Dynamics and Complexity of a New 4D Chaotic Laser System
Abstract
1. Inroduction
- (i)
- We derive a new 4D chaotic laser system with three equilibria from Lorenz-Haken equations;
- (ii)
- We investigate the stability of the symmetric equilibria, and the existence of coexisting multiple Hopf bifurcations on these equilibria;
- (iii)
- We analyze the presence of complex coexisting behaviors in the laser system;
- (iv)
- We use the complexity of the laser system time series to locate the regions of coexisting attractors when the parameters and initial values vary;
- (v)
- Based on the complexity of the system time series, we study the randomness of multistability regions.
2. A New 4D Chaotic Laser System From Lorenz-Haken Model
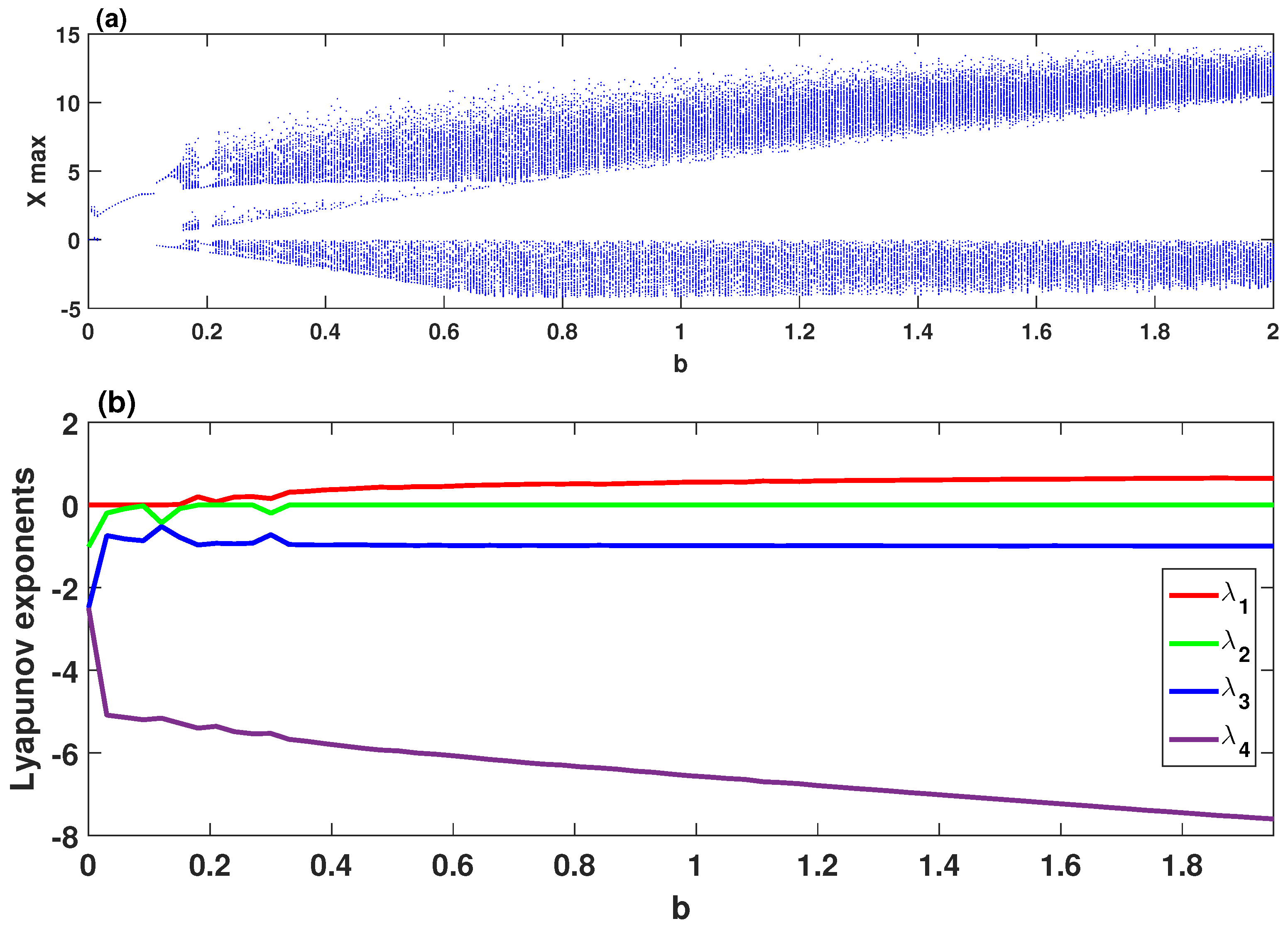
2.1. Chaotic Behavior Regions
2.2. Dissipation and Symmetry
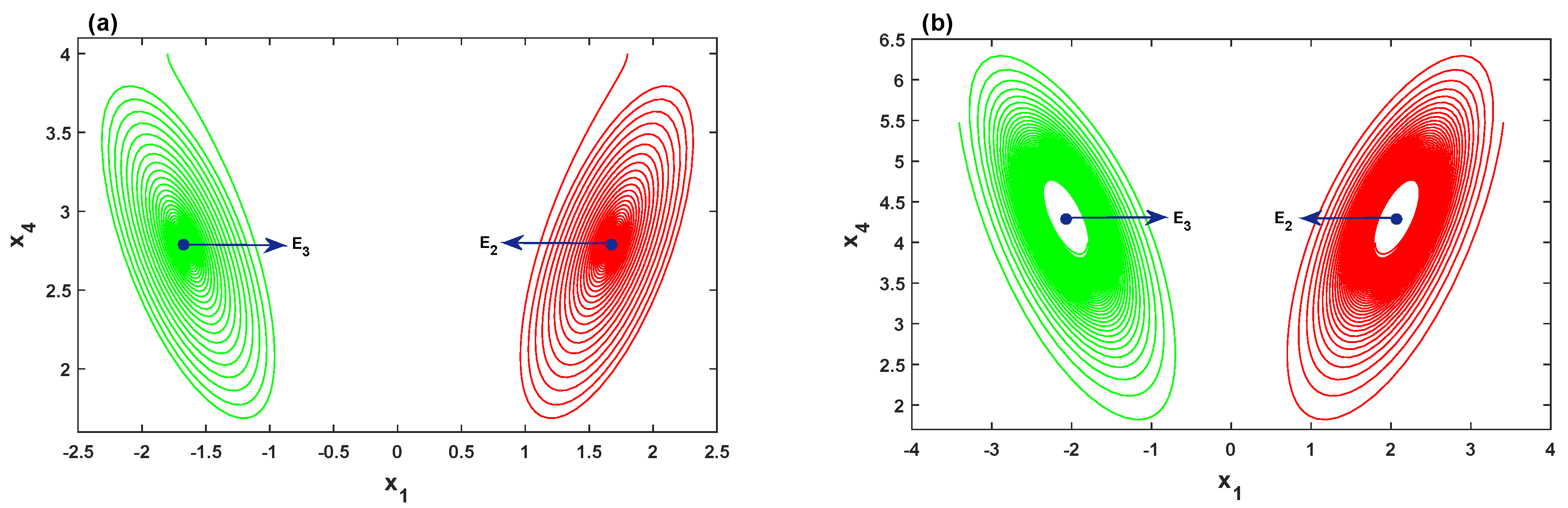
2.3. Equilibria and Stability
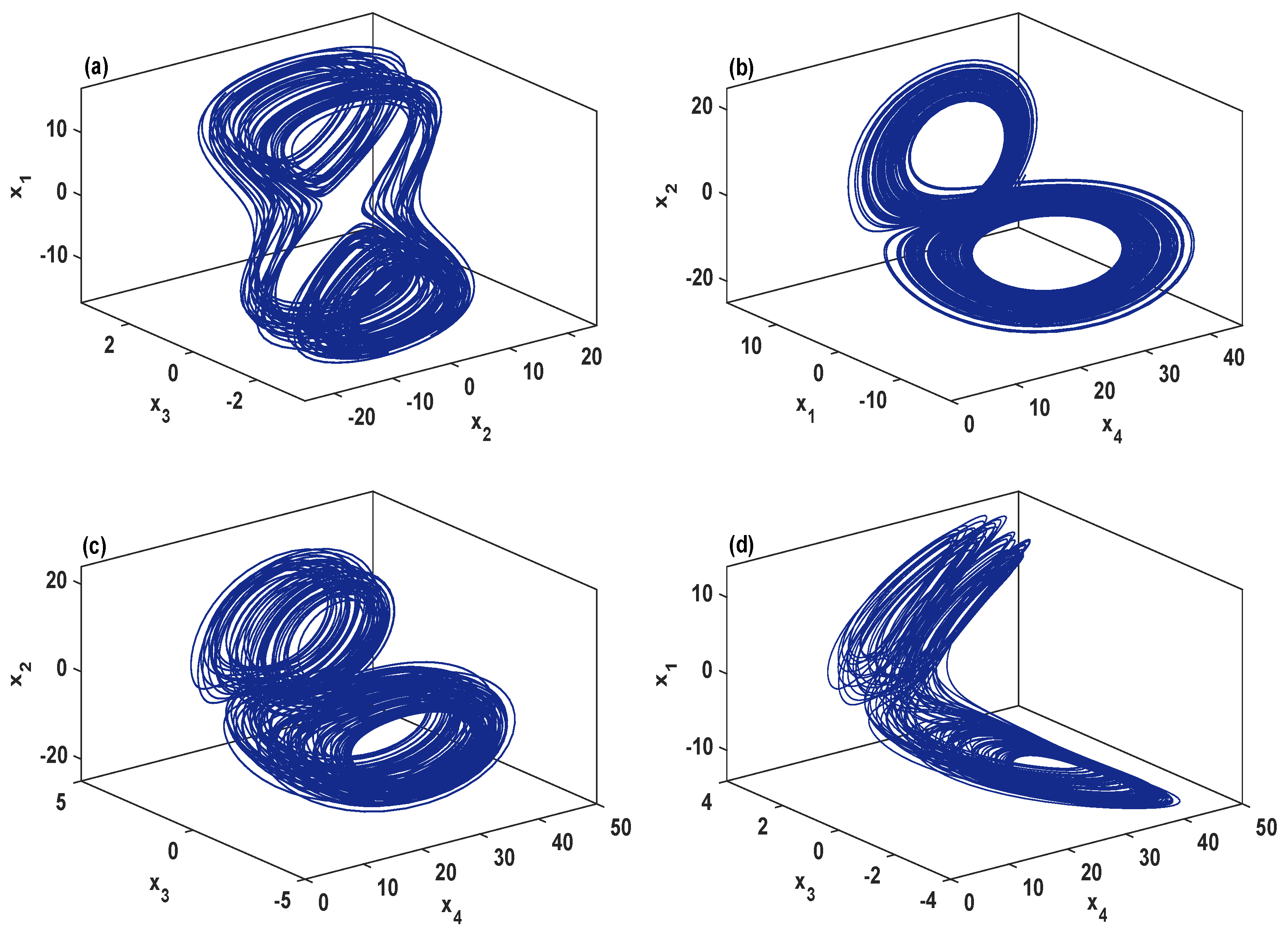
3. Local Bifurcation Analysis and Numerical Simulations
3.1. Hopf Bifurcation
- (A)
- nondegeneracy condition: the Jacobian matrix has one pair of purely imaginary roots, and other roots have nonzero real parts;
- (B)
- transversality condition: the real part of differentiation characteristic equation with respect to the parameter satisfy
- (C)
- the first Lyapunov coefficient is nonzero.
