Feasibility of the Machine Learning Network to Diagnose Tympanic Membrane Lesions without Coding Experience
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition of Tympanic Membrane Images
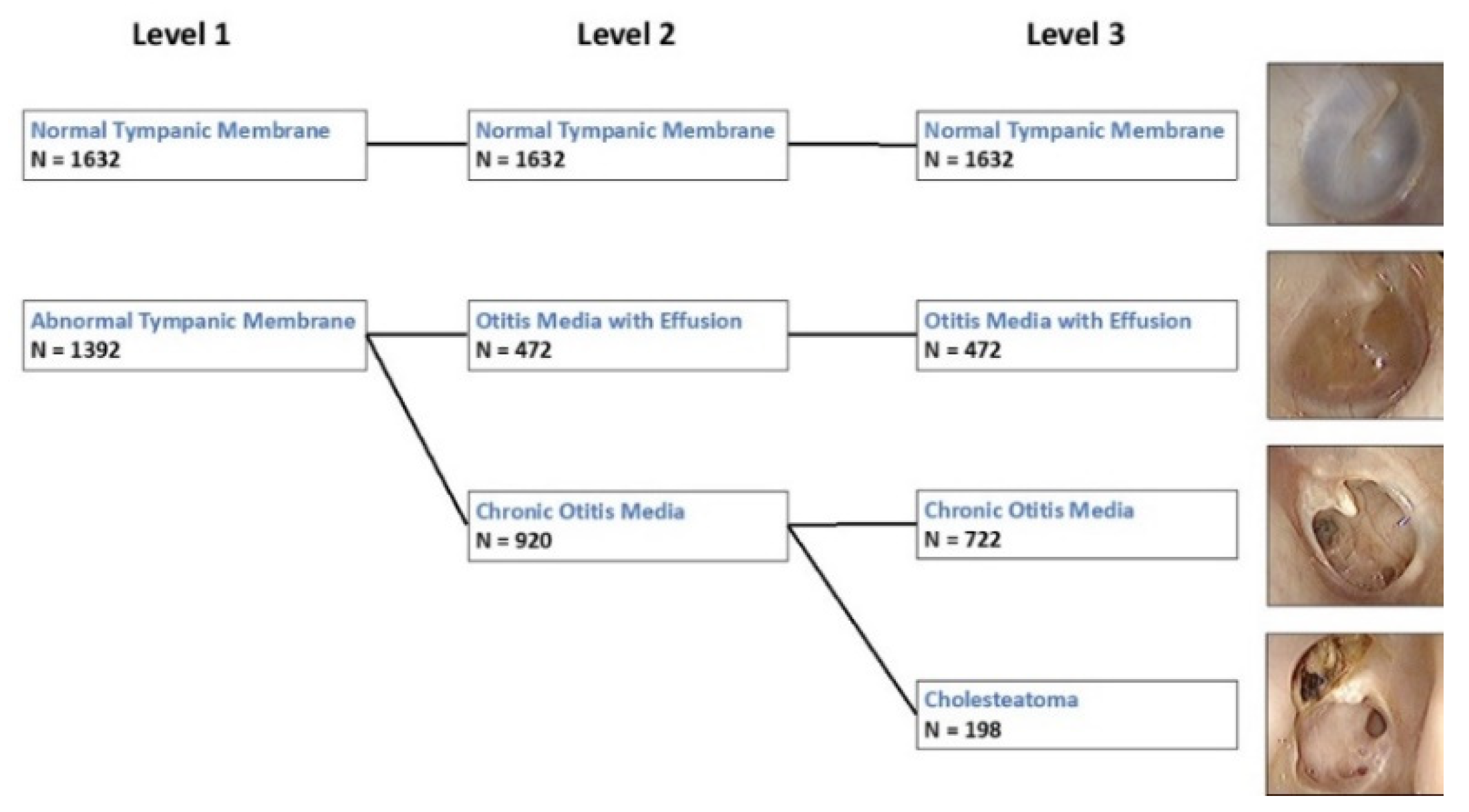
2.2. Image Annotation and Classifications
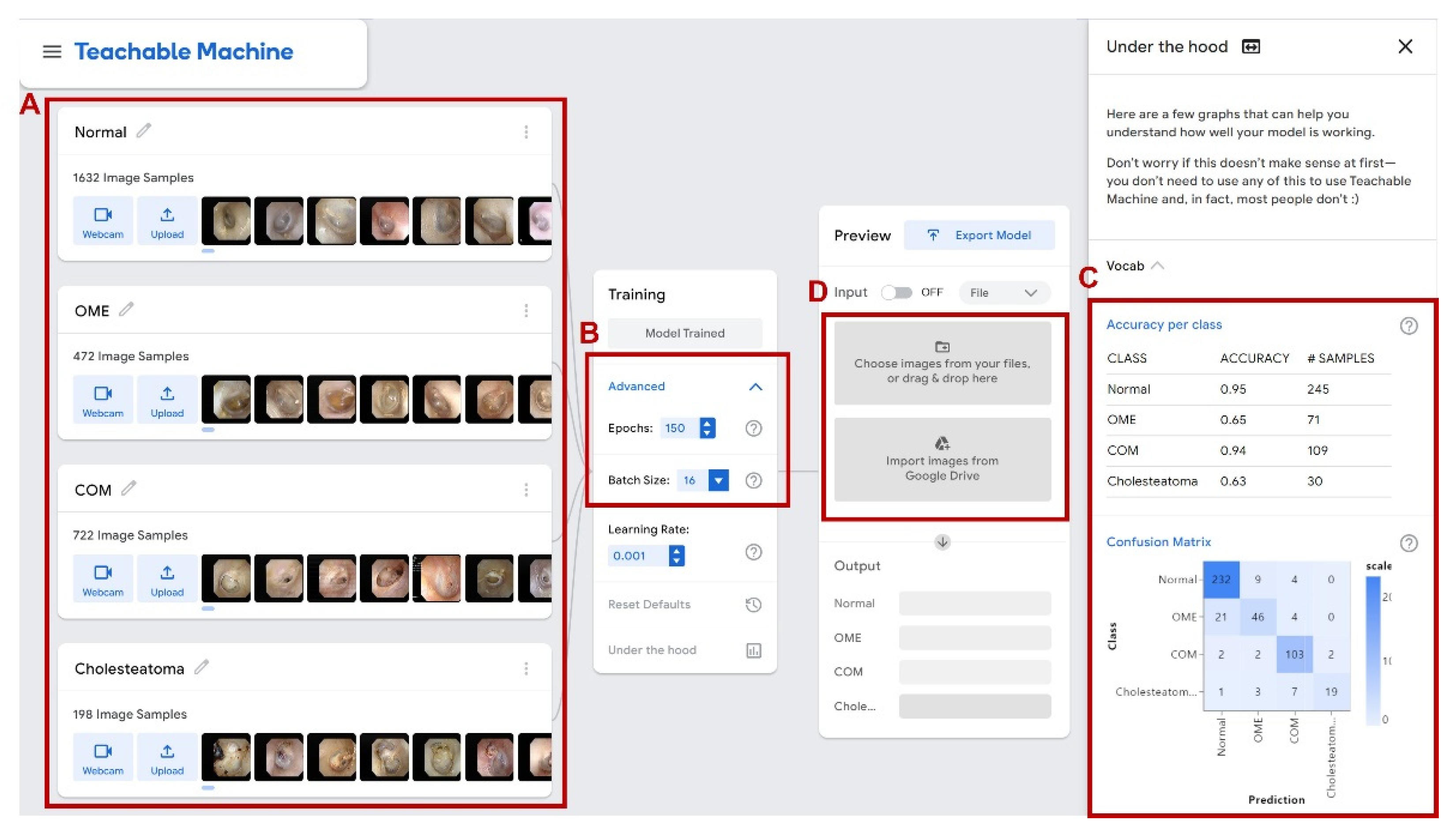
2.3. Teachable Machine
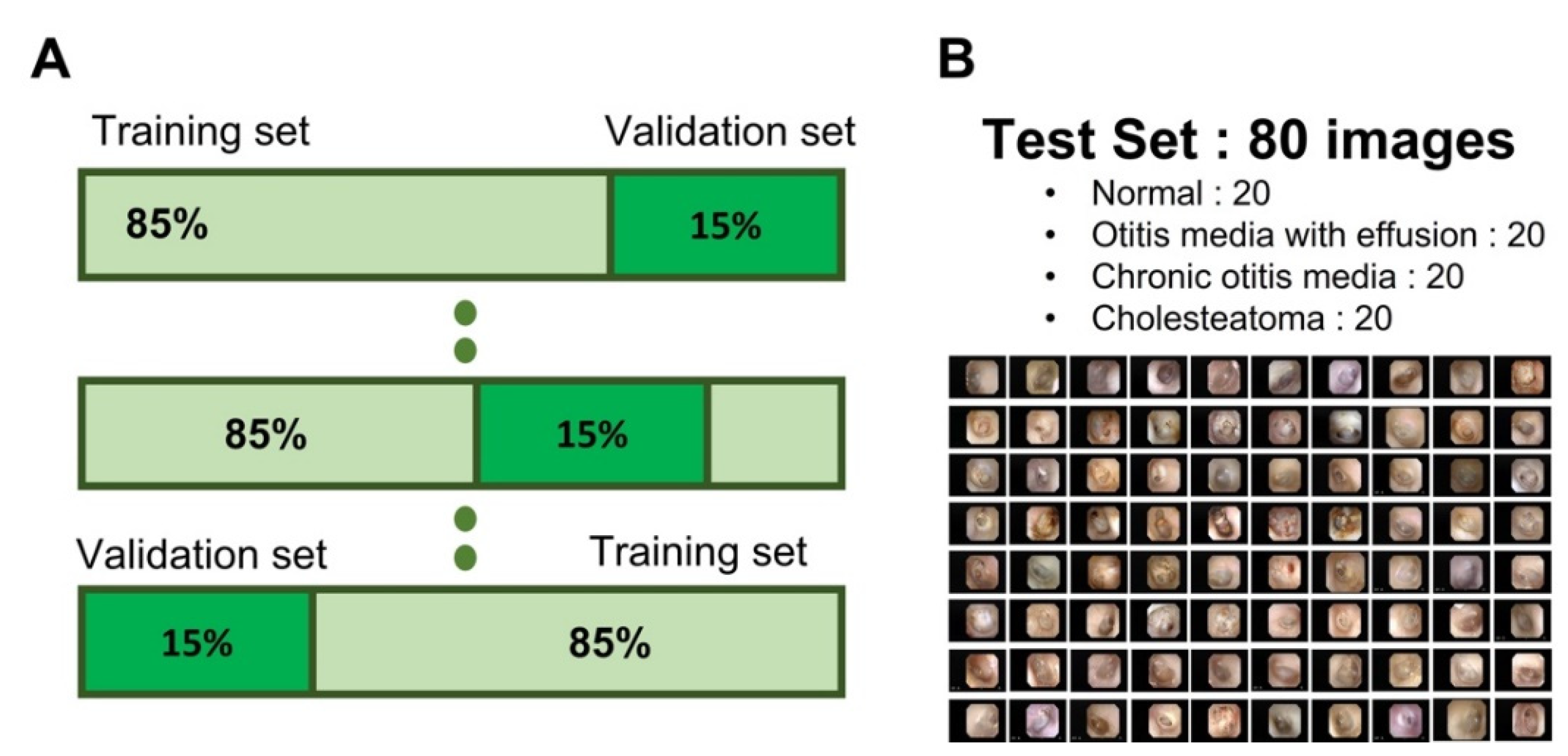
2.4. Network Performance and Validation
2.5. Ethical Issues
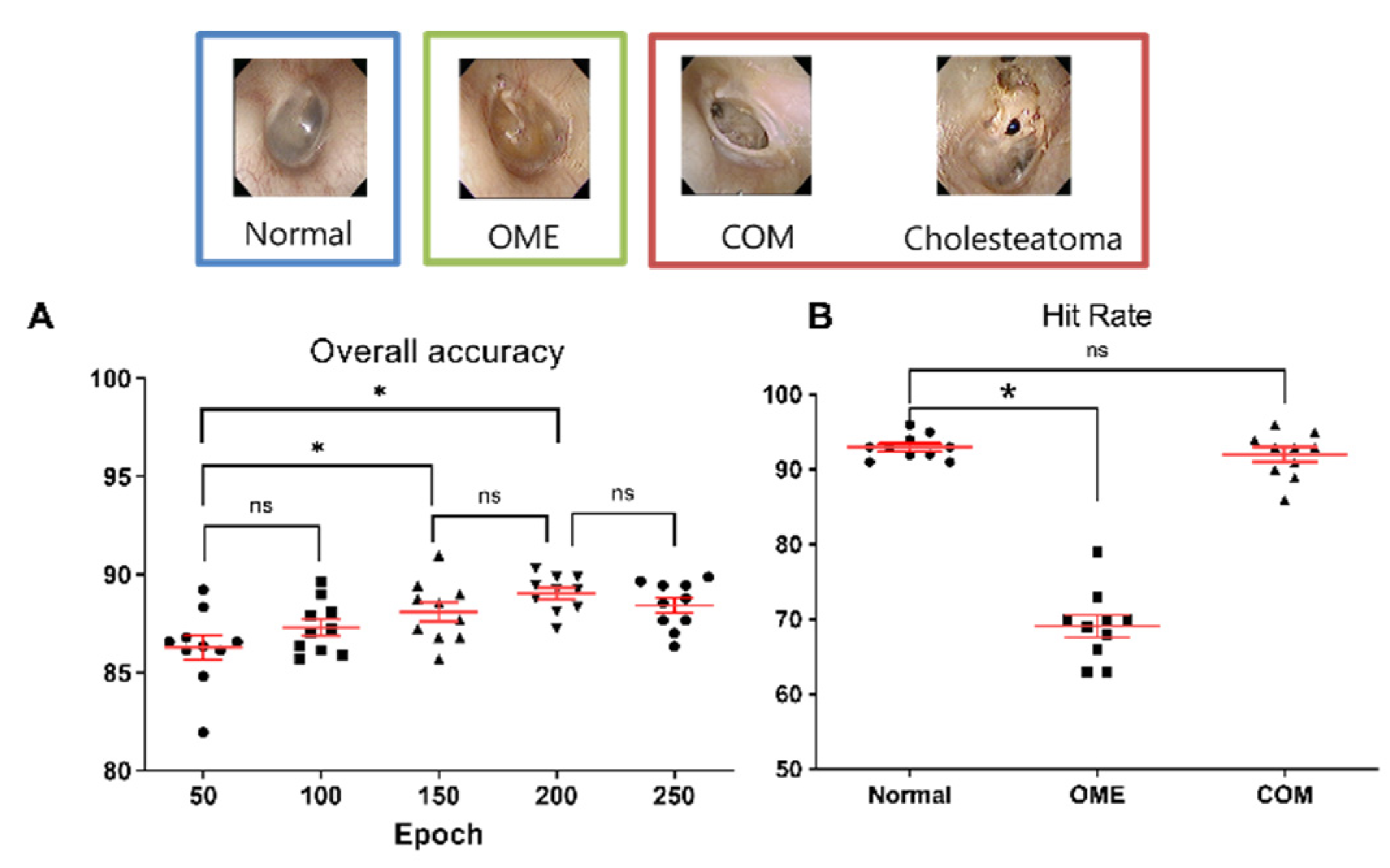
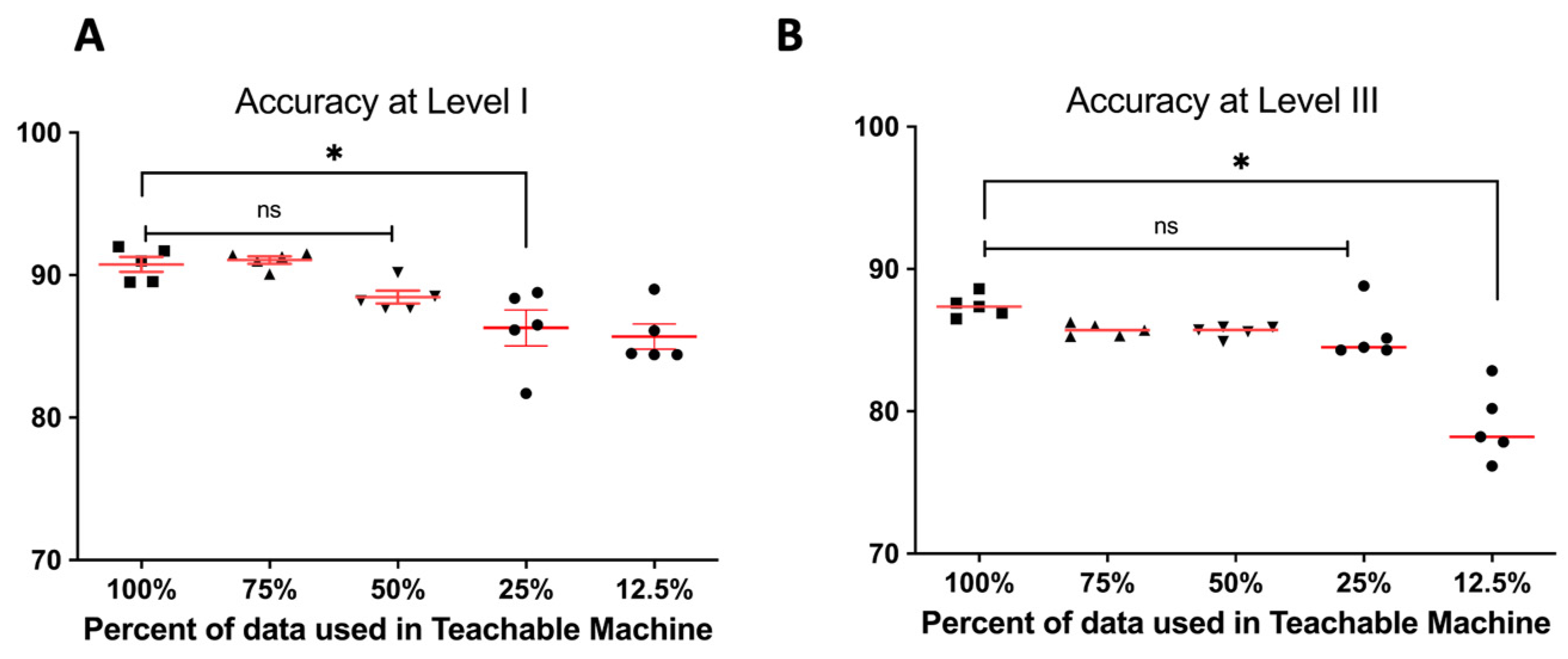
3. Results
3.1. Tympanic Membrane Images
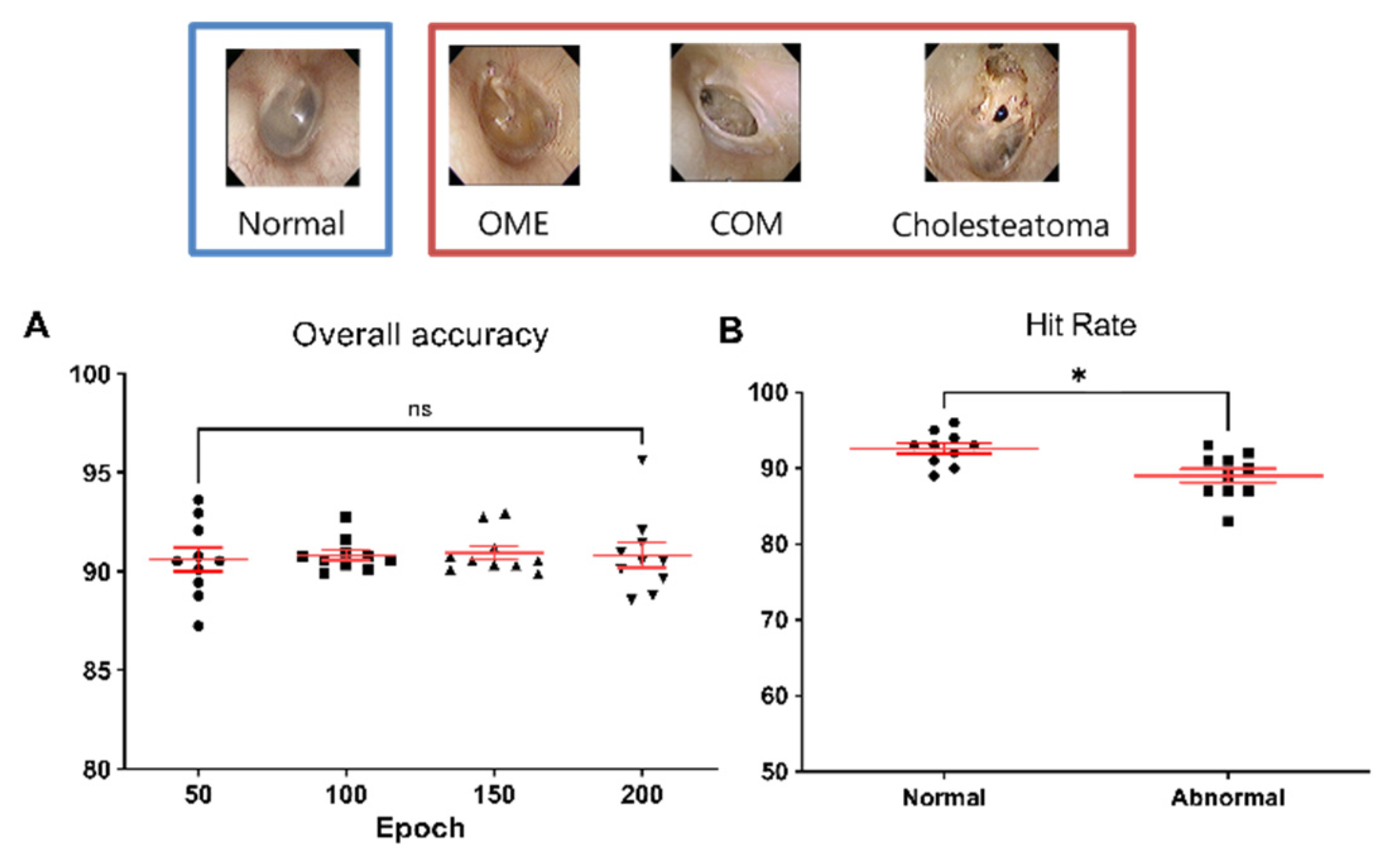
3.2. Network Verification
3.3. Diagnostic Performance According to the Number of Tympanic Membrane Image
3.4. Performance of the Network with Representative
Tympanic Membrane Images
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buchanan, C.M.; Pothier, D.D. Recognition of paediatric otopathology by General Practitioners. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 72, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichichero, M.E. Can Machine Learning and AI Replace Otoscopy for Diagnosis of Otitis Media? Pediatrics 2021, 147, e2020049584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, H.; Yu, S.; Oh, J.; Bae, J.; Yoon, M.S.