Dynamic Softening Mechanism of Platinum Thermomechanically Deformed at Low Strain Rate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
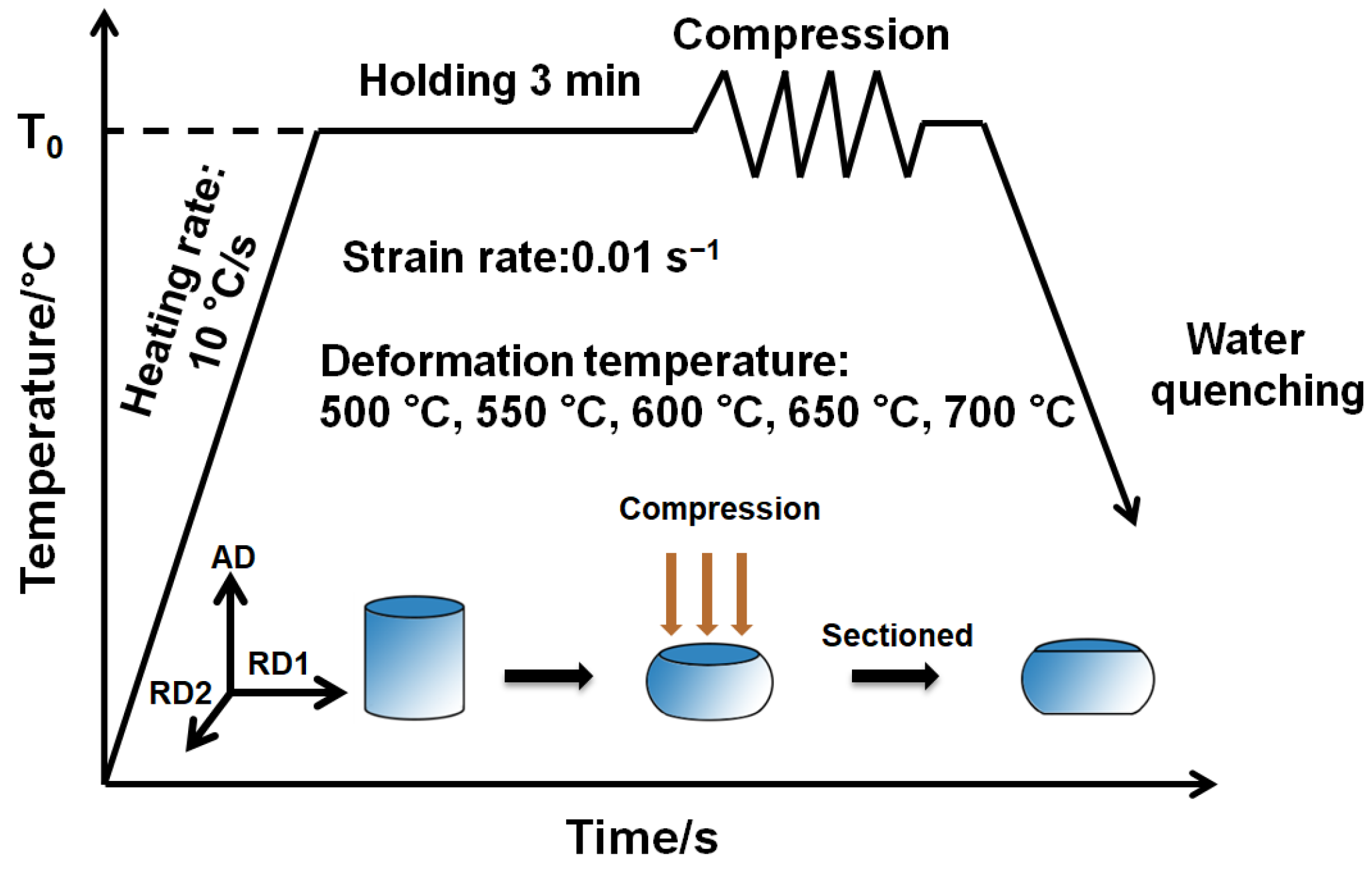
2. Experimental
3. Results
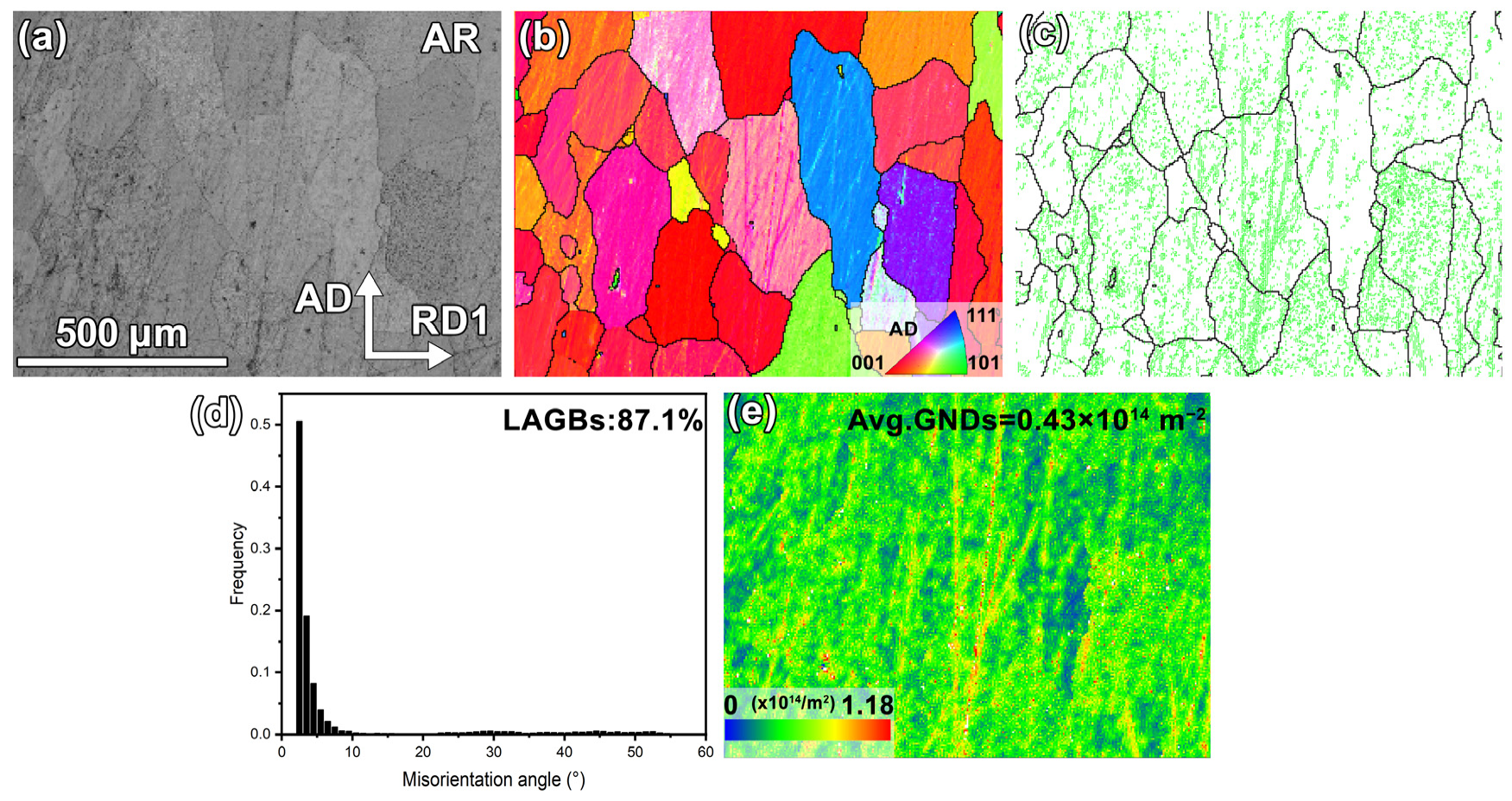
3.1. Initial Microstructure
