L for malic. The metal extraction efficiency of Si nanoparticles was 19%. The vibration peaks in the FTIR were characteristic of the presence of silica nanoparticles in wavenumbers 1020 cm−1 and 1150 cm−1. Finally, a prototype solar radiation test bench for parabolic systems was built and provided with a radiation source that falls on a translucent pipe that transports the nanoparticles, which has a pump and a series of thermocouples. The heat capacity of the biotechnologically produced silica nanoparticle suspension was 0.72 ± 0.05 kJ/kgK, using material and energy balances in the flow circuit.
1. Introduction
Global energy consumption is underpinning a growing level of demand that will reach 778 Zettajoules by 2035 [1]. Factors such as industrialization, commercial development, and the massive use of electronic devices increase the dependence on energy sources by 1.52% per year [2,3], thereby affecting global environmental conditions in terms of CO2 [4,5,6], and other greenhouse gases [7].
Solar energy as a source of energy can cover a large portion of global consumption. Existing solar energy technologies include photovoltaic panels, thermal collectors, and hybrid photovoltaic/thermal panels [8,9]. However, photovoltaics technologies incorporate toxic metallic materials that include Germanium, Chromium, Gallium, and Cadmium [9,10].
Solar thermal collectors are a feasible alternative to photovoltaics technologies since they capture solar radiation and store it in thermal fluids and then transfer the heat to steam generating systems [11]. The recent research to optimize thermal collectors is focused mainly on the increase of heat transfer via structural design or improving the inner convection coefficient by increasing the thermal conductivity of the base fluid, incorporating chemically synthesized nanoparticles in the form of nanosuspensions, and applying sonication at the laboratory level [12]. The most studied base fluids are deionized water, oil, ethylene glycol, and polymer solutions. The most suitable nanoparticles comprise silica modified with copper [13], Cu–Ag/biochar [11], copper oxide, aluminum oxide, carbon nanotubes, or heavy metals such as nickel, iron, zinc, gold, and silver [14].
Although these solutions are effective, obtaining nanoparticles via a chemical process consumes high amounts of energy and generates residuals that can be toxic to people and ecosystems. Biological methods are an alternative to synthesize green nanoparticles [14], especially those that contain silica. Nanoparticles are synthesized by different microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, fungi, and viruses. Studies include minerals, solutions, or metal oxides [15]. In addition, microorganisms such as fungi are used in the bio-dissolution of valuable metals in solid matrices [16], and studies have been mainly focused on medical applications [17].
As we found in our literature review, no studies report the direct application of biosynthesized silica nanoparticles from a fermented broth in parabolic solar panels. The interaction between the biomolecules such as the amino acids, organic acids from the fermentation, and nanoparticles could favor the stability of the suspension, thereby avoiding the nanoparticle sedimentation [18].
Additionally, in cited studies, the analysis of the thermal improvement of nanofluids is performed using empirical observations, and few thermic models are applied to develop predictive mathematical models that are useful in the design and implementation of pilot parabolic solar panels.
Based on the current situation, this paper proposes the biological synthesis of silica nanoparticles from a fungal fermentation and construction sand to generate a nanosuspension that serves directly as thermal fluid in parabolic solar panels.
Finally, to evaluate the thermal conductivity of the nanosuspension, a prototype test bench for solar radiation was proposed, as well as a mathematical model based on differential equations for the thermal analysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silica Nanoparticles Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of silica nanoparticles was carried out in two stages. In the first, a fermented broth rich in extracellular proteins, enzymes, and organic acids was produced by a biological process and in the second, the fermented broth was brought into contact with sand as a source of silica for its extraction and biosynthesis of nanoparticles.
Initially, duplicate fermentation was carried out in a liquid state in a 1 L bioreactor and a working volume of 750 mL, using a 10% inoculum of Aspergillus niger in culture medium proposed by Papagianni [19] at 200 rpm, under constant aeration, and without adjustment of the initial pH for nine days.
