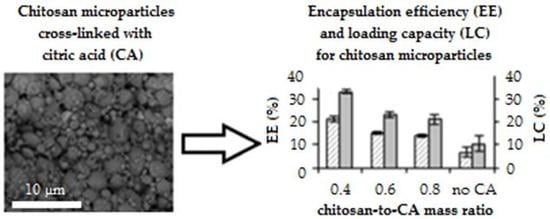
Modulation of Entrapment Efficiency and In Vitro Release Properties of BSA-Loaded Chitosan Microparticles Cross-Linked with Citric Acid as a Potential Protein–Drug Delivery System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
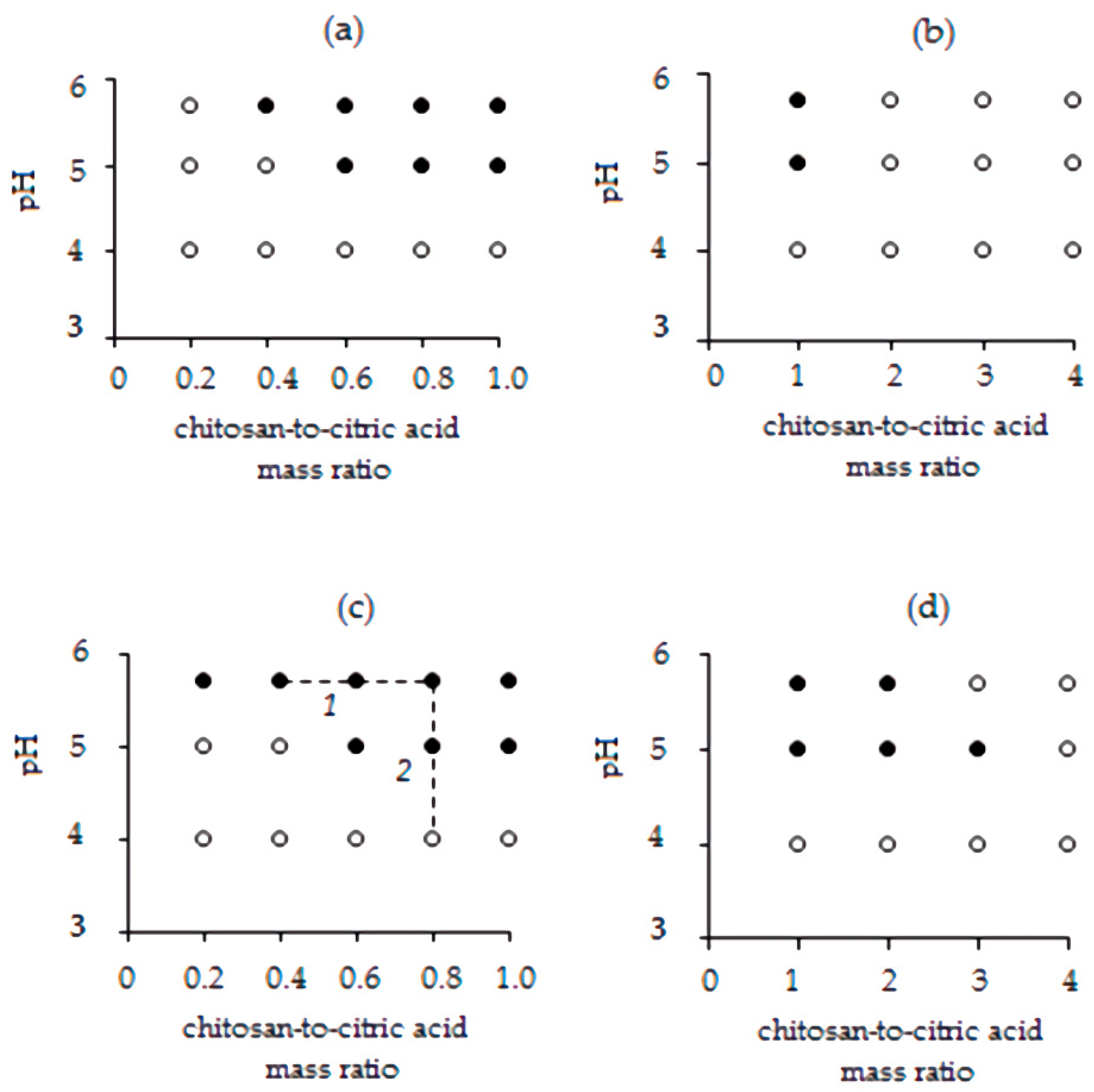
2.2. Study of the Interaction between Chitosan and Citric Acid
2.3. Preparation of Chitosan Microparticles
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.5. X-ray Diffraction Studies
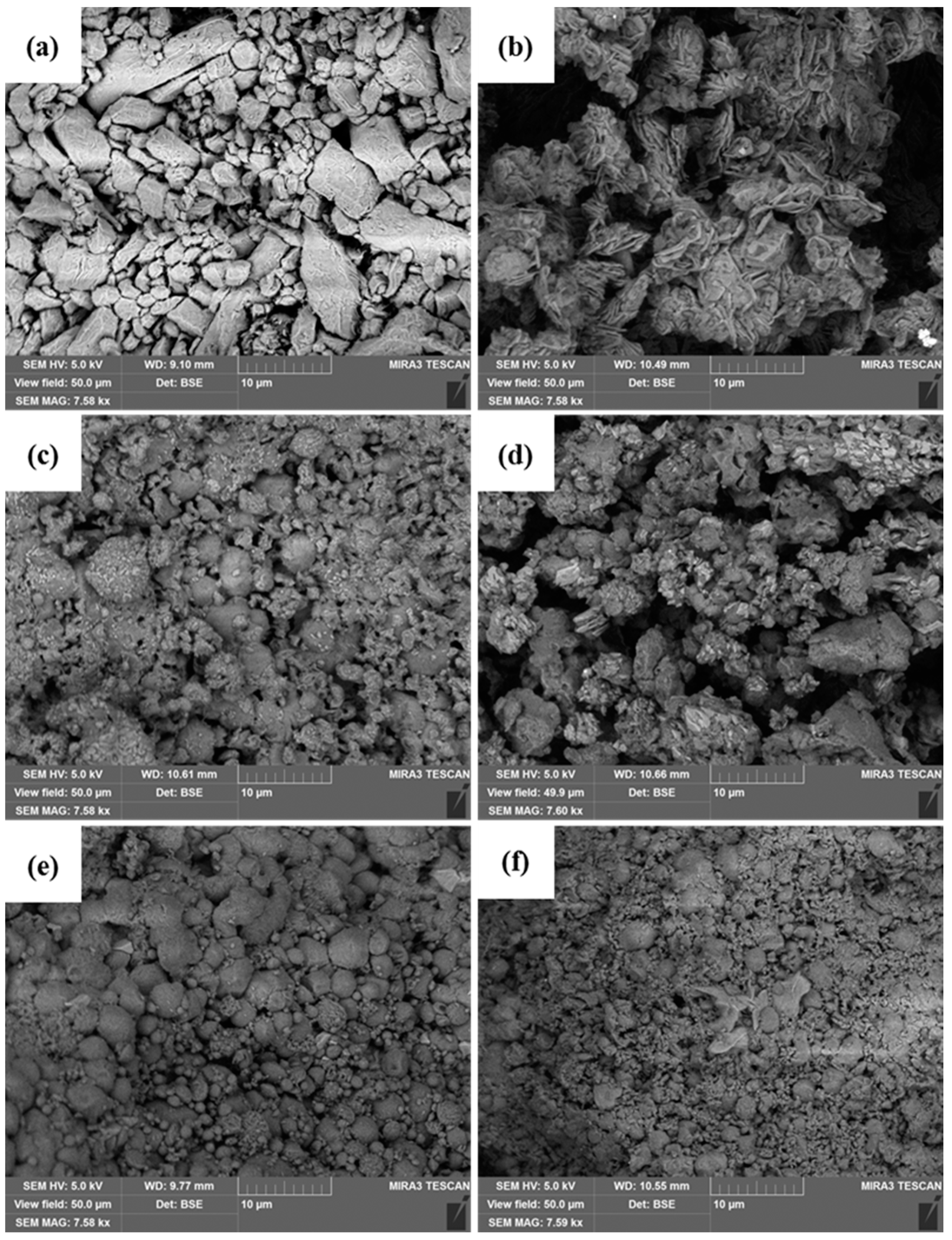
2.6. Surface Morphology and Particle Size
2.7. Zeta Potential
2.8. Erosion Studies
2.9. Microparticle Loading—Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) and Loading Capacity (LC)
2.10. In Vitro Release Study
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Study of the Interaction between Citrate and Chitosan
3.2. Characterization of Microparticles
3.2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.2.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
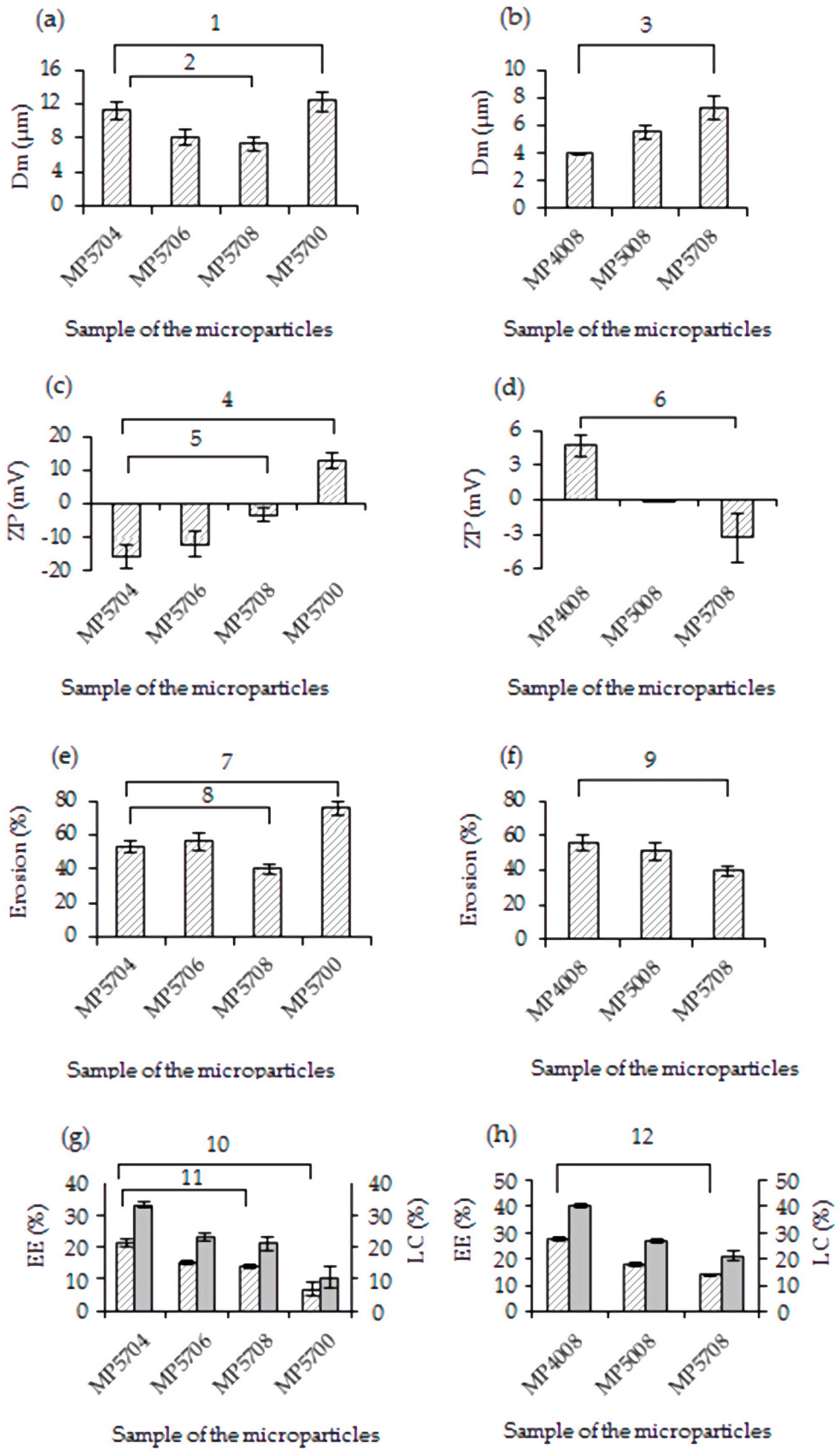
3.2.4. Size and Zeta Potential of Chitosan Microparticles
3.2.5. Erosion of the Microparticles
3.3. Encapsulation Efficiency and Loading Capacity
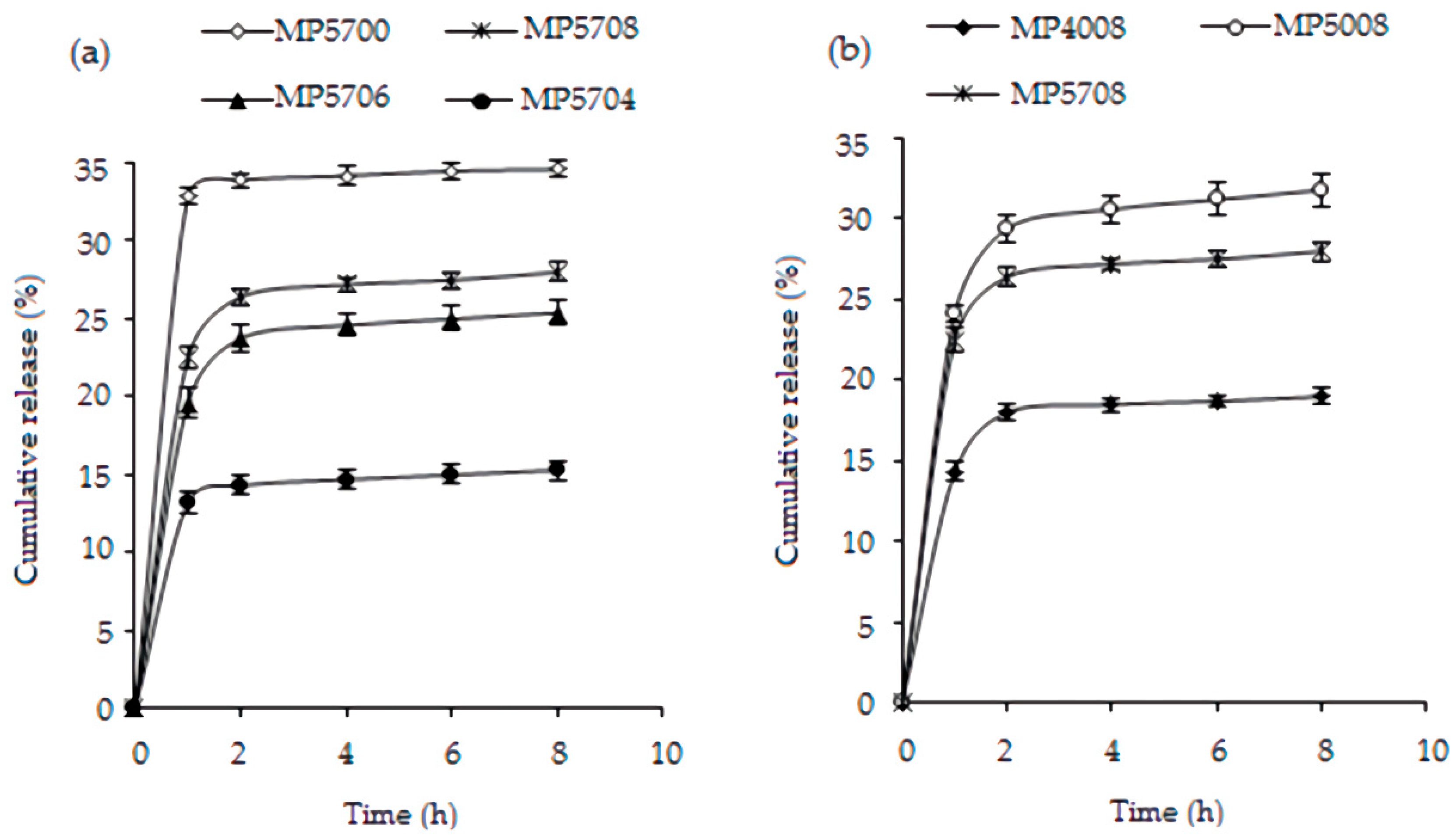
3.4. In Vitro BSA Release
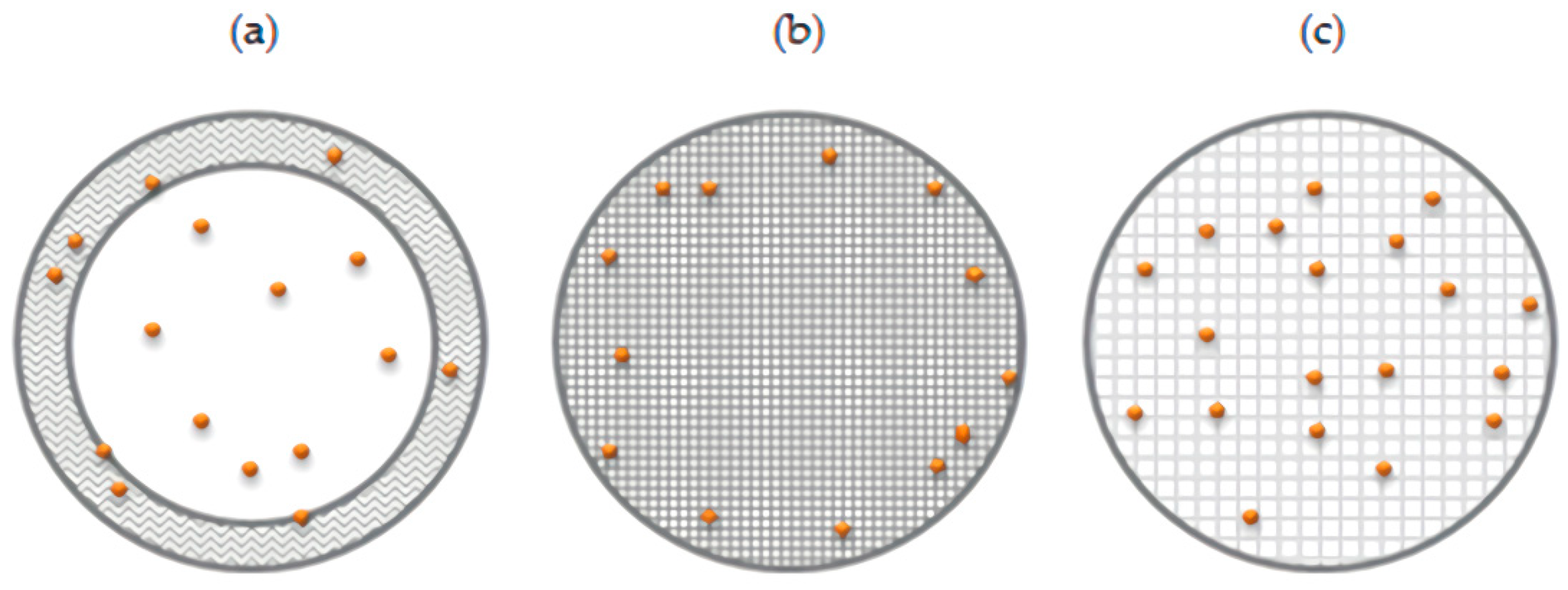
3.5. Role of the Surfactant and Proposed Structure of the Microparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Drug Delivery Systems: Entering the Mainstream. Science 2004, 303, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kona, S.; Specht, D.; Rahimi, M.; Shah, B.P.; Gilbertson, T.; Nguyen, K.T. Targeted biodegradable nanoparticles for drug delivery to smooth muscle cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyam, J.; Labhasetwar, V. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.; Titball, R.; Williamson, D. Vaccine delivery using nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilczewska, A.; Niemirowicz, K.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Car, H. Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, A.; Moghimi, S.M. Smart polymers in drug delivery: A biological perspective. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A.; Caccamo, M.T. Smart Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Application: Development of Versatile Nanocarrier Platforms in Biotechnology and Nanomedicine. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luss, A.L.; Kulikov, P.P.; Romme, S.B.; Andersen, C.L.; Pennisi, C.P.; Docea, A.O.; Kuskov, A.; Velonia, K.; Mezhuev, Y.O.; Shtilman, M.I.; et al. Nanosized carriers based on amphiphilic poly-N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone for intranuclear drug delivery. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamskov, I.A.; Kuskov, A.; Babievsky, K.K.; Berezin, B.B.; Krayukhina, M.A.; Samoylova, N.A.; Tikhonov, V.E.; Shtilman, M.I. Novel liposomal forms of antifungal antibiotics modified by amphiphilic polymers. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2008, 44, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuskov, A.; Kulikov, P.; Shtilman, M.; Rakitskii, V.; Tsatsakis, A. Amphiphilic poly-N-vynilpyrrolidone nanoparticles: Cytotoxicity and acute toxicity study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villemson, A.L.; Kuskov, A.; Shtilman, M.I.; Galebskaya, L.V.; Ryumina, E.V.; Larionova, N.I. Interaction of Polymer Aggregates