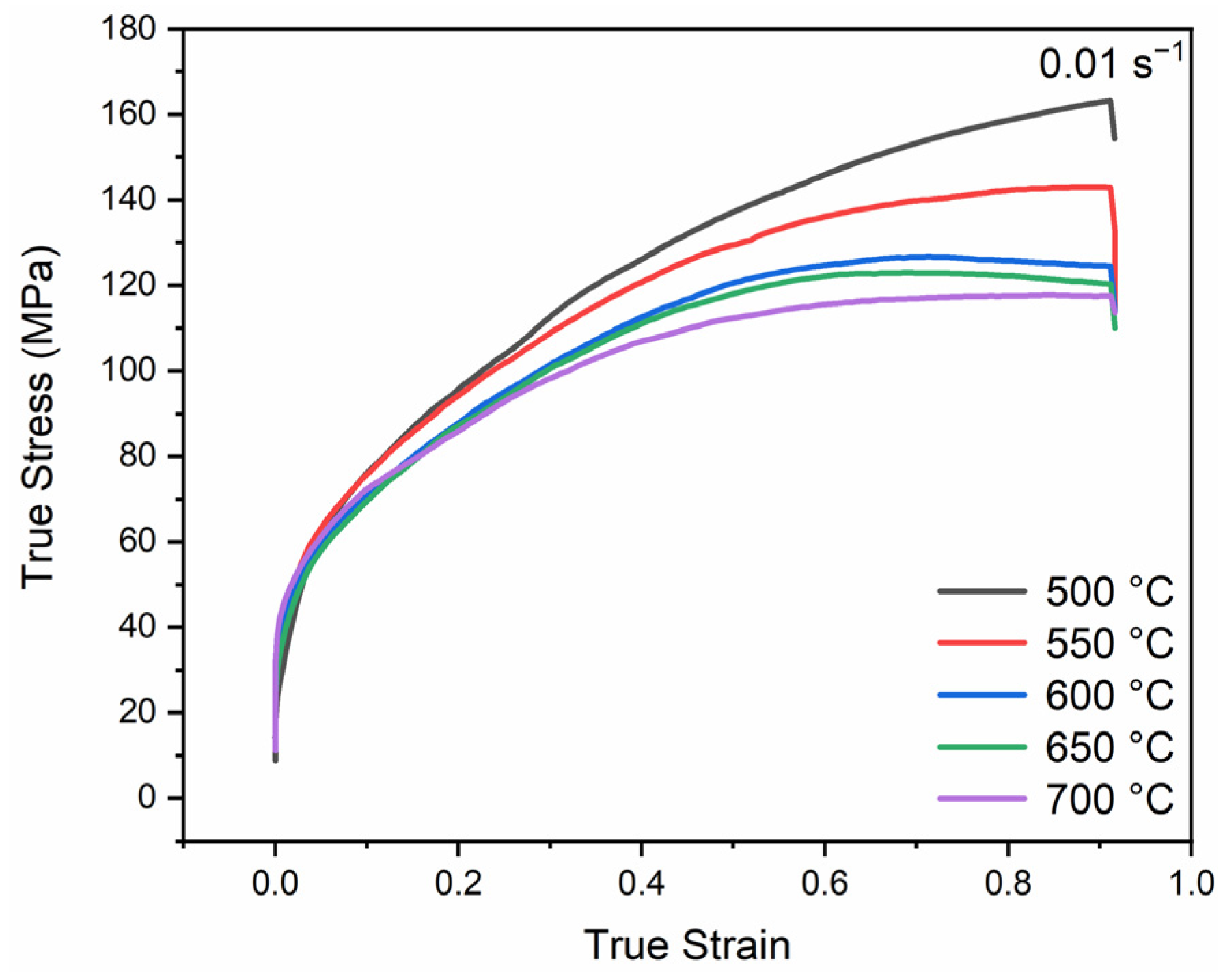
3.2. Thermocompression Flow Behavior
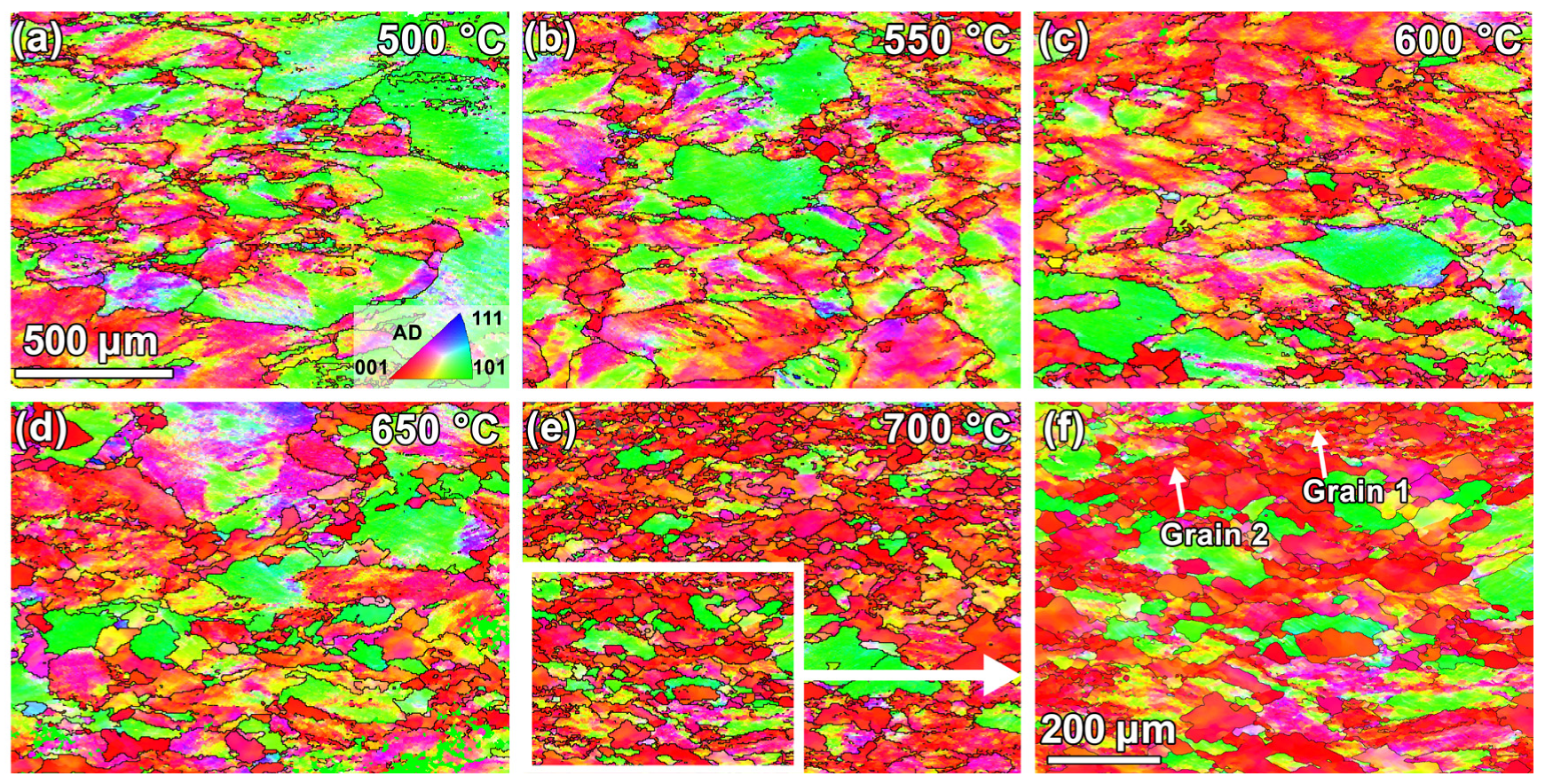
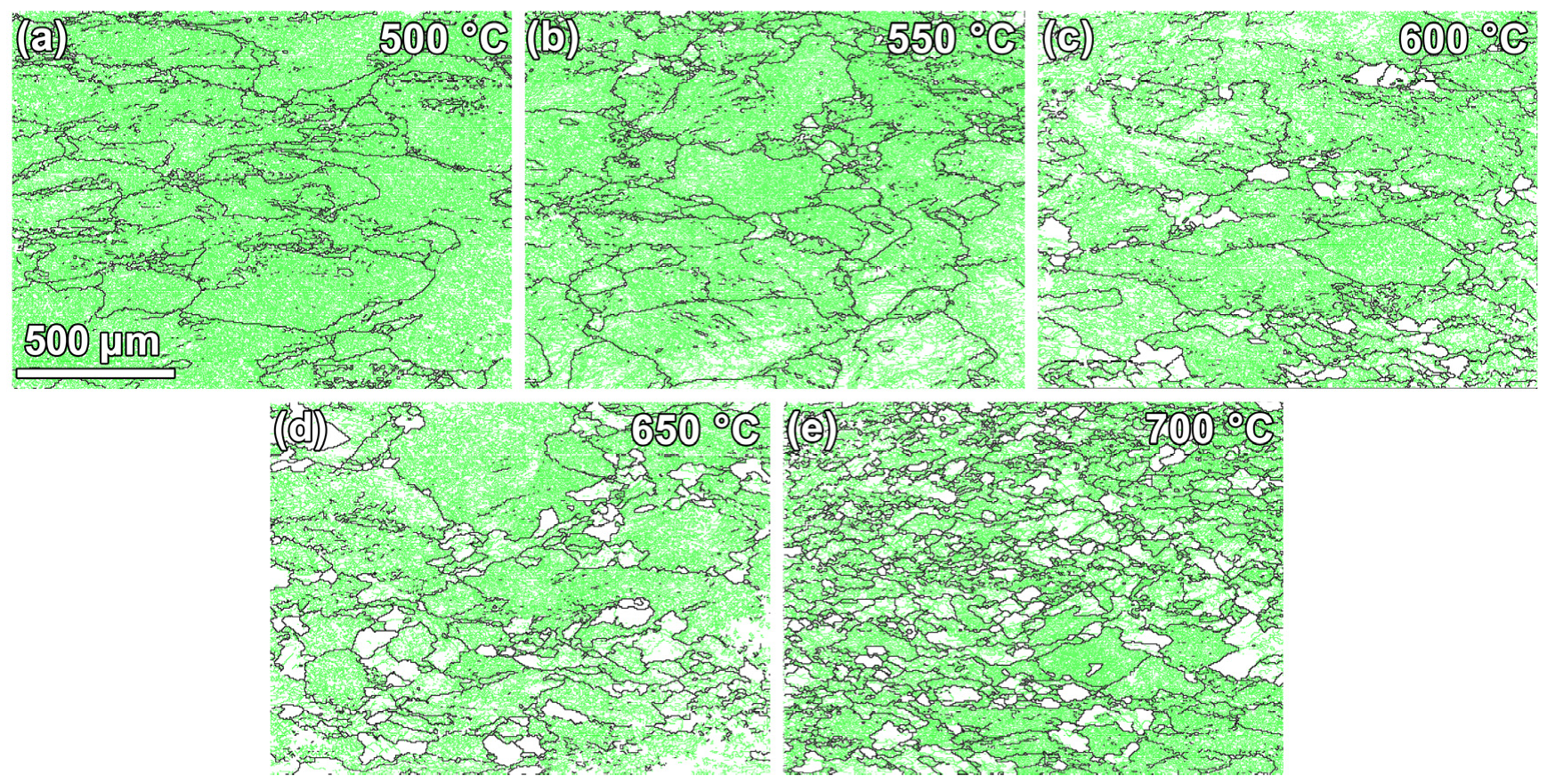
