Genetics and Pathogenicity of Natural Reassortant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Emerging in Latvia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
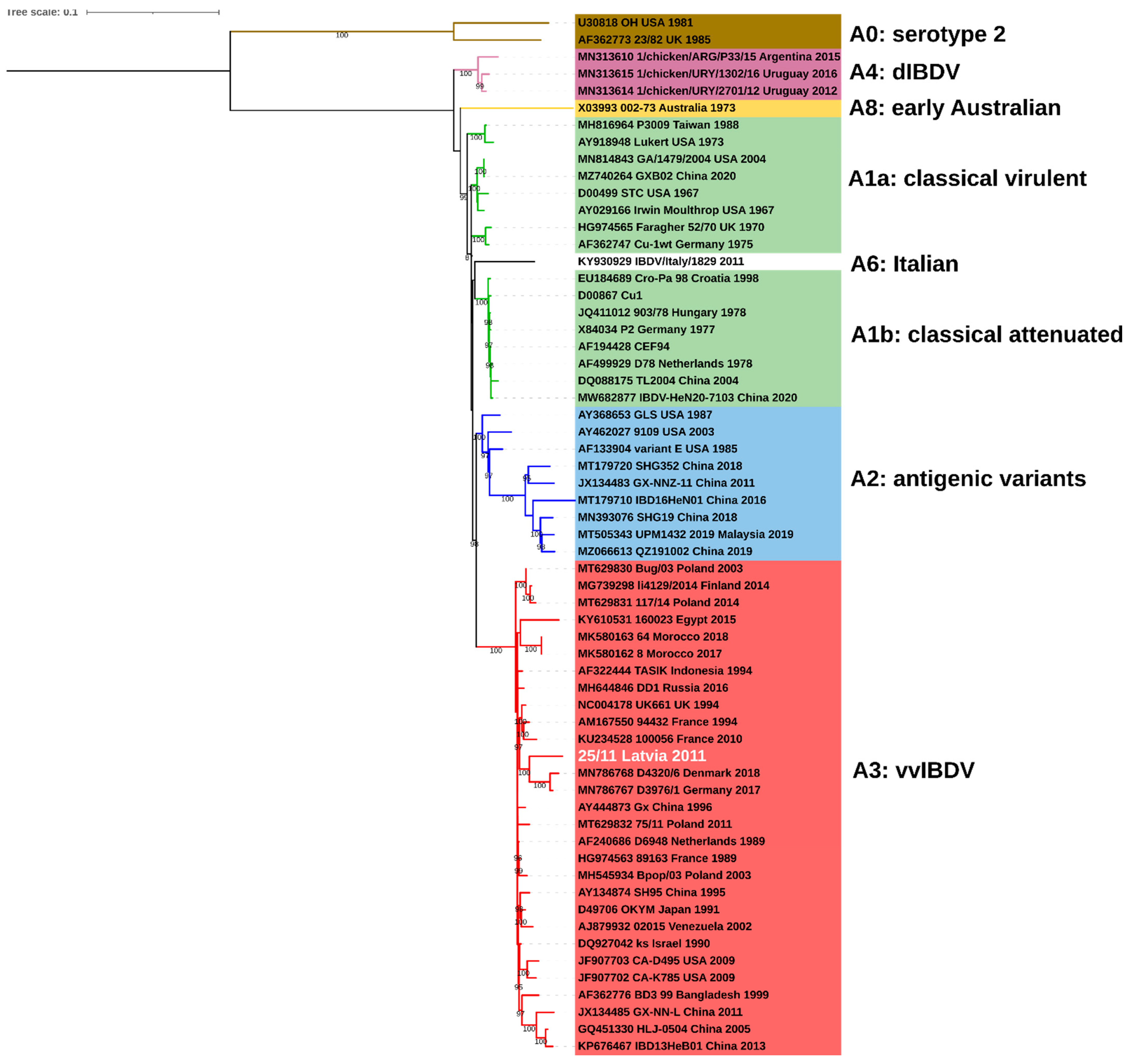
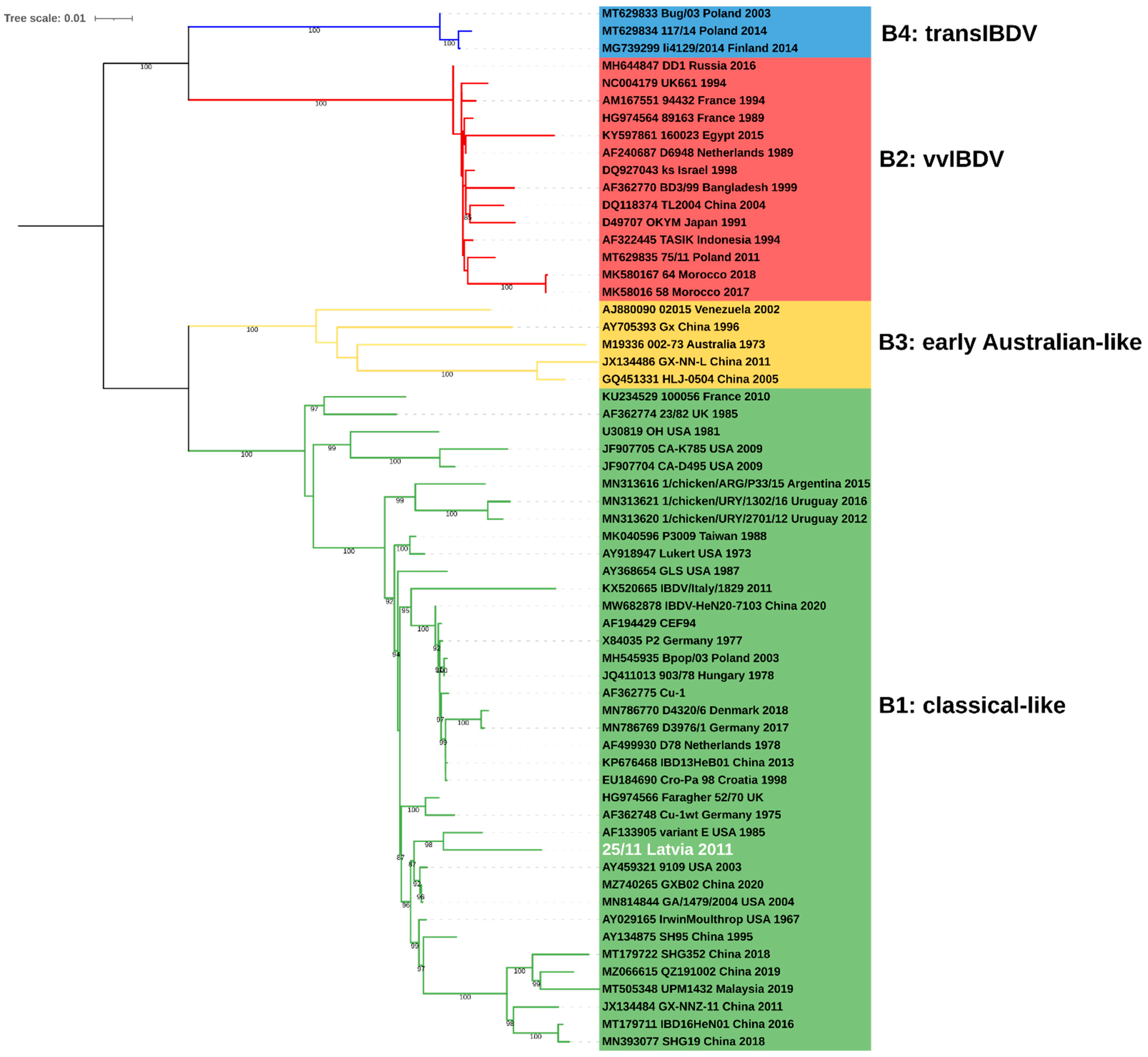
2.1. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2. Animal Experimental Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Full-length Genome Sequencing
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Animal Experimental Study
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobos, P.; Hill, B.J.; Hallett, R.; Kells, D.T.; Becht, H.; Teninges, D. Biophysical and biochemical characterization of five animal viruses with bisegmented double-stranded RNA genomes. J. Virol. 1979, 32, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulibaly, F.; Chevalier, C.; Gutsche, I.; Pous, J.; Navaza, J.; Bressanelli, S.; Delmas, B.; Rey, F.A. The birnavirus crystal structure reveals structural relationships among icosahedral viruses. Cell 2005, 120, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Einem, U.I.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Schirrmeier, H.; Behrens, S.E.; Letzel, T.; Mundt, E. VP1 of infectious bursal disease virus is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, E.; Han, X.; Yu, Z.; Liu, H. VP1 and VP3 Are Required and Sufficient for Translation Initiation of Uncapped Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Genomic Double-Stranded RNA. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01345-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escaffre, O.; Le Nouen, C.; Amelot, M.; Ambroggio, X.; Ogden, K.M.; Guionie, O.; Toquin, D.; Muller, H.; Islam, M.R.; Eterradossi, N. Both Genome Segments Contribute to the Pathogenicity of Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2767–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eterradossi, N.; Saif, Y.M. Infectious bursal disease. In Diseases of Poultry, 14th ed.; Swayne, D.E., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 257–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eterradossi, N.; Arnauld, C.; Toquin, D.; Rivallan, G. Critical amino acid changes in VP2 variable domain are associated with typical and atypical antigenicity in very virulent infectious bursal disease viruses. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.J.; Wu, T.T.; Wang, Y.L.; Hussain, A.; Jiang, N.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.L.; Liu, C.J.; Cui, H.Y.; et al. Novel variants of infectious bursal disease virus can severely damage the bursa of fabricius of immunized chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, O.; Suwanruengsri, M.; Araki, K.; Izzati, U.Z.; Pornthummawat, A.; Nueangphuet, P.; Fuke, N.; Hirai, T.; Jackwood, D.J.; Yamaguchi, R. Bursa atrophy at 28 days old caused by variant infectious bursal disease virus has a negative economic impact on broiler farms in Japan. Avian Pathol. 