Nutritional Assessment in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)—Development of the Groningen IBD Nutritional Questionnaires (GINQ)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
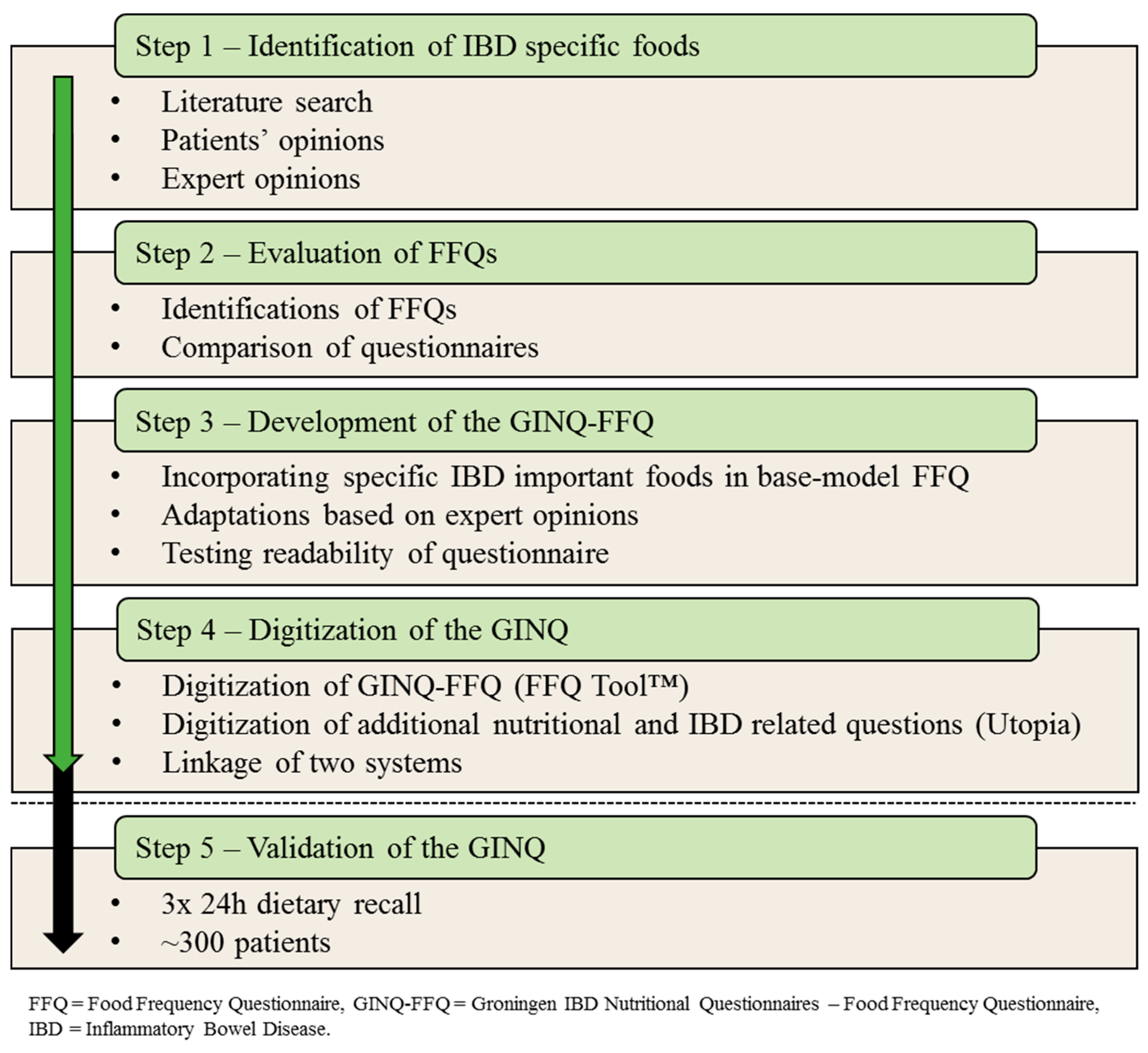
2.1. Step 1—Identification of IBD Specific Foods
2.2. Step 2—Evaluation of Current Methods
2.3. Step 3—Composition of the GINQ-FFQ
2.4. Step 4—Digitization of the GINQ
2.5. Step 5—Validation of the GINQ-FFQ
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| FFQ | Food Frequency Questionnaire |
| GINQ | Groningen IBD Nutritional Questionnaires |
| GINQ-FFQ | FFQ part of the GINQ |
| NEVO table | Dutch Food Composition Database |
| WUR | Wageningen University and Research |
| RDS | Research Data Support |
| MIAH | Monitor IBD at home questionnaire |
| UMCG | University Medical Centre Groningen |
| FR-QoL | Food-related Quality of Life questionnaire |
| IMID | Immune-mediated Inflammatory Disease |
References
- Aleksandrova, K.; Romero-Mosquera, B.; Hernandez, V. Diet, gut microbiome and epigenetics: Emerging links with inflammatory bowel diseases and prospects for management and prevention. Nutrients 2017, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomer, M.C.E. Dietary and nutritional considerations for inflammatory bowel disease. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2001, 70, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, V.; Tigchelaar, E.; Campmans-Kuijpers, M.; Sheedfar, F.; Imhann, F.; Dekens, J.; Wijmenga, C.; Swertz, M.; Franke, L.; Weersma, R.; et al. Habitual dietary intake of IBD patients differs from population controls: A case-control study. Nutrients. under review.