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, T.H. An Assistive Role of a Machine Learning Network in Diagnosis of Middle Ear Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Li, L.; Pan, H.; Chen, G.; Fu, Y.; Qiu, Q. Deep Learning for Classification of Pediatric Otitis Media. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E2344–E2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Kwon, S.; Choo, J.; Hong, S.M.; Kang, S.H.; Park, I.H.; Kim, S.K.; Hong, S.J. Automatic detection of tympanic membrane and middle ear infection from oto-endoscopic images via convolutional neural networks. Neural Netw. 2020, 126, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Luo, W.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Shi, J.; Wu, K.; Liu, T.; Lin, X.; et al. Efficient and accurate identification of ear diseases using an ensemble deep learning model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhudhaif, A.; Cömert, Z.; Polat, K. Otitis media detection using tympanic membrane images with a novel multi-class machine learning algorithm. PeerJ. Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, A.R.; Kajbafzadeh, M.; Hasan, Z.; Wong, E.; Gunasekera, H.; Perry, C.; Sacks, R.; Kumar, A.; Singh, N. Artificial intelligence to classify ear disease from otoscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2022, 47, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korot, E.; Guan, Z.; Ferraz, D.; Wagner, S.K.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Faes, L.; Pontikos, N.; Finlayson, S.G.; Khalid, H.; et al. Code-free deep learning for multi-modality medical image classification. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H. Feasibility Study of Google’s Teachable Machine in Diagnosis of Tooth-Marked Tongue. J. Dent. Hyg. Sci. 2020, 20, 206–212. [Google Scholar]
- Oyewumi, M.; Brandt, M.G.; Carrillo, B.; Atkinson, A.; Iglar, K.; Forte, V.; Campisi, P. Objective Evaluation of Otoscopy Skills Among Family and Community Medicine, Pediatric, and Otolaryngology Residents. J. Surg. Educ. 2016, 73, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichichero, M.E.; Poole, M.D. Assessing diagnostic accuracy and tympanocentesis skills in the management of otitis media. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2001, 155, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.-H.; Chung, J.W. Automated Classification of the Tympanic Membrane Using a Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsutsumi, K.; Goshtasbi, K.; Risbud, A.; Khosravi, P.; Pang, J.C.; Lin, H.W.; Djalilian, H.R.; Abouzari, M. A Web-Based Deep Learning Model for Automated Diagnosis of Otoscopic Images. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e1382–e1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, D.; Pae, C.; Seong, S.B.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, H.J. Automated diagnosis of ear disease using ensemble deep learning with a big otoendoscopy image database. EBioMedicine 2019, 45, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crowson, M.G.; Hartnick, C.J.; Diercks, G.R.; Gallagher, T.Q.; Fracchia, M.S.; Setlur, J.; Cohen, M.S. Machine Learning for Accurate Intraoperative Pediatric Middle Ear Effusion Diagnosis. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e2020034546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Yu, J.G.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Xiao, L.; Grais, E.M.; Zhao, F.; Lan, L.; Zeng, S.; Zeng, J.; et al. Investigating the use of a two-stage attention-aware convolutional neural network for the automated diagnosis of otitis media from tympanic membrane images: A prediction model development and validation study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e041139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, D.; Talai, A.S.; Chau, J.; Forkert, N.D. Building an Otoscopic screening prototype tool using deep learning. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2019, 48, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Myburgh, H.C.; Jose, S.; Swanepoel, D.W.; Laurent, C. Towards low cost automated smartphone- and cloud-based otitis media diagnosis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 39, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viscaino, M.; Maass, J.C.; Delano, P.H.; Torrente, M.; Stott, C.; Auat Cheein, F. Computer-aided diagnosis of external and middle ear conditions: A machine learning approach. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study | Tympanic Membrane Classification | Number of Classification | Algorithm Used | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The present study | Normal versus Abnormal | 2 | Teachable Machine® | 90.8 ± 1.5% |
| Normal, OME, and COM | 3 | Teachable Machine® | 87.8 ± 1.7% | |
| Normal, OME, perforation, cholesteatoma | 4 | Teachable Machine® | 85.4 ± 1.7% | |
| Alhudhaif et al. (2021) [7] | Normal, AOM, CSOM, Earwax, | 4 | CBAM | 98.26% |
| Crowson et al. (2021) [16] | Normal versus OME | 2 | ResNet34 | 84.06% |
| Tsutsumi et al. (2021) [14] | Normal versus abnormal | 2 | InceptionV3 | 73.0% |
| MobileNetV2 | 77.0% | |||
| Habib et al. (2020) [8] | Normal versus Perforation | 2 | InceptionV3 | 76.00% |
| Cai et al. (2021) [17] | Normal, OME, CSOM | 3 | Resnet50 | 93.4% |
| Wu et al. (2021) [4] | Normal, AOM, OME | 3 | Xception | 90.66% |
| 3 | MobileNetV2 | 88.56% | ||
| Cha et al. (2019) [15] | Normal versus Abnormal | 2 | InceptionV3 | 93.31% |
| 2 | ResNet101 | 91.88% | ||
| 2 | Ensemble Network | 94.17% | ||
| Livingstone et al. (2019) [18] | Normal, Earwax, Tympanostomy tube | 3 | CNN | 84.44% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Byun, H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Oh, J.; Chung, J.H. Feasibility of the Machine Learning Network to Diagnose Tympanic Membrane Lesions without Coding Experience. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111855
Byun H, Lee SH, Kim TH, Oh J, Chung JH. Feasibility of the Machine Learning Network to Diagnose Tympanic Membrane Lesions without Coding Experience. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(11):1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111855
Chicago/Turabian StyleByun, Hayoung, Seung Hwan Lee, Tae Hyun Kim, Jaehoon Oh, and Jae Ho Chung. 2022. "Feasibility of the Machine Learning Network to Diagnose Tympanic Membrane Lesions without Coding Experience" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 11: 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111855
APA StyleByun, H., Lee, S. H., Kim, T. H., Oh, J., & Chung, J. H. (2022). Feasibility of the Machine Learning Network to Diagnose Tympanic Membrane Lesions without Coding Experience. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11), 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111855






