Interaction Information Along Lifespan of the Resting Brain Dynamics Reveals a Major Redundant Role of the Default Mode Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Participants
2.2. Imaging Acquisition
2.3. Imaging Preprocessing
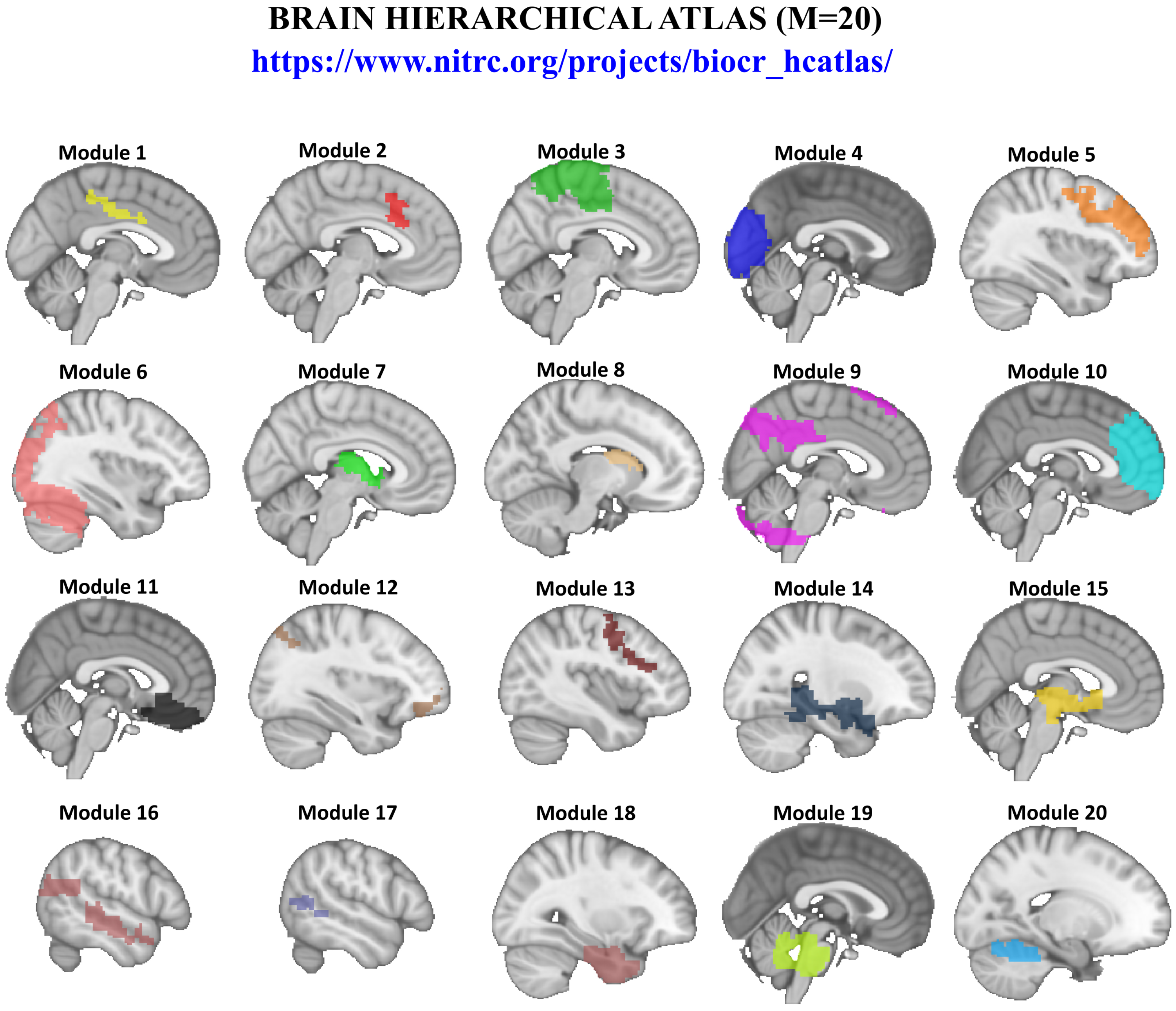
2.4. Brain Hierarchical Atlas
2.5. Shannon Entropy
2.6. Interaction Information
2.7. Calculation of II
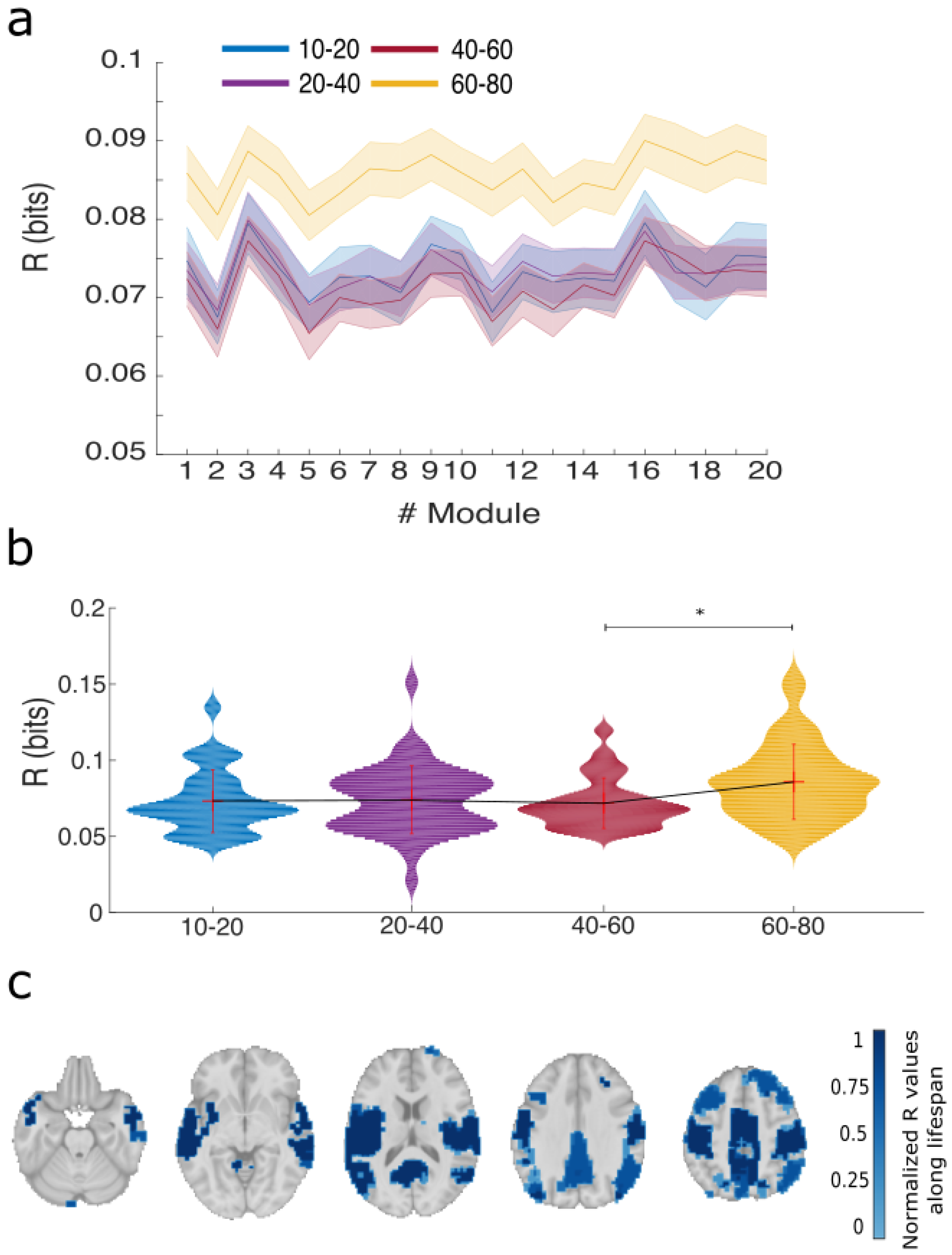
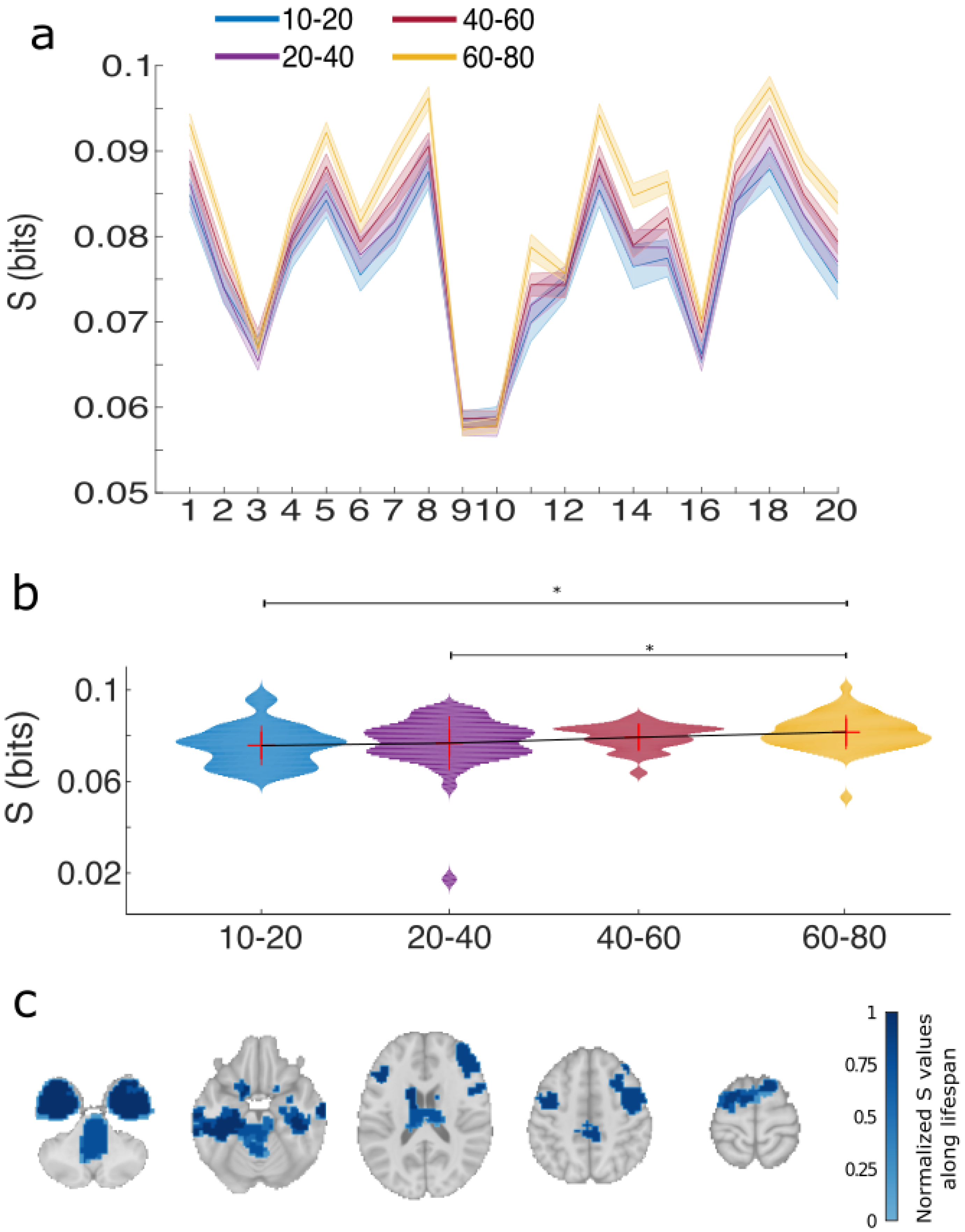
2.8. Per Module R and S
2.9. Statistical Analysis
2.10. Mask of the Resting State Networks
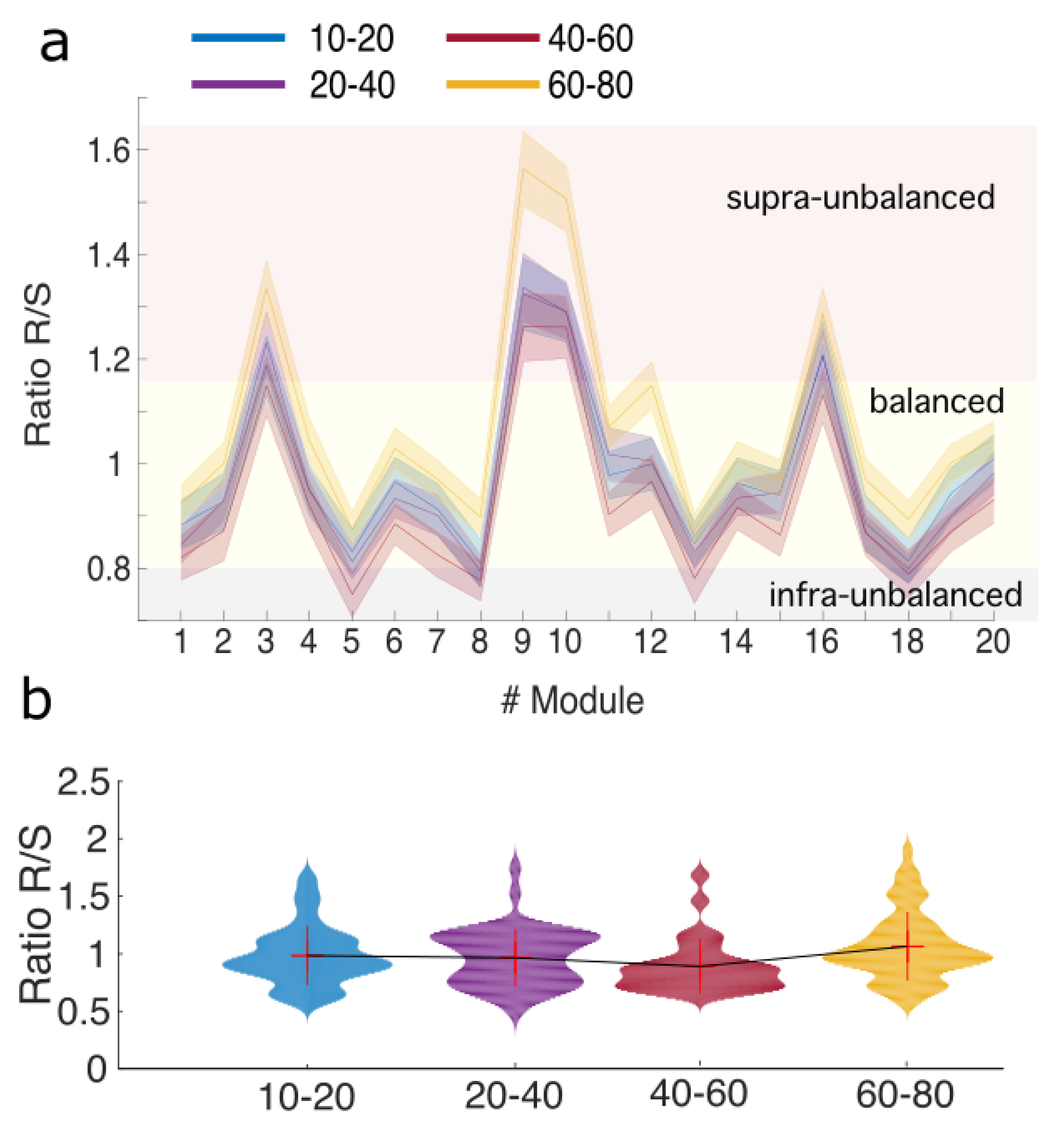
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| II | interaction information |
| MI | mutual information |
| R | redundancy |
| S | synergy |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| DMN | default mode network |
| RSN | resting state network |
| BHA | brain hierarchical atlas |
References
- McGill, W.J. Multivariate Information Transmission. Psychometrika 1954, 19, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erramuzpe, A.; Ortega, G.; Pastor, J.; de Sola, R.; Marinazzo, D.; Stramaglia, S.; Cortes, J. Identification of redundant and synergetic circuits in triplets of electrophysiological data. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 066007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneidman, E.; Bialek, W.; Berry, M. Synergy, redundancy, and independence in population codes. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 11539–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, A. Exploration of synergistic and redundant information sharing in static and dynamical Gaussian systems. Phys. Rev. E 2015, 91, 052802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, W.; Ince, R. Exact Partial Information Decompositions for Gaussian Systems Based on Dependency Constraints. Entropy 2018, 20, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizier, J.T.; Atay, F.M.; Jost, J. Information Storage, Loop Motifs, and Clustered Structure in Complex Networks. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 026110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibral, M.; Lizier, J.T.; Vögler, S.; Priesemann, V.; Galuske, R. Local Active Information Storage as a Tool to Understand Distributed Neural Information Processing. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettencourt, L.; Gintautas, V.; Ham, M. Information Subgraphs in Complex Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 238701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stramaglia, S.; Cortes, J.; Marinazzo, D. Synergy and redundancy in the Granger causal analysis of dynamical networks. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramaglia, S.; Wu, G.R.; Pellicoro, M.; Marinazzo, D. Expanding the transfer entropy to identify information circuits in complex systems. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 066211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conger, A.J. A Revised Definition for Suppressor Variables: A Guide To Their Identification and Interpretation. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1974, 34, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.V.; Tetko, I.V.; Mader, M.T.; Budczies, J.; Mewes, H.W. Optimization Models for Cancer Classification: Extracting Gene Interaction Information from Microarray Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Saito, M.; Bisikirska, B.C.; Alvarez, M.J.; Lim, W.K.; Rajbhandari, P.; Shen, Q.; Nemenman, I.; Basso, K.; Margolin, A.A.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of Post-Translational Modulators of Transcription Factor Activity in Human B Cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinazzo, D.; Gosseries, O.; Boly, M.; Ledoux, D.; Rosanova, M.; Massimini, M.; Noirhomme, Q.; Laureys, S. Directed information transfer in scalp electroencephalographic recordings: Insights on disorders of consciousness. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2014, 45, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stramaglia, S.; Angelini, L.; Wu, G.; Cortes, J.M.; Faes, L.; Marinazzo, D. Synergetic and Redundant Information Flow Detected by Unnormalized Granger Causality: Application to Resting State fMRI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 2518–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, M.; Snyder, A.; Vincent, J.; Corbetta, M.; Essen, D.V.; Raichle, M. The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9673–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichle, M.; Mintum, M. Brain work and brain imaging. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 449–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswal, B.; Zerrin Yetkin, F.; Haughton, V.M.; Hyde, J.S. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar mri. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, C.F.; DeLuca, M.; Devlin, J.T.; Smith, S.M. Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2005, 360, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIntosh, A.R.; Lobaugh, N.J. Partial least squares analysis of neuroimaging data: Applications and advances. NeuroImage 2004, 23 (Suppl. 1), S250–S263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Fox, P.T.; Miller, K.L.; Glahn, D.C.; Fox, P.M.; Mackay, C.E.; Filippini, N.; Watkins, K.E.; Toro, R.; Laird, A.R.; et al. Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13040–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boveroux, P.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Bruno, M.A.; Noirhomme, Q.; Lauwick, S.; Luxen, A.; Degueldre, C.; Plenevaux, A.; Schnakers, C.; Phillips, C.; et al. Breakdown of Within- and between-Network Resting State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Connectivity during Propofol-Induced Loss of Consciousness. Anesthesiology 2010, 113, 1038–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noirhomme, Q.; Soddu, A.; Lehembre, R.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Boveroux, P.; Boly, M.; Laureys, S. Brain Connectivity in Pathological and Pharmacological Coma. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, L.; Soddu, A.; Gómez, F.; Vanhaudenhuyse, A.; Tshibanda, L.; Thonnard, M.; Charland-Verville, V.; Kirsch, M.; Laureys, S.; Demertzi, A. Resting State Networks and Consciousness. Front. Psychol. 