Scaling-Laws of Flow Entropy with Topological Metrics of Water Distribution Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Topological Metrics
2.2. Entropic Metrics
2.3. Maximum Entropy and Network Robustness
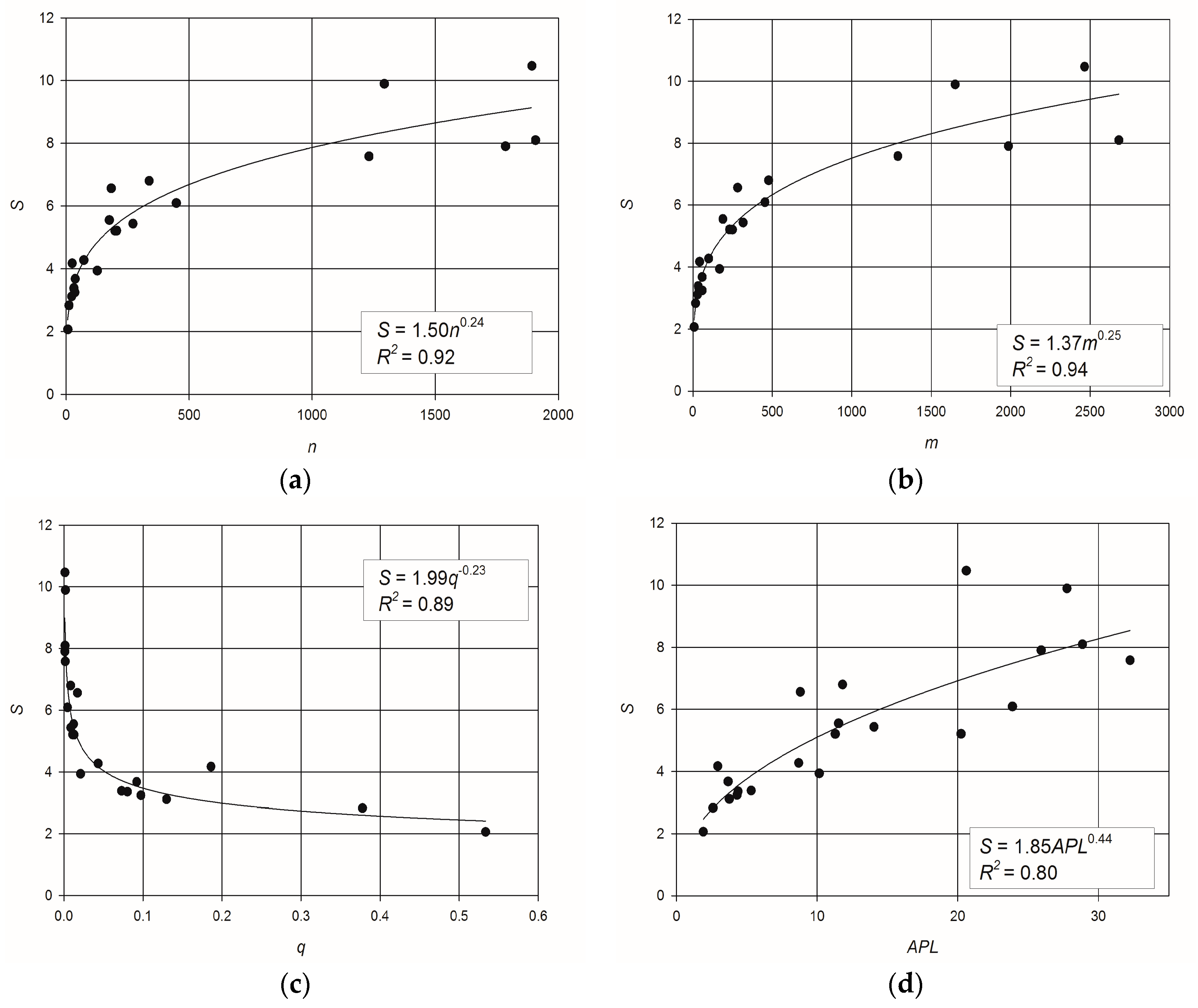
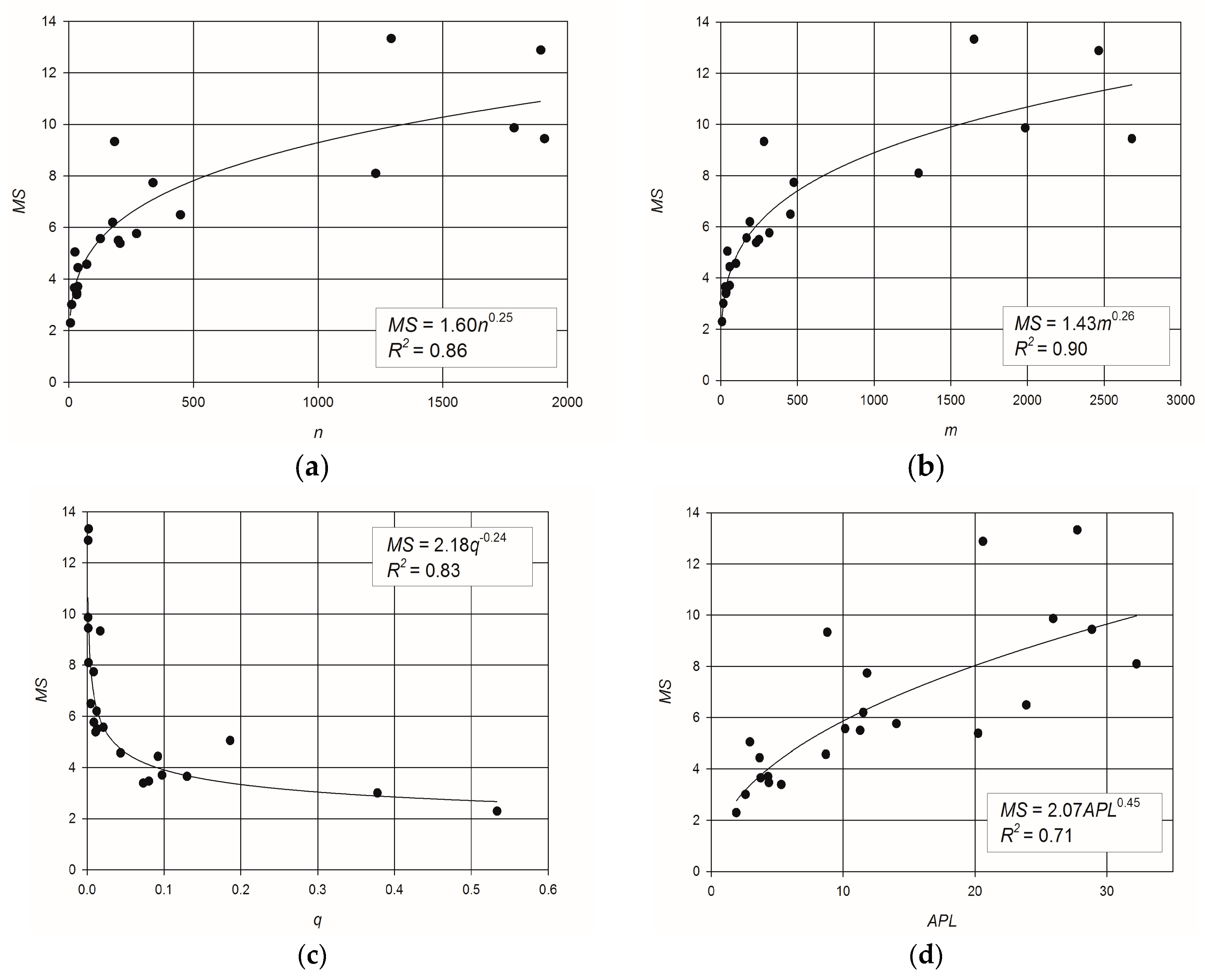
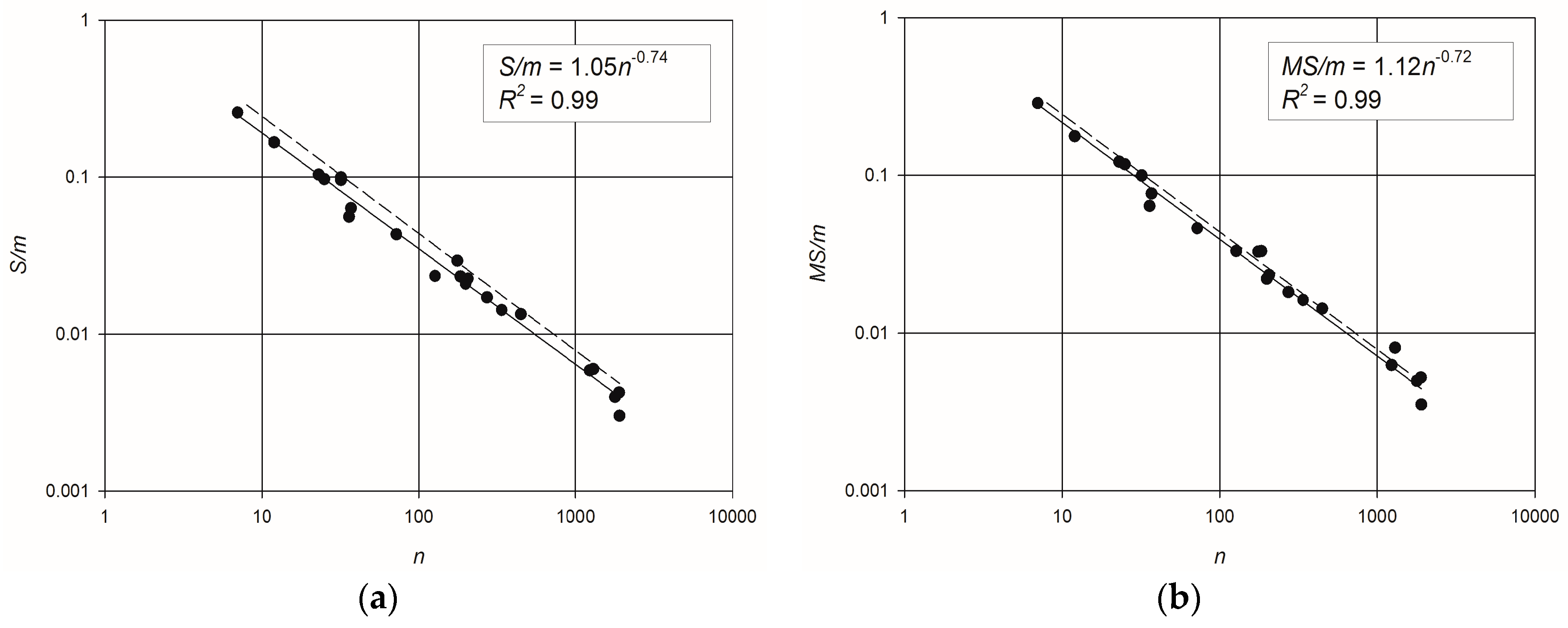
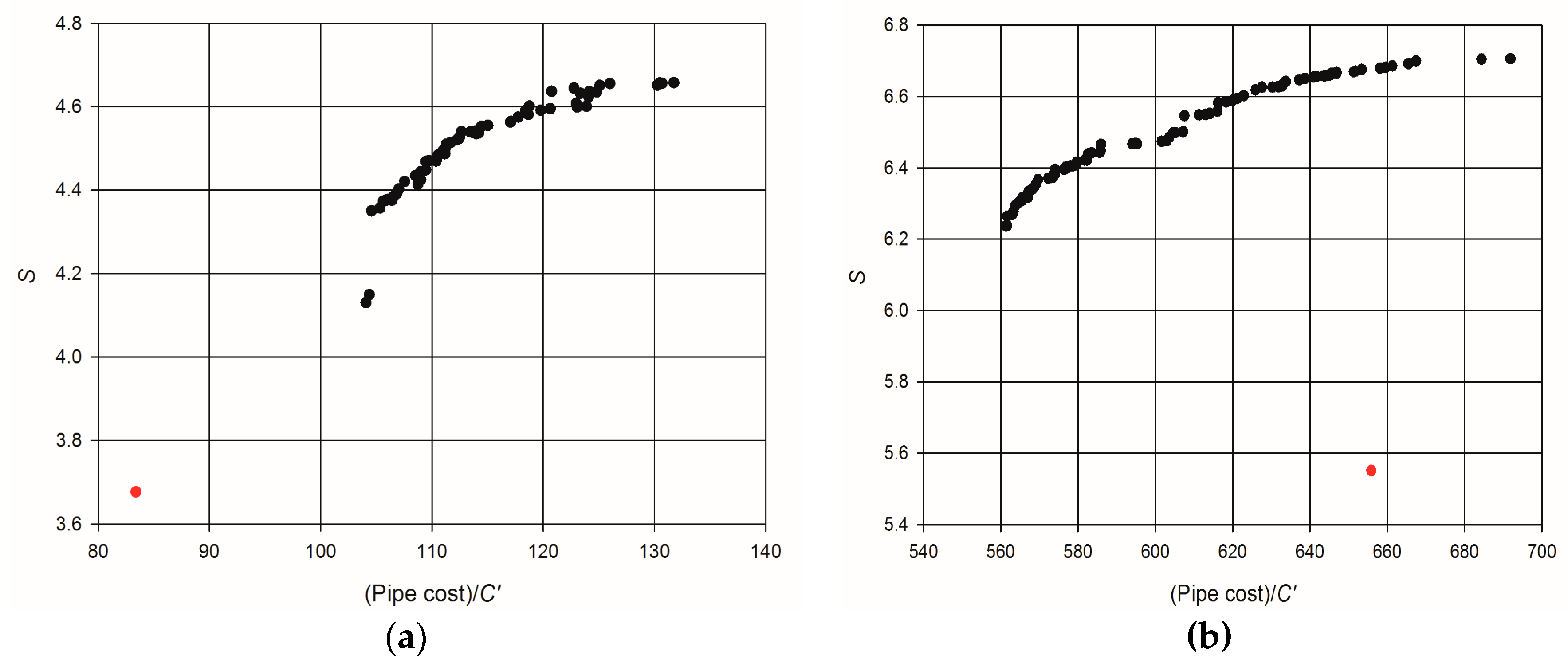
3. Results and Discussions
- dimension: the smallest network has a number of nodes n = 6 (Two Loop), while the largest has n = 1890 (Exnet);
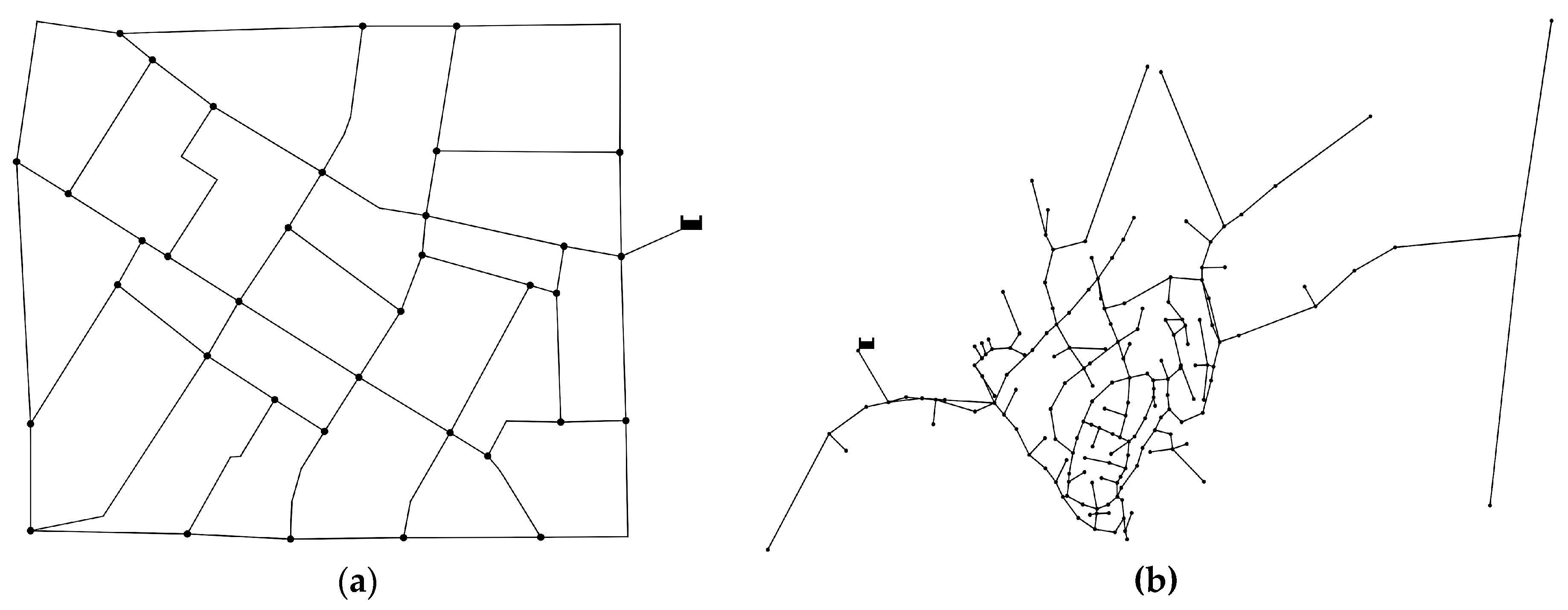
- layout: looped networks as well as branched ones are included, i.e., Balerma Irrigation can be considered a tree-network, while networks such as Parete and Sector Centro Real are very looped; compact and elongated networks are included, with low values of APL coupled with high values of density being representative of compact network layouts;
- robustness: the set of networks includes systems with very small deviation of actual entropyfrom maximum entropy, like Hanoi and Modena (the entropy deviation is equal to 0.0032 and 0.0616, respectively), and networks with high deviation of entropy, like Parete and BWSN2008-1(entropy deviations of 0.297 and 0.292, respectively).
4. Examples of Application
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greco, R.; Di Nardo, A.; Santonastaso, G.F. Resilience and entropy as indices of robustness of water distribution networks. J. Hydroinform. 2012, 14, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A. Scaling Laws. In Mechanics over Micro and Nano Scales; Chakraborty, S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Rinaldo, A. Fractal River Basins: Chance and Self Organization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; ISBN 0521473985. [Google Scholar]