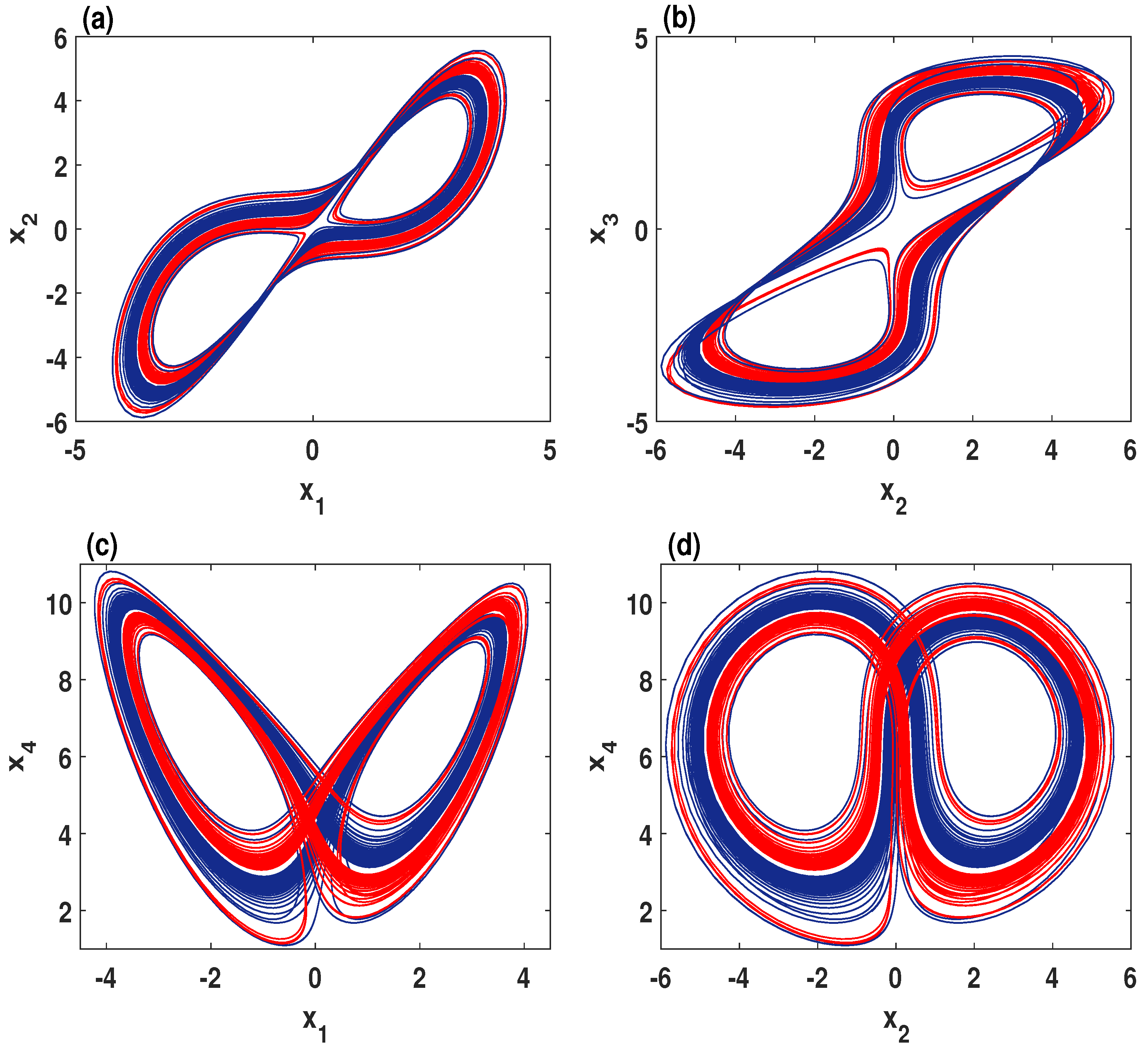
3.2. Numerical Simulations
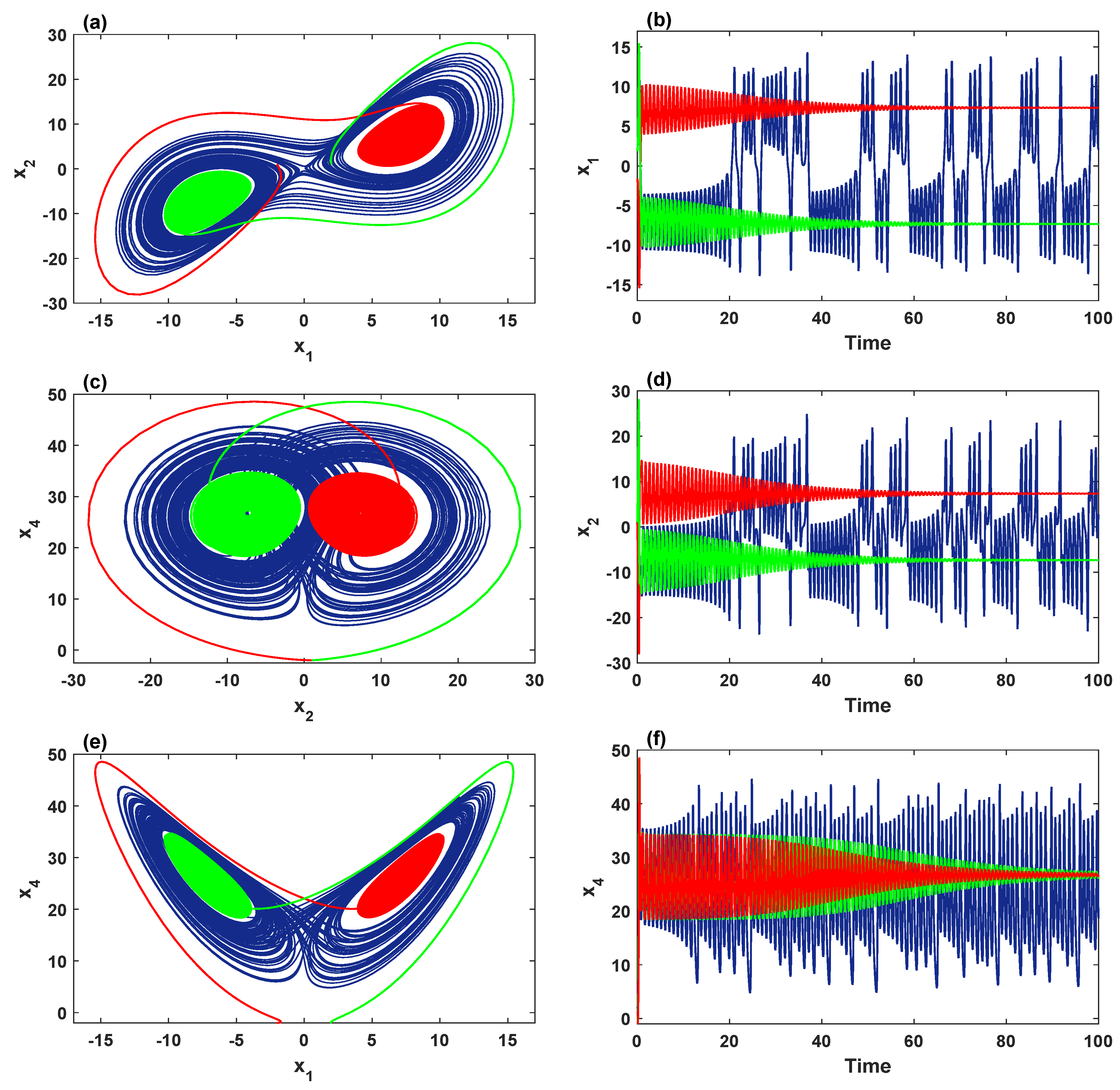
4. Multistability Behavior
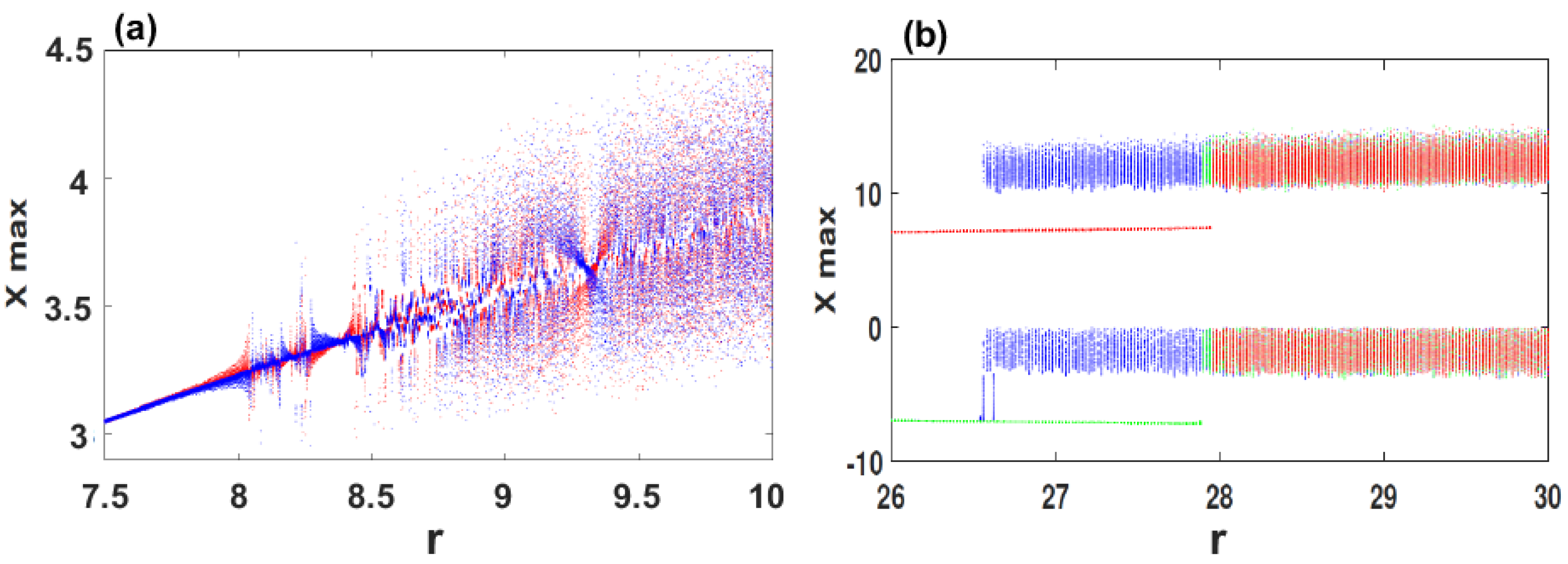
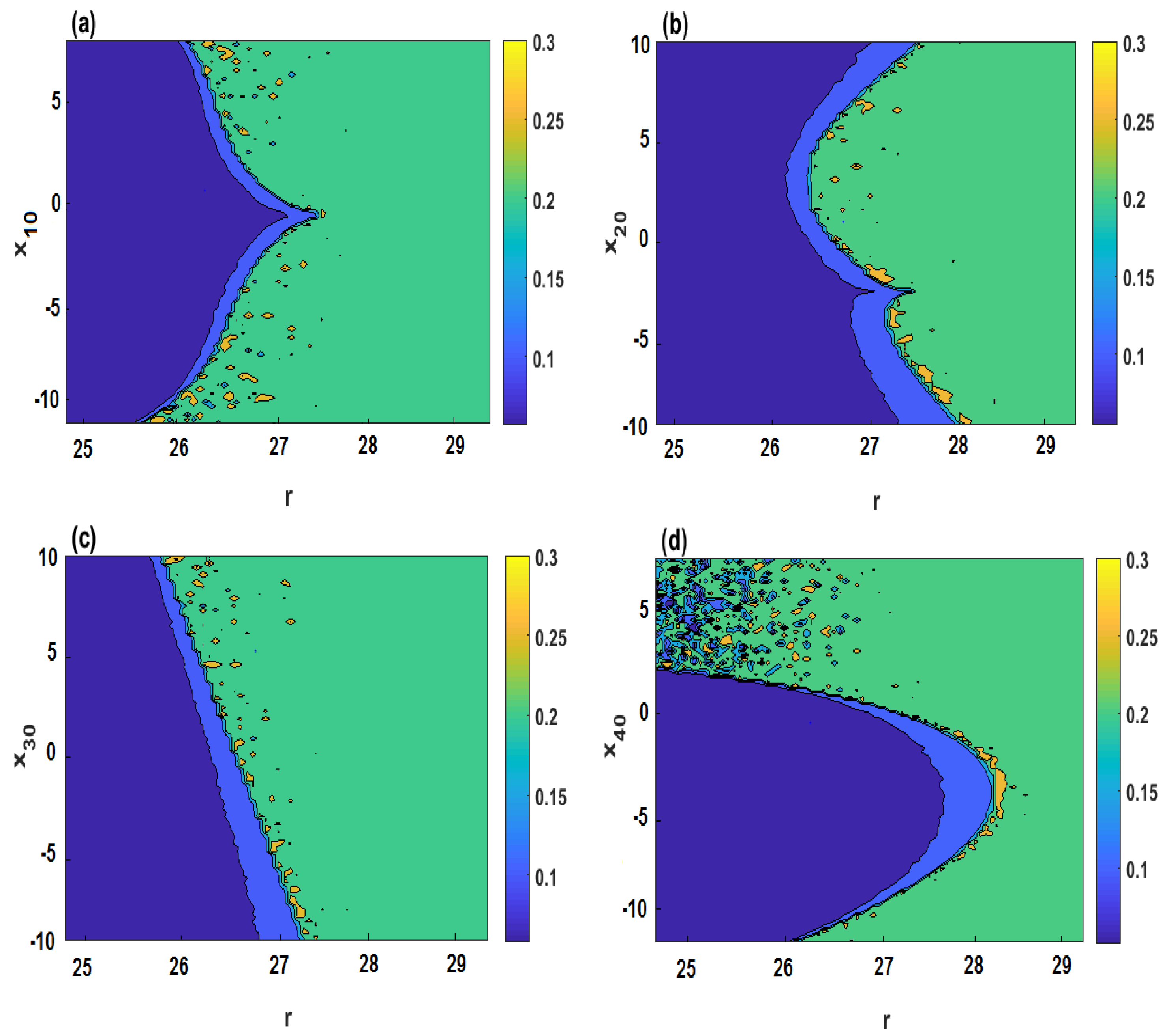
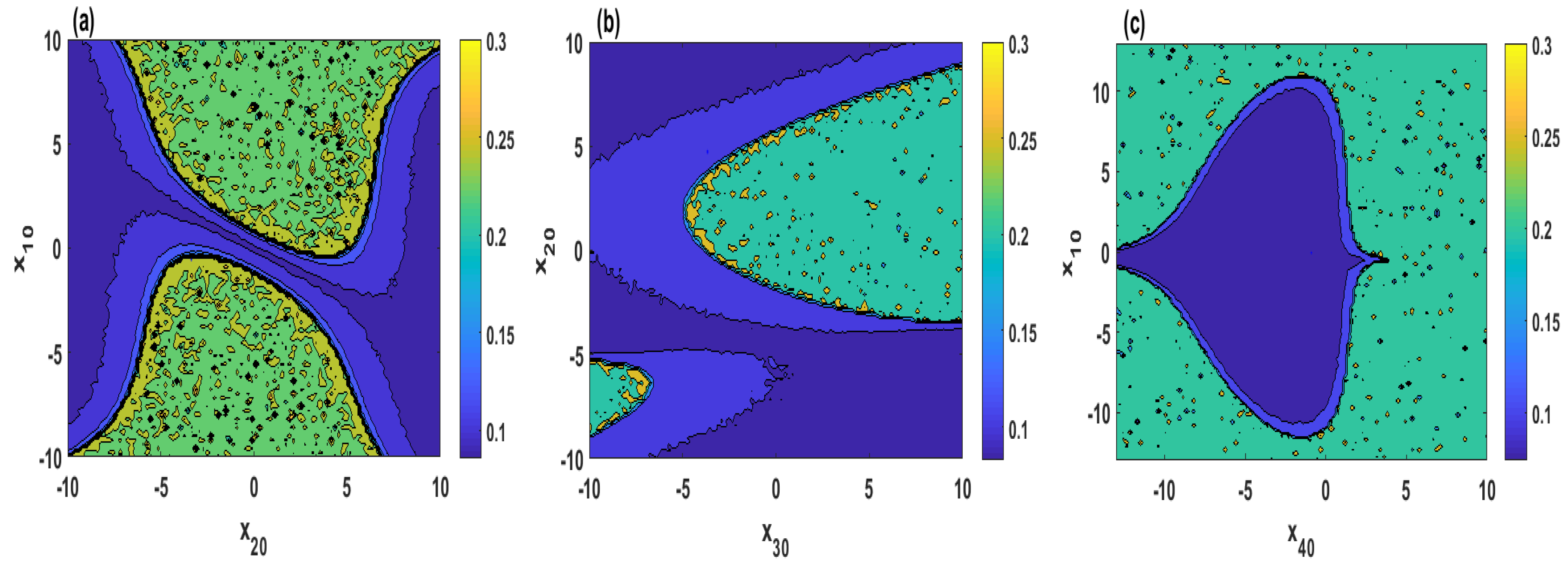
5. Complexity and Randomness of Multistability Regions
5.1. Sample Entropy
- (A)
- Reconstructing phase-space: for a given embedding dimension m and time delay , the reconstruction sequences are given bywhere .
- (B)
- Counting the vector pairs: let be the number of vector such thatwhere r is the tolerance parameter, and is the distance between and , which is defined by
- (C)
- Calculating probability: according to the obtained number of vector pairs, we can obtainthen calculate the probability by
- (D)
- Calculating SamEn: repeating the above steps we can obtain , then SamEn is given by
5.2. Chaos-Based PRNG
| Algorithm 1 The generation of chaos-based PRNG |
Input: The initial values of system (2).
|
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banerjee, S.; Rondoni, L.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Misra, A.P. Synchronization of spatiotemporal semiconductor lasers and its application in color image encryption. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 2278–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valli, D.; Banerjee, S.; Ganesan, K.; Muthuswamy, B.; Subramaniam, C.K. Chaotic time delay systems and field programmable gate array realization. In Chaos, Complexity and Leadership 2012; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Saha, P.; Chowdhury, A.R. Chaotic scenario in the Stenflo equations. Phys. Scr. 2001, 63, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Banerjee, S.; He, S.; Said, M.R.M.; Kilicman, A. Designing an M-dimensional nonlinear model for producing hyperchaos. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 114, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Banerjee, S.; Chowdhury, A.R. Synchronization between variable time-delayed systems and cryptography. Europhys. Lett. 2007, 80, 30006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S. (Ed.) Chaos Synchronization and Cryptography for Secure Communications: Applications for Encryption; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, P.; Banerjee, S.; Chowdhury, A.R. Chaos, signal communication and parameter estimation. Phys. Lett. A 2004, 326, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fataf, N.A.A.; Palit, S.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Said, M.R.M.; Son, D.H.; Banerjee, S. Communication scheme using a hyperchaotic semiconductor laser model: Chaos shift key revisited. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Pizzi, M.; Rondoni, L. Modulation of output power in the spatio-temporal analysis of a semi conductor laser. Opt. Commun. 2012, 285, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondoni, L.; Ariffin, M.R.K.; Varatharajoo, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Palit, S.K.; Banerjee, S. Optical complexity in external cavity semiconductor laser. Opt. Commun. 2017, 387, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Palit, S.K.; Banerjee, S.; Ariffin, M.R.K.; Rondoni, L.; Bhattacharya, D.K. Can complexity decrease in congestive heart failure? Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2015, 439, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Palit, S.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ariffin, M.R.K.; Rondoni, L. Complexity in congestive heart failure: A time-frequency approach. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2016, 26, 033105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.-T.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Volos, C.K.; Jafari, S. Hidden attractors in a chaotic system with an exponential nonlinear term. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2015, 224, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonov, G.A.; Kuznetsov, N.V. Hidden attractors in dynamical systems. From hidden oscillations in Hilbert–Kolmogorov, Aizerman, and Kalman problems to hidden chaotic attractor in Chua circuits. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2013, 23, 1330002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.T.; Volos, C.; Jafari, S.; Wang, X.; Vaidyanathan, S. Hidden hyperchaotic attractor in a novel simple memristive neural network. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 2014, 8, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Dudkowski, D.; Jafari, S.; Kapitaniak, T.; Kuznetsov, N.V.; Leonov, G.A.; Prasad, A. Hidden attractors in dynamical systems. Phys. Rep. 2016, 637, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; de la Fraga, L.G.; Pham, V.T.; Volos, C.; Jafari, S.; de Jesus Quintas-Valles, A. Dynamics, FPGA realization and application of a chaotic system with an infinite number of equilibrium points. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.-T.; Volos, C.; Gambuzza, L.V. A memristive hyperchaotic system without equilibrium. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 368986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natiq, H.; Said, M.R.M.; Ariffin, M.R.K.; He, S.; Rondoni, L.; Banerjee, S. Self-excited and hidden attractors in a novel chaotic system with complicated multistability. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pham, V.T.; Jafari, S.; Volos, C.; Munoz-Pacheco, J.M.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E. A new chaotic system with stable equilibrium: From theoretical model to circuit implementation. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 8851–8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Sprott, J.C. Simple chaotic flows with a line equilibrium. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2013, 57, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.T.; Jafari, S.; Volos, C.; Giakoumis, A.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Kapitaniak, T. A chaotic system with equilibria located on the rounded square loop and its circuit implementation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2016, 63, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecchi, F.; Meucci, R.; Puccioni, G.; Tredicce, J. Experimental evidence of subharmonic bifurcations, multistability, and turbulence in a q-switched