Biotin-Linked Ursolic Acid Conjugates as Selective Anticancer Agents and Target-Identification Tools for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
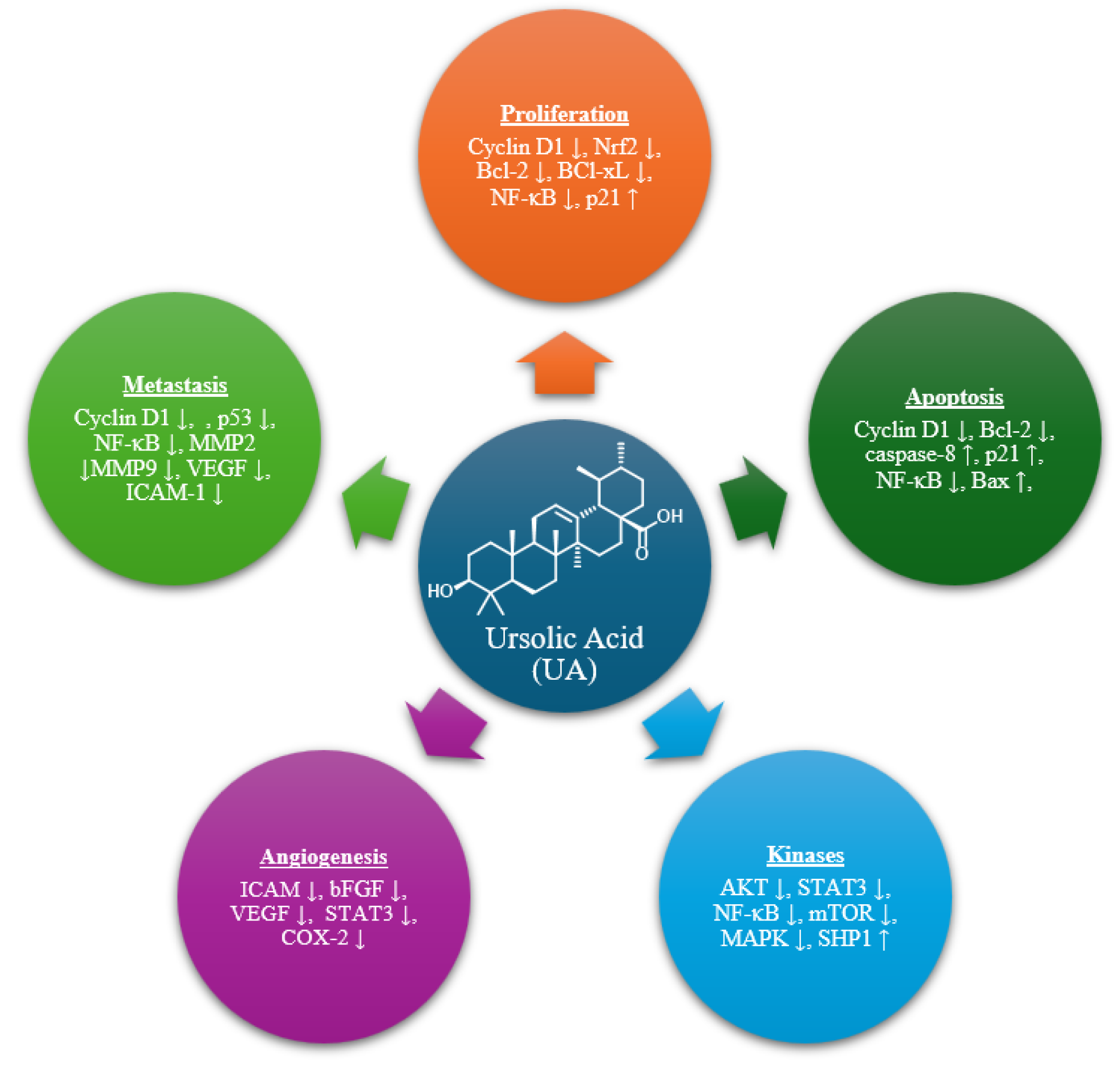
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
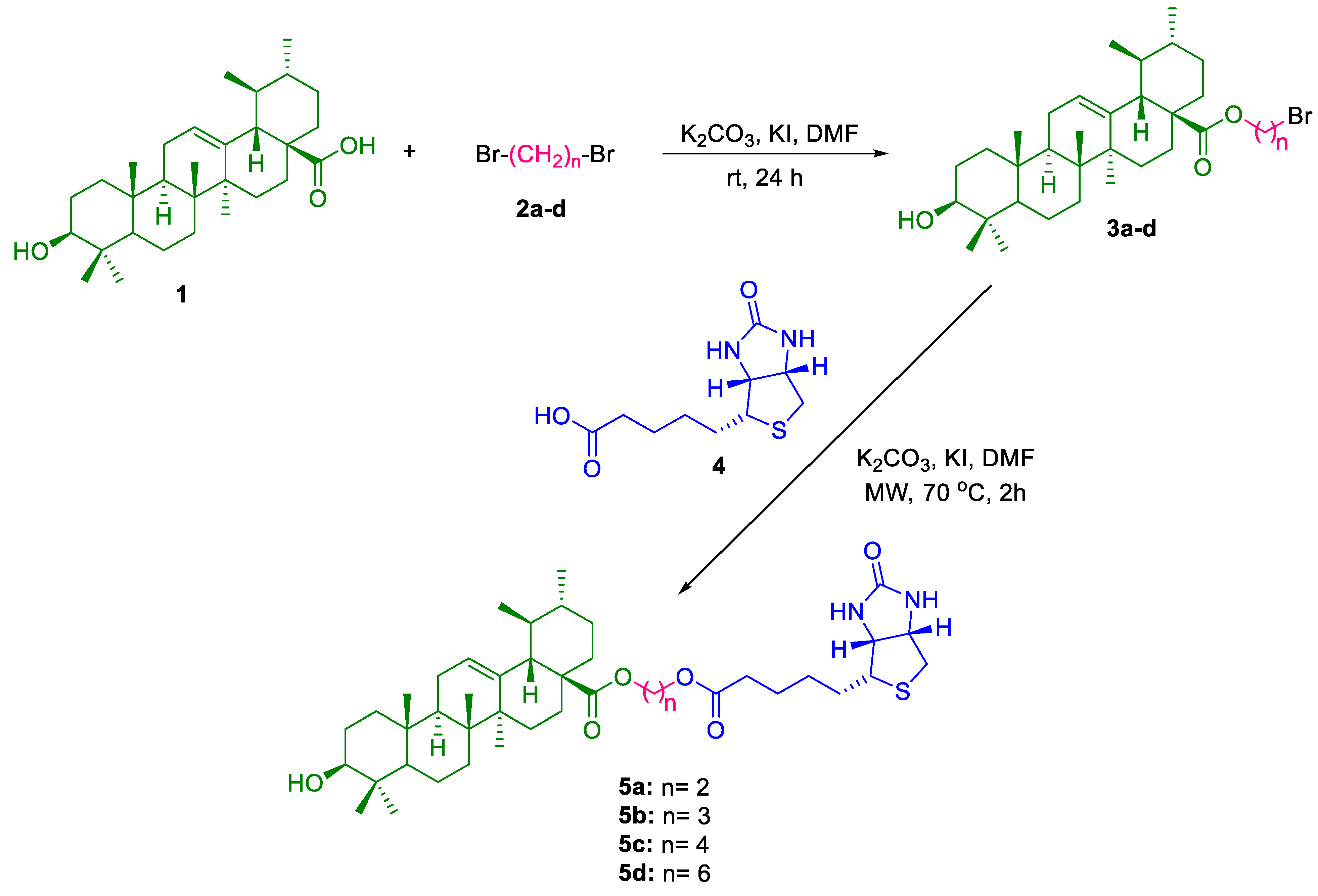
2.1. Chemistry
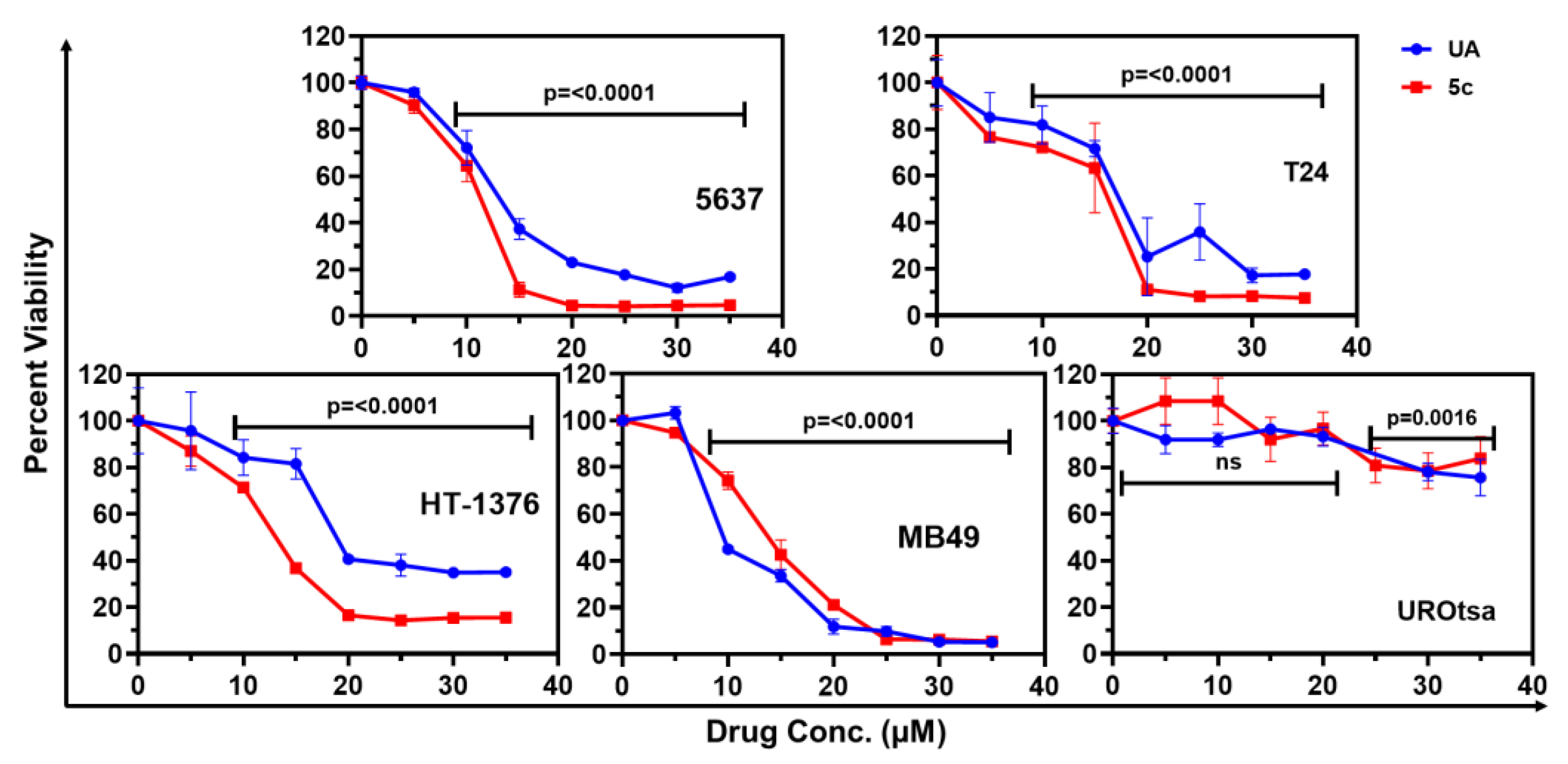
2.2. Antiproliferative Activity
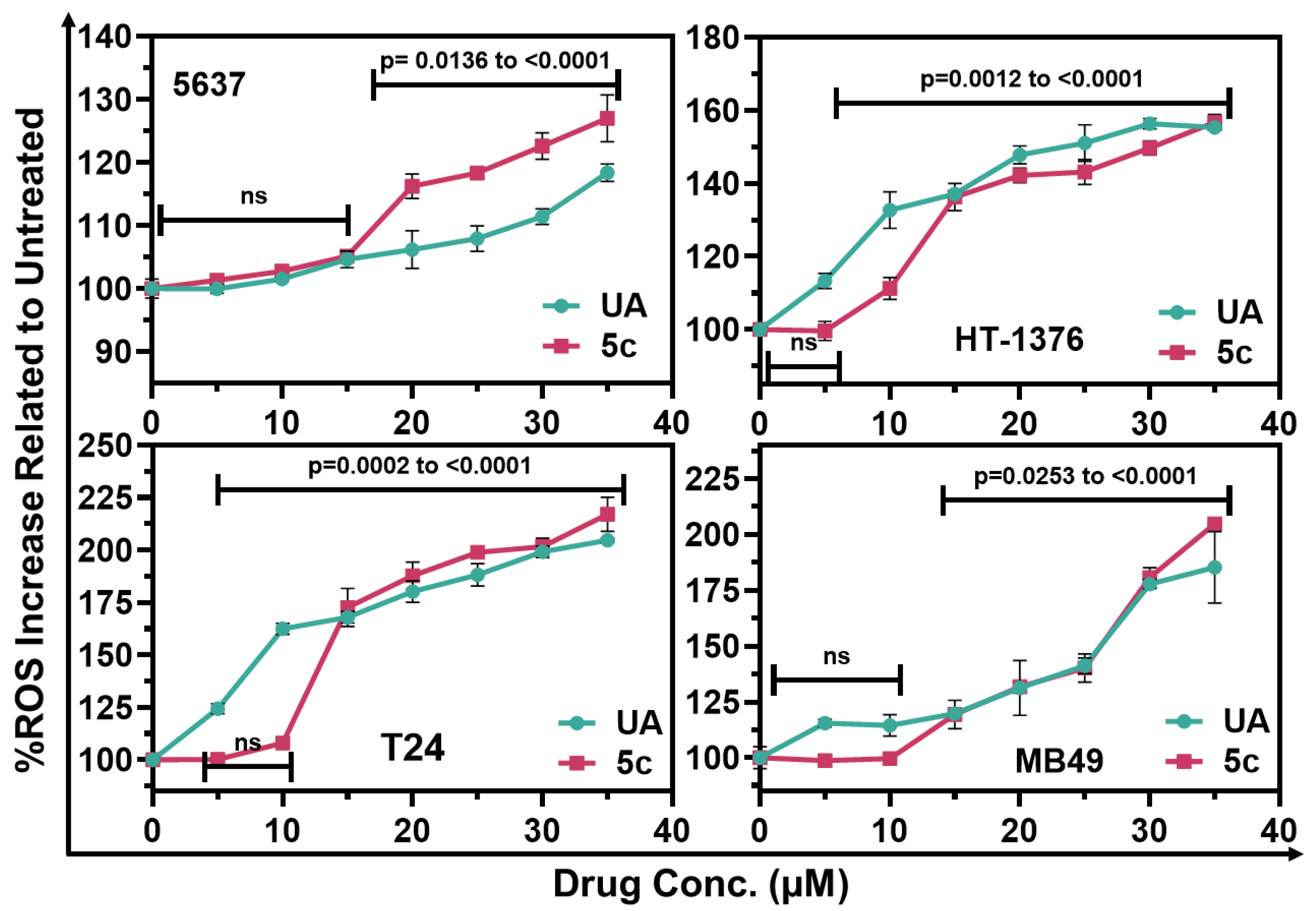
2.3. Induction of Reactive Oxygen Species by UA and Compound 5c in Bladder Cancer Cells
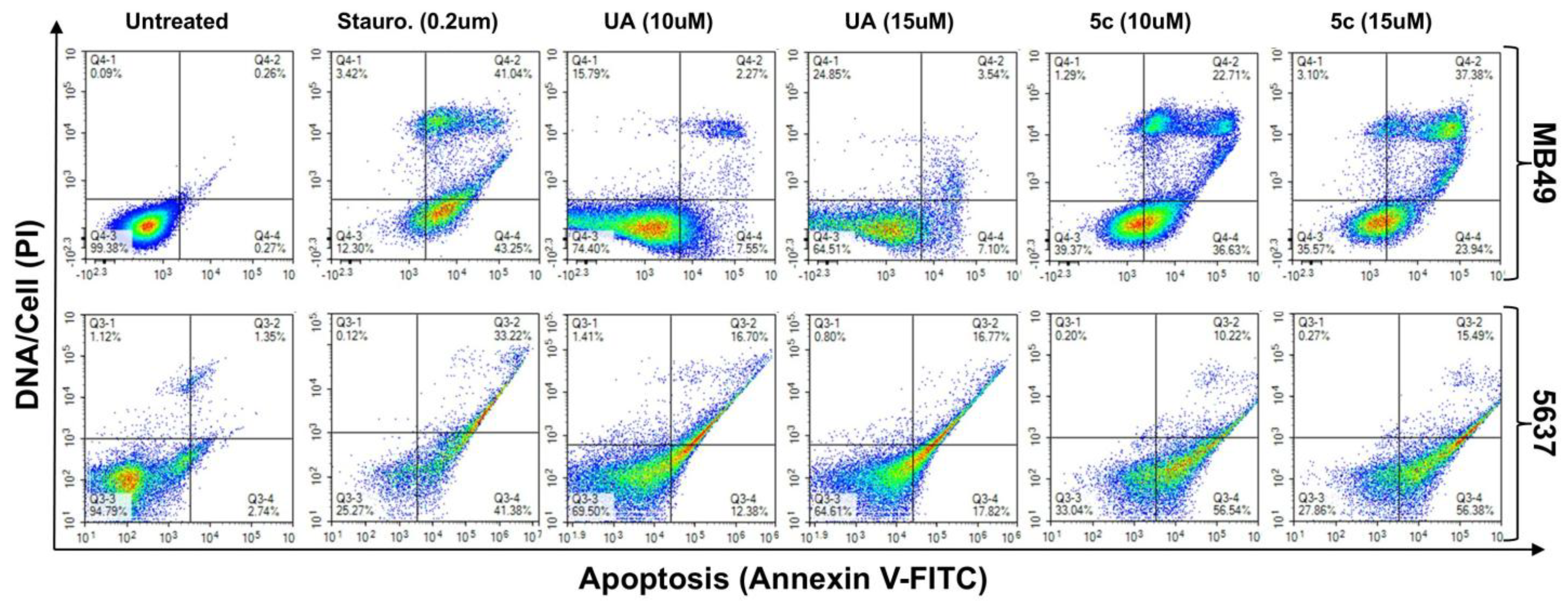
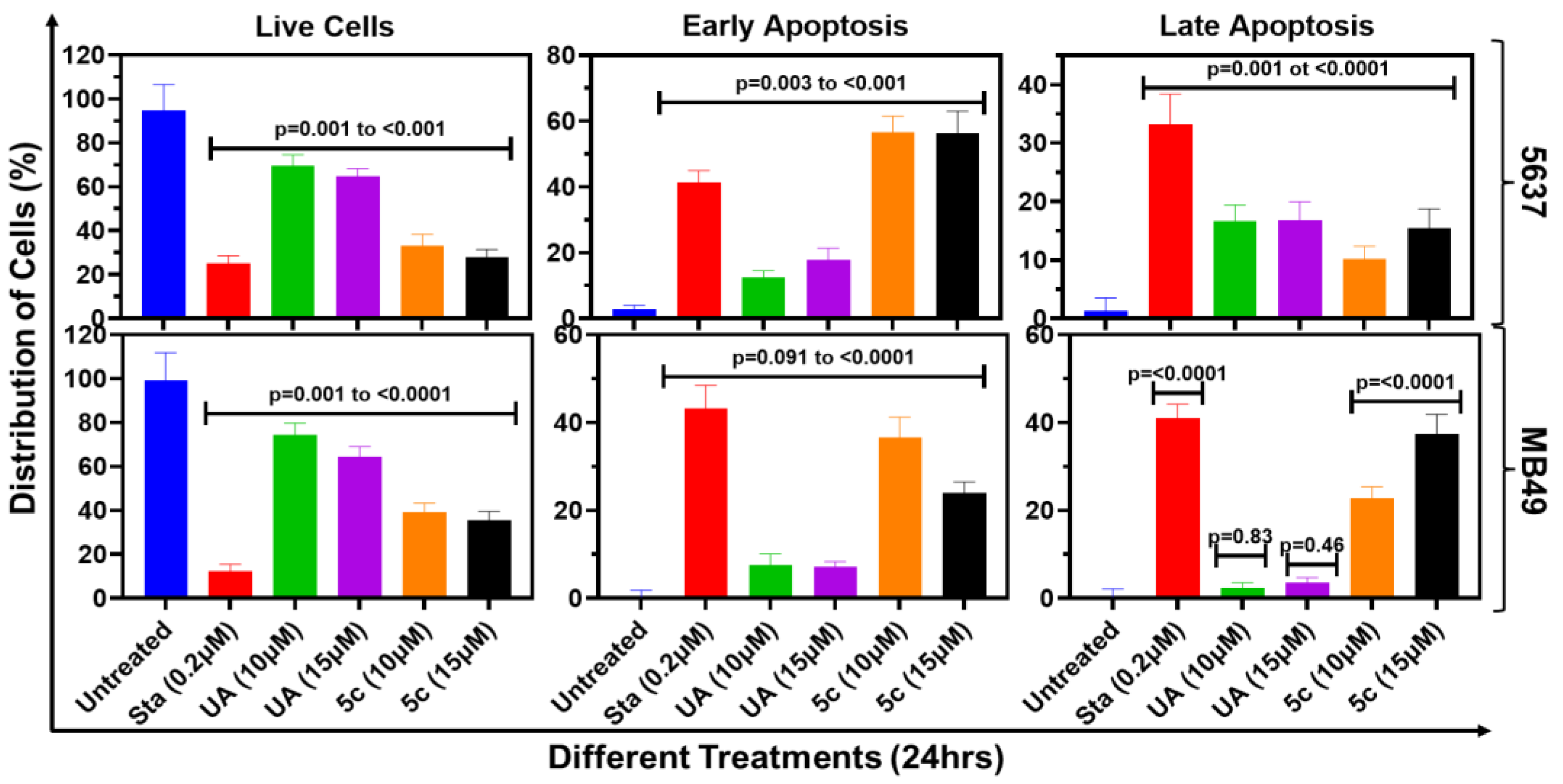
2.4. Apoptosis Induction by UA and 5c in Bladder Cancer Cells
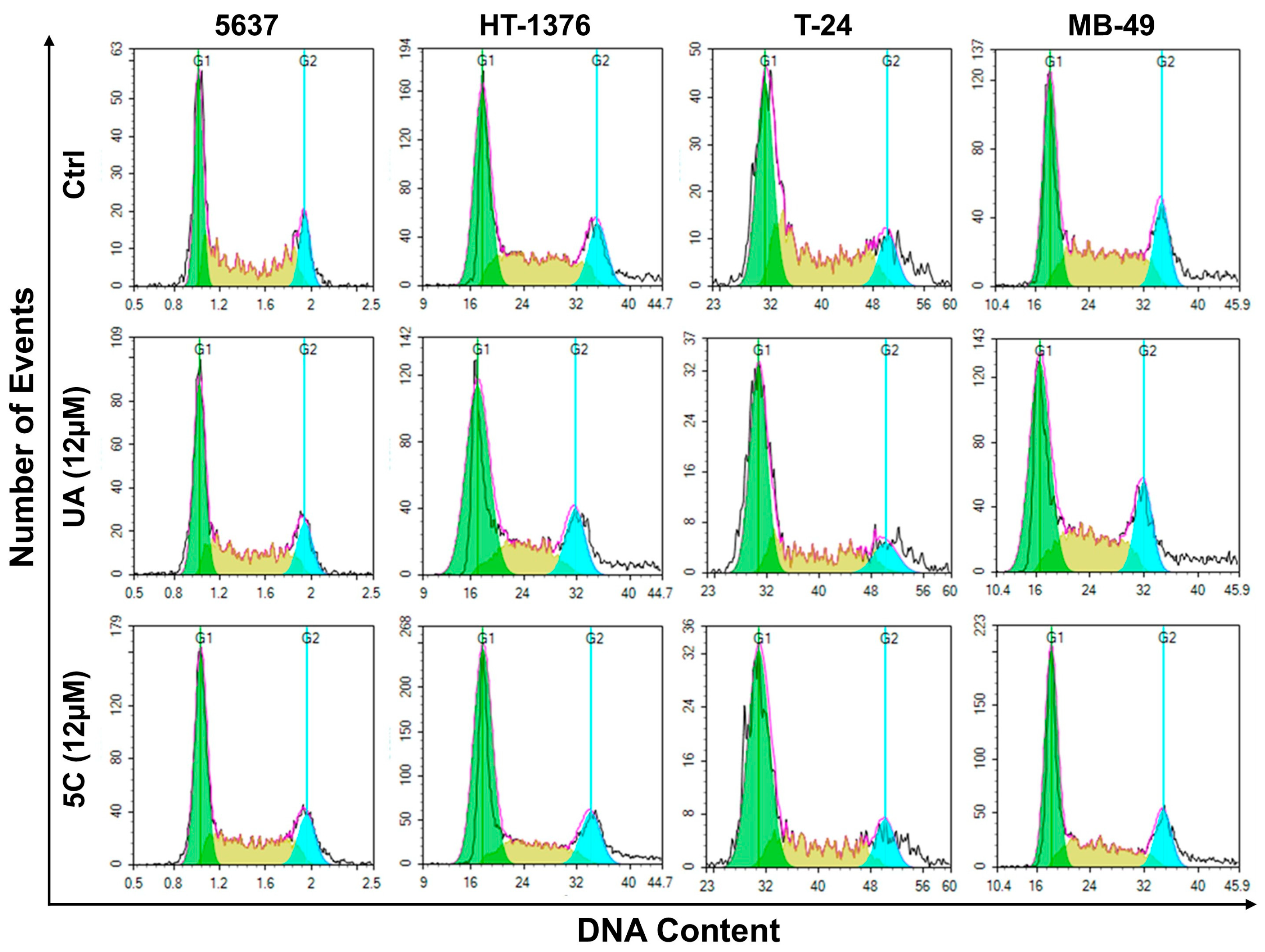
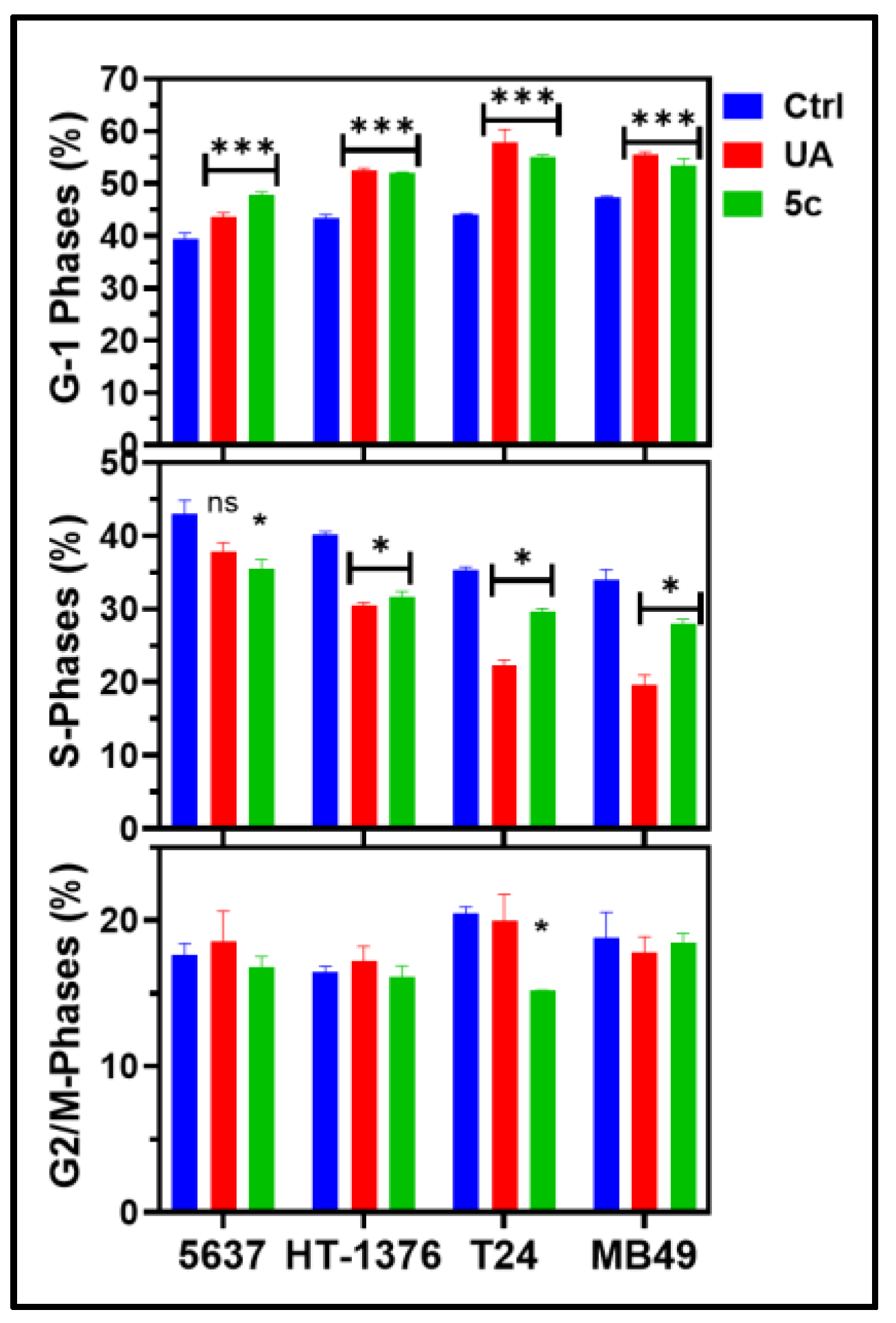
2.5. Cell-Cycle Analysis of Bladder Cancer Cells Treated with 5c
3. Proteomics to Identify Protein Targets of 5c in Bladder Cancer Cells
3.1. Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and ATP Synthase Complex
3.2. Translation Machinery and Elongation Factors
3.3. Stress Response and Chaperone Networks
3.4. RNA Processing and Splicing Factors
3.5. Cytoskeletal Remodeling
3.6. Chromatin Dynamics and Histone Variants
4. Conclusions
5. Experimental Section
5.1. General Method for Preparation of Compounds 3a–d [16]
5.2. General Method for the Preparation of Compounds 5a-d
5.3. Cell Culture and Maintenance
5.4. Testing the Compounds for Antiproliferative Activity
5.5. Estimation of Total Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
5.6. Cell Cycle Phase Fractionation Study Through Flow Cytometry
5.7. Assay to Measure Apoptosis Activity
5.8. Biotinylated Pull-Down of Protein Followed by LC-MS/MS Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arulnangai, R.; Thabassoom, H.A.; Banu, H.V.; Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Ganesamoorthy, R. Recent Developments on Ursolic Acid and Its Potential Biological Applications. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 101900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlala, S.; Oyedeji, A.O.; Gondwe, M.; Oyedeji, O.O. Ursolic Acid and Its Derivatives as Bioactive Agents. Molecules 2019, 24, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.Y.; Lee, S.R.; Heo, J.W.; No, M.H.; Rhee, B.R.; Ko, K.S.; Kwak, H.B.; Han, J. Ursolic Acid in Health and Disease. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Hortas, L.; Perez-Larran, P.; Gonzalez-Munoz, M.J.; Falque, E.; Dominguez, H. Recent Developments on the Extraction and Application of Ursolic Acid: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.N.; Ullevig, S.L.; Short, J.D.; Wang, L.; Ahn, Y.J.; Asmis, R. Ursolic acid and related analogues: Triterpenoids with broad health benefits. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.B.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Thangaraju, M.; Panda, S.S.; Lokeshwar, B.L. Cytotoxic Autophagy: A Novel Treatment Paradigm against Breast Cancer Using Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid. Cancers 2024, 16, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornel, A.; Nadile, M.; Tsiani, E. Evidence of the Beneficial Effects of Ursolic Acid against Lung Cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornel, A.; Nadile, M.; Retsidou, M.I.; Sakellakis, M.; Gioti, K.; Beloukas, A.; Sze, N.S.K.; Klentrou, P.; Tsiani, E. Ursolic Acid against Prostate and Urogenital Cancers: A Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Wu, R.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, D.; Yang, Y.; Androulakis, I.P.; Kong, A.N. Synergistic Effects of Ursolic Acid and Curcumin on the Suppression of Inflammatory Pathways in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 3709–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limami, Y.; Pinon, A.; Wahnou, H.; Oudghiri, M.; Liagre, B.; Simon, A.; Duval, R.E. Ursolic Acid’s Alluring Journey: One Triterpenoid vs. Cancer Hallmarks. Molecules 2023, 28, 7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Khan, K.; Hafeez, A.; Irfan, M.; Armaghan, M.; ur Rahman, A.; Gürer, E.S.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Butnariu, M.; Bagiu, I.