Abstract
The present paper is concerned with the analysis of inherent irreversibility in hydromagnetic boundary layer flow of variable viscosity fluid over a semi-infinite flat plate under the influence of thermal radiation and Newtonian heating. Using local similarity solution technique and shooting quadrature, the velocity and temperature profiles are obtained numerically and utilized to compute the entropy generation number. The effects of magnetic field parameter, Brinkmann number, the Prandtl number, variable viscosity parameter, radiation parameter and local Biot number on the fluid velocity profiles, temperature profiles, local skin friction and local Nusselt number are presented. The influences of the same parameters and the dimensionless group parameter on the entropy generation rate in the flow regime and Bejan number are calculated, depicted graphically and discussed quantitatively. It is observed that the peak of entropy generation rate is attained within the boundary layer region and plate surface act as a strong source of entropy generation and heat transfer irreversibility.
Keywords:
flat plate; variable viscosity; Newtonian heating; Thermal radiation; magnetic field; entropy generation rate PACS Codes:
44.10.+a; 47.11.-j; 47.15.gm
1. Introduction
Theoretical study of thermodynamic irreversibility in hydromagnetic boundary layer flow in the presence of thermal radiation appears to be increasingly important due to its various applications in engineering and industries [1,2] such as in the design of cooling systems for electronic devices, in the field of solar energy collection, geothermal reservoirs, heat exchangers, thermal insulation, enhanced oil recovery, packed-bed catalytic reactors, cooling of nuclear reactors, etc. Moreover, many engineering processes occur at high temperature and acknowledge radiation heat transfer become very important for the design of pertinent equipment [3,4,5]. Nuclear power plants, gas turbines and the various propulsion devices for air craft, missiles, satellites and space vehicles are other example of such applications. Several excellent studies on hydromagnetic boundary layer flows with thermal radiation have been communicated [6,7,8]. These forgoing research works have covered a wide range of problems involving the hydromagnetic boundary layer flow and heat transfer phenomenon; they have been restricted, from thermodynamic point of view, to only the first law analysis. The contemporary trend in the field of fluid flow, heat transfer and thermal design is the second law of thermodynamics analysis and its related concept of entropy generation minimization [9]. Entropy generation is closely associated with thermodynamic irreversibility, which is encountered in all heat transfer processes [10]. Different sources are responsible for entropy generation like heat transfer along a temperature gradient, fluid friction, magnetic field effect, thermal radiation effect, etc. The analysis of thermodynamic irreversibility enables us to identify the irreversibility associated with various components and to avoid loss of available energy. Such information can be employed to design thermal systems, guide efforts to reduce sources of irreversibility, estimate the cost of engineering systems and optimize complex systems. In a pioneering work, Bejan [11,12] introduced the theoretical concept of entropy generation minimization based on the second-law analysis into heat transfer and thermal design problems. Thereafter, several works on entropy generation minimisation have appeared in the literature [13,14,15]. Makinde and Aziz [16] gave an analytical and numerical analysis of the second law for a variable viscosity plane Poiseuille flow with asymmetric convective heat transfer. The study of entropy generation in a falling variable viscosity liquid film along an inclined heated plate with convective cooling was carried out by Makinde [17]. Mahmud et al. [18] studied the effect of a magnetic field on the entropy generation in a mixed convection channel flow. Makinde and Beg [19] applied the second law analysis to the problem of inherent irreversibility in a reactive hydromagnetic channel flow. The double-diffusive (natural) convection in vertical annuluses with opposing temperature and concentration gradients was report by Chen et al. [20]. They proposed that lattice Boltzmann-based numerical method is an effective alternative to traditional CFD for evaluating the irreversibility due to viscosity with a more straightforward way. Chen and his co-workers [21,22,23,24] made use of this important numerical approach to investigate the entropy generation rate in several flow related problems, such as impinging flow confined by planar opposing jets, natural convection in a rectangle cavity, premixed hydrogen-air combustion, etc.
In this paper, our main focus is on the entropy generation characteristics for hydromagnetic boundary layer flow under the influence of thermal radiation and Newtonian heating at the plate surface. This study extends the work of Aziz [25] to include the combined effects of magnetic field, viscous dissipation, radiative heat transfer and entropy generation analysis. Pertinent results on the effects of various embedded parameters controlling the system are presented in tabular and graphical forms and discussed quantitatively.
2. Mathematical Model
The steady two-dimensional hydromagnetic boundary layer flow with heat transfer over a flat plate in a stream of variable viscosity electrically conducting fluid at temperature T∞ in the presence of magnetic field and thermal radiation is considered. It is assumed that the lower surface of the plate is heated by convection from a hot fluid at temperature Tf which provides a heat transfer coefficient hf. The fluid on the upper side of the plate is then subjected to Newtonian heating and its property variations due to temperature are limited to viscosity. A uniform transverse magnetic field B0 is imposed along the y-axis as shown in Figure 1. Both the induced magnetic field due to the motion of the electrically-conducting fluid and the electric field due to the polarization of charges are assumed to be negligible.
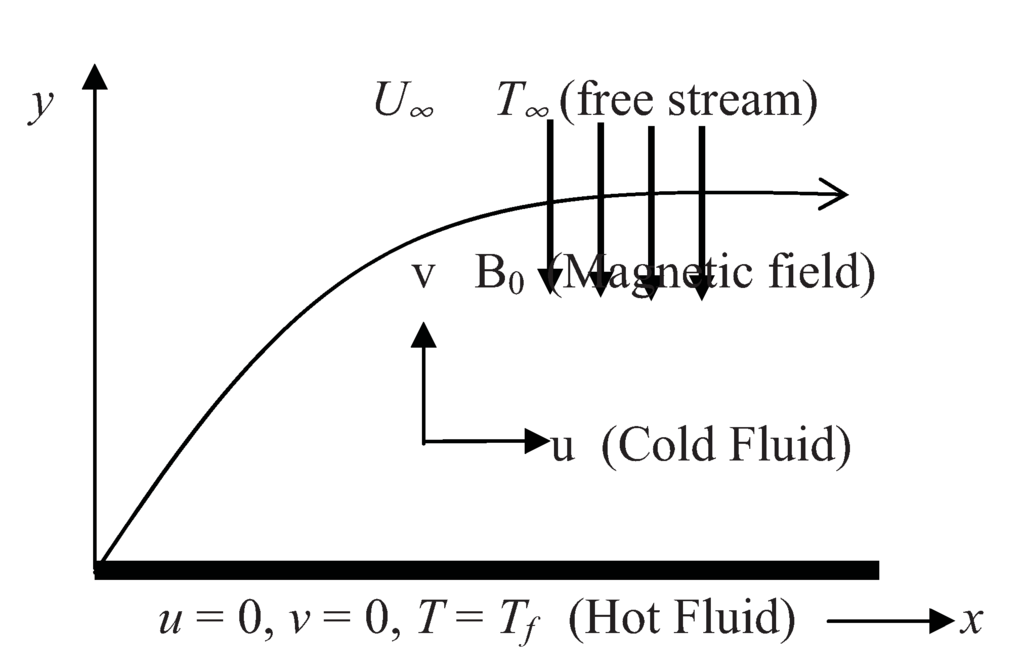
Figure 1.
Flow configuration and coordinate system.
Under the usual boundary layer approximations, the flow is governed by the following Equations [6,7,8,19]:
where U∞ is the free stream velocity, cp is the specific heat at constant pressure, α is the thermal diffusivity, ρ is the fluid density, σ is the fluid electrical conductivity. The fluid dynamical viscosity µ is assumed to be an inverse linear function of temperature, Lai and Kulacki [26], as given by:
where is cold fluid viscosity and γ is a constant. Using the Rosseland approximation [3] for radiation, the radiative heat flux is simplified as:
where is the Stephan-Boltzmann constant and k* is the mass absorption coefficient. The temperature differences within the flow are assumed to be sufficiently small so that T4 may be expressed as a linear function of temperature T using a truncated Taylor series about the free stream temperature i.e.,
The boundary conditions at the plate surface and far into the free stream may be written as:
where k is the thermal conductivity coefficient. The stream function ψ, satisfies the continuity Equation (1) automatically with:
A similarity solution of Equations (1)–(8) is obtained by defining an independent variable η and a dependent variable f in terms of the stream function ψ as:
After introducing Equation (9) into Equations (1)–(8), we obtain:
where and β = 1 corresponds to the absence of thermal radiation influence. The prime symbol represents the derivative with respect to η and:
It is noteworthy that the local parameters Ha and Bi in Equations (10)–(13) are functions of x. In order to have a similarity solution, all the parameters must be constant and we therefore assume [6,7,18]:
where c, and l are constants.
2.1. Numerical Procedure
The set of Equations (10) and (11) under the boundary conditions (12) have been solved numerically by applying the Nachtsheim and Swigert [27] shooting iteration technique together with Runge-Kutta sixth-order integration scheme. Let , , , , , Equations (10) and (11) are transformed into a system of first order differential equations as follows:
subject to the following initial conditions:
The unspecified initial conditions and are assumed and Equation (15) is then integrated numerically as an initial valued problem to a given terminal point. Improvement is made on the values of assumed missing initial conditions by iteratively comparing the calculated value of the dependent variable at the terminal point with its given value there. The computations were done by a written program which uses a symbolic and computational computer language MAPLE. A step size of = 0.001 was selected to be satisfactory for a convergence criterion of 10−7 in nearly all cases. From the process of numerical computation, the plate surface temperature, the local skin-friction coefficient and the local Nusselt number which are respectively proportional to θ(0), and , are also worked out and their numerical values are presented in a tabular form.