gas laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Pacheco, J.; Zambrano-Serrano, E.; Volos, C.; Jafari, S.; Kengne, J.; Rajagopal, K. A new fractional-order chaotic system with different families of hidden and self-excited attractors. Entropy 2018, 20, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ding, Q. A New Two-Dimensional Map with Hidden Attractors. Entropy 2018, 20, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sprott, J.C.; Hu, W.; Xu, Y. Infinite multistability in a self-reproducing chaotic system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2017, 27, 1750160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, C. The Lorenz Equations: Bifurcations, Chaos, and Strange Attractors; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, U.; Coullet, P.; Tirapegui, E. The Bogdanov—Takens normal form: A minimal model for single neuron dynamics. Entropy 2015, 17, 7859–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Ma, J.; Ren, W. Research entropy complexity about the nonlinear dynamic delay game model. Entropy 2017, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ma, J.; Si, F.; Ren, W. Entropy complexity and stability of a nonlinear dynamic game model with two delays. Entropy 2016, 18, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.S.; Palit, S.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Hoang, T.M.; Banerjee, S. Complexity and synchronization in stochastic chaotic systems. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2016, 225, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Sun, K.; Wang, H. Complexity analysis and DSP implementation of the fractional-order Lorenz hyperchaotic system. Entropy 2015, 17, 8299–8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ma, X.; Lou, W. Analysis of the Complexity Entropy and Chaos Control of the Bullwhip Effect Considering Price of Evolutionary Game between Two Retailers. Entropy 2016, 18, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, C.; Sun, K.; Jafari, S. Multivariate Multiscale Complexity Analysis of Self-Reproducing Chaotic Systems. Entropy 2018, 20, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haken, H. Analogy between higher instabilities in fluids and lasers. Phys. Lett. A 1975, 53, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Saha, P.; Chowdhury, A.R. Chaotic aspects of lasers with host-induced nonlinearity and its control. Phys. Lett. A 2001, 291, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tartwijk, G.H.M.; Agrawal, G.P. Nonlinear dynamics in the generalized Lorenz-Haken model. Opt. Commun. 1997, 133, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.A. Numerical Analysis of Bifurcations. In Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 505–585. [Google Scholar]
- Kaffashi, F.; Foglyano, R.; Wilson, C.G.; Loparo, K.A. The effect of time delay on approximate & sample entropy calculations. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2008, 237, 3069–3074. [Google Scholar]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volos, C.K.; Kyprianidis, I.M.; Stouboulos, I.N. Fingerprint images encryption process based on a chaotic true random bits generator. Int. J. Multimedia Intell. Secur. 2010, 1, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Booz-Allen and Hamilton Inc.: Mclean, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Natiq, H.; Al-Saidi, N.M.G.; Said, M.R.M.; Kilicman, A. A new hyperchaotic map and its application for image encryption. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Orozco, E.; García-Guerrero, E.; Inzunza-Gonzalez, E.; López-Bonilla, O.; Flores-Vergara, A.; Cárdenas-Valdez, J.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E. FPGA-based Chaotic Cryptosystem by Using Voice Recognition as Access Key. Electronics 2018, 7, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
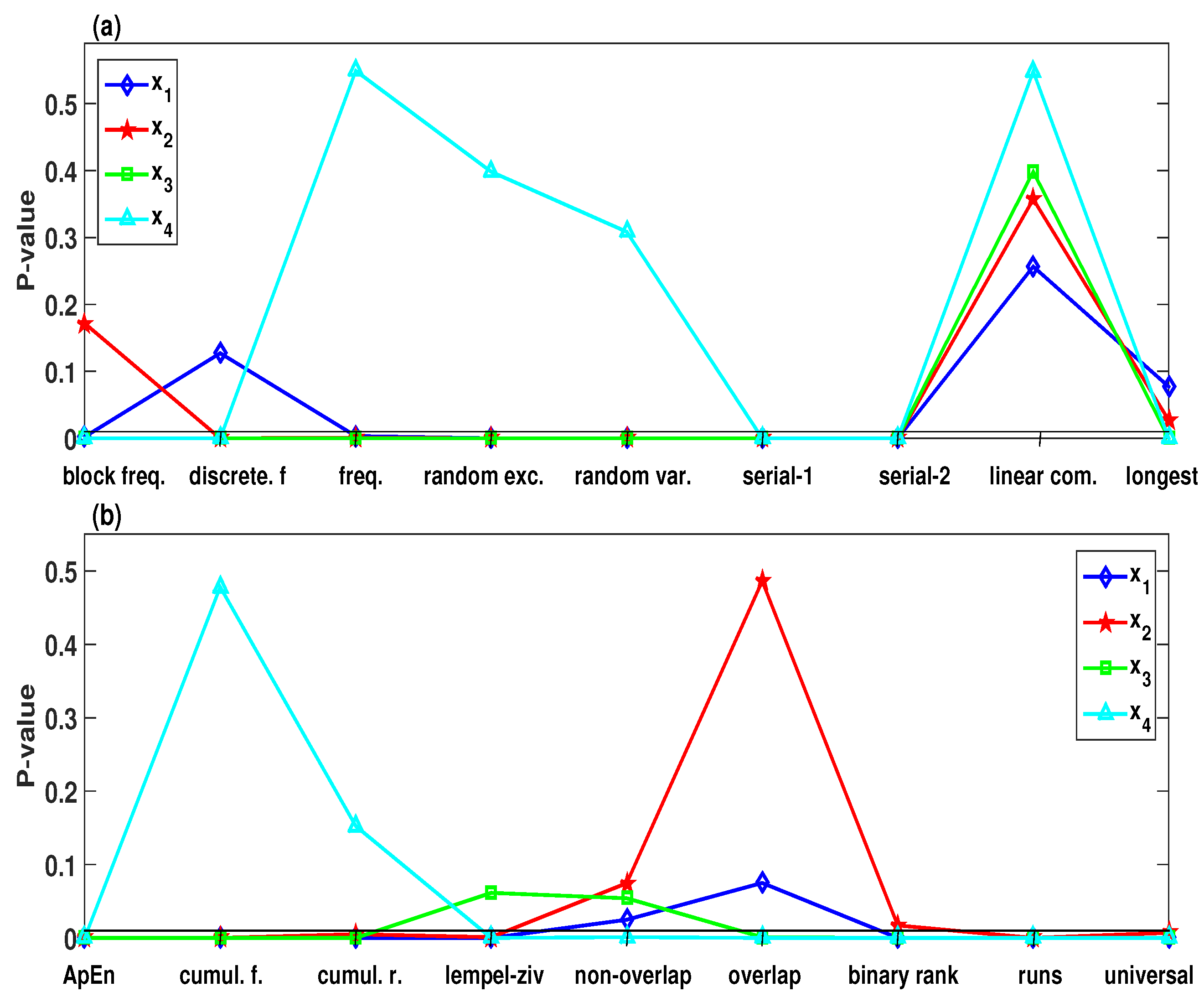
| Each Sequence to be Tested Consists of 1,000,000 Bits | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIST-800-22 Tests | -Value () | -Value () | -Value () | -Value () | Result | |
| 1. | Block-Frequency (m = 128) | 0.2116 | 0.8460 | 0.8313 | 0.0210 | Random |
| 2. | Frequency (Monobit) | 0.7611 | 0.0380 | 0.6570 | 0.3503 | Random |
