Microplastic Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) by Natural Coagulation: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microplastics from Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs)
2.1. Microplastic Removal in WWTPs
2.2. Advanced Removal Technologies
2.3. Wastewater Management in Southeast Asia
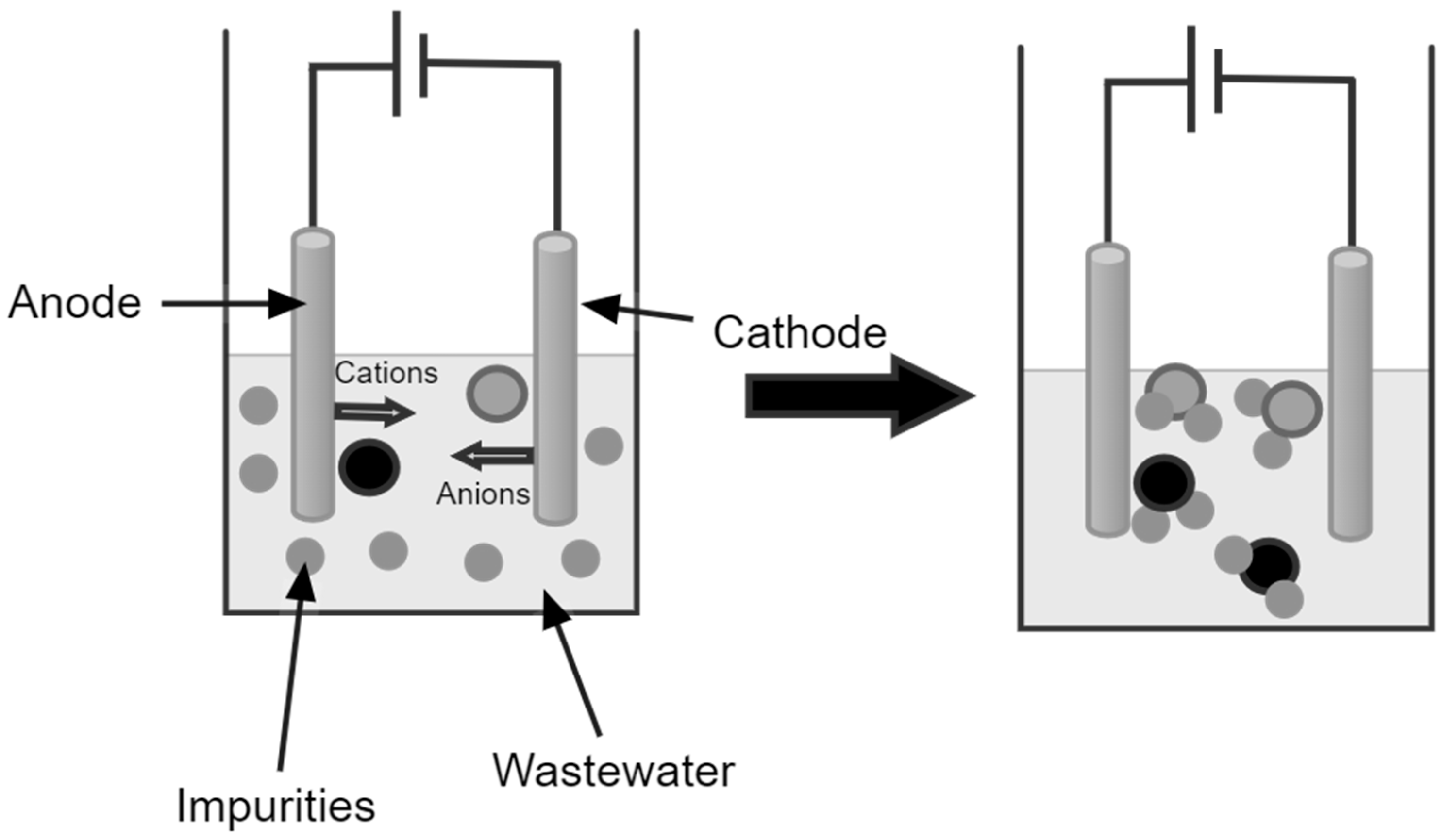
3. Coagulation
3.1. Mechanism
3.2. Factors Affecting Coagulation
3.3. Chemical Coagulants
3.4. Natural Coagulants
3.5. Use of Natural Coagulants in Southeast Asia
4. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hale, R.C.; Seeley, M.E.; La Guardia, M.J.; Mai, L.; Zeng, E.Y. A Global Perspective on Microplastics. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125, e2018JC014719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C. Microplastics in freshwater sediment: A review on methods, occurrence, and sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Plastic Pollution is Growing Relentlessly as Waste Management and Recycling Fall Short, Says OECD; OECD: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rochman, C.M.; Brookson, C.; Bikker, J.; Djuric, N.; Earn, A.; Bucci, K.; Athey, S.; Huntington, A.; McIlwraith, H.; Munno, K.; et al. Rethinking microplastics as a diverse contaminant suite. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith, K.L. Plastics on the Sargasso sea surface. Science 1972, 175, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtiniemi, M.; Hartikainen, S.; Näkki, P.; Engström-Öst, J.; Koistinen, A.; Setälä, O. Size matters more than shape: Ingestion of primary and secondary microplastics by small predators. Food Webs 2018, 17, e00097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curren, E.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Yoshida, T.; Leong, S.C.Y. Marine microplastics in the ASEAN region: A review of the current state of knowledge. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, S.; Friedrich, C.; Brinker, A. Uptake routes of microplastics in fishes: Practical and theoretical approaches to test existing theories. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, L.J.J.; van Emmerik, T.; van der Ent, R.; Schmidt, C.; Lebreton, L. More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eaaz5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Behbehani, M. An assessment of microplastic inputs into the aquatic environment from wastewater streams. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, E.E.; Boxall, A.B.A. Microplastics in the aquatic environment: Evidence for or against adverse impacts and major knowledge gaps. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2776–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.A.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D.L. Wastewater treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: Development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res. 2017, 112, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.Q. The role of coagulation in water treatment. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2015, 8, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Bachmann, R.T. A contemporary review on plant-based coagulants for applications in water treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 72, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, N.M.; Priyatharishini, M.; Kristanti, R.A. Study on the Effectiveness of Banana Peel Coagulant in Turbidity Reduction of Synthetic Wastewater. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2019, 6, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, F.P.; Sousa, V.S.; Bergamasco, R.; Ribau Teixeira, M. The use of Moringa oleifera as a natural coagulant in surface water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- De Falco, F.; Di Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Avella, M. The contribution of washing processes of synthetic clothes to microplastic pollution. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M. Reducing microplastics from facial exfoliating cleansers in wastewater through treatment versus consumer product decisions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.L.; Pramanik, B.K.; Shah, K.; Roychand, R. Pathway, classification and removal efficiency of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Chen, L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.; Lü, F. Municipal solid waste (MSW)landfill: A source of microplastics? -Evidence of microplastics in landfill leachate. Water Res. 2019, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, T. A review of the removal of microplastics in global wastewater treatment plants: Characteristics and mechanisms. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, Q.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Ni, B.J. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res. 2019, 152, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajith, N.; Arumugam, S.; Parthasarathy, S.; Manupoori, S.; Janakiraman, S. Global distribution of microplastics and its impact on marine environment—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25970–25986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater Treatment Works (WwTW) as a Source of Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kross, S.M.; Armstrong, J.B.; Bogan, M.T.; Darling, E.S.; Green, S.J.; Smyth, A.R.; Veríssimo, D. Scientific Evidence Supports a Ban on Microbeads. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10759–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.A.; Telles Silveira, I.; Chua, A.; Leusch, F.D.L. An audit of microplastic abundance throughout three Australian wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, K.; Xiong, X. Microplastic pollution in inland waters focusing on Asia. Handb. Environ. Chem. 2018, 58, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauziah, S.H.; Rizman-Idid, M.; Cheah, W.; Loh, K.H.; Sharma, S.; Noor, N.M.; Bordt, M.; Praphotjanaporn, T.; Samah, A.A.; bin Sabaruddin, J.S.; et al. Marine debris in Malaysia: A review on the pollution intensity and mitigating measures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadsuwan, K.; Babel, S. Microplastic abundance and removal via an ultrafiltration system coupled to a conventional municipal wastewater treatment plant in Thailand. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongprasith, N.; Kittimethawong, C.; Lertluksanaporn, R.; Eamchotchawalit, T.; Kittipongvises, S.; Lohwacharin, J. IR microspectroscopic identification of microplastics in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18557–18564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayana, D. Fsm Case Study Sanitation and Sewerage Management: The Malaysian Experience. ADBI Policy Brief No. 2020-8 (December) ISSN 2411-6734. Available online: https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/publication/659216/adbi-pb2020-8.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Phu, H.; Thi Ngoc Han, H.; Ly Ngoc Thao, N.; Thi Minh Ha, T. Microplastics and solutions to remove microplastics in wastewater from wastewater treatment plants in the Saigon–Dong Nai river basin, Vietnam. J. Hydrometeorol. 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.M.T.; Truong, T.N.S.; Nguyen, P.D.; Le, Q.D.T.; Tran, Q.V.; Le, T.T.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Kieu-Le, T.C.; Strady, E. Evaluation of microplastic removal efficiency of wastewater-treatment plants in a developing country, Vietnam. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 102994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radityaningrum, A.D.; Trihadiningrum, Y.; Mar’atusholihah; Soedjono, E.S.; Herumurti, W. Microplastic contamination in water supply and the removal efficiencies of the treatment plants: A case of Surabaya City, Indonesia. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, J.; Olmos, S.; López-Castellanos, J. Microplastics in an urban wastewater treatment plant: The influence of physicochemical parameters and environmental factors. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.T.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Chung, J.; Kim, E.J. Microplastic removal in conventional drinking water treatment processes: Performance, mechanism, and potential risk. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xiang, X.M.; Dong, K.Y.; Gong, Y.Y.; Li, Z.J. Surfactant stealth effect of microplastics in traditional coagulation process observed via 3-D fluorescence imaging. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; Brandsma, S.H.; Van Velzen, M.J.M.