-C.; et al. Ursolic Acid: A Natural Modulator of Signaling Networks in Different Cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Luo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Development of a Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Ursolic Acid in Rat Plasma and Tissue: Application to the Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distribution Study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Wei, G.; Si, D.; Liu, C. Determination of Ursolic Acid in Human Plasma by LC–MS/MS and Its Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.S.; Thangaraju, M.; Lokeshwar, B.L. Ursolic Acid Analogs as Potential Therapeutics for Cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 8981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seremak, R.; Gupta, K.B.; Bonigala, S.; Liu, E.; Marshall, B.; Zhi, W.; Bokhtia, R.M.; Panda, S.S.; Lokeshwar, V.B.; Lokeshwar, B.L. Targeting Chemoresistance in Advanced Bladder Cancers with a Novel Adjuvant Strategy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2024, 23, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhtia, R.M.; Pham, A.M.; Gupta, K.B.; Warang, S.S.; Venugopal, N.; Shakuja, R.; Somanath, P.R.; Liu, F.; Jeon, Y.C.; Guimaraes, G.J.; et al. Ursolic Acid Conjugates: A New Frontier in Anticancer Drug Development. ChemBioChem 2024, 25, e202400376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamah, F.E.; Mazandu, G.K.; Hassan, R.; Bope, C.D.; Thomford, N.E.; Ghansah, A.; Chimusa, E.R. Computational/In Silico Methods in Drug Target and Lead Prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 21, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.-R.; You, Z.-H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; An, J.-Y. Prediction of Drug–Target Interaction Networks from the Integration of Protein Sequences and Drug Chemical Structures. Molecules 2017, 22, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, S.; Di Stefano, M.; Martinelli, E.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T. Recent Advances in In Silico Target Fishing. Molecules 2021, 26, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechter, S.; Thomas, D.R.; Jans, D.A. Application of In Silico and HTS Approaches to Identify Nuclear Import Inhibitors for Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus Capsid Protein: A Case Study. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 573121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabana, Y.; Babu, D.; Fahlman, R.; Siraki, A.G.; Barakat, K. Target Identification of Small Molecules: An Overview of the Current Applications in Drug Discovery. BMC Biotechnol. 2023, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, H.; Gu, L.; Zhang, J.; Fang, L. Therapeutic Target Identification and Drug Discovery Driven by Chemical Proteomics. Biology (Basel) 2024, 13, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.; Pries, V.; Hedberg, C.; Waldmann, H. Target Identification for Small Bioactive Molecules: Finding the Needle in the Haystack. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 2744–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomenick, B.; Hao, R.; Jonai, N.; Huang, J. Target Identification Using Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21984–21989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Tan, L.; Tao, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. CETSA and Thermal Proteome Profiling Strategies for Target Identification and Drug Discovery of Natural Products. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, E.O.J.; Steel, P.G. Activity-Based Protein Profiling: A Graphical Review. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2023, 5, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bergen, W.; Žuna, K.; Fiala, J.; Pohl, E.E.; Heck, A.J.R.; Baggelaar, M.P. Dual-Probe Activity-Based Protein Profiling Reveals Site-Specific Differences in Protein Binding of EGFR-Directed Drugs. ACS Chem. Biol. 2024, 19, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Yin, L.; Niu, T.; Rehman, A.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, K. Target Discovery-Directed Pharmacological Mechanism Elucidation of Bioactive Natural Products. Med. Rev. 2025, 5, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, D.B. Biotin’s Lessons in Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 