Unveiling the Mineral and Sugar Richness of Moroccan Honeys: A Study of Botanical Origins and Quality Indicators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sugar Content
2.2. Mineral Content
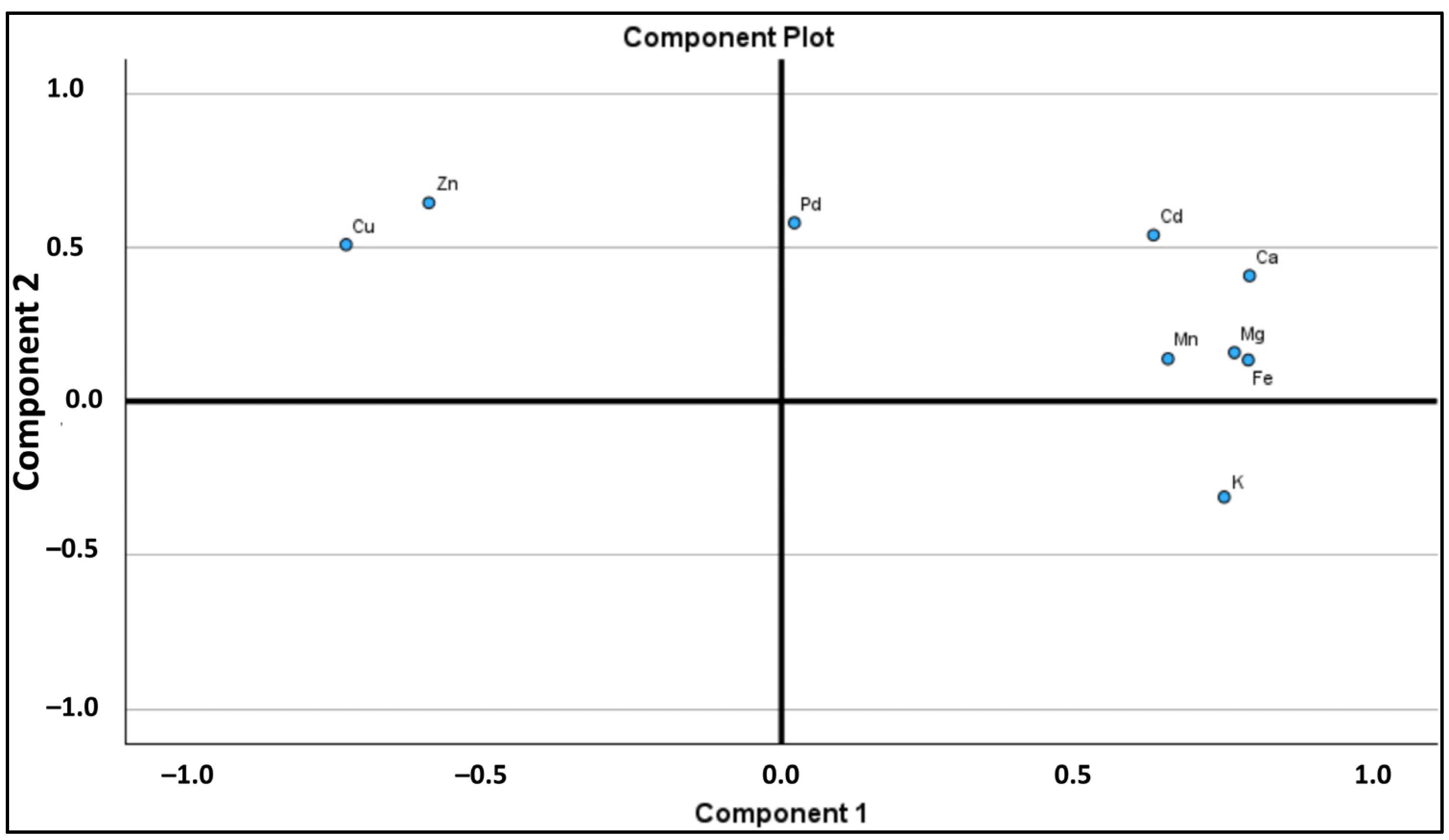
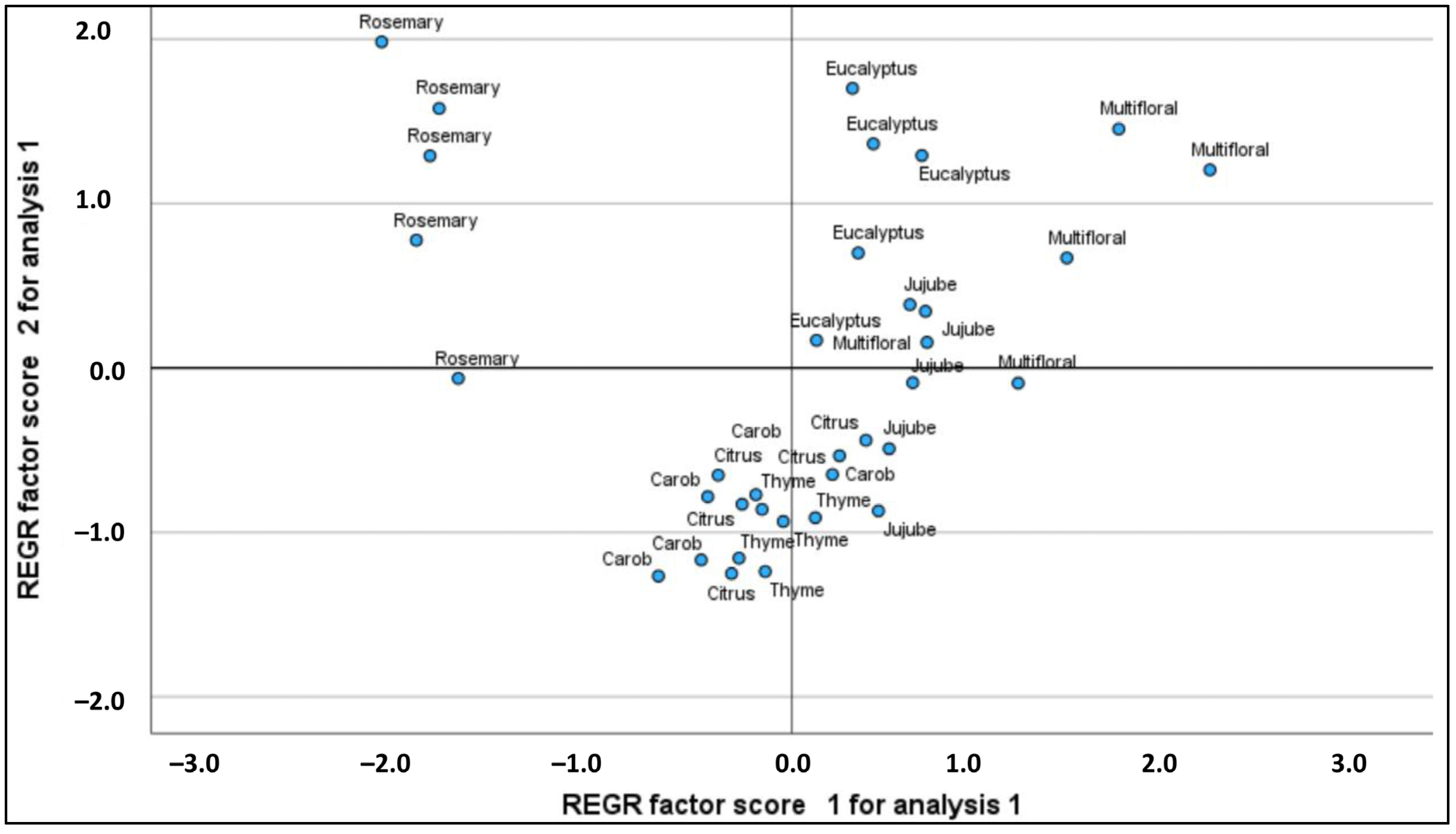
2.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Collection and Preparation of Honey Samples
3.2. GC-FID Determination of Sugars
3.3. Analysis of the Mineral Content
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alqarni, A.S.; Owayss, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Hannan, M.A. Mineral Content and Physical Properties of Local and Imported Honeys in Saudi Arabia. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Yung An, C.; Rao, P.V.; Hawlader, M.N.I.; Azlan, S.A.B.M.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. Identification of Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids in Monofloral Honey from Bangladesh by High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Determination of Antioxidant Capacity. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 737490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golob, T.; Doberšek, U.; Kump, P.; Nečemer, M. Determination of Trace and Minor Elements in Slovenian Honey by Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachman, J.; Kolihová, D.; Miholová, D.; Košata, J.; Titěra, D.; Kult, K. Analysis of Minority Honey Components: Possible Use for the Evaluation of Honey Quality. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç Altun, S.; Dinç, H.; Paksoy, N.; Temamoğulları, F.K.; Savrunlu, M. Analyses of Mineral Content and Heavy Metal of Honey Samples from South and East Region of Turkey by Using ICP-MS. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 2017, 6391454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solayman, M.; Islam, M.A.; Paul, S.; Ali, Y.; Khalil, M.I.; Alam, N.; Gan, S.H. Physicochemical Properties, Minerals, Trace Elements, and Heavy Metals in Honey of Different Origins: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. food Sci. food Saf. 2016, 15, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squadrone, S.; Brizio, P.; Stella, C.; Mantia, M.; Pederiva, S.; Brusa, F.; Mogliotti, P.; Garrone, A.; Abete, M.C. Trace Elements and Rare Earth Elements in Honeys from the Balkans, Kazakhstan, Italy, South America, and Tanzania. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 12646–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacoppo, S.; Galuppo, M.; Calabrò, R.S.; D’Aleo, G.; Marra, A.; Sessa, E.; Bua, D.G.; Potortì, A.G.; Dugo, G.; Bramanti, P.; et al. Heavy Metals and Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Observational Study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 161, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.J.; Blizard, R.A. Autism Genes Are Selectively Targeted by Environmental Pollutants Including Pesticides, Heavy Metals, Bisphenol A, Phthalates and Many Others in Food, Cosmetics or Household Products. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 101, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.E.A. Factors Affecting the Physicochemical Properties and Chemical Composition of Bee’s Honey. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, W.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Shahnawaz, M.; Schmelzer, J.D.; Boeve, B.F.; Sletten, D.M.; Gehrking, T.L.; Gehrking, J.A.; Olson, A.D.; Savica, R.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers and Neurofilament Light Chain in Spinal Fluid Differentiate Multiple System Atrophy from Lewy Body Synucleinopathies. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Honey as a Source of Dietary Antioxidants: Structures, Bioavailability and Evidence of Protective Effects against Human Chronic Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belay, A.; Solomon, W.K.; Bultossa, G.; Adgaba, N.; Melaku, S. Physicochemical Properties of the Harenna Forest Honey, Bale, Ethiopia. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3386–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aykas, D.P. Determination of Possible Adulteration and Quality Assessment in Commercial Honey. Foods 2023, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaerjani, W.M.A.; Abu-Melha, S.; Alshareef, R.M.H.; Al-Farhan, B.S.; Ghramh, H.A.; Al-Shehri, B.M.A.; Bajaber, M.A.; Khan, K.A.; Alrooqi, M.M.; Modawe, G.A.; et al. Biochemical Reactions and Their Biological Contributions in Honey. Molecules 2022, 27, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, M.C.; Chirife, J. Determination of Water Activity Change Due to Crystallization in Honeys from Argentina. Food Control 2006, 17, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oroian, M.; Dranca, F.; Ropciuc, S.; Pauliuc, D. A Comparative Study Regarding the Adulteration Detection of Honey: Physicochemical Parameters vs. Impedimetric Data. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Mironescu, M.; Drouza, C.; Mironescu, I.D.; Agriopoulou, S. Insight into the Recent Application of Chemometrics in Quality Analysis and Characterization of Bee Honey during Processing and Storage. Foods 2023, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska-Matysek, M.; Teter, A.; Skałecki, P.; Topyła, B.; Domaradzki, P.; Poleszak, E.; Florek, M. Residues of Pesticides and Heavy Metals in Polish Varietal Honey. Foods 2022, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Han, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qian, L.; Huang, M.; Luo, B.