Fibrilar Polymorphism of the Bacterial Extracellular Matrix Protein TasA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Native TasA Purification
2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy
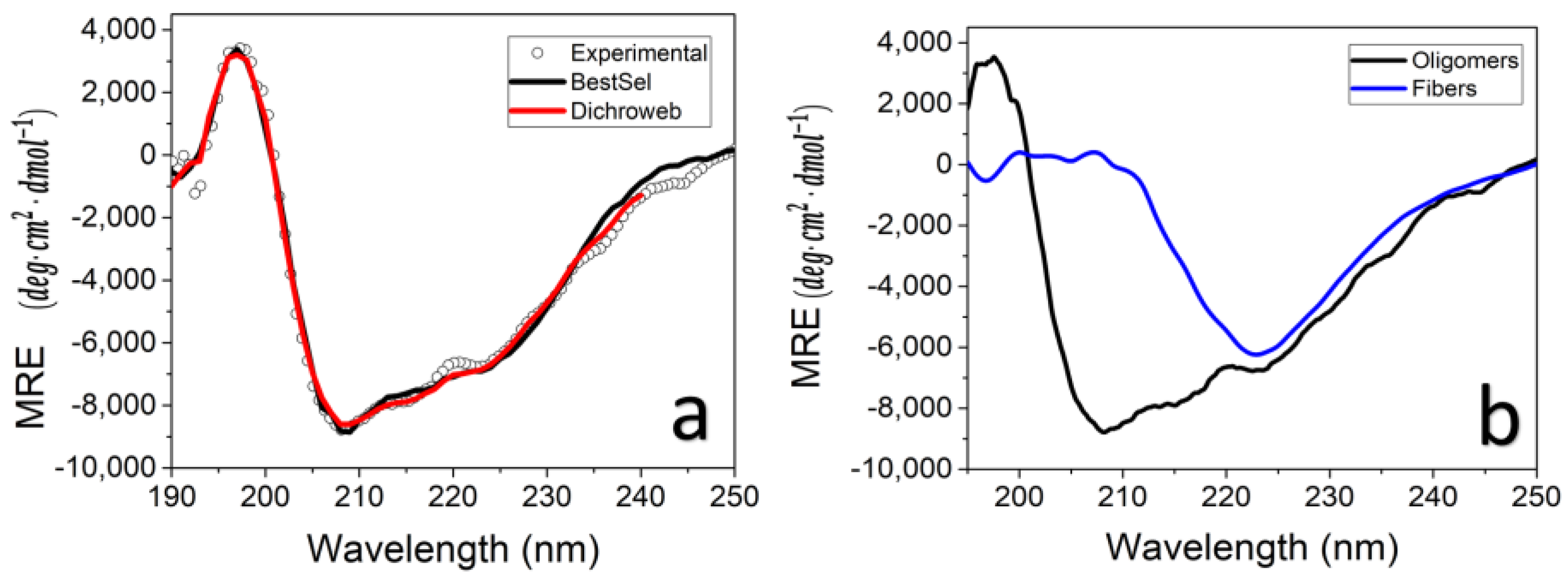
2.4. Circular Dichroism
2.5. Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy (Cryo-TEM)
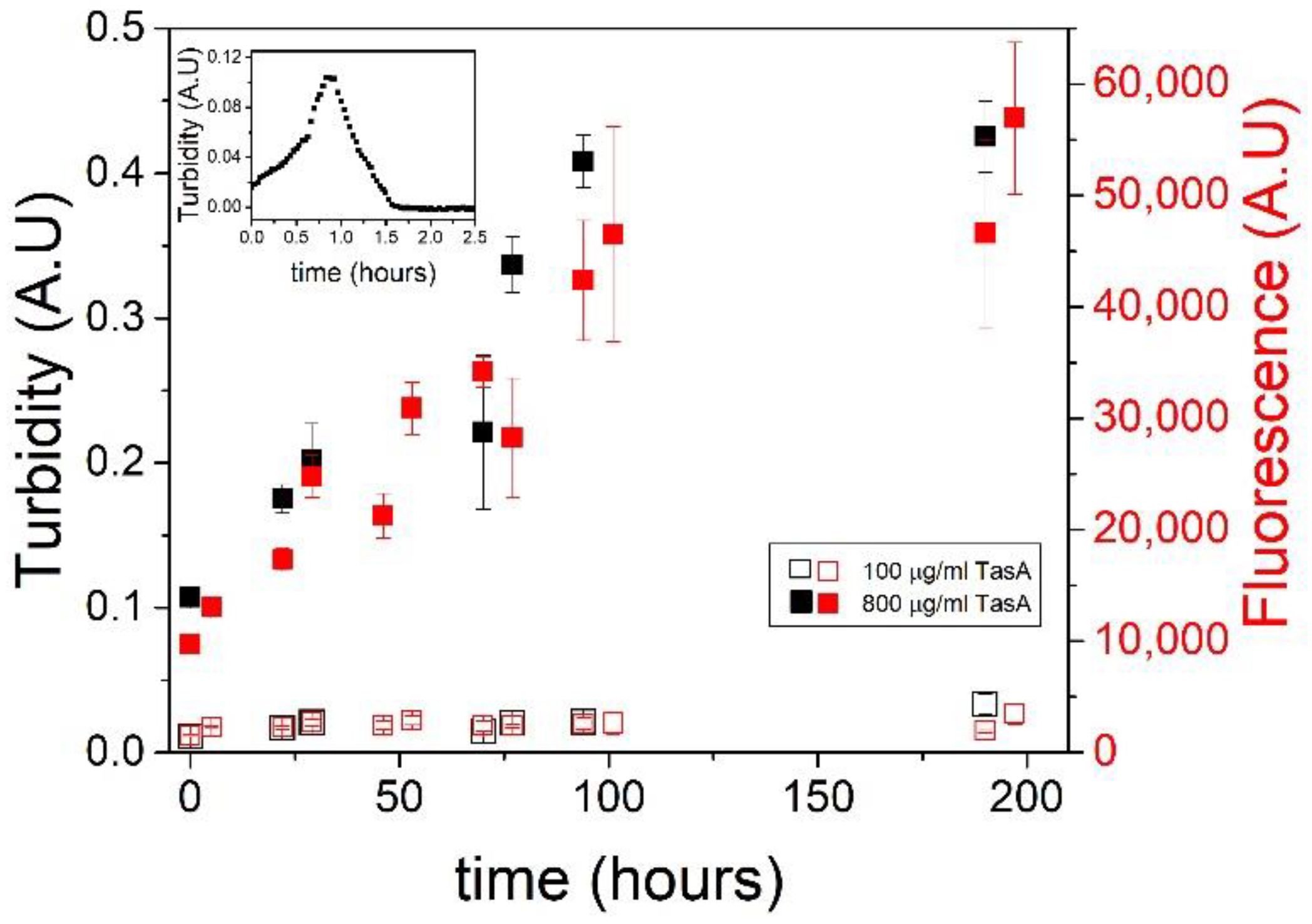
2.6. Turbidity Measurements
2.7. Thioflavin-T (ThT) Fluorescence
2.8. Fiber Preparation
3. Results
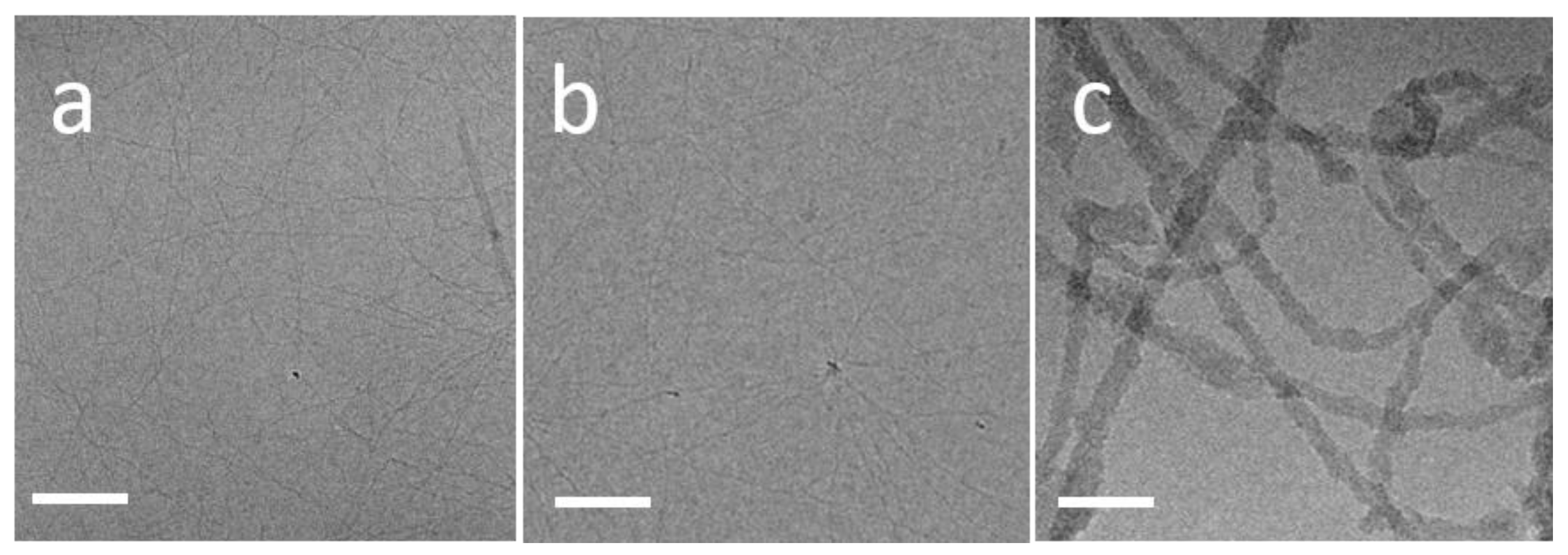
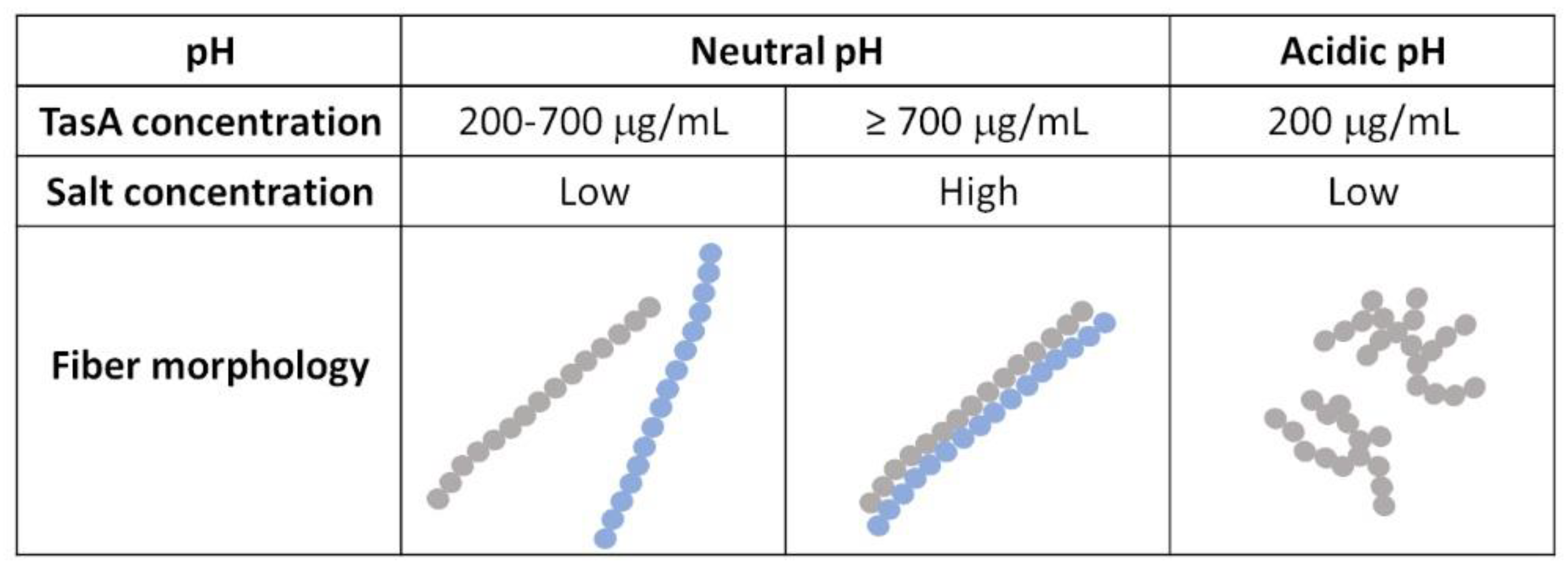
3.1. TasA Forms Fibers with Different Morphologies Depending on the Environmental Conditions
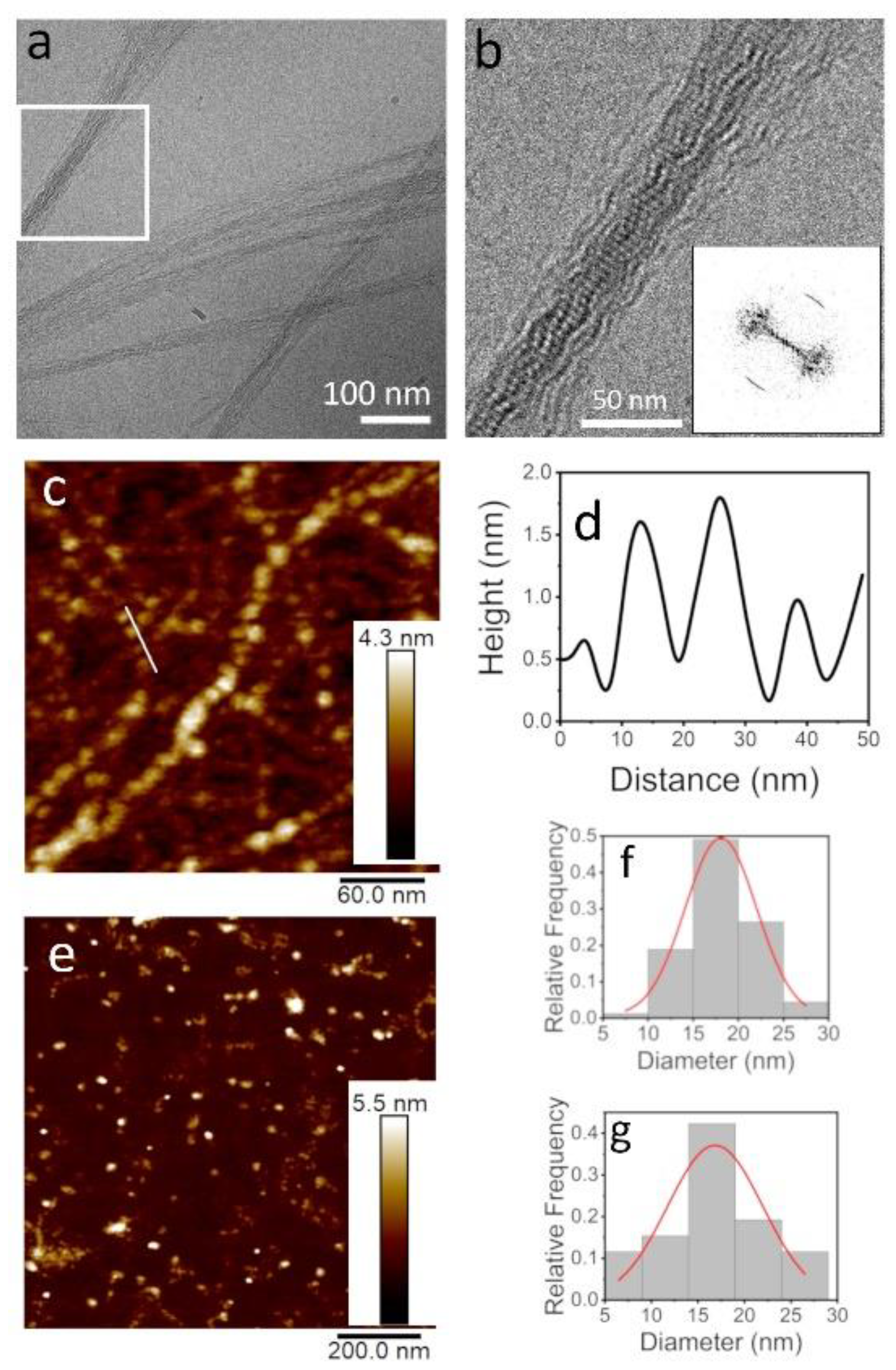
3.2. TasA Fibers Carry a Distinct Periodicity
3.3. Fiber Morphology Depends on Aggregation Kinetics
3.4. TasA Bundles Contain Twisted β Sheets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costerton, J.W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.E.; Korber, D.R.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Microbial Biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 711–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, H.-C.F.J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.A.R.S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Pu, J.; Ba, F.; Xue, S.; Ye, H.; Zhao, T.; Li, K.; et al. Programmable and printable Bacillus subtilis biofilms as engineered living materials. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 15, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ido, N.; Lybman, A.; Hayet, S.; Azulay, D.N.; Ghrayeb, M.; Liddawieh, S.; Chai, L. Bacillus subtilis biofilms characterized as hydrogels. Insights on water uptake and water binding in biofilms. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 6180–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.R.; Robinson, L.S.; Pinkner, J.S.; Roth, R.; Heuser, J.; Hammar, M.; Normark, S.; Hultgren, S.J. Role of Escherichia coli Curli Operons in Directing Amyloid Fiber Formation. Science 2002, 295, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, M.M.; Chapman, M.R. Curli Biogenesis and Function. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueholm, M.S.; Petersen, S.V.; Sønderkaer, M.; Larsen, P.; Christiansen, G.; Hein, K.L.; Enghild, J.J.; Nielsen, J.L.; Nielsen, K.L.; Nielsen, P.H.; et al. Functional amyloid in Pseudomonas. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb-Fligelman, E.; Tabachnikov, O.; Moshe, A.; Goldshmidt-Tran, O.; Sawaya, M.R.; Coquelle, N.; Colletier, J.-P.; Landau, M. The cytotoxic Staphylococcus aureus PSMα3 reveals a cross-α amyloid-like fibril. Science 2017, 355, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, K.; Syed, A.K.; Stephenson, R.E.; Rickard, A.H.; Boles, B.R. Functional Amyloids Composed of Phenol Soluble Modulins Stabilize Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D.; Vlamakis, H.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. An accessory protein required for anchoring and assembly of amyloid fibres in B. subtilis biofilms. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D.; Aguilar, C.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Amyloid fibers provide structural integrity to Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2230–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mammeri, N.; Hierrezuelo, J.; Tolchard, J.; Cámara-Almirón, J.; Caro-Astorga, J.; Álvarez-Mena, A.; Dutour, A.; Berbon, M.; Shenoy, J.; Morvan, E.; et al. Molecular architecture of bacterial amyloids in Bacillus biofilms. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 12146–12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pansieri, J.; Halim, M.A.; Vendrely, C.; Dumoulin, M.; Legrand, F.; Sallanon, M.M.; Chierici, S.; Denti, S.; Dagany, X.; Dugourd, P.; et al. Mass and charge distributions of amyloid fibers involved in neurodegenerative diseases: Mapping heterogeneity and polymorphism† (†Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental section and supplementary figures. See doi:10.1039/c7sc04542e). Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.L.; Nettleton, E.J.; Bouchard, M.; Robinson, C.V.; Dobson, C.M.; Saibil, H.R. The protofilament structure of insulin amyloid fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9196–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeters, S.J.; Iyer, A.; Pletikapić, G.; Kogan, V.; Subramaniam, V.; Woutersen, S. Evidence for Intramolecular Antiparallel Beta-Sheet Structure in Alpha-Synuclein Fibrils from a Combination of Two-Dimensional Infrared Spectroscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsbury, C.; Frey, P.; Olivieri, V.; Aebi, U.; Müller, S.A. Multiple Assembly Pathways Underlie Amyloid-β Fibril Polymorphisms. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 352, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Y.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Polymorphism in Alzheimer Aβ Amyloid Organization Reflects Conformational Selection in a Rugged Energy Landscape. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4820–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ge, P.; Murray, K.A.; Sheth, P.; Zhang, M.; Nair, G.; Sawaya, M.R.; Shin, W.S.; Boyer, D.R.; Ye, S.; et al. Cryo-EM of full-length α-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tycko, R. Physical and structural basis for polymorphism in amyloid fibrils. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.W.P.; Falcon, B.; Michel, G.; Murzin, A.G.; Murshudov, G.; Garringer, H.J.; Crowther, R.A.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M.; Scheres, S.H.W. Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 547, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Roeters, S.J.; Kogan, V.; Woutersen, S.; Claessens, M.M.A.E.; Subramaniam, V. C-Terminal Truncated α-Synuclein Fibrils Contain Strongly Twisted β-Sheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15392–15400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.-C.; Liang, C.; Mehta, A.K.; Lynn, D.G.; Grover, M.A. Multistep Conformation Selection in Amyloid Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17007–17010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madine, J.; Jack, E.; Stockley, P.G.; Radford, S.E.; Serpell, L.C.; Middleton, D.A. Structural Insights into the Polymorphism of Amyloid-Like Fibrils Formed by Region 20−29 of Amylin Revealed by Solid-State NMR and X-ray Fiber Diffraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14990–15001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsburyab, C.; Goldie, K.; Pellaud, J.; Seelig, J.; Frey, P.; Müller, S.; Kistler, J.; Cooperbf, G.J.S.; Aebi, U. Amyloid Fibril Formation from Full-Length and Fragments of Amylin. J. Struct. Biol. 2000, 130, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, K.; Gührs, K.-H.; Koehler, R.; Schmidt, M.; Michel, H.; Loos, C.; Gaffney, P.M.; Sigurdson, C.J.; Hegenbart, P.D.U.; Schönland, P.D.S.; et al. Polymorphism of Amyloid Fibrils In Vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4822–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gath, J.; Bousset, L.; Habenstein, B.; Melki, R.; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B.H. Unlike Twins: An NMR Comparison of Two α-Synuclein Polymorphs Featuring Different Toxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Romero, D.; Kayatekin, C.; Akabayov, B.; Vlamakis, H.