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics en route: Field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koistinen, A.; Setälä, O. Solutions to microplastic pollution–Removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Zhao, H.; Sun, H.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Y. Abundance, morphology, and removal efficiency of microplastics in two wastewater treatment plants in Nanjing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9327–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, W.; Di, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Transfer and fate of microplastics during the conventional activated sludge process in one wastewater treatment plant of China. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gies, E.A.; LeNoble, J.L.; Noël, M.; Etemadifar, A.; Bishay, F.; Hall, E.R.; Ross, P.S. Retention of microplastics in a major secondary wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, C.B.; Won, E.J.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, M.C.; Hwang, D.S.; Hwang, U.K.; Zhou, B.; Souissi, S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.S. Microplastic Size-Dependent Toxicity, Oxidative Stress Induction, and p-JNK and p-p38 Activation in the Monogonont Rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, R.Y.; Manikandan, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Karmegam, N.; Kim, W.; Govarthanan, M. Recent approaches and advanced wastewater treatment technologies for mitigating emerging microplastics contamination–A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrício Silva, A.L. New frontiers in remediation of (micro)plastics. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 28, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, C.; Deniz, F. Electrocoagulation/Electroflotation Process for Removal of Organics and Microplastics in Laundry Wastewater. Clean-Soil Air Water 2021, 49, 2000146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, W.; Wojtasik, A.; Cai, Q. Removal of Microbeads from Wastewater Using Electrocoagulation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam Babu, D.; Anantha Singh, T.S.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Suresh Kumar, M. Industrial wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation process. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 3195–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatib, D.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.; Carissimi, E. Electrocoagulation applied for the removal of microplastics from wastewater treatment facilities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 118877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkhosh, F.; Lashanizadegan, M.; Mahjoub, A.R.; Cheshme Khavar, A.H. One pot synthesis of CuFeO2 @ expanding perlite as a novel efficient floating catalyst for rapid degradation of methylene blue under visible light illumination. Solid State Sci. 2019, 91, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; Huang, J.; Louangsouphom, B.; Zhao, J. Floating photocatalysts based on loading Bi/N-doped TiO2 on expanded graphite C/C (EGC) composites for the visible light degradation of diesel. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71922–71931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Louangsouphom, B.; Song, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Synthesis of expanded graphite C/C composites (EGC) based Ni-N-TiO2 floating photocatalysts for in situ adsorption synergistic photocatalytic degradation of diesel oil. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 347, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.N.; Borghei, S.M.; Vossoughi, M.; Taghavinia, N. Immobilization of TiO2 on perlite granules for photocatalytic degradation of phenol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 74, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, J.; López-Castellanos, J.; Olmos, S. Membrane bioreactor and rapid sand filtration for the removal of microplastics in an urban wastewater treatment plant. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotelo, T.J.; Satoh, H.; Mino, T. Assessing wastewater management in the developing countries of Southeast Asia: Underlining flexibility in appropriateness. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2019, 17, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, K.P.; Mara, D.D.; Angelakis, A.N. Application of cost criteria for selection of municipal wastewater treatment systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 142, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W.; Ho, G. Small scale sanitation technologies. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.H.; Visvanathan, C.; Jegatheesan, V. Performance Evaluation of Septic Tanks as onsite Sanitation System. Southeast Asian Water Environ. 2009, 3, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Roomratanapun, W. Introducing centralised wastewater treatment in Bangkok: A study of factors determining its acceptability. Habitat Int. 2001, 25, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xue, W.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Li, L. Characteristics of microplastic removal via coagulation and ultrafiltration during drinking water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.E.; Morad, N.; Teng, T.T.; Poh, B.T. Development, characterization and the application of hybrid materials in coagulation/flocculation of wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, H.; Huang, M.; Yang, H.; Li, A. A review on chitosan-based flocculants and their applications in water treatment. Water Res. 2016, 95, 59–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Li, H.; Fei, L.; Wei, B.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, H. The removal of microplastics from water by coagulation: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidayaturrahman, H.; Lee, T.G. A study on characteristics of microplastic in wastewater of South Korea: Identification, quantification, and fate of microplastics during treatment process. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, G.; Jia, X.; Song, Y.; Guo, A.; Wang, A.; Zhang, S.; Ji, M. Microplastic abundance, characteristics and removal in large-scale multi-stage constructed wetlands for effluent polishing in northern China. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C.; Wu, R.; Lam, P.K.S. A preliminary screening of HBCD enantiomers transported by microplastics in wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guibal, E.; Van Vooren, M.; Dempsey, B.A.; Roussy, J. A review of the use of chitosan for the removal of particulate and dissolved contaminants. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 2487–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renault, F.; Sancey, B.; Badot, P.M.; Crini, G. Chitosan for coagulation/flocculation processes-An eco-friendly approach. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, J.; Yan, Y.; Yang, L.; Xing, G.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Wang, M.; Zheng, H. Application of coagulation/flocculation in oily wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Demissie, H.; Jiao, R.; An, G.; Wang, D. Removal characteristics and mechanism of microplastics and tetracycline composite pollutants by coagulation process. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Improving nanoplastic removal by coagulation: Impact mechanism of particle size and water chemical conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mao, J.; Zhao, Q.; He, S.; Ma, J. Effect of AlCl3 concentration on nanoparticle removal by coagulation. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 38, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jiao, R.; Xu, H.; An, G.; Wang, D. The influence of particle size and concentration combined with pH on coagulation mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 82, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, H.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shu, S.; Zhang, J. Removal of polystyrene and polyethylene microplastics using PAC and FeCl3 coagulation: Performance and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Li, G. Coagulation efficiency and flocs characteristics of recycling sludge during treatment of low temperature and micro-polluted water. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, K.; Grönfors, O.; Hesampour, M.; Mikola, A. Removal of microplastics from secondary wastewater treatment plant effluent by coagulation/flocculation with iron, aluminum and polyamine-based chemicals. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Gao, B.; Ren, J.