- Hubert, P.; Tessier, Y.; Lovejoy, S.; Schertzer, D.; Schmitt, F.; Ladoy, P.; Carbonnel, J.P.; Violette, S. Multifractals and extreme rainfall events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1993, 20, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, A.H. World’s greatest observed point rainfalls. Mon. Weather Rev. 1950, 78, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmarini, S.; Steyn, D.G.; Ainslie, B. The scaling law relating world point-precipitation records to duration. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A.N. The local structure of turbulence in incompressible viscous fluid for very large Reynolds numbers. Proc. R. Soc. A 1991, 434, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, U.; Sulem, P.; Nelkin, M. A simple dynamical model of intermittent fully developed turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 87, 719–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrault, J.; Arnéodo, A.; Davis, A.; Marshak, A. Wavelet based multifractal analysis of rough surfaces: Application to cloud models and satellite data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badin, G.; Domeisen, D.I.V. Nonlinear stratospheric variability: Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis and singularity spectra. Proc. R. Soc. A 2016, 472, 20150864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Moon, W.; Wettlaufer, J. Trends, noise and re-entrant long-term persistence in Arctic sea ice. Proc. R. Soc. A 2012, 468, 2416–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabási, A.-L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletti, S.; Latora, V.; Moreno, Y.; Chavez, M. Hwanga, D.U. Complex networks: Structure and dynamics. Phys. Rep. 2006, 424, 175–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.R.; Lence, B.J.; Tolson, B.A.; Foschi, R.O. First-order reliability method for estimating reliability, vulnerability, and resilience. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, A.; Jeffrey, P. A complex network approach to robustness and vulnerability of spatially organized water distribution networks. Phys. Soc. 2010, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Mays, L.W. Model for water distribution system reliability. J. Hydrual. Eng. 1990, 116, 1119–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargano, R.; Pianese, D. Reliability as a tool for hydraulic network planning. J. Hydrual. Eng. ASCE 2000, 126, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, A. Reliability analysis of water distribution systems. J. Hydroinform. 2004, 6, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.M.; Shamir, U.; Marks, D.H. Water distribution reliability: Analytical methods. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1988, 114, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P. Entropy Theory and Its Application in Environmental and Water Engineering, 1st ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-119-97656-1. [Google Scholar]
- Awumah, K.; Goulter, I.; Bhatt, S.K. Assessment of reliability in water distribution networks using entropy based measures. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 1990, 4, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Templeman, A.B. A quantified assessment of the relationship between the reliability and entropy of water distribution systems. Eng. Optim. 2000, 33, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Sheahan, C. A maximum entropy based approach to the layout optimization of water distribution systems. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2002, 19, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiadi, Y.; Tanyimboh, T.T.; Templeman, A.B. Modelling errors, entropy and the hydraulic reliability of water distribution systems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2005, 36, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Savic, D.; Kapelan, Z.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, H. A diameter-sensitive flow entropy method for reliability consideration in water distribution system design. Water. Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5597–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Templeman, A.B. Calculating maximum entropy flows in networks. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1993, 44, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Templeman, A.B. Using entropy in water distribution networks. In Integrated Computer Applications in Water Supply, 1st ed.; Coulbeck, B., Ed.; Research Studies Press Ltd.: Taunton, UK, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 77–90. ISBN 086380-154-4. [Google Scholar]
- Perelman, L.; Housh, M.; Ostfeld, A. Robust optimization for water distribution systems least cost design. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6795–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.H.A.; Tanyimboh, T.T. Optimal design of water distribution systems based on entropy and topology. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 28, 3555–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.W. Water Distribution Systems Handbook, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 780071342131. [Google Scholar]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Greco, R.; Santonastaso, G.F. Complex network and fractal theory for the assessment of water distribution network resilience to pipe failures. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2017, 17, ws2017124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.; Strogatz, S. Collective dynamics of small world networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabasi, A.L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 797–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, A.; Jeffrey, P. Robustness and Vulnerability Analysis of Water Distribution Networks Using Graph Theoretic and Complex Network Principles. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference on Water Distribution Systems Analysis (WDSA), Tucson, AZ, USA, 12–15 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.A.; Herrera, M.; Pérez-García, R.; Ramos-Martínez, E. Application of graph-spectral methods in the vulnerability assessment of water supply networks. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 57, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Abraham, E.; Stoianov, I. A graph-theoretic framework for assessing the resilience of sectorised water distribution networks. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 30, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisi, A.; Naser, G. Multistate Reliability of Water-Distribution Systems: Comparison of Surrogate Measures. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.T. Informational entropy: A failure tolerance and reliability surrogate for water distribution networks. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 31, 3189–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creaco, E.; Fortunato, A.; Franchini, M.; Mazzola, M.R. Comparison between entropy and resilience as indirect measures of reliability in the framework of water distribution network design. Proc. Eng. 2014, 70, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todini, E. Looped water distribution networks design using a resilience index based heuristic approach. Urban Water 2000, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, T.D.; Park, N.S. Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithms for Design of Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 2004, 130, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaabel, J.; Ainola, L.; Koppel, T. Hydraulic power analysis for determination of characteristics of a water. In Proceedings of the Eighth Annual Water Distribution Systems Analysis Symposium (WDSA), Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdani, A.; Jeffrey, P. Complex network analysis of water distribution systems. Chaos 2011, 21, 016111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Greco, R.; Santonastaso, G.F. Water supply network partitioning based on weighted spectral clustering. Stud. Comp. Intell. 2017, 693, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Izquierdo, J.; Pérez-Garcìa, R.; Montalvo, I. Multi-agent adaptive boosting on semi supervised water supply clusters. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2012, 50, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, G.; Namey, E.E. Public Health Research Methods, 1st ed.; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Musmarra, D.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Simone, A. Water Distribution System Clustering and Partitioning Based on Social Network Algorithms. Proc. Eng. 2015, 119, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khinchin, A.I. Mathematical Foundations of Statistical Mechanics; Dover: New York, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, W.K.; Jowitt, P.W. Path entropy method for multiple-source water distribution networks. J. Eng. Optim. 2005, 37, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A. EPANET2 Users Manual; US EPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2000.