2021, 50, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, T.; Tatar-Kis, T.; Felfoldi, B.; Jansson, D.S.; Homonnay, Z.; Banyai, K.; Palya, V. Occurrence and spread of a reassortant very virulent genotype of infectious bursal disease virus with altered VP2 amino acid profile and pathogenicity in some European countries. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 245, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Fan, L.; Niu, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Identification and Pathogenicity Evaluation of a Novel Reassortant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (Genotype A2dB3). Viruses 2021, 13, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikuła, A.; Lisowska, A.; Jasik, A.; Perez, L.J. The Novel Genetic Background of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Strains Emerging from the Action of Positive Selection. Viruses 2021, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.H.; Al Saegh, H.A.; FS, A.L. Sequence diversity and evolution of infectious bursal disease virus in Iraq. F1000Research 2021, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drissi Touzani, C.; Fellahi, S.; Fihri, O.F.; Gaboun, F.; Khayi, S.; Mentag, R.; Lico, C.; Baschieri, S.; El Houadfi, M.; Ducatez, M. Complete genome analysis and time scale evolution of very virulent infectious bursal disease viruses isolated from recent outbreaks in Morocco. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 77, 104097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammiranta, N.; Ek-Kommonen, C.E.; Rossow, L.; Huovilainen, A. Circulation of very virulent avian infectious bursal disease virus in Finland. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legnardi, M.; Franzo, G.; Tucciarone, C.M.; Koutoulis, K.; Duarte, I.; Silva, M.; Le Tallec, B.; Cecchinato, M. Detection and molecular characterization of a new genotype of infectious bursal disease virus in Portugal. Avian Pathol. 2022, 51, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikula, A.; Domanska-Blicharz, K.; Cepulis, R.; Smietanka, K. Identification of infectious bursal disease virus with atypical VP2 amino acid profile in Latvia. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 61, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, T.; Medveczki, A.; Kiss, I. Research Note: "Hidden" infectious bursal disease virus infections in Central Europe. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Nooruzzaman, M.; Rahman, T.; Mumu, T.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Eterradossi, N.; Muller, H. A unified genotypic classification of infectious bursal disease virus based on both genome segments. Avian Pathol. 2021, 50, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrard, S.R.; Li, L.; Barrett, A.D.; Nichol, S.T. Ngari virus is a Bunyamwera virus reassortant that can be associated with large outbreaks of hemorrhagic fever in Africa. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8922–8926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.I.; Viboud, C.; Simonsen, L.; Bennett, R.T.; Griesemer, S.B.; George, K.S.; Taylor, J.; Spiro, D.J.; Sengamalay, N.A.; Ghedin, E.; et al. Multiple reassortment events in the evolutionary history of H1N1 influenza A virus since 1918. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, C.C.; Lam, T.Y.; Drummond, A.; Rambaut, A.; Lee, Y.F.; Yip, C.W.; Zeng, F.; Lam, P.Y.; Ng, P.T.; Leung, F.C. Phylogenetic analysis reveals a correlation between the expansion of very virulent infectious bursal disease virus and reassortment of its genome segment B. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8503–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.H.; Lu, P.; Yan, Y.X.; Hua, X.G.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Y. Sequence and analysis of genomic segment A and B of very virulent infectious bursal disease virus isolated from China. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2003, 50, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.P.; Hong, L.L.; Ye, J.X.; Huang, Z.Y.; Zhou, J.Y. The VP5 protein of infectious bursal disease virus promotes virion release from infected cells and is not involved in cell death. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Hou, L.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J. Infectious bursal disease virus activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway by interaction of VP5 protein with the p85alpha subunit of PI3K. Virology 2011, 417, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; Zheng, S.J. Critical role for voltage-dependent anion channel 2 in infectious bursal disease virus-induced apoptosis in host cells via interaction with VP5. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, F.; de Garay, T.; Rodriguez, D.; Rodriguez, J.F. Infectious bursal disease virus VP5 polypeptide: A phosphoinositide-binding protein required for efficient cell-to-cell virus dissemination. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackwood, D.J.; Sommer-Wagner, S.E. Amino acids contributing to antigenic drift in the infectious bursal disease Birnavirus (IBDV). Virology 2011, 409, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Ogawa, M.; Inoshima, Y.; Miyoshi, M.; Fukushi, H.; Hirai, K. Identification of sequence changes responsible for the attenuation of highly virulent infectious bursal disease virus. Virology 1996, 223, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, C.P.; Mertens, J.; Fontana, J.; Luque, D.; Allende-Ballestero, C.; Reguera, D.; Trus, B.L.; Steven, A.C.; Carrascosa, J.L.; Caston, J.R. The RNA-Binding Protein of a Double-Stranded RNA Virus Acts like a Scaffold Protein. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00968-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacken, M.G.; Peeters, B.P.; Thomas, A.A.; Rottier, P.J.; Boot, H.J. Infectious bursal disease virus capsid protein VP3 interacts both with VP1, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, and with viral double-stranded RNA. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11301–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, H.J.; ter Huurne, A.A.; Hoekman, A.J.; Pol, J.M.; Gielkens, A.L.; Peeters, B.P. Exchange of the C-terminal part of VP3 from very virulent infectious bursal disease virus results in an attenuated virus with a unique antigenic structure. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10346–10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Qi, X.L.; Kang, Z.H.; Yu, F.; Qin, L.T.; Gao, H.L.; Gao, Y.L.; Wang, X.M. A single amino acid in the C-terminus of VP3 protein influences the replication of attenuated infectious bursal disease virus in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2010, 87, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, J.; Rautenschlein, S. Infectious bursal disease virus’ interferences with host immune cells: What do we know? Avian Pathol. 2022, 51, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, K.; Qi, X.; et al. Naturally occurring reassortant infectious bursal disease virus in northern China. Virus Res. 2015, 203, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubies, S.M.; Courtillon, C.; Briand, F.X.; Queguiner-Leroux, M.; Courtois, D.; Amelot, M.; Grousson, K.; Morillon, P.; Herin, J.B.; Eterradossi, N. Identification of a European interserotypic reassortant strain of infectious bursal disease virus. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Nouen, C.; Rivallan, G.; Toquin, D.; Darlu, P.; Morin, Y.; Beven, V.; de Boisseson, C.; Cazaban, C.; Comte, S.; Gardin, Y.; et al. Very virulent infectious bursal disease virus: Reduced pathogenicity in a rare natural segment-B-reassorted isolate. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.; Soubies, S.; Courtillon, C.; Briand, F.X.; Allee, C.; Amelot, M.; De Boisseson, C.; Lucas, P.; Blanchard, Y.; Belahouel, A.; et al. Infectious bursal disease virus in Algeria: Detection of highly pathogenic reassortant viruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 60, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jang, I.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Choi, K.S. Genome Sequence of a Novel Reassortant and Very Virulent Strain of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00730-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikuła, A.; Śmietanka, K.; Perez, L.J. Emergence and expansion of novel pathogenic reassortant strains of infectious bursal disease virus causing acute outbreaks of the disease in Europe. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Niu, X.; Huang, M.; Gao, Y.; Liu, A.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Pan, Q.; et al. Genotyping and Molecular Characterization of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Identified in Important Poultry-Raising Areas of China During 2019 and 2020. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 759861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arowolo, O.A.; George, U.E.; Luka, P.D.; Maurice, N.A.; Atuman, Y.J.; Shallmizhili, J.J.; Shittu, I.; Oluwayelu, D.O. Infectious bursal disease in Nigeria: Continuous circulation of reassortant viruses. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikuła, A.; Lisowska, A.; Jasik, A.; Śmietanka, K. Identification and assessment of virulence of a natural reassortant of infectious bursal disease virus. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, D.J.; Sommer-Wagner, S.E.; Crossley, B.M.; Stoute, S.T.; Woolcock, P.R.; Charlton, B.R. Identification and pathogenicity of a natural reassortant between a very virulent serotype 1 infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) and a serotype 2 IBDV. Virology 2011, 420, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Segment A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VP5 | VP2 | VP4 | VP3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IBDV Strain | Genogroup | 9 | 14 | 19 | 45 | 47 | 74 | 112 | 134 | 219 | 220 | 222 | 242 | 254 | 256 | 279 | 280 | 284 | 545 | 553 | 570 | 680 | 905 | 935 | 960 | 990 | |
| D6948 | A3 | vv | D | E | N | R | A | F | A | H | Q | Y | A | I | G | I | D | N | A | A | R | M | Y | L | A | E | A |
| 25/11 | A3 | vv | A | K | . | . | T | L | V | N | L | F | . | . | D | . | N | T | . | T | . | V | F | P | V | D | V |
| D3976 | A3 | vv | - | K | D | . | . | L | V | . | L | . | . | . | D | . | N | T | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | V |
| D4320 | A3 | vv | - | K | D | . | . | L | V | . | L | . | . | . | D | . | N | T | . | . | K | . | . | . | . | . | V |
| Bpop/03 | A3 | vv | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| SH95 | A3 | vv | - | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | V |
| GA/1479/2004 | A1 | cv | . | K | . | G | . | I | . | . | . | . | P | V | . | V | . | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . |
| Variant E | A2 | av | . | K | . | G | . | I | . | . | . | . | T | V | S | V | N | . | . | . | . | . | C | . | . | . | . |
| 117/04 | A3 | vv | . | K | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | V |
| 02015.1 | A3 | vv | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | V |
| HLJ-0504 | A3 | vv | . | K | . | . | . | . | . | N | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| 100056 | A3 | vv | . | K | . | . | . | L | . | . | . | . | . | . | S | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | P | . | . | V |
| 160021 | A3 | vv | . | K | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | F | . | . | S | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Segment B | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VP1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IBDV Strain | Genogroup | 4 | 13 | 61 | 71 | 145 | 146 | 147 | 157 | 242 | 275 | 287 | 390 | 393 | 455 | 508 | 511 | 515 | 562 | 646 | 682 | 685 | 687 | 695 | 759 | 859 | |
| GA/1479/2004 | B1 | cl | I | K | V | E | N | E | D | Q | D | I | T | L | E | T | R | R | D | S | G | R | V | S | K | K | T |
| 25/11 | B1 | cl | . | . | . | D | . | . | . | L | . | . | . | . | . | S | . | . | . | . | . | . | I | P | . | R | . |
| D3976 | B1 | cl | . | T | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | L | . | . | . | . | . | K | . | . | . | K | . | . | . | . | V |