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Antibiotic Residues in Honey in the Chinese Market and Human Health Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailli, A.; Zibouh, K.; Eddamsyry, B.; Drioiche, A.; Fetjah, D.; Ayyad, F.Z.; Mothana, R.A.; Hawwal, M.F.; Radi, M.; Tarik, R.; et al. Physicochemical Characterization of Moroccan Honey Varieties from the Fez-Meknes Region and Their Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties. Metabolites 2024, 14, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouddine, T.; Laaroussi, H.; Bakour, M.; Guirrou, I.; Khallouki, F.; Mazouz, H.; Hajjaj, H.; Hajji, L. Organic Honey from the Middle Atlas of Morocco: Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Properties, Pollen Spectra, and Sugar Profiles. Foods 2022, 11, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, S.A.; Mahmood, D.; Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Khan, M.I.; Ashfaq, F.; Patel, M.; Snoussi, M.; Kieliszek, M.; Adnan, M. Exposure to Pesticide Residues in Honey and Its Potential Cancer Risk Assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 180, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeslami, A.; El Farissi, H.; El Bachiri, A.; Sindic, M.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Bruneau, E.; Talhaoui, A. Exploring the Physicochemical and Antioxidant Characteristics of Honey from Eastern Morocco: Insights into Potential Health Benefits and Molecular Docking Analysis. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchemoukh, S.; Amessis-Ouchemoukh, N.; Gómez-Romero, M.; Aboud, F.; Giuseppe, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Characterisation of Phenolic Compounds in Algerian Honeys by RP-HPLC Coupled to Electrospray Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuredo, O.; Dobre, I.; Fernández-González, M.; Seijo, M.C. Contribution of Botanical Origin and Sugar Composition of Honeys on the Crystallization Phenomenon. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, I.; Georgescu, L.A.; Alexe, P.; Escuredo, O.; Seijo, M.C. Rheological Behavior of Different Honey Types from Romania. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornuk, F.; Karaman, S.; Ozturk, I.; Toker, O.S.; Tastemur, B.; Sagdic, O.; Dogan, M.; Kayacier, A. Quality Characterization of Artisanal and Retail Turkish Blossom Honeys: Determination of Physicochemical, Microbiological, Bioactive Properties and Aroma Profile. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 46, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Se, K.W.; Ibrahim, R.K.R.; Wahab, R.A.; Ghoshal, S.K. Accurate Evaluation of Sugar Contents in Stingless Bee (Heterotrigona itama) Honey Using a Swift Scheme. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 66, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siok Peng Kek Nyuk Ling Chin, Y.A.Y.S.W.T.; Chua, L.S. Classification of Entomological Origin of Honey Based on Its Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S2723–S2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuttong, B.; Chanbang, Y.; Sringarm, K.; Burgett, M. Physicochemical Profiles of Stingless Bee (Apidae: Meliponini) Honey from South East Asia (Thailand). Food Chem. 2016, 192, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenaoui, N.; Mouhoubi-Tafinine, Z.; Amessis-Ouchemoukh, N.; Saimi, M.; Saidi, H.; Ayad, R.; Sadou, D.; Moumeni, L.; Ouchemoukh, S. Pollen Profiles, Physico-Chemical Parameters, in Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Honeys and Anti-Browning Effect of Honeys on Apple. Med. J. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 17, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, E.; Sanz, M.L.; Martínez-Castro, I.; Sanz, J.; Ruiz-Matute, A.I. Volatile and Carbohydrate Composition of Rare Unifloral Honeys from Spain. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Arquillué, C.; Conchello, P.; Ariño, A.; Juan, T.; Herrera, A. Physicochemical Attributes and Pollen Spectrum of Some Unifloral Spanish Honeys. Food Chem. 1995, 54, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, Y.; Yesli, A.; Bengana, M.; Sadoudi, R.; Amrouche, T. Physico-Chemical and Microbiological Assessment of Honey from Algeria. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 9, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Pasupuleti, V.R.; Arigela, C.S.; Gan, S.H.; Salam, S.K.N.; Krishnan, K.T.; Rahman, N.A.; Jeffree, M.S. A Review on Oxidative Stress, Diabetic Complications, and the Roles of Honey Polyphenols. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8878172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obia, O.; Ogwa, C.; Ojeka, S.; Ajah, A.; Chuemere, A. Effect of Honey on the Body Weight of Glibenclamide Treated Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Apither. 2016, 1, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Brenciani, A.; Mazzoni, L.; Gasparrini, M.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Morroni, G.; Simoni, S.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; et al. Apis Mellifera vs Melipona Beecheii Cuban Polifloral Honeys: A Comparison Based on Their Physicochemical Parameters, Chemical Composition and Biological Properties. LWT 2018, 87, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, T.C.; Moran, B.J.; Sugarbaker, P.H.; Levine, E.A.; Glehen, O.; Gilly, F.N.; Baratti, D.; Deraco, M.; Elias, D.; Sardi, A.; et al. Early- and Long-Term Outcome Data of Patients with Pseudomyxoma Peritonei from Appendiceal Origin Treated by a Strategy of Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, R.; Pérez-Bernal, J.L.; Bello-López, M.