2012, 3, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäki-Marttunen, V.; Diez, I.; Cortes, J.M.; Chialvo, D.R.; Villarreal, M. Disruption of Transfer Entropy and Inter-Hemispheric Brain Functional Connectivity in Patients with Disorder of Consciousness. Front. Neuroinform. 2013, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, N.D.; Rogers, B.; Heckers, S. Functional Resting-State Networks Are Differentially Affected in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 130, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbasforoushan, H.; Woodward, N.D. Resting-State Networks in Schizophrenia. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2404–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Mantini, D.; Ding, J.; Duan, X.; Luo, C.; Lu, G.; Chen, H. Altered Functional Connectivity and Small-World in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Li, Z.; Wu, G.; Zhang, M.J.; Franczak, M.; Antuono, P.G. Alzheimer Disease: Evaluation of a Functional MR Imaging Index as a Marker. Radiology 2002, 225, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greicius, M.D.; Srivastava, G.; Reiss, A.L.; Menon, V. Default-Mode Network Activity Distinguishes Alzheimer’s Disease from Healthy Aging: Evidence from Functional MRI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4637–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombouts, S.A.; Barkhof, F.; Goekoop, R.; Stam, C.J.; Scheltens, P. Altered Resting State Networks in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Alzheimer’s Disease: An fMRI Study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2005, 26, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewijzend, M.A.; Schoonheim, M.M.; Sanz-Arigita, E.; Wink, A.M.; van der Flier, W.M.; Tolboom, N.; Adriaanse, S.M.; Damoiseaux, J.S.; Scheltens, P.; van Berckel, B.N.; et al. Resting-State fMRI Changes in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheline, Y.I.; Raichle, M.E. Resting State Functional Connectivity in Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews-Hanna, J.; Snyder, A.; Vincent, J.; Lustig, C.; Head, D.; Raichle, M.; Buckner, R. Disruption of large-scale brain systems in advanced