Short-Term Effect of Ozone Exposure on Small Airway Function in Adult Asthma Patients with PM2.5 Exacerbating the Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Lung Function Tests
2.3. Environmental Exposures
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
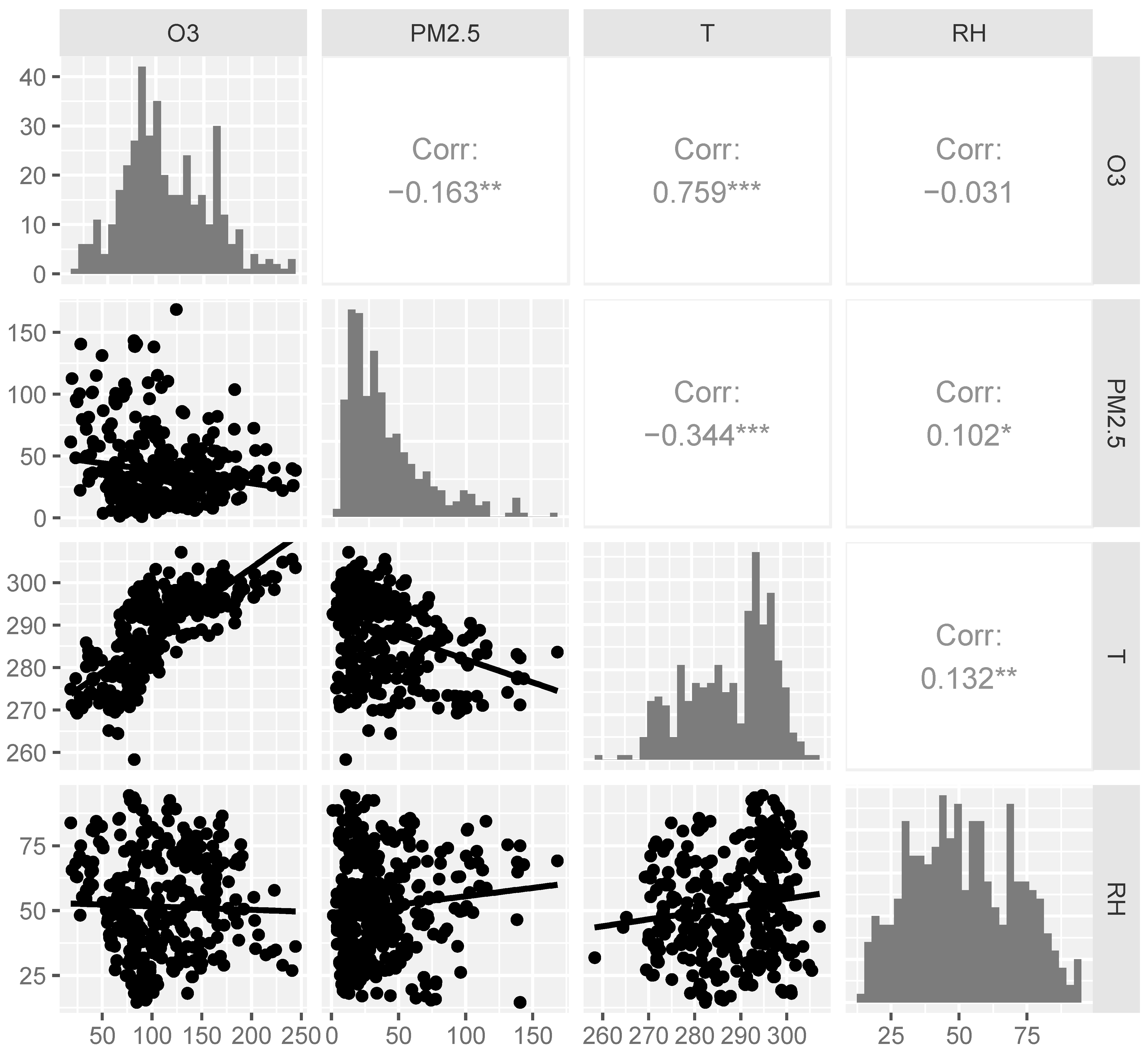
3.1. Study Population and Environmental Variables
3.2. Effects of Ambient O3 on Small Airway Function in Patients with Asthma
3.3. Interactions of Ambient O3 with PM2.5
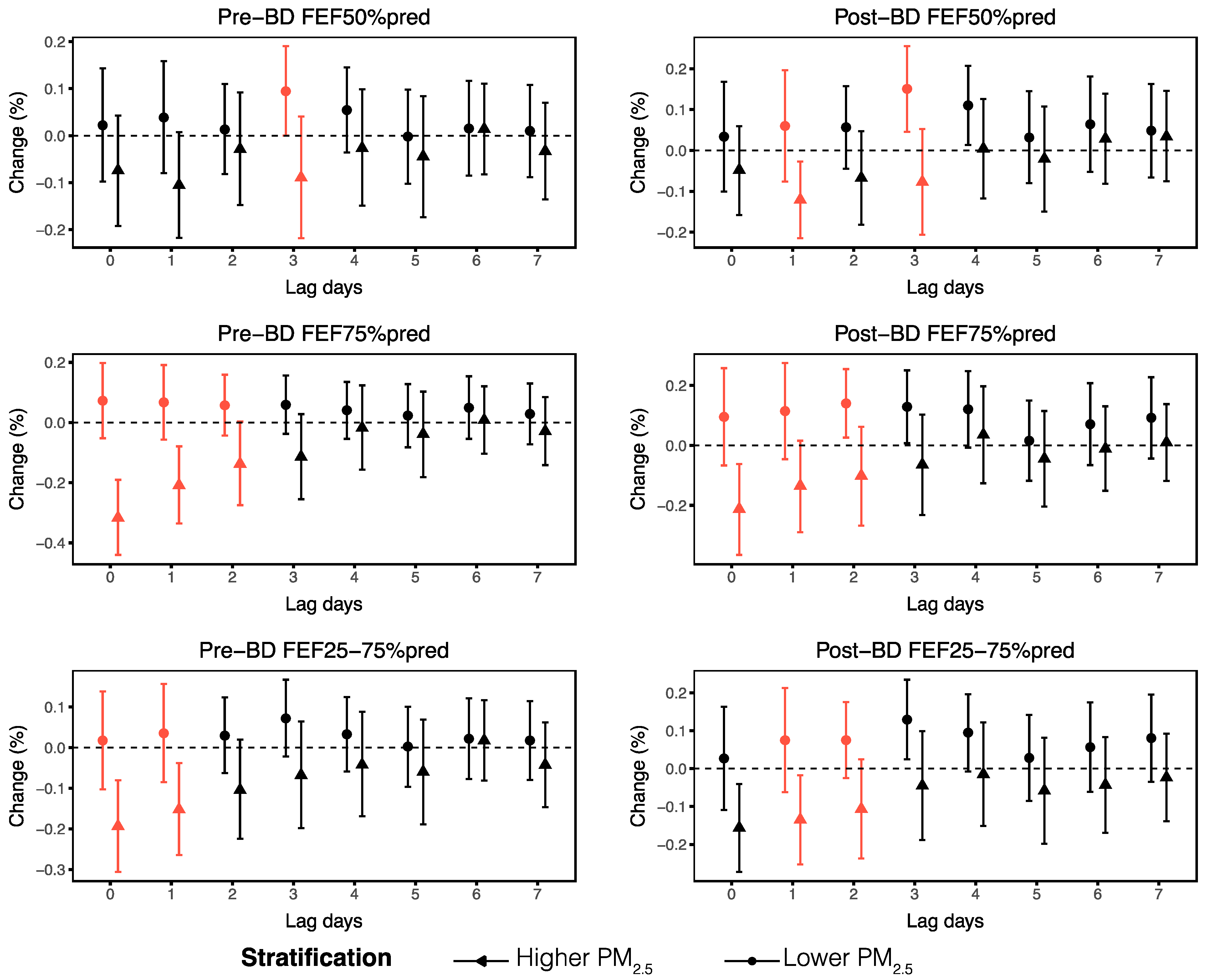
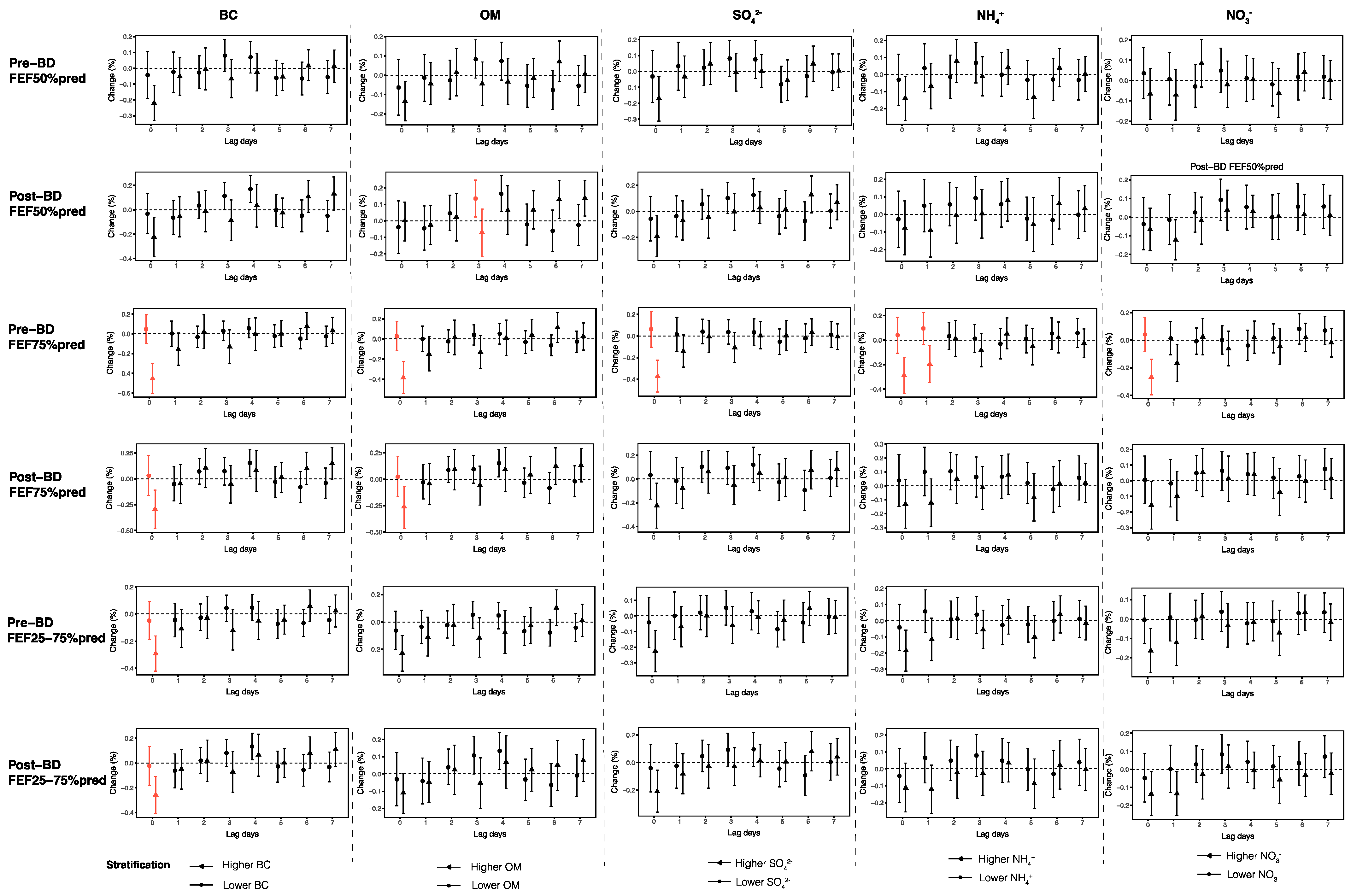
3.4. Stratified Analyses
3.5. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| BC | black carbon |
| FEF | forced expiratory flow |
| FVC | forced vital capacity |
| FEF50% | forced expiratory flow at 50% of forced vital capacity |
| FEF75% | forced expiratory flow at 75% of forced vital capacity |
| FEF25–75% | forced expiratory flow at 25–75% of forced vital capacity |
| FEV1 | forced expiratory volume in one second |
| NOx | nitrogen oxides |
| NO3− | nitrate |
| NH4+ | ammonium |
| O3 | ozone |
| OM | organic matter |
| PM2.5 | fine particulate matter |
| Pre-BD | prebronchodilator |
| Post-BD | postbronchodilator |
| RH | relative humidity |
| SO42− | sulfate |
| SAD | small airway dysfunction |
| T | temperature |
| VOCs | volatile organic compounds |
References
- Diseases, G.B.D.; Injuries, C. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer, K.; Lesosky, M.; Garcia-Marcos, L.; Asher, M.I.; Pearce, N.; Ellwood, E.; Bissell, K.; El Sony, A.; Ellwood, P.; Marks, G.B.; et al. The burden of asthma, hay fever and eczema in adults in 17 countries: GAN Phase I study. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Yang, T.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; Kang, J.; Ran, P.; Shen, H.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of asthma in China: A national cross-sectional study. Lancet 2019, 394, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agache, I.; Canelo-Aybar, C.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Cecchi, L.; Rigau, D.; Rodriguez-Tanta, L.Y.; Nieto-Gutierrez, W.; Song, Y.; Cantero-Fortiz, Y.; Roque, M.; et al. The impact of outdoor pollution and extreme temperatures on asthma-related outcomes: A systematic review for the EAACI guidelines on environmental science for allergic diseases and asthma. Allergy 2024, 79, 1725–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Yildizhan, H.; Udristioiu, M.T.; Pekdogan, T.; Ameen, A. Observational study of ground-level ozone and climatic factors in Craiova, Romania, based on one-year high-resolution data. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26733. [Google Scholar]