3. Entropy Generation Analysis
The hydromagnetic boundary layer flow past a flat surface under the influence of thermal radiation and Newtonian heating is inherently irreversible. This is due to the exchange of energy and momentum, within the fluid and solid boundaries leading to continuous entropy generation [9,10,11,12]. Two major of entropy production can be identified. One part is due to the combined effects of heat transfer and thermal radiation in the direction of finite temperature gradients while the other arises due to the combined effects of fluid friction and Joule heating. Following Woods [1], the local volumetric rate of entropy generation in the presence of a magnetic field is given by:
The first term in Equation (17) is the irreversibility due to heat transfer, the second term is the entropy generation due to viscous dissipation and the third term is the local entropy generation due to the effect of the magnetic field. Using Equation (9), we express the entropy generation number in dimensionless form as:
where is the temperature difference parameter and Re = U∞x/ν is the local Reynolds number. We assigned N1 to the first term in Equation (18) due to heat transfer and the second term due to the combined effects of viscous dissipation and magnetic field as N2, i.e.,
The irreversibility distribution ratio is then given as Ф = N2/N1. Therefore, whenever 0 ≤ Ф < 1, the heat transfer irreversibility dominates. The fluid friction together with magnetic field dominates when Ф > 1. The contribution of both heat transfer and fluid friction with magnetic field to entropy generation are equal when Ф = 1. However, in many engineering designs and energy optimisation problems, the contribution of heat transfer entropy (N1) and fluid friction with magnetic field effect (N2) to overall local entropy generation rate Nsx is needed. In order to achieve this, we define the following Bejan numbers (Be) mathematically as:
From Equation (20), it is very obvious that the Bejan number ranges from 0 to 1. The zero value of the Bejan number corresponds to the limit where the irreversibility is dominated by the combined effects of fluid friction and magnetic field while Be = 1 is the limit where the irreversibility due to heat transfer by virtue of finite temperature differences dominates the flow system. The contributions of both the factors to entropy generation are equal when Bejan number is equal to half.
4. Results and Discussion
The boundary layer flow and heat transfer in a variable viscosity fluid under the influence of a transverse uniform magnetic field and thermal radiation has been solved numerically using shooting iteration technique together with Runge-Kutta integration scheme and numerical expressions of the velocity and temperature have been used to compute the entropy generation. This type of problem arises in many industrial applications such as geothermal reservoirs, cooling of nuclear reactors, thermal insulation, petroleum reservoirs, electronic packages and microelectronic devices during their operation. In order to study the influence of all parameters involved on the flow and thermal fields along with their entropy generation characteristics, a selected set of graphical results is presented in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19, Figure 20 and Figure 21. I emphasize here that an increase in the parameter a > 0 indicates a decrease in the fluid viscosity. Extensive calculations have been performed to obtain the local skin friction and local Nusselt number for a wide range of parameters. Also, the results have been compared with the one reported by Aziz [18] as shown in Table 1 for constant viscosity fluid without the magnetic field, thermal radiation and viscous dissipation effects and it is found that they are in good agreement. This serves as a benchmark for the accuracy of our numerical procedure. Table 2 shows the effect of various thermophysical parameters on the local skin friction (), Nusselt number () and plate surface temperature variation (). I notice that both the local skin friction and local Nusselt number increase with an increase in the parameter values of Bi, Br, a. This can be attributed to the fact that as the convective heat transfer from the hot fluid on the lower side of the plate to the upper side increases due to Newtonian heating, the fluid viscosity on the upper side of the plate decreases leading to an increase in velocity gradient and viscous dissipation. It is interesting to note that the local skin friction decreases while the surface heat transfer rate increases with an increase in thermal radiation (Ra) and Prandtl number (Pr). The physical reason for this trend is that at higher Prandtl number and radiation, the fluid thermal boundary layer becomes thinner leading to an increase in the temperature gradient. Moreover, an increase in magnetic field intensity (Ha) causes a decrease in the local Nusselt number and an increase in local skin friction.

Table 1.
Computations showing comparison with Aziz [18] results for Hax = Br = a = 0, β = 1, Pr = 0.72.
Bi | Aziz [18] | − Aziz [18] | Present | − Present |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.1447 | 0.0428 | 0.14466 | 0.04276 |
| 0.60 | 0.6699 | 0.1981 | 0.66991 | 0.19805 |
| 1.00 | 0.7718 | 0.2282 | 0.77182 | 0.22817 |
| 5.00 | 0.9441 | 0.2791 | 0.94417 | 0.27913 |
| 20.00 | 0.9854 | 0.2913 | 0.98543 | 0.29132 |

Table 2.
Computation showing , , and for various values of key parameters.
| Bi | a | Br | Ra | Pr | Ha | − | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.46167359 | 0.06417756 | 0.35822438 |
| 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.47460353 | 0.16490527 | 0.83509472 |
| 10 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.47847240 | 0.19577586 | 0.98042241 |
| 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.49847466 | 0.06463133 | 0.35368667 |
| 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.53980796 | 0.06510562 | 0.34894370 |
| 0.1 | −0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.44170340 | 0.06391808 | 0.36081912 |
| 0.1 | −0.5 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.39774382 | 0.06331171 | 0.36688289 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.46903194 | 0.03335240 | 0.66647595 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 10 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.52982570 | 0.24134507 | 3.41345073 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 5.0 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.46104375 | 0.06820145 | 0.31798541 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 10.0 | 0.72 | 0.1 | 0.46100454 | 0.06856032 | 0.31439674 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 3.00 | 0.1 | 0.45924014 | 0.07604897 | 0.23951024 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 7.10 | 0.1 | 0.45801360 | 0.08146073 | 0.18539265 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 0.5 | 0.78699049 | 0.06242200 | 0.37577998 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 1.0 | 1.06625574 | 0.06065042 | 0.39349571 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.72 | 2.0 | 1.47684794 | 0.05773749 | 0.42262501 |
4.1. Effect of Parameter Variation on Velocity Profiles
Figure 2 shows the variation of longitudinal velocity as a function of η at different values of magnetic field parameter. The fluid velocity is lowest at the plate surface and increases to the free stream value satisfying the far field boundary condition. Application of the magnetic field creates a resistive force similar to the drag force that acts in the opposite direction of the fluid motion, thus causing the velocity of the fluid to overshoot towards the plate surface. Similar trend is observed in Figure 3 with a decrease in the fluid viscosity (i.e., as parameter a increases). Since as fluid viscosity decreases, the momentum boundary layer becomes thinner, leading to an increase in the fluid velocity gradient.
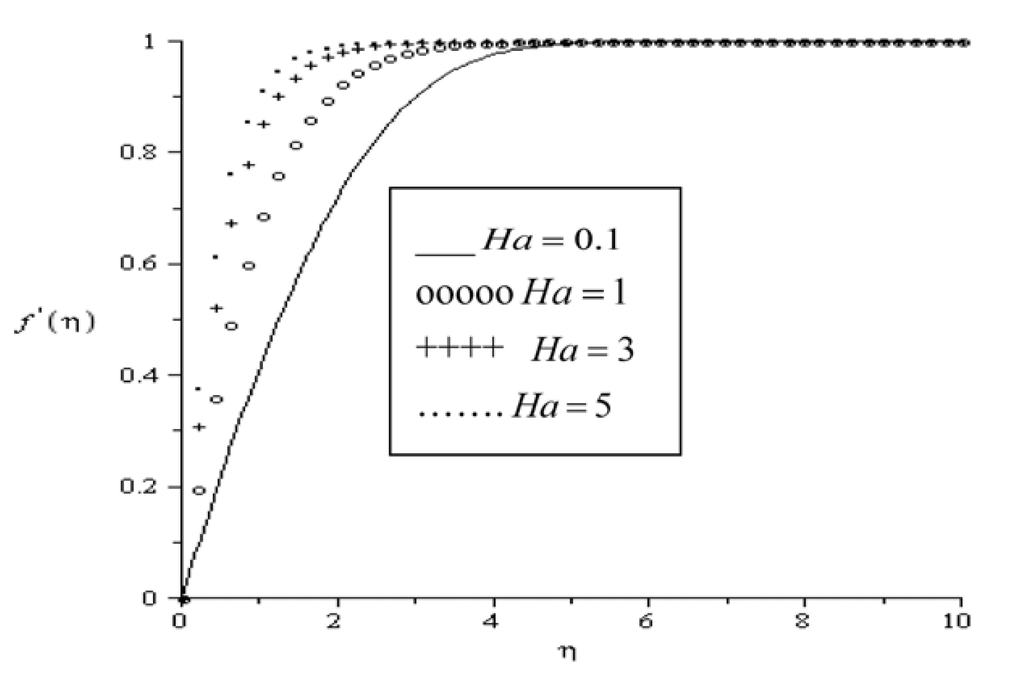
Figure 2.
Velocity profile for Pr = 0.72, Br = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, a = 0.1, Bi = 0.1.