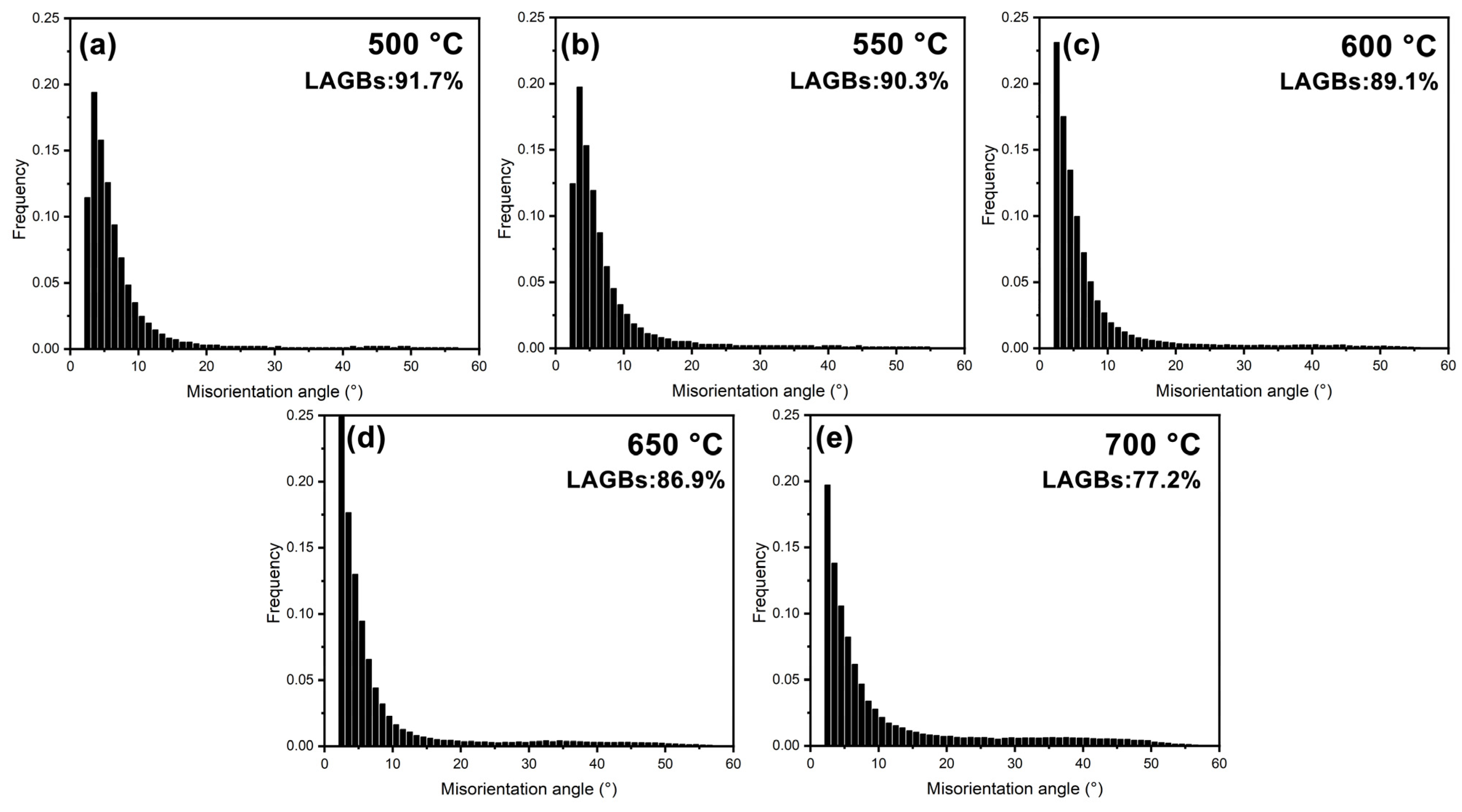
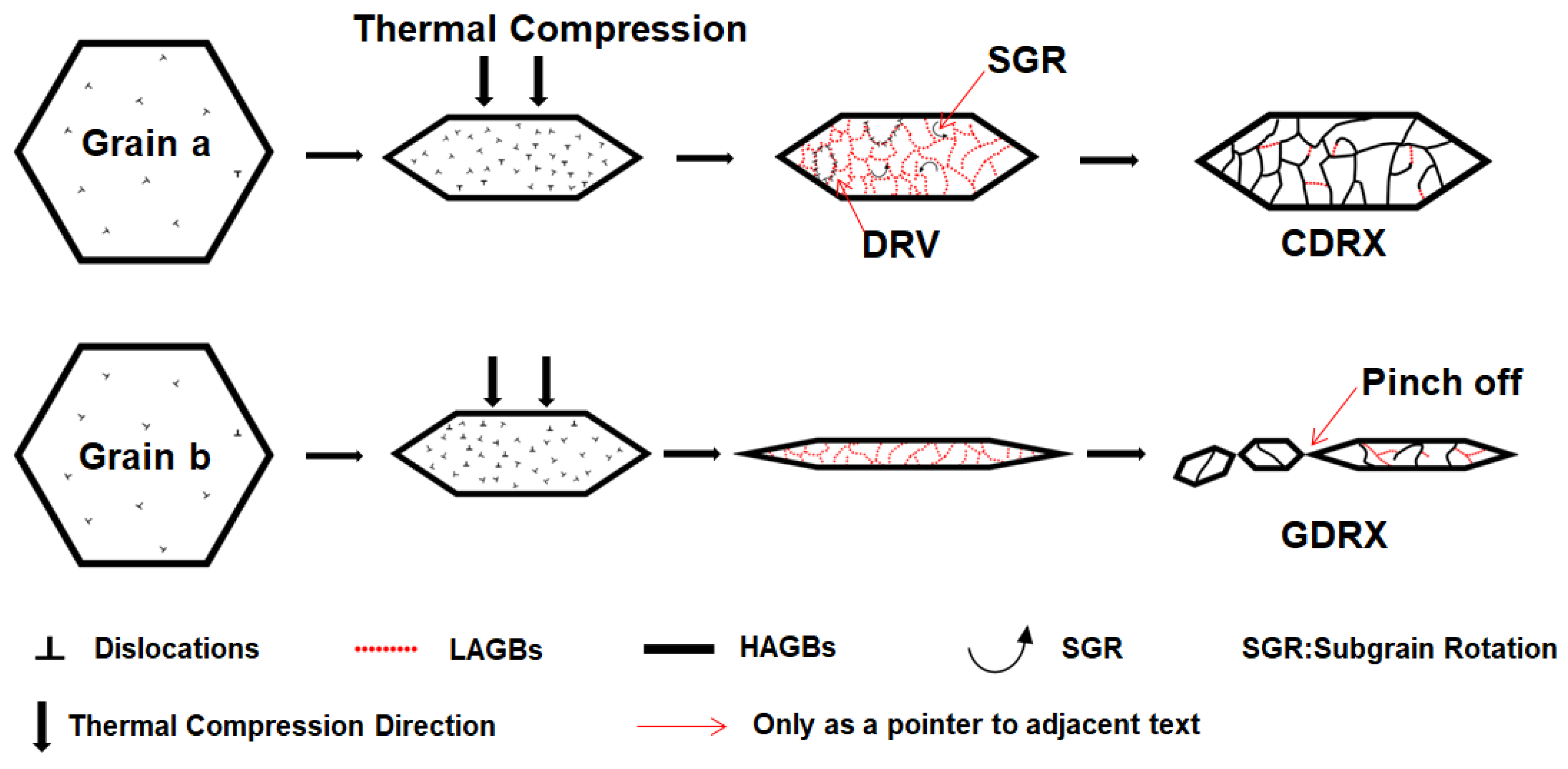
3.3. Microstructural Characteristics After Thermal Deformation
