Myeloid Differentiation Protein 2 Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Ang II Increases Liver MD2 Expression
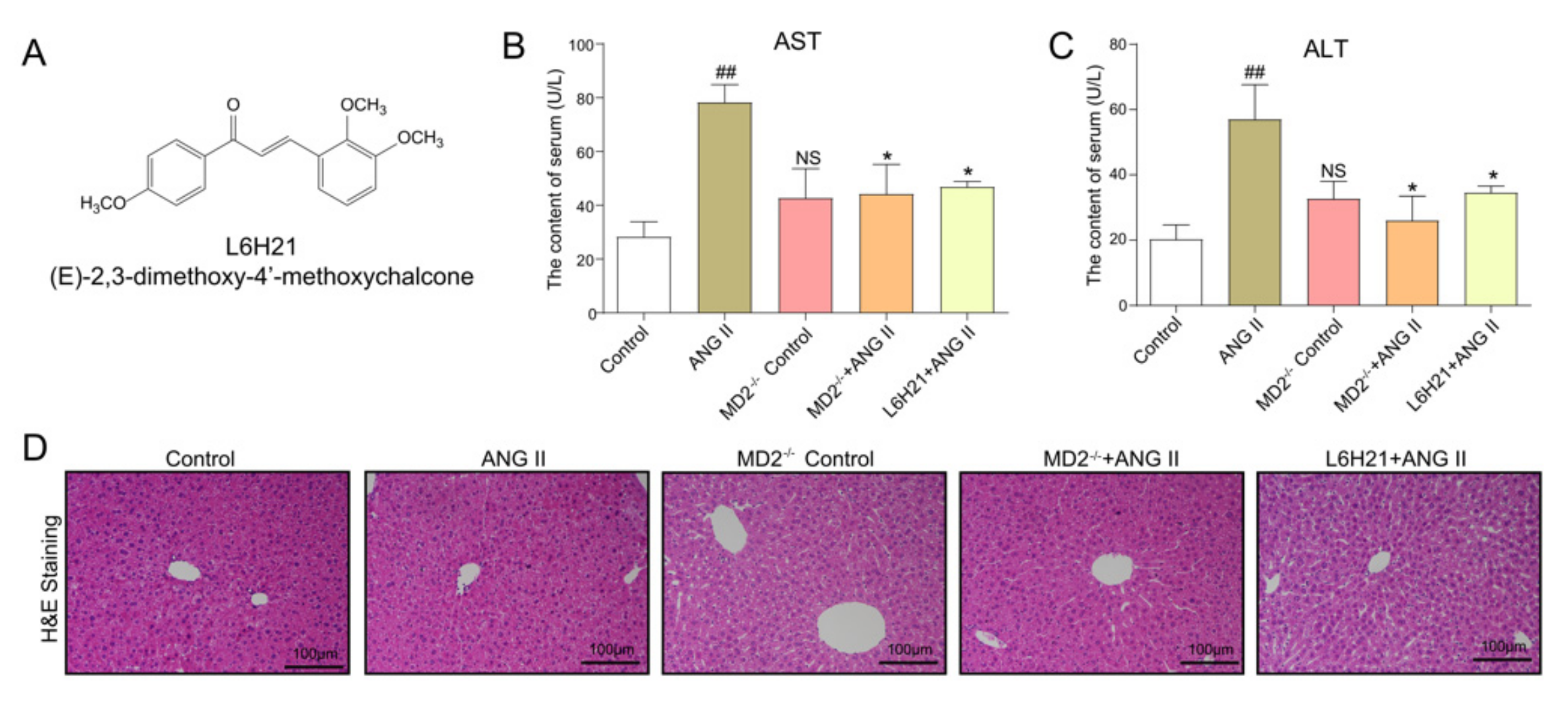
2.2. MD2 Inhibition and Knockout Protected Mice from Ang II-Induced Liver Injury and Dysfunction
2.3. MD2 Inhibition and Knockout Protected Mice from Ang II-Induced Liver Fibrosis
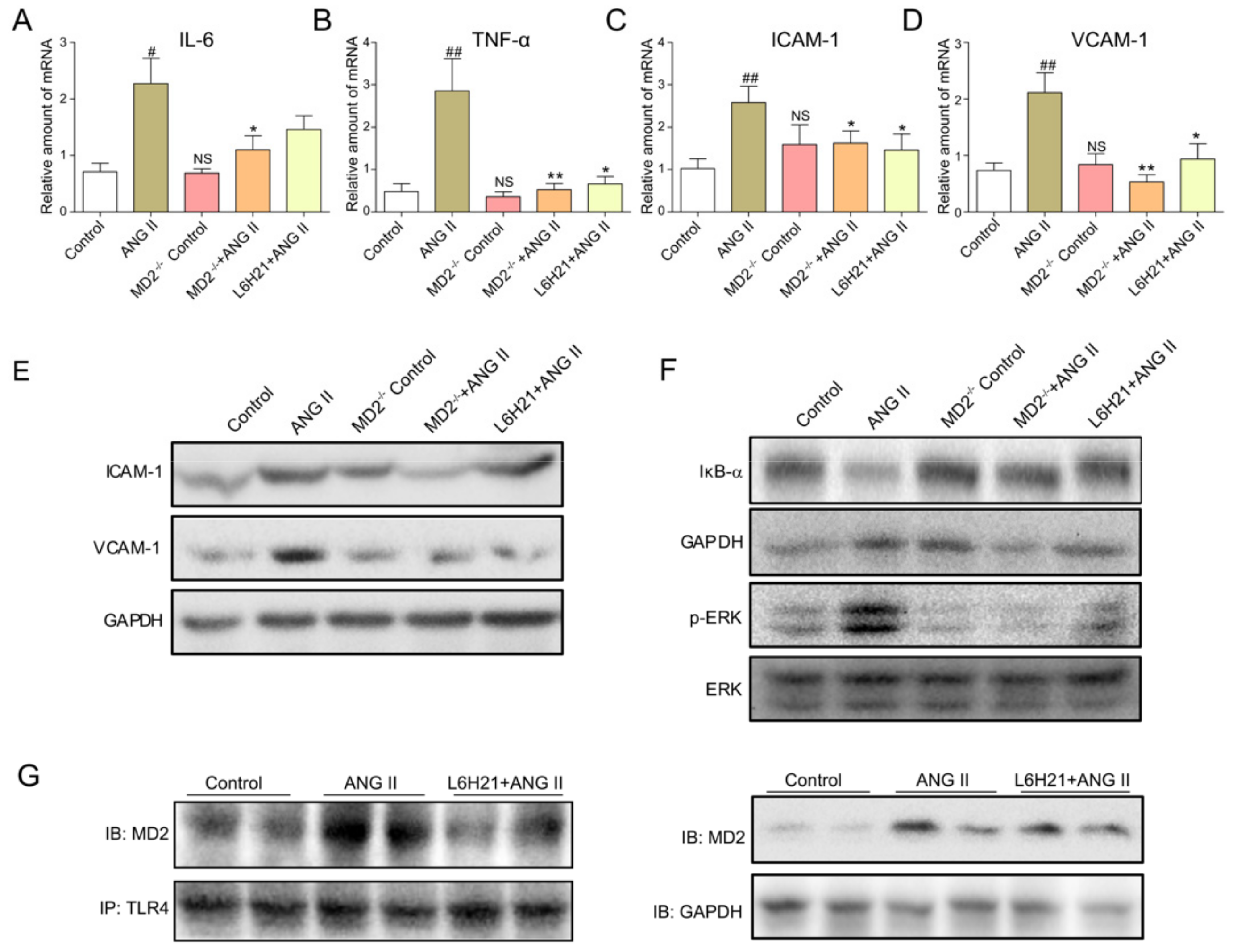
2.4. MD2 Inhibition and MD2 Knockout Protected Mice from Ang II-Induced Liver Inflammation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Histopathologic Analysis
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Measurement of ALT and AST in Serum
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.8. Reverse Transcription and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Talukdar, A.D.; Nath, R.; Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Sahu, J.; Choudhury, M.D. Role of Natural Phenolics in Hepatoprotection: A Mechanistic Review and Analysis of Regulatory Network of Associated Genes. Front Pharm. 2019, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira de Macedo, S.; Guimaraes, T.A.; Feltenberger, J.D.; Sousa Santos, S.H. The role of renin-angiotensin system modulation on treatment and prevention of liver diseases. Peptides 2014, 62, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyhrquist, F.; Saijonmaa, O. Renin-angiotensin system revisited. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataller, R.; Gabele, E.; Schoonhoven, R.; Morris, T.; Lehnert, M.; Yang, L.; Brenner, D.A.; Rippe, R.A. Prolonged infusion of angiotensin II into normal rats induces stellate cell activation and proinflammatory events in liver. Am. J. Physiology. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G642–G651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beom Seok, P.; Hyun, S.D.; Ho Min, K.; Byong-Seok, C.; Hayyoung, L.; Jie-Oh, L. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature 2009, 458, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Pan, Z.; Ge, X.; Sun, C.; Lu, C.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Dai, Y. Shikonin inhibits myeloid differentiation protein-2 to prevent lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Targeting myeloid differentiation 2 for treatment of sepsis. Front. Biosci. 2014, 19, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Fang, Q.; Zhong, P.