Development and Evaluation of an Internet-Based Diabetes Nutrition Education Resource
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
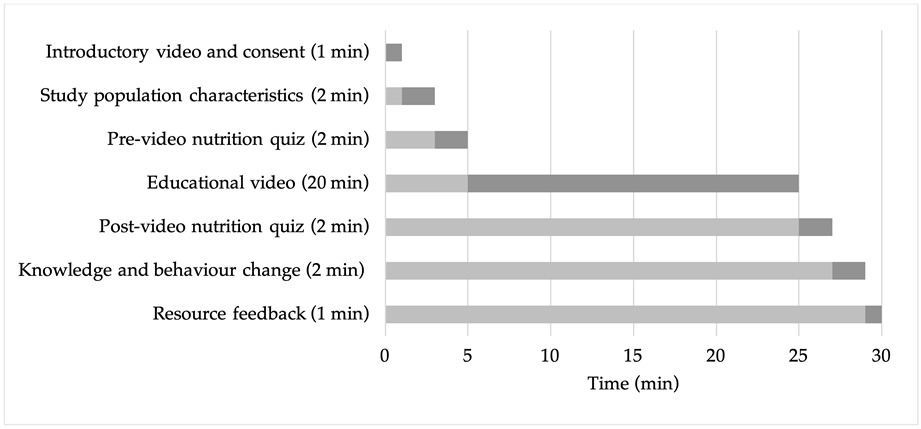
2.2. The IDNET
2.3. Validation Study (Control Group)
2.4. IDNET Video Development (Needs Assessment)
- 1)
- Pathology of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes;
- 2)
- Foods and beverages that impact blood glucose;
- 3)
- Meal portions and a healthy plate model;
- 4)
- Meal and snack ideas;
- 5)
- Exercise and nutrition tips for managing pre- and type 2 diabetes.
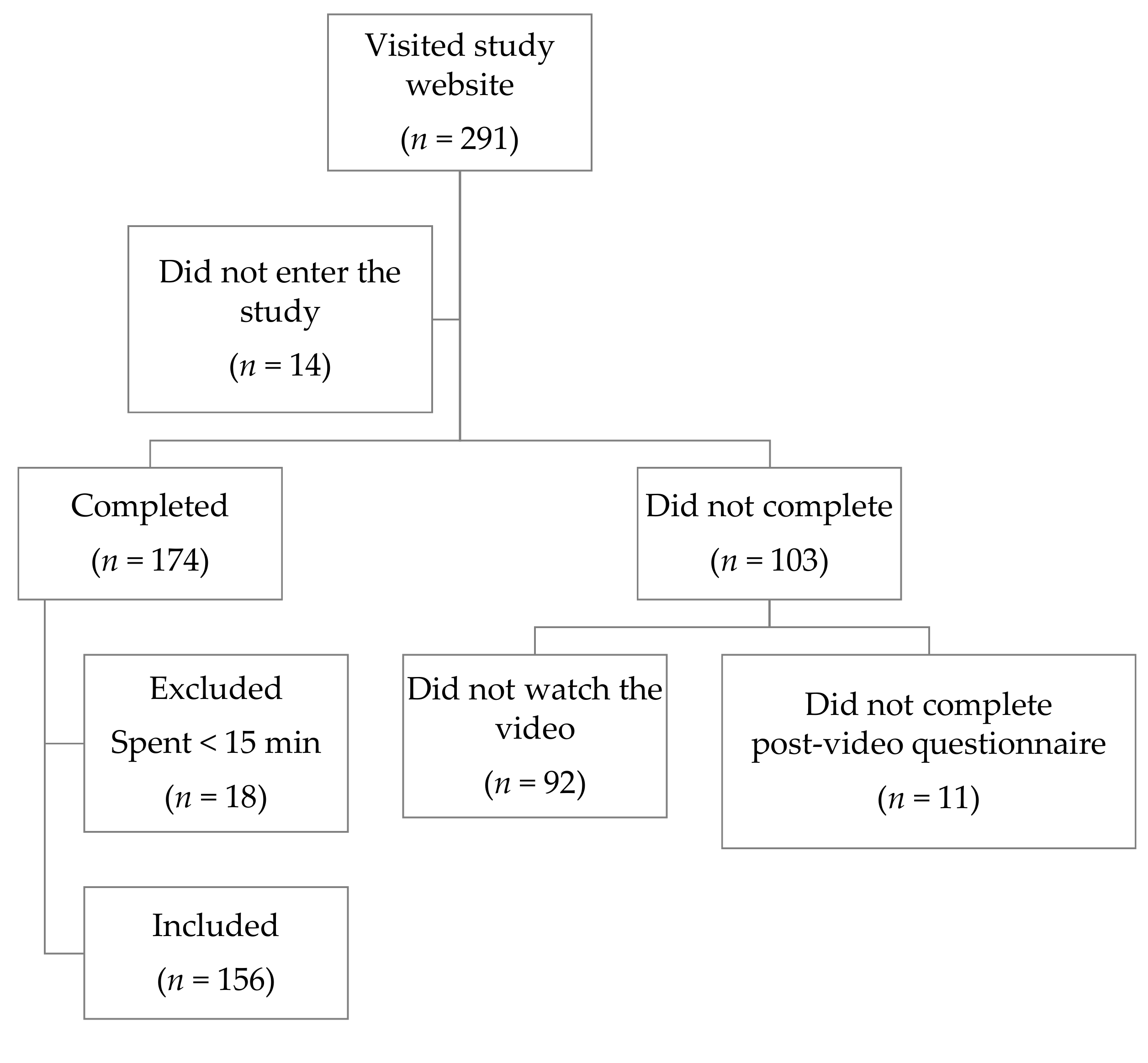
2.5. Participants and Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Needs Assessment Result
3.2. Validation Study
3.3. IDNET Participants’ Characteristics
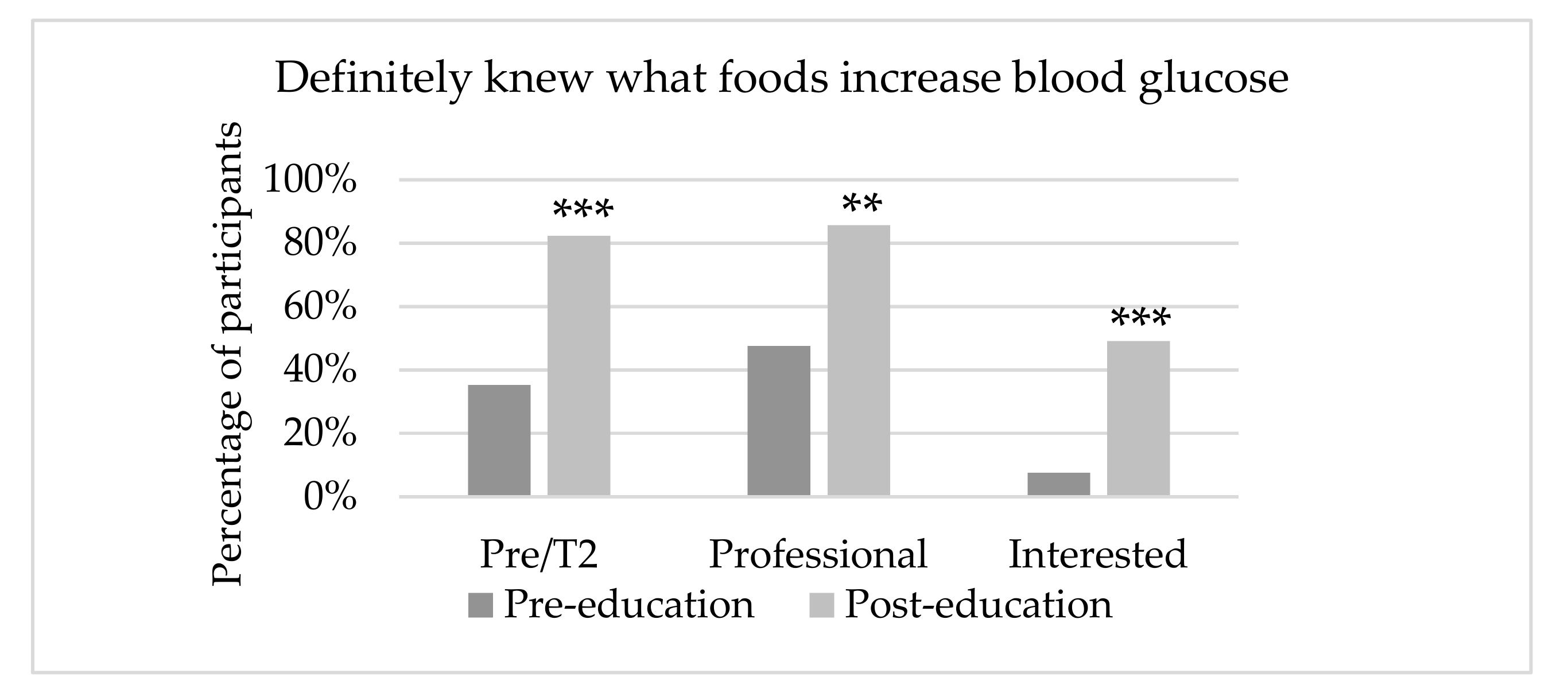
3.4. IDNET Quiz
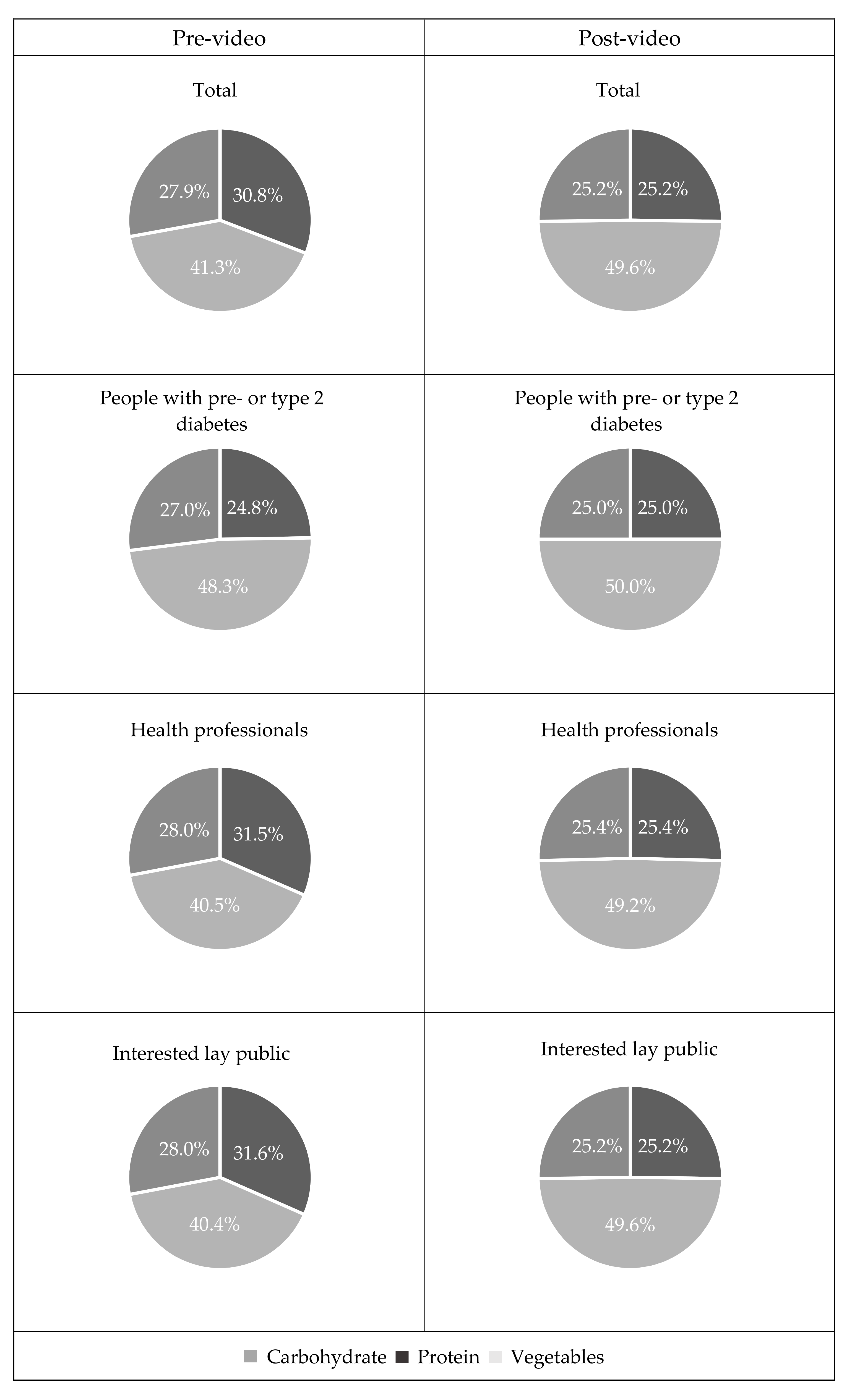
3.5. Perceived Dietary and Behaviour Change
3.6. IDNET Feedback
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 8th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guariguata, L.; Whiting, D.R.; Hambleton, I.; Beagley, J.; Linnenkamp, U.; Shaw, J.E. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, S.L.; Engelgau, M.M.; Venkat Narayan, K.M. Effectiveness of Self-Management Training in Type 2 Diabetes: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 561–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, G.M.V.; Kegels, G. Effects of the First Line Diabetes Care (FiLDCare) self-management education and support project on knowledge, attitudes, perceptions, self-management practices and glycaemic control: A quasi-experimental study conducted in the Northern Philippines. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinsbekk, A.; Rygg, L.; Lisulo, M.; Rise, M.B.; Fretheim, A. Group based diabetes self-management education compared to routine treatment for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2012, 12, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, Z.; Ba, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wen, Y. Nutritional and eating education improves knowledge and practice of patients with type 2 diabetes concerning dietary intake and blood glucose control in an outlying city of China. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deakin, T.; McShane, C.E.; Cade, J.E.; Williams, R. Group based training for self-management strategies in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-C.; Hsu, C.-C.; Wang, H.-S.; Shin, S.-J. Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial to Evaluate Effectiveness of Registered Dietitian–Led Diabetes Management on Glycemic and Diet Control in a Primary Care Setting in Taiwan. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odgers-Jewell, K.; Ball, L.; Kelly, J.; Isenring, E.; Reidlinger, D.; Thomas, R. Effectiveness of group-based self-management education for individuals with Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analyses and meta-regression. Diabetic Med. 2017, 34, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes UK. Improving Supported Self-Management for People with Diabetes; Diabetes UK: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Attridge, M.; Creamer, J.; Ramsden, M.; Cannings-John, R.; Hawthorne, K. Culturally appropriate health education for people in ethnic minority groups with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 9, CD006424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.; Duggan, M. Health Online 2013; Pew Research Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, A.; Miller, M.; Smith, P.; Bell, A.; Crothers, C. The Internet in New Zealand 2013; Institute of Culture, Discourse & Communication, AUT University: Auckland, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lustria, M.L.; Smith, S.A.; Hinnant, C.C. Exploring digital divides: An examination of eHealth technology use in health information seeking, communication and personal health information management in the USA. Health Inform. J 2011, 17, 224–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reininger, B.; Mecca, L.P.; Stine, K.M.; Schultz, K.; Ling, L.; Halpern, D. A Type 2 Diabetes Prevention Website for African Americans, Caucasians, and Mexican Americans: Formative Evaluation. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2013, 2, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, K.; Eastwood, S.V.; Michie, S.; Farmer, A.; Barnard, M.L.; Peacock, R.; Wood, B.; Edwards, P.; Murray, E. Computer-based interventions to improve self-management in adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadas, A.; Quek, K.F.; Chan, C.K.Y.; Oldenburg, B. Web-based interventions for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review of recent evidence. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2011, 80, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadas, A.; Chan, C.K.; Oldenburg, B.; Hussien, Z.; Quek, K.F. A web-based dietary intervention for people with type 2 diabetes: Development, implementation, and evaluation. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2015, 22, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weymann, N.; Dirmaier, J.; von Wolff, A.; Kriston, L.; Härter, M. Effectiveness of a Web-based tailored interactive health communication application for patients with type 2 diabetes or chronic low back pain: Randomized controlled trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2015, 17, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, S.J.; Chapman-Novakofski, K.M.; Scherer, J.A. Your Guide to Diet and Diabetes: Web-based diabetes education tailored to Hispanics. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2009, 41, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, B.S.; Brodsky, I.G.; Lawless, K.A.; Smolin, L.I.; Arozullah, A.M.; Smith, E.V.; Berbaum, M.L.; Heckerling, P.S.; Eiser, A.R. Implementation and Evaluation of a Low-Literacy Diabetes Education Computer Multimedia Application. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorig, K.; Ritter, P.L.; Laurent, D.D.; Plant, K.; Green, M.; Jernigan, V.B.B.; Case, S. Online diabetes self-management program. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.; Cranch, H.; Littlemore, K.; Mortimer, J.; Platts, J.; Stephens, J.W. A pilot service-evaluation examining change in HbA1c related to the prescription of internet-based education films for type 2 diabetes. Prim. Care Diabetes 2017, 11, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijdenes, M.; Henneman, L.; Qureshi, N.; Kostense, P.J.; Cornel, M.C.; Timmermans, D.R. Using web-based familial risk information for diabetes prevention: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasgow, R.E.; Wagner, E.H.; Kaplan, R.M.; Vinicor, F.; Smith, L.; Norman, J. If diabetes is a public health problem, why not treat it as one? A population-based approach to chronic illness. Ann. Behav. Med. 1999, 21, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, D.; Moshang, J.; Jabbour, S. Diabetes Knowledge: Are Resident Physicians and Nurses Adequately Prepared to Manage Diabetes? Endocr. Pract. 2007, 13, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, M.L.; Herring, S.J.; Sood, M.; Shah, N.R.; Kalet, A.L. What do resident physicians know about nutrition? An evaluation of attitudes, self-perceived proficiency and knowledge. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2008, 27, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Monro, J.; Venn, B. Carbohydrate Knowledge and Expectations of Nutritional Support among Five Ethnic Groups Living in New Zealand with Pre-and Type 2 Diabetes: A Qualitative Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2017. Diabetes Care 2017, 40 (Suppl. 1), s4–s5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Zealand Guidelines Group. Guidance on the Management of Type 2 Diabetes 2011; New Zealand Guidelines Group: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, E.; de Nooijer, J.; Schaper, N.C.; Schoonus-Spit, M.H.; Janssen, M.A.; de Vries, N.K. Evaluation of the web-based Diabetes Interactive Education Programme (DIEP) for patients with type 2 diabetes. Patient Educ. Couns. 2011, 86, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, P.