Plastic Smell: A Review of the Hidden Threat of Airborne Micro and Nanoplastics to Human Health and the Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sources of Airborne MPs/NPs
2.1. The Common Type of MPs/NPs (Fibers, Fragments, Microbeads)
2.2. Road Dust
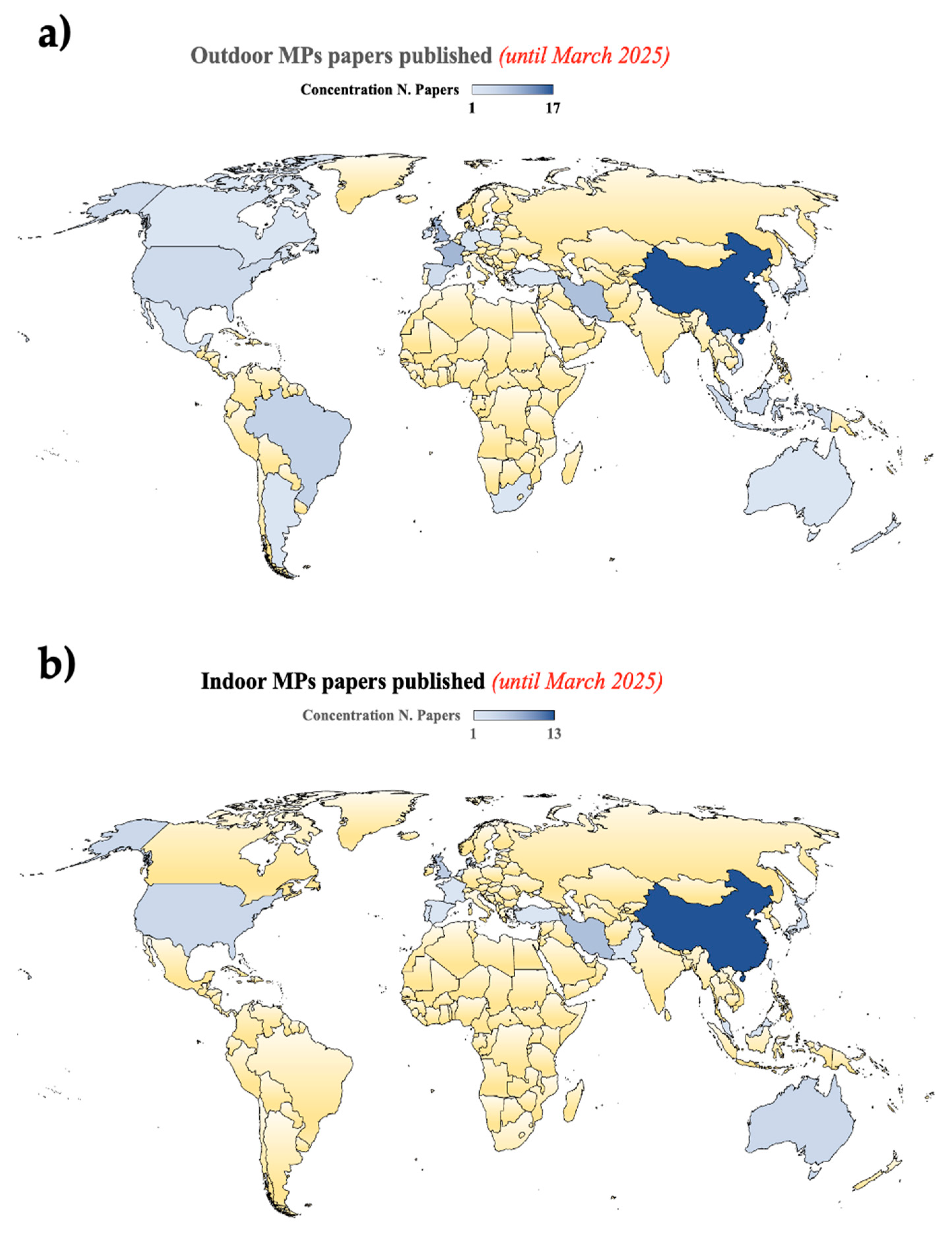
2.3. Outdoor/Indoor MPs/NPs
3. Key Sampling Techniques for MPs/NPs as Well as Challenges with Identification and Quantification
3.1. Sampling Techniques
3.2. Separation Treatments
3.3. Visual Identification
3.4. Thermochemical Analytical Methods
3.5. Spectroscopy Analytical Techniques
3.6. Novel MPs/NPs Detection Methods
4. Environmental Risk of Airborne MPs/NPs
5. Possible Risks to Human Health by Airborne MPs/NPs
| Location | MP/NP Type | MP/NP Shape | MPs/NPs Particle Size (µm) | Implications on Human Health | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | PA, PE, PET, PP, PS, PVC | Fibers, fragments | 0.1–40 | Extrathoracic and bronchial regions (upper airways), respiratory tissues | [76] |
| China | PS | Microbeads | 0.50–0.52 | Renal injury (NR4A1/CASP3, TF/F12, and HK-2). Renal tubular injury, glomerular mural epithelial cell proliferation, and immune cell infiltration | [77] |
| China | PE | Microbeads | 1.0–5.0 | Asthma, higher degree of inflammatory cell infiltration, bronchial goblet cell hyperplasia, oxidative stress injury in the lung (cytokine IL-33 in the BALF) | [181] |
| China | PS | Microbeads | 0.1–1 | Liver fibrosis, oxidative stress in AML12 cells, liver inflammation (increasing JNK, JAK1, NF-κB, STAT1, TNF-α, and P38 MAPK) | [182] |
| China | PHA, PP | Fibers, microbeads | 5.0 | Intestinal microbiome dysbiosis, intestinal and serum metabolome disruption, hepatic transcriptome disturbances, and hepatotoxicity | [192] |
| China | PE, PET, PP, PS, PTFE, PVC | Fibers, fragments, films, microbeads | 0.5–5.0 | Thorax and alveoli, lung tissue, BEAS−2B cells, lung fibrosis damage, COPD, ARDS | [78] |
| Australia, Bangladesh, USA | PA, PAN, PE, PES, PET, PP, PVC | Fibers, fragments, films, microbeads | 0.1–5.0 | Hormonal imbalance, undesirable pregnancy outcomes, sexual dysfunction and infertility, asthma, impaired renal function | [193] |
| Iran | PE, PET, PP, PS | Fibers, fragments, films, microbeads | 200–5000 | Extrathoracic and bronchial regions (upper airways), respiratory tissues | [20] |
| China | PAN, PE, PET, PP, PS, PVC | Fibers, fragments, films, microbeads | 0.1–5.0 | DNA damage, altered gene and protein expression, cell/tissue apoptosis, loss of cell viability, oxidative stress, elevated calcium levels, and inflammation | [163] |
| China | PS | Microbeads | 0.5–3.0 | Inflammation in multiple organs, infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages, increased Toll-like receptors (TLRs), myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MyD88) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), as well as proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1β) in the lungs, thymus, spleen, liver, and kidneys | [194] |
| China | PS | Microbeads | 0.50–0.52 | Glucose metabolism disorder (hyperglycemia), liver damage, liver fibrosis | [195] |
| China, New Zealand | PS | Microbeads | 0.1–5.0 | Airway dysbiosis, altered nasal microbiota, altered lung microbiota | [196] |
| China | EVA, PA, PAN, PE, PET, PMMA, PP, PS, PTFE, PVC | Fibers, fragments, films, microbeads | 0.1–500 | Extrathoracic and bronchial regions (upper airways), respiratory tissues | [197] |
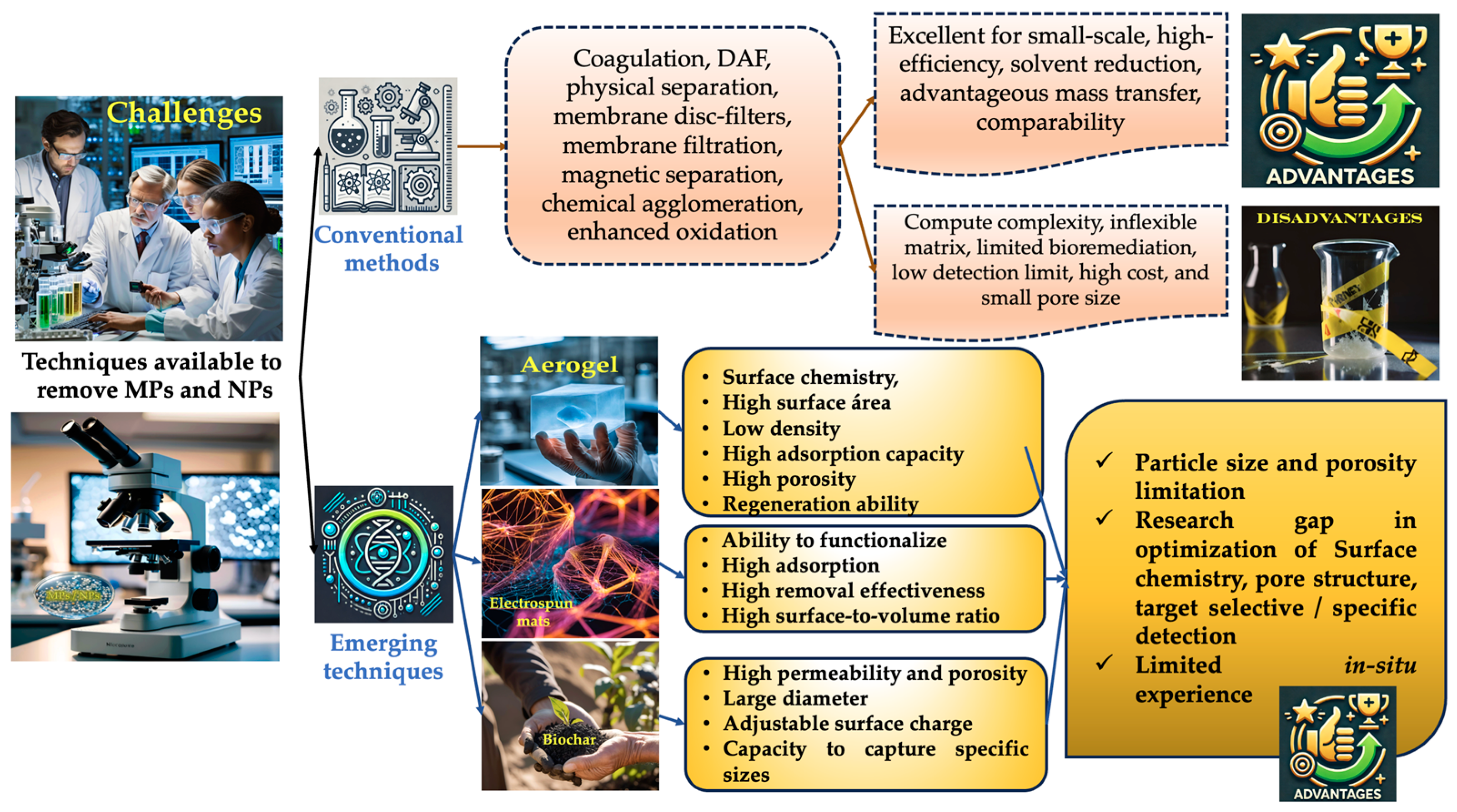
6. Future Perspectives and Potential Solutions
- ○
- Physicochemical characteristics: Dimensions, type of plastic, and shape.
- ○
- Clinical methodology: Amounts of MPs/NPs entering and leaving the body, possible degradation of ingested MPs/NPs’ particles, possible clinical interactions between MPs/NPs and physiological homeostasis and target organs/tissues, permeability/adsorption of MPs/NPs by each target tissue, possible measurement of the Trojan horse effect, and studies of signaling pathways.
- ○
- Pathological investigations: Examination of MPs/NPs that initiate, accelerate, and propagate possible carcinogenesis in organs and tissues. For better clinical evaluations, the link between cellular alterations and high MPs/NPs’ concentrations or dosages must be confirmed.
- ○
- Biochemical studies: The possible biochemical processes that contribute to the reduction and destruction of airborne MPs/NPs in tissues and organs must be assessed.
- ○
- Comparative investigation: How MPs/NPs differ from other similar particles that the human body can absorb in terms of absorption, toxicity, and pathological effects (i.e., TiO2 nanoparticles) must be examined.
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| ABS | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
| AFM-IR | Atomic force microscopy-based infrared |
| AI | Alveolar-interstitial regions |
| ARDSS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| ASA | Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate |
| ATR-FTIR | Attenuated total reflectance–Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases |
| EPDM | Polyethylenepropylene-diene |
| EVA | Ethylene vinyl acetate |
| FPA | Focal plane array |
| FSEI | Fusion and solvent evaporation ionization |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| GI | Gastrointestinal system |
| HDPE | High-density polyethylene |
| LDIR | Laser-direct infrared |
| LDPE | Low-density polyethylene |
| LIBS | Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy |
| MO | Microorganisms |
| MPs | Microplastics |
| MPS | Medical Polymer Science |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| NEE | Non-exhaust emission |
| NPs | Nanoplastics |
| NY | Nylon |
| OS | Oxidative stress |
| PA | Polyamide |
| PA-6,6 | Polyamide 6,6 |
| PFAS | Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| PFOA | Perfluorooctanoic acid |
| PAH | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon |
| PAI-TOFMS | Photoinduced associative ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| PAN/PS/PMA | Poly(acrylonitrile:styrene:methyl acrylate) |
| PB | Polybutylene |
| PBA | Poly(11-bromoundecyl acrylate) |
| PBD | Polybutadiene |
| PBDE | Polybrominated diphenyl ethers |
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| PCB | Polychlorinated biphenyl |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| PDMS | Polydimethyl siloxane |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon) |
| PES | Polyester |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoates |
| PHB | Polyhydroxy butyrate |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| PLE | Pressurized liquid extraction |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| PMMA | Polymethylmethacrylate |
| POM | Polyoxymethylene |
| POPs | Persistent organic pollutants |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PUPA | Polyurethane and poly(amido-amine) |
| Py-GC/MS | Pyrolisis GC/MS spectrometry |
| RA | Rayon |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SAN | Styrene acrylonitrile |
| SBR | Styrene-butadiene |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SERS | Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| TWPs | Tire wear particles |
| WWTPs | Wastewater treatment plants |
| µFTIR | Micro Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
References
- Casella, C.; Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Microplastics in Sewage Sludge: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63382–63415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, C.; Ballaz, S.J. Genotoxic and neurotoxic potential of intracellular nanoplastics: A review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 1657–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP-WCMC; IUCN; NGS. Protected Planet Report; UNEP-WCMC, IUCN and NGS: Cambridge, UK; Gland, Switzerland; Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Available online: https://protectedplanetreport2020.protectedplanet.net/pdf/Protected_Planet_Report_2018.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Plastics Europe 2024—The Fast Facts 2024 Plastics Europe. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2023 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Moss, K.; Le Roux, G.; Phoenix, V.R.; Sonke, J.E. Examination of the ocean as a source for atmospheric microplastics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Mirande, C.; Tassin, B. Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: A source of microplastics in the environment? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahedi, F.; Fard, N.J.H.; Turner, A. A Systematic Review of Biomonitoring Microplastics in Environmental Matrices: Emphasis on Airborne Particles, Dry Deposits, and Comparative Analysis with Traditional Methods. Environ. Adv. 2025, 19, 100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuri, G.; Karanasiou, A.; Lacorte, S. Microplastics: Human exposure assessment through air, water, and food. Environ. Int. 2023, 179, 108150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, G.; Wang, S.; Walters, S.; Lichtig, P.; Li, C. Microplastics in the Atmosphere: A Global Perspective. 2023. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-3186780/v1 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Xiao, S.; Cui, Y.; Brahney, J.; Mahowald, N.M.; Li, Q. Long-distance atmospheric transport of microplastic fibres influenced by their shapes. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C. Airborne microplastics: Consequences to human health? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xue, Y.; Sha, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Suvdantsetseg, B.; Wang, L. Influence of regional environmental variables on the radiative forcing of atmospheric microplastics. Eco-Environ. Health 2024, 4, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, T.; Casillas, G.; Zarus, G.M.; Barr, D.B. Systematic review of microplastics and nanoplastics in indoor and outdoor air: Identifying a framework and data needs for quantifying human inhalation exposures. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2024, 34, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A. Indoor Microplastics and Microfibers: Sources and Impacts on Human Health. In Microfibre Pollution from Textiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 285–307. Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.1201/9781003331995-16/indoor-microplastics-microfibers-mansoor-ahmad-bhat (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Jung, C.C.; Chao, Y.C.; Hsu, H.T.; Gong, D.W. Spatial and seasonal variations of atmospheric microplastics in high and low population density areas at the intersection of tropical and subtropical regions. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 119996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Glamoclija, M.; Murphy, A.; Gao, Y. Characterization of microplastics in indoor and ambient air in northern New Jersey. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinnerton, S.; Su, J.; Tsai, C.S. The emission and physicochemical properties of airborne microplastics and nanoplastics generated during the mechanical recycling of plastic via shredding. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beres, N.; Burkart, J.; Graf, E.; Zeder, Y.; Niederberger, E.; Dailey, L.A.; Weinzierl, B. A novel online method for the detection, analysis, and classification of airborne microplastics. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2023; p. EGU-12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Gaga, E.O.; Gedik, K. How can contamination be prevented during laboratory analysis of atmospheric samples for microplastics? Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2024, 196, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaydi, N.; Jorfi, S.; Takdastan, A.; Haghighifard, N.J.; Khafaie, M.A. Morphological and Chemical Analysis of Indoor Airborne Microplastics: Implications for Human Health in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ. Geochem. Health 2025, 47, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaydi, N.; Jorfi, S.; Takdastan, A.; Jaafarzadeh Haghighifard, N.; Khafaie, M.A. Source identification and apportionment of ambient air microplastics: A systematic review. Disc. Appl. Sci. 2024, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Behbehani, M. Microplastics in the atmosphere: A review. J. Environ. Expo. Assess 2022, 1, 10–20517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levermore, J.M.; Smith, T.E.; Kelly, F.J.; Wright, S.L. Detection of microplastics in ambient particulate matter using Raman spectral imaging and chemometric analysis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 8732–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhu, J.; Su, K.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Deng, M.; Zhang, C. Tracing the Transport and Residence Times of Atmospheric Microplastics Using Natural Radionuclides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 15702–15710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.P.; Chauhan, P.; Staudinger, U.; Satapathy, B.K. Exploring sustainable adsorbents to mitigate micro-/nano-plastic contamination: Perspectives on electrospun fibrous constructs, biochar, and aerogels. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, 1217–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Chen, R.; Gao, T.; Allen, S. Atmospheric emissions of microplastics entrained with dust from potential source regions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Tian, X.; Guo, Z.; Chang, C.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Wang, R.; Li, Q.; et al. Effect of dry soil aggregate size on microplastic distribution and its implications for microplastic emissions induced by wind erosion. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Bushnaq, H.; Munro, C.; Gibert, Y.; Sharma, R.; Mishra, V.; Dumée, L.F. Perspectives on transport pathways of microplastics across the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. npj Clean Water 2024, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Riksen, M.J.; Sirjani, E.; Sameni, A.; Geissen, V. Wind erosion as a driver for transport of light density microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Lu, X.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Microplastic emission from soil-air interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghardt, T.E.; Pashkevich, A.; Babić, D.; Mosböck, H.; Babić, D.; Żakowska, L. Microplastics and road markings: The role of glass beads and loss estimation. Transport. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 102, 103123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathna, K.S.D.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Vithanage, M. Microplastics in road dust and surrounding environment: Sources, Fate and Analytical Approaches. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 45, e00256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, A.; Arp, H.P.H.; Escher, B.I.; Gewert, B.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Ogonowski, M.; Potthoff, A.; Rummel, C.; Schmitt-Jansen, M.; et al. Reducing uncertainty and confronting ignorance about the possible impacts of weathering plastic in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.C.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Roy, P.D.; Martínez, I.E. Occurrence and characteristics of atmospheric microplastics in Mexico City. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. The chemical behaviors of microplastics in marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deylami, S.; Cárdenas-Escudero, J.; Ochoa, M.L.; Ayuso-Haro, J.; Galán-Madruga, D.; Ruiz, J.L.U.; Cáceres, J.O. Microplastics in Antarctic air: Revealing current findings. Antarct. Sci. 2025, 37, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Junaid, M.; Liao, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J. Eco-corona formation and associated ecotoxicological impacts of nanoplastics in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Lang, M.; Yu, X.; Wu, R.; Yang, X.; Guo, X. Aging mechanism of microplastics with UV irradiation and its effects on the adsorption of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.E.; Neale, P.J.; Hylander, S.; Rose, K.C.; Figueroa, F.L.; Robinson, S.A.; Häder, D.-P.; Wängberg, S.; Worrest, R.C. The interactive effects of stratospheric ozone depletion, UV radiation, and climate change on aquatic ecosystems. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 717–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Santos, T.A.; Duarte, A.C. Characterization and Analysis of Microplastics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 75, Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/handbook/comprehensive-analytical-chemistry/vol/75?page-size=100&page=1 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Acharya, S.; Rumi, S.S.; Hu, Y.; Abidi, N. Microfibers from synthetic textiles as a major source of microplastics in the environment: A review. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 2136–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järlskog, I.; Jaramillo-Vogel, D.; Rausch, J.; Gustafsson, M.; Strömvall, A.M.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Concentrations of tire wear microplastics and other traffic-derived non-exhaust particles in the road environment. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Meng, Y.; Liu, G. Mitigating airborne microplastics pollution from perspectives of precipitation and underlying surface types. Water Res. 2023, 243, 120385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Ulke, J.; Font, A.; Chan, K.L.A.; Kelly, F.J. Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Turner, A.; Sharifi, R.; Nematollahi, M.J.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Moghtaderi, T. Microplastics in the school classrooms of Shiraz, Iran. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, M.; Isobe, A.; Uchida, K.; Tokai, T.; Kitakado, T.; Yoshitake, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Mukai, T.; Imai, K.; Shimizu, K.; et al. Abundance and potential sources of floating polystyrene foam macro-and microplastics around Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gao, M.; Nowack, B. Formation of microplastic fibers and fibrils during abrasion of a representative set of 12 polyester textiles. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 862, 160758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xing, Y.; Liu, K.; Ling, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Pei, Z.; et al. Review of research on migration, distribution, biological effects, and analytical methods of microfibers in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafina, P.R.; Yudison, A.P.; Sembiring, E.; Irsyad, M.; Tomo, H.S. Identification of fibrous suspended atmospheric microplastics in Bandung Metropolitan Area, Indonesia. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; dos Santos Galvão, L.; Wiebeck, H.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Mauad, T. Atmospheric microplastic fallout in outdoor and indoor environments in São Paulo megacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, M.; Valencia, B.G.; Lucas-Solis, O.; Calero, J.L.; Maisincho, L.; Conicelli, B.; Moulatlet, G.M.; Capparelli, M.V. A new method for microplastic sampling and isolation in mountain glaciers: A case study of one antisana glacier, Ecuadorian Andes. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2020, 2, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materić, D.; Ludewig, E.; Brunner, D.; Röckmann, T.; Holzinger, R. Nanoplastics transport to the remote, high-altitude Alps. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Duan, Y.; Han, X.; Sun, X.; Munyaneza, J.; Ma, J.; Xiu, G. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in the megalopolis (Shanghai) during rainy season: Characteristics, influence factors, and source. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.; Han, G.M.; Shim, W.J. Rapid production of micro-and nanoplastics by fragmentation of expanded polystyrene exposed to sunlight. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11191–11200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Ma, T.; Liu, X.; Wei, H.; Meng, H.; Fu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J. Distribution and possible sources of atmospheric microplastic deposition in a valley basin city (Lanzhou, China). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 233, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.R.; Le Roux, G.; Durántez Jiménez, P.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Xing, B. Environmental source, fate, and toxicity of microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, R.S.; Yang, X.; van Dam, J. Rainfall-induced microplastic fate and transport in unsaturated dutch soils. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 268, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, M.C.; Pawlak, J.J.; Daystar, J.; Ankeny, M.; Cheng, J.J.; Venditti, R.A. Microfibers generated from the laundering of cotton, rayon and polyester based fabrics and their aquatic biodegradation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)-A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, N.K.; Mawaddah, N.; Shiddiq, M.D.; Alam, F.C.; Fajar, M. Atmospheric Microplastic Particulate in Urban Roadside: Case of Bandar Lampung City, Indonesia. Research Square, 2024; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaneros, S.M.; Chapman, E.; Hansen, M.; Williams, B.; Rotchell, J. Automatic pre-screening of outdoor airborne microplastics in micrographs using deep learning. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 372, 125993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margenat, H.; Hagelskjaer, O.; Le Roux, G.; Hansson, S.V. Plastics in Upper Vicdessos-Bridging the gapS for a Better Understanding of Atmospheric Microplastics in Mountain Environments (PVC#2). In ohmpyr2024: Séminaire de Restitution des Projets 2022–2024 de l’OHM Pyrénées Haut Vicdessos, (LabEx DRIIHM). 2024. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-04828850/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Mutshekwa, T.; Mulaudzi, F.; Maiyana, V.P.; Mofu, L.; Munyai, L.F.; Murungweni, F.M. Atmospheric deposition of microplastics in urban, rural, forest environments: A case study of Thulamela Local Municipality. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0313840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindelaub, J.D.; Salmond, J.A.; Fan, W.; Miskelly, G.M.; Dirks, K.N.; Henning, S.; Conrath, T.; Stratmann, F.; Coulson, G. Aerosol mass concentrations and dry/wet deposition of atmospheric microplastics at a remote coastal location in New Zealand. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 372, 126034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.; Chang, C.; Peng, C.; Liu, K.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Fu, T.; Han, Y.; et al. Atmospheric microplastics emission source potentials and deposition patterns in semi-arid croplands of Northern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmosp. 2024, 129, e2024JD041546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winijkul, E.; Latt, K.Z.; Limsiriwong, K.; Pussayanavin, T.; Prapaspongsa, T. Depositions of airborne microplastics during the wet and dry seasons in Pathum Thani, Thailand. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 102242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peries, S.D.; Sewwandi, M.; Sandanayake, S.; Kwon, H.H.; Vithanage, M. Airborne Transboundary Microplastics–A Swirl Around the Globe. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 353, 124080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Lee, S.; Tobino, T.; Nakajima, F. Efficient pretreatment method for analyzing microplastics in urban road dust containing composite materials. Water Environ. Res. 2025, 97, e70028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, P.W.; Jung, C.C. Concentrations, characteristics, influencing factors, and interactions of indoor and outdoor microplastics during the hot season at the intersection between tropical and subtropical zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 970, 179051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Habibi, N.; Sajid, S.; Dupont, S.; Behbehani, M. A preliminary assessment of size-fractionated microplastics in indoor aerosol—Kuwait’s baseline. Toxics 2022, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Lim, E.; Ni, Y.; Wei, J.; Kurosu, S.; Takeuchi, J.; Takemura, A. Investigation of indoor microplastics in settled indoor house dust in single-person residential buildings in Japan. Jpn. Arch. Rev. 2025, 8, e70013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewika, M.; Markandan, K.; Nagaratnam, S.; Irfan, N.A.; Abdah, M.A.A.M.; Ruwaida, J.N.; Sara, Y.Y.; Khalid, M. Assessing the concentration, distribution and characteristics of suspended microplastics in the Malaysian indoor environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 959, 178049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Liao, C.M. Regional and population-scale trends in human inhalation exposure to airborne microplastics: Implications for health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 371, 125950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Han, B.; Yang, S.; Guo, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, P.; Hong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Qi, S.; et al. Toxicological effects and mechanisms of renal injury induced by inhalation exposure to airborne nanoplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Airborne micro-and nanoplastics: Emerging causes of respiratory diseases. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petters, S.S.; Kjærgaard, E.R.; Hasager, F.; Massling, A.; Glasius, M.; Bilde, M. Morphology and hygroscopicity of nanoplastics in sea spray. Phys. Chem. Chem. Physic. 2023, 25, 32430–32442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageel, H.K.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.E. Microplastics in indoor air from Birmingham, UK: Implications for inhalation exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, H.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Y.; Tan, Z.; Liao, Z.; Ou, H. Disinfection inducing release of contaminants from baby play mats: Microplastics and volatile organic compounds. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 366, 125497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Mao, R.; Hu, E.; Xiao, C.; Yang, C.; Guo, X. The indoor exposure of microplastics in different environments. Gondw. Res. 2022, 108, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A. Unravelling the microplastic contamination: A comprehensive analysis of microplastics in indoor house dust. Indoor Built Environ. 2024, 33, 1420326X241248054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Liao, Z.; Ji, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C.; Shi, C.; Chen, Z.; Ge, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Microplastic ingestion from atmospheric deposition during dining/drinking activities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærgaard, E.R.; Hasager, F.; Petters, S.S.; Glasius, M.; Bilde, M. Bubble-mediated generation of airborne nanoplastic particles. Environ. Sci. Proc. Imp. 2024, 26, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorimotlagh, Z.; Hopke, P.K.; Mirzaee, S.A. A systematic review of airborne microplastics emissions as emerging contaminants in outdoor and indoor air environments. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Wang, P.; Lou, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, L.; Hu, Y.; Luan, Y.; Quan, C.; Fang, J.; Zou, H.; et al. A review of airborne micro-and nano-plastics: Sampling methods, analytical techniques, and exposure risks. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yao, K.; Guo, H. Characterization and sources of indoor and outdoor microplastics and PM2. 5: Possible relationships. Air Qual. Atmosph. Health 2024, 18, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Guo, H.; Fu, H.; Yao, K. Microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments in China: Characteristic and human exposure risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 287, 117328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Rosales, A.; Ferreiro, B.; Andrade, J.; Fernández-Amado, M.; González-Pleiter, M.; López-Mahía, P.; Rosal, R.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S. A reliable method to determine airborne microplastics using quantum cascade laser infrared spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Girão, A.V.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Identifying a quick and efficient method of removing organic matter without damaging microplastic samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, I.; Qadir, A.; Levermore, J.M.; Kelly, F.J. Dynamics of airborne microplastics, appraisal and distributional behaviour in atmosphere; a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, I.; Qadir, A.; Levermore, J.M.; Kelly, F.J. Nature, depositional dynamics, sources, and health risk assessment of indoor microplastics in three cities of Punjab, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, J.; He, S.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Xiayihazi, N. Evaluation of microplastic pollution in Shihezi city, China, using pine needles as a biological passive sampler. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.T.; Diamond, M.; Ward, E.; Adams, J.; Cherin-Hall, A.; Gamberg, M.; Obediah, T.; Palmer, M.; Platt, A.; Worthy, C.; et al. Snow as an Indicator of Atmospheric Transport of Anthropogenic Particles (Microplastics and Microfibers) from Urban to Arctic Regions. Arct. Sci. 2024, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Turner, A.; Kelly, F.J.; Dominguez, A.O.; Jaafarzadeh, N. Distribution and potential health impacts of microplastics and microrubbers in air and street dusts from Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, E.; Woo, M.; Steele, C.; Sukumaran, S.; Anderson, S. Microplastics differ between indoor and outdoor air masses: Insights from multiple microscopy methodologies. Appl. Spectros. 2020, 74, 1079–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Verla, A.W.; Verla, E.N.; Ibe, F.C.; Amaobi, C.E. Airborne microplastics: A review study on method for analysis, occurrence, movement and risks. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 2019, 191, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Pereira, R. Morphological and physical characterization of microplastics. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 75, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutroneo, L.; Reboa, A.; Geneselli, I.; Capello, M. Considerations on salts used for density separation in the extraction of microplastics from sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, W.; Fu, L.; Yin, C.; Fernandez, C.; Karimi-Maleh, H. Current development and future challenges in microplastic detection techniques: A bibliometrics-based analysis and review. Sci. Progr. 2022, 105, 00368504221132151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erni-Cassola, G.; Gibson, M.I.; Thompson, R.C.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Lost, but found with Nile red: A novel method for detecting and quantifying small microplastics (1 mm to 20 µm) in environmental samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13641–13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Wontor, K.; Cizdziel, J.V. Labeling microplastics with fluorescent dyes for detection, recovery, and degradation experiments. Molecules 2022, 27, 7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Tan, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Tan, X.; Chen, Q. Characteristic of microplastics in the atmospheric fallout from Dongguan city, China: Preliminary research and first evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24928–24935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, A.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.; Nagraik, R. An insight into different microplastic detection methods. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 5721–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, Q.; Luo, J.; Pan, Y.; Feng, H. Fusion and Solvent Evaporation Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Rapid Detection of Microplastics (MPs). Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 4687–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albignac, M.; de Oliveira, T.; Landebrit, L.; Miquel, S.; Auguin, B.; Leroy, E.; Maria, E.; Mingotaud, A.F.; ter Halle, A. Tandem mass spectrometry enhances the performances of pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for microplastic quantification. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2023, 172, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.Y.; Lai, Y.J.; Yu, S.J.; Li, Q.C.; Zhou, Q.X.; Liu, J.F. Quantitation of atmospheric suspended polystyrene nanoplastics by active sampling prior to pyrolysis–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10754–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.; Okoffo, E.D.; O’Brien, J.W.; Ribeiro, F.; Wang, X.; Wright, S.L.; Samanipour, S.; Rauert, C.; Toapanta, T.Y.A.; Albarracin, R.; et al. Airborne emissions of microplastic fibres from domestic laundry dryers. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 747, 141175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermabessiere, L.; Himber, C.; Boricaud, B.; Kazour, M.; Amara, R.; Cassone, A.L.; Laurentie, M.; Paul-Pont, I.; Soudant, P.; Dehaut, A.; et al. Optimization, performance, and application of a pyrolysis-GC/MS method for the identification of microplastics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6663–6676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, F.; Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Song, J.; Wang, W.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yan, J. Influence of interaction on accuracy of quantification of mixed microplastics using Py-GC/MS. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Chu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liao, Z.; Ji, X.; Ju, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, Z.; Dahlgren, R.; et al. Micro-and Nano-plastics in the atmosphere: A review of occurrence, properties and human health risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Guo, S.; Shen, D.; Shentu, J.; Lu, L.; Qi, S.; Zhu, M.; Long, Y. Characteristics and release potential of microplastics in municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Gómez, I.; Suarez-Suarez, M.; Moreno, J.M.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Negral, L.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; López-García, I.; Peñalver, R. A novel application of thermogravimetry-mass spectrometry for polystyrene quantification in the PM10 and PM2. 5 fractions of airborne microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalver, R.; Costa-Gómez, I.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Moreno, J.M.; López-García, I.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Córdoba, M.H. Assessing the level of airborne polystyrene microplastics using thermogravimetry-mass spectrometry: Results for an agricultural area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorolla-Rosario, D.; Llorca-Porcel, J.; Pérez-Martínez, M.; Lozano-Castelló, D.; Bueno-López, A. Microplastics’ analysis in water: Easy handling of samples by a new Thermal Extraction Desorption-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (TED-GC/MS) methodology. Talanta 2023, 253, 123829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ma, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X. Pretreatment, identification and quantification of submicro/nano-plastics in complex environmental matrices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, W.; Han, B.; Wu, T.; Yan, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Online in situ detection of atmospheric microplastics based on laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. J. Laser Appl. 2025, 37, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukotaka, A.; Kataoka, T.; Nihei, Y. Rapid analytical method for characterization and quantification of microplastics in tap water using a Fourier-transform infrared microscope. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netema, B.N.; Chakraborty, T.K.; Nice, M.S.; Islam, K.R.; Debnath, P.C.; Chowdhury, P.; Rahman, S.; Halder, M.; Zaman, S.; Ghosh, G.C.; et al. Appraisal of microplastic pollution and its related risks for urban indoor environment in Bangladesh using machine learning and diverse risk evolution indices. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 360, 124631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, J.J. Characterization of Microplastics Using Fourier Infrared Spectroscopy. In Microplastics and Pollutants: Interactions, Degradations and Mechanisms; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-54565-8_6 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Veerasingam, S.; Ranjani, M.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Bagaev, A.; Mukhanov, V.; Litvinyuk, D.; Mugilarasan, M.; Gurumoorthi, K.; Guganathan, L.; Aboobacker, V.M.; et al. Contributions of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy in microplastic pollution research: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 2681–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Savino, I.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to assess the degree of alteration of artificially aged and environmentally weathered microplastics. Polymers 2023, 15, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, M.; Kang, J.H.; Kwon, O.Y.; Han, G.M.; Shim, W.J. Large accumulation of micro-sized synthetic polymer particles in the sea surface microlayer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9014–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oßmann, B.E. Microplastics characterization by Raman microscopy. In Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Methods for sampling and detection of microplastics in water and sediment: A critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Levermore, J.M.; Kelly, F.J. Raman spectral imaging for the detection of inhalable microplastics in ambient particulate matter samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8947–8956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, B.; Aherne, J.; Paterson, A.M.; Yao, H.; McConnell, C. Atmospheric deposition of anthropogenic particles and microplastics in south-central Ontario, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L.; Mallach, G.; Kulka, R.; Halappanavar, S. Microplastics and nanoplastics science: Collecting and characterizing airborne microplastics in fine particulate matter. Nanotoxicol. 2021, 15, 1253–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.; Seo, K.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.; Tanaka, M.; Lee, K.; Choi, J. Methods of analyzing microsized plastics in the environment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.; Liddle, C.R.; Williams, B.; Hilmer, E.; Quick, L.J.; Garcia, A.G.; Suárez, D.C.; White, D.; Bunting, M.J.; Walker, P.; et al. Airborne microplastic monitoring: Developing a simplified outdoor sampling approach using pollen monitoring equipment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokammel, A.; Naddafi, K.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Nabizadeh, R.; Faridi, S.; Noruzzade, E.; Yaghmaeian, K. Airborne Microplastics Pollution in Municipal Solid Waste Processing and Disposal Complex: Concentration, Characterization, and Composition. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 11, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, D.; Pei, J.; Fei, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y. Identification and quantification of microplastics using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy: Current status and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 18, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.; Lee, C.; Belchez, C.; Shipper, A.G.; Wiens, K.E. Microplastics in Urban Ambient Air: A Rapid Review of Active Sampling and Analytical Methods for Human Risk Assessment. Environments 2024, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizi, L.; Simon-Sánchez, L.; Vianello, A.; Nielsen, A.H.; Vollertsen, J. Every breath you take: High concentration of breathable microplastics in indoor environments. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Mutalib, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Jaafar, J. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy. In Membrane Characterization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Dana, P.; Gaga, E.O.; Gedik, K. Analytical Challenges and Strategies for Particle-Based Analysis of Airborne Micro (nano) plastics in Size-Fractionated Samples Using Microscopy, SEM/EDX, and Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 20622–20634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, L.E.; Kuma, P.; Le Ru, E.C.; Somerville, W.R.; Gaw, S. Direct radiative effects of airborne microplastics. Nature 2021, 598, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, L.; Aves, A.; MacDonald, A.; Allen, D.; Allen, S.; Materic, D.; Gaw, S.; Davy, P.; Naeher, S. Quantifying the uncertainty and errors between common analytical methods for measuring airborne microplastics. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2023; p. EGU-1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Rivera, D.M.; Quintanilla-Villanueva, G.E.; Luna-Moreno, D.; Sánchez-Álvarez, A.; Rodríguez-Delgado, J.M.; Cedillo-González, E.I.; Kaushik, G.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.M. Exploring Innovative Approaches for the Analysis of Micro-and Nanoplastics: Breakthroughs in (Bio) Sensing Techniques. Biosensors 2025, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Zheng, B.; Huang, W.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Fu, R. A scalable molecular-templating strategy toward well-defined microporous carbon aerogels for efficient water treatment and electrocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latiza, R.J.P.; Olay, J.; Eguico, C.; Yan, R.J.; Rubi, R.V. Environmental applications of carbon dots: Addressing microplastics, air and water pollution. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H.M.; Yang, K.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Ying, K.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Zhang, K.; et al. Advancing the Understanding of Microplastic Weathering: Insights from a Novel Polarized Light Scattering Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 19004–19015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Nie, Z.; Meng, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, Y.; Chai, G. Influence of meteorological conditions on atmospheric microplastic transport and deposition. Environ. Res. 2024, 265, 120460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzl, J.; Seifried, T.M.; Stolzenburg, D.; Grothe, H. A fluorescence approach for an online measurement technique of atmospheric microplastics. Environ. Sci. Atmosp. 2024, 4, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rednikin, A.R.; Frank, Y.A.; Rozhin, A.O.; Vorobiev, D.S.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Airborne Microplastics: Challenges, Prospects, and Experimental Approaches. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunnbauer, L.; Jirku, M.; Quarles Jr, C.D.; Limbeck, A. Capabilities of simultaneous 193 nm-LIBS/LA-ICP-MS imaging for microplastics characterization. Talanta 2024, 269, 125500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Song, Z.; Li, D. Efficient transport of atmospheric microplastics onto the continent via the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Okochi, H.; Tani, Y.; Hayami, H.; Minami, Y.; Katsumi, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Sorimachi, A.; Fujii, Y.; Kajino, M.; et al. Airborne hydrophilic microplastics in cloud water at high altitudes and their role in cloud formation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Good, K.D. Microplastics and PFAS air-water interaction and deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Dong, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Ni, G.; Guo, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Airborne nanoplastics exposure inducing irreversible glucose increase and complete hepatic insulin resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3108–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Wei, N.; Ye, H.; Cong, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Qu, L.; Zhu, L.; et al. Global inventory of atmospheric fibrous microplastics input into the ocean: An implication from the indoor origin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafea, T.H.; Chan, F.K.S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Ji, D.; Xiao, H.; He, J. Microplastics Aloft: A comprehensive exploration of sources, transport, variations, interactions and their implications on human health in the atmospheric realm. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 255, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, B.O.; Souza, A.K.M.D.; Soares, P.L.; Palma, A.R.T.; Vendel, A.L. How to control the airborne contamination in laboratory analyses of microplastics? Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2022, 65, e22210399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Lee, Y.; Ro, C.U. Single-particle investigation of airborne microplastics of inhalable size (<10 µm) using fluorescence microscopy, Raman microspectrometry, and scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry in combination. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2023; p. EGU-11138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, W.; Pan, Q.; Li, J. Metal-organic framework-based wood aerogel for effective removal of micro/nano plastics. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2022, 38, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoellner, A. Measuring airborne nanoplastics using aerosol physics. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifried, T.M.; Nikkho, S.; Morales Murillo, A.; Andrew, L.J.; Grant, E.R.; Bertram, A.K. Microplastic particles contain ice nucleation sites that can be inhibited by atmospheric aging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 15711–15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Shin, Y.; Song, I.G.; Lim, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Weon, S. Atmospheric Microplastics: Challenges in Site-and Target-Specific Measurements. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 178, 117859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Feng, Q.; Wang, J. Mini-review of microplastics in the atmosphere and their risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Liu, K.; Zhu, L.; Song, Z.; Li, D. Atmospheric microplastic over the South China Sea and East Indian Ocean: Abundance, distribution and source. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, G.; An, L.; Fang, W.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Bing, X.; Song, Q.; Zhou, Q.; et al. A comprehensive risk assessment of microplastics in soil, water, and atmosphere: Implications for human health and environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Lyu, H.; Tang, J. Adsorption of PCBs on microplastics mitigated greenhouse gas emission by changing C/N metabolism in freshwater sediment. J. Clean. Product. 2024, 434, 139883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M. Trending Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Microplastics (MPs) and Nano-plastics (NPs) in Different Physical Environments and Their Role in Various Emerging Environmental Issues: A Review. 2024. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5095223 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Zhang, T.; Luo, X.S.; Kumar, A.; Liu, X.; Tong, X.; Yao, X.; Fan, J.; Chen, Z.; Chaturvedi, S. Effects of micro-nano plastics on the environmental biogeochemical cycle of nitrogen: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2024, 357, 142079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Li, Y.; Jones, T.; Santosh, M.; Liu, P.; Zhang, M.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Lu, J.; Yang, C.-X.; et al. Airborne microplastics: A review of current perspectives and environmental implications. J. Clean. Product. 2022, 347, 131048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Azevedo, A.; Pinto, E.C.; de Cata Preta Correa, G.A.; Bouskela, E. SARS-CoV-2 infection causes pulmonary shunt by vasodilatation. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prattichizzo, F.; Ceriello, A.; Pellegrini, V.; La Grotta, R.; Graciotti, L.; Olivieri, F.; Paolisso, G. Micro-nanoplastics and cardiovascular diseases: Evidence and perspectives. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, ehae552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattanasit, U.; Kongpran, J.; Keda, A. Airborne microplastics: A narrative review of potential effects on the human respiratory system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, D. Enemies of the hormones: Microplastics and endocrine disruptors impacting public health. In Health and Climate Change; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 119–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Saha, G. Effect of microplastics deposition on human lung airways: A review with computational benefits and challenges. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, U.; Kumari, P.; Ghosh, A.; Sinha, A.; Jena, S.; Kirti, A.; Gupta, A.; Choudhury, A.; Simnani, F.Z.; Nandi, A.; et al. Detrimental consequences of micropolymers associated plasticizers on endocrinal disruption. Mater. Today Bio 2024, 27, 101139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, K.S.; Khokhar, M.F.; Parvez, S.; Niazi, M.B.K. Emerging environmental challenge: A critical review of airborne microplastics. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 092003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kek, H.Y.; Tan, H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Ho, W.S.; Sheng, D.D.C.V.; Wong, K.Y. Critical review on airborne microplastics: An indoor air contaminant of emerging concern. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 118055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portugal, J.; Bedia, C.; Amato, F.; Juárez-Facio, A.T.; Stamatiou, R.; Lazou, A.; Piña, B. Toxicity of airborne nanoparticles: Facts and challenges. Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.P. Understanding the dynamics and implications of airborne microplastics in atmosphere. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2024, 17, 2661–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozunu, A.; Irankunda, E.; Valeria, P.O.P.; Cui, Z.; Crăciun, A.I. The Critical Analysis of Air Pollution and Soil Pollution with Microplastics and Heavy Metal in Rwanda, Roumania and China. Rev. Roum. Chim 2024, 69, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarska, E.; Jutel, M.; Zemelka-Wiacek, M. The potential impact of nano-and microplastics on human health: Understanding human health risks. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, C.; Song, J.; Yu, S.; Liao, G.; Zou, P.; Tang, K.H.D.; Wu, C. Airborne microplastics: Occurrence, sources, fate, risks and mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Q.; Wang, C.C.; Ma, R.X.; Qi, S.Q.; Fu, W.; Zhong, J.; Cao, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Gao, Y.D. Co-exposure to polyethylene microplastics and house dust mites aggravates airway epithelial barrier dysfunction and airway inflammation via CXCL1 signaling pathway in a mouse model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 146, 113921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Yang, W.; Dong, H.; Liu, T.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Co-Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics and Bisphenol A Contributes to the Formation of Liver Fibrosis in Mice through Inhibition of the BMAL1/E-Cad Signaling Pathway. J. Agricult. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 7405–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Larpruenrudee, P.; Arsalanloo, A.; Beni, H.M.; Islam, M.A.; Sauret, E. How microplastics are transported and deposited in realistic upper airways? Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 063319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, S.V.; Liddle, C.R.; Atherall, C.A.; Chapman, E.; Watkins, M.; Calaminus, S.D.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastics in human blood: Polymer types, concentrations and characterisation using µFTIR. Environ. Int. 2024, 188, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Chen, J.; Ni, B.-J. Toxicity of micro/nanoplastics in the environment: Roles of plastisphere and eco-corona. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Dalu, T.; Kadushkin, A.; Singh, J.; Fakhrullin, R.; Wang, F.; Cai, X.; Li, R. Coronas of micro/nano plastics: A key determinant in their risk assessments. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Guo, Y.; He, L.; Liao, X.; Chen, X.; He, L.; Lu, Z.; Qian, Z.-J.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; et al. Nanoplastics aggravate the toxicity of arsenic to AGS cells by disrupting ABC transporter and cytoskeleton. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, K.; Zhang, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, W. Cellular internalization and release of polystyrene microplastics and nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Qu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Xiong, F.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Sun, R. Research progress on the cellular toxicity caused by microplastics and nanoplastics. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2023, 43, 1576–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Ha, E.-S.; Jung, Y.-S.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Cationic nanoplastic causes mitochondrial dysfunction in neural progenitor cells and impairs hippocampal neurogenesis. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2023, 208, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, J.; Annangi, B.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A.; Catalán, J. Insights into the potential carcinogenicity of micro-and nano-plastics. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2023, 791, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.; Li, S.; Zhuge, A.; Shen, J.; Yao, Y.; Chang, K.; Li, L. Hazard assessment of airborne and foodborne biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates microplastics and non-biodegradable polypropylene microplastics. Environ. Int. 2025, 196, 109311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Salam, A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Bari, A.; Aich, N.; Jahan, F.; Rahman, M.; Islam, Z.; Kabir, H.; Shaikh, A.A.; et al. Understanding the occurrence and fate of atmospheric microplastics and their potential risks to human health: A study protocol for cross-sectional analysis. JMIR Res. Prot. 2024, 13, e60289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wei, Y.; Hu, L.J.; Zeng, F.M.; Chen, Y.W.; Xu, D.; He, M. Inhalation of Microplastics Induces Inflammatory Injuries in Multiple Murine Organs via the Toll-like Receptor Pathway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 18603–18618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, T.; Ge, Y.