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, X. Author Correction: Saturated palmitic acid induces myocardial inflammatory injuries through direct binding to TLR4 accessory protein MD2. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fu, W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Liang, G. Recent progress in the discovery of myeloid differentiation 2 (MD2) modulators for inflammatory diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1187–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoki, K.; Boldogh, I.; Leopoldo, A.A.; Sun, Q.; Itazawa, T.; Hazra, T.; Brasier, A.R.; Kurosky, A.; Sur, S. Myeloid differentiation protein 2 facilitates pollen- and cat dander-induced innate and allergic airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1506–1513.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, H.; Ge, X.; Ying, S.; Hu, M.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, C. Inhibition of MD2-dependent inflammation attenuates the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 22 (Suppl. 1), 936–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csak, T.; Velayudham, A.; Hritz, I.; Petrasek, J.; Levin, I.; Lippai, D.; Catalano, D.; Mandrekar, P.; Dolganiuc, A.; Kurtjones, E. Deficiency in myeloid differentiation factor-2 and toll-like receptor 4 expression attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Zou, C.; Mei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; You, S.; Pan, Y.; Xu, Z.; Bai, B.; Huang, W. MD2 mediates angiotensin II-induced cardiac inflammation and remodeling via directly binding to Ang II and activating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2017, 112, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Han, J.; Zou, C.; Huang, W.; Yu, W.; Shan, X.; Lum, H.; Li, X.; Liang, G. Angiotensin II induces kidney inflammatory injury and fibrosis through binding to myeloid differentiation protein-2 (MD2). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.; Xiaoou, S.; Gaozhi, C.; Lili, J.; Zhe, W.; Qilu, F.; Xing, L.; Jingying, W.; Yali, Z.; Wencan, W. MD-2 as the target of a novel small molecule, L6H21, in the attenuation of LPS-induced inflammatory response and sepsis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 4391–4405. [Google Scholar]