Á.; Callejón-Mochón, M.; Jiménez-Sánchez, J.C.; Guiraúm-Pérez, A. Mineral Content and Botanical Origin of Spanish Honeys. Talanta 2005, 65, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.R.; Videira, R.; Monteiro, A.P.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B. Honey from Luso Region (Portugal): Physicochemical Characteristics and Mineral Contents. Microchem. J. 2009, 93, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlin, A.; Kočar, D.; Imperl, J.; Kolar, M.; Marolt, G.; Petrova, P. Honey Origin Authentication via Mineral Profiling Combined with Chemometric Approaches. Foods 2023, 12, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhanen, L.P.; Emmertz, A.; Savage, G.P. Mineral Analysis of Mono-Floral New Zealand Honey. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hungerford, N.L.; Tinggi, U.; Tan, B.L.L.; Farrell, M.; Fletcher, M.T. Mineral and Trace Element Analysis of Australian/Queensland Apis Mellifera Honey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria Rizelio, V.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Borges, G.D.S.C.; França Maltez, H.; Costa, A.C.O.; Fett, R. Fast Determination of Cations in Honey by Capillary Electrophoresis: A Possible Method for Geographic Origin Discrimination. Talanta 2012, 99, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czipa, N.; Andrási, D.; Kovács, B. Determination of Essential and Toxic Elements in Hungarian Honeys. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereksi-Reguig, D.; Bouchentouf, S.; Allali, H.; Adamczuk, A.; Kowalska, G.; Kowalski, R. Trace Elements and Heavy Metal Contents in West Algerian Natural Honey. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2022, 2022, 7890856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S.; Lülmann, C.; Martin, P.; Von Der Ohe, W.; Russmann, H.; Vorwohl, G.; Persano Oddo, L.; Sabatini, A.-G.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Piro, R.; et al. Honey Quality, Methods of Analysis and International Regulatory Standards: Review of the Work of the International Honey Commission the Collaborative Work of the International Honey. Swiss Bee Res. Cent. 2000, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Pisani, A.; Protano, G.; Riccobono, F. Minor and Trace Elements in Different Honey Types Produced in Siena County (Italy). Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.; El-Haty, M.; Mohamed, S.M. Bee Honey as Environmental Indicator for Pollution with Heavy Metals. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2009, 91, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S.; Lüllmann, C.; Martin, P.; von der Ohe, W.; Russmann, H.; Vorwohl, G.; Oddo, L.P.; Sabatini, A.