Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. Current Recommendations for Salt Intake
3.1.1. Salt Requirement Recommendations for the General Population
3.1.2. Salt Restriction Recommendations in Particular Situations: HF and CKD
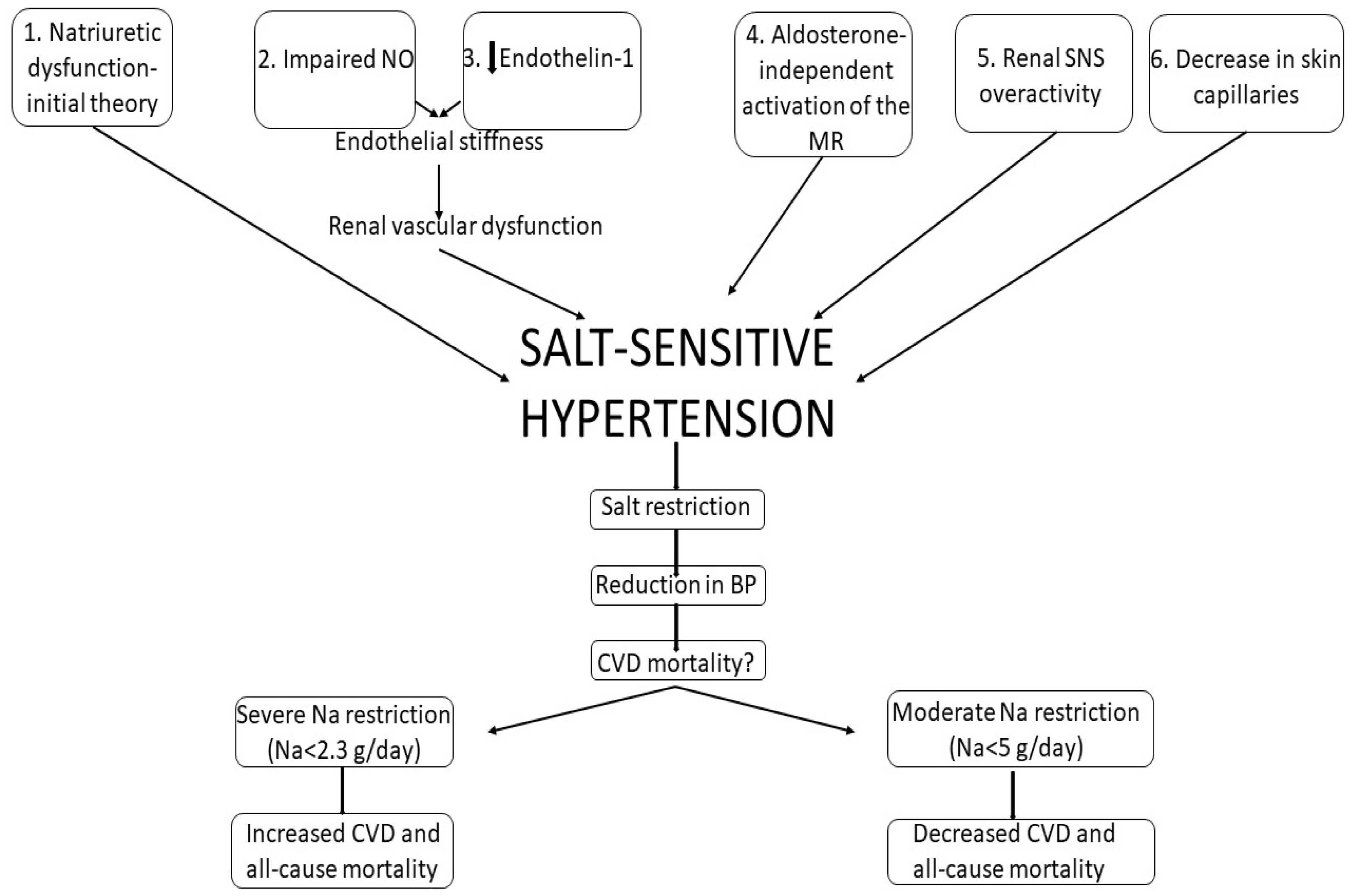
3.2. Salt-Sensitive versus Salt-Resistant Hypertension
3.3. Salt and Cardiovascular Events
3.4. Low-Salt Diet—Advantages
3.4.1. Low-Salt Diet and BP
| Outcome | Evidence from Meta-Analyses |
|---|---|
| BP | Dose-response relationship between salt reduction and BP decrease (He 2013 [47], Taylor 2011 [48], Graudal 2020 [32], Aburto 2013 [49]) |
| CV events |
|
| HF | Severe salt restriction: |
| Lipids | Salt restriction: |
| Kidney function | Salt reduction:
|
3.4.2. Salt Intake and CKD
3.4.3. Salt Intake and Stroke
3.4.4. Salt Intake and HF
3.5. “Salt Not Always an Enemy”: The Deleterious Effects of Salt Restriction
3.5.1. CVD and All-Cause Mortality
3.5.2. HF
3.5.3. Metabolic Parameters
3.5.4. Hypotension
4. Conclusions
Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, R.; Sutradhar, R.; Yao, Z.; Wodchis, W.P.; Rosella, L.C. Smoking, drinking, diet and physical activity—Modifiable lifestyle risk factors and their associations with age to first chronic disease. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. A comprehensive review on salt and health and current experience of worldwide salt reduction programmes. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2008, 23, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Ippolito, R.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Strazzullo, P. Habitual salt intake and risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suckling, R.J.; Swift, P.A. The health impacts of dietary sodium and a low-salt diet. Clin. Med. (Northfield Il) 2015, 15, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.A.; Tekle, D.; Rosewarne, E.; Flexner, N.; Cobb, L.; Al-Jawaldeh, A.; Kim, W.J.; Breda, J.; Whiting, S.; Campbell, N.; et al. A Systematic Review of Salt Reduction Initiatives Around the World: A Midterm Evaluation of Progress Towards the 2025 Global Non-Communicable Diseases Salt Reduction Target. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1768–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.R.; Cutler, J.A.; Obarzanek, E.; Buring, J.E.; Rexrode, K.M.; Kumanyika, S.K.; Appel, L.J.; Whelton, P.K. Long term effects of dietary sodium reduction on cardiovascular disease outcomes: Observational follow-up of the trials of hypertension prevention (TOHP). BMJ 2007, 334, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, D.S.A.; Prieto, M.C.; Navar, L.G. Salt-Sensitive Hypertension: Perspectives on Intrarenal Mechanisms. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2015, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Ingole, S.; Jain, R. Salt sensitivity and its implication in clinical practice. Indian Heart J. 2018, 70, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T. Mechanism of Salt-Sensitive Hypertension: Focus on Adrenal and Sympathetic Nervous Systems. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.; Mente, A.; Alderman, M.H.; Brady, A.J.B.; Diaz, R.; Gupta, R.; López-Jaramillo, P.; Luft, F.C.; Lüscher, T.F.; Mancia, G.; et al. Salt and cardiovascular disease: Insufficient evidence to recommend low sodium intake. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 3363–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Sodium Intake for Adults and Children. In Guidel Sodium Intake Adults Child; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, e13–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, e895–e1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Outcomes Blood Pressure Work Group I; Disease, K.; Cheung, A.K.; Chang, T.I.; Cushman, W.C.; Furth, S.L.; Hou, F.F.; Ix, J.H.; Knoll, G.A.; Muntner, P.; et al. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Blood Pressure in Chronic Kidney Disease. Pract. Guidel. 2021, 99, S1–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.C.; Coleman, T.G.; Granger, H.J. Circulation: Overall Regulation. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1972, 34, 13–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, T.W.; DiCarlo, S.E.; Pravenec, M.; Morris, R.C. The pivotal role of renal vasodysfunction in salt sensitivity and the initiation of salt-induced hypertension. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2018, 27, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, T.W.; DiCarlo, S.E.; Pravenec, M.; Morris, R.C. Changing views on the common physiologic abnormality that mediates salt sensitivity and initiation of salt-induced hypertension: Japanese research underpinning the vasodysfunction theory of salt sensitivity. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 42, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, I.S.; Tavares-Mordwinkin, R.; Castejon, A.M.; Alfieri, A.B.; Cubeddu, L.X. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphism, nitric oxide production, salt sensitivity and cardiovascular risk factors in Hispanics. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2005, 19, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Vos, I.; Shaw, S.; Boer, P.; D’Uscio, L.V.; Gröne, H.J.; Rabelink, T.J.; Lattmann, T.; Moreau, P.; Lüscher, T.F. Dysfunctional renal nitric oxide synthase as a determinant of salt-sensitive hypertension: Mechanisms of renal artery endothelial dysfunction and role of endothelin for vascular hypertrophy and Glomerulosclerosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnock, D.G.; Kusche-Vihrog, K.; Tarjus, A.; Sheng, S.; Oberleithner, H.; Kleyman, T.R.; Jaisser, F. Blood pressure and amiloride-sensitive sodium channels in vascular and renal cells. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusche-Vihrog, K.; Tarjus, A.; Fels, J.; Jaisser, F. The epithelial Na+ channel. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertuglu, L.A.; Elijovich, F.; Laffer, C.L.; Kirabo, A. Salt-Sensitivity of Blood Pressure and Insulin Resistance. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuPont, J.J.; Greaney, J.L.; Wenner, M.M.; Lennon-Edwards, S.L.; Sanders, P.W.; Farquhar, W.B.; Edwards, D.G. High Dietary Sodium Intake Impairs Endothelium-Dependent Dilation in Healthy Salt-Resistant Humans. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, P.W. Vascular consequences of dietary salt intake. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elia, L.; Galletti, F.; Fata ELa Sabino, P.; Strazzullo, P. Effect of dietary sodium restriction on arterial stiffness: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the randomized controlled trials. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarazaki, H.; Ando, K.; Fujita, M.; Matsui, H.; Nagae, A.; Muraoka, K.; Kawarasaki, C.; Fujita, T. Mineralocorticoid receptor activation: A major contributor to salt-induced renal injury and hypertension in young rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 300, F1402–F1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Amodeo, C. Salt Appetite and Aging. Arq. Bras. De Cardiol. 2019, 113, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, W.M.; Sacks, F.M.; Ard, J.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; Conlin, P.R.; Svetkey, L.P.; Erlinger, T.P.; Moore, T.J.; et al. Effects of diet and sodium intake on blood pressure: Subgroup analysis of the DASH-sodium trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 135, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Oniki, H. High salt intake promotes a decline in renal function in hypertensive patients: A 10-year observational study. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 36, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, L.; Rossi, G.; Di Cola, M.S.; Savino, I.; Galletti, F.; Strazzullo, P. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Dietary Sodium Restriction with or without Concomitant Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System-Inhibiting Treatment on Albuminuria. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graudal, N.A.; Hubeck-Graudal, T.; Jurgens, G. Effects of low sodium diet versus high sodium diet on blood pressure, renin, aldosterone, catecholamines, cholesterol, and triglyceride. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison-Bernard, L.M. The renal renin-angiotensin system. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2009, 33, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, M.; Matsui, H.; Shibata, S.; Gotoda, T.; Fujita, T. Salt-induced nephropathy in obese spontaneously hypertensive rats via paradoxical activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor: Role of oxidative stress. Hypertens 2007, 50, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, S.; Nagase, M.; Yoshida, S.; Kawarazaki, W.; Kurihara, H.; Tanaka, H.; Miyoshi, J.; Takai, Y.; Fujita, T. Modification of mineralocorticoid receptor function by Rac1 GTPase: Implication in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohama, D.; Nishimoto, M.; Ayuzawa, N.; Kawarazaki, W.; Fujii, W.; Oba, S.; Shibata, S.; Marumo, T.; Fujita, T. Activation of Rac1-Mineralocorticoid Receptor Pathway Contributes to Renal Injury in Salt-Loaded db/db Mice. Hypertens 2021, 78, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonios, T.F.T.; Singer, D.R.J.; Markandu, N.D.; Mortimer, P.S.; MacGregor, G.A. Structural skin capillary rarefaction in essential hypertension. Hypertens 1999, 33, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze, J.; Dahlmann, A.; Lerchl, K.; Kopp, C.; Rakova, N.; Schrö Der, A.; Luft, F.C. Spooky sodium balance. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajah, V.; Connolly, K.; McEniery, C.; Wilkinson, I. Skin Sodium and Hypertension: A Paradigm Shift? Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, P.; D’Elia, L.; Kandala, N.B.; Cappuccio, F.P. Salt intake, stroke, and cardiovascular disease: Meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ 2009, 339, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto, N.J.; Ziolkovska, A.; Hooper, L.; Elliott, P.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Meerpohl, J.J. Effect of lower sodium intake on health: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ 2013, 346, f1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graudal, N.; Jürgens, G.; Baslund, B.; Alderman, M.H. Compared with usual sodium intake, low- and excessive-sodium diets are associated with increased mortality: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Hypertens. 2014, 27, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.; Mente, A.; Rangarajan, S.; McQueen, M.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Yan, H.; Lee, S.F.; Mony, P.; Devanath, A.; et al. Urinary Sodium and Potassium Excretion, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Yusuf, S.; Mente, A.; Gao, P.; Mann, J.F.; Teo, K.; Sleight, P.; Sharma, A.M.; Dans, A.; Probstfield, J.; et al. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion and risk of cardiovascular events. JAMA 2011, 306, 2229–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayedi, A.; Ghomashi, F.; Zargar, M.S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary sodium, sodium-to-potassium ratio, and risk of stroke: A systematic review and nonlinear dose-response meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. Intersalt: An international study of electrolyte excretion and blood pressure. Results for 24 hour urinary sodium and potassium excretion. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. BMJ 1988, 297, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.J.; Li, J.; MacGregor, G.A. Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2013, 346, f1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.S.; Ashton, K.E.; Moxham, T.; Hooper, L.; Ebrahim, S. Reduced dietary salt for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (cochrane review). Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, A.; O’Donnell, M.; Yusuf, S. Sodium Intake and Health: What Should We Recommend Based on the Current Evidence? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Khan, M.U.; Riaz, H.; Valavoor, S.; Zhao, D.; Vaughan, L.; Okunrintemi, V.; Riaz, I.B.; Khan, M.S.; Kaluski, E.; et al. Effects of Nutritional Supplements and Dietary Interventions on Cardiovascular Outcomes An Umbrella Review and Evidence Map: An Umbrella Review and Evidence Map. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtani, K.R.; Heneghan, C.; Onakpoya, I.; Tierney, S.; Aronson, J.K.; Roberts, N.; Hobbs, F.D.R.; Nunan, D. Reduced Salt Intake for Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, E.J.; Campbell, K.L.; Bauer, J.D.; Mudge, D.W.; Kelly, J.T. Altered dietary salt intake for people with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 6, CD010070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Borrelli, S.; Provenzano, M.; De Stefano, T.; Vita, C.; Chiodini, P.; Minutolo, R.; de Nicola, L.; Conte, G. Dietary Salt Restriction in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2018, 10, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Zou, M.; Zhen, Z.; Xue, Y. Effect of a sodium restriction diet on albuminuria and blood pressure in diabetic kidney disease patients: A meta-analysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juraschek, S.P.; Woodward, M.; Sacks, F.M.; Carey, V.J.; Miller, E.R.; Appel, L.J. Time Course of Change in Blood Pressure from Sodium Reduction and the DASH Diet. Hypertension 2017, 70, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerbass, F.B.; Morais, J.G.; dos Santos, R.G.; Kruger, T.S.; Sczip, A.C.; da Luz Filho, H.A. Factors associated to salt intake in chronic hemodialysis patients. Braz. J. Nephrol. 2013, 35, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.F.F.; Peixoto, A.J. Sodium balance in maintenance hemodialysis. Semin. Dial. 2010, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze, J.; Krause, H.; Hecht, H.; Dietsch, P.; Rittweger, J.; Lang, R.; Kirsch, K.A.; Hilgers, K.F. Reduced osmotically inactive Na storage capacity and hypertension in the Dahl model. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2002, 283, F134–F141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitiyakara, C.; Chabrashvili, T.; Chen, Y.; Blau, J.; Karber, A.; Aslam, S.; Welch, W.J.; Wilcox, C.S. Salt intake, oxidative stress, and renal expression of NADPH oxidase and superoxide dismutase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketonen, J.; Merasto, S.; Paakkari, I.; Mervaala, E.M.A. High sodium intake increases vascular superoxide formation and promotes atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Blood Press. 2005, 14, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, C.K.; Michellazzo, S.M.; De Nucci, G.; Zatz, R. Sodium excess aggravates hypertension and renal parenchymal injury in rats with chronic NO inhibition. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, F697–F705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.M.; Burrell, L.M.; Black, M.J.; Wu, L.L.; Dilley, R.J.; Cooper, M.E.; Johnston, C.I. Salt induces myocardial and renal fibrosis in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Circulation 1998, 98, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safar, M.E.; Temmar, M.; Kakou, A.; Lacolley, P.; Thornton, S.N. Sodium intake and vascular stiffness in hypertension. Hypertension 2009, 54, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Patel, Y.; Joseph, J. Sodium Intake and Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.W.; Huang, L.H.; Ku, C.H. Use of dietary sodium intervention effect on neurohormonal and fluid overload in heart failure patients: Review of select research based literature. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2018, 42, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.; Mente, A.; Yusuf, S. Sodium Intake and Cardiovascular Health. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.W.; Hailpern, S.M.; Fang, J.; Alderman, M.H. Sodium intake and mortality in the NHANES II follow-up study. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 275.e1–275.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, T.; Kuklina, E.V.; Flanders, W.D.; Hong, Y.; Gillespie, C.; Chang, M.; Gwinn, M.; Dowling, N.; Khoury, M.J.; et al. Sodium and potassium intake and mortality among US adults: Prospective data from the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterna, S.; Gaspare, P.; Fasullo, S.; Sarullo, F.M.; Di Pasquale, P. Normal-sodium diet compared with low-sodium diet in compensated congestive heart failure: Is sodium an old enemy or a new friend? Clin. Sci. 2008, 114, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado d’Almeida, K.S.; Rabelo-Silva, E.R.; Souza, G.C.; Trojahn, M.M.; Santin Barilli, S.L.; Aliti, G.; EduardoRohde, L.; Biolo, A.; Beck-da-Silv, L. Aggressive fluid and sodium restriction in decompensated heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Results from a randomized clinical trial. Nutrition 2018, 54, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricio, C.G.; Tanaka, D.M.; de Souza Gentil, J.R.; Ferreira Amato, C.A.; Marques, F.; Schwartzmann, P.V.; Schmidt, A.; Simões, M.V. A normal sodium diet preserves serum sodium levels during treatment of acute decompensated heart failure: A prospective, blind and randomized trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 32, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyas, E.; Jeitler, K.; Horvath, K.; Semlitsch, T.; Hemkens, L.G.; Pignitter, N.; Siebenhofer, A. Benefit assessment of salt reduction in patients with hypertension: Systematic overview. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulowicz, W.; Radziszewski, A. Pathogenesis and treatment of dialysis hypotension. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, S36–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kilpatrick, R.D.; McAllister, C.J.; Greenland, S.; Kopple, J.D. Reverse epidemiology of hypertension and cardiovascular death in the hemodialysis population: The 58th annual fall conference and scientific sessions. Hypertension 2005, 45, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hogas, M.; Statescu, C.; Padurariu, M.; Ciobica, A.; Bilha, S.C.; Haisan, A.; Timofte, D.; Hogas, S. Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective. Medicina 2022, 58, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091175
Hogas M, Statescu C, Padurariu M, Ciobica A, Bilha SC, Haisan A, Timofte D, Hogas S. Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective. Medicina. 2022; 58(9):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091175
Chicago/Turabian StyleHogas, Mihai, Cristian Statescu, Manuela Padurariu, Alin Ciobica, Stefana Catalina Bilha, Anca Haisan, Daniel Timofte, and Simona Hogas. 2022. "Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective" Medicina 58, no. 9: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091175
APA StyleHogas, M., Statescu, C., Padurariu, M., Ciobica, A., Bilha, S. C., Haisan, A., Timofte, D., & Hogas, S. (2022). Salt, Not Always a Cardiovascular Enemy? A Mini-Review and Modern Perspective. Medicina, 58(9), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091175