- Granzow, M.; Schierwagen, R.; Klein, S.; Kowallick, B.; Huss, S.; Linhart, M.; Mazar, I.G.; Gortzen, J.; Vogt, A.; Schildberg, F.A.; et al. Angiotensin-II type 1 receptor-mediated Janus kinase 2 activation induces liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benigni, A.; Cassis, P.; Remuzzi, G. Angiotensin II revisited: New roles in inflammation, immunology and aging. Embo. Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Ramalho, L.N.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Ramalho, F.; Abraldes, J.G.; Colmenero, J.; Dominguez, M.; Egido, J.; Arroyo, V.; et al. Atorvastatin attenuates angiotensin II-induced inflammatory actions in the liver. Am. J. Physiology. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G147–G156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Sun, C.; Zhang, B.; Bai, B.; Wu, D.; Xiao, Z.; Lum, H.; et al. Inhibition of myeloid differentiation factor 2 by baicalein protects against acute lung injury. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2019, 63, 152997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jianzhang, W.; Jianling, L.; Yuepiao, C.; Yong, P.; Faqing, Y.; Yali, Z.; Yunjie, Z.; Shulin, Y.; Xiaokun, L.; Guang, L. Evaluation and discovery of novel synthetic chalcone derivatives as anti-inflammatory agents. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8110–8123. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not available. |


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Jia, W.; Qi, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H. Myeloid Differentiation Protein 2 Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010025
Zhang Y, Liu H, Jia W, Qi J, Zhang W, Zhang W, Liang G, Zhang Y, Chen H. Myeloid Differentiation Protein 2 Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice. Molecules. 2020; 25(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yi, Hui Liu, Wenjing Jia, Jiayu Qi, Wentao Zhang, Wenxin Zhang, Guang Liang, Yali Zhang, and Hongjin Chen. 2020. "Myeloid Differentiation Protein 2 Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice" Molecules 25, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010025
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, H., Jia, W., Qi, J., Zhang, W., Zhang, W., Liang, G., Zhang, Y., & Chen, H. (2020). Myeloid Differentiation Protein 2 Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice. Molecules, 25(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010025



