Brand Image of Beijing’s Time-Honored Restaurants: An Analysis Through Large Language Model-Driven Review Mining
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Perspective limitation: Most existing studies remain at a descriptive level, failing to uncover different brand image typologies from a holistic and structural perspective. In other words, while we may know “which brands perform better or worse,” we still lack an understanding of “what types of ‘good’ brand images exist, and how these types are constructed.”
- Methodological limitation: Prior studies primarily rely on traditional machine learning or deep learning models (e.g., BERT), without fully leveraging the remarkable potential of LLMs in handling complex semantics, multi-faceted sentiment, and zero-shot learning. As a result, existing analyses fall short of delivering more precise, fine-grained insights.
2. Related Research
2.1. China Time-Honored Brands
2.2. Brand Image
2.3. Application of UGC Data in Brand Image Research
3. Materials and Methods
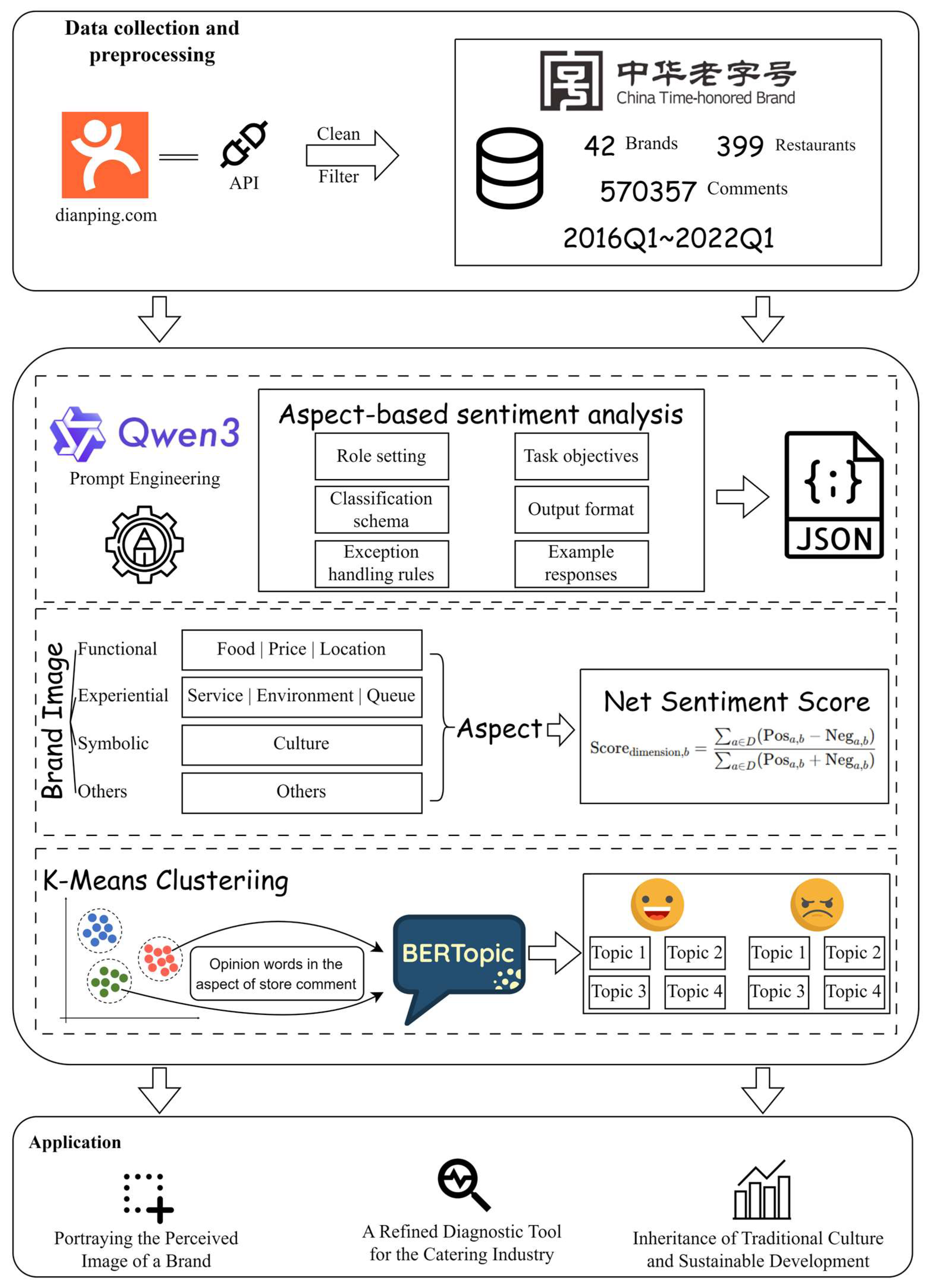
3.1. Research Framework
3.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
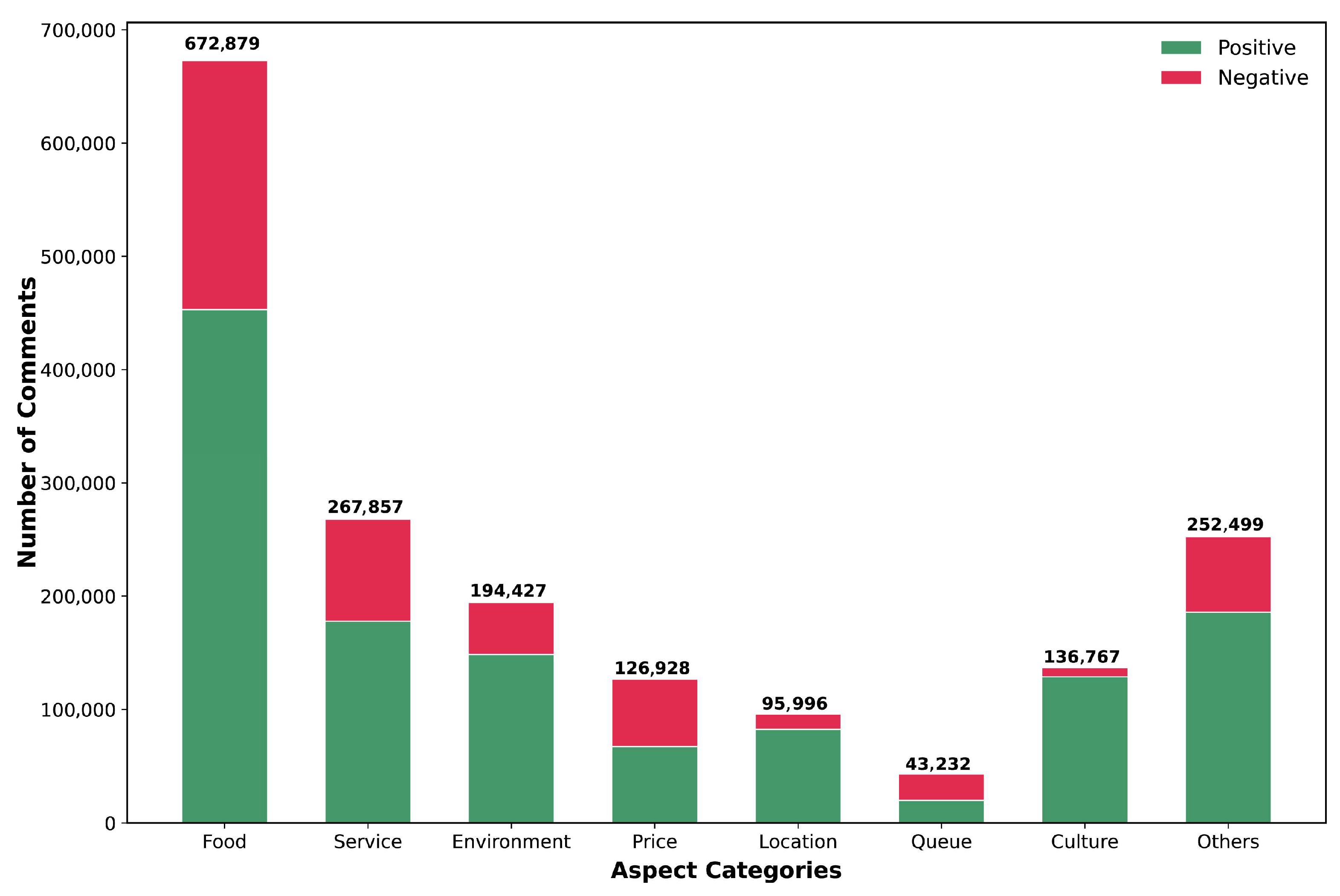
3.3. Aspect Selection and Dimension Mapping
3.4. ABSA
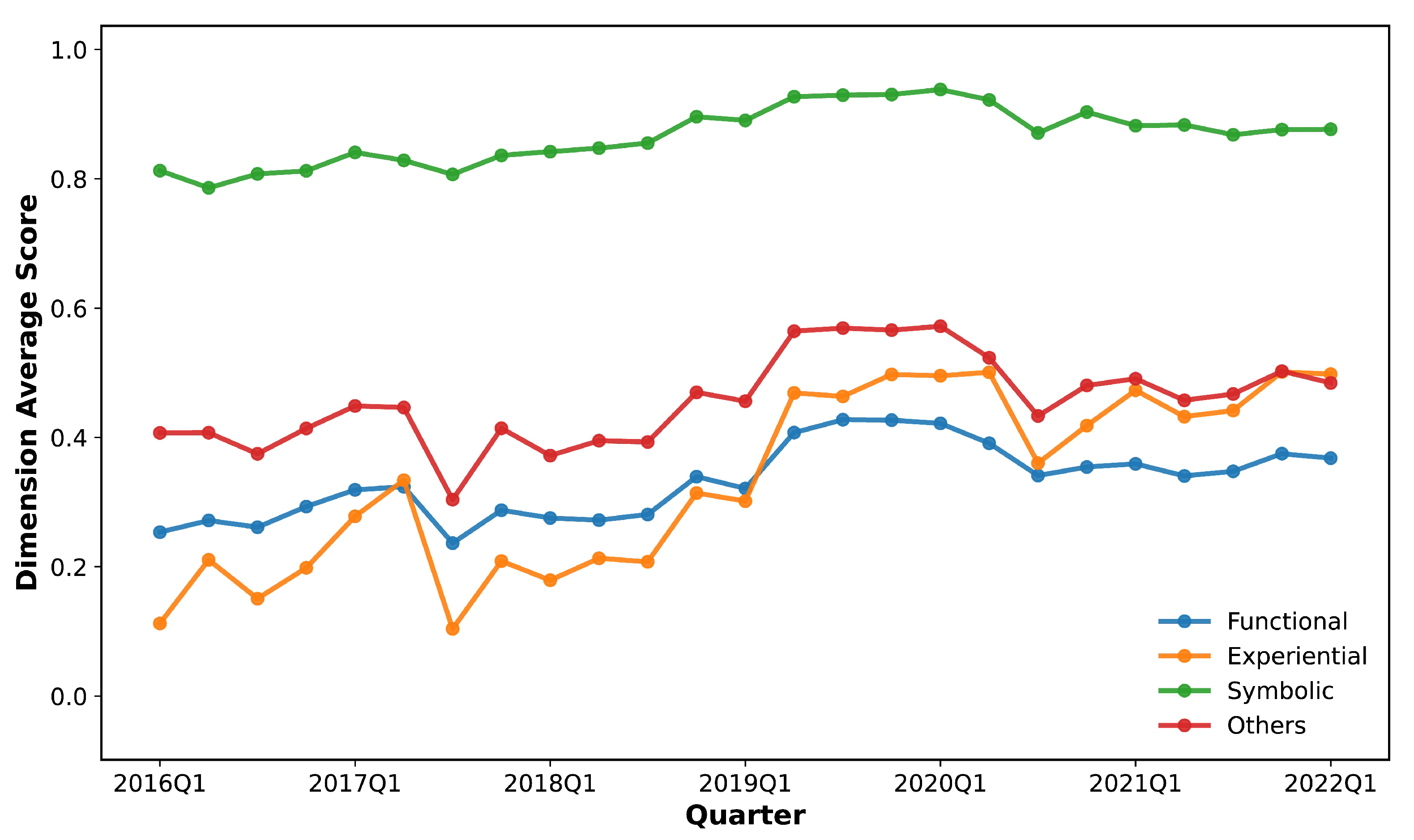
3.5. Quantifying Brand Image Dimension Scores
3.6. Identifying Brand Image Types via Clustering Analysis
3.7. BERTopic for Topic Modeling
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Clustering Results Analysis
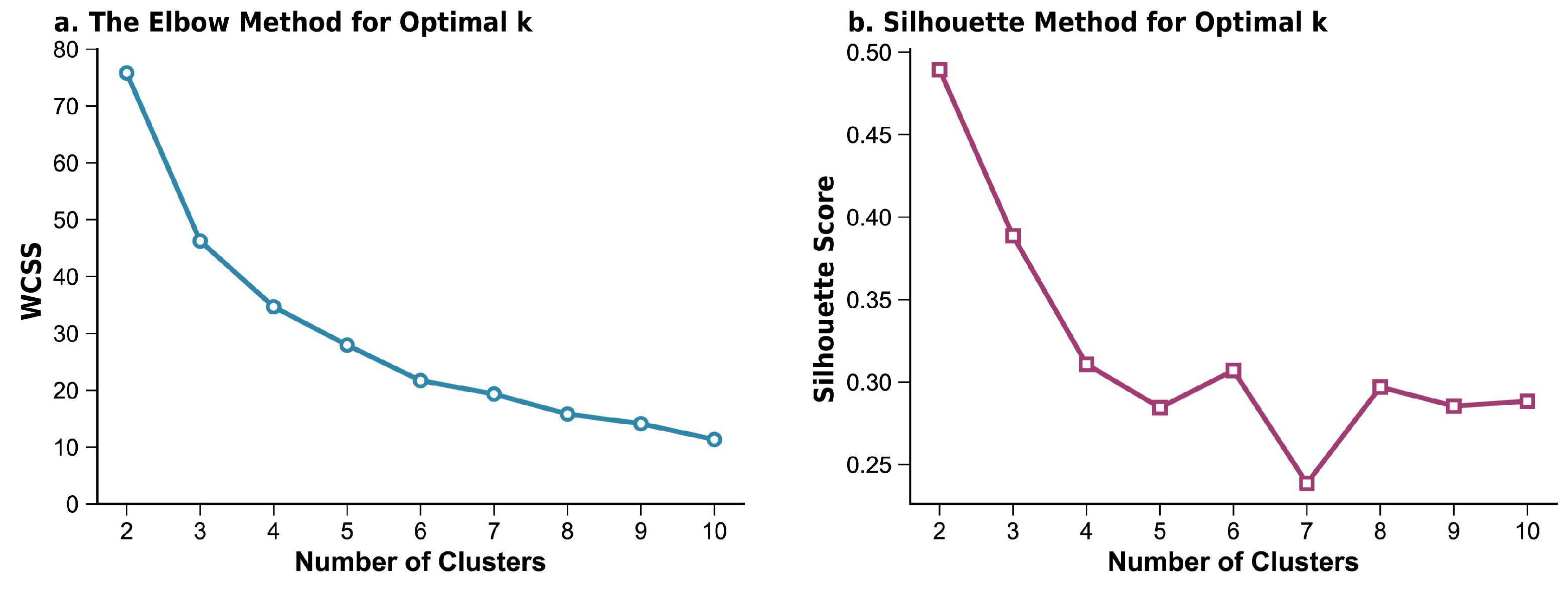