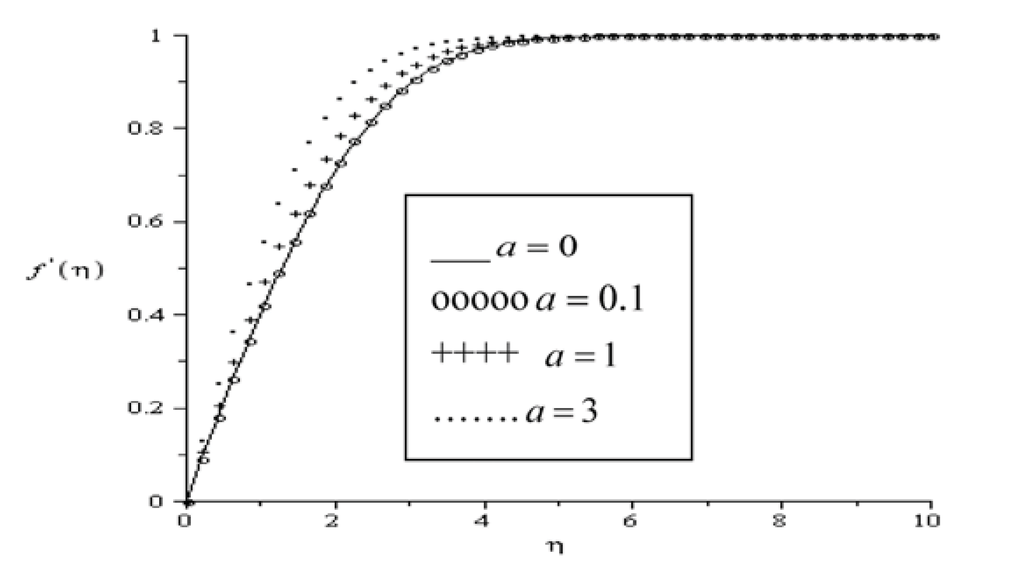
Figure 3.
Velocity profile for Pr = 0.72, Br = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Ha = 0.1, Bi = 0.1.
4.2. Effects of Parameter Variation on Temperature Profiles
Dimensionless temperatures θ are plotted as a function of transverse distance η in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9. Generally, the fluid temperature is highest at the plate surface and decreases exponentially to the free stream zero value away from the plate satisfying the boundary condition. As it can be seen in Figure 4, the fluid temperature increases with an increase in Ha accordingly leading to an increase in thermal boundary layer. As explained above, the transverse magnetic field gives rise to a resistive force known as the Lorentz force of an electrically conducting fluid. This force makes the fluid experience a resistance by increasing the friction between its layers and thus increases its temperature. Similar trend is observed in Figure 5 and Figure 6 with increasing values of Br and Bi. The thermal boundary layer generates energy due to combined effects of viscous heating and Newtonian heating. This causes the temperature of the fluid to increase. In Figure 7, it is noteworthy that the fluid temperature decreases with an increase in radiation parameter (Ra) leading to a decrease in the thermal boundary layer thickness. Figure 8 represents graphs of temperature profiles taking different values of the variable viscosity parameter (a). It can be seen that thermal boundary layer decreases due to a decrease in the fluid viscosity and this causes the temperature of the fluid to decrease. Figure 9 depicts the temperature profiles for different values of the Prandtl number. The fluid temperature decreases with an increase in Prandtl number, consequently the thermal boundary layer decreases.
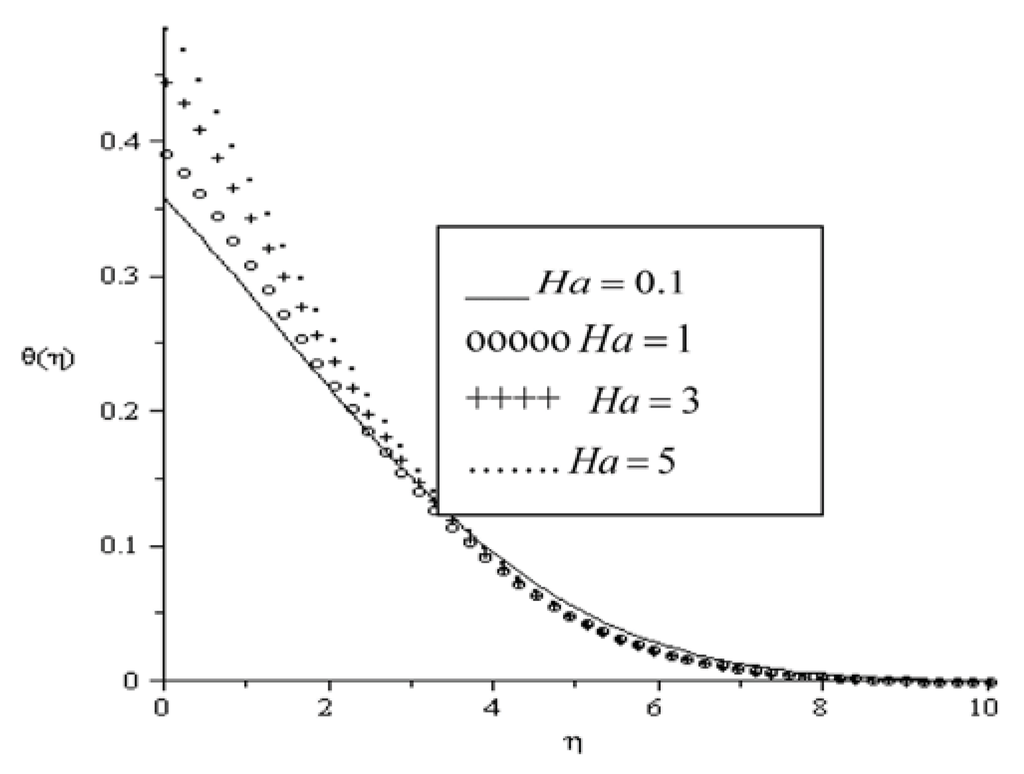
Figure 4.
Temperature profiles for Pr = 0.72, Br = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, a = 0.1, Bi = 0.1.
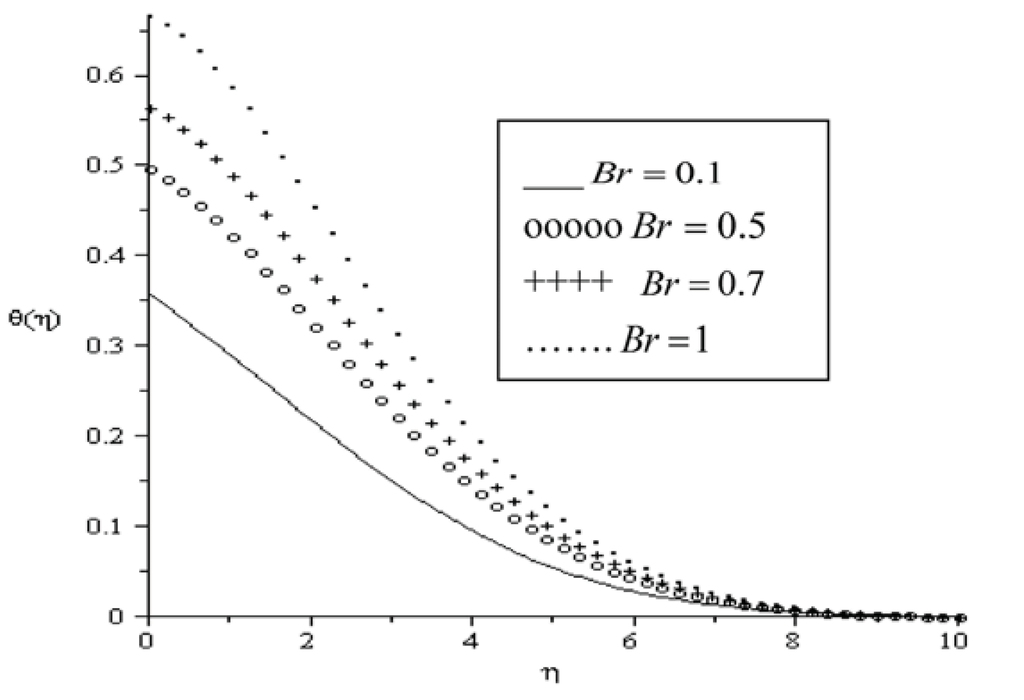
Figure 5.
Temperature profiles for Pr = 0.72, Ha = 0.1, Bi = 0.1, Ra = 0.1, a = 0.1.