| D4320 | B1 | cl | . | T | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | L | . | . | . | . | . | K | . | . | . | K | . | . | . | . | V |
| Bpop/03 | B1 | cl | . | T | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | E | . | . | K | . | . | . | . | . |
| SH95 | B1 | cl | . | T | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | K | . | . | . | . | K | . | . | . | . | I |
| Variant E | B1 | cl | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | I | . | . | . | . |
| 117/04 | B4 | trans | V | . | I | . | S | . | G | . | . | . | A | M | . | . | K | S | E | . | S | K | . | . | . | . | I |
| 02015.1 | B3 | eA | V | . | . | . | T | . | S | . | . | . | A | . | D | . | K | S | E | . | S | K | . | P | . | . | I |
| HLJ-0504 | B3 | eA | V | . | I | . | T | . | G | . | . | . | A | . | . | . | K | S | E | . | S | K | . | P | . | . | . |
| 100056 | B1 | cl | . | . | . | . | . | . | G | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | K | S | E | A | . | K | . | . | . | . | . |
| 160021 | B2 | vv | . | . | I | . | T | D | N | . | E | . | A | M | D | . | K | S | E | P | S | K | . | P | R | . | . |
| D6948 | B2 | vv | V | . | I | . | T | D | N | . | E | . | A | M | D | . | K | S | E | P | S | K | . | P | R | . | . |
| No. | IBDV Strain | Genotype | Origin | Segment A | Segment B | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Date | |||||
| 1 | 002-73 | A8B3 | Australia | 1973 | X03993 | M19336 |
| 2 | 02015.1 | A3B3 | Venezuela | 2002 | AJ879932 | AJ880090 |
| 3 | 1/chicken/ARG/P33/15 | A4B1 | Argentina | 2015 | MN313610 | MN313616 |
| 4 | 1/chicken/URY/1302/16 | A4B1 | Uruguay | 2016 | MN313615 | MN313621 |
| 5 | 1/chicken/URY/2701/12 | A4B1 | Uruguay | 2012 | MN313614 | MN313620 |
| 6 | 100056 | A3B1 | France | 2010 | KU234528 | KU234529 |
| 7 | 117/14/Poland/2014 | A3B4 | Poland | 2014 | MT629831 | MT629834 |
| 8 | 160023 | A3B2 | Egypt | 2015 | KY610531 | KY597861 |
| 9 | 23/82 | A0B1 | UK | 1985 | AF362773 | AF362774 |
| 10 | 64 | A3B2 | Morocco | 2018 | MK580163 | MK580167 |
| 11 | 75/11/Poland/2011 | A3B2 | Poland | 2011 | MT629832 | MT629835 |
| 12 | 8 | A3B2 | Morocco | 2017 | MK580162 | MK580165 |
| 13 | 89163 | A3B2 | France | 1989 | HG974563 | HG974564 |
| 14 | 903/78 | A1bB1 | Hungary | 1978 | JQ411012 | JQ411013 |
| 15 | 9109 | A2B1 | USA | 2003 | AY462027 | AY459321 |
| 16 | 94432 | A3B2 | France | 1994 | AM167550 | AM167551 |
| 17 | BD3/99 | A3B2 | Bangladesh | 1999 | AF362776 | AF362770 |
| 18 | Bpop/03/Poland/2003 | A3B1 | Poland | 2003 | MH545934 | MH545935 |
| 19 | Bug/03/Poland/2003 | A3B4 | Poland | 2003 | MT629830 | MT629833 |
| 20 | CA-D495 | A3B1 | USA | 2009 | JF907703 | JF907704 |
| 21 | CA-K785 | A3B1 | USA | 2009 | JF907702 | JF907705 |
| 22 | CEF94 | A1bB1 | - | - | AF194428 | AF194429 |
| 23 | Cro-Pa/98 | A1bB1 | Croatia | 1998 | EU184689 | EU184690 |
| 24 | Cu-1 | A1bB1 | vaccine | - | D00867 | AF362775 |
| 25 | Cu-1wt | A1aB1 | Germany | 1975 | AF362747 | AF362748 |
| 26 | D3976/1 | A3B1 | Germany | 2017 | MN786767 | MN786769 |