- Anenberg, S.C.; Henze, D.K.; Tinney, V.; Kinney, P.L.; Raich, W.; Fann, N.; Malley, C.S.; Roman, H.; Lamsal, L.; Duncan, B.; et al. Estimates of the Global Burden of Ambient [Formula: See text], Ozone, and [Formula: See text] on Asthma Incidence and Emergency Room Visits. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 107004. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Qiu, X.; Sabath, M.B.; Yazdi, M.D.; Yin, K.; Li, L.; Peralta, A.A.; Wang, C.; Koutrakis, P.; Zanobetti, A.; et al. Air Pollutants and Asthma Hospitalization in the Medicaid Population. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Markevych, I.; Fuertes, E.; de Hoogh, K.; Accordini, S.; Boudier, A.; Casas, L.; Forsberg, B.; Garcia Aymerich, J.; Gnesi, M.; et al. Impact of long-term exposure to ambient ozone on lung function over a course of 20 years (The ECRHS study): A prospective cohort study in adults. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2023, 34, 100729. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Na, G.; Jang, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.C.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, H.C.; et al. The impact of ambient air pollution on lung function and respiratory symptoms in elite athletes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158862. [Google Scholar]
- Vinikoor-Imler, L.C.; Owens, E.O.; Nichols, J.L.; Ross, M.; Brown, J.S.; Sacks, J.D. Evaluating potential response-modifying factors for associations between ozone and health outcomes: A weight-of-evidence approach. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Usmani, O.S.; Singh, D.; Spinola, M.; Bizzi, A.; Barnes, P.J. The prevalence of small airways disease in adult asthma: A systematic literature review. Respir. Med. 2016, 116, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Postma, D.S.; Brightling, C.; Baldi, S.; Van den Berge, M.; Fabbri, L.M.; Gagnatelli, A.; Papi, A.; Van der Molen, T.; Rabe, K.F.; Siddiqui, S.; et al. Exploring the relevance and extent of small airways dysfunction in asthma (ATLANTIS): Baseline data from a prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toumpanakis, D.; Usmani, O.S. Small airways in asthma: Pathophysiology, identification and management. Chin. Med. J. Pulm. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 1, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Huang, K.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; Kang, J.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of small airway dysfunction, and association with smoking, in China: Findings from a national cross-sectional study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.G.; Lee, P.H.; Choi, S.M.; An, M.H.; Jang, A.S. Effects of Air Pollutants on Airway Diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, M.; Fine, R.D.; Saha, S.; Wang, Z.; Zang, C.; Li, M.; Smith, J.S. Fob1-dependent condensin recruitment and loop extrusion on yeast chromosome III. PLoS Genet. 2023, 19, e1010705. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Yang, T.; Gu, X.; Chen, R.; Meng, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; et al. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Small Airway Dysfunction: The China Pulmonary Health (CPH) Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 450–458. [Google Scholar]
- Global Initiative for Athma (GINA). Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2021. Available online: https://ginasthma.org (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Xiao, Q.; Geng, G.; Xue, T.; Liu, S.; Cai, C.; He, K.; Zhang, Q. Tracking PM2.5 and O3 Pollution and the Related Health Burden in China 2013–2020. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6922–6932. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yue, X.; Liu, Y.; Yin, C. Evaluation of IMERG and ERA5 precipitation products over the Mongolian Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21776. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Guo, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, L.; Silang, Y.; Hong, F.; et al. Long-term Exposure to Ambient PM2.5 and Its Components Associated With Diabetes: Evidence From a Large Population-Based Cohort From China. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Akar-Ghibril, N.; Casale, T.; Custovic, A.; Phipatanakul, W. Allergic Endotypes and Phenotypes of Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tager, I.B.; Balmes, J.; Lurmann, F.; Ngo, L.; Alcorn, S.; Kunzli, N. Chronic exposure to ambient ozone and lung function in young adults. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Yang, L.; Dou, S.; Li, X.; Wen, S.; Yan, L.