aging. Neuron 2008, 56, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damoiseaux, J.; Beckmann, C.; Arigita, E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Stam, C.; Smith, S.; Rombouts, S. Reduced resting-state brain activity in the “default network” in normal aging. Cereb Cortex 2007, 18, 1856–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, M.; Park, D.; Savalia, N.; Petersen, S.; Wig, G. Decreased segregation of brain systems across the healthy adult lifespan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4997–E5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagmann, P.; Sporns, O.; Madan, N.; Cammoun, L.; Pienaar, R.; Wedeen, V.; Meuli, R.; Thiran, J.; Grant, P. White matter maturation reshapes structural connectivity in the late developing human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19067–19072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marinazzo, D.; Pellicoro, M.; Wu, G.; Angelini, L.; Cortés, J.M.; Stramaglia, S. Information Transfer and Criticality in the Ising Model on the Human Connectome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alonso-Montes, C.; Diez, I.; Remaki, L.; Escudero, I.; Mateos, B.; Rosseel, Y.; Marinazzo, D.; Stramaglia, S.; Cortes, J.M. Lagged and Instantaneous Dynamical Influences Related to Brain Structural Connectivity. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amor, T.A.; Russo, R.; Diez, I.; Bharath, P.; Zirovich, M.; Stramaglia, S.; Cortes, J.M.; de Arcangelis, L.; Chialvo, D.R. Extreme Brain Events: Higher-Order Statistics of Brain Resting Activity and Its Relation with Structural Connectivity. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2015, 111, 68007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, I.; Erramuzpe, A.; Escudero, I.N.; Mateos, B.; Cabrera, A.; Marinazzo, D.; Sanz-Arigita, E.J.; Stramaglia, S.; Cortes Diaz, J.M.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Information Flow Between Resting-State Networks. Brain Connect. 2015, 5, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasero, J.; Pellicoro, M.; Angelini, L.; Cortes, J.M.; Marinazzo, D.; Stramaglia, S. Consensus Clustering Approach to Group Brain Connectivity Matrices. Netw. Neurosci. 