The kinetics of the fermentation was performed by reading the pH and quantifying malic acid, citric acid, and sucrose using the HPLC technique with a mobile phase of sulfuric acid at 4 mM, with a flow of 0.52 mL/min and 70 °C in an oven. The column used was Monosaccharide H + Phenomenex, using 10 µL per sample injection. Detectors were employed at a 210 nm wavelength.
After the fermentation, the separation process of a fraction of the broth was carried out for day 5 and day 9 of the fermentation and each supernatant was contacted with 18% construction sand (average diameter 0.125 mm, #115 mesh, SiO2 concentration 96.21%) in a 500 L reactor with mechanical agitation, at a temperature of 25 ºC and contact time of 30 min. Subsequently, the separation process was carried out by centrifugation at 3500 rpm for 10 min.
Silica nanoparticles were analyzed by SEM/EDS. A dry sample of supernatant was subjected to NeoScopeTM JCM-6000 Plus equipped with an Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometer (EDS) for elemental analysis at 15 kV.
The supernatant was analyzed by FTIR spectrophotometry between 4000 to 400 cm−1 to determine the production of Silica nanoparticles. For this analysis, two samples were evaluated: the one on day 5 with a pH value of 2.62 and the one on day 9 with a pH value of 1.71.
The silica concentration of the process was quantified from the aqueous phase and the sand after acid digestion by UV-VIS spectrophotometry using the standard molybdate method [20].
2.2. Solar Panel Bench
A prototype radiation test bench was built, consisting of a wooden body in the shape of a 28 cm × 28 cm × 115 cm cubic parallelepiped, insulated on its walls, and lined with a reflective aluminum material. Inside, a parabolic mirror was designed and installed to cover the front face of the test bench with a focal length (P) of 1.8 cm, which describes a line according to Equation (1):
where P is the focal length and 4P equals the length of the aperture, Y is the vertical coordinate axis, and X is the horizontal coordinate axis.
A translucent pipe was installed along the focal axis that transports the nanoparticles, which are powered by a peristaltic pump. The temperature was monitored using a pair of K-type thermocouples and the flow was determined by volumetry using a test tube. The tests were performed in triplicate to assess their statistical variation. Figure 1 shows the prototype test bench for solar radiation.
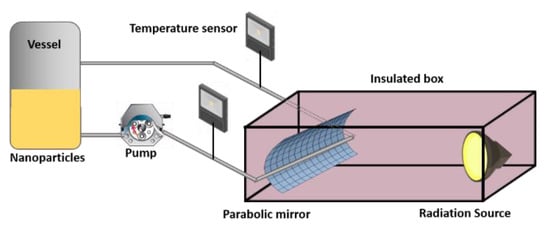
Figure 1.
Prototype test bench for solar radiation.
The heat capacity of the silica nanoparticle suspension produced by material and energy balances in the flow circuit was determined, using the first law of thermodynamics in conjunction with a model for internal convection using Equations (2)–(4) based on the model proposed by [21]:
where dr is the pipe diameter, hnf is the heat transfer coefficient W/m2 K, Is is the Source radiation intensity, W/m2, m is the the mass flow of the nanofluidic stream, kg/s, Tw is the Temperature of the nanosuspension, Tf is the Temperature of the fluid, z represent the axial direction, and Cp,nf is the Heat capacity of nanofluids kJ/kgK.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Silica Nanoparticles Biosynthesis
In this research, we worked with Aspergillus niger because of its capability to synthesize a wide range of nanoparticles. The cultivation and the bioconversion can be controlled to obtain the desired nanoparticles [18]. Furthermore, A. niger solubilizes metals [16] due to the production of organic acids, mainly citric, gluconic, and oxalic acids as its primary metabolites during its development. These bio-produced acids are the most critical leaching agents in the process [22].