- Yassin-Kassab, A.; Templeman, A.B.; Tanyimboh, T.T. Calculating maximum entropy flows in multi-source, multi-demand networks. Eng. Optim. 1999, 31, 695–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alperovits, E.; Shamir, U. Design of optimal water distribution systems. Water Resour. Res. 1977, 13, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessler, J. Pipe network optimization by enumeration. Proceedings of Computer Applications in Water Resources, ASCE Specialty Conference, Buffalo, NY, USA, 10–12 June 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Walski, T.; Brill, E.; Gessler, J.; Goulter, I.; Jeppson, R.; Lansey, K.; Lee, H.; Liebman, J.; Mays, L.; Morgan, D.; et al. Battle of the network models: Epilogue. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 1987, 113, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, Y.N. A study on the pipe network system design using non-linear programming. J. Korean Water Resour. Assoc. 1994, 27, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sherali, H.D.; Subramanian, S.; Loganathan, G. Effective relaxations and partitioning schemes for solving water distribution network design problems to global optimality. J. Global. Optim. 2001, 19, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, O.; Khang, D.B. A two-phase decomposition method for optimal design of looped water distribution networks. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Lee, S.I. Genetic algorithms for optimal augmentation of water distribution networks. J. Korean Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 34, 567–575. [Google Scholar]
- Bragalli, C.; D'Ambrosio, C.; Lee, J.; Lodi, A.; Toth, P. On the Optimal Design of Water Distribution Networks: A Practical MINLP Approach. Optim. Eng. 2012, 13, 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, A.; Uber, J.G.; Salomons, E.; Berry, J.W.; Hart, W.E.; Phillips, C.A.; Watson, J.; Dorini, G.; Jonkergouw, P.; Kapelan, Z.; et al. The Battle of the Water Sensor Networks (BWSN): A Design Challenge for Engineers and Algorithms. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2008, 134, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Laspidou, C.; Morlando, F.; Santonastaso, G.F.; Kofinas, D. Spectral analysis and topological and energy metrics for water network partitioning of Skiathos island. Eur. Water 2017, 58, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Gisonni, C.; Iervolino, M. A genetic algorithm for demand pattern and leakage estimation in a water distribution network. J. Water Supply Res. Tech. Aqua 2015, 64, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Canu, S.; Karatzoglou, A.; Perez-Garcıa, R.; Izquierdo, J. An approach to water supply clusters by semi-supervised learning. In Proceedings of theInternational Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software Modelling (iEMSs) 2010 for Environment’s Sake, Fifth Biennial Meeting, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 5–8 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Reca, J.; Martinez, J. Genetic algorithms for the design of looped irrigation water distribution networks. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W05416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzatchkov, V.G.; Alcocer-Yamanaka, V.H.; Ortìz, V.B. Graph Theory Based Algorithms for Water Distribution Network Sectorization Projects. In Proceedings of the Eighth Annual Water Distribution Systems Analysis (WDSA) Symposium, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 27–30 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lippai, I. Colorado Springs Utilities Case Study: Water System Calibration Optimization. In Proceedings of the ASCE Pipeline Division Specialty Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 21–24 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Farmani, R.; Savic, D.A.; Walters, G.A. Evolutionary multi-objective optimization in water distribution network design. Eng. Optim. 