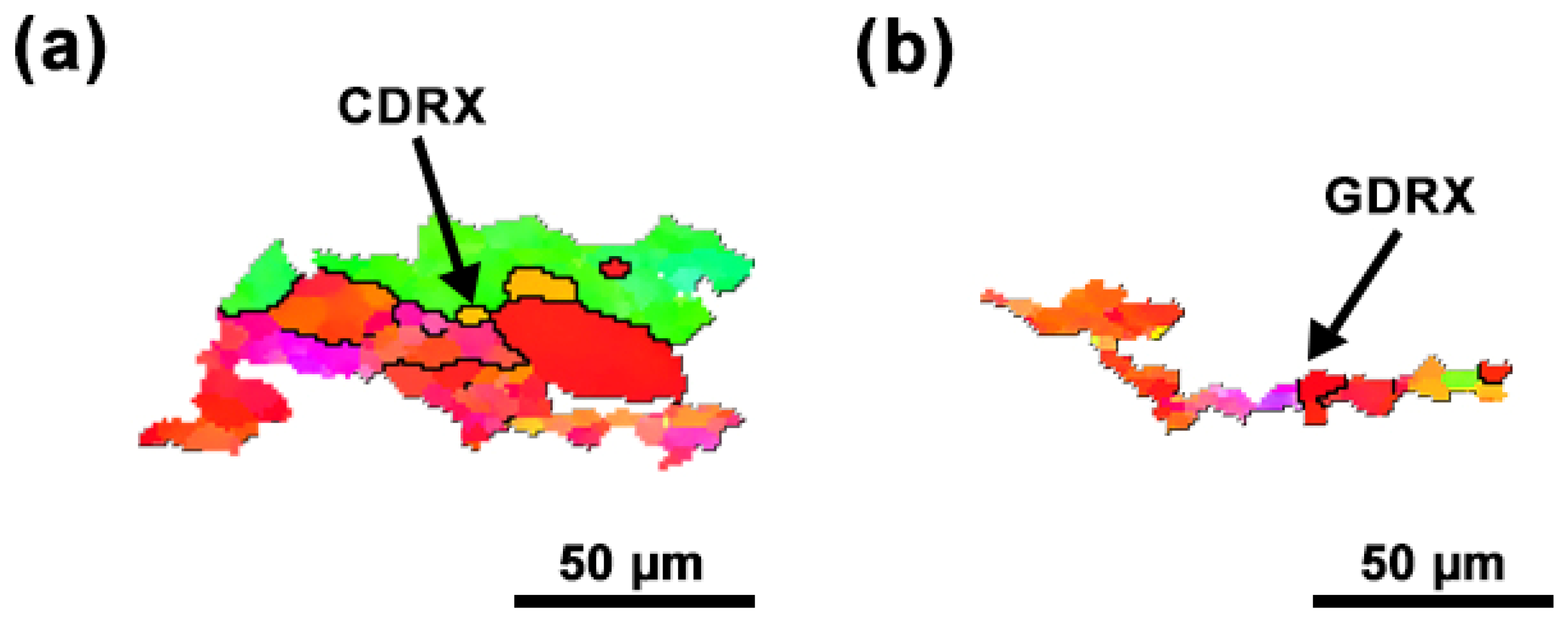
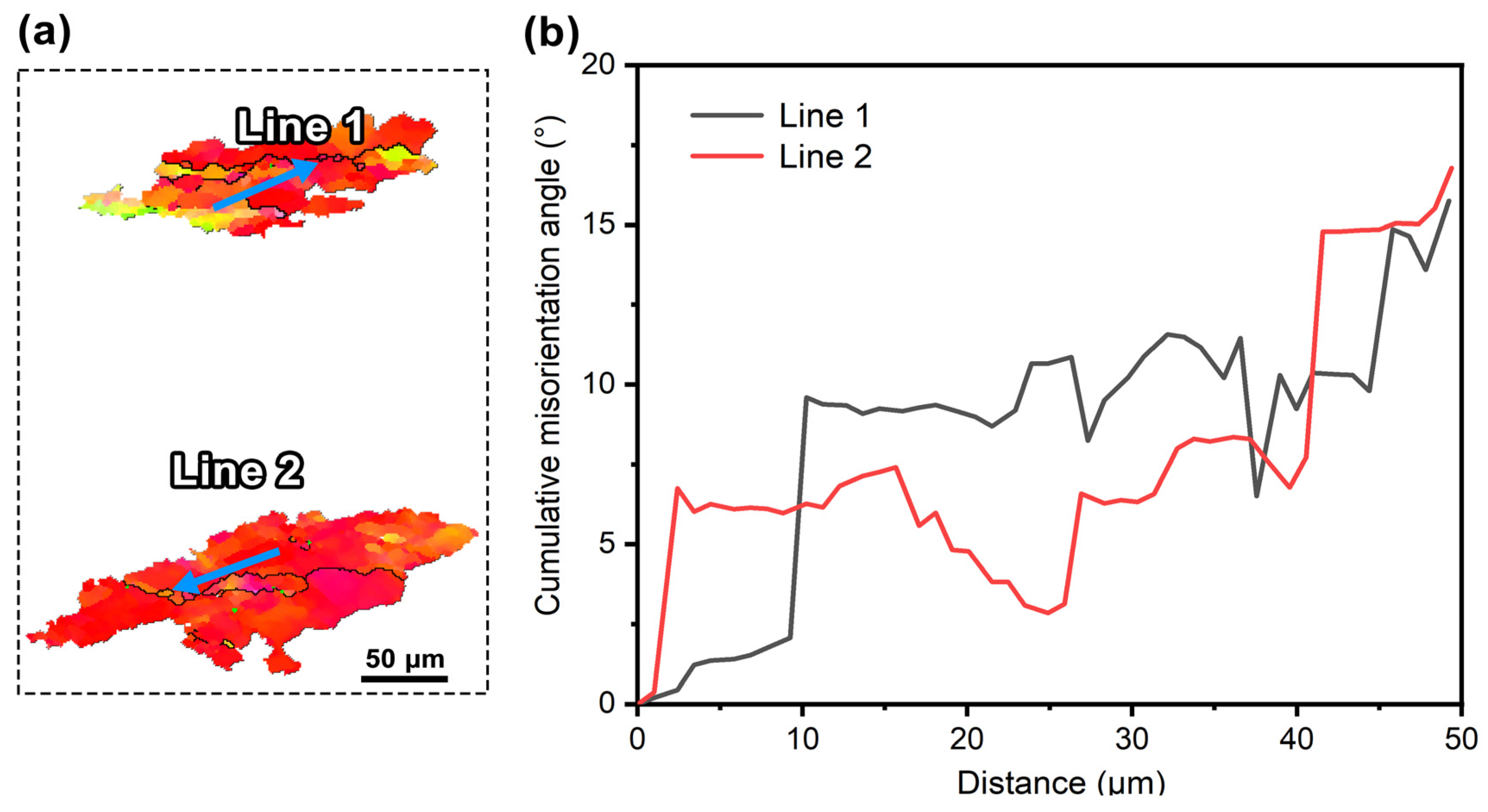
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- During thermal compression deformation at 0.01 s−1, the grain size, LAGBs fractions, and dislocation density of pure Pt generally decrease with increasing temperature.
- DRV based on dislocation cross-slip/climb is always found as a softening mechanism for pure Pt compressed at 500–700 °C.