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Isolation, Characterization, and Aggregation of a Structured Bacterial Matrix Precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17559–17568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, A.; Roske, Y.; Ball, L.; Chowdhury, A.; Hiller, M.; Molière, N.; Kramer, R.; Stöppler, D.; Worth, C.L.; Schlegel, B.; et al. Structural changes of TasA in biofilm formation of Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3237–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Chapman, M.R. Bacterial functional amyloids: Order from disorder. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöver, A.G.; Driks, A. Secretion, Localization, and Antibacterial Activity of TasA, a Bacillus subtilis Spore-Associated Protein. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, N.; Keren-Paz, A.; Hou, Q.; Doron, S.; Yanuka-Golub, K.; Olender, T.; Hadar, R.; Rosenberg, G.; Jain, R.; Cámara-Almirón, J.; et al. The extracellular matrix protein TasA is a developmental cue that maintains a motile subpopulation within Bacillus subtilis biofilms. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaaw8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, N.; Povolotsky, T.L.; Landau, M.; Kolodkin-Gal, I. Emerging Roles of Functional Bacterial Amyloids in Gene Regulation, Toxicity, and Immunomodulation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 85, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branda, S.S.; Chu, F.; Kearns, D.B.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. A major protein component of the Bacillus subtilis biofilm matrix. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Kernya, L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Goto, Y.; Réfrégiers, M.; Kardos, J. Accurate secondary structure prediction and fold recognition for circular dichroism spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3095–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Bulyáki, É.; Kun, J.; Moussong, É.; Lee, Y.-H.; Goto, Y.; Réfrégiers, M.; Kardos, J. BeStSel: A web server for accurate protein secondary structure prediction and fold recognition from the circular dichroism spectra. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. DICHROWEB, an online server for protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W668–W673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. Protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopy: Methods and reference databases. Biopolymers 2007, 89, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erskine, E.; Morris, R.J.; Schor, M.; Earl, C.; Gillespie, R.M.C.; Bromley, K.M.; Sukhodub, T.; Clark, L.; Fyfe, P.K.; Serpell, L.C.; et al. Formation of functional, non-amyloidogenic fibres by recombinant Bacillus subtilis TasA. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 110, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azulay, D.N.; Ghrayeb, M.; Ktorza, I.B.; Nir, I.; Nasser, R.; Harel, Y.S.; Chai, L. Colloidal-like aggregation of a functional amyloid protein. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 23286–23294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichner, T.; Radford, S.E. A Diversity of Assembly Mechanisms of a Generic Amyloid Fold. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.I.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M.; Knowles, T.P. From Macroscopic Measurements to Microscopic Mechanisms of Protein Aggregation. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 421, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancalana, M.; Koide, S. Molecular mechanism of Thioflavin-T binding to amyloid fibrils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momotani, Y.; Arie, R.; Takagi, T. Novel transient circular dichroic spectra with a trough near 230 nm observed in the denaturation processes of lectins by sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. 1981, 668, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malishev, R.; Abbasi, R.; Jelinek, R.; Chai, L. Bacterial Model Membranes Reshape Fibrillation of a Functional Amyloid Protein. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5230–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghrayeb, M.; Hayet, S.; Lester-Zer, N.; Levi-Kalisman, Y.; Chai, L. Fibrilar Polymorphism of the Bacterial Extracellular Matrix Protein TasA. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030529
Ghrayeb M, Hayet S, Lester-Zer N, Levi-Kalisman Y, Chai L. Fibrilar Polymorphism of the Bacterial Extracellular Matrix Protein TasA. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(3):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030529
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhrayeb, Mnar, Shahar Hayet, Neta Lester-Zer, Yael Levi-Kalisman, and Liraz Chai. 2021. "Fibrilar Polymorphism of the Bacterial Extracellular Matrix Protein TasA" Microorganisms 9, no. 3: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030529
APA StyleGhrayeb, M., Hayet, S., Lester-Zer, N., Levi-Kalisman, Y., & Chai, L. (2021). Fibrilar Polymorphism of the Bacterial Extracellular Matrix Protein TasA. Microorganisms, 9(3), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030529