Figure 2 shows the kinetics of the fermentation process, showing that the Aspergillus niger requires a nutrient medium that stimulates its proliferation. It is observed that an increase in sucrose within the medium is directly related to greater excretion of organic acids. Similarly, the sucrose concentration decreases as it is consumed by the fungus, generating an increase in the biomass or metabolites produced [23,24].
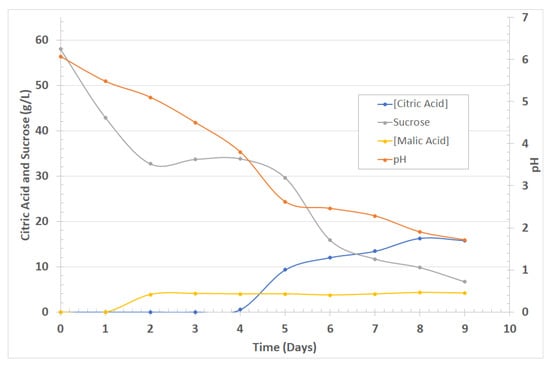
Figure 2.
Kinetics for the fermentation process.
Sucrose was used in this research because it is the most affordable carbon source for sugars such as fructose, lactose, and galactose. A. niger has a potent mycelial-bound extracellular invertase that is active at low pH values and hydrolyzes sucrose rapidly [25].
The production of organic acids (citric and malic acid) was the main leaching agent, resulting from the metabolism of Aspergillus niger. However, A. niger is also capable of excreting other types of acids, which leads to multiple dissolution mechanisms of mineral species [26].
Figure 2 shows the results of the fermentation. On day 5 citric and malic acid were 9.31 g/L and 3.99 g/L, respectively, and the pH was 2.62, evidencing the affinity between the substrate and the microorganism; at this stage, the production of citric acid rose uniformly. During day 9 the pH was 1.71, and acid concentrations remained constant, indicating the end of the bioprocess. The silica extracted after contacting the sand with the fermented broth was 19%, using both the fifth- and ninth-day broth. This result was verified by UV/Vis spectrophotometry using the standard molybdate method [20].
Organic acids possess interesting properties as potential leaching agents, although they cannot be applied to all minerals due to the limitations associated with their chemistry. They are presented as an alternative to consider in the future [23]. In general, organic acids are less corrosive, allow greater selectivity, and can be easily obtained from the processing of materials found in nature [26]. Finally, organic acids are presented as interesting options for leaching from different species [27].
Organic acids are weak acids, which are partially ionized in water [28]. The acidity of carboxylic acids is based on the greater polarity of the O-H bond in the center of reactivity of the molecule and the resonance stabilization of the carboxylate anion after ionization or neutralization of the acid [24,29,30,31].
These organic acids can be obtained as a product of the metabolic activity of different microorganisms, some of them capable of synthesizing several organic acids simultaneously. Species like B. megaterium, B. Circulans, and A. niger can produce these acids. However, A. niger is considered to be the most affordable for metal recovery [23,24].
The mechanism associated with this phenomenon could be explained when the protons resulting from the dissociation of carboxylic acid allowed the dissolution of species; then as a result of this chemical dissolution process, the formation of stable complexes could occur, where the dissociated carboxylates form stable complexes with the cations in solution, which drives greater dissociation of organic acids or an electrochemical dissolution mechanism. Thus, carboxylates react by exchanging electrons with suspension components [32].
Organic acids experience limitations in their dissociation at relatively low concentrations since the dissolution of mineral species is attributed to the presence of carboxylic ions in solution, influencing the process kinetics and the degree of extraction of metallic species [33]. However, there are other factors associated with the solubilization process of metals, such as amino acids (aspartic acid, histidine, serine, alanine, and glycine) [34] and enzyme activity that is directly correlated to the production of organic acids [35].