4.2.1. Determination of the Optimal K
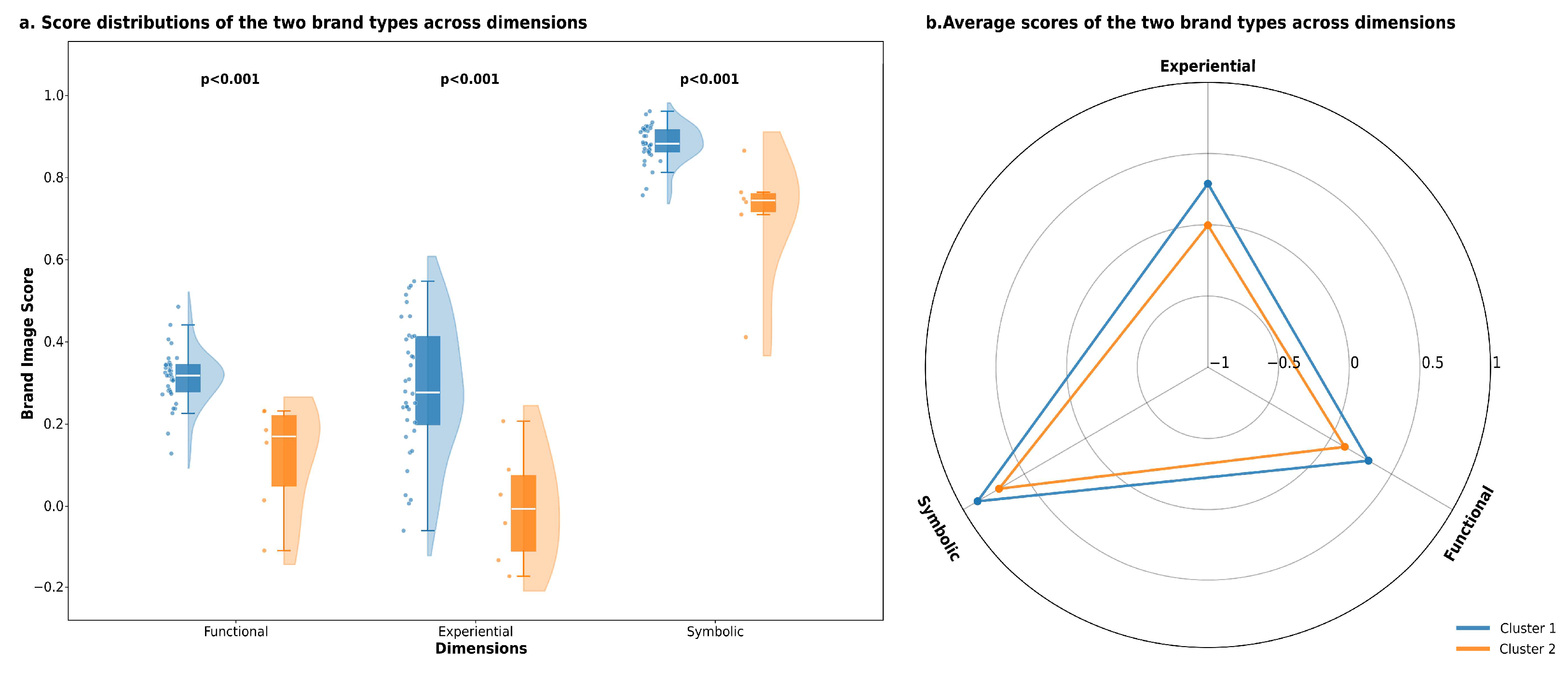
4.2.2. Cluster Characteristics of CTHBs Restaurants
- Cluster 1: Comprehensive Performers (n = 36).
- Cluster 2: Heritage Strugglers (n = 6).
4.3. Fine-Grained Diagnosis of Brand Image Based on Topic Modeling
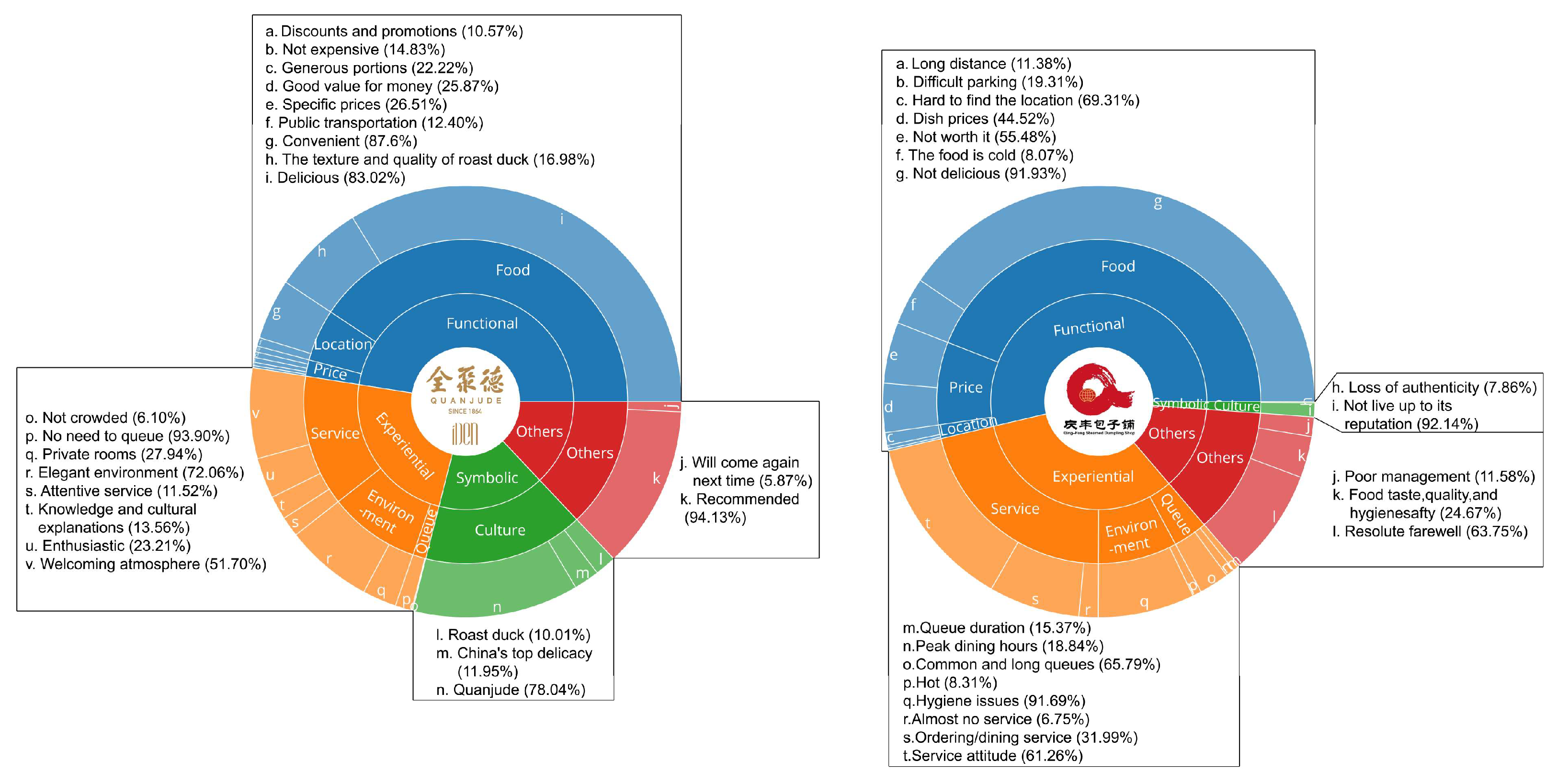
4.3.1. Success Factors of Comprehensive Performers: The Case of Quanjude
4.3.2. Diagnosing the Pain Points of “Heritage Strugglers”: The Case of Qingfeng Stuffed Bun House
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpreting Brand Image: The Dual Structure of CTHBs
5.2. Theoretical and Methodological Contributions
5.3. Managerial Implications
5.4. Limitations and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
- Strengthen operations before emphasizing heritage: Ensure that products, services, and environments exceed consumer expectations.
- Embed culture into experiences rather than treating it as ornamentation: Innovate service processes to transform history and culture into tangible consumer experiences.
- Use dynamic data as a mirror for continuous improvement: Establish long-term monitoring mechanisms for brand image health through real-time data such as online reviews.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LLMs | Large Language Models |
| ABSA | Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis |
| CTHBs | China Time-honored Brands |
| UGC | User-generated content |
| eWOM | Electronic Word of Mouth |