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liang, G. Inhalation exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics induces chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-like lung injury in mice through multi-dimensional assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, H.; Xia, J.; Li, S.; Lv, J.; Zhuge, A.; Tang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Chang, K.; Li, L. Airborne polystyrene microplastics and nanoplastics induce nasal and lung microbial dysbiosis in mice. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Jia, H. Is the impact of atmospheric microplastics on human health underestimated? Uncertainty in risk assessment: A case study of urban atmosphere in Xi’an, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.T.; Hou, S.N.; Miao, Y.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Cui, H.; Zhu, H. Synergistic effects of microplastics and sulfonamide on greenhouse gas emissions in agricultural ditch sediments: Insights into microbial interactions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakes, L.C.; Patmore, I.R.; Bancone, C.E.; Rose, N.L. High temporal resolution records of outdoor and indoor airborne microplastics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 39246–39257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, F.; Sorrentino, M.C.; Granata, A.; Vergara, A.; Alberico, M.; Rossi, M.; Spagnuolo, V.; Giordano, S. Optimizing moss and lichen transplants as biomonitors of airborne anthropogenic microfibers. Biology 2023, 12, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, C.; Vadivel, D.; Dondi, D. The current situation of the legislative gap on microplastics (MPs) as new pollutants for the environment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqash, A.; Anwar, J.; Qadir, A.; Hussain, R.; Jamil, N. Source identification, characteristics, and spatial distribution of airborne microplastic deposition in Lahore City, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 54905–54919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciolà, A.; Visalli, G.; Pruiti Ciarello, M.; Di Pietro, A. Newly emerging airborne pollutants: Current knowledge of health impact of micro and nanoplastics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapea, A. A scientific perspective on microplastics in nature and society. In Science Advice for Policy by European Academies; ALLEA Secretariat: Berlin, Germany, 2019; Available online: https://allea.org/science-advice-for-policy-by-european-academies/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Jafarova, M.; Grifoni, L.; Aherne, J.; Loppi, S. Comparison of lichens and mosses as biomonitors of airborne microplastics. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Do, H.T.; Nguyen, T.L.; Thi, L.A.P.; Dang, T.H.L. Microplastics in the atmosphere: Transportation and impact on humans. In Microplastics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 181–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, S. Airborne microplastics: A review on the occurrence, migration and risks to humans. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shi, G.; Revell, L.E.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, C.; Wang, D.; Le Ru, E.C.; Wu, G.; Mitrano, D.M. Long-range atmospheric transport of microplastics across the southern hemisphere. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollo, M.S.; Villagra, E.L.; Gomez, J.J. Atmospheric microplastic accumulation in Ramalina celastri (Sprengel) Krog & Swinscow Thalli: A transplant study across different levels of urbanization. Folia Oecologica 2025, 52, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.C.; Chen, K.Y. Assessing the impact of marine litter hotspot on atmospheric microplastics: A study of a coastal village. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Wang, H.; Gu, X.; Liu, S.; Xiong, Y.; Deng, S.; Li, S. Atmospheric Microplastics Emission from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Power Plant: Field Evidence and Characterizations. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2025, 6, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamahara, S.; Nakata, H. Road dust-associated microplastics as a carrier of plastic additives in urban small-scale river sediment. Environ. Monit. Contam. Res. 2025, 5, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Hashemi, N.; Khodabakhshloo, N.; Mina, M.; Yousefi, M.R.; Turner, A. Transport and deposition of microplastics and microrubbers during a dust storm (Sarakhs, northeast Iran). Aeol. Res. 2024, 70, 100942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnahas, A.; Gray, A.; Lee, J.; AlAmiri, N.; Pokhrel, N.; Allen, S.; Foroutan, H. Atmospheric Deposition of Microplastics in South Central Appalachia in the United States. ACS EST Air 2024, 2, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, G.M.; de Moraes, A.D.S.; Dos Santos, G.B.; de Miranda, I.T.; Zucolotto, V.; Urban, R.C. Atmospheric microplastics deposition assessment in a countryside municipality in Southeastern Brazil: A case study at a state elementary school. Chemosphere 2024, 369, 143886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejano, J.B.B.; Araña, K.N.D.; Eleccion, E.B.; Laya-og, M.E.; Palasol, C.D.S.; Pimentel, C.S.; Bacosa, H.P. Microplastics in the Road Dust of Iligan City, the Philippines. Philip. J. Sci. 2024, 153, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Tian, X.; Bai, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Rillig, M.C.; Huang, Y.; Hu, M. Atmospheric microplastic input into wetlands: Spatiotemporal patterns, drivers, and unique ecological impacts. Water Res. 2024, 268, 122601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Zahedi, A.; Ravanbakhsh, M.; Abbaszadeh, S.; Turner, A. Microplastics in the atmosphere of Ahvaz City, Iran. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 126, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.Y.; Jeong, S.; Shin, J.; Park, J.; Park, C.R.; Choi, S.; Chun, C.-H.; Chae, M.-Y.; Lim, B.C. First quantification and chemical characterization of atmospheric microplastics observed in Seoul, South Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 327, 121481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, C.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Leganes, F.; Gómez, M.; Martínez, I.; Herrera, A.; Hernández-Sánchez, C.; González-Sálamo, J.; Borges, J.H.; López-Castellanos, J.; et al. A nationwide monitoring of atmospheric microplastic deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hee, Y.Y.; Hanif, N.M.; Weston, K.; Latif, M.T.; Suratman, S.; Rusli, M.U.; Mayes, A.G. Atmospheric microplastic transport and deposition to urban and pristine tropical locations in Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Costa, N.D.S.X.; Dantas, K.C.; dos Santos Galvão, L.; Moralles, F.N.; Lombardi, S.C.F.S.; Júnior, A.M.; Lindoso, J.A.L.; Ando, R.A.; Lima, F.G.; et al. Airborne microplastics and SARS-CoV-2 in total suspended particles in the area surrounding the largest medical centre in Latin America. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Sadofsky, L.R.; Danopoulos, E.; Rotchell, J.M. Household indoor microplastics within the Humber region (United Kingdom): Quantification and chemical characterisation of particles present. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, L.; Scibetta, L.; Markuszewski, P.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Drozdowska, V.; Makuch, P.; Jutrzenka-Trzebiatowska, P.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Andò, S.; Saliu, F.; et al. Airborne and marine microplastics from an oceanographic survey at the Baltic Sea: An emerging role of air-sea interaction? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.; Ziajahromi, S.; Bengtson Nash, S.; Manage, P.M.; Leusch, F.D. Airborne microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments of a developing country in south asia: Abundance, distribution, morphology, and possible sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16676–16685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwiyanto, A.I.S.; Prartono, T.; Riani, E.; Naulita, Y.; Cordova, M.R.; Koropitan, A.F. The deposition of atmospheric microplastics in Jakarta-Indonesia: The coastal urban area. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2022, 174, 113195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wei, N.; Liu, K.; Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Zong, C.; Li, D. Exponential decrease of airborne microplastics: From megacity to open ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Dobaradaran, S.; Torkmahalleh, M.A.; Saeedi, R.; Aibaghi, R.; Ghasemi, F.F. Suspended fine particulate matter (PM2.5), microplastics (MPs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in air: Their possible relationships and health implications. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Baladima, F.; Phoenix, V.R.; Thomas, J.L.; Le Roux, G.; Sonke, J.E. Evidence of free tropospheric and long-range transport of microplastic at Pic du Midi Observatory. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, M.; Gong, P.; Wang, C. Microplastics in a remote lake basin of the Tibetan Plateau: Impacts of atmospheric transport and glacial melting. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12951–12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Edo, C.; Aguilera, Á.; Viúdez-Moreiras, D.; Pulido-Reyes, G.; González-Toril, E.; Osuna, S.; de Diego-Castilla, G.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; et al. Occurrence and transport of microplastics sampled within and above the planetary boundary layer. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, T.; Yan, M.; Yang, L.; Gong, H.; Wang, W.; Qing, X.; Wang, J. Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a subtropical urban environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Ji, X.; Ma, Y.; Lv, B.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X.; Fang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Dahlgren, R.; et al. Airborne microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments of a coastal city in Eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.N.S.; Strady, E.; Kieu-Le, T.C.; Tran, Q.V.; Le, T.M.T.; Thuong, Q.T. Microplastic in atmospheric fallouts of a developing Southeast Asian megacity under tropical climate. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Huang, W.; Fang, M.; Liao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Mu, Q.; Shi, C.; Lu, C.; Deng, H.; et al. Airborne microplastic concentrations in five megacities of northern and southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12871–12881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahney, J.; Hallerud, M.; Heim, E.; Hahnenberger, M.; Sukumaran, S. Plastic rain in protected areas of the United States. Science 2020, 368, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Feng, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, D. Airborne fiber particles: Types, size and concentration observed in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roblin, B.; Ryan, M.; Vreugdenhil, A.; Aherne, J. Ambient atmospheric deposition of anthropogenic microfibers and microplastics on the western periphery of Europe (Ireland). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11100–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trainic, M.; Flores, J.M.; Pinkas, I.; Pedrotti, M.L.; Lombard, F.; Bourdin, G.; Gorsky, G.; Boss, E.; Rudich, Y.; Vardi, A.; et al. Airborne microplastic particles detected in the remote marine atmosphere. Comm. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastic abundance in atmospheric deposition within the Metropolitan area of Hamburg, Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Fang, T.; Xu, P.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Wei, N.; Song, Z.; Li, D. Accurate quantification and transport estimation of suspended atmospheric microplastics in megacities: Implications for human health. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Zong, C.; Wei, N.; Li, D. Consistent transport of terrestrial microplastics to the ocean through atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10612–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, T.; Johnson, M.; Nathanail, P.; MacNaughtan, W.; Gomes, R.L. Freshwater and airborne textile fibre populations are dominated by ‘natural’, not microplastic, fibres. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafei, A.D.; Nurasrin, N.R.; Assomadi, A.F.; Boedisantoso, R. Microplastic pollution in the ambient air of Surabaya, Indonesia. Curr. World Environ. 2019, 14, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.T.; Yurtsever, M.; Bayraktar, S.C. Ubiquitous exposure to microfiber pollution in the air. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Delshab, H.; Soltani, N.; Sorooshian, A. Investigation of microrubbers, microplastics and heavy metals in street dust: A study in Bushehr city, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Tian, C.; Luo, Y. Various forms and deposition fluxes of microplastics identified in the coastal urban atmosphere. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 3902–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fang, L.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Lan, T.; Dong, J.; Lu, Z.; Li, Q.; et al. Unveiling the Systemic Impact of Airborne Microplastics: Integrating Breathomics and Machine Learning with Dual-Tissue Transcriptomics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, I.; Qadir, A.; Ahmad, S.R. A preliminary assessment of microplastics in indoor dust of a developing country in South Asia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Chen, C.; Gan, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Zeng, W.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, L.; Lu, Z.; et al. Indoor microplastics and bacteria in the atmospheric fallout in urban homes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashfi, F.S.; Ramavandi, B.; Arfaeinia, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Saeedi, R.; De-la-Torre, G.E.; Dobaradaran, S. Occurrence and exposure assessment of microplastics in indoor dusts of buildings with different applications in Bushehr and Shiraz cities, Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nematollahi, M.J.; Zarei, F.; Keshavarzi, B.; Zarei, M.; Moore, F.; Busquets, R.; Kelly, F.J. Microplastic occurrence in settled indoor dust in schools. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Skoczynska, E.; Siddhanti, D.; van Putten, R.J.; Leslie, H.A.; Gruter, G.J.M. Quantification of polyethylene terephthalate microplastics and nanoplastics in sands, indoor dust and sludge using a simplified in-matrix depolymerization method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Agullo, A.; Karanasiou, A.; Moreno, T.; Lacorte, S. Airborne microplastic particle concentrations and characterization in indoor urban microenvironments. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Y. Inhalable microplastics prevails in air: Exploring the size detection limit. Environ. Int. 2022, 162, 107151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liao, K.; Wu, P.; Jin, H. Microplastics in dust from different indoor environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, N.S.; Taylor, M.P.; Wilson, S.P. Quantification and exposure assessment of microplastics in Australian indoor house dust. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xumiao, L.; Prata, J.C.; Alves, J.R.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Cerqueira, M. Airborne microplastics and fibers in indoor residential environments in Aveiro, Portugal. Environ. Adv. 2021, 6, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Tang, X.; Gong, X.; Dai, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Development and application of a mass spectrometry method for quantifying nylon microplastics in environment. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13930–13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Du, F.; Cai, H.; Wang, G.; Shi, H. Microplastic fallout in different indoor environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6530–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Kannan, K. Microplastics in house dust from 12 countries and associated human exposure. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, J.; Gao, Y.; Sun, H. Widespread distribution of PET and PC microplastics in dust in urban China and their estimated human exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianello, A.; Jensen, R.L.; Liu, L.; Vollertsen, J. Simulating human exposure to indoor airborne microplastics using a Breathing Thermal Manikin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, A.I.; Macchia, V.; Sanderson, W.G.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Low levels of microplastics (MP) in wild mussels indicate that MP ingestion by humans is minimal compared to exposure via household fibres fallout during a meal. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casella, C.; Cornelli, U.; Ballaz, S.; Zanoni, G.; Merlo, G.; Ramos-Guerrero, L. Plastic Smell: A Review of the Hidden Threat of Airborne Micro and Nanoplastics to Human Health and the Environment. Toxics 2025, 13, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050387
Casella C, Cornelli U, Ballaz S, Zanoni G, Merlo G, Ramos-Guerrero L. Plastic Smell: A Review of the Hidden Threat of Airborne Micro and Nanoplastics to Human Health and the Environment. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050387
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasella, Claudio, Umberto Cornelli, Santiago Ballaz, Giuseppe Zanoni, Gabriele Merlo, and Luis Ramos-Guerrero. 2025. "Plastic Smell: A Review of the Hidden Threat of Airborne Micro and Nanoplastics to Human Health and the Environment" Toxics 13, no. 5: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050387
APA StyleCasella, C., Cornelli, U., Ballaz, S., Zanoni, G., Merlo, G., & Ramos-Guerrero, L. (2025). Plastic Smell: A Review of the Hidden Threat of Airborne Micro and Nanoplastics to Human Health and the Environment. Toxics, 13(5), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050387







