Natural Cellulose-Based Multifunctional Nanofibers for the Effective Removal of Particulate Matter and Volatile Organic Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
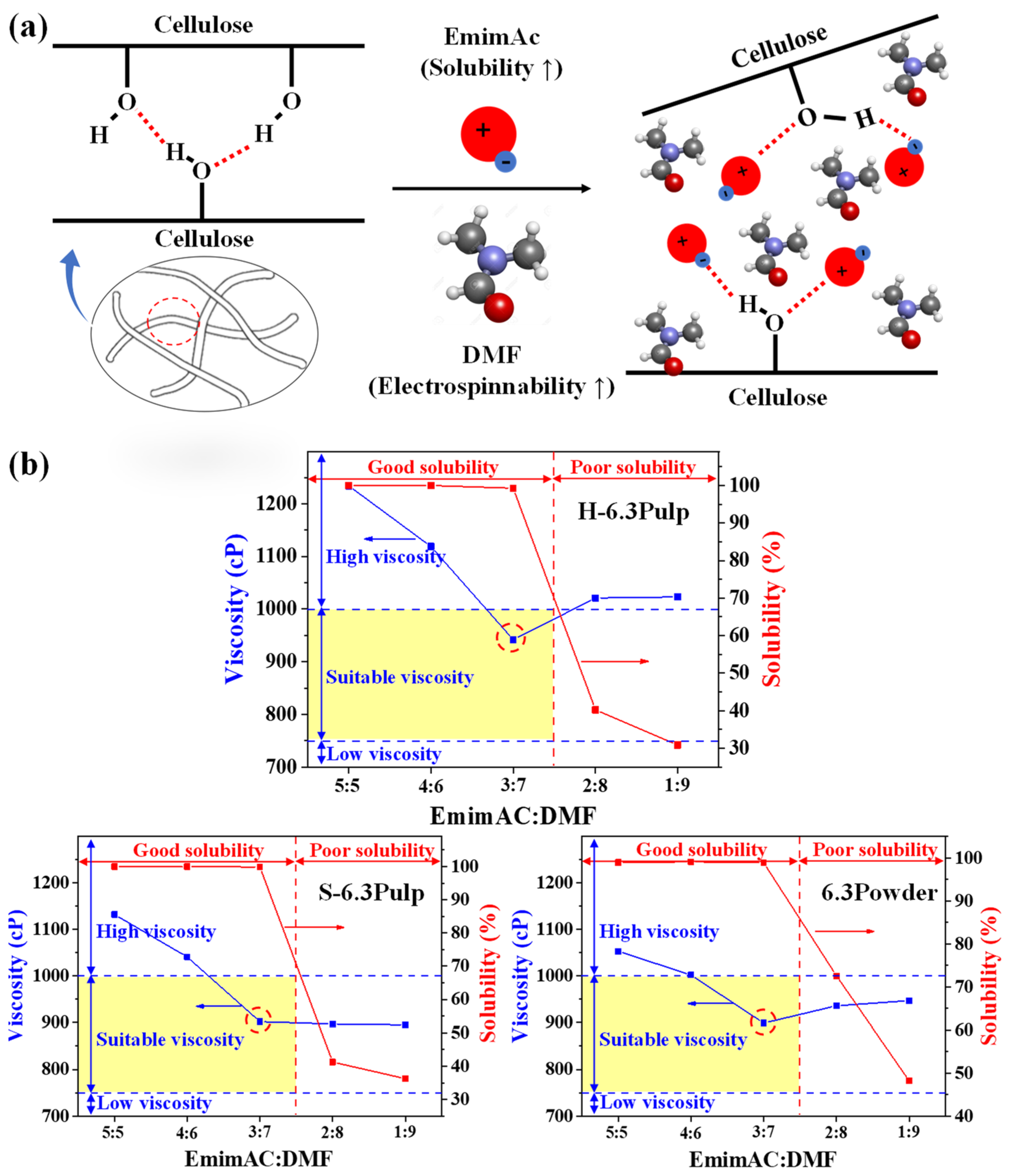
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navas-Martín, M.Á.; Oteiza, I.; Cuerdo-Vilches, T. Dwelling in Times of COVID-19: An Analysis on Habitability and Environmental Factors of Spanish Housing. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 60, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, P.; Östman, C.; Sällsten, G. Indoor Levels of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Homes with or Without Wood Burning for Heating. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5074–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Z. The Hematologic Effects of BTEX Exposure Among Elderly Residents in Nanjing: A Cross-Sectional Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 10552–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, D.Y.H.; Chen, S.-C.; Zuo, Z. PM2.5 in China: Measurements, Sources, Visibility and Health Effects, and Mitigation. Particuology 2014, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Azadi, E.; Hussain, C.M. Fabrication of Air Filters with Advanced Filtration Performance for Removal of Viral Aerosols and Control the Spread of COVID-19. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 303, 102653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, J. Surface Modification of Coconut Shell Based Activated Carbon for the Improvement of Hydrophobic VOC Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.-N.; Chen, S.-C. Simultaneous Removal of VOCs and PM2.5 by Metal-Organic Framework Coated Electret Filter Media. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Low, Z.X.; Feng, S.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Z. Multifunctional Hybrid Porous Filters with Hierarchical Structures for Simultaneous Removal of Indoor VOCs, Dusts and Microorganisms. Nanoscale. 2017, 9, 5433–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, S.; Pierpaoli, M.; Riderelli, L.; Qi, S.; Ruello, M.L. Preparation and Characterization of an Electrospun PLA-Cyclodextrins Composite for Simultaneous High-Efficiency PM and VOC Removal. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karzar Jeddi, M.K.; Laitinen, O.; Liimatainen, H. Magnetic Superabsorbents Based on Nanocellulose Aerobeads for Selective Removal of Oils and Organic Solvents. Mater. Des. 2019, 183, 108115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.D.; Ang, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, C.; Chen, F.; Ng, B.F.; Wan, M.P.; Wong, S.-C.; Li, Z.; et al. Highly Porous Polymer Nanofibrous Aerogels Cross-Linked via Spontaneous Inter-fiber Stereocomplexation and Their Potential for Capturing Ultrafine Airborne Particles. Polymer 2019, 179, 121649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fang, Y.; Ni, X.; Wu, K.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Riffat, S.B. Fabrication and Characterization of a Novel Konjac Glucomannan-Based Air Filtration Aerogels Strengthened by Wheat Straw and Okara. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, R.; Haghighat Mamaghani, A.H.; Boluk, Y.; Hashisho, Z. Synthesis and Characterization of Electrospun PAN-based Activated Carbon Nanofibers Reinforced with Cellulose Nanocrystals for Adsorption of VOCs. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Trabzon, L.; Kilic, A.; Zaidi, S.J. Recent Advances in Nanofibrous Membranes: Production and Applications in Water Treatment and Desalination. Desalination 2020, 478, 114178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hong, F.F.; Yuan, J.; Li, L.; Fang, M.; Wei, W.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y. Super Solvent of Cellulose with Extra High Solubility for Tunable Cellulose Structure with Versatile Application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Tsuchii, K. Dissolution Behavior of Cellulose in a Novel Cellulose Solvent. Carbohydr. Res. 2022, 511, 108490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, D.; Ning, X. Multifunctional Composite Membrane Based on BaTiO3@PU/PSA Nanofibers for High-Efficiency PM2.5 Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Lee, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chu, S.; et al. Nanofiber Air Filters with High-Temperature Stability for Efficient PM2.5 Removal from the Pollution Sources. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugly, E.; Pauliukaityte, I.; Ciuzas, D.; Bulota, M.; Peciulyte, L.; Martuzevicius, D. Cellulose Electrospinning from Ionic Liquids: The Effects of Ionic Liquid Removal on the Fiber Morphology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 285, 119260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zugenmaier, P. Crystalline Cellulose and Derivatives: Characterization and Structures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kadokawa, J.I. Cellulose Crystal Dissolution in Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids: A Theoretical Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casasola, R.; Thomas, N.L.; Trybala, A.; Georgiadou, S. Electrospun Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) Fibres: Effect of Different Solvent Systems on Fibre Morphology and Diameter. Polymer 2014, 55, 4728–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Xue, Y.; Xuan, H.; Yuan, H. A Solvent System Involved Fabricating Electrospun Polyurethane Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakai, F.; Akatsu, T. Anisotropic Viscosities and Shrinkage Rates in Sintering of Particles Arranged in a Simple Orthorhombic Structure. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, B.V.M.; Ramires, E.C.; Santos, R.P.O.; Frollini, E.J. Ultrathin and Nanofibers via Room Temperature Electrospinning from Trifluoroacetic Acid Solutions of Untreated Lignocellulosic Sisal Fiber or Sisal Pulp. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Lee, H.W.; Ye, M.; Zheng, G.; Liu, N.; Li, W.; Cui, Y. Transparent Air Filter for High-Efficiency PM2.5 Capture. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Zhou, L.; Wu, H.; Yang, L. Alkylation Modified Pistachio Shell-Based Biochar to Promote the Adsorption of VOCs in High Humidity Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 295, 118714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ece, M.Ş.; Kutluay, S. Comparative and Competitive Adsorption of Gaseous Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylene onto Natural Cellulose-Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Adsorption Efficiency (%) | Pressure Drop | Air Permeability | PM2.5 Quality Factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM0.5 | PM1.0 | PM2.5 | (Pa) | (cm3/cm2/s) | (Pa–1) | |
| H-6.0NF | 85.36 | 88.14 | 89.12 | 98 | 277 | 0.24 |
| H-6.3NF | 92.25 | 97.25 | 97.38 | 105 | 284 | 0.28 |
| H-6.5NF | 88.25 | 93.22 | 95.25 | 97 | 270 | 0.23 |
| S-6.0NF | 83.24 | 87.15 | 92.36 | 96 | 274 | 0.22 |
| S-6.3NF | 86.25 | 88.83 | 94.21 | 102 | 283 | 0.27 |
| S-6.5NF | 83.12 | 89.12 | 95.31 | 93 | 269 | 0.21 |
| P-6.0NF | 74.15 | 76.81 | 79.17 | 88 | 281 | 0.19 |
| P-6.3NF | 75.43 | 77.22 | 81.21 | 99 | 277 | 0.25 |
| P-6.5NF | 73.25 | 76.22 | 80.05 | 86 | 264 | 0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, S.H.; Yun, J.S. Natural Cellulose-Based Multifunctional Nanofibers for the Effective Removal of Particulate Matter and Volatile Organic Compounds. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111720
Ji SH, Yun JS. Natural Cellulose-Based Multifunctional Nanofibers for the Effective Removal of Particulate Matter and Volatile Organic Compounds. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(11):1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111720
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Sang Hyun, and Ji Sun Yun. 2023. "Natural Cellulose-Based Multifunctional Nanofibers for the Effective Removal of Particulate Matter and Volatile Organic Compounds" Nanomaterials 13, no. 11: 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111720
APA StyleJi, S. H., & Yun, J. S. (2023). Natural Cellulose-Based Multifunctional Nanofibers for the Effective Removal of Particulate Matter and Volatile Organic Compounds. Nanomaterials, 13(11), 1720. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13111720