-G.; Marcazzan, G.L.; Piro, R.; et al. Honey Quality and International Regulatory Standards: Review by the International Honey Commission. Bee World 1999, 80, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucholobek, G.; de Andrade, C.K.; Rigobello, E.S.; Wielewski, P.; de Toledo, V.d.A.A.; Quináia, S.P. Determination of the Ca, Mn, Mg and Fe in Honey from Multiple Species of Stingless Bee Produced in Brazil. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Honey Type | Jujube | Multifloral | Citrus | Eucalyptus | Thyme | Carob | Rosemary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar | Composition | ||||||
| Fructose (%) | 36.92 ± 0.73 b | 40.14 ± 0.32 a | 38.51 ± 0.37 a | 34.44 ± 0.25 a | 35.95 ± 0.45 b | 38.56 ± 0.76 b | 33.88 ± 0.38 a |
| Glucose (%) | 28.09 ± 0.31 a | 35.69 ± 0.39 a | 29.17 ± 0.45 b | 27.02 ± 0.28 a | 26.52 ± 0.45 b | 29.62 ± 0.49 b | 33.82 ± 0.54 b |
| Maltose (%) | 3.96 ± 0.09 c | 4.23 ± 0.16 a | 5 ± 0.22 a | 3.66 ± 0.12 a | 4.88 ± 0.38 a | 3.16 ± 0.23 a | 3.52 ± 0.39 a |
| Turanose (%) | 1.80 ± 0.29 a | 1.49 ± 0.12 a | 1 ± 0.36 a | 0.85 ± 0.28 a | 1.48 ± 0.34 a | 0.93 ± 0.27 a | 0.99 ± 0.13 a |
| Erlose (%) | 1.58 ± 0.06 c | 0.63 ± 0.01 c | 0.22 ± 0.03 c | 1.64 ± 0.05 c | 0.52 ± 0.02 c | 0.37 ± 0.04 c | 0.59 ± 0.02 c |
| Palatinose (%) | 0.68 ± 0.09 c | 0.38 ± 0.06 c | 0.32 ± 0.04 c | 0.26 ± 0.05 c | 0.47 ± 0.07 c | 0.05 ± 0.02 c | 0.18 ± 0.01 c |
| Sucrose (%) | 0.51 ± 0.51 a | 1.00 ± 0.13 a | 0.15 ± 0.19 a | 0.15 ± 0.23 a | 0.17 ± 0.29 a | 0.66 ± 0.31 a | 0.29 ± 0.21 a |
| Rafinose (%) | 0.015 ± 0.01 c | nd | 0.27 ± 0.10 a | nd | 0.41 ± 0.08 c | 0.06 ± 0.09 c | 0.07 ± 0.07 c |
| Melezitose (%) | 0.13 ± 0.03 c | 0.09 ± 0.04 c | nd | nd | 0.20 ± 0.06 c | 0.41 ± 0.03 c | nd |
| Panose (%) | 0.05 ± 0.01 c | 0.02 ± 0.01 c | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Granulation indexes | |||||||
| Total sugar content | 73.73 ± 0.21 a | 83.67 ± 2.25 d | 74.64 ± 3.95 d | 68.02 ± 4.76 e | 70.6 ± 2.98 d | 73.82 ± 5.43 e | 73.34 ± 3.19 d |
| F + G | 65.01 ± 1.04 d | 75.83 ± 0.71 b | 67.68 ± 0.82 d | 61.46 ± 0.53 b | 62.47 ± 0.9 b | 68.18 ± 1.25 d | 67.2 ± 0.92 d |
| F/G ratio | 1.31 ± 0.07 c | 1.12 ± 0.06 c | 1.32 ± 0.06 c | 1.27 ± 0.05 c | 1.35 ± 0.02 c | 1.30 ± 0.01 c | 1.00 ± 0.03 c |
| Elements (mg/kg) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Honey Type | Potassium | Calcium | Magnesium | Iron | Zinc | Manganese | Copper | Cadmium | Lead |
| Jujube | 395.53 ± 20.87 f | 107.81 ± 8.37 d | 38.66 ± 9.73 d | 16.65 ± 1.52 b | 5.50 ± 0.58 a | 2.46 ± 1.13 b | 1.22 ± 0.87 a | 0.0019 ± 0.01 a | 0.17 ± 0.027 a |
| Multifloral | 452.66 ± 18.34 f | 145.24 ± 10.78 d | 33.37 ± 5.23 c | 23.2 ± 0.86 a | 2.40 ± 0.18 a | 3.08 ± 1.08 b | 1.23 ± 0.75 a | 0.018 ± 0.09 a | 0.19 ± 0.012 a |