16319–16327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjiappan, S.; Pavadai, P.; Vellaichamy, S.; Pandian, S.R.K.; Ravishankar, V.; Palanisamy, P.; Govindaraj, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Premanand, A.; Sankaranarayanan, M.; et al. Surface Receptor-Mediated Targeted Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Cancer Treatment: A State-of-the-Art Review. Drug Dev. Res. 2020, 82, 309–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A.; Rangra, S.; Patil, R.; Desai, N.; Jyothi, V.G.S.S.; Salave, S.; Amate, P.; Benival, D.; Kommineni, N. Receptor-Targeted Nanomedicine for Cancer Therapy. Receptors 2024, 3, 323–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Kuznetsova, L.; Wong, S.S.; Ojima, I. Mechanism-Based Tumor-Targeting Drug Delivery System: Validation of Efficient Vitamin Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis and Drug Release. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzoldt, J.L.; Leigh, I.M.; Duffy, P.G.; Sexton, C.; Masters, J.R. Immortalisation of Human Urothelial Cells. Urol. Res. 1995, 23, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimowska, W.; Motyl, T.; Skierski, J.; Balasinska, B.; Ploszaj, T.; Orzechowski, A.; Filipecki, M. Apoptosis and Bcl-2 Protein Changes in L1210 Leukaemic Cells Exposed to Oxidative Stress. Apoptosis 1997, 2, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Guglani, A.; Ghorpade, R.; Wang, B. Biotin Conjugates in Targeted Drug Delivery: Is It Mediated by a Biotin Transporter, a Yet to Be Identified Receptor, or (an)Other Unknown Mechanism(s)? J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 2276663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Xu, T.; Yu, S.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J. Mitochondrial Metabolism and Cancer Therapeutic Innovation. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2025, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truitt, M.L.; Ruggero, D. New Frontiers in Translational Control of the Cancer Genome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoter, A.; El-Sabban, M.E.; Naim, H.Y. The HSP90 Family: Structure, Regulation, Function, and Implications in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ni, X.; Tao, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, F.; Gu, F.; Cui, X.; Jiang, S.; Li, Q.; Lu, H.; et al. Targeting PUF60 Prevents Tumor Progression by Retarding mRNA Decay of Oxidative Phosphorylation in Ovarian Cancer. Cell Oncol. 