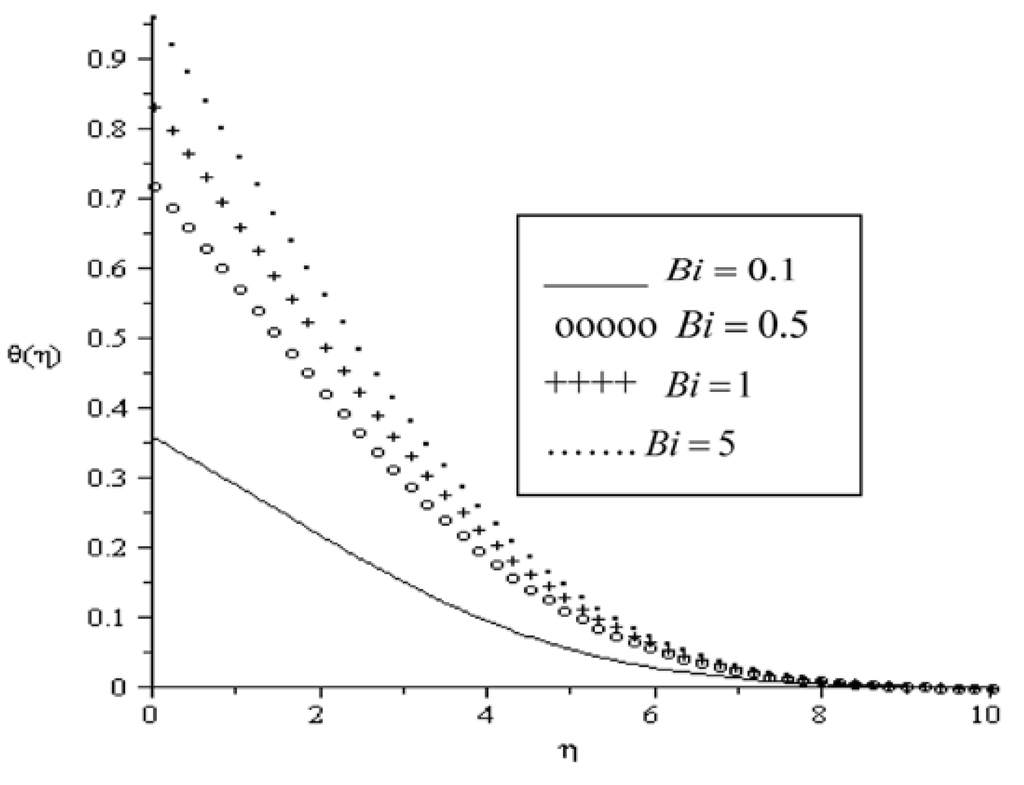
Figure 6.
Temperature profiles for Pr = 0.72, Ha = 0.1, a = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Br = 0.1.
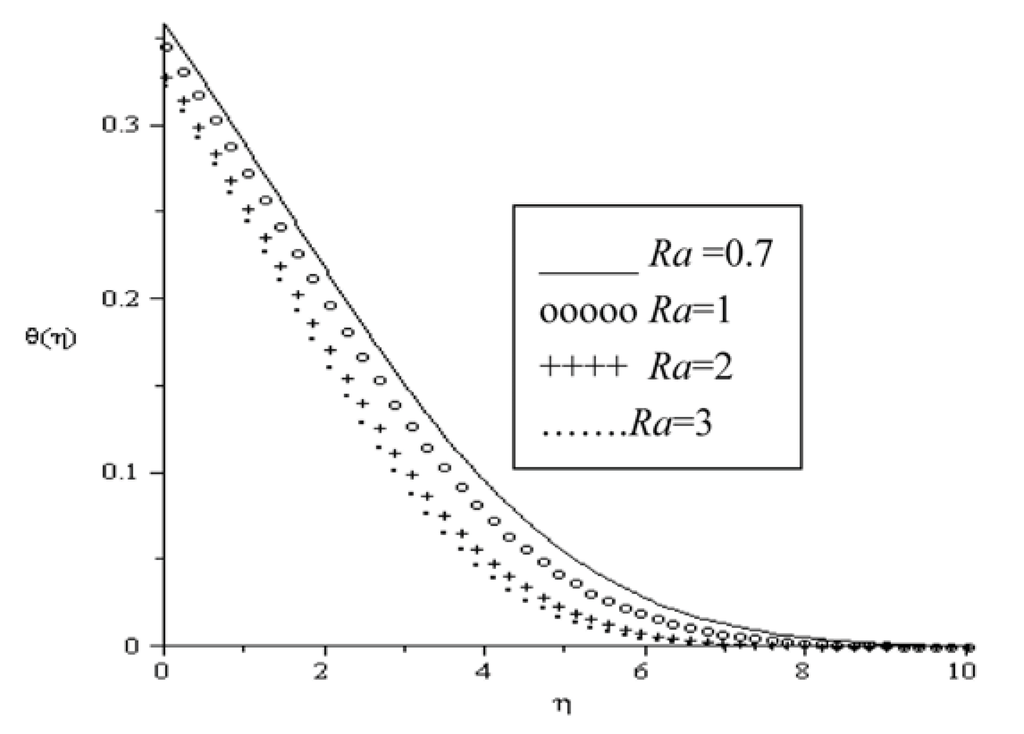
Figure 7.
Temperature profiles for Pr = 0.72, Ha = 0.1, a = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Br = 0.1.
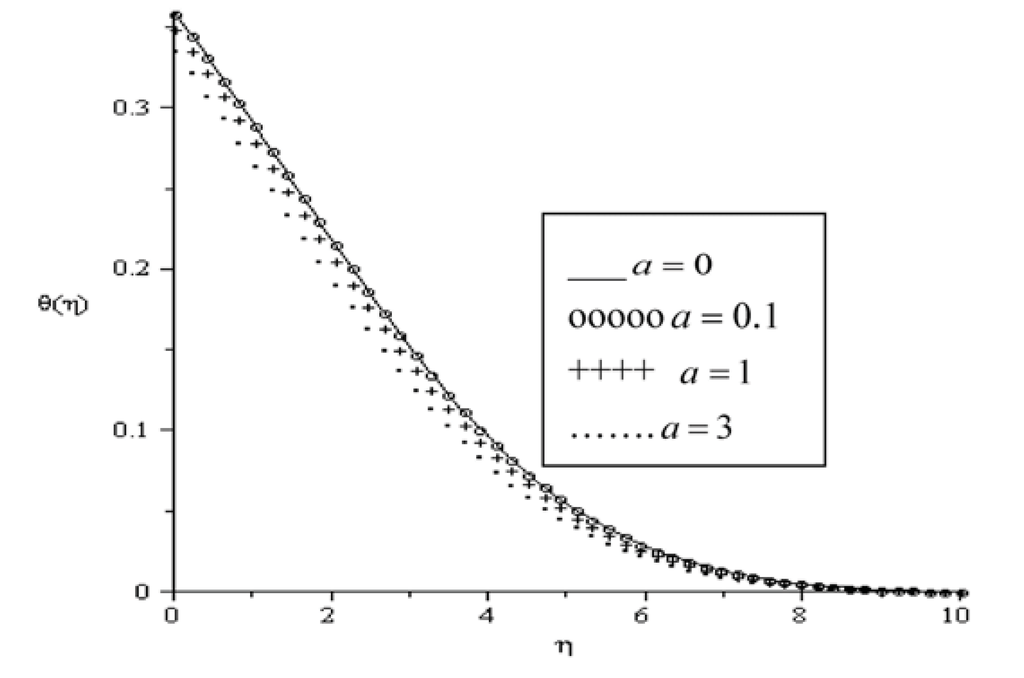
Figure 8.
Temperature profiles for Pr = 0.72, Br = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Ha = 0.1, Bi = 0.1.
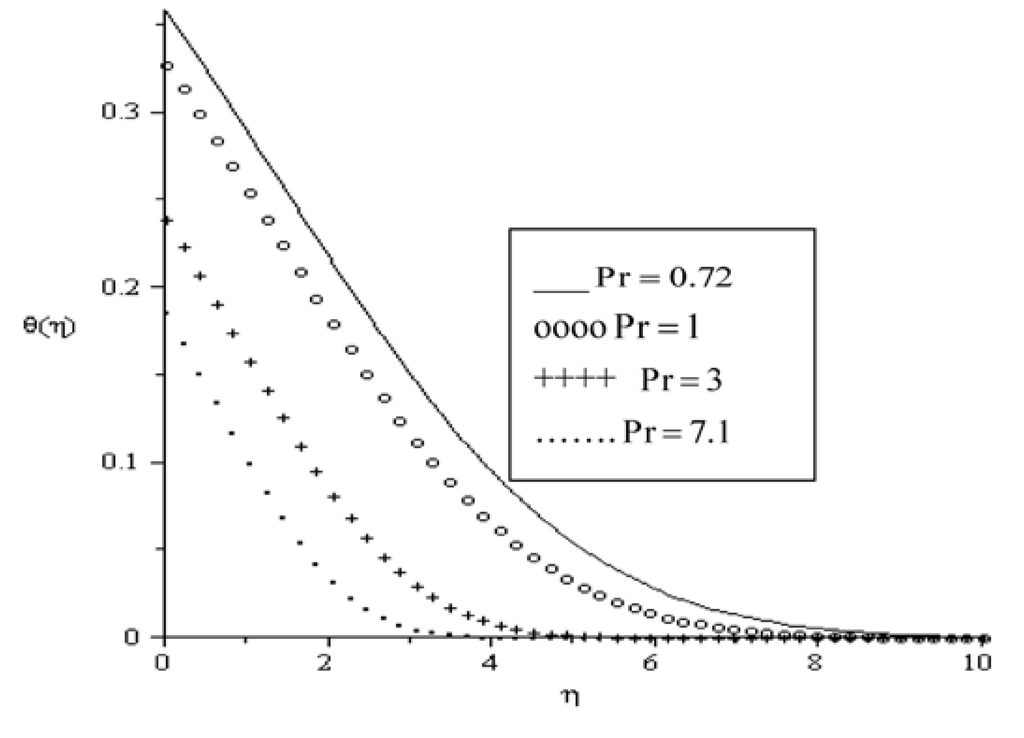
Figure 9.