Based on Stearoyl-poly-N-vinylpyrrolidone with Blood Components. Biochemistry 2004, 69, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuskov, A.; Villemson, A.L.; Shtilman, M.I.; Larionova, N.I.; Tsatsakis, A.; Tsikalas, I.; Rizos, A.K. Amphiphilic poly-N-vinylpyrrolidone nanocarriers with incorporated model proteins. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 205139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonia, T.A.; Sharma, C.P. Chitosan and Its Derivatives for Drug Delivery Perspective. Fortschr. der Hochpolym. Forsch. 2011, 243, 23–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Fangueiro, J.; Smitha, J.; Cinu, T.; Chacko, A.; Premaletha, K.; Souto, E.B. Cross-linked chitosan microspheres for oral delivery of insulin: Taguchi design and in vivo testing. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2012, 92, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirzhanova, E.A.; Pechenkin, M.A.; Demina, N.B.; Balabushevich, N.G. Alginate–chitosan micro- and nanoparticles for transmucosal delivery of proteins. Mosc. Univ. Chem. Bull. 2016, 71, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtat, D.; Mahlous, M.; Benamer, S.; Khodja, A.N.; Oussedik-Oumehdi, H.; Fatima, L.-D. Oral delivery of insulin from alginate/chitosan crosslinked by glutaraldehyde. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2013, 58, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walke, S.; Srivastava, G.; Nikalje, M.; Doshi, J.; Kumar, R.; Ravetkar, S.; Doshi, P. Fabrication of chitosan microspheres using vanillin/TPP dual crosslinkers for protein antigens encapsulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 128, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.; Felt, O.; Peppas, N.; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhao, X.; Ye, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, H. Preparation and drug release behavior of pH-responsive bovine serum albumin-loaded chitosan microspheres. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.; Singla, A.K.; Sinha, V.R. Evaluation of mucoadhesive properties of chitosan microspheres prepared by different methods. AAPS PharmSciTech 2004, 5, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dambies, L.; Vincent, T.; Domard, A.; Guibal, E. Preparation of Chitosan Gel Beads by Ionotropic Molybdate Gelation. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.A.; Park, H.J.; Hwang, S.-J.; Park, J.B.; Lee, J.S. Preparation and characterization of chitosan microparticles intended for controlled drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 249, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X. Novel pH-sensitive citrate cross-linked chitosan film for drug controlled release. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 212, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierszewska-Drużyńska, M.; Ostrowska-Czubenko, J.; Kwiatkowska, A. Effect of ionic crosslinking on density of hydrogel chitosan membranes. Prog. Chemi. Appl. Chitin Deriv. 2013, 18, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa, J.; Miyoshi, N.; Sakurai, K. Characterization of chitosan/citrate and chitosan/acetate films and applications for wound healing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, P.; Muxika, A.; Zarandona, I.; De La Caba, K. Crosslinking of chitosan films processed by compression molding. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, D.; Sakkara, S.; Meghwal, M.; Reddy, N. Crosslinked chitosan films with controllable properties for commercial applications. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lei, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, R.; Xiao, D.; Jiao, C.; Xia, R.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effect of citric acid induced crosslinking on the structure and properties of potato starch/chitosan composite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orienti, I.; Aiedeh, K.; Gianasi, E.; Bertasi, V.; Zecchi, V. Indomethacin loaded chitosan microspheres. Correlation between the erosion process and release kinetics. J. Microencapsul. 1996, 13, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshosaz, J.; Alinagari, R. Effect of citric acid as cross-linking agent on insulin loaded chitosan microspheres. Iranian Polym. J. 2005, 14, 647–656. [Google Scholar]
- Sedyakina, N.; Silaeva, A.O.; Krivoshchepov, A.F.; Avramenko, G.V. Preparation and properties of chitosan microspheres based on polyglycerol polyricinoleate stabilized emulsions. Mendeleev Commun. 2018, 28, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedyakina, N.; Zakharov, A.; Krivoshchepov, A.F.; Pribytkova, A.P.; Bogdanova, Y.A.; Feldman, N.B.; Lutsenko, S.; Avramenko, G.V. Effect of carbon chain length of dicarboxylic acids as cross-linking agents on morphology, encapsulation, and release features of protein-loaded chitosan microparticles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedyakina, N.; Feldman, N.B.; Lutsenko, S.V.; Avramenko, G.V. Fabrication and drug release behavior of ionically cross-linked chitosan microspheres. Mendeleev Commun. 