| 3. | Discrete Fourier Transform | 0.3602 | 0.1792 | 0.1478 | 0.1225 | Random |
| 4. | Approximate Entropy (m = 10) | 0.9592 | 0.6512 | 0.6343 | 0.3659 | Random |
| 5. | Cumulative Sums (Forward) | 0.7617 | 0.0721 | 0.7280 | 0.5832 | Random |
| Cumulative Sums (Reverse) | 0.5578 | 0.0320 | 0.5106 | 0.1816 | Random | |
| 6. | Serial-1 (m = 16) | 0.7937 | 0.2948 | 0.1635 | 0.9706 | Random |
| Serial-2 (m = 16) | 0.8885 | 0.7628 | 0.5357 | 0.9530 | Random | |
| 7. | Runs | 0.9649 | 0.6196 | 0.4751 | 0.1530 | Random |
| 8. | Longest Run of Ones | 0.2568 | 0.0965 | 0.8242 | 0.2420 | Random |
| 9. | Overlapping Template (m = 9) | 0.7032 | 0.6461 | 0.5603 | 0.7085 | Random |
| 10. | Non-overlapping Template (m = 9) | 0.4960 | 0.5403 | 0.5150 | 0.5117 | Random |
| 11. | Linear Complexity (m = 500) | 0.4091 | 0.7263 | 0.1607 | 0.8582 | Random |
| 12. | Binary Matrix Rank | 0.2618 | 0.1029 | 0.2843 | 0.2376 | Random |
| 13. | Lempel-ziv Compression | 0.0769 | 0.2343 | 0.1411 | 0.9581 | Random |
| 14. | Random Excursions | 0.4628 | 0.2379 | 0.4787 | 0.3931 | Random |
| 15. | Random Excursions Variant | 0.6141 | 0.1814 | 0.3977 | 0.2865 | Random |
| 16. | Universal Statistical | 0.4931 | 0.7326 | 0.6056 | 0.1038 | Random |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Natiq, H.; Said, M.R.M.; Al-Saidi, N.M.G.; Kilicman, A. Dynamics and Complexity of a New 4D Chaotic Laser System. Entropy 2019, 21, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010034
Natiq H, Said MRM, Al-Saidi NMG, Kilicman A. Dynamics and Complexity of a New 4D Chaotic Laser System. Entropy. 2019; 21(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleNatiq, Hayder, Mohamad Rushdan Md Said, Nadia M. G. Al-Saidi, and Adem Kilicman. 2019. "Dynamics and Complexity of a New 4D Chaotic Laser System" Entropy 21, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010034
APA StyleNatiq, H., Said, M. R. M., Al-Saidi, N. M. G., & Kilicman, A. (2019). Dynamics and Complexity of a New 4D Chaotic Laser System. Entropy, 21(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/e21010034