The fungi additionally perform the biosynthesis of nanoparticles due to the presence of bioactive metabolites, high accumulation, and improved production. Fungi react differently with metal ions for the synthesis of metal nanoparticles. The synthesis method in this work is extracellular, where amicroorganism secretes the enzyme reductase used in the bioreduction of metal ions into metal nanoparticles [18].
In general, microorganisms use various mechanisms for the synthesis of nanoparticles, including the formation of metal complexes, extracellular precipitation, changes in solubility, biosorption, toxicity through oxidation-reduction, the absence of specific transporters, and efflux pumps [18].
Scanning electron microscopy images of the dried silica nanoparticles showed mostly spherical particles of a size below 300 nm, as shown in Figure 3.
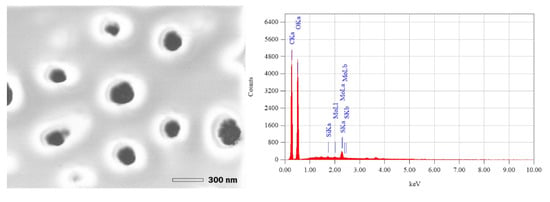
Figure 3.
SEM/EDS analysis for nanoparticle suspension obtained with sand in contact with the fermented broth from A. niger at a pH of 1.71.
Elemental mapping of nanoparticle samples shows the presence of Silicon at 1.739 keV (0.15 ± 0.01% mass). Other compounds such as Carbon (40.21 ± 0.10% mass), Oxygen (57.34 ± 0.26% mass), and Sulfur (0.48 ± 0.02% mass) are present due to the interaction of the construction sand and biomolecules from the fermented broth to produce the nanoparticles.
Figure 4 shows the FTIR spectra of the liquids coming from the treatment between the sand and the fermented broth from A. niger. It presents two samples at different pH values: 1.71 and 2.62.
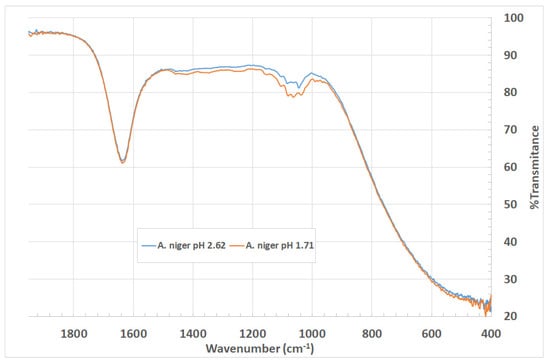
Figure 4.
FTIR spectrum for nanoparticle suspension obtained with sand in contact with the fermented broth from A. niger. Samples were obtained at pH values of 1.71 and 2.62.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis is used to characterize and confirm the presence of nanoparticles [18]. The spectra shown in Figure 4 are similar to the results obtained by Li et al. in the production of Si nanocomposites in resin matrices [36].
As shown in Figure 4, there are peak characteristics of silica nanoparticles. In the fingerprint region, the wavenumbers 1020 cm−1 and 1150 cm−1 represent the asymmetric stretching vibrations Si-O-Si. The weak bands at 900 cm−1 and 949 cm−1 are possibly attributed to the symmetric stretching vibrations Si-OH and Si-O-Si in amorphous silica. Among the two treatments, a pH of 1.71 exhibits higher absorbance, which reflects a higher concentration of silica nanoparticles in quantitative terms.
The results showed that the broth produced by Aspergillus niger at pH 1.71 provides the best conditions to produce Silica nanoparticles, thereby coinciding with the conditions reported by Ovais et al. on the importance of pH in the production of citric acids from the fermentation of Aspergillus niger, and its contribution in the formation, size, and structure of nanoparticles [18].
The production of Silicon (Si) nanoparticles, using Aspergillus niger, is believed to occur due to the production of extracellular enzymes such as acetyl xylan esterase, cellobiohydrolase D, glucosidase, and β-glucosidase, which are relevant in the biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles [37].