Temperature profiles for Bi = 0.1, Ha = 0.1, Br = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, a = 0.1.
4.3. Effects of Parameter Variation on Entropy Generation Rate
The influence of various parameters on entropy generation rate is displayed in Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15. In Figure 10, we notice that the entropy generation number is higher for higher magnetic parameter (Ha). The presence of the magnetic field creates entropy in the fluid. The effects of the local Biot number Bi and the group parameter BrΩ−1 on the entropy generation number is represented in Figure 11 and Figure 12. It seems that these parameters have similar effect on the entropy generation number by creating more entropy in the fluid. However, it is interesting to note that the entropy generated in the fluid attained it maximum value at a distance near the plate surface within the boundary layer region. The influence of the Prandtl number on the entropy generation number is shown in Figure 13. As the Prandtl number increases, the entropy generation number increases gradually from the plate surface, then to its highest value within the boundary layer and decreases to its lowest zero value at the free stream. It is noteworthy that the entropy generation rate peak value for Pr = 0.72 (Air) is higher than that of Pr = 7.1 (Water). Similar trend is observed in Figure 14 and Figure 15 with increasing value of parameters a and Ra. As the fluid viscosity decreases and thermal radiation increases, the entropy generation rate increases from the plate surface, reaching its peak values and then decreases to zero value at free stream. The peak value for Ra = 0.7 is higher to that of Ra = 3.
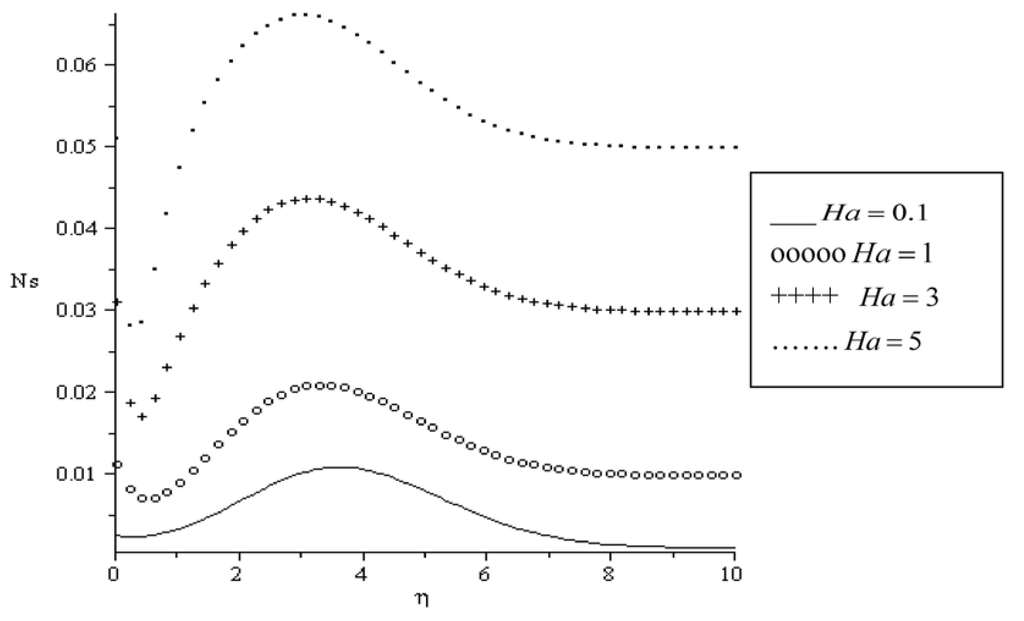
Figure 10.
Entropy generation rate for Pr = 0.72, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, Re= 0.1, Bi = 0.1, a = 0.1, Ra = 0.7.
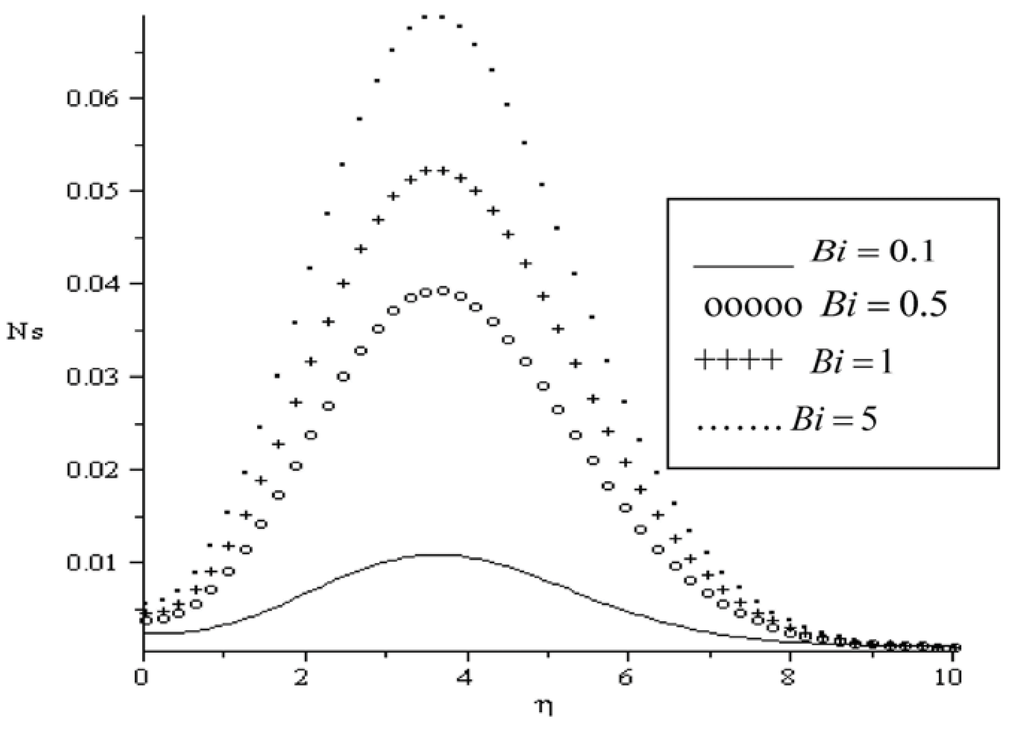
Figure 11.
Entropy generation rate for Pr = 0.72, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, a = 0.1.
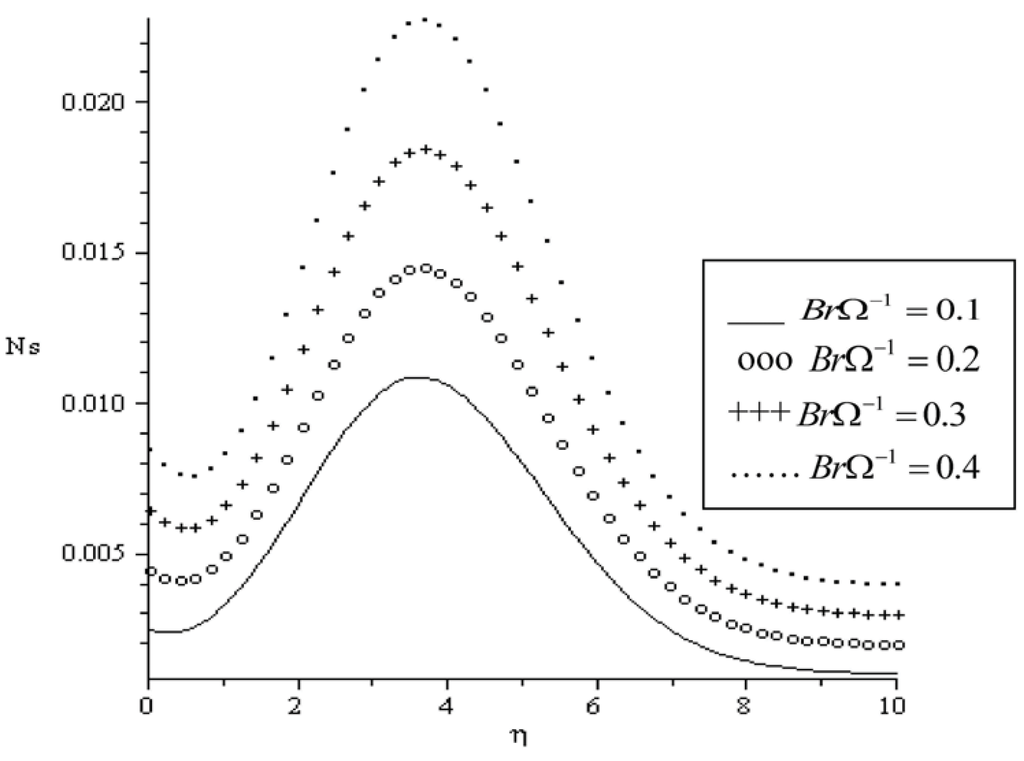
Figure 12.
Entropy generation rate for Pr = 0.72, Bi = 0.1, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1, a = 0.1, Ra = 0.7.