2024, 47, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Ge, H.; Güngör, C.; Gong, X.; Chen, Y. Cytoskeletal and Cytoskeleton-Associated Proteins: Key Regulators of Cancer Stem Cell Properties. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, G.-L.; Bleakley, M.; Bradley, R.K.; Malik, H.S.; Henikoff, S.; Molaro, A.; Sarthy, J. Short H2A Histone Variants Are Expressed in Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, N.S.; Ooi, L. A Simple Microplate Assay for Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Rapid Cellular Protein Normalization. Bio Protoc. 2021, 11, e3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.B.; Taylor, T.L.; Panda, S.S.; Thangaraju, M.; Lokeshwar, B.L. Curcumin-Dichloroacetate Hybrid Molecule as an Antitumor Oral Drug Against Multidrug-Resistant Advanced Bladder Cancers. Cancers 2024, 16, 3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokeshwar, B.L.; Selzer, M.G.; Zhu, B.Q.; Block, N.L.; Golub, L.M. Inhibition of Cell Proliferation, Invasion, Tumor Growth and Metastasis by an Oral Non-Antimicrobial Tetracycline Analog (COL-3) in a Metastatic Prostate Cancer Model. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.K.; Hasanali, S.L.; Wang, J.; Kallifatidis, G.; Morera, D.S.; Jordan, A.R.; Terris, M.K.; Klaassen, Z.; Bollag, R.; Lokeshwar, V.B.; et al. Promotion of Epithelial Hyperplasia by Interleukin-8-CXCR Axis in Human Prostate. Prostate 2020, 80, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| S. No | Compd. | IC50 Values in µM (Mean ± SD) (SI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5637 | T24 | MCF-12A | ||
| 1 | 5a | 39.31 ± 21.17 (15.92) | 14.57 ± 4.97 (42.96) | 626.00 ± 34.69 |
| 2 | 5b | >10,000 | 107.7 ± 24.41 (0.68) | 73.33 ± 0.12 |
| 3 | 5c | 10.97 ± 0.19 (7.58) | 14.20 ± 1.01 (5.85) | 83.11 ± 0.30 |
| 4 | 5d | >10,000 | 581.50 (6.57) | 3823.00 |