2017, 1, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stramaglia, S.; Pellicoro, M.; Angelini, L.; Amico, E.; Aerts, H.; Cortés, J.M.; Laureys, S.; Marinazzo, D. Ising Model with Conserved Magnetization on the Human Connectome: Implications on the Relation Structure-Function in Wakefulness and Anesthesia. Chaos 2017, 27, 047407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordes, D.; Haughton, V.M.; Arfanakis, K.; Carew, J.D.; Turski, P.A.; Moritz, C.H.; Quigley, M.A.; Meyerand, M.E. Frequencies Contributing to Functional Connectivity in the Cerebral Cortex in “Resting-State” Data. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.G.; Cheung, B.; Kelly, C.; Colcombe, S.; Craddock, R.C.; Di Martino, A.; Li, Q.; Zuo, X.N.; Castellanos, F.X.; Milham, M.P. A Comprehensive Assessment of Regional Variation in the Impact of Head Micromovements on Functional Connectomics. NeuroImage 2013, 76, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez, I.; Bonifazi, P.; Escudero, I.n.; Mateos, B.; Muñoz, M.A.; Stramaglia, S.; Cortes, J.M. A Novel Brain Partition Highlights the Modular Skeleton Shared by Structure and Function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez, I.; Drijkoningen, D.; Stramaglia, S.; Bonifazi, P.; Marinazzo, D.; Gooijers, J.; Swinnen, S.P.; Cortes, J.M. Enhanced Prefrontal Functional–Structural Networks to Support Postural Control Deficits after Traumatic Brain Injury in a Pediatric Population. Netw. Neurosci. 2017, 1, 116–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifazi, P.; Erramuzpe, A.; Diez, I.; Gabilondo, I.; Boisgontier, M.; Pauwels, L.; Stramaglia, S.; Swinnen, S.; Cortes, J. Structure-function multi-scale connectomics reveals a major role of the fronto-striato-thalamic circuit in brain aging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NITRC. Brain Hierarchical Atlas: A brain atlas where the regions of interest are relevant for both structure and function. Available online: https://www.nitrc.org/projects/biocr_hcatlas/ (accessed on 31 July 2018).
- GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/compneurobilbao/bha (accessed on 31 July 2018).
- Jaynes, E.T. Information Theory and Statistical Mechanics. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ince, R.; Giordano, B.; Kayser, C.; Rousselet, G.; Gross, J.; Schyns, P. A statistical framework for neuroimaging data analysis based on mutual information estimated via a Gaussian copula. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 1541–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/robince/gcmi/ (accessed on 31 July 2018).
- Smith, S.; Fox, P.; Miller, K.; Glahn, D.; Fox, P.; Mackay, C.; Filippini, N.; Watkins, K.; Toro, R.; Laird, A.; et al. Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13040–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Johnson, B.; Gay, M.; Horovitz, S.; Hallett, M.; Sebastianelli, W.; Slobounov, S. Default mode network in concussed individuals in response to the YMCA physical stress test. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, K.; Shenk, T.; Poole, V.; Breedlove, E.; Leverenz, L.; Nauman, E.; Talavage, T.; Robinson, M. Alteration of default mode network in high school football athletes due to repetitive subconcussive mild traumatic brain injury: A resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Brain Connect. 2015, 5, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, A.; Chhatwal, J.; Hedden, T.; Mormino, E.; Hanseeuw, B.; Sepulcre, J.; Huijbers, W.; LaPoint, M.; Buckley, R.; Johnson, K.; et al. Phases of Hyperconnectivity and Hypoconnectivity in the Default Mode and Salience Networks. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mevel, K.; Chételat, G.; Eustache, F.; Desgranges, B. The default mode network in healthy aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 2011, 13040–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, M.; Seidl-Rathkopf, K.; Kastner, S. Functions of the human frontoparietal attention network: Evidence from neuroimaging. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2015, 1, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