| F-E-S | Functional–Experiential–Symbolic |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| c-TF-IDF | class-based Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| WCSS | Within-Cluster Sum of Squares |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| LDA | Latent Dirichlet Allocation |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. ABSA Prompts

Appendix A.2. Model Links and Computing Environment
| Component | Specification | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Hygon 7390 32C/64T @ 2.7 GHz | 2 |
| GPU | NVIDIA A6000 (48 GB VRAM) | 2 |
| RAM | 32 GB 3200 MHz DDR4 ECC RDIMM | 16 |
| Storage | Enterprise SSD (SATA) 1 TB | 2 |
| Enterprise SSD (SATA) 4 TB | 3 | |
| RAID card | LSI9361-8i | 1 |
References
- Notice of the Ministry of Commerce and 14 Other Departments on Issuing the “Several Opinions on Protecting and Promoting the Development of Time-Honored Brands. Available online: https://www.mofcom.gov.cn/zcfb/zgdwjjmywg/art/2008/art_5d39c753700f475ab2b21680eeeff129.html (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of Chinese Time-Honored Catering Brands in the Five Northwestern Provinces. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, J.B.; Kim, J.-H. Nostalgic Experiences in Time-Honored Restaurants: Antecedents and Outcomes. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 99, 103080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cui, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, N. Brand Revitalization of Heritage Enterprises for Cultural Sustainability in the Digital Era: A Case Study