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Coagulation/flocculation in dewatering of sludge: A review. Water Res. 2018, 143, 608–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.A.; Dixon, D.R.; Eldridge, R.J.; King, S.J. The Use of Cationic Polymers as Primary Coagulants in Water Treatment. In Chemical Water and Wastewater Treatment V, Proceedings of the 8th Gothenburg Symposium 1998, Prague, Czech Republic, 7–9 September 1998; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mathuram, M.; Meera, R.; Vijayaraghavan, G. Application of Locally Sourced Plants as Natural Coagulants For Dye Removal from Wastewater: A Review. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 2508, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Shang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Chen, A.; Qian, X.; Yang, H.; Cheng, R. The flocculating properties of chitosan-graft-polyacrylamide flocculants (II)—Test in pilot scale. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, N.K.; Maeng, M.; Kim, D.; Dockko, S. Removal behavior of microplastics using alum coagulant and its enhancement using polyamine-coated sand. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 141, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, T.; Chen, W. Occurrence and removal of microplastics in an advanced drinking water treatment plant (ADWTP). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayarathne, H.N.P.; Angove, M.J.; Aryal, R.; Abuel-Naga, H.; Mainali, B. Removal of natural organic matter from source water: Review on coagulants, dual coagulation, alternative coagulants, and mechanisms. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Busquets, R.; Moruzzi, R.B.; Campos, L.C. Preliminary study on low-density polystyrene microplastics bead removal from drinking water by coagulation-flocculation and sedimentation. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Gregory, J. Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniak, S.L.; Almuhtaram, H.; McKie, M.J.; Hermabessiere, L.; Yuan, C.; Rochman, C.M.; Andrews, R.C. Conventional and biological treatment for the removal of microplastics from drinking water. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonský, M.; Pivokonská, L.; Novotná, K.; Čermáková, L.; Klimtová, M. Occurrence and fate of microplastics at two different drinking water treatment plants within a river catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Diehl, A.; Lewandowski, A.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Baker, T. Removal efficiency of micro- and nanoplastics (180 nm–125 μm) during drinking water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monira, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Haque, N.; Pramanik, B.K. Assess the performance of chemical coagulation process for microplastics removal from stormwater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Tian, S.; Lu, J.; Mu, R.; Yuan, H. Coagulation removal of microplastics from wastewater by magnetic magnesium hydroxide and PAM. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 43, 102250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Huang, Z. Sedimentation of nanoplastics from water with Ca/Al dual flocculants: Characterization, interface reaction, effects of pH and ion ratios. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvaniti, O.S.; Antonopoulou, G.; Tsagkogianni, D.; Stasinakis, A.S. Screening on the sorption of emerging contaminants to polystyrene and polyethylene and use of coagulation–Flocculation process for microplastics’ removal. Glob. Nest J. 2021, 23, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Albahnasawi, A.; Ali, G.A.M.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Nassani, D.E.; Al Maskari, T.; Amr, S.S.A.; Abujazar, S.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Albahnasawi, A.; et al. Application of Natural Coagulants for Pharmaceutical Removal from Water and Wastewater: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupińska, I. Aluminium Drinking Water Treatment Residuals and Their Toxic Impact on Human Health. Molecules 2020, 25, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Ghouri, A.S.; Ahmad, A. Pine cone extract as natural coagulant for purification of turbid water. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawakkoly, B.; Alizadehdakhel, A.; Dorosti, F. Evaluation of COD and turbidity removal from compost leachate wastewater using Salvia hispanica as a natural coagulant. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenazi, M.; Hashim, K.S.; Hassan, A.A.; Muradov, M.; Kot, P.; Abdulhadi, B. Turbidity removal using natural coagulants derived from the seeds of strychnos potatorum: Statistical and experimental approach. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Baghdad, Iraq, 15–16 December 2020; Volume 888. [Google Scholar]