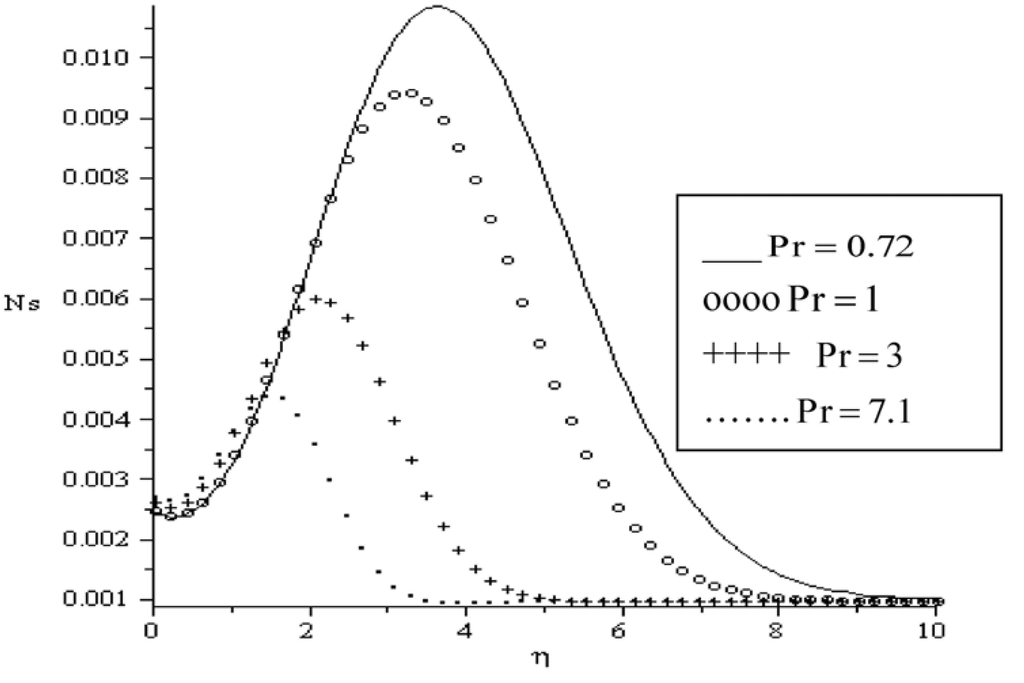
Figure 13.
Entropy generation rate for Bi = 0.1, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1, a = 0.1.
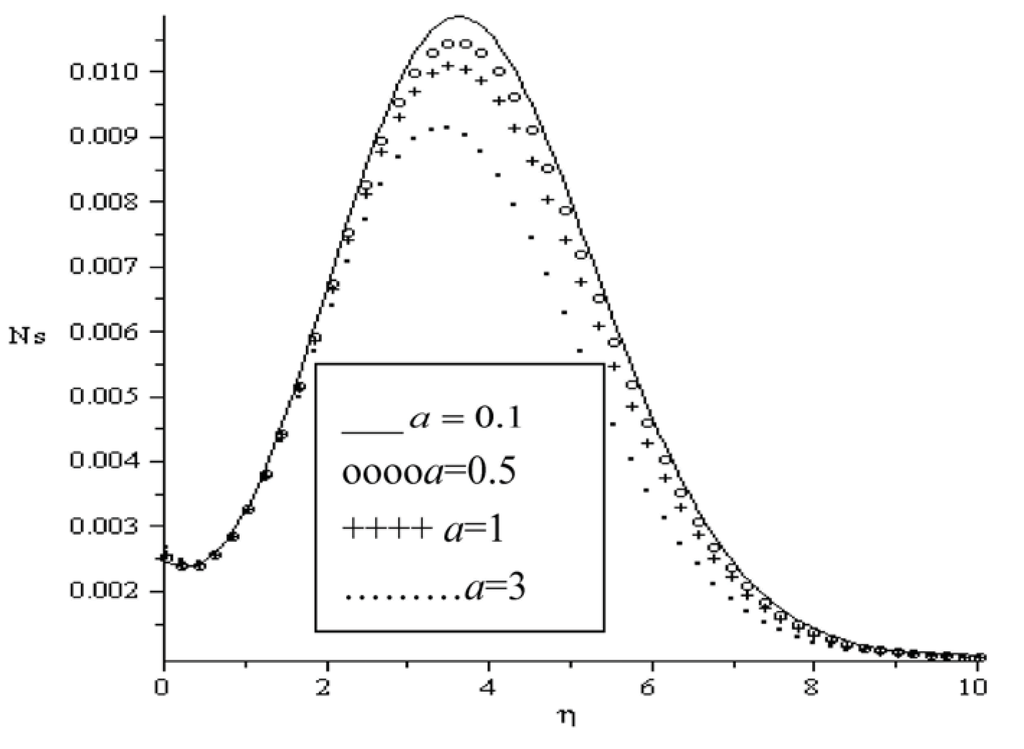
Figure 14.
Entropy generation rate for Bi = 0.1, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1.
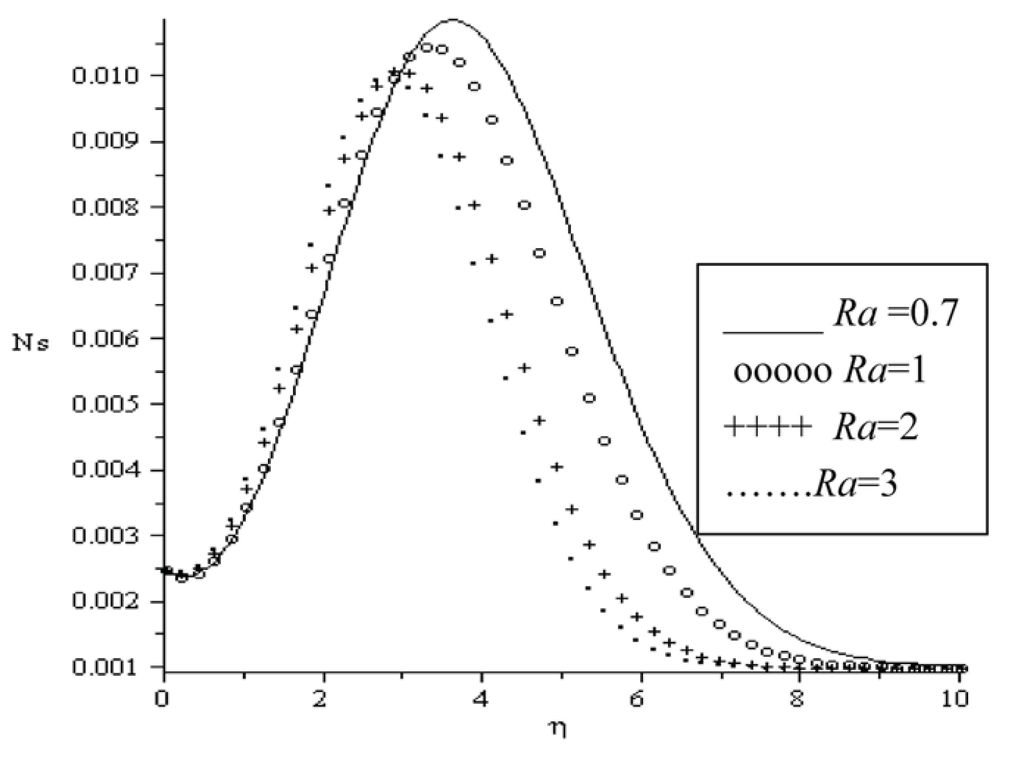
Figure 15.
Entropy generation rate for Bi = 0.1, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, a = 0.1, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1.
4.4. Effects of Parameter Variation on Bejan Number
In Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19, Figure 20 and Figure 21, the Bejan number is displayed as a function of the transverse distance η. It is interesting to note that the heat transfer irreversibility dominates within the boundary layer while the viscous dissipation and magnetic field irreversibility dominate at the plate surface and in the free stream region. Meanwhile, the dominant effect of heat transfer irreversibility within the boundary layer region decreases with an increase in magnetic field intensity (Ha), group parameter BrΩ−1, variable viscosity parameter (a) and Prandtl number (Pr) as illustrated in Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19 and Figure 20. In Figure 21, we notice that the effect of heat transfer irreversibility increases as the local Biot number (Bi) parameter increase due to Newtonian heating of the plate surface. Hence, the plate surface acts as a strong source of heat transfer irreversibility.