in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.W.; Jaworski, B.J.; MacInnis, D.J. Strategic Brand Concept-Image Management. J. Mark. 1986, 50, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Tsuda, K. A Management Method of the Corporate Brand Image Based on Customers’ Perception. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 126, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Leung Ng, Y.; Luk, E.K. Impact of Celebrity Endorsement in Advertising on Brand Image among Chinese Adolescents. Young Consum. 2013, 14, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S. The Drivers of Green Brand Equity: Green Brand Image, Green Satisfaction, and Green Trust. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 93, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumeyer, A.; Kottemann, P.; Böger, D.; Decker, R. Measuring Brand Image: A Systematic Review, Practical Guidance, and Future Research Directions. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2019, 13, 227–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. Knowing How Satisfied/Dissatisfied Is Far from Enough: A Comprehensive Customer Satisfaction Analysis Framework Based on Hybrid Text Mining Techniques. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2023, 36, 873–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L. How Far Is Reality from Vision: An Online Data-Driven Method for Brand Image Assessment and Maintenance. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Rodriguez, L.M.; Castillo-Abdul, B. Toward State-of-the-Art on Social Marketing Research in User-Generated Content (UGC) and Influencers. JMD 2023, 42, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzate, M.; Arce-Urriza, M.; Cebollada, J. Mining the Text of Online Consumer Reviews to Analyze Brand Image and Brand Positioning. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 67, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.A.; Hassan, H.M.K.; Asheq, A.A.; Islam, K.M.A. The Interplay between eWOM Information and Purchase Intention on Social Media: Through the Lens of IAM and TAM Theory. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Hung, Y.-C.; Liu, W. Cultural Differences in Hospitality Service Evaluations: Mining Insights of User Generated Content. Electron. Mark. 2022, 32, 1061–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Pathania, A. Reading between the Lines: Untwining Online User-Generated Content Using Sentiment Analysis. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2021, 15, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Deep Learning Mechanism and Big Data in Hospitality and Tourism: Developing Personalized Restaurant Recommendation Model to Customer Decision-Making. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 121, 103803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liao, H.; Kóczy, L.T. Preference Mining and Fuzzy Inference for Hotel Selection Based on Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis from User-Generated Content. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2025, 76, 1414–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding 2019.