- Czuber-Dochan, W.; Morgan, M.; Hughes, L.D.; Lomer, M.C.E.; Lindsay, J.O.; Whelan, K. Perceptions and psychosocial impact of food, nutrition, eating and drinking in people with inflammatory bowel disease: A qualitative investigation of food-related quality of life. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaldaferri, F.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Musca, T.; Ingravalle, F.; Sicignano, L.L.; Mentella, M.; Miggiano, G.; Mele, M.C.; Gaetani, E.; et al. Nutrition and IBD: Malnutrition and/or Sarcopenia? A Practical Guide. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 8646495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, M.J.; van der Meulen-de Jong, A.E.; Romberg-Camps, M.J.; Becx, M.C.; Maljaars, J.P.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; Mahmmod, N.; Markus, T.; Hameeteman, W.M. Risk of impaired nutritional status and flare occurrence in IBD outpatients. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar]
- Haskey, N.; Gibson, D.L. An examination of diet for the maintenance of remission in inflammatory bowel disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, E.V. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1504–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eussen, S.J.; van Dongen, M.C.; Wijckmans, N.E.; Meijboom, S.; Brants, H.A.; de Vries, J.H.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Geelen, A.; Sluik, D.; Feskens, E.J.; et al. A national FFQ for the Netherlands (the FFQ-NL1.0): Development and compatibility with existing Dutch FFQs. Public Health Nutr. 2018, 21, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, J.H.M.; Dijkhuizen, M.; Tap, P.; Witteman, B.J.M. Patient’s Dietary Beliefs and Behaviours in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. 2019, 37, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streppel, M.T.; de Vries, J.H.; Meijboom, S.; Beekman, M.; de Craen, A.J.; Slagboom, P.E.; Feskens, E.J. Relative validity of the food frequency questionnaire used to assess dietary intake in the Leiden Longevity Study. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagianos, K.; Clara, I.; Carr, R.; Graff, L.A.; Walker, J.R.; Targownik, L.E.; Lix, L.M.; Rogala, L.; Miller, N.; Bernstein, C.N. What Are Adults With Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Eating? A Closer Look at the Dietary Habits of a Population-Based Canadian IBD Cohort. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 40, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Public Health and Environment. Dutch Food Composition Dataset (NEVO), 1st ed.; EuroFIR AISBL: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Keshteli, A.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Rajaie, S.; Askari, G.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Adibi, P. A Dish-based Semi-quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire for Assessment of Dietary Intakes in Epidemiologic Studies in Iran: Design and Development. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hughes, L.D.; King, L.; Morgan, M.; Ayis, S.; Direkze, N.; Lomer, M.C.; Lindsay, J.O.; Whelan, K. Food-related quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease: Development and validation of a questionnaire. J. Crohn Colitis 2015, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, M.J.; Roosen, D.; Degens, J.H.R.J.; van den Heuvel, T.R.A.; Romberg-Camps, M.; Hameeteman, W.; Bodelier, A.G.L.; Romanko, I.; Lukas, M.; Winkens, B.; et al. Development and Validation of a Patient-reported Score to Screen for Mucosal Inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns. Colitis 2019, 13, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baecke, J.A.; Burema, J.; Frijters, J.E. A short questionnaire for the measurement of habitual physical activity in epidemiological studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 36, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, R.; Hirata, S.; Yamada, M.; Nishiyama, T.; Kurosaka, M.; Tamura, Y. Reliability and validity of the Baecke physical activity questionnaire in adult women with hip disorders. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2007, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashvand, S.; Somi, M.H.; Rashidkhani, B.; Hekmatdoost, A. Dietary fatty acid intakes are related to the risk of ulcerative colitis: A case-control study. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2015, 30, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Khalili, H.; Konijeti, G.G.; Higuchi, L.M.; de Silva, P.; Korzenik, J.R.; Fuchs, C.S.; Willett, W.C.; Richter, J.M.; Chan, A.T. A prospective study of long-term intake of dietary fiber and risk of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, R.; Whitten, K.E.; Woodhead, H.; Leach, S.T.; Lemberg, D.A.; Day, A.S. Dietary intakes of children with Crohn’s disease. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 102, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatenstein, B.; Amre, D.; Jabbour, M.; Feguery, H. Examining the relative validity of an adult food frequency questionnaire in children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzan, M.I.E.; Mofarreh, M.A.A.; Sarkhy, A.A.A.; Assiri, A.M.; Hamed, Y.M. Pre-illness diet as risk factor in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili, H.; de Silva, P.S.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Lochhead, P.; Joshi, A.; Garber, J.J.; Richter, J.R.; Sauk, J.; Chan, A.T. Dietary Iron and Heme Iron Consumption, Genetic Susceptibility, and Risk of Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, J.S.; Gibson, P.R. Development and validation of a comprehensive semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire that includes FODMAP intake and glycemic index. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.B.; Lee, D.; Long, M.D.; Kappelman, M.D.; Martin, C.F.; Sandler, R.S.; Lewis, J.D. Dietary patterns and self-reported associations of diet with symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, M.; Nakane, K.; Takayama, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Ohno, H.; Ishii, H.; Tsuda, S.; Tsuji, T.; Komastu, M.; Sugawara, T. Development and Application of a Plant-Based Diet Scoring System for Japanese Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Perm. J. 2016, 20, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jowett, S.L.; Seal, C.J.; Phillips, E.; Gregory, W.; Barton, J.R.; Welfare, M.R. Dietary beliefs of people with ulcerative colitis and their effect on relapse and nutrient intake. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limdi, J.K.; Aggarwal, D.; McLaughlin, J.T. Dietary Practices and Beliefs in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 22, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zallot, C.; Quilliot, D.; Chevaux, J.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, C.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.M.; Freling, E.; Collet-Fenetrier, B.; Williet, N.; Ziegler, O.; Bigard, M.A.; et al. Dietary beliefs and behavior among inflammatory bowel disease patients. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holt, D.Q.; Strauss, B.J.; Moore, G.T. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease and their treating clinicians have different views regarding diet. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 30, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marion-Letellier, R.; Savoye, G.; Ghosh, S. IBD: In Food we Trust. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2015, 10, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christ, A.; Latz, E. The Western lifestyle has lasting effects on metaflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, M.J.; van der Meulen-de Jong, A.E.; Romberg-Camps, M.J.; Becx, M.C.; Maljaars, J.P.; Cilissen, M.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; Mahmmod, N.; Markus, T.; Hameeteman, W.M. Telemedicine for management of inflammatory bowel disease (myIBDcoach): A pragmatic, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peters, V.; Alizadeh, B.Z.; de Vries, J.H.; Dijkstra, G.; Campmans-Kuijpers, M.J. Nutritional Assessment in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)—Development of the Groningen IBD Nutritional Questionnaires (GINQ). Nutrients 2019, 11, 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112739
Peters V, Alizadeh BZ, de Vries JH, Dijkstra G, Campmans-Kuijpers MJ. Nutritional Assessment in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)—Development of the Groningen IBD Nutritional Questionnaires (GINQ). Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112739
Chicago/Turabian StylePeters, Vera, Behrooz Z Alizadeh, Jeanne HM de Vries, Gerard Dijkstra, and Marjo JE Campmans-Kuijpers. 2019. "Nutritional Assessment in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)—Development of the Groningen IBD Nutritional Questionnaires (GINQ)" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112739
APA StylePeters, V., Alizadeh, B. Z., de Vries, J. H., Dijkstra, G., & Campmans-Kuijpers, M. J. (2019). Nutritional Assessment in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)—Development of the Groningen IBD Nutritional Questionnaires (GINQ). Nutrients, 11(11), 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112739