| Citrus | 305.90 ± 14.55 e | 69.56 ± 7.15 c | 16.57 ± 5.98 c | 12.57 ± 0.74 a | 2.19 ± 0.13 a | 2.12 ± 0.87 a | 0.99 ± 0.45 a | 0.0017 ± 0.04 a | 0.18 ± 0.042 a |
| Eucalyptus | 115.37 ± 17.22 f | 150 ± 5.44 c | 33.75 ± 10.27 d | 5.45 ± 1.67 b | 5.08 ± 0.21 a | 3.27 ± 1.54 b | 1.30 ± 0.60 a | 0.011 ± 0.03 a | 0.13 ± 0.040 a |
| Thyme | 330.52 ± 18.16 f | 40.33 ± 4.12 b | 27.23 ± 4.12 b | 4.67 ± 0.63 a | 2.88 ± 0.30 a | 2.98 ± 0.97 a | 1.27 ± 0.37 a | 0.0014 ± 0.07 a | 0.09 ± 0.002 a |
| Carob | 180.20 ± 14.44 e | 29.68 ± 6.18 c | 24.78 ± 3.34 b | 7.30 ± 0.85 a | 1.49 ± 0.19 a | 2.38 ± 0.73 a | 1.31 ± 0.29 a | 0.0016 ± 0.01 a | 0.10 ± 0.002 a |
| Rosemary | 49.31 ± 14.56 e | 12.33 ± 8.31 d | 12.03 ± 6.55 c | 2.15 ± 0.39 a | 12.46 ± 0.12 a | 1.45 ± 0.64 a | 3.32 ± 0.92 a | 0.017 ± 0.04 a | 0.14 ± 0.011 a |
| Variance Explained Factor Loading | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | Eigenvalues | % of Variance | % Cumulative | K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Zn | Mn | Cu | Pd | Cd |
| 1 | 5.031 | 56.143 | 56.143 | 0.751 | 0.794 | 0.768 | 0.791 | –0.598 | 0.655 | –0.738 | 0.022 | 0.631 |
| 2 | 1.751 | 19.586 | 75.730 | –0.311 | 0.407 | 0.158 | 0.134 | 0.645 | 0.138 | 0.509 | 0.579 | 0.540 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abeslami, A.; El Farissi, H.; Cacciola, F.; El Bachiri, A.; Sindic, M.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Bruneau, E.; Talhaoui, A. Unveiling the Mineral and Sugar Richness of Moroccan Honeys: A Study of Botanical Origins and Quality Indicators. Molecules 2025, 30, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010150
Abeslami A, El Farissi H, Cacciola F, El Bachiri A, Sindic M, Fauconnier M-L, Bruneau E, Talhaoui A. Unveiling the Mineral and Sugar Richness of Moroccan Honeys: A Study of Botanical Origins and Quality Indicators. Molecules. 2025; 30(1):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010150
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbeslami, Azzedine, Hammadi El Farissi, Francesco Cacciola, Ali El Bachiri, Mariane Sindic, Marie-Laure Fauconnier, Etienne Bruneau, and Abdelmonaem Talhaoui. 2025. "Unveiling the Mineral and Sugar Richness of Moroccan Honeys: A Study of Botanical Origins and Quality Indicators" Molecules 30, no. 1: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010150
APA StyleAbeslami, A., El Farissi, H., Cacciola, F., El Bachiri, A., Sindic, M., Fauconnier, M.-L., Bruneau, E., & Talhaoui, A. (2025). Unveiling the Mineral and Sugar Richness of Moroccan Honeys: A Study of Botanical Origins and Quality Indicators. Molecules, 30(1), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30010150