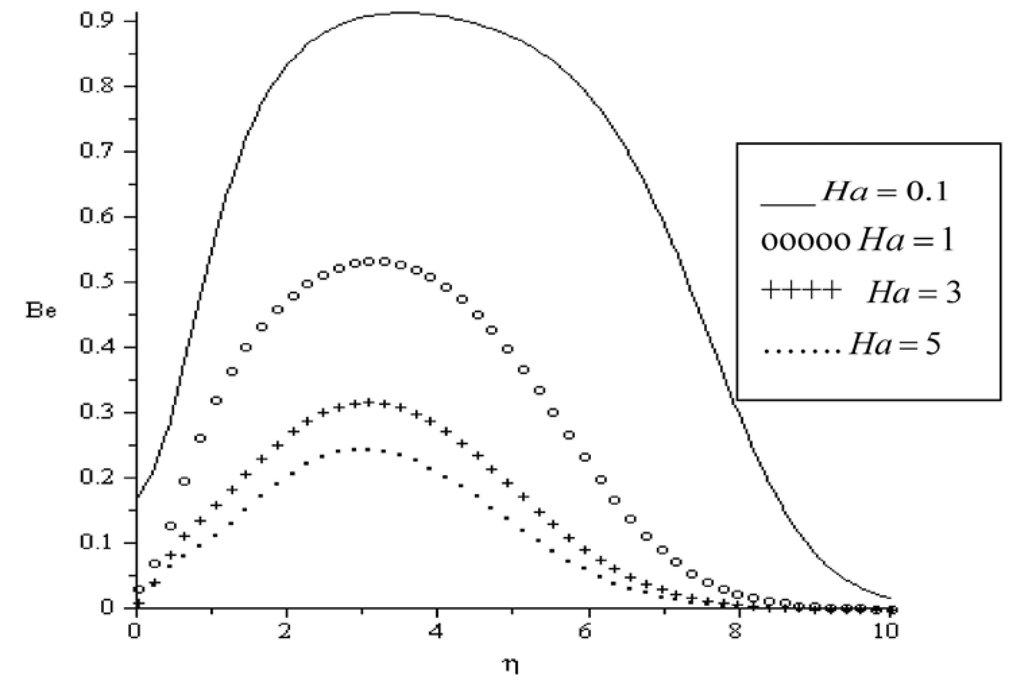
Figure 16.
Bejan number for Bi = 0.1, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, a = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Re = 0.1.
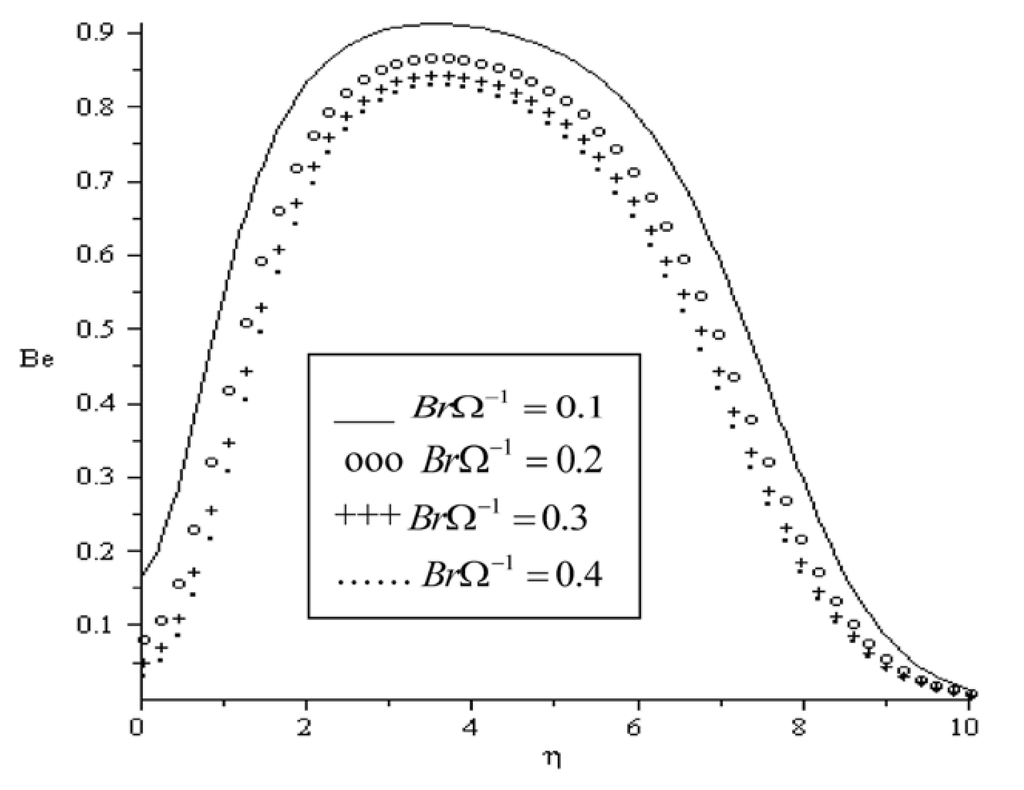
Figure 17.
Bejan number for Pr = 0.72, Bi = 0.1, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1, a = 0.1, Ra = 0.7.
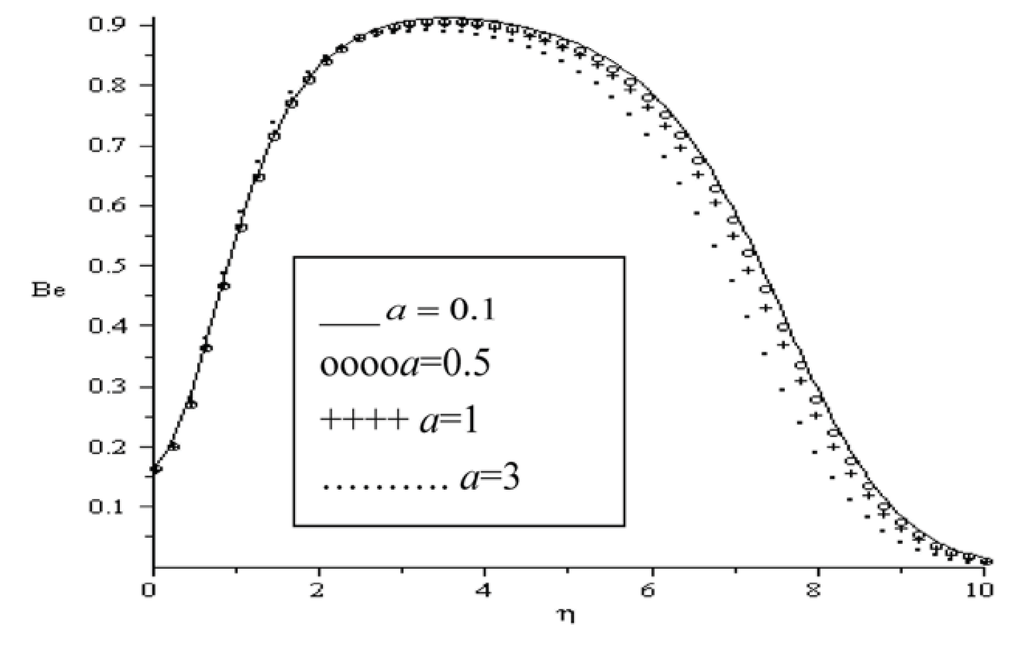
Figure 18.
Bejan number for Bi = 0.1, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1.
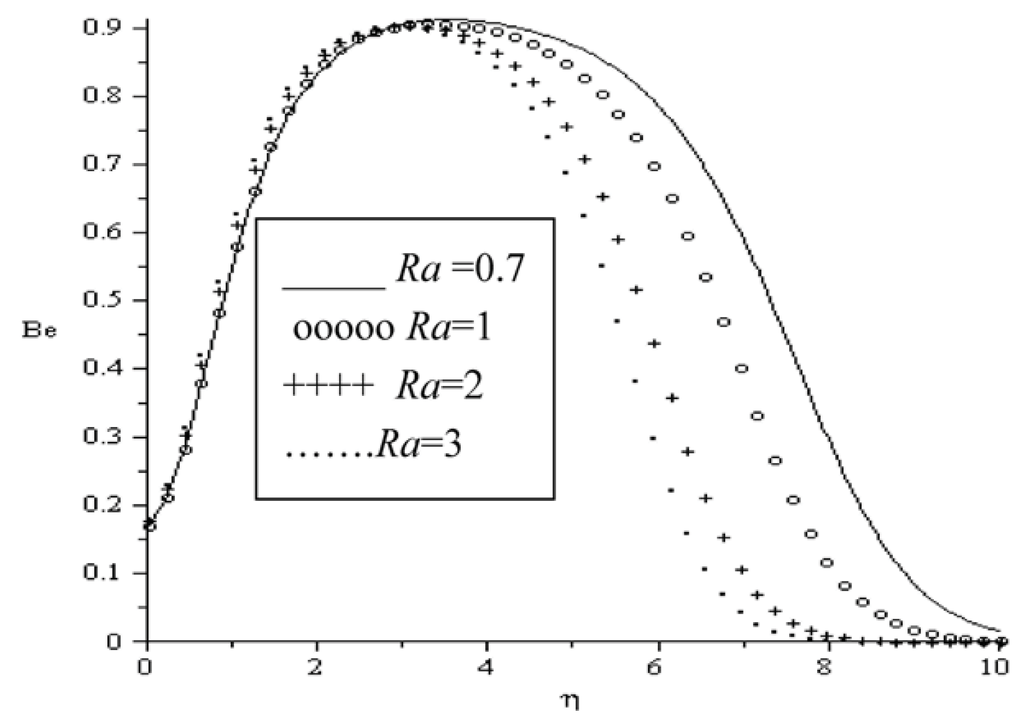
Figure 19.
Bejan number for Bi = 0.1, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, a = 0.1, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1.