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, B.; Yuan, L.; et al. Associations between long-term ozone exposure and small airways function in Chinese young adults: A longitudinal cohort study. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.Y.; Chao, H.J.; Chan, C.C.; Lee, C.T.; Wu, H.P.; Cheng, T.J.; Chen, C.C.; Guo, Y.L. Effects of ambient particulate matter and fungal spores on lung function in schoolchildren. Pediatrics 2011, 127, e690–e698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Chan, C.C.; Chen, B.Y.; Cheng, T.J.; Leon Guo, Y. Effects of particulate air pollution and ozone on lung function in non-asthmatic children. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dauchet, L.; Hulo, S.; Cherot-Kornobis, N.; Matran, R.; Amouyel, P.; Edme, J.L.; Giovannelli, J. Short-term exposure to air pollution: Associations with lung function and inflammatory markers in non-smoking, healthy adults. Environ. Int. 2018, 121 Pt 1, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaudel, C.; Mackowiak, C.; Maillet, I.; Fauconnier, L.; Akdis, C.A.; Sokolowska, M.; Dreher, A.; Tan, H.T.; Quesniaux, V.F.; Ryffel, B.; et al. Ozone exposure induces respiratory barrier biphasic injury and inflammation controlled by IL-33. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 942–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, G.G.; Weidenbach-Gerbase, M.; Foster, W.M.; Zacur, H.; Frank, R. Evidence for ozone-induced small-airway dysfunction: Lack of menstrual-cycle and gender effects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjomandi, M.; Witten, A.; Abbritti, E.; Reintjes, K.; Schmidlin, I.; Zhai, W.; Solomon, C.; Balmes, J. Repeated exposure to ozone increases alveolar macrophage recruitment into asthmatic airways. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, A.S.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.S.; Park, C.S. Prolonged ozone exposure in an allergic airway disease model: Adaptation of airway responsiveness and airway remodeling. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, B.; Mu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W. Short-term effects of real-time individual fine particulate matter exposure on lung function: A panel study in Zhuhai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 65140–65149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duan, R.; Niu, H.; Yu, T.; Huang, K.; Cui, H.; Chen, C.; Yang, T.; Wang, C. Adverse effects of short-term personal exposure to fine particulate matter on the lung function of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma: A longitudinal panel study in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 47463–47473. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Analysis of influencing factors and a predictive model of small airway dysfunction in adults. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, R.; Gu, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; Kang, J.; Ran, P.; et al. Association of fine particulate matter air pollution and its constituents with lung function: The China Pulmonary Health study. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106707. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Y.; Jin, C.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, B. Water soluble and insoluble components of urban PM2.5 and their cytotoxic effects on epithelial cells (A549) in vitro. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Majumder, N.; Goldsmith, W.T.; Kodali, V.K.; Velayutham, M.; Friend, S.A.; Khramtsov, V.V.; Nurkiewicz, T.R.; Erdely, A.; Zeidler-Erdely, P.C.; Castranova, V.; et al. Oxidant-induced epithelial alarmin pathway mediates lung inflammation and functional decline following ultrafine carbon and ozone inhalation co-exposure. Redox Biol. 2021, 46, 102092. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, T.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Effects of Ambient O3 on Respiratory Mortality, Especially the Combined Effects of PM2.5 and O3. Toxics 2023, 11, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowell, J.D.; Sun, Y.; Gause, E.L.; Spangler, K.R.; Schwartz, J.; Bernstein, A.; Wellenius, G.A.; Nori-Sarma, A. Warm season ambient ozone and children’s health in the USA. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 53, dyae035. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; Peng, L.; Yang, T.; Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Shi, S.; Liu, C.; Kan, H.; et al. Non-optimum ambient temperature may decrease pulmonary function: A longitudinal study with intensively repeated measurements among asthmatic adult patients in 25 Chinese cities. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107283. [Google Scholar]