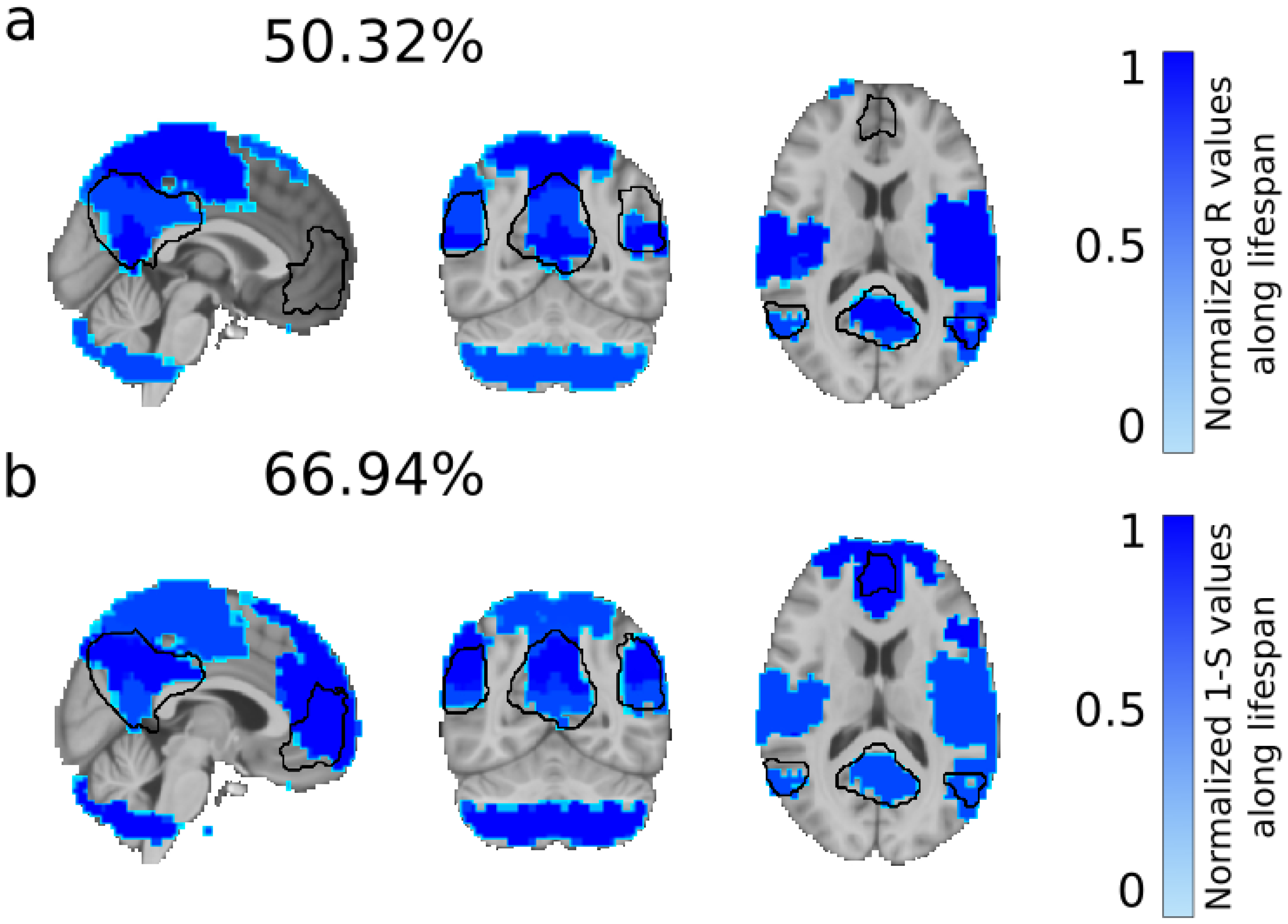
| Infra-Balanced (%) | Balanced (%) | Supra-Balanced (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default Mode | 0.2246 | 19.0583 | 69.1893 |
| Auditory | 0.0284 | 38.1631 | 55.2979 |
| Cerebellum | 0 | 84.3334 | 0.8268 |
| Executive Control | 5.176 | 37.3482 | 30.9205 |
| Frontoparietal | 9.5896 | 39.358 | 39.5368 |
| Sensorimotor | 1.72 | 11.7076 | 57.8549 |
| Visual | 0 | 77.7678 | 5.9748 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camino-Pontes, B.; Diez, I.; Jimenez-Marin, A.; Rasero, J.; Erramuzpe, A.; Bonifazi, P.; Stramaglia, S.; Swinnen, S.; Cortes, J.M. Interaction Information Along Lifespan of the Resting Brain Dynamics Reveals a Major Redundant Role of the Default Mode Network. Entropy 2018, 20, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20100742
Camino-Pontes B, Diez I, Jimenez-Marin A, Rasero J, Erramuzpe A, Bonifazi P, Stramaglia S, Swinnen S, Cortes JM. Interaction Information Along Lifespan of the Resting Brain Dynamics Reveals a Major Redundant Role of the Default Mode Network. Entropy. 2018; 20(10):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20100742
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamino-Pontes, Borja, Ibai Diez, Antonio Jimenez-Marin, Javier Rasero, Asier Erramuzpe, Paolo Bonifazi, Sebastiano Stramaglia, Stephan Swinnen, and Jesus M. Cortes. 2018. "Interaction Information Along Lifespan of the Resting Brain Dynamics Reveals a Major Redundant Role of the Default Mode Network" Entropy 20, no. 10: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20100742
APA StyleCamino-Pontes, B., Diez, I., Jimenez-Marin, A., Rasero, J., Erramuzpe, A., Bonifazi, P., Stramaglia, S., Swinnen, S., & Cortes, J. M. (2018). Interaction Information Along Lifespan of the Resting Brain Dynamics Reveals a Major Redundant Role of the Default Mode Network. Entropy, 20(10), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/e20100742