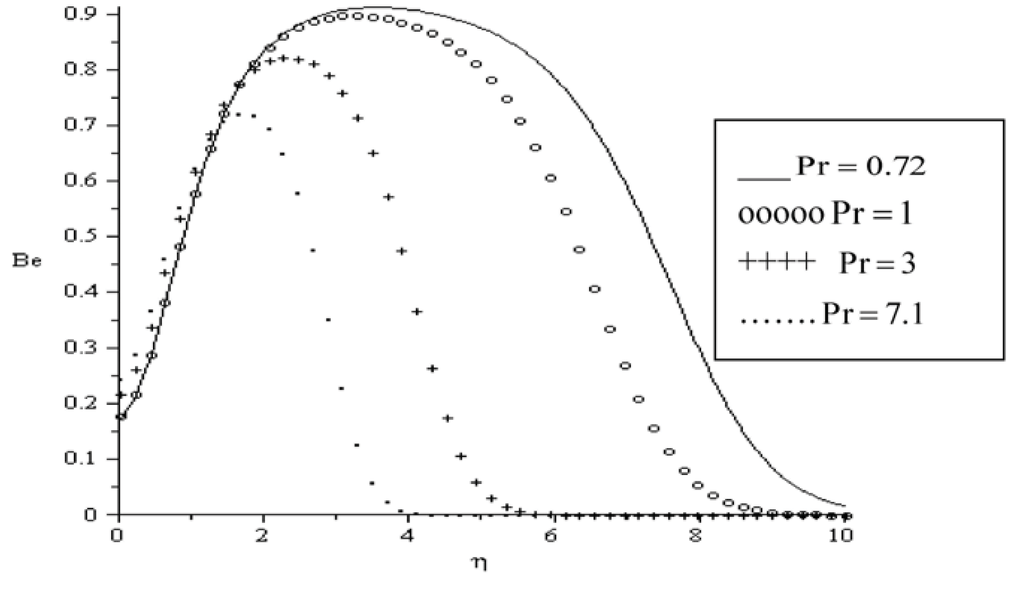
Figure 20.
Bejan number for Bi = 0.1, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1, a = 0.1.
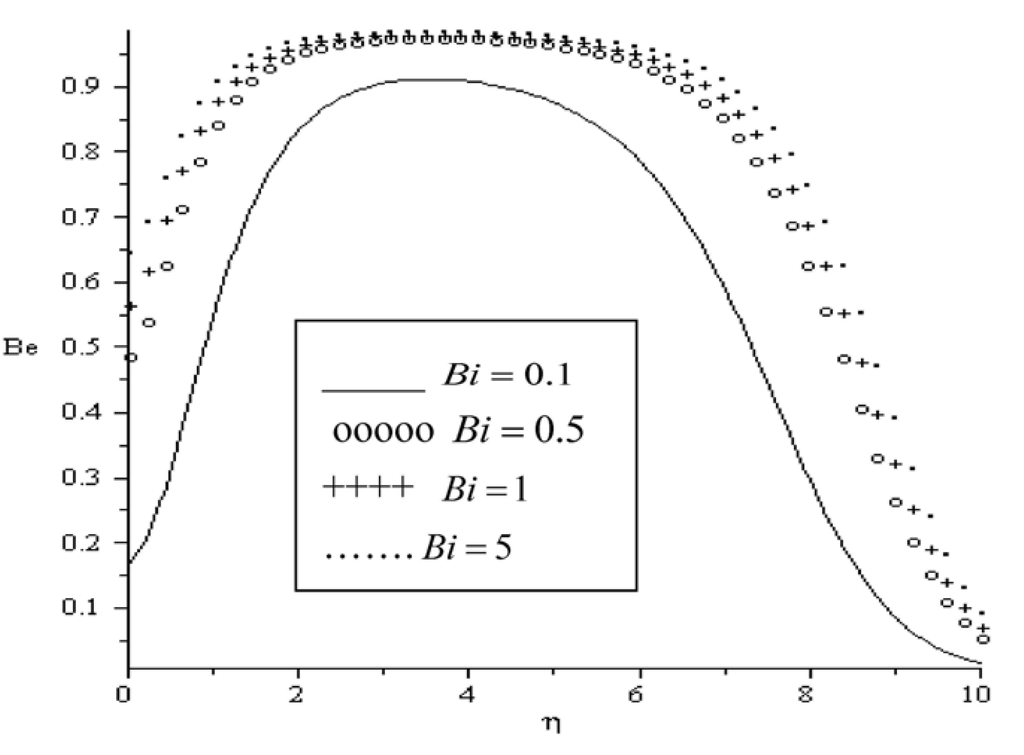
Figure 21.
Bejan number for Pr = 0.72, BrΩ−1 = 0.1, Re = 0.1, Ha = 0.1, Ra = 0.7, a = 0.1.
5. Conclusions
Analysis of entropy generation rate in hydromagnetic boundary layer flow of a variable viscosity fluid in the presence of thermal radiation, viscous dissipation and Newtonian heating is carried out. The velocity and temperature profiles are obtained numerically and used to compute the entropy generation number. The effects of the magnetic parameter, the Prandtl number, local Biot number, variable viscosity parameter and radiation parameter on velocity and temperature profiles are presented. The influences of the same parameters and the dimensionless group parameter on the entropy generation rate and Bejan number are also discussed. From the results the following conclusions could be drawn:
- The skin friction and the Nusselt number increase with increasing values of Bi, Br, a. An increase Ha causes a decrease in the Nusselt number and an increase in the skin friction. As Ra and Pr increase, the skin friction decreases while the Nusselt number increases.
- The velocity boundary layer thickness decreases with Ha, a.
- The thermal boundary layer thickness increases with Ha, Br, Bi and decreases with Ra, Pr, a.
- The plate surface act as a strong source of entropy generation and heat transfer irreversibility. However, the peak of entropy generation rate is attained within the boundary layer region.
- The entropy generation number increases as Ha, Bi and BrΩ−1 increase while it decreases as the Pr, Ra and a increase.
- The optimum design and efficient performance of the flow system can be enhanced by the ability to clearly identify the source and location of entropy generation. The present results show that minimum entropy generation in the flow system can be achieved with appropriate choice and combination of the various thermophysical parameters.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the National Research Foundation of South Africa Thuthuka programme for financial support.
References
- Woods, L.C. Thermodynamics of Fluid Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Aıboud, S.; Saouli, S. Entropy analysis for viscoelastic magnetohydrodynamic flow over a stretching surface. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2010, 45, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, E.M.; Cess, R.D. Radiation Heat Transfer; Harpercollins College Div: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Raptis, A.; Perdikis, C.; Takhar, H.S. Effect of thermal radiation on MHD flow. Appl. Math. Comput. 2004, 153, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbeledogu, I.U.; Amakiri, A.R.C.; Ogulu, A. Unsteady MHD free convection flow of a compressible fluid past a moving vertical plate in the presence of radiative heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataller, R.C. Radiation effects for the Blasius and Sakiadis flows with a convective surface boundary condition. Appl. Math. Comput. 2008, 206, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D.; Aziz, A. MHD mixed convection from a vertical plate embedded in a porous medium with a convective boundary condition. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D. On MHD heat and mass transfer over a moving vertical plate with a convective surface boundary condition. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 88, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narusawa, U. The second-law analysis of mixed convection in rectangular ducts. Heat Mass Transf. 1998, 37, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.Z. Second law analysis of laminar viscous flow through a duct subjected to constant wall temperature. J. Heat Transf. 1998, 120, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A. Second-law analysis in heat transfer and thermal design. Adv. Heat Transf. 1982, 15, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bejan, A. Entropy Generation Minimization; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kobo, N.S.; Makinde, O.D. Second law analysis for a variable viscosity reactive Couette flow under Arrhenius kinetics. Math. Probl. Eng. 2010, 2010, 278104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaal, M.; Ganji, D.D.; Ahmadi, G. Analytical investigation on acceleration motion of a vertically falling spherical particle in incompressible Newtonian media. Adv. Powder Technol. 2010, 21, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaal, M.; Ganji, D.D. An analytical study on motion of a sphere rolling down an inclined plane submerged in a Newtonian fluid. Powder Technol. 2010, 198, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D.; Aziz, A. Second law analysis for a variable viscosity plane Poiseuille flow with asymmetric convective cooling. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 60, 3012–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D. Thermodynamic second law analysis for a gravity driven variable viscosity liquid film along an inclined heated plate with convective cooling. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S; Tasnim, S.H.; Mamun, H.A.A. Thermodynamic analysis of mixed convection in a channel with transverse hydromagnetic effect. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2003, 42, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinde, O.D.; Beg, O.A. On inherent irreversibility in a reactive hydromagnetic channel flow. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 19, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tolke, J.; Krafczyk, M. Numerical investigation of double-diffusive (natural) convection in vertical annuluses with opposing temperature and concentration gradients. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2010, 31, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zheng, C. Entropy generation in impinging flow confined by planar opposing jets. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Du, R. Entropy generation of turbulent double-diffusive natural convection in a rectangle cavity. Energy 2011, 36, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Analysis of entropy generation in counter-flow premixed hydrogen-air combustion. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zheng, C. Analysis of entropy generation in hydrogen-enriched ultra-lean counter-flow methane–air non-premixed combustion. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 12491–12501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A. A similarity solution for laminar thermal boundary layer over a flat plate with a convective surface boundary condition. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 14, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.C.; Kulacki, F.A. The effect of variable viscosity on convective heat and mass transfer in saturated porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1991, 33, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtsheim, P.R.; Swigert, P. Satisfaction of the Asymptotic Boundary Conditions in Numerical Solution of the System of Nonlinear Equations of Boundary Layer Type; NASA TND-3004; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).