| 5 | 1 | 13.43 ± 0.35 (4.19) | 17.52 ± 0.98 (3.21) | 56.39 ± 7.60 |
| IC50 Concentrations (µM) ± SD (SI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| S. No. | Cell Line | UA | 5c |
| 1 | 5637 | 13.43 ± 0.35 (4.99) | 10.97 ± 0.19 (5.74) |
| 2 | HT-1376 | 21.9 ± 1.14 (3.06) | 12.68 ± 0.40 (4.96) |
| 3 | T-24 | 17.52 ± 0.98 (3.82) | 14.20 ± 1.01 (4.43) |
| 4 | MB49 | 10.71 ± 0.36 (6.26) | 13.58 ± 0.18 (4.63) |
| 5 | UROtsa | 67.01 ± 7.15 | 62.90 ± 3.84 |
| S. No. | Description | 5637 | MB-49 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change 10 min/Ctrl | Fold Change 1 h/Ctrl | Fold Change 10 min/Ctrl | Fold Change 1 h/Ctrl | ||
| 1 | ATP synthase subunit alpha | 1.63 | 2 | 1.26 | 1.26 |
| 2 | ATP synthase subunit beta | 3.29 | 5 | 1.31 | 1.82 |
| 3 | ATP synthase subunit O | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 4 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family A | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
| 5 | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase | 15 | 10 | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| 7 | DNA topoisomerase | 0.08 | 0.11 | 1 | 1.75 |
| 8 | Elongation factor 1-beta (EF1β) | 2.35 | 2.35 | 5 | 5 |
| 9 | Elongation factor 1-delta (EF1δ) | 8 | 7 | 1.4 | 2 |
| 10 | Elongation factor 1-gamma (EF1γ) | 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 |
| 11 | Elongation factor 2 (eEF2) | 44 | 50 | 3 | 2 |
| 12 | Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A (eIF4A) | 22 | 19 | 1 | 3 |
| 13 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2) | 14 | 7 | 2 | 0 |
| 14 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5B (eIF5B) | 32 | 34 | 3 | 2.75 |
| 15 | Filamin-A (FLNA) | 16 | 18 | 3.33 | 4 |
| 16 | HSC 71 | 5.25 | 6.25 | 1.5 | 2 |
| 17 | HSP 90-alpha (HSP90α) | 119 | 111 | 1.07 | 1.25 |
| 18 | HSP 90-beta (HSP90β) | 93 | 97 | 1.40 | 1.71 |
| 19 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U (HNRNPU) | 4.33 | 4.33 | 2.38 | 2.13 |
| 20 | Poly(U)-binding-splicing factor 60 (PUF60) | 6 | 5 | 2.33 | 3.33 |
| 21 | Rab-like protein 6 (RABL6) | 1.33 | 2.67 | 3 | 5.5 |
| 22 | Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 | 3.5 | 2.25 | 1 | 3 |