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Farrant, S.; Fromson, S.; Meadows, K. Effect of computer-based learning on diabetes knowledge and control. Diabetes Care 1986, 9, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrenson, R.; Joshy, G.; Eerens, Y.; Johnstone, W. How do newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes in the Waikato get their diabetes education? J. Prim. Health Care 2010, 2, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, H.; Reynolds, A.N.; Venn, B.J. Perceptions of the Healthfulness of Foods of New Zealand Adults Living With Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 339–345.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, Y.; Lindgren, T.G.; Bonnet, K.; Kamitani, E. Perception and sense of control over eating behaviors among a diverse sample of adults at risk for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2014, 40, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, C.; Ryan, M.; Gibney, M.J.; O’Shea, D. Diabetes-related nutrition knowledge and dietary intake among adults with type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.C.; Roediger, H.L. Testing improves long-term retention in a simulated classroom setting. Eur. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2007, 19, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, N.D. Teaching and Learning Styles: VARK Strategies; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Houts, P.S.; Doak, C.C.; Doak, L.G.; Loscalzo, M.J. The role of pictures in improving health communication: A review of research on attention, comprehension, recall, and adherence. Patient Educ. Couns. 2006, 61, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test | Re-Test | ∆Score (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validation | 12.7 | 12.9 | 5.4% (−1.7%, 12.3%) | 0.394 |
| Characteristics | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Age, average (range) years | 34.3 (19–76) |
| Female, n (%) | 126 (81%) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |
| European | 110 (70%) |
| Non-European | 56 (30%) |
| Education, university, n (%) | 133 (85%) |
| Average years of diagnosis, years | |
| Pre-diabetes | 2.7 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 9.1 |
| Pre- or type 2 diabetes, n (%) | 17 (11%) |
| Health professionals, n (%) | 21 (14%) |