2018, 28, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.B.; Sawant, K.K. Chitosan microspheres as a delivery system for nasal insufflation. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozie-Nwachukwu, S.; Danyuo, Y.; Obayemi, J.; Odusanya, O.; Malatesta, K.; Soboyejo, W. Extraction and encapsulation of prodigiosin in chitosan microspheres for targeted drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, S.; Shanumugasundaram, N.; Adhirajan, N.; Lakshmi, T.R.; Babu, M. Preparation and characterization of chitosan microspheres for doxycycline delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.R.; Parikh, R.H. Two-stage optimization process for formulation of chitosan microspheres. AAPS PharmSciTech 2009, 5, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.K.; Ichikawa, H.; Fukumori, Y. Gadolinium diethylenetriaminopentaacetic acid-loaded chitosan microspheres for gadolinium neutron-capture therapy. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2835–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Qu, G.; Wu, X.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Yu, L.; Ping, Q. Preparation and characterization of galactosylated chitosan coated BSA microspheres containing 5-fluorouracil. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analyt. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayukhina, M.A.; Samoilova, N.A.; Erofeev, A.S.; Yamskov, I.A. Complexation of chitosan with maleic acid copolymers. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2010, 52, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeesh, S.; Sharma, C.P. Interpolymer complex microparticles based on polymethacrylic acid-chitosan for oral insulin delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 99, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaonkar, D.; Gaikwad, S.; Rai, M. Catharanthus roseus leaf extract-synthesized chitosan nanoparticles for controlled in vitro release of chloramphenicol and ketoconazole. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sedyakina, N.; Kuskov, A.; Velonia, K.; Feldman, N.; Lutsenko, S.; Avramenko, G. Modulation of Entrapment Efficiency and In Vitro Release Properties of BSA-Loaded Chitosan Microparticles Cross-Linked with Citric Acid as a Potential Protein–Drug Delivery System. Materials 2020, 13, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081989
Sedyakina N, Kuskov A, Velonia K, Feldman N, Lutsenko S, Avramenko G. Modulation of Entrapment Efficiency and In Vitro Release Properties of BSA-Loaded Chitosan Microparticles Cross-Linked with Citric Acid as a Potential Protein–Drug Delivery System. Materials. 2020; 13(8):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081989
Chicago/Turabian StyleSedyakina, Natalia, Andrey Kuskov, Kelly Velonia, Nataliya Feldman, Sergey Lutsenko, and Grigory Avramenko. 2020. "Modulation of Entrapment Efficiency and In Vitro Release Properties of BSA-Loaded Chitosan Microparticles Cross-Linked with Citric Acid as a Potential Protein–Drug Delivery System" Materials 13, no. 8: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081989
APA StyleSedyakina, N., Kuskov, A., Velonia, K., Feldman, N., Lutsenko, S., & Avramenko, G. (2020). Modulation of Entrapment Efficiency and In Vitro Release Properties of BSA-Loaded Chitosan Microparticles Cross-Linked with Citric Acid as a Potential Protein–Drug Delivery System. Materials, 13(8), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081989