| 27 | D4320/6 | A3B1 | Denmark | 2018 | MN786768 | MN786770 |
| 28 | D6948 | A3B2 | Netherlands | 1989 | AF240686 | AF240687 |
| 29 | D78 | A1bB1 | Netherlands | 1978 | AF499929 | AF499930 |
| 30 | DD1 | A3B2 | Russia | 2016 | MH644846 | MH644847 |
| 31 | Faragher 52/70 | A1aB1 | UK | 1970 | HG974565 | HG974566 |
| 32 | GA/1479/2004 | A1aB1 | USA | 2004 | MN814843 | MN814844 |
| 33 | GLS | A2B1 | USA | 1987 | AY368653 | AY368654 |
| 34 | Gx | A3B3 | China | 1996 | AY444873 | AY705393 |
| 35 | GXB02 | A1aB1 | China | 2020 | MZ740264 | MZ740265 |
| 36 | GX-NN-L | A3B3 | China | 2011 | JX134485 | JX134486 |
| 37 | GX-NNZ-11 | A2B1 | China | 2011 | JX134483 | JX134484 |
| 38 | HLJ-0504 | A3B3 | China | 2005 | GQ451330 | GQ451331 |
| 39 | IBD13HeB01 | A3B1 | China | 2013 | KP676467 | KP676468 |
| 40 | IBD16HeN01 | A2B1 | China | 2016 | MT179710 | MT179711 |
| 41 | IBDV/Italy/1829/2011 | A6B1 | Italy | 2011 | KY930929 | KX520665 |
| 42 | IBDV-HeN20-7103 | A1bB1 | China | 2020 | MW682877 | MW682878 |
| 43 | Irwin Moulthrop | A1aB1 | USA | 1967 | AY029164 | AY029165 |
| 44 | ks | A3B2 | Israel | 1990 | DQ927042 | DQ927043 |
| 45 | li4129/2014 | A3B4 | Finland | 2014 | MG739298 | MG739299 |
| 46 | Lukert | A1aB1 | USA | 1973 | AY918948 | AY918947 |
| 47 | OH | A0B1 | USA | 1981 | U30818 | U30819 |
| 48 | OKYM | A3B2 | Japan | 1991 | D49706 | D49707 |
| 49 | P2 | A1bB1 | Germany | 1977 | X84034 | X84035 |
| 50 | P3009 | A1aB1 | Taiwan | 1988 | MH816964 | MK040596 |
| 51 | QZ191002 | A2B1 | China | 2019 | MZ066613 | MZ066615 |
| 52 | SH95 | A3B1 | China | 1995 | AY134874 | AY134875 |
| 53 | SHG19 | A2B1 | China | 2018 | MN393076 | MN393077 |
| 54 | SHG352 | A2B1 | China | 2018 | MT179720 | MT179722 |
| 55 | STC | A1a | USA | 1967 | D00499 | - |
| 56 | TASIK | A3B2 | Indonesia | 1994 | AF322444 | AF322445 |
| 57 | TL2004 | A1bB2 | China | 2004 | DQ088175 | DQ118374 |
| 58 | UK661 | A3B2 | UK | 1994 | NC004178 | NC004179 |
| 59 | UPM1432/2019 | A2B1 | Malaysia | 2019 | MT505343 | MT505348 |
| 60 | variant E | A2B1 | USA | 1985 | AF133904 | AF133905 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pikuła, A.; Lisowska, A. Genetics and Pathogenicity of Natural Reassortant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Emerging in Latvia. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101081
Pikuła A, Lisowska A. Genetics and Pathogenicity of Natural Reassortant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Emerging in Latvia. Pathogens. 2022; 11(10):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101081
Chicago/Turabian StylePikuła, Anna, and Anna Lisowska. 2022. "Genetics and Pathogenicity of Natural Reassortant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Emerging in Latvia" Pathogens 11, no. 10: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101081
APA StylePikuła, A., & Lisowska, A. (2022). Genetics and Pathogenicity of Natural Reassortant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Emerging in Latvia. Pathogens, 11(10), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11101081