- Zhou, C.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, K.; Ji, C.; Yan, Q.; He, L.; et al. A Comprehensive Survey on Pretrained Foundation Models: A History from BERT to ChatGPT. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cyber. 2024, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrati, Z.; Imran, A.S.; Kurti, A. Weakly Supervised Framework for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis on Students’ Reviews of MOOCs. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 106799–106810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Bing, L.; Lam, W. A Survey on Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis: Tasks, Methods, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 11019–11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Hao, C.; Wang, Z. User Needs Insights from UGC Based on Large Language Model. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2025, 65, 103268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P. Large Language Models (LLMs): Survey, Technical Frameworks, and Future Challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; He, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, K.; Han, Q.-L.; Tang, Y. A Brief Overview of ChatGPT: The History, Status Quo and Potential Future Development. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2023, 10, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jin, H.; Tang, R.; Han, X.; Feng, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhong, S.; Yin, B.; Hu, X. Harnessing the Power of LLMs in Practice: A Survey on ChatGPT and Beyond. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2024, 18, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X.; Wu, N. Zero-Shot Information Extraction from Radiological Reports Using ChatGPT. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2024, 183, 105321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.; Shiwakoti, S.; Shah, S.B.; Adhikari, S.; Veeramani, H.; Nasim, M.; Naseem, U. Large Language Models (LLM) in Computational Social Science: Prospects, Current State, and Challenges. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2025, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. How to Revitalize China Time-Honored Brand through Marketing. In Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Economic Management and Cultural Industry (ICEMCI 2022), Chongqing, China, 14–16 October 2022; Appolloni, A., Caracciolo, F., Ding, Z., Gogas, P., Huang, G., Nartea, G., Ngo, T., Striełkowski, W., Joshi, S., Eds.; Atlantis Press International BV: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 231, pp. 1391–1399. ISBN 978-94-6463-097-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-N.; Li, Y.-Q.; Liu, C.-H.; Ruan, W.-Q. A Study on China’s Time-Honored Catering Brands: Achieving New Inheritance of Traditional Brands. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 58, 102290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.; Miller, D.; Merrilees, B. Restoring Luxury Corporate Heritage Brands: From Crisis to Ascendency. J. Brand. Manag. 2015, 22, 448–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, A.R.; Korsager, E.M.; Heller, M. A Bittersweet Past: The Negative Equity of Corporate Heritage Brands. J. Consum. Cult. 2021, 21, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Economic Daily. How Do Chinese Time-Honored Brands Unleash New Vitality. 2016. Available online: http://paper.ce.cn/jjrb/html/2016-12/09/content_319795.htm (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Chen, Q.; Huang, R.; Hou, B. Perceived Authenticity of Traditional Branded Restaurants (China): Impacts on Perceived Quality, Perceived Value, and Behavioural Intentions. Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 23, 2950–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Huang, R.; Liang, S.; Liao, X. Consumer Perceived Brand Innovativeness and Authenticity of Chinese Time-Honored Brand Restaurants: The Moderated Mediation Effect of Personal Traits. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag. 2023, 16, 2481–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xiang, J.; Wang, J. Extension of Heritage Brands and Consumer Purchase Intention with the Moderating Role of Pop Culture Involvement: An Empirical Analysis of Time-Honoured Brands in China. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2023, 36, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X. “New and Old”: Consumer Evaluations of Co-Branding between New Brands and Chinese Time-Honored Brands. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2023, 73, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hui, M.K.; Zhou, L.; Li, S. Cultural Congruity and Extensions of Corporate Heritage Brands: An Empirical Analysis of Time-Honored Brands in China. J. Consum. Behav. 2022, 21, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sishun, H. The Reshaping of the Time-Honored Brand Image under the New Media Environment; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 633–636. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; He, C.; Ma, Y. Research on the Visual Image Design and Communication Studies of China’s Time-Honored Brands; Athena Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- DuBois, D.T. China’s Old Brands: Commercial Heritage and Creative Nostalgia. Int. J. Asian Stud. 2021, 18, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, B.B.; Levy, S.J. The Product and the Brand. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1955, 33, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Aaker, D.A. Managing Brand Equity; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; ISBN 978-0-02-900101-1. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, K.L. Conceptualizing, Measuring, and Managing Customer-Based Brand Equity. J. Mark. 1993, 57, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, M.N.; Noor, N.M.; Noor, N.M. Purchase Intentions of Foreign Luxury Brand Handbags among Consumers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2016, 35, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Jebarajakirthy, C.; Sivapalan, A. How Consumption Values and Perceived Brand Authenticity Inspire Fashion Masstige Purchase? An Investigation. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 68, 103023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, N. An Exploratory Investigation of the Elements of B2B Brand Image and Its Relationship to Price Premium. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2010, 39, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brečić, R.; Filipović, J.; Gorton, M.; Ognjanov, G.; Stojanović, Ž.; White, J. A Qualitative Approach to Understanding Brand Image in an International Context: Insights from Croatia and Serbia. Int. Mark. Rev. 2013, 30, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohs, R.; Reisinger, H. Sponsorship Effects on Brand Image: The Role of Exposure and Activity Involvement. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Yu, J.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Han, H. Exploring the Impact of Functional, Symbolic, and Experiential Image on Approach Behaviors among State-Park Tourists from India, Korea, and the USA. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, M.; Torres, P. Effects of Brand Attitude and eWOM on Consumers’ Willingness to Pay in the Banking Industry: Mediating Role of Consumer-Brand Identification and Brand Equity. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2018, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, G.; Elviana, E. Effect of Brand Image, Celebrity Endorsement, EWOM, Brand Awareness and Social Media Communication on Purchase Intention with Brand Trust as a Mediation Variable on Smartphone Users in Batam City. Conf. Bus. Soc. Sci. Technol. (CoNeScINTech) 2022, 2, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Kudeshia, C.; Kumar, A. Social eWOM: Does It Affect the Brand Attitude and Purchase Intention of Brands? Manag. Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 310–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ren, P.; Lv, X.; Li, S. Service Experience and Customers’ eWOM Behavior on Social Media Platforms: The Role of Platform Symmetry. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2024, 119, 103735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustak, M.; Hallikainen, H.; Laukkanen, T.; Plé, L.; Hollebeek, L.D.; Aleem, M. Using Machine Learning to Develop Customer Insights from User-Generated Content. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2024, 81, 104034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Kwon, J.; Chae, B.; Kim, S.-B. What Are the Salient and Memorable Green-Restaurant Attributes? Capturing Customer Perceptions From User-Generated Content. SAGE Open 2021, 11, 21582440211031546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Seo, H.J.; Song, T.H. Do All the Service Attributes Matter? Application of Customer Review-Based Attribute Extraction Considering Brand Status. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2025, 87, 104345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.; Garain, A.; Sarkar, R. An Ensemble-Based Hotel Recommender System Using Sentiment Analysis and Aspect Categorization of Hotel Reviews. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 98, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, P.; Dias, S. Enhancing Restaurant Management through Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis and NLP Techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 237, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, B.X.B.; Li, G.; Gao, H. Restaurant Survival Prediction Using Customer-Generated Content: An Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis of Online Reviews. Tour. Manag. 2023, 96, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahhosseini, M.; Khalili Nasr, A. What Attributes Affect Customer Satisfaction in Green Restaurants? An Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis Approach. J. Travel. Tour. Mark. 2024, 41, 472–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Jin, Y. ChatGPT and Finetuned BERT: A Comparative Study for Developing Intelligent Design Support Systems. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2024, 21, 200308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Chakraborty, I.; Nishimura, Y. AI–Human Hybrids for Marketing Research: Leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) as Collaborators. J. Mark. 2025, 89, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatora, P.S.; Hosseini, S.E.; Pervez, S.; Iqbal, M.J.; Shaukat, N. Sentiment Analysis of Product Reviews Using Machine Learning and Pre-Trained LLM. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantano, E.; Serravalle, F.; Priporas, C.-V. The Form of AI-Driven Luxury: How Generative AI (GAI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) Are Transforming the Creative Process. J. Mark. Manag. 2024, 40, 1771–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Y. Exploring the Relationship between Urban Polycentricity and Consumer Amenity Development: An Empirical Study Using Dianping Data in China. Cities 2025, 166, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić Rosario, A.; de Valck, K.; Sotgiu, F. Conceptualizing the Electronic Word-of-Mouth Process: What We Know and Need to Know about eWOM Creation, Exposure, and Evaluation. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2020, 48, 422–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S. (Sixue) Measuring Tourists’ Meal Experience by Mining Online User Generated Content about Restaurants. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour. 2019, 19, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cankül, D.; Kaya, S.; Kızıltaş, M.Ç. The Effect of Gastronomic Experience on Restaurant Image, Customer Perceived Value, Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2024, 36, 100908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Salirrosas, E.E.; Escobar-Farfán, M.; Esponda-Perez, J.A.; Millones-Liza, D.Y.; Villar-Guevara, M.; Haro-Zea, K.L.; Gallardo-Canales, R. The Impact of Perceived Value on Brand Image and Loyalty: A Study of Healthy Food Brands in Emerging Markets. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1482009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.V.; Phan, T.N.; Le-Hoang, V.P. Positioning Customer-Based Convenience Store Image: A Multidimensional Scaling Approach via Perceptual Map. J. Distrib. Sci. 2021, 19, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Lee, S.; Huffman, L. Impact of Restaurant Experience on Brand Image and Customer Loyalty: Moderating Role of Dining Motivation. J. Travel Tour. Mark. 2012, 29, 532–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heung, V.C.S.; Gu, T. Influence of Restaurant Atmospherics on Patron Satisfaction and Behavioral Intentions. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2012, 31, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J.; Roy, D.; De Koster, R. Worth the Wait? How Restaurant Waiting Time Influences Customer Behavior and Revenue. J. Oper. Manag. 