- Kristianto, H.; Rahman, H.; Prasetyo, S.; Sugih, A.K. Removal of Congo red aqueous solution using Leucaena leucocephala seed’s extract as natural coagulant. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Ray, M.B.; Neogi, S. Evaluation of the potential application of cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) as a bio-coagulant for pre-treatment of oil sands process-affected water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huzir, N.M.; Aziz, M.M.A.; Ismail, S.B.; Mahmood, N.A.N.; Umor, N.A.; Faua’ad Syed Muhammad, S.A. Optimization of coagulation-flocculation process for the palm oil mill effluent treatment by using rice husk ash. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 139, 111482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, G.; Sasikala, S. Removal of turbidity from drinking water using natural coagulants. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukić, D.V.; Šćiban, M.B.; Prodanović, J.M.; Tepić, A.N.; Vasić, M.A. Extracts of fava bean (Vicia faba L.) seeds as natural coagulants. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daverey, A.; Tiwari, N.; Dutta, K. Utilization of extracts of Musa paradisica (banana) peels and Dolichos lablab (Indian bean) seeds as low-cost natural coagulants for turbidity removal from water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34177–34183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, N.S.; Muda, K.; Abdul Rahman, M.A.; al Aina Nadhillah Muhamad, N.; Fatihah Juhari, N.; Noorazurah Mohamad, I. Efficiency of Natural Plant-Based Coagulants for Water Treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 616, 012075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneenoon, K.; Sirirugsa, P.; Sridith, K. Ethnobotany of Dioscorea L. (Dioscoreaceae), a major food plant of the sakai tribe at Banthad Range, Peninsular Thailand. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2008, 6, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yusoff, M.S.; Juni, F.; Ahmed, Z.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Aziz, H.A. Dioscorea hispida starch as a novel natural coagulant in textile wastewater treatment. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2021, 53, 210207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BPS Badan Pusat Statistik. 2021. Available online: https://sulut.bps.go.id/indicator/55/956/1/produksi-buah-buahan-dan-sayuran-tahunan-menurut-jenis-tanaman.html (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- Ahmad, A.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Hasan, H.A.; Othman, A.R.; Ismail, N. ‘Izzati Potential of local plant leaves as natural coagulant for turbidity removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 2579–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megersa, M.; Gach, W.; Beyene, A.; Ambelu, A.; Triest, L. Effect of salt solutions on coagulation performance of Moringa stenopetala and Maerua subcordata for turbid water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, N.T.; Hue, C.T. Enhanced water treatment by Moringa oleifera seeds extract as the bio-coagulant: Role of the extraction method. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-AQUA 2018, 67, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.N.; Bridgeman, J. A fluorescence-based assessment of the fate of organic matter in water treated using crude/purified Hibiscus seeds as coagulant in drinking water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsnejati, S.; Chaibakhsh, N.; Pendashteh, A.R.; Hayeripour, S. Mucilaginous seed of Ocimum basilicum as a natural coagulant for textile wastewater treatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W. State of the art and sustainability of natural coagulants in water and wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Location | Coagulant | Dosage of Coagulant | Sample | pH | Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ontario, Canada | Aluminum hydroxide | 40 mg/L | River water | 7.8 | 71% | [91] |