2005, 37, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyimboh, T.T.; Saleh, S.H.A. Global maximum entropy minimum cost design of water distribution systems. In Proceedings of the ASCE/EWRI World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2011, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, D.E. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine Learning; Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co. Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Tricarico, C.; Gargano, R.; Kapelan, Z.; Savic, D.; de Marinis, G. Economic Level of Reliability for the Rehabilitation of Hydraulic Networks. J. Civ. Eng. Environ. Syst. 2006, 23, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Network | n | m | q | APL | S | MS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two Loop * [53] | 7 | 8 | 0.5333 | 1.90 | 2.063 | 2.296 | 0.101 |
| Two Reservoirs * [54] | 12 | 17 | 0.3778 | 2.59 | 2.829 | 3.008 | 0.059 |
| Anytown * [55] | 25 | 43 | 0.1861 | 2.94 | 4.172 | 5.048 | 0.174 |
| GoYang * [56] | 23 | 30 | 0.1299 | 3.75 | 3.113 | 3.658 | 0.149 |
| Blacksburg * [57] | 32 | 35 | 0.0805 | 4.37 | 3.358 | 3.473 | 0.033 |
| Hanoi * [58] | 32 | 34 | 0.0731 | 5.31 | 3.384 | 3.395 | 0.003 |
| BakRyan * [59] | 36 | 58 | 0.0975 | 4.30 | 3.243 | 3.709 | 0.126 |
| Fossolo [60] | 37 | 58 | 0.0921 | 3.67 | 3.677 | 4.441 | 0.172 |
| Pescara [60] | 72 | 99 | 0.0435 | 8.69 | 4.273 | 4.572 | 0.065 |
| BWSN2008-1 * [61] | 127 | 168 | 0.0213 | 10.15 | 3.939 | 5.567 | 0.292 |
| Skiathos [62] | 176 | 189 | 0.0124 | 11.52 | 5.551 | 6.196 | 0.104 |
| Parete [1] | 184 | 282 | 0.0171 | 8.80 | 6.561 | 9.331 | 0.297 |
| Villaricca [1] | 199 | 249 | 0.0130 | 11.29 | 5.206 | 5.497 | 0.053 |
| Monteruscello [63] | 206 | 231 | 0.0110 | 20.24 | 5.211 | 5.385 | 0.032 |
| Modena [60] | 272 | 317 | 0.0089 | 14.04 | 5.436 | 5.764 | 0.057 |
| Celaya [64] | 338 | 477 | 0.0086 | 11.81 | 6.8 | 7.734 | 0.121 |
| Balerma Irrigation [65] | 448 | 454 | 0.0046 | 23.89 | 6.091 | 6.489 | 0.061 |
| Castellammare | 1231 | 1290 | 0.0017 | 32.25 | 7.583 | 8.094 | 0.063 |
| Matamoros [66] | 1293 | 1651 | 0.0020 | 27.76 | 9.896 | 13.325 | 0.257 |
| Wolf Cordera Ranch [67] | 1786 | 1985 | 0.0013 | 25.94 | 7.905 | 9.865 | 0.199 |
| Exnet * [68] | 1893 | 2465 | 0.0014 | 20.60 | 10.466 | 12.882 | 0.188 |
| San Luis Rio Colorado [66] | 1908 | 2681 | 0.0015 | 28.86 | 8.097 | 9.443 | 0.143 |
| FossoloDN (mm) | SkiathosDN (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 16.00 | 73.60 | 40.00 | 125.00 |
| 20.40 | 90.00 | 50.00 | 140.00 |
| 26.00 | 102.20 | 63.00 | 150.00 |
| 32.60 | 147.20 | 75.00 | 160.00 |
| 40.80 | 184.00 | 80.00 | 225.00 |
| 51.40 | 204.6 | 90.00 | |
| 61.40 | 229.2 | 110.00 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santonastaso, G.F.; Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudicianni, C.; Greco, R. Scaling-Laws of Flow Entropy with Topological Metrics of Water Distribution Networks. Entropy 2018, 20, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20020095
Santonastaso GF, Di Nardo A, Di Natale M, Giudicianni C, Greco R. Scaling-Laws of Flow Entropy with Topological Metrics of Water Distribution Networks. Entropy. 2018; 20(2):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20020095
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantonastaso, Giovanni Francesco, Armando Di Nardo, Michele Di Natale, Carlo Giudicianni, and Roberto Greco. 2018. "Scaling-Laws of Flow Entropy with Topological Metrics of Water Distribution Networks" Entropy 20, no. 2: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20020095
APA StyleSantonastaso, G. F., Di Nardo, A., Di Natale, M., Giudicianni, C., & Greco, R. (2018). Scaling-Laws of Flow Entropy with Topological Metrics of Water Distribution Networks. Entropy, 20(2), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20020095