Aspergillus niger was used to produce ZnO nanoparticles as an antibacterial potential, to degrade inks [38], and to produce cobalt oxide nanoparticles [39].
Different filamentous fungi are satisfactory for the biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles. Fungal compounds and media composition play a role in stabilizing nanoparticles. Furthermore, the fungal proteins are responsible for the production of nanoparticles [18].
Bioreduction is a green method for the synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Through this approach, the plant extracts or the microorganisms used for the reduction of the metal salt are converted into nano-sized, non-toxic, and stable metals [15].
Nanoparticle biosynthesis is competitive due to its easy production and scaling, as well as its well-defined morphologies, and improved biocompatibility if compared with physiochemical-based nanoparticles, making it more effective than nanoparticles synthesized by non-biological means [18].
3.2. Parabolic Solar Panels
As shown in Figure 5, the thermodynamic model, based on Equations (2)–(4), was accurate for predicting the thermal behavior of the solar test bench. In the monitoring of the temperature for thermal fluid, a progressive increase in the outlet temperature was evidenced. When adjusting the parameters, the heat capacity was used as a correlation parameter between experimental data and the model, minimizing the total square error in the MS Excel solver.
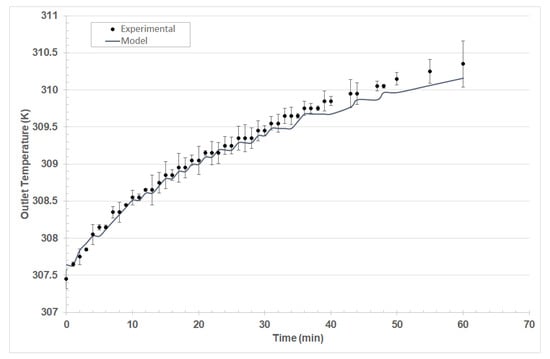
Figure 5.
Energy balances used in conjunction with Equations (2)–(4) to predict the outlet temperature of the solar panel bench.
Solving Equations (2)–(4), a heat capacity of 0.72 ± 0.05 kJ/kgK was obtained for the nanosuspension, which is within the expected range of commercial nanoparticles obtained by chemical synthesis between 0.714–0.765 kJ/kgK, according to the results presented by Bait [21].
On the other hand, the thermal conductivity of nanofluids increases with increasing temperature and volume fraction [13]; therefore, its application in the design of thermal solar panels is highly relevant.
Since heat transfer is a surface phenomenon between the interface of the fluid and the particles, the heat transfer rate will increase significantly on a nanometric scale by increasing the surface area of the nanoparticles, consequently providing an increase in thermal conductivity of nanofluids [13].
Several studies have shown how the nanoparticles of Al2O3, Cu2O, MgO, SiO2, TiO2, and ZnO are effective in increasing thermophysical properties, such as density, viscosity, the thermal conductivity, and specific heat with efficiencies of 79.9% [21].
4. Conclusions
The fermented broth for day 9 was revealed to be more efficient for the biosynthesis process of Si nanoparticles, presenting a pH value of 1.71 and acid concentrations of 15.78 g/L for citric and 4.16 g/L for malic acid, and peaks of vibration in the FTIR characteristic of the presence of silica nanoparticles in the fingerprint region, specifically in the wavenumbers 1020 cm−1 and 1150 cm−1 which represent the vibrations of asymmetric stretching Si-O-Si.
Biosynthesized Si nanoparticles are amorphous due to the weak bands found in the FTIR at 900 cm−1 and 949 cm−1, which can possibly be attributed to symmetric stretching vibrations Si-OH and Si-O-Si.
The SEM/EDS analysis determined that the biosynthesized Si nanoparticles are in the nanometric domain, showing spherical particles below a 300 nm diameter.