- Kahle, J.J.; Neas, L.M.; Devlin, R.B.; Case, M.W.; Schmitt, M.T.; Madden, M.C.; Diaz-Sanchez, D. Interaction effects of temperature and ozone on lung function and markers of systemic inflammation, coagulation, and fibrinolysis: A crossover study of healthy young volunteers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, W.D.; Ivins, S.; Alexis, N.E.; Wu, J.; Bromberg, P.A.; Brar, S.S.; Travlos, G.; London, S.J. Effect of Obesity on Acute Ozone-Induced Changes in Airway Function, Reactivity, and Inflammation in Adult Females. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordeide Kuiper, I.; Svanes, C.; Markevych, I.; Accordini, S.; Bertelsen, R.J.; Braback, L.; Heile Christensen, J.; Forsberg, B.; Halvorsen, T.; Heinrich, J.; et al. Lifelong exposure to air pollution and greenness in relation to asthma, rhinitis and lung function in adulthood. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenquist, N.A.; Metcalf, W.J.; Ryu, S.Y.; Rutledge, A.; Coppes, M.J.; Grzymski, J.J.; Strickland, M.J.; Darrow, L.A. Acute associations between PM2.5 and ozone concentrations and asthma exacerbations among patients with and without allergic comorbidities. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, A.; Yang, H.; Ji, J.; Chen, Y.; Bao, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Ben, S. Involvements of p38 MAPK and oxidative stress in the ozone-induced enhancement of AHR and pulmonary inflammation in an allergic asthma model. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Poon, R.; Chen, L.; Frescura, A.M.; Montuschi, P.; Ciabattoni, G.; Wheeler, A.; Dales, R. Acute effects of air pollution on pulmonary function, airway inflammation, and oxidative stress in asthmatic children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Descriptive Information of 312 Participates | ||
|---|---|---|
| Variables | N (%) | |
| Age (years) | ||
| Mean (SD) | 40.87 (14.78) | |
| >40 | 136 (43.6) | |
| ≤40 | 176 (56.4) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) 1 | Mean (SD) | 24.26 (3.70) |
| ≥25 | 120 (38.5) | |
| <25 | 192 (61.5) | |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 172 (55.1) | |
| Male | 140 (44.9) | |
| Smoking status | ||
| Ex-smoker | 8 (2.6) | |
| Current smoker | 20 (6.4) | |
| Non-smoker | 284 (91.0) | |
| Allergic asthma 2 | ||
| Yes | 154 (49.4) | |
| No | 114 (36.5) | |
| Medication use | ||
| Yes | 149 (47.8) | |
| No | 163 (52.2) | |
| Small airway function parameters 3 | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) |
| Pre-BD FEF50%pred (%) | 71.74 (27.00) | 70.20 (38.80) |
| Pre-BD FEF75%pred (%) | 61.96 (28.08) | 59.15 (34.83) |
| Pre-BD FEF25–75%pred (%) | 70.71 (26.43) | 69.85 (38.15) |
| Post-BD FEF50%pred (%) | 79.57 (27.34) | 77.15 (35.00) |
| Post-BD FEF75%pred (%) | 70.93 (30.34) | 68.00 (42.40) |
| Post-BD FEF25–75%pred (%) | 78.86 (26.65) | 76.80 (37.15) |
| Variables | Mean (SD) | Median (IQR) | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3 (μg/m3) 1 | 111.01 (45.01) | 102.35 (63.97) | 18.40 | 244.10 |
| Warm season | 129.72 (38.65) | 125.75 (63.57) | 67.60 | 244.10 |
| Cold season | 70.64 (28.14) | 70.15 (28.47) | 18.40 | 165.60 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) 2 | 37.49 (30.07) | 29.60 (33.90) | 1.00 | 168.40 |
| Warm season | 28.42 (20.23) | 24.30 (25.10) | 1.00 | 140.60 |
| Cold season | 57.02 (37.64) | 49.25 (57.60) | 3.70 | 168.40 |
| BC 3 | 1.44 (1.13) | 1.11 (1.23) | 0.04 | 6.35 |
| OM 4 | 7.83 (5.96) | 6.23 (6.93) | 0.27 | 37.56 |
| SO42− | 4.78 (4.33) | 3.56 (4.59) | 0.13 | 30.50 |
| NO3− | 6.83 (7.66) | 4.30 (6.34) | 0.12 | 42.99 |
| NH4+ | 4.15 (4.53) | 2.61 (3.85) | 0.09 | 25.28 |
| Temperature (K) | 288.71 (9.54) | 291.78 (15.36) | 258.30 | 307.09 |
| Relative humidity (%) | 51.54 (19.12) | 50.56 (31.59) | 14.57 | 94.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Li, Z.; Mu, X.; Han, X.; Xie, X.; Fu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Short-Term Effect of Ozone Exposure on Small Airway Function in Adult Asthma Patients with PM2.5 Exacerbating the Effect. Toxics 2025, 13, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040279
Shang Y, Liang Y, Jiang D, Li Z, Mu X, Han X, Xie X, Fu G, Zhang Y, Sun Y, et al. Short-Term Effect of Ozone Exposure on Small Airway Function in Adult Asthma Patients with PM2.5 Exacerbating the Effect. Toxics. 2025; 13(4):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040279
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Ying, Yanjing Liang, Dongxia Jiang, Zhengxiong Li, Xianlin Mu, Xuehu Han, Xinzhuo Xie, Guanglong Fu, Yunshu Zhang, Yongchang Sun, and et al. 2025. "Short-Term Effect of Ozone Exposure on Small Airway Function in Adult Asthma Patients with PM2.5 Exacerbating the Effect" Toxics 13, no. 4: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040279
APA StyleShang, Y., Liang, Y., Jiang, D., Li, Z., Mu, X., Han, X., Xie, X., Fu, G., Zhang, Y., Sun, Y., Huang, S., & Chang, C. (2025). Short-Term Effect of Ozone Exposure on Small Airway Function in Adult Asthma Patients with PM2.5 Exacerbating the Effect. Toxics, 13(4), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13040279