| Czech Republic | Alum | - | Drinking water treatment plant | 3.5 | 61.65% | [92] |
| Surabaya City, Indonesia | Aluminum sulfate (Al2(SO4)3) | - | River water | - | 17% | [37] |
| Daegu, Republic of Korea | PAC | WWTP A—32.4 mg/L WWTP B—30.5 mg/L WWTP C—29.3 mg/L | Wastewater treatment plant | - | WWTP A—53.8% WWTP B—81.6% WWTP C—47.1% | [69] |
| Tianjin, China | PAC, PAM, Fe3O4 | - | Constructed wetland | - | 73.8% (sunny days) 77.9% (rainy days) | [70] |
| Detroit, MI, USA | Aluminum sulfate | 20 ppm | Water treatment plant | 7.43–7.59 | 13.6% (particle size 45–53 µm) | [93] |
| Australia | Alum, PAM | 50–250 mg/L | Simulated stormwater | 3–11 | Maximum: 96% at 150 mg/L alum and 15 mg/L PAM | [94] |
| Finland | Ferric chloride, polyaluminum chloride | 0.017–1.4 mmol/L | Wastewater | 6.5 | Ferric chloride—99.4% Polyaluminum chloride—98.2% | [81] |
| China | Magnetic magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2, iron oxide (Fe3O4) | 200 mg/L Mg(OH)2 120 mg/L Fe3O4 | Simulated wastewater | 7 | 66.3 to 87.1% | [95] |
| - | Iron (III) chloride (FeCl3) PAC | 30 to 180 mg/L (30 increments) | Simulated water | 7 | PS—77.83% PE—29.70% | [79] |
| China | Aluminum chloride (AlCl3), calcium chloride (CaCl2) | - | Lake water | 3–10 | More than 80% at pH > 6 | [96] |
| Greece | Iron sulfate (FeSO4), iron (III) chloride (FeCl3), magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) | 496–993 mg/L FeSO4 483–964 mg/L FeCl3 1025–2050 mg/L MgSO4 | Tap water | 8 | 92.4% for Fe2+ ion 89.1–90.4 for Mg2+ ion | [97] |
| Coagulant | Dosage of Coagulant | Sample | pH | Efficiency | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinecone extract | 0.5 mL/L | Synthetic turbid water | 2 and 12 | Maximum turbidity removal: 82% | [100] |
| Salvia hispanica (chia) | 40 g/L | Landfill leachate | 7 | Turbidity: 62.4% COD: 39.76% | [101] |
| Strychnos potatorum | 40.0 mg/L | Artificial water | 7 | Kaolinite turbidity: 93% | [102] |
| Leucaena leucocephala | 10 mL/L | Synthetic wastewater | 3 | Congo red dye: 99.9% | [103] |
| Cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) | 1500 mg/L | Oil sand process-affected water | 7–8 | Turbidity: 98% | [104] |
| Rice husk ash | 6.0 g | Palm oil mill effluent | 3.6 | COD: 52.38% TS: 83.88% | [105] |
| Moringa oleifera | 50 mg/L | Surface water | 7.03–7.70 | Turbidity: 85% | [17] |
| Phaseolus vulgaris | 0.5 M | Synthetic turbid water | 7.4 | Turbidity: 85% | [106] |
| Fava bean seeds (Vicia fava L.) | 0.125–0.25 mL/L | Synthetic water | 10 | Turbidity: 51.5 to 54% | [107] |
| Musa paradisica (banana) peels | 0.6 mL/L | Simulated turbid water | 11 | Turbidity: 98.14% | [108] |
| Dolichos lablab (Indian beans) | 0.6 mL/L | Simulated turbid water | 11 | Turbidity: 98.84% | [108] |
| Soybean | 120 mg/L | Surface water | - | Turbidity: 23.2% Color removal: 30.4% | [109] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reza, T.; Mohamad Riza, Z.H.; Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.; Abu Hasan, H.; Ismail, N.‘I.; Othman, A.R. Microplastic Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) by Natural Coagulation: A Literature Review. Toxics 2024, 12, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010012
Reza T, Mohamad Riza ZH, Sheikh Abdullah SR, Abu Hasan H, Ismail N‘I, Othman AR. Microplastic Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) by Natural Coagulation: A Literature Review. Toxics. 2024; 12(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleReza, Taskeen, Zahratul Huda Mohamad Riza, Siti Rozaimah Sheikh Abdullah, Hassimi Abu Hasan, Nur ‘Izzati Ismail, and Ahmad Razi Othman. 2024. "Microplastic Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) by Natural Coagulation: A Literature Review" Toxics 12, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010012
APA StyleReza, T., Mohamad Riza, Z. H., Sheikh Abdullah, S. R., Abu Hasan, H., Ismail, N. ‘I., & Othman, A. R. (2024). Microplastic Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) by Natural Coagulation: A Literature Review. Toxics, 12(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010012