The heat capacity of the biotechnologically produced silica nanoparticle suspension was 0.72 ± 0.05 kJ/kgK, which was obtained using material and energy balances in the flow circuit.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R.-C. and C.O.-L.; methodology, L.R.-C., M.R.-C. and C.O.-L.; validation, C.O.-L.; formal analysis, L.R.-C., M.R.-C. and C.O.-L.; investigation, E.C.-D., L.P.-M. and A.R.-C.; data curation, C.O.-L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.O.-L. and E.C.-D.; visualization, E.C.-D., L.P.-M. and A.R.-C.; supervision, M.R.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Government of Antioquia, and MINCIENCIAS, grant number CT 579-2019. Contract 80740-009-2019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study is available in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the technical support received from the engineer Rubén Darío Giraldo-Aristizabal in the construction of the test bench system and chemical engineering student Alejandro Arango-Calle for his support in monitoring some of the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmad, R.; Kaveh, R.K. Renewable Hybridization of Oil and Gas Supply Chains. In Polygeneration with Polystorage for Chemical and Energy Hubs; Khalilpour, K.R., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 331–372. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, S.A.; Marques, A.C.; Fuinhas, J.A. On the drivers of peak electricity demand: What is the role played by battery electric cars? Energy 2018, 159, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeq, J.; Najjar, Y. Modeling and Simulation of Solar Thermal Power System Using Parabolic Trough Collector. Energy Eng. 2017, 143, 04016056. [Google Scholar]
- Broumand, M.; Albert-Green, S.; Yun, S.; Hong, Z.; Thomson, M.J. Spray combustion of fast pyrolysis bio-oils: Applications, challenges, and potential solutions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2020, 79, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.; Singh, B.R. Global Trends of Fossil Fuel Reserves and Climate Change in the 21st Century. In Fossil Fuel and the Environment; Khan, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 167–191. [Google Scholar]
- Abokyi, E.; Appiah-Konadu, P.; Abokyi, F.; Oteng-Abayie, E.F. Industrial growth and emissions of CO2 in Ghana: The role of financial development and fossil fuel consumption. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. OECD Green Growth Studies: Energy? OCDE Publishing: París, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sorknæs, P.; Lund, H.; Skov, I.; Djørup, S.; Skytte, K.; Morthorst, P.; Fausto, F. Smart Energy Markets―Future electricity, gas and heating markets. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2020, 119, 109655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daabo, A.M.; Hammo, K.E.; Mohammed, O.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Lattimore, T. Performance investigation and design optimization of micro scale compressed air axial turbine for domestic solar powered Brayton cycle. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 37, 100583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Xu, T.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Liang, L.; Hong, K. Experimental study on thermal properties and thermal performance of eutectic hydrated salts/expanded perlite form-stable phase change materials for passive solar energy utilization. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 188, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.L.; Huang, Z.H.; Chu, Y.C.; Lin, H.P.; Chang, Y.J. Application of metallic nanoparticle-biochars with ionic liquids for thermal transfer fluids. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kalbasi, R.; Nguyen, Q.; Afrand, M. Effects of sonication duration and nanoparticles concentration on thermal conductivity of silica-ethylene glycol nanofluid under different temperatures: An experimental study. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 404–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrajab, R.; Noghrehabadi, A.; Hajidavalloo, E.; Behbahani, M. Investigation of thermal conductivity of a new hybrid nanofluids based on mesoporous silica modified with copper nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and experimental study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 300, 112337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, M.; Giovanela, M.; Roesch-Ely, M.; Devine, D.M.; da Silva Crespo, J. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles: A review of the synthesis methodology and mechanism of formation. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 15, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun-Do, K.; Prakash Patila, M. Marine microorganisms for synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Haragobinda, S.; Ranjan Kumar, M.; Pankaj Kumar, P. Bioleaching approach for extraction of metal values from secondary solid wastes: A critical review. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105122. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanan Pillai, A.; Sankar Sivasankarapillai, V.; Rahdar, A.; Joseph, J.; Sadeghfar, F.; Anuf, R. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles with antibacterial and antifungal activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1211, 128107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovais, M.; Talha Khalil, A.; Ayaz, M.; Ahmad, I.; Kumar Nethi, S. Biosynthesis of Metal Nanoparticles via Microbial Enzymes: A Mechanistic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagianni, M. Advances in citric acid fermentation by Aspergillus niger: Biochemical aspects, membrane transport and modeling. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 244–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotza, D.; Ramírez-Carmona, M.; Pineda-Vásquez, T.; Casas-Botero, A.; Torres-Taborda, M.; Soares, C.L. Biogeneration of Silica Nanoparticles from Rice Husk Ash Using Fusarium oxysporum in Two Different Growth Media. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6959–6965. [Google Scholar]
- Bait, O. Direct and indirect solar–powered desalination processes loaded with nanoparticles: A review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 37, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddanna, M.H.; Baral, S.S. A comparative study of the extraction of metals from the spent fluid catalytic cracking catalyst using chemical leaching and bioleaching by Aspergillus niger. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, I.D.M.; Fietto, J.L.R.; Vieira, R.X.; Trópia, M.J.M.; Campos, L.M.M.D.; Paniago, E.B.; Brandão, R.L. Bioleaching of zinc and nickel from silicates using Aspergillus niger cultures. Hydrometallurgy 2000, 57, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wu, T. Biosorption behavior of heavy metals in bioleaching process of MSWI fly ash by Aspergillus niger. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 46, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaloo-Hore, N.; Mousavi, S.M. Enhanced recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries through optimization of organic acids produced by Aspergillus niger. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaerun, S.K.; Sulistyo, R.S.; Minwal, W.P.; Mubarok, M.Z. Indirect bioleaching of low-grade nickel limonite and saprolite ores using fungal metabolic organic acids generated by Aspergillus niger. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 174, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Rastegar, S.; Beigzadeh, R.; Gu, T. Ultrasound-assisted leaching of spent lithium ion batteries by natural organic acids and H2O2. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.S.J.; Bailey, C.A. Química Orgánica: Conceptos y Aplicaciones; Prentice Hall Hispanoamericana: Ciudad de México, México, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- McMurry, J. Química Orgánica; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ascensio, J.S. Equilibrios Químicos; Visión Libros: Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, Z.I.; Ashraf, M. Selective leaching kinetics of calcareous phosphate rock in lactic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 131, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Kim, D.J.; Ahn, J.G.; Rhee, Y.H. Bioleaching: A microbial process of metal recovery; A review. Met. Mater. Int. 2005, 11, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrille, A.D.; Edith, K.K.; Marius, N.P.; Bilé, A.; Bernadette, E.; Henri, A.K. Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Oxalic Acid Dissociation in Water-Ethanol Solvents. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2015, 4, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Gadd, G.M. Fungal Production of Citric and Oxalic Acid: Importance in Metal Speciation, Physiology and Biogeochemical Processes. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1999, 41, 47–92. [Google Scholar]
- Burgstaller, W.; Müller, B.; Schinner, F. The in vivo effect of glucose and extracellular pH on the plasma membrane H+-ATPase of Penicillium simplicissimum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 147, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, E.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Haoran, Z. Effects of silane coupling agents on the electrical properties of silica/epoxy nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. 2016, 2, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Ovais, M.; Khalil, A.T.; Islam, N.U.; Ahmad, I.; Ayaz, M. Role of Plant Phytochemicals and Microbial Enzymes in Biosynthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6799–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalpana, V.N.; Kataru, B.A.S.; Sravani, N.; Vigneshwari, T.; Panneerselvam, P.; Rajeswari, V.D. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using culture filtrates of Aspergillus niger: Antimicrobial textiles and dye degradation studies. OpenNano 2018, 3, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanandan, A.S.; Balakrishnan, R.M. Biosynthesis of cobalt oxide nanoparticles using endophytic fungus Aspergillus nidulans. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).