Structural Change in Ni-Fe-Ga Magnetic Shape Memory Alloys after Severe Plastic Deformation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Microstructure Analysis
3.2. SEM Analysis
3.3. TEM Analysis
3.4. EDX Analysis
3.5. Microhardness Considerations
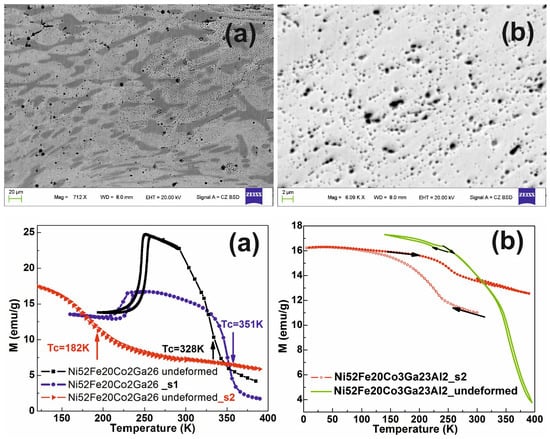
3.6. Thermo-Magnetic Data
4. Conclusions
- For the first time, buttons of Ni-Fe-Ga (with and without Co and Al substitution) in the as-cast condition were successfully severely plastically deformed by HSHPT at room temperature.
- The microstructure of the two-phase Heusler Ni-Fe-Ga FSM alloys Ni57Fe18Ga25, Ni50Fe22Ga25Co3, Ni52Fe20Co2Ga26, and Ni52Fe20Co3Ga23Al2 after SPD was explored after SPD with an optical microscope, SEM-EDX, as well as TEM.
- Martensitic transformation that takes place in severely deformed Ni-Fe-Ga alloys with Co and Al substitutions has been highlighted by magnetic measurements.
- In the temperature range over which the martensitic transformation occurs a microstructural change take place producing discontinuities in the thermal dependence of magnetization.
- The severe deformation at 0.95 logarithmic degree induces a decrease in MT temperatures, an increase in Tc and a decrease in magnetization, while a 2.2 degree of deformation induces a loss of the shape memory effect in the Ni52Fe20Co2Ga26 alloy, and unstable austenite in the Ni52Fe20Co3Ga23Al2 alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bahador, A.; Hamzah, E.; Kondoh, K.; Asma Abubakar, T.; Yusof, F.; Umeda, J.; Saud, S.N.; Ibrahim, M.K. Microstructure and superelastic properties of free forged Ti–Ni shape-memory alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Ed.) 2018, 28, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, L.; Mino, J.; Ryba, T.; Gamcova, J.; Dzubinska, A.; Reiffers, M.; Diko, P.; Kavecansky, V.; Milkovic, O.; Kravcak, J.; et al. Novel compositions of Heusler-based glass-coated microwires for practical applications using shape memory effect. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 747, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, M.P.; Berkowitz, A.E.; Armstrong, A.; Müllner, P.; Solomon, C.V. 4D printing of net shape parts made from Ni-Mn-Ga magnetic shape-memory alloys. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.H.; Cong, D.Y.; Li, S.H.; Gui, W.Y.; Nie, Z.H.; Zhang, M.H.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.D. Simultaneously achieved large reversible elastocaloric and magnetocaloric effects and their coupling in a magnetic shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 151, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, J.; Cesari, E.; Seguí, C.; Masdeu, F.; Santamarta, R. Ferromagnetic shape memory alloys: Alternatives to Ni–Mn–Ga. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 481482, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, P.; Infante, V.; Deus, A.M. ScienceDirect Thermo-mechanical modeling of a high pressure turbine blade of an airplane gas turbine engine. Struct. Integr. Procedia 2016, 1, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofronie, M.; Tolea, F.; Crisan, A.D.; Popescu, B.; Valeanu, M. Magnetoelastic properties in polycrystalline ferromagnetic shape memory Heusler alloys. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2016, 2, 1530–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- González-Legarreta, L.; Rosa, W.O.; García, J.; Ipatov, M.; Nazmunnahar, M.; Escoda, L.; Suñol, J.J.; Prida, V.M.; Sommer, R.L.; González, J.; et al. Annealing effect on the crystal structure and exchange bias in Heusler Ni45.5Mn43.0In11.5alloy ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 582, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.H.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.J.; Hu, Q.D.; Li, J.G. A study of microstructure and crystal orientation in directionally solidified Ni-Fe-Ga-Co magnetic shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 572, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Krishnan, M. Deformation Studies of Ni 55 Fe 19 Ga 26 Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloy. Phys. Procedia 2010, 10, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.H.; Lin, Q.Y.; Sha, G.; Huang, M.X.; Ringer, S.P.; Zhu, Y.T.; Liao, X.Z. Microstructural evolution and phase transformation in twinning-induced plasticity steel induced by high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2016, 109, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurǎu, G.; Gurǎu, C.; Potecaşu, O.; Alexandru, P.; Bujoreanu, L.-G. Novel high-speed high pressure torsion technology for obtaining Fe-Mn-Si-Cr shape memory alloy active elements. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleu, V.; Gurau, G.; Comaneci, R.I.; Sampath, V.; Gurau, C.; Bujoreanu, L.-G. A new application of Fe-28 Mn-6 Si-5 Cr (mass. %) shape memory alloy, for self-adjustable axial preloading of ball bearings. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurau, G.; Gurau, C.; Bujoreanu, L.G.; Sampath, V. A Versatile Method for Nanostructuring Metals, Alloys and Metal Based Composites. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing, China, 24–27 October 2017; Volume 209. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xin, Y.; Chai, L.; Ma, Y.; Xu, H. Microstructures and shape memory characteristics of dual-phase Co–Ni–Ga high-temperature shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3655–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurau, G.; Gurau, C.; Sampath, V. Investigation of microhardness evolution in an ultrafine grained NiTi alloy formed via high speed high pressure torsion (HSHPT). MATEC Web Conf. 2015, 33, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.; Sehitoglu, H. Deformation physics of shape memory alloys—Fundamentals at atomistic frontier. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 88, 49–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample. | Ms (K) | Mf (K) | As(K) | Af (K) | Tc (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni52Fe20Co2Ga26 _undeformed | 243 | 218 | 250 | 258 | 328 |
| Ni52Fe20Co2Ga26_s1 | 224 | 207 | 230 | 238 | 351 |
| Ni52Fe20Co2Ga26_s2 | - | - | - | - | 182 |
| Ni52Fe20Co3Ga23Al2_undeformed | 236 | 210 | 245 | 260 | 355 |
| Ni52Fe20Co3Ga23Al2_s2 | 240 | 145 | 238 | 267 | >400 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gurau, G.; Gurau, C.; Tolea, F.; Sampath, V. Structural Change in Ni-Fe-Ga Magnetic Shape Memory Alloys after Severe Plastic Deformation. Materials 2019, 12, 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121939
Gurau G, Gurau C, Tolea F, Sampath V. Structural Change in Ni-Fe-Ga Magnetic Shape Memory Alloys after Severe Plastic Deformation. Materials. 2019; 12(12):1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121939
Chicago/Turabian StyleGurau, Gheorghe, Carmela Gurau, Felicia Tolea, and Vedamanickam Sampath. 2019. "Structural Change in Ni-Fe-Ga Magnetic Shape Memory Alloys after Severe Plastic Deformation" Materials 12, no. 12: 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121939
APA StyleGurau, G., Gurau, C., Tolea, F., & Sampath, V. (2019). Structural Change in Ni-Fe-Ga Magnetic Shape Memory Alloys after Severe Plastic Deformation. Materials, 12(12), 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121939