| 23 | Receptor of activated protein C kinase 1 (RACK1) | 6 | 6 | 0.88 | 1.29 |
| 24 | Ribosomal L1 domain-containing protein 1 (RSL1D1) | 5 | 4 | 1.33 | 1.56 |
| 25 | RNA-binding protein 39 (RBM39) | 3.5 | 3 | 2 | 1.71 |
| 26 | Splicing factor U2AF 65 kDa subunit (U2AF65) | 14 | 10 | 4 | 3 |
| 27 | T-complex protein 1 subunit theta | 14 | 12 | 2 | 3 |
| 28 | Histone H2A type 2-C (HIST2H2AC) | 3.48 | 3.04 | 1.58 | 1.27 |
| 29 | Histone H2A.Z | 5.85 | 4.78 | 1.86 | 1.20 |
| 30 | Histone H2B type 1-M | 3.16 | 1.37 | 2.04 | 1.81 |
| 31 | Histone H4 | 13.23 | 11.08 | 1.64 | 1.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bokhtia, R.M.; Gupta, K.B.; Natalini, A.; Srinivasan, T.V.; Amineni, N.; Ying, S.; Shakuja, R.; Verbeck, G.F.; Lokeshwar, B.L.; Panda, S.S. Biotin-Linked Ursolic Acid Conjugates as Selective Anticancer Agents and Target-Identification Tools for Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2025, 30, 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234588
Bokhtia RM, Gupta KB, Natalini A, Srinivasan TV, Amineni N, Ying S, Shakuja R, Verbeck GF, Lokeshwar BL, Panda SS. Biotin-Linked Ursolic Acid Conjugates as Selective Anticancer Agents and Target-Identification Tools for Cancer Therapy. Molecules. 2025; 30(23):4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234588
Chicago/Turabian StyleBokhtia, Riham M., Kunj Bihari Gupta, Annabella Natalini, Theerth Vikas Srinivasan, Nihal Amineni, Sophia Ying, Rajeev Shakuja, Guido F. Verbeck, Bal L. Lokeshwar, and Siva S. Panda. 2025. "Biotin-Linked Ursolic Acid Conjugates as Selective Anticancer Agents and Target-Identification Tools for Cancer Therapy" Molecules 30, no. 23: 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234588
APA StyleBokhtia, R. M., Gupta, K. B., Natalini, A., Srinivasan, T. V., Amineni, N., Ying, S., Shakuja, R., Verbeck, G. F., Lokeshwar, B. L., & Panda, S. S. (2025). Biotin-Linked Ursolic Acid Conjugates as Selective Anticancer Agents and Target-Identification Tools for Cancer Therapy. Molecules, 30(23), 4588. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30234588