- After the deformation temperature exceeds 650 °C, both CDRX and GDRX occur, facilitating improving the microstructural homogeneity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rakhtsaum, G. Platinum Alloys: A Selective Review of the Available Literature. Platin. Met. Rev. 2013, 57, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffths, W.P. Rare Platinum Metals. Nature 1968, 218, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, P.; Cornish, L.; Fairbank, G. New developments in high-temperature platinum alloys. JOM 2001, 53, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthey, J. Platinum 2003. Platin. Met. Rev. 2003, 47, 122. [Google Scholar]
- Maurice, C.; Driver, J. Hot rolling textures of fcc metals-part II. numerical simulations. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 4639–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, B.R.; Pratsinis, S.E. Flame Synthesis of Supported Platinum Group Metals for Catalysis and Sensors. Platin. Met. Rev. 2009, 53, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.S. Rhodium-Platinum alloys. Platin. Met. Rev 1961, 5, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Logé, R.E. A review of dynamic recrystallization phenomena in metallic materials. Mater. Des. 2016, 111, 548–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, F.; Bouzy, E.; Kou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Grain fragmentation associated continuous dynamic recrystallization (CDRX) of hexagonal structure during uniaxial isothermal compression: High-temperature α phase in TiAl alloys. Intermetallics 2021, 129, 107028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, G.; Jia, Z.; Ma, W. Investigation on deformation behaviors and dynamic recrystallization mechanism of spray formed Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy under hot compression. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 4401–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changizian, P.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R. On the recrystallization behavior of homogenized AZ81 magnesium alloy: The effect of mechanical twins and γ precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D. Explaining texture weakening and improved formability in magnesium rare earth alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chu, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, K.; Meng, Z.; Chen, L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, G. Dynamic precipitation and recrystallization behavior during hot deformation of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy: Experiment and modeling. Int. J. Plast. 2024, 178, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.; Cao, L.; Liao, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q. Hot deformation and dynamic recrystallization in Al-Mg-Si alloy. Mater. Charact. 2021, 173, 110976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhangani, S.; Masa, S.K.; Mathew, R.T.; Prasad, M.J.N.V.; Sujata, M. Microstructural evolution in Al–Mg–Sc alloy (AA5024): Effect of thermal treatment, compression deformation and friction stir welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wu, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, X.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Shan, A. Transition of deformation behavior and its related microstructure evolution in Nimonic 80A under hot-to-warm working. Mater. Charact. 2015, 106, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Fan, X.G.; Li, H.W.; Zhan, M.; Li, S.H. Grain morphology related microstructural developments in bulk deformation of 2219 aluminum alloy sheet at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 760, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; He, J.J.; Pi, L.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, W.Y.; Cheng, J.; Bai, S.W.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Y. Flow behavior and dynamic softening mechanism of Pt–10Ir precious alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2025, 35, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, F.J. Review—Grain and subgrain characterisation by electron backscatter diffraction. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 3833–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.A.; Hansen, N. The microstructural origin of work hardening stages. Acta Mater. 2018, 148, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Nunes, J.M.; de Carvalho, M.C.N.; Rodrigues, M.V.G.; Ferreira, J.C.; Silva, K.L.; Reyes, A.E.S.; da Silva Lima, M.N.; Siciliano, F.; Reis, G.S.; de Abreu, H.F.G.; et al. Stacking fault energy during DRV-DRX competition in high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel used in orthopedic implants. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 5322–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, H.J. Development of dynamic recrystallization theory. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 387–389, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samman, T.; Gottstein, G. Dynamic recrystallization during high temperature deformation of magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 490, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Fan, J.; Cheng, W.; Roven, H.J.; Xu, B.; Dong, H. Improved mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy plates by pre-rolling followed by warm compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 618, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi-Varzaneh, S.M.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Beladi, H. Dynamic recrystallization in AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 456, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Li, X.; Peng, Z.; Lai, J. Microstructure evolution and physical-based diffusion constitutive analysis of Al-Mg-Si alloy during hot deformation. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitdikov, O.; Kaibyshev, R. Dynamic recrystallization in pure magnesium. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| As-Received | 500 °C | 550 °C | 600 °C | 650 °C | 700 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 121.9 | 60.1 | 59.8 | 61.8 | 57.3 | 43.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Luan, B.; Chai, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, M.; Wu, B. Dynamic Softening Mechanism of Platinum Thermomechanically Deformed at Low Strain Rate. Materials 2025, 18, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040783
Tang H, Luan B, Chai L, Zhang F, Liu H, Xiao Y, Zhong M, Wu B. Dynamic Softening Mechanism of Platinum Thermomechanically Deformed at Low Strain Rate. Materials. 2025; 18(4):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040783
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Huiyi, Baifeng Luan, Linjiang Chai, Fuen Zhang, Hongliang Liu, Yuchen Xiao, Mingyao Zhong, and Baoan Wu. 2025. "Dynamic Softening Mechanism of Platinum Thermomechanically Deformed at Low Strain Rate" Materials 18, no. 4: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040783
APA StyleTang, H., Luan, B., Chai, L., Zhang, F., Liu, H., Xiao, Y., Zhong, M., & Wu, B. (2025). Dynamic Softening Mechanism of Platinum Thermomechanically Deformed at Low Strain Rate. Materials, 18(4), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18040783