2018, 63, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.Y.; Khoo-Lattimore, C.; Wang, Y. Food and Cuisine Image in Destination Branding: Toward a Conceptual Model. Tour. Hosp. Res. 2019, 19, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Papageorgiou, H.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Manandhar, S.; Al-Smadi, M.; Al-Ayyoub, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, B.; de Clercq, O.; et al. SemEval-2016 Task 5: Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2016), San Diego, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2016; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Pavlopoulos, J.; Papageorgiou, H.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Manandhar, S. SemEval-2014 Task 4: Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014), Dublin, Ireland, 23–29 August 2014; Nakov, P., Zesch, T., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Kerrville, TX, USA, 2014; pp. 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Li, A.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Hui, B.; Zheng, B.; Yu, B.; Gao, C.; Huang, C.; Lv, C.; et al. Qwen3 Technical Report. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.09388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Langrené, N.; Zhu, S. Unleashing the Potential of Prompt Engineering for Large Language Models. Patterns 2025, 6, 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappeman, J.; Clark, R.; Evans, J.; Sierra-Rubia, L.; Gordon, P. Studying Social Media Sentiment Using Human Validated Analysis. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, N.A.; Fanany, M.I.; Budi, I. Twitter Sentiment to Analyze Net Brand Reputation of Mobile Phone Providers. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 72, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikotun, A.M.; Ezugwu, A.E.; Abualigah, L.; Abuhaija, B.; Heming, J. K-Means Clustering Algorithms: A Comprehensive Review, Variants Analysis, and Advances in the Era of Big Data. Inf. Sci. 2023, 622, 178–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Franco, M.J.; Rey-Moreno, M. Do Travelers’ Reviews Depend on the Destination? An Analysis in Coastal and Urban Peer-to-Peer Lodgings. Psychol. Mark. 2022, 39, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, T.; Meng, B.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S. Analysis of Tourist Behavior Patterns and Perceptions in Beijing Based on User-Generated Content Data. Appl. Spat. Anal. 2025, 18, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Pattnaik, D.; Hughes, L.; Nedungadi, P. Unveiling the Dynamics of AI Applications: A Review of Reviews Using Scientometrics and BERTopic Modeling. J. Innov. Knowl. 2024, 9, 100517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaker, D.A. Should You Take Your Brand to Where the Action Is? Harv. Bus. Rev. 1997, 75, 135–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dion, D.; Mazzalovo, G. Reviving Sleeping Beauty Brands by Rearticulating Brand Heritage. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 5894–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urde, M.; Greyser, S.A.; Balmer, J.M.T. Corporate Brands with a Heritage. J. Brand. Manag. 2007, 15, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppelwieser, V.G.; Klaus, P.; Manthiou, A.; Hollebeek, L.D. The Role of Customer Experience in the Perceived Value–Word-of-Mouth Relationship. J. Serv. Mark. 2022, 36, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, M.; Elayan, S.; Hodgkinson, I.R.; Jackson, T.W.; West, A. The Power of Emotions: Leveraging User Generated Content for Customer Experience Management. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 144, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, J.L.; Mellinas, J.P.; Martín-Fuentes, E. The Halo Effect: A Longitudinal Approach. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 83, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richetin, J.; Demartini, E.; Gaviglio, A.; Ricci, E.C.; Stranieri, S.; Banterle, A.; Perugini, M. The Biasing Effect of Evocative Attributes at the Implicit and Explicit Level: The Tradition Halo and the Industrial Horn in Food Products Evaluations. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 61, 101890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Pan, B.; Hu, T.; Chen, K.; Qiao, L.; Zhu, J. Beyond Self-Selection: The Multilayered Online Review Biases at the Intersection of Users, Platforms and Culture. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2021, 4, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xiao, J. Factors Affecting Users’ Satisfaction with Urban Parks through Online Comments Data: Evidence from Shenzhen, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, N.; Radaideh, M.I.; Kwon, O.H.; Verma, A.; Radaideh, M.I. On the Impact of Language Nuances on Sentiment Analysis with Large Language Models: Paraphrasing, Sarcasm, and Emojis 2025. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.05603. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, A.; Soltangheis, M.; Arabzadeh, N.; Salamat, S.; Zihayat, M.; Bagheri, E. Benchmarking Prompt Sensitivity in Large Language Models. In Advances in Information Retrieval; Hauff, C., Macdonald, C., Jannach, D., Kazai, G., Nardini, F.M., Pinelli, F., Silvestri, F., Tonellotto, N., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 303–313. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhou, A.; Meng, B.; Wang, R. Brand Image of Beijing’s Time-Honored Restaurants: An Analysis Through Large Language Model-Driven Review Mining. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20040300
Li X, Zhou A, Meng B, Wang R. Brand Image of Beijing’s Time-Honored Restaurants: An Analysis Through Large Language Model-Driven Review Mining. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research. 2025; 20(4):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20040300
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaohang, Aihua Zhou, Bin Meng, and Ruize Wang. 2025. "Brand Image of Beijing’s Time-Honored Restaurants: An Analysis Through Large Language Model-Driven Review Mining" Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research 20, no. 4: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20040300
APA StyleLi, X., Zhou, A., Meng, B., & Wang, R. (2025). Brand Image of Beijing’s Time-Honored Restaurants: An Analysis Through Large Language Model-Driven Review Mining. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 20(4), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20040300