| Interested lay public, n (%) | 118 (75%) |
| At risk of type 2 diabetes | 7 (5%) |
| Look after people with type 2 diabetes | 6 (4%) |
| Have type 1 diabetes | 2 (1%) |
| Study or research diabetes | 27 (17%) |
| Personal interest | 76 (49%) |
| n | Pre-video | Post-video | ∆ Knowledge (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| People with pre- or type 2 diabetes | 17 | 13.2 | 15.1 | 17.4% (5.3%, 29.7%) | 0.013 |
| Health professionals | 21 | 14.8 | 16.4 | 12.8% (5.1%, 20.6%) | 0.003 |
| Interested lay public | 118 | 13.6 | 15.2 | 16.3% (11.1%, 21.5%) | <0.001 |
| European | 110 | 13.8 | 15.5 | 16.7% (11.7, 21.7%) | <0.001 |
| Non-European | 46 | 13.5 | 14.9 | 14.1% (5.9%, 22.3%) | 0.003 |
| Total | 156 | 13.7 | 15.4 | 16.0% (4.3, 20.2%) | <0.001 |
| n | Δ Meal Composition Pre-video (95% CI) | Δ Meal Composition Post-video (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| People with pre- or type 2 diabetes | 17 | 3.6 (0.9–6.4) | 0.0 (0.0, 0.0) | 0.018 |
| Health professionals | 21 | 5.4 (3.1–7.8) | 0.4 (−0.4, 1.1) | <0.001 |
| Interested lay public | 118 | 5.9 (4.9–6.9) | 0.3 (0.1, 0.6) | <0.001 |
| Total | 156 | 5.6 (4.7–6.5) | 0.8 (0.1, 0.5) | <0.001 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Monro, J.; Venn, B.J. Development and Evaluation of an Internet-Based Diabetes Nutrition Education Resource. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061217
Zhang Z, Monro J, Venn BJ. Development and Evaluation of an Internet-Based Diabetes Nutrition Education Resource. Nutrients. 2019; 11(6):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061217
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhuoshi, John Monro, and Bernard J. Venn. 2019. "Development and Evaluation of an Internet-Based Diabetes Nutrition Education Resource" Nutrients 11, no. 6: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061217
APA StyleZhang, Z., Monro, J., & Venn, B. J. (2019). Development and Evaluation of an Internet-Based Diabetes Nutrition Education Resource